Food Addiction and Grazing—The Role of Difficulties in Emotion Regulation and Negative Urgency in University Students
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Sociodemographic and Clinical Questionnaire
2.2.2. Portuguese Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 (P-YFAS 2.0; [29,30])
2.2.3. Repetitive Eating Questionnaire (Rep(eat)-Q; [18])
2.2.4. Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale–Short Form (DERS-SF; [24,32,33])
2.2.5. UPPS-P–Negative Urgency Subscale (UPPS-P; [34,35])
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characterization
3.2. Association between Food Addiction Symptomatology, Grazing, and the Variables under Study
3.3. Measurement Model
3.3.1. Dimensionality
3.3.2. Reliability: Internal Consistency
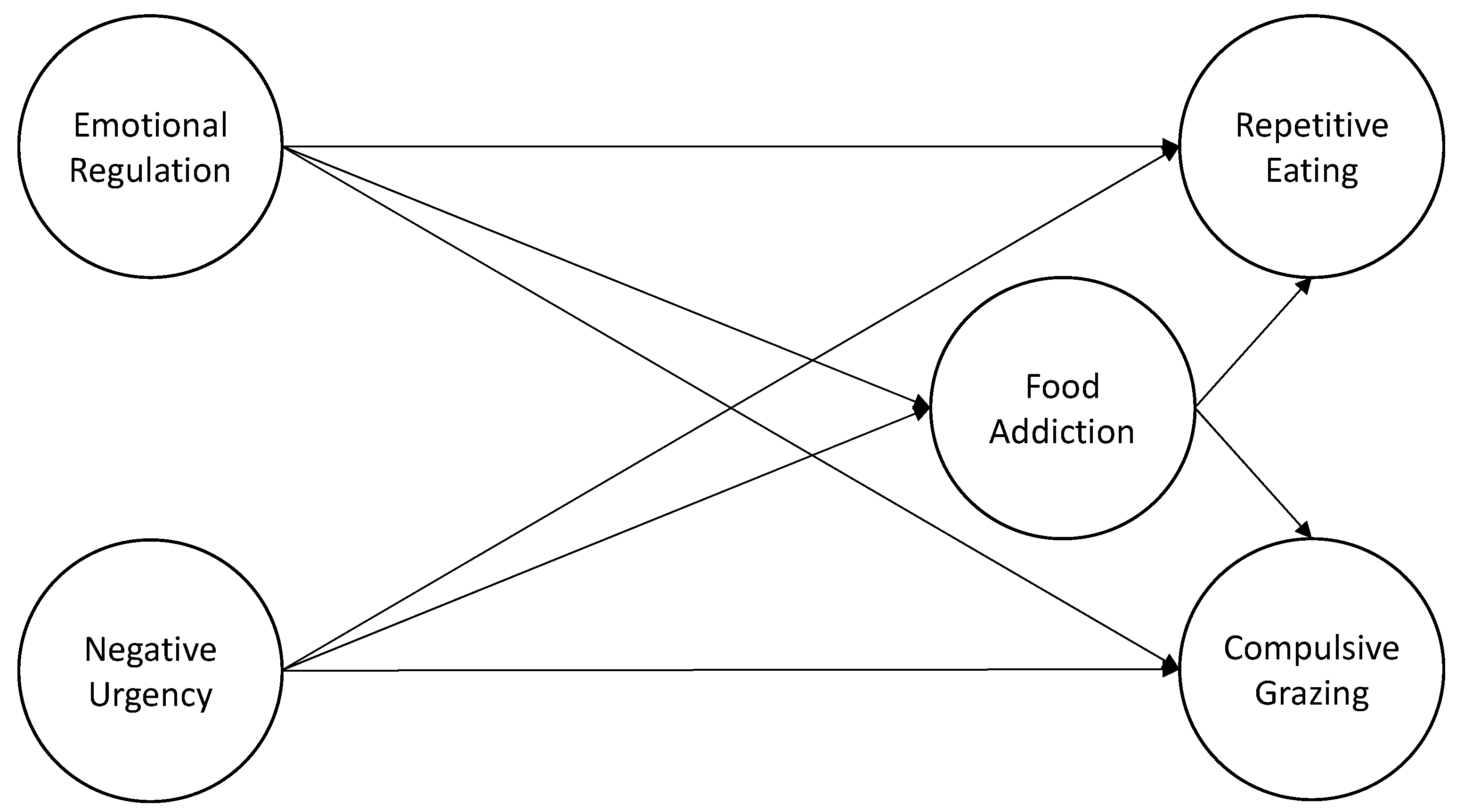
3.4. Testing the Proposed Structural Model
4. Discussion
4.1. The Mediation Model
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papadaki, A.; Hondros, G.; Scott, J.A.; Kapsokefalou, M. Eating habits of University students living at, or away from home in Greece. Appetite 2007, 49, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogari, G.; Velez-Argumedo, C.; Gómez, M.I.; Mora, C. College students and eating habits: A study using an ecological model for healthy behavior. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrkou, C.; Tsakoumaki, F.; Fotiou, M.; Dimitropoulou, A.; Symeonidou, M.; Menexes, G.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Michaelidou, A.-M. Changing trends in nutritional behavior among university students in Greece, between 2006 and 2016. Nutrients 2018, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, P.; Hanck, C.; Neisingh, M.; Prak, D.; Groen, H.; Faas, M.M. Weight gain in freshman college students and perceived health. Prev. Med. Rep. 2015, 2, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stok, F.M.; Renner, B.; Clarys, P.; Lien, N.; Lakerveld, J.; Deliens, T. Understanding eating behavior during the transition from adolescence to young adulthood: A literature review and perspective on future research directions. Nutrients 2018, 10, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, S.; Félix, S.; Martins, F.; Lapenta, O.; Machado, B.C.; Conceição, E.M. Food Addiction Problems in College Students: The Relationship between Weight-Related Variables, Eating Habits, and Food Choices. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursey, K.M.; Stanwell, P.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Collins, C.E.; Burrows, T.L. The prevalence of food addiction as assessed by the yale food addiction scale: A systematic review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4552–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; Corbin, W.R.; Brownell, K.D. Preliminary validation of the Yale Food Addiction Scale. Appetite 2009, 52, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; White, M.A.; Potenza, M.N. Binge eating disorder and food addiction. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2011, 4, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najem, J.; Saber, M.; Aoun, C.; El Osta, N.; Papazian, T.; Khabbaz, L.R. Prevalence of food addiction and association with stress, sleep quality and chronotype: A cross-sectional survey among university students. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hone-Blanchet, A.; Fecteau, S. Overlap of food addiction and substance use disorders definitions: Analysis of animal and human studies. Neuropharmacology 2014, 85, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonder, R.; Davis, C.; Kuk, J.L.; Loxton, N.J. Compulsive “grazing” and addictive tendencies towards food. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2018, 26, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C. Evolutionary and neuropsychological perspectives on addictive behaviors and addictive substances: To the “food addiction” construct. Subst. Abuse Rehabil. 2014, 2014, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J. Food additives, food and the concept of ‘food addiction’: Is stimulation of the brain reward circuit by food sufficient to trigger addiction? Pathophysiology 2018, 25, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.J.; Tomasi, D.; Baler, R.D. Obesity and addiction: Neurobiological overlaps. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C. A commentary on the associations among ‘food addiction’, binge eating disorder, and obesity: Overlapping conditions with idiosyncratic clinical features. Appetite 2017, 115, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, E.M.; Mitchell, J.E.; Engel, S.G.; Machado, P.P.; Lancaster, K.; Wonderlich, S.A. What is “grazing”? Reviewing its definition, frequency, clinical characteristics, and impact on bariatric surgery outcomes, and proposing a standardized definition. Surg. Obes. Relate Dis. 2014, 10, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, E.M.; Mitchell, J.E.; Machado, P.P.; Vaz, A.R.; Pinto-Bastos, A.; Ramalho, S.; Brandao, I.; Simoes, J.B.; de Lourdes, M.; Freitas, A.C. Repetitive eating questionnaire [Rep(eat)-Q]: Enlightening the concept of grazing and psychometric properties in a Portuguese sample. Appetite 2017, 117, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, E.M.; de Lourdes, M.; Pinto-Bastos, A.; Vaz, A.R.; Brandão, I.; Ramalho, S. Problematic eating behaviors and psychopathology in patients undergoing bariatric surgery: The mediating role of loss of control eating. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 51, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivarunas, B.; Conner, B.T. Impulsivity and emotion dysregulation as predictors of food addiction. Eat Behav. 2015, 19, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsi, E.; Kamal, A.; Turvill, A.; Holler, R. Emotion dysregulation and loneliness as predictors of food addiction. J. Health Soc. Sci. 2019, 4, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunio, L.K.; Battles, J.A.; Loverich, T.M. The nuances of emotion regulation difficulties and mindfulness in food addiction. Addict. Res. Theory 2021, 29, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innamorati, M.; Imperatori, C.; Harnic, D.; Erbuto, D.; Patitucci, E.; Janiri, L.; Lamis, D.A.; Pompili, M.; Tamburelloo, S.; Fabbricatore, M. Emotion Regulation and Mentalization in People at Risk for Food Addiction. Behav. Med. 2017, 43, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, K.L.; Roemer, L. Multidimensional Assessment of Emotion Regulation and Dysregulation: Development, Factor Structure and Initial Validation of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale. Psychopathol. Behav. Asessment 2004, 26, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, U.; Chen, E.; Neighbors, C.; Hunter, D.; Lo, T.; Larimer, M. Difficulties regulating emotions: Do binge eaters have fewer strategies to modulate and tolerate negative affect? Eat. Behav. 2007, 8, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolz, I.; Granero, R.; Fernández-Aranda, F. A comprehensive model of food addiction in patients with binge-eating symptomatology: The essential role of negative urgency. Compr. Psychiatry 2017, 74, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.M.; Stojek, M.K.; MacKillop, J. Interrelationships among impulsive personality traits, food addiction, and Body Mass Index. Appetite 2014, 73, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolz, I.; Hilker, I.; Granero, R.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Dieguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Menchón, J.M.; Fernández-Aranda, F. “Food Addiction” in Patients with Eating Disorders is Associated with Negative Urgency and Difficulties to Focuson Long-Term Goals. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; Corbin, W.R.; Brownell, K.D. Development of the Yale Food Addiction Scale Version 2.0. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2016, 30, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.; Moreira, C.; Machado, B.; Bastos, B.; Vieira, A.I. Psychometric properties and convergent and divergent validity of the Portuguese Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 (P-YFAS 2.0). Eat Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM-5: Manual Diagnóstico e Estatístico de Transtornos Mentais; Climepsi Editores: Forte da Casa, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, E.A.; Xia, M.; Fosco, G.; Yaptangco, M.; Skidmore, C.R.; Crowell, S.E. The Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale Short Form (DERS-SF): Validation and Replication in Adolescent and Adult Samples. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2016, 38, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, H.; Gouveia, M.J.; Canavarro, M.C. A bifactor analysis of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale—Short Form (DERS-SF) in a sample of adolescents and adults. Curr. Psychol. 2022, 41, 757–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, A.J. Análise das Caraterísticas Psicométricas da Escala de Impulsividade UPPS-P na População Portuguesa Mediante o Modelo de Rasch. 2015. Available online: http://recil.grupolusofona.pt/handle/10437/6432 (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Whiteside, S.P.; Lynam, D.; Miller, J.; Reynolds, S. Validation of the UPPS impulsive behavior scale: A four factor model of impulsivity. Eur. J. Pers. 2005, 19, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Version 4.3.1; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2023.
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R, Version 2023.3.0.386; Posit Software, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rosseel, Y. Lavaan: An R Package for Structural Equation Modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, B.M. Structural Equation Modeling with AMOS: Basic Concepts, Applications, and Programming, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.A. Confirmatory Factor Analysis for Applied Research, 2nd ed.; Guildford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Muthén, B. Latent variable structural equation modeling with categorical data. J. Econom. 1983, 22, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Response to Leslie Hayduk’s review of principles and practice of structural equation modeling, 4th edition. Can. Stud. Popul. 2023, 45, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, T.D.; Pornprasertmanit, S.; Schoemann, A.M.; Rosseel, Y. SemTools: Useful Tools for Structural Equation Modeling, R Package Version 0.5-6.922; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, J.; Colombarolli, M.S.; Cordás, T.A. Prevalence and correlates of food addiction: Systematic review of studies with the YFAS 2.0. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 15, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzenstadler, L.; Soares, C.; Karila, L.; Khazaal, Y. Systematic Review of Food Addiction as Measured with the Yale Food Addiction Scale: Implications for the Food Addiction Construct. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heatherton, T.F.; Baumeister, R.F. Binge eating as escape from self-awareness. Psychol. Bull. 1991, 110, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxton, S.J.; Diggens, J. Avoidance coping, binge eating, and depression: An examination of the escape theory of binge eating. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1997, 22, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.E.M.; El Rasheed, A.H.; Azzam, H.M.; ElZoheiry, A.K.; ElSerafi, D.M.; ElGhamry, R.H.; Naguib, R.M. Personality profile and affect regulation in relation to food addiction among a sample of Egyptian Females. Addict. Disord. Their Treat. 2016, 15, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivezaj, V.; Ashley, A.W.; Lawson, J.L.; Grilo, C.M. Food Addiction in Sleeve Gastrectomy Patients with Loss-of-Control Eating. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | M | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Symptomatology of Food Addiction | 1.29 | 2.40 | ----- | |||||
| 2. DERS-SF: Total | 39.84 | 12.65 | 0.420 *** | ----- | ||||
| 3. UPPS–UN subscale | 26.67 | 7.38 | 0.411 *** | 0.613 *** | ---- | |||
| 4. Rep(Eat)-Q: Total | 1.82 | 1.47 | 0.666 *** | 0.442 *** | 0.503 *** | ----- | ||
| 5. Rep(Eat)-Q: CG | 1.44 | 1.34 | 0.675 *** | 0.443 *** | 0.476 *** | 0.928 *** | ---- | |
| 6. Rep(Eat)-Q: RE | 1.59 | 1.30 | 0.556 *** | 0.374 *** | 0.457 *** | 0.924 *** | 0.716 *** | ---- |
| Path | B | se | z | p | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effects (Y ⇐ X) | ||||||
| FA <- ER | 0.489 | 0.061 | 0.486 | 8.084 | <0.001 | (0.371; 0.608) |
| FA <- NU | 0.099 | 0.042 | 0.126 | 2.336 | 0.019 | (0.016; 0.181) |
| CG <- FA | 0.984 | 0.062 | 0.776 | 15.934 | <0.001 | (0.863; 1.105) |
| CG <- ER | 0.005 | 0.071 | 0.004 | 0.077 | 0.939 | (−0.134; 0.145) |
| CG <- NU | 0.105 | 0.041 | 0.105 | 2.531 | 0.011 | (0.024; 0.186) |
| RE <- FA | 0.718 | 0.059 | 0.575 | 12.200 | <0.001 | (0.603; 0.834) |
| RE <- ER | −0.042 | 0.075 | −0.033 | −0.560 | 0.576 | (−0.190; 0.105) |
| RE <- NU | 0.225 | 0.047 | 0.229 | 4.772 | <0.001 | (0.132; 0.317) |
| Indirect Effects (Y ⇐ M ⇐ X) | ||||||
| CG <- FA <- ER | 0.482 | 0.067 | 0.377 | 7.196 | <0.001 | (0.350; 0.613) |
| RE <- FA <- ER | 0.351 | 0.054 | 0.279 | 6.537 | <0.001 | (0.246; 0.457) |
| CG <- FA <- NU | 0.097 | 0.042 | 0.098 | 2.324 | 0.020 | (0.015; 0.179) |
| RE <- FA <- NU | 0.071 | 0.031 | 0.072 | 2.279 | 0.023 | (0.010; 0.132) |
| Total Effects (Y ⇐ X + [Y ⇐ M ⇐ X]) | ||||||
| CG <- ER + (CG <- FA <- ER) | 0.487 | 0.080 | 0.381 | 6.067 | <0.001 | (0.330; 0.644) |
| RE <- ER + (RE <- FA <- ER) | 0.309 | 0.076 | 0.246 | 4.092 | <0.001 | (0.161; 0.457) |
| CG <- NU + (CG <- FA <- NU) | 0.202 | 0.059 | 0.203 | 3.395 | 0.001 | (0.085; 0.318) |
| RE <- NU + (RE <- FA <- NU) | 0.295 | 0.056 | 0.302 | 5.319 | <0.001 | (0.187; 0.404) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, A.; Sinval, J.; Félix, S.; Guimarães, C.; Machado, B.C.; Gonçalves, S.; de Lourdes, M.; Conceição, E.M. Food Addiction and Grazing—The Role of Difficulties in Emotion Regulation and Negative Urgency in University Students. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204410
Ribeiro A, Sinval J, Félix S, Guimarães C, Machado BC, Gonçalves S, de Lourdes M, Conceição EM. Food Addiction and Grazing—The Role of Difficulties in Emotion Regulation and Negative Urgency in University Students. Nutrients. 2023; 15(20):4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204410
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Andreia, Jorge Sinval, Sílvia Félix, Carolina Guimarães, Bárbara César Machado, Sónia Gonçalves, Marta de Lourdes, and Eva M. Conceição. 2023. "Food Addiction and Grazing—The Role of Difficulties in Emotion Regulation and Negative Urgency in University Students" Nutrients 15, no. 20: 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204410
APA StyleRibeiro, A., Sinval, J., Félix, S., Guimarães, C., Machado, B. C., Gonçalves, S., de Lourdes, M., & Conceição, E. M. (2023). Food Addiction and Grazing—The Role of Difficulties in Emotion Regulation and Negative Urgency in University Students. Nutrients, 15(20), 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15204410








