Human Pancreatic Islets React to Glucolipotoxicity by Secreting Pyruvate and Citrate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethic Statement
2.2. Human Islet Isolation and Culture
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Insulin Assay
2.5. Triglyceride Assay
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Oil Red O Staining
2.8. Oxygen Consumption Rate
2.9. Sample Preparation for NMR Analyses
2.10. NMR Analysis and Data Processing
2.11. Metabolite Identification and Quantification
2.12. Multivariate Analysis on Exometabolome
2.13. Correlogram and Heat Map
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
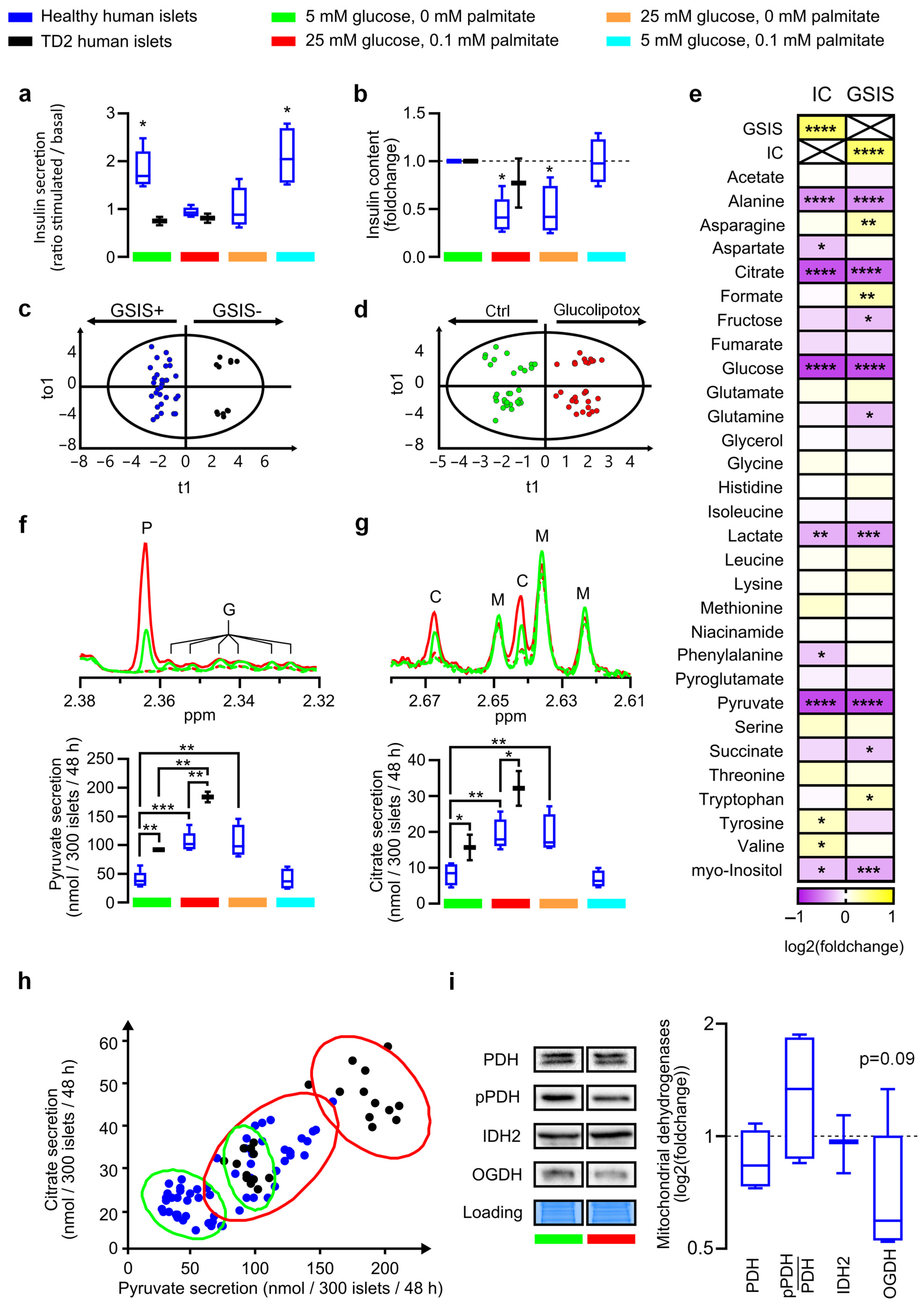
3.1. Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Increased Glucose Intake Promotes Loss of Function of Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion and Secretome Remodeling in Human Islets
3.2. Pyruvate and Citrate Secretion Are Biomarkers of Healthy Islets Alteration in the Glycolysis–TCA–Insulin Secretion Pathways
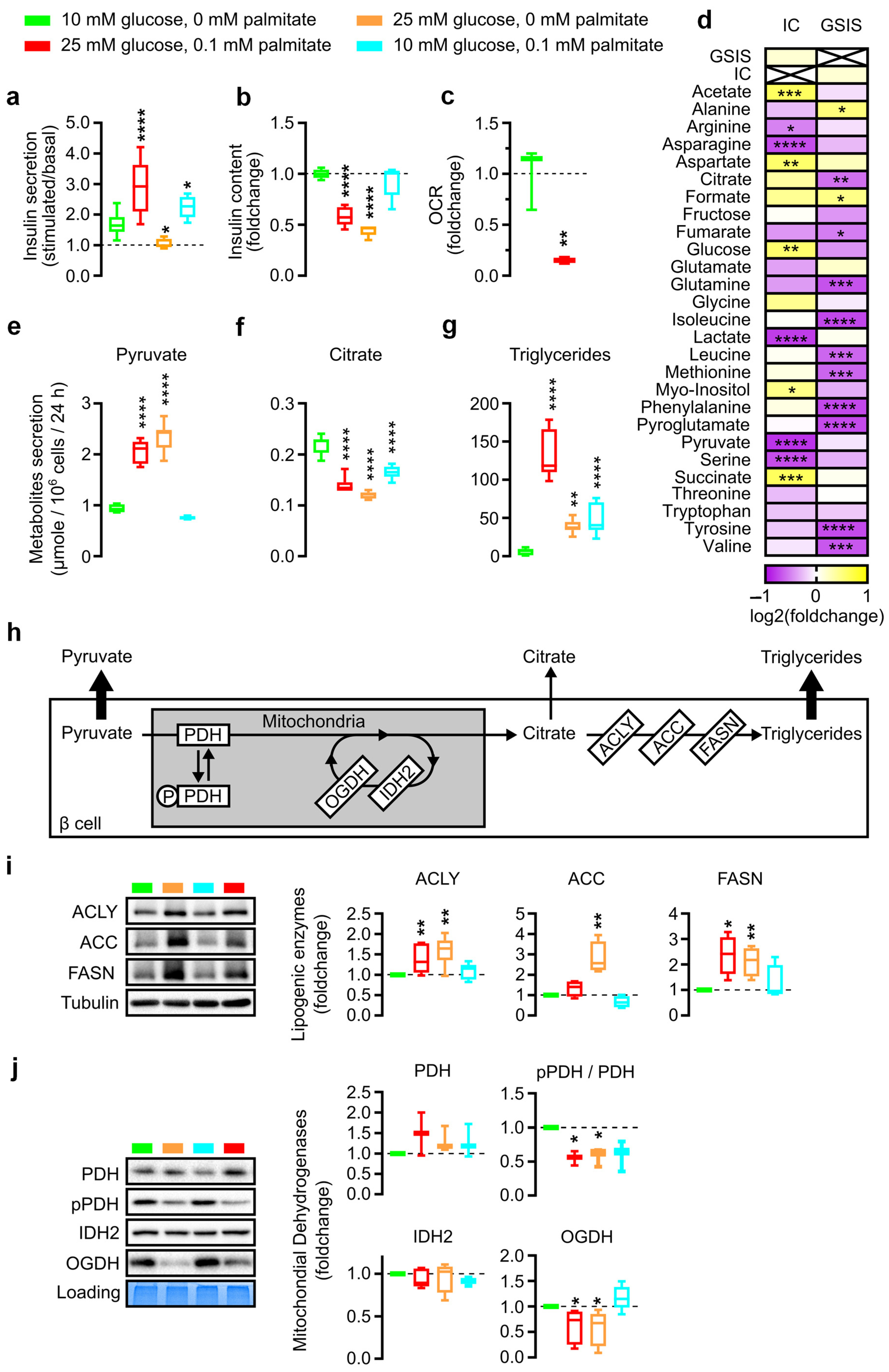
3.3. Rodent INS-1E Beta Cells Confirm and Modulate Glucolipotoxicity-Related Stopper in Glycolysis–TCA–Insulin Pathways
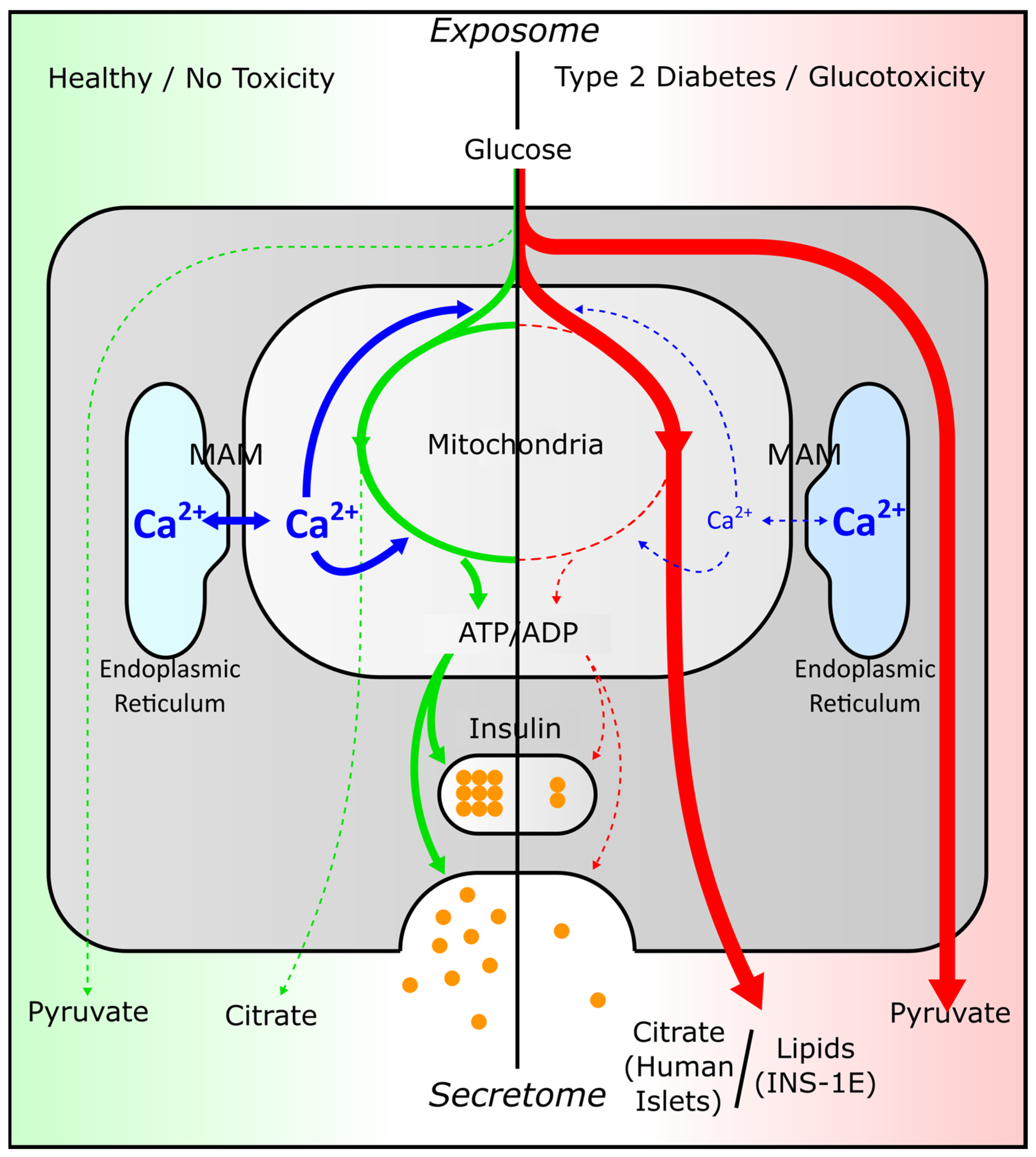
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bensellam, M.; Laybutt, D.R.; Jonas, J.-C. The Molecular Mechanisms of Pancreatic β-Cell Glucotoxicity: Recent Findings and Future Research Directions. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 364, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Korbutt, G.S.; Hellerström, C. Prolonged Exposure of Human Pancreatic Islets to High Glucose Concentrations In Vitro Impairs the Beta-Cell Function. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.B.; Alonso, L.C. Lipotoxicity in the Pancreatic Beta Cell: Not Just Survival and Function, but Proliferation as Well? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, G.C. Glucolipotoxicity, β-Cells, and Diabetes: The Emperor Has No Clothes. Diabetes 2020, 69, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, G.C.; Butler, P.C.; Bonner-Weir, S. The β-Cell Glucose Toxicity Hypothesis: Attractive but Difficult to Prove. Metabolism 2021, 124, 154870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmgren, S.; Nicholls, D.G.; Taneera, J.; Bacos, K.; Koeck, T.; Tamaddon, A.; Wibom, R.; Groop, L.; Ling, C.; Mulder, H.; et al. Tight Coupling between Glucose and Mitochondrial Metabolism in Clonal Beta-Cells Is Required for Robust Insulin Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32395–32404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, H.; Maechler, P.; Gjinovci, A.; Herrera, P.-L.; Wollheim, C.B. Islet Beta-Cell Secretion Determines Glucagon Release from Neighbouring Alpha-Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Matschinsky, F.M.; Madiraju, S.R.M. Metabolic Signaling in Fuel-Induced Insulin Secretion. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 162–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuit, F.C.; De Vos, A.; Moens, K.; Quartier, E.; Heimberg, H. Glucose-Induced B-Cell Recruitment and the Expression of Hexokinase Isoenzymes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1997, 426, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, N.; Cirulli, V.; Regazzi, R.; Brown, L.J.; Gine, E.; Tamarit-Rodriguez, J.; Girotti, M.; Marie, S.; MacDonald, M.J.; Woll-heim, C.B. Low Lactate Dehydrogenase and High Mitochondrial Glycerol Phosphate Dehydrogenase in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Potential Role in Nutrient Sensing. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitout, V.; Robertson, R.P. Glucolipotoxicity: Fuel Excess and Beta-Cell Dysfunction. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Raalte, D.H.; Diamant, M. Glucolipotoxicity and Beta Cells in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Target for Durable Therapy? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93 (Suppl. S1), S37–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Geng, B.; Cui, Q.; Guan, Y.; Yang, J. Intracellular and Extracellular Adenosine Triphosphate in Regulation of Insulin Secretion from Pancreatic β Cells (β). J. Diabetes 2014, 6, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antinozzi, P.A.; Ishihara, H.; Newgard, C.B.; Wollheim, C.B. Mitochondrial Metabolism Sets the Maximal Limit of Fuel-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in a Model Pancreatic Beta Cell: A Survey of Four Fuel Secretagogues. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11746–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.; Whelan, H.; Brennan, L. Metabolomic Analysis of Pancreatic Beta Cells Following Exposure to High Glucose. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousf, S.; Sardesai, D.M.; Mathew, A.B.; Khandelwal, R.; Acharya, J.D.; Sharma, S.; Chugh, J. Metabolic Signatures Suggest O-Phosphocholine to UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Ratio as a Potential Biomarker for High-Glucose and/or Palmitate Exposure in Pancreatic β-Cells. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugabo, Y.; Zhao, S.; Lamontagne, J.; Al-Mass, A.; Peyot, M.-L.; Corkey, B.E.; Joly, E.; Madiraju, S.R.M.; Prentki, M. Meta-bolic Fate of Glucose and Candidate Signaling and Excess-Fuel Detoxification Pathways in Pancreatic β-Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 7407–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haythorne, E.; Rohm, M.; van de Bunt, M.; Brereton, M.F.; Tarasov, A.I.; Blacker, T.S.; Sachse, G.; Silva Dos Santos, M.; Ter-ron Exposito, R.; Davis, S.; et al. Diabetes Causes Marked Inhibition of Mitochondrial Metabolism in Pancreatic β-Cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, F.; Seelig, A.; Humphrey, S.J.; Krahmer, N.; Volta, F.; Reggio, A.; Marchetti, P.; Gerdes, J.; Mann, M. Phosphoprote-omics Reveals the GSK3-PDX1 Axis as a Key Pathogenic Signaling Node in Diabetic Islets. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1422–1432.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spégel, P.; Mulder, H. Metabolomics Analysis of Nutrient Metabolism in β-Cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 1429–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.M.J.; Pokrywczynska, M.; Ricordi, C. Clinical Pancreatic Islet Transplantation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingreville, F.; Panthu, B.; Thivolet, C.; Ducreux, S.; Gouriou, Y.; Pesenti, S.; Chauvin, M.-A.; Chikh, K.; Errazuriz-Cerda, E.; Van Coppenolle, F.; et al. Differential Effect of Glucose on ER-Mitochondria Ca2+ Exchange Participates in Insulin Secretion and Glucotoxicity-Mediated Dysfunction of β-Cells. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1778–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefevre, C.; Panthu, B.; Naville, D.; Guibert, S.; Pinteur, C.; Elena-Herrmann, B.; Vidal, H.; Rautureau, G.J.P.; Mey, A. Met-abolic Phenotyping of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Reveals a Unique Signature and Intrinsic Differences between Fat Pads. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9323864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckonert, O.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Bundy, J.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic Profiling, Metabo-lomic and Metabonomic Procedures for NMR Spectroscopy of Urine, Plasma, Serum and Tissue Extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mili, M.; Panthu, B.; Madec, A.-M.; Berger, M.-A.; Rautureau, G.J.P.; Elena-Herrmann, B. Fast and Ergonomic Extraction of Adherent Mammalian Cells for NMR-Based Metabolomics Studies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 5453–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautureau, G.J.P.; Morio, B.; Guibert, S.; Lefevre, C.; Perrier, J.; Alves, A.; Chauvin, M.A.; Pinteur, C.; Monet, M.A.; Godet, M.; et al. Dietary Obesity in Mice Is Associated with Lipid Deposition and Metabolic Shifts in the Lungs Sharing Features with the Liver. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2018. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.-S.; Hyeon, J.-S.; Hwang, G.-S. Software-Assisted Serum Metabolite Quantification Using NMR. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 934, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Guo, M.; Li, Q.; Peng, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Cai, C. Plasma Metabolomic Profiling to Reveal Antipyretic Mechanism of Shuang-Huang-Lian Injection on Yeast-Induced Pyrexia Rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonville, J.M.; Richards, S.E.; Barton, R.H.; Boulange, C.L.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Dumas, M.-E. The Evolution of Partial Least Squares Models and Related Chemometric Approaches in Metabonomics and Metabolic Phenotyping. J. Chemom. 2010, 24, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, R.M.; Ghiasi, S.M.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Meier, S.; Lerche, M.H.; Ardenkjær-Larsen, J.H.; Jensen, P.R. Pancre-atic β-Cells Respond to Fuel Pressure with an Early Metabolic Switch. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.J.; Longacre, M.J.; Stoker, S.W.; Kendrick, M.; Thonpho, A.; Brown, L.J.; Hasan, N.M.; Jitrapakdee, S.; Fukao, T.; Hanson, M.S.; et al. Differences between Human and Rodent Pancreatic Islets: Low Pyruvate Carboxylase, Atp Citrate Lyase, and Pyruvate Carboxylation and High Glucose-Stimulated Acetoacetate in Human Pancreatic Islets. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 18383–18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerczyk, A.; Damblon, C.; Elena-Herrmann, B.; Panthu, B.; Rautureau, G.J.P. Metabolomic Approaches to Study Chemi-cal Exposure-Related Metabolism Alterations in Mammalian Cell Cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, Z.; Zhong, W.; Hao, Q.; Lei, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, D.; Xu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Temporal Transcriptomic and Proteomic Landscapes of Deteriorating Pancreatic Islets in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2188–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensellam, M.; Van Lommel, L.; Overbergh, L.; Schuit, F.C.; Jonas, J.C. Cluster Analysis of Rat Pancreatic Islet Gene mRNA Levels after Culture in Low-, Intermediate- and High-Glucose Concentrations. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, E.; Assimacopoulos-Jeannet, F.; Witters, L.A.; Perruchoud, B.; Yaney, G.; Corkey, B.; Asfari, M.; Prentki, M. Induction by Glucose of Genes Coding for Glycolytic Enzymes in a Pancreatic Beta-Cell Line (INS-1). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichler, M.; Borgmann, D.; Krumsiek, J.; Buck, A.; MacDonald, P.E.; Fox, J.E.M.; Lyon, J.; Light, P.E.; Keipert, S.; Jastroch, M.; et al. N-Acyl Taurines and Acylcarnitines Cause an Imbalance in Insulin Synthesis and Secretion Provoking β Cell Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1334–1347.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madec, A.-M.; Perrier, J.; Panthu, B.; Dingreville, F. Role of Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane (MAMs) Interactions and Calcium Exchange in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 363, 169–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Donor | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | D11 | Mean | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| identifier | HP 1907 | HP 1905 | HP 1908 | HO 2001 | HP 1910 | HI-28 | HI-29 | HI-20 | HM 88 | HM 84 | HM 92 | ||
| Origin of islets | CEED | CEED | CEED | CEED | CEED | ECIT | ECIT | ECIT | LCTD | LCTD | LCTD | ||
| isolation centre | Strasbourg | Strasbourg | Strasbourg | Strasbourg | Strasbourg | Geneva | Geneva | Geneva | Montpellier | Montpellier | Montpellier | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.9 | 19.1 | 20.5 | 26.7 | 27.8 | 21.9 | 25.6 | 27.2 | 26 | 30.5 | 30.1 | 25.6 | 3.7 |
| age (years) | 58 | 60 | 86 | 64 | 61 | 55 | 59 | 46 | 26 | 62 | 68 | 58.6 | 14.6 |
| Sex (M/F) | M | M | F | F | M | F | M | M | M | M | M | 27% F/73% M | |
| plasma glucose test | <11.1 mmol/L | <11.1 mmol/L | ND | ND | <11.1 mmol/L | <11.1 mmol/L | <11.1 mmol/L | <11.1 mmol/L | ND | <11.1 mmol/L | ND | ||
| cause of death | Stroke | Stroke | subdural hematoma | Stroke | Stroke | no death (auto-transplantation) | Stroke | Stroke | Suicide | Trauma | Trauma | ||
| Warm ischemia time | 54 min | 2 min 30 | 35 min | <2 h | <2 h | <2 h | <2 h | 62 min | <2 h | <2 h | <2 h | ||
| Donor history of diabete? | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | T2D | T2D | ||
| therapy at time of death | Metformin | Metformin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perrier, J.; Nawrot, M.; Madec, A.-M.; Chikh, K.; Chauvin, M.-A.; Damblon, C.; Sabatier, J.; Thivolet, C.H.; Rieusset, J.; Rautureau, G.J.P.; et al. Human Pancreatic Islets React to Glucolipotoxicity by Secreting Pyruvate and Citrate. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224791
Perrier J, Nawrot M, Madec A-M, Chikh K, Chauvin M-A, Damblon C, Sabatier J, Thivolet CH, Rieusset J, Rautureau GJP, et al. Human Pancreatic Islets React to Glucolipotoxicity by Secreting Pyruvate and Citrate. Nutrients. 2023; 15(22):4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224791
Chicago/Turabian StylePerrier, Johan, Margaux Nawrot, Anne-Marie Madec, Karim Chikh, Marie-Agnès Chauvin, Christian Damblon, Julia Sabatier, Charles H. Thivolet, Jennifer Rieusset, Gilles J. P. Rautureau, and et al. 2023. "Human Pancreatic Islets React to Glucolipotoxicity by Secreting Pyruvate and Citrate" Nutrients 15, no. 22: 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224791
APA StylePerrier, J., Nawrot, M., Madec, A.-M., Chikh, K., Chauvin, M.-A., Damblon, C., Sabatier, J., Thivolet, C. H., Rieusset, J., Rautureau, G. J. P., & Panthu, B. (2023). Human Pancreatic Islets React to Glucolipotoxicity by Secreting Pyruvate and Citrate. Nutrients, 15(22), 4791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15224791







