Effect of Gestational Weight Gain during the First Half of Pregnancy on the Incidence of GDM, Results from a Pregnant Cohort in Northern Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Variables and Population Characteristics
2.2. Calculation of Weight Gain
2.3. Estimation of Expected Weight Gain Ranges
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolu, P.; Raitanen, J.; Rissanen, P.; Luoto, R. Health care costs associated with gestational diabetes mellitus among high-risk women—Results from a randomised trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2012, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Dainelli, L.; Yu, K.; Ma, L.; Zolezzi, I.S.; Detzel, P.; Fang, H. The short-term health and economic burden of gestational diabetes mellitus in China: A modelling study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e018893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42 (Suppl. S1), S13–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Catalano, P.; Zhang, C.; Desoye, G.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Damm, P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, É.D.; Saunders, C.; do Carmo, C.N.; de Aquino Lacerda, E.M.; Zajdenverg, L.; de Castro, M.B.; de Almeida, N.F.; de Carvalho Padilha, P. Gestational weight gain and adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes among women with gestational diabetes mellitus according to International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Group (IADPSG) criteria: A cross sectional study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 50, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, M.; Langen, E.; Davis, M.B. Pregnancy Complications as a Window to Future Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiol. Rev. 2020, 28, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.B.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Hull, R.L.; Tong, J.; Wallace, T.M.; Kodama, K.; Shofer, J.B.; Heckbert, S.R.; Boyko, E.J.; Fujimoto, W.Y.; et al. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Increases the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Women with a Family History of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2078–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, L.; Casas, J.-P.; Hingorani, A.D.; Williams, D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2009, 373, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranidou, A.; Dagklis, T.; Tsakiridis, I.; Siargkas, A.; Apostolopoulou, A.; Mamopoulos, A.; Goulis, D.G.; Chourdakis, M. Risk of developing metabolic syndrome after gestational diabetes mellitus—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 44, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S.E.V.; Chávez-González, E.L. Obstetric-Neonatal Complications of Gestational Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Mex. J. Med. Res. ICSA 2023, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaza, N.; Masete, M.; Adam, S.; Dias, S.; Nyawo, T.; Pheiffer, C. A Systematic Review to Compare Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Women with Pregestational Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, E.C.; Denison, F.C.; Norman, J.E.; Reynolds, R.M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms, Treatment, and Complications. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, Y.; Marks, D.J.; Grossman, B.; Yoon, M.; Loudon, H.; Stone, J.; Halperin, J.M. Exposure to gestational diabetes mellitus and low socioeconomic status: Effects on neurocognitive development and risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in offspring. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2012, 166, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Ornoy, A.; Reece, E.A.; Pavlinkova, G.; Kappen, C.; Miller, R.K. Effect of maternal diabetes on the embryo, fetus, and children: Congenital anomalies, genetic and epigenetic changes and developmental outcomes. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2015, 105, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenoue, S.; Miyakoshi, K.; Kasuga, Y.; Ochiai, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Tanaka, M. Impaired fetal growth in mothers with inadequate gestational weight gain: A retrospective study in Japanese uncomplicated pregnancy. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2018, 33, 2227–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedderson, M.M.; Gunderson, E.P.; Ferrara, A. Gestational Weight Gain and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 115, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine; National Research Council. Weight Gain during Pregnancy: Re-Examining the Guidelines; Rasmussen, K.M., Yaktine, A.L., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; 1. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Gao, J.; He, Z.; Ji, J.; Zhang, W.; Wu, P.; Guo, X.; Cao, D.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.; et al. What is an appropriate gestational weight gain for women with gestational diabetes mellitus: Based on the adverse pregnancy outcomes of over 12 thousand participants? Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.-H.; Chen, S.-F.; Hsu, J.-J.; Hsieh, T.-T. Gestational weight gain and risks for adverse perinatal outcomes: A retrospective cohort study based on the 2009 Institute of Medicine guidelines. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 54, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.Y.; Callaghan, W.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Schmid, C.H.; Lau, J.; England, L.J.; Dietz, P.M. Maternal Obesity and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiridis, I.; Giouleka, S.; Mamopoulos, A.; Kourtis, A.; Athanasiadis, A.; Filopoulou, D.; Dagklis, T. Diagnosis and Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: An Overview of National and International Guidelines. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2021, 76, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, P.M. Trying to understand gestational diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powe, C.E.; Allard, C.; Battista, M.-C.; Doyon, M.; Bouchard, L.; Ecker, J.L.; Perron, P.; Florez, J.C.; Thadhani, R.; Hivert, M.-F. Heterogeneous Contribution of Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion Defects to Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C. Gestational diabetes: Risks, management, and treatment options. Int. J. Women’s Health 2010, 2, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, C.L.; Lombard, C.B.; Strauss, B.J.; Teede, H.J. Optimizing healthy gestational weight gain in women at high risk of gestational diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Obesity 2013, 21, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskovi-Kaplan, Z.A.; Ozgu-Erdinc, A.S. Management of gestational diabetes mellitus. In Diabetes: From Research to Clinical Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Hellenic Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology Emergency. Gestational Diabetes and Pregnancy: Gestational Diabetes; Guideline No 36; EMGE: Athens, Greece, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- International Association of Diabetes; Pregnancy Study Groups Consensus Panel. International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, C.B.; Jan, A. BMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ren, X.; He, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W. Maternal age and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of over 120 million participants. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwash, S.M.; McIntyre, H.D.; Mamun, A. The association of general obesity, central obesity and visceral body fat with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 15, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboudi-Gandevani, S.; Amiri, M.; Bidhendi Yarandi, R.; Ramezani Tehrani, F. The impact of diagnostic criteria for gestational diabetes on its prevalence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, K.S.; Waters, T.P.; Catalano, P.M. Maternal Weight Gain in Women Who Develop Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 119, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Sharma, A.J.; Sappenfield, W.; Wilson, H.G.; Salihu, H.M. Association of Maternal Body Mass Index, Excessive Weight Gain, and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus with Large-for-Gestational-Age Births. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 123, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberico, S.; Montico, M.; Barresi, V.; Monasta, L.; Businelli, C.; Soini, V.; Erenbourg, A.; Ronfani, L.; Maso, G.; for the Multicentre Study Group on Mode of Delivery in Friuli Venezia Giulia. The role of gestational diabetes, pre-pregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain on the risk of newborn macrosomia: Results from a prospective multicentre study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2014, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Chung, J.H.; Kurbisch-Block, I.; Inturrisi, M.; Shafer, S.; Caughey, A.B. Gestational weight gain and gestational diabetes mellitus: Perinatal outcomes. Obstet.Gynecol. 2008, 112, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautredou, M.; Pan-Petesch, B.; Dupré, P.-F.; Drugmanne, G.; Nowak, E.; Anouilh, F.; Briend, D.; Salomon, C.; Gourhant, L.; Le Moigne, E.; et al. Excessive gestational weight gain is an independent risk factor for gestational diabetes mellitus in singleton pregnancies: Results from a French cohort study. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2022, 275, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Jin, J.; Hu, K.-L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D. Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Gestational Weight Gain Restriction in Overweight/Obese Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.; Vermeulen, M.; Shapiro, J.; Kenshole, A. Maternal and neonatal outcomes in pregestational and gestational diabetes mellitus, and the influence of maternal obesity and weight gain: The DEPOSIT study. Qjm Int. J. Med. 2001, 94, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komem, D.; Salman, L.; Krispin, E.; Arbib, N.; Bardin, R.; Wiznitzer, A.; Hadar, E. Gestational weight gain and weight loss among women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 141, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hortelano, J.A.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Garrido-Miguel, M.; Soriano-Cano, A.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V. Monitoring gestational weight gain and prepregnancy BMI using the 2009 IOM guidelines in the global population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhalima, K.; Van Crombrugge, P.; Moyson, C.; Verhaeghe, J.; Vandeginste, S.; Verlaenen, H.; Vercammen, C.; Maes, T.; Dufraimont, E.; De Block, C.; et al. Characteristics and pregnancy outcomes across gestational diabetes mellitus subtypes based on insulin resistance. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2118–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Qiu, D.; Liu, X.; Xing, Q.; Liu, R.; Hu, Y. The incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus among women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ni, Y. Association between Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2022, 87, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosdou, J.K.; Anagnostis, P.; Goulis, D.G.; Lainas, G.T.; Tarlatzis, B.C.; Grimbizis, G.F.; Kolibianakis, E.M. Risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in women achieving singleton pregnancy spontaneously or after ART: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2020, 26, 514–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, M.H.; Sacks, D.A.; Xiang, A.H.; Lawrence, J.M. The Relative Contribution of Prepregnancy Overweight and Obesity, Gestational Weight Gain, and IADPSG-Defined Gestational Diabetes Mellitus to Fetal Overgrowth. Diabetes Care 2012, 36, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, K.; Aoki, S.; Toma, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Sakamaki, K.; Hirahara, F. Pregnancy Outcomes Based on Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index in Japanese Women. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Song, W.O. Prepregnancy body mass index is an independent risk factor for gestational hypertension, gestational diabetes, preterm labor, and small- and large-for-gestational-age infants. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2014, 28, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Chen, L.; Tan, K.; Ang, L.T.; Ho, C.; Wong, G.; Soh, S.E.; Tan, K.H.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Godfrey, K.M.; et al. Population-centric risk prediction modeling for gestational diabetes mellitus: A machine learning approach. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 185, 109237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisset, A.-S.; Tchernof, A.; Dubé, M.-C.; Veillette, J.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Robitaille, J. Weight Gain Measures in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Women’s Health 2011, 20, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, N.; Hendrickson, A.F.; Schellenbaum, G.D.; Mueller, B.A. Weight Change and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes in Obese Women. Epidemiology 2004, 15, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GDM (n = 325) | Non-GDM (n = 5623) | Statistic [CI] for Incidence or Likelihood of GDM | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA (years) mean ± sd | 33.7 ± 5.47 | 31.6 ± 5.25 | 1.99 [1.39, 2.60] | <0.0001 |
| MA > 35 years old (n%) | 124 (38.2%) | 1464 (26%) | 1.75 [1.37, 2.22] | <0.0001 |
| Smoking (n%) | 48 (14.8%) | 759 (13.5%) | 1.18 [0.79, 1.52] | 0.50 |
| Thyroid disease (n%) | 19 (5.85%) | 348 (6.19%) | 1.19 [0.55, 1.51] | 0.90 |
| Parity (n%) | 142 (43.7%) | 2665 (47.4%) | 0.86 [0.68, 1.08] | 0.20 |
| Gravidity mean ± sd | 0.55 ± 0.7 | 0.61 ± 0.78 | −5.34 × 10−5 [−2.18, 8.15] | 0.41 |
| Conception with ART (n%) | 29 (8.92%) | 252 (4.48%) | 2.08 [1.34, 3.13] | 0.01 |
| Wt pre (kg) mean ± sd | 72.6 ± 16.6 | 65.6 ± 13.6 | 5.99 [4.50, 7.00] | <0.0001 |
| BMI pre mean ± sd | 26.5 ± 5.75 | 23.9 ± 4.7 | 2.20 [1.70, 2.70] | <0.0001 |
| UW pre (n%) | 10 (3.08%) | 292 (5.19%) | 0.57 [0.27, 1.09] | 0.11 |
| NW pre (n%) | 153 (47.1%) | 3615 (64.3%) | 0.49 [0.39, 0.62] | <0.0001 |
| OW pre (n%) | 81 (24.9%) | 1100 (19.6%) | 1.36 [1.03, 1.77] | 0.021 |
| OB1 pre (n%) | 53 (16.3%) | 422 (7.5%) | 2.40 [1.72, 3.29] | <0.0001 |
| OB2 pre (n%) | 17 (5.23%) | 145 (2.58%) | 2.08 [1.16, 3.51] | 0.008 |
| OB3 pre (n%) | 11 (3.38%) | 49 (0.87%) | 3.98 [1.84–7.86] | 0.0003 |
| GWG (kg) mean ± sd | 6.57 ± 4.41 | 6.49 ± 3.93 | 7.01 [−5.73, 0.30] | 0.95 |
| UW now (n%) | 2 (0.62%) | 32 (0.57%) | 1.08 [0.12, 4.27] | 0.79 |
| NW now (n%) | 90 (27.7%) | 2647 (47.1%) | 0.43 [0.33, 0.55] | <0.0001 |
| OW now (n%) | 118 (36.3%) | 1911 (34%) | 1.10 [0.86, 1.40] | 0.39 |
| OB1 now (n%) | 70 (21.5%) | 713 (12.7%) | 1.89 [1.41, 2.50] | <0.0001 |
| OB2 now (n%) | 25 (7.7%) | 244 (4.34%) | 2.82 [1.14, 2.83] | 0.008 |
| OB3 now (n%) | 20 (6.15%) | 76 (1.35%) | 4.78 [2.73, 8.03] | <0.0001 |
| BMI now mean ± sd | 28.9 ± 5.8 | 26.4 ± 4.7 | 2.36 [1.84, 2.89] | <0.0001 |
| Gestational Weight Gain Category | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wgcat Less n (%) | Wgcat Normal n (%) | Wgcat More n (%) | |||||||
| GDM | Non-GDM | p Value | GDM | Non-GDM | p Value | GDM | Non-GDM | p Value | |
| UW pre | 3 (5%) | 46 (5.5%) | 1 | 3 (5.08%) | 92 (6.72%) | 0.79 | 4 (1.94%) | 154 (4.51%) | 0.11 |
| NW pre | 21 (35%) | 483 (57.7%) | 0.0007 | 29 (49.2%) | 967 (70.6%) | 0.0008 | 103 (50%) | 2165 (63.4%) | 0.0001 |
| OW pre | 13 (21.7%) | 162 (19.4%) | 0.61 | 14 (23.7%) | 177 (12.9%) | 0.03 | 54 (26.2%) | 761 (22.3%) | 0.2 |
| OB1 pre | 12 (20%) | 80 (9.56%) | 0.02 | 10 (17%) | 95 (6.94%) | 0.009 | 31 (15.1%) | 247 (7.23%) | 0.0002 |
| OB2 pre | 4 (6.67%) | 48 (5.73%) | 0.77 | 2 (3.39%) | 30 (2.19%) | 0.38 | 11 (5.34%) | 67 (1.96%) | 0.004 |
| OB3 pre | 7 (11.7%) | 18 (2.15%) | 0.0008 | 1 (1.69%) | 8 (0.58%) | 0.31 | 3 (1.46%) | 23 (0.67%) | 0.18 |
| Total | 60 | 837 | - | 59 | 1369 | - | 206 | 3417 | - |
| Mean Weight Changes for All Subgroups (kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDM (Ν = 325) | Non-GDM (Ν = 5623) | ||||
| UW | 10 | 6.4 ± 3.34 | 292 | 7.26 ± 3.68 | |
| NW | 153 | 7.22 ± 3.94 | 3616 | 6.79 ± 3.43 | |
| OW | 81 | 6.84 ± 4.43 | 1100 | 6.36 ± 4.19 | |
| OB1 | 53 | 5.16 ± 4.64 | 422 | 5.34 ± 5.01 | |
| OB2 | 17 | 7.06 ± 6.22 | 145 | 3.48 ± 5.26 | |
| OB3 | 11 | 1.73 ± 3.2 | 49 | 1.71 ± 7.69 | |
| UW | NW | OW | OB1 | OB2 | OB3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic [CI] | p | Statistic [CI] | p | Statistic [CI] | p | Statistic [CI] | p | Statistic [CI] | p | Statistic [CI] | p | Statistic Name | |
| MA > 35 years | 3.54 [0.7, 15.6] | 1 | 1.72 [1.21, 2.44] | 0.13 | 1.51 [0.90, 2.48] | 1 | 1.30 [0.67, 2.48] | 1 | 1.90 [0.59, 5.96] | 1 | 4.25 [0.91, 23.1] | 1 | Odds ratio |
| Parity | 0.74 [0.12, 3.33] | 1 | 0.77 [0.54, 1.09] | 0.53 | 0.68 [0.42, 1.10] | 1 | 0.73 [0.39, 1.36] | 1 | 1.09 [0.35, 3.59] | 1 | 1.97 [0.40, 13.0] | 1 | Odds ratio |
| Hypothyroidism | - | - | 1.46 [0.56, 3.18] | 0.92 | 1.69 [0.13, 2.20] | 1 | 0.43 [0.01, 2.85] | 1 | 1.00 [0.10, 4.95] | 1 | 1.93 [0.16, 14.4] | 1 | Odds ratio |
| Wt pre | 0.05 [−2.59, 2.73] | 0.97 | 1.99 [0.99, 2.99] | 0.003 | 1.76 [−1.0, 1.99] | 0.86 | 1.00 [−0.99, 3.99] | 0.84 | −0.99 [−5.00, 3.90] | 0.66 | −0.20 [−8.99, 7.33] | 0.95 | W statistic |
| Wt now | −0.41 [−4.52, 2.95] | 0.97 | 2.00 0.99, 3.00] | 0.002 | 0.99 [−1.0, 2.99] | 0.77 | 1.00 [−1.0, 4.0] | 0.84 | 0.99 [−2.64, 8.05] | 0.38 | 3.77 [−7.00, 6.99] | 0.95 | W statistic |
| BMI now | −0.39 [−1.46, 0.73] | 0.97 | 0.79 [0.42, 1.16] | 0.0002 | 0.33 [−0.13, 0.75] | 0.44 | 0.21 [−0.45, 0.85] | 0.84 | 3.16 [0.69, 2.99] | 0.03 | −0.53 [−2.08, 1.20] | 0.95 | W statistic |
| GWG | −0.99 [−3.00, 1.50] | 0.97 | 1.07 [−6.65, 0.99] | 0.20 | 3.00 [−0.99, 1.00] | 0.77 | −2.60 [−1.99, 1.00] | 0.84 | 2.60 [0.87, 6.30] | 0.06 | −1.00 [−4.99, 1] | 0.95 | W statistic |
| Weight Gain Categories | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wgcat Less | Wgcat Normal | Wgcat More | |
| WGextra | 1.09 [0.98, 1.24] | 0.87 [0.59, 1.27] | 1.03 [0.98, 1.07] |
| MA | 1.05 [1.003, 1.11] | 1.08 [1.02, 1.15] | 1.09 [1.05, 1.12] |
| Gravidity | 0.87 [0.59, 1.24] | 0.96 [0.67, 1.31] | 0.65 [0.51, 0.80] |
| Smoking | 1.004 [0.37, 2.28] | 1.44 [0.67, 2.83] | 0.98 [0.65, 1.45] |
| Thyroid disease | 0.32 [0.05, 1.12] | 0.57 [0.13, 1.61] | 0.99 [0.53, 1.69] |
| BMI pre | 1.08 [1.04, 1.12] | 1.09 [1.04, 1.14] | 1.09 [1.06, 1.12] |
| Conception ART | 0.83 [0.18, 2.57] | 1.54 [0.47, 4.10] | 1.10 [0.62, 1.84] |
| UW Pre | NW Pre | OW Pre | OB1 Pre | OB2 Pre | OB3 Pre | Total Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wgcat less | 3.37 [0.65, 14.71] | 1.09 [0.66, 1.73] | 1.18 [0.60, 2.14] | 1.27 [0.61, 2.49] | 0.63 [0.15, 2.10] | 4.17 [0.82, 25.56] | 1.18 [0.86, 1.58] |
| Wgcat normal | 1.07 [0.22, 4.13] | 0.67 [0.43, 1.00] | 1.09 [0.57, 1.94] | 0.86 [0.39, 1.73] | 0.55 [0.08, 2.30] | 0.34 [0.01, 2.67] | 0.78 [0.57, 1.03] |
| Wgcat more | 0.43 [0.10, 1.63] | 1.28 [0.91, 1.83] | 0.85 [0.52, 1.41] | 0.93 [0.51, 1.69] | 1.98 [0.66, 6.48] | 0.40 [0.05, 2.24] | 1.07 [0.85, 1.36] |
| WGextra | 0.85 [0.68, 1.03] | 1.01 [0.97, 1.06] | 1.01 [0.95, 1.06] | 0.99 [0.93, 1.04] | 1.12 [1.01, 1.26] | 0.97 [0.86, 1.12] | 1.01 [0.99, 1.04] |
| MA | 1.18 [1.02, 1.39] | 1.09 [1.05, 1.12] | 1.07 [1.02, 1.13] | 1.05 [1.00, 1.12] | 1.06 [0.96, 1.19] | 1.26 [1.04, 1.63] | 1.08 [1.06, 1.11] |
| Gravidity | 0.94 [0.28, 2.47] | 0.67 [0.51, 0.86] | 0.74 [0.53, 1.01] | 0.77 [0.51, 1.10] | 0.89 [0.43, 1.60] | 0.54 [0.16, 1.60] | 0.75 [0.63, 0.88] |
| Smoking | 1.83 [0.34, 8.27] | 0.80 [0.44, 1.34] | 1.00 [0.49, 1.89] | 1.14 [0.53, 2.28] | 1.94 [0.48, 6.67] | 1.91 [0.39, 9.70] | 1.06 [0.76, 1.45] |
| Thyroid disease | 3.68 [0.18, 26.94] | 0.84 [0.39, 1.61] | 0.39 [0.09, 1.10] | 0.60 [0.09, 2.11] | 0.89 [0.13, 3.60] | 2.06 [0.24, 13.11] | 0.73 [0.43, 1.16] |
| BMI pre | 0.86 [0.38, 2.36] | 1.24 [1.13, 1.37] | 1.09 [0.92, 1.29] | 1.04 [0.84, 1.28] | 1.36 [0.93, 2.00] | 0.92 [0.63, 1.21] | 1.09 [1.07, 1.11] |
| Conception ART | 4.68 [0.21, 41.06] | 1.11 [0.58, 1.99] | 1.67 [0.67, 3.76] | 0.54 [0.08, 2.12] | 0.75 [0.03, 5.28] | 0.29 [0.008, 4.29] | 1.15 [0.73, 1.77] |
| UW Now | NW Now | OW Now | OB1 Now | OB2 Now | OB3 Now | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wgcat less | - | 1.17 [0.66, 1.98] | 1.34 [0.70, 2.43] | 1.35 [0.58, 2.98] | 1.03 [0.20, 4.16] | 5.00 [1.14, 23.69] |
| Wgcat normal | - | 0.90 [0.55, 1.41] | 0.65 [0.36, 1.10] | 0.96 [0.45, 1.91] | 1.24 [0.33, 3.79] | 0.34 [0.01, 2.17] |
| Wgcat more | - | 0.99 [0.63, 1.55] | 1.19 [0.75, 1.93] | 0.84 [0.43, 1.65] | 0.80 [0.25, 2.65] | 0.47 [0.12, 1.75] |
| WGextra | - | 0.98 [0.90, 1.05] | 0.99 [0.92, 1.05] | 1.05 [0.97, 1.14] | 0.97 [0.84, 1.10] | 0.95 [0.84, 1.06] |
| MA | - | 1.09 [1.05, 1.14] | 1.06 [1.02, 1.11] | 1.10 [1.04, 1.16] | 0.99 [0.92, 1.07] | 1.19 [1.04, 1.39] |
| Gravidity | - | 0.59 [0.40, 0.85] | 0.82 [0.63, 1.05] | 0.60 [0.41, 0.86] | 0.93 [0.52, 1.51] | 0.80 [0.35, 1.76] |
| Smoking | - | 1.16 [0.55, 2.20] | 0.70 [0.36, 1.25] | 1.28 [0.64, 2.40] | 1.16 [0.40, 3.01] | 1.56 [0.45, 5.13] |
| Thyroid disease | - | 1.20 [0.45, 2.63] | 0.47 [0.16, 1.08] | 0.81 [0.23, 2.13] | 0.38 [0.02, 1.98] | 2.27 [0.41, 10.49] |
| BMI pre | - | 1.21 [1.06, 1.38] | 1.12 [1.02, 1.23] | 1.05 [0.95, 1.16] | 0.88 [0.74, 1.05] | 0.96 [0.81, 1.11] |
| Conception ART | - | 1.20 [0.51, 2.51] | 0.89 [0.37, 1.89] | 2.03 [0.80, 4.80] | 0.64 [0.03, 3.9] | 1.23 [0.11, 10.4] |
| BMI Shifts | BMI Classification Shifts at 20+0–23+6 Weeks of Gestation | |
|---|---|---|
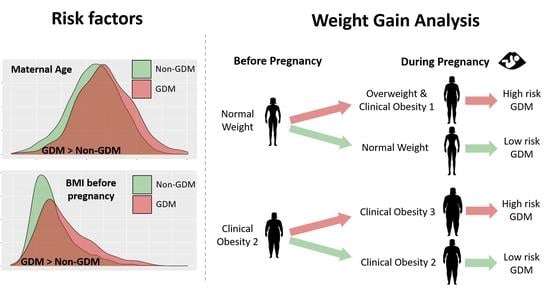
| NW pre → NW now | 0.60 [0.43, 0.85] | Lower in GDM |
| NW pre → OW now | 1.52 [1.08, 2.14] | Higher in GDM |
| NW pre → OB1 now | 4.38 [1.08, 13.13] | Higher in GDM |
| OB1 pre → OB1 now | 0.77 [0.41, 1.46] | NS |
| OB1 pre → OB2 now | 1.19 [0.61, 2.26] | NS |
| OB2 pre → OB2 now | 0.26 [0.07, 0.81] | Lower in GDM |
| OB2 pre → OB3 now | 4.85 [1.50, 15.95] | Higher in GDM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tranidou, A.; Magriplis, E.; Tsakiridis, I.; Pazaras, N.; Apostolopoulou, A.; Chourdakis, M.; Dagklis, T. Effect of Gestational Weight Gain during the First Half of Pregnancy on the Incidence of GDM, Results from a Pregnant Cohort in Northern Greece. Nutrients 2023, 15, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040893
Tranidou A, Magriplis E, Tsakiridis I, Pazaras N, Apostolopoulou A, Chourdakis M, Dagklis T. Effect of Gestational Weight Gain during the First Half of Pregnancy on the Incidence of GDM, Results from a Pregnant Cohort in Northern Greece. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040893
Chicago/Turabian StyleTranidou, Antigoni, Emmanuela Magriplis, Ioannis Tsakiridis, Nikolaos Pazaras, Aikaterini Apostolopoulou, Michail Chourdakis, and Themistoklis Dagklis. 2023. "Effect of Gestational Weight Gain during the First Half of Pregnancy on the Incidence of GDM, Results from a Pregnant Cohort in Northern Greece" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040893
APA StyleTranidou, A., Magriplis, E., Tsakiridis, I., Pazaras, N., Apostolopoulou, A., Chourdakis, M., & Dagklis, T. (2023). Effect of Gestational Weight Gain during the First Half of Pregnancy on the Incidence of GDM, Results from a Pregnant Cohort in Northern Greece. Nutrients, 15(4), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040893