Is Circulating Vitamin D Status Associated with the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism? A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources of Data and Search Strategies
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Outcomes and Definitions
2.5. Data Synthesis and Analysis
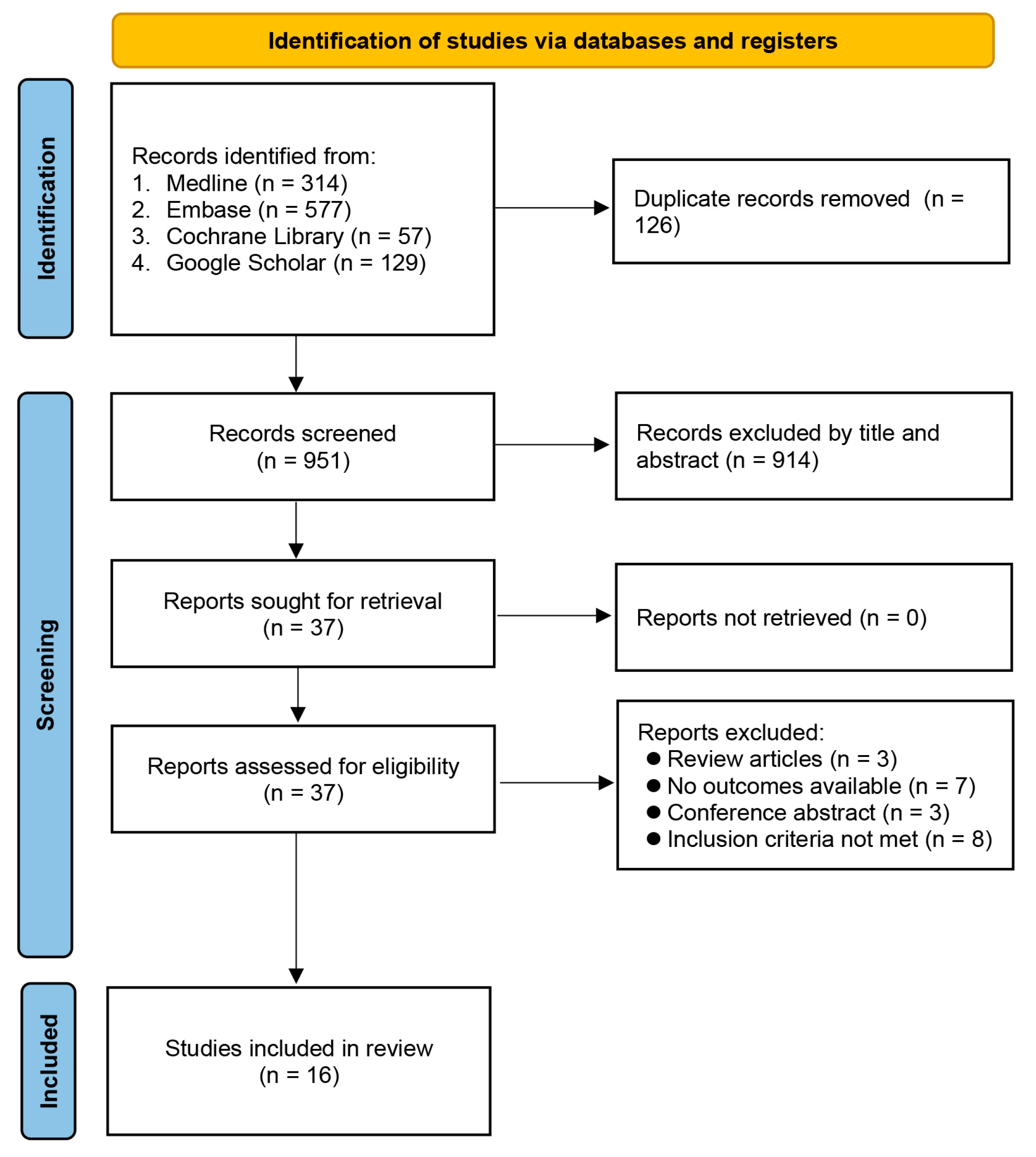
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection, Characteristics of Studies, and Risk of Bias Assessment
3.2. Outcomes
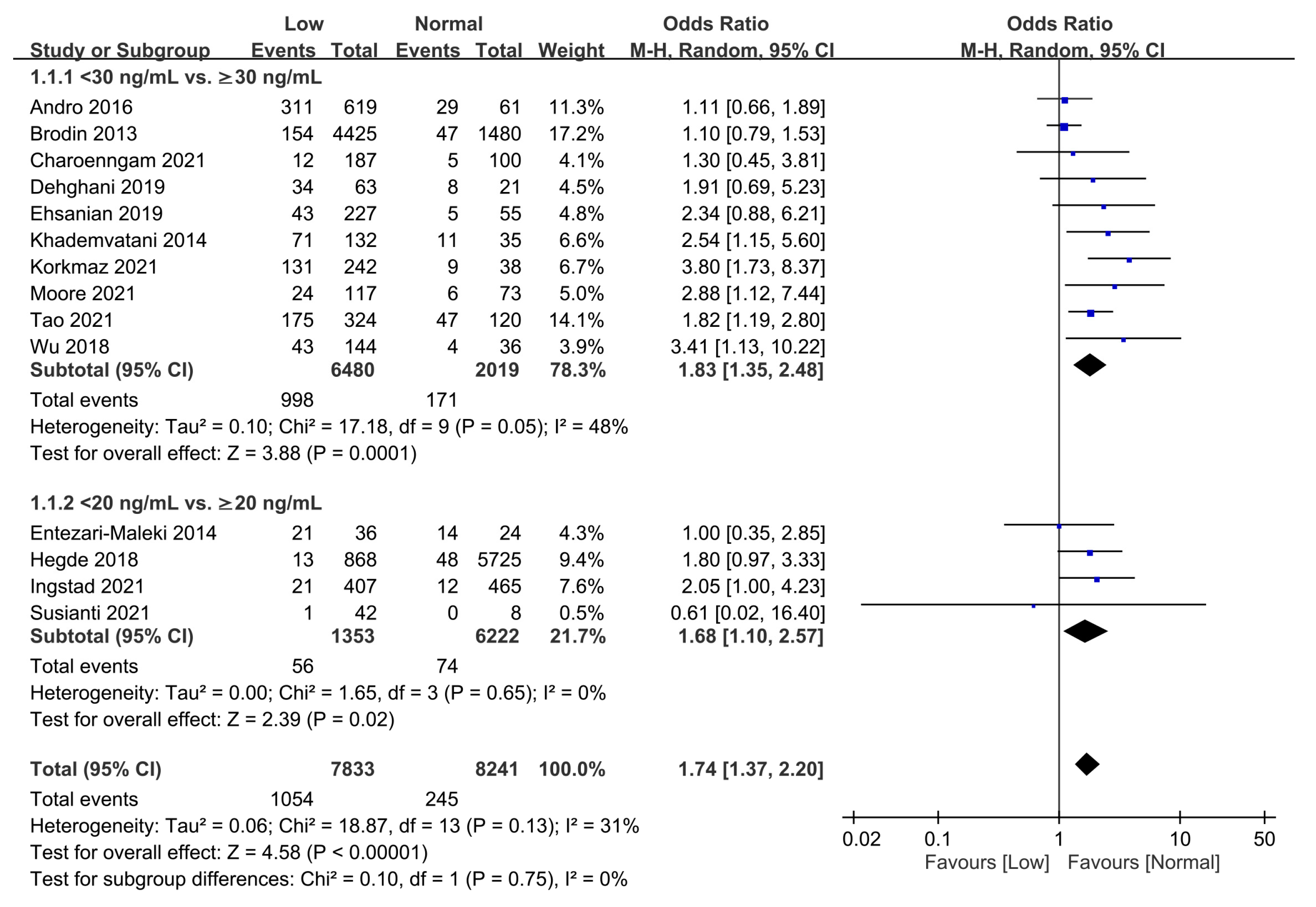
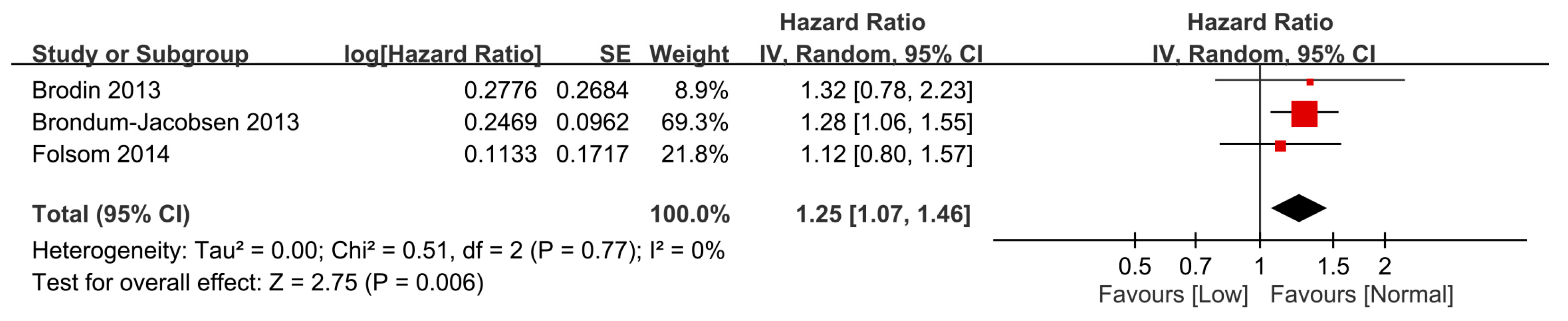
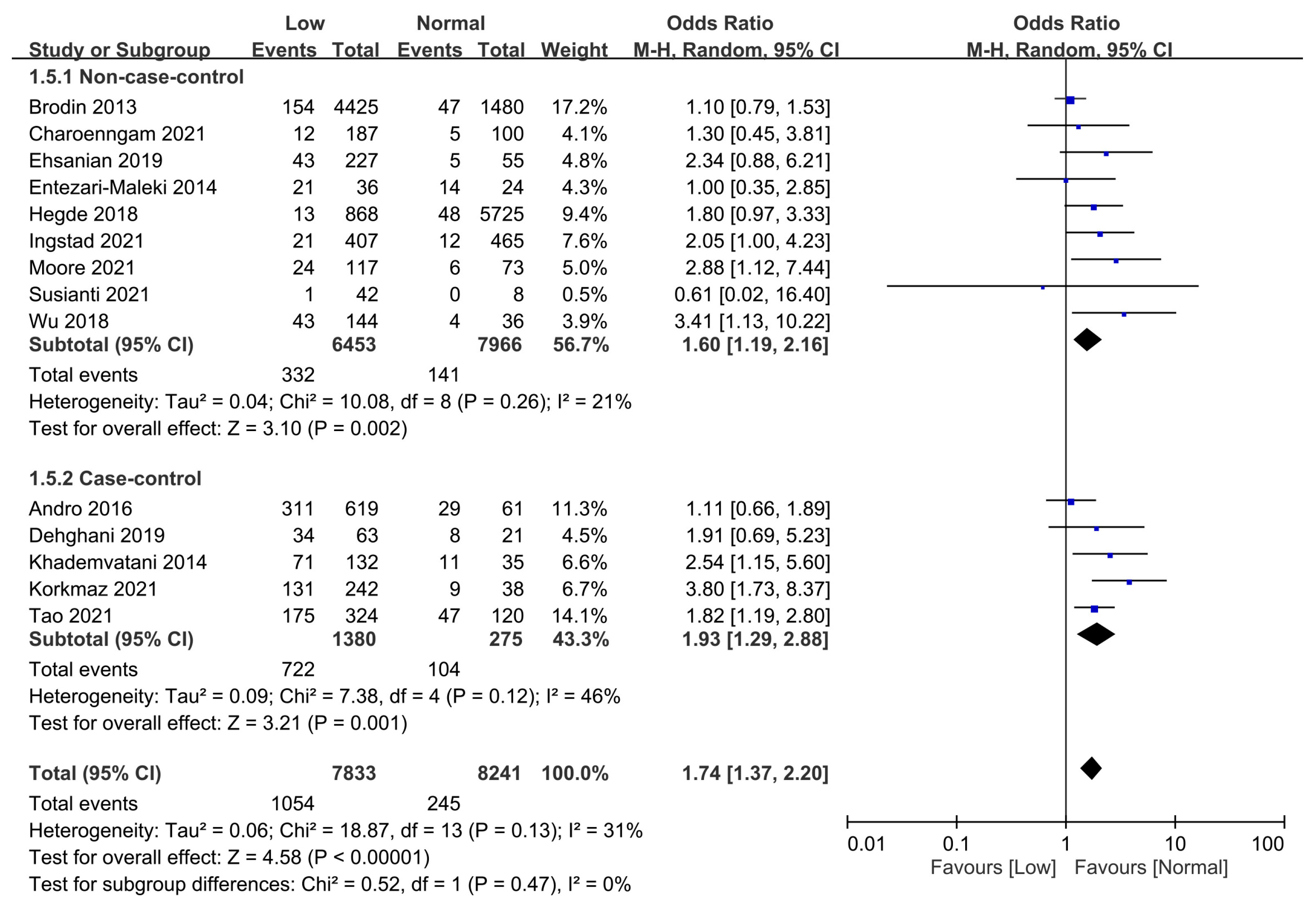
3.2.1. Association of Vitamin D Status with the Overall Risk of VTE
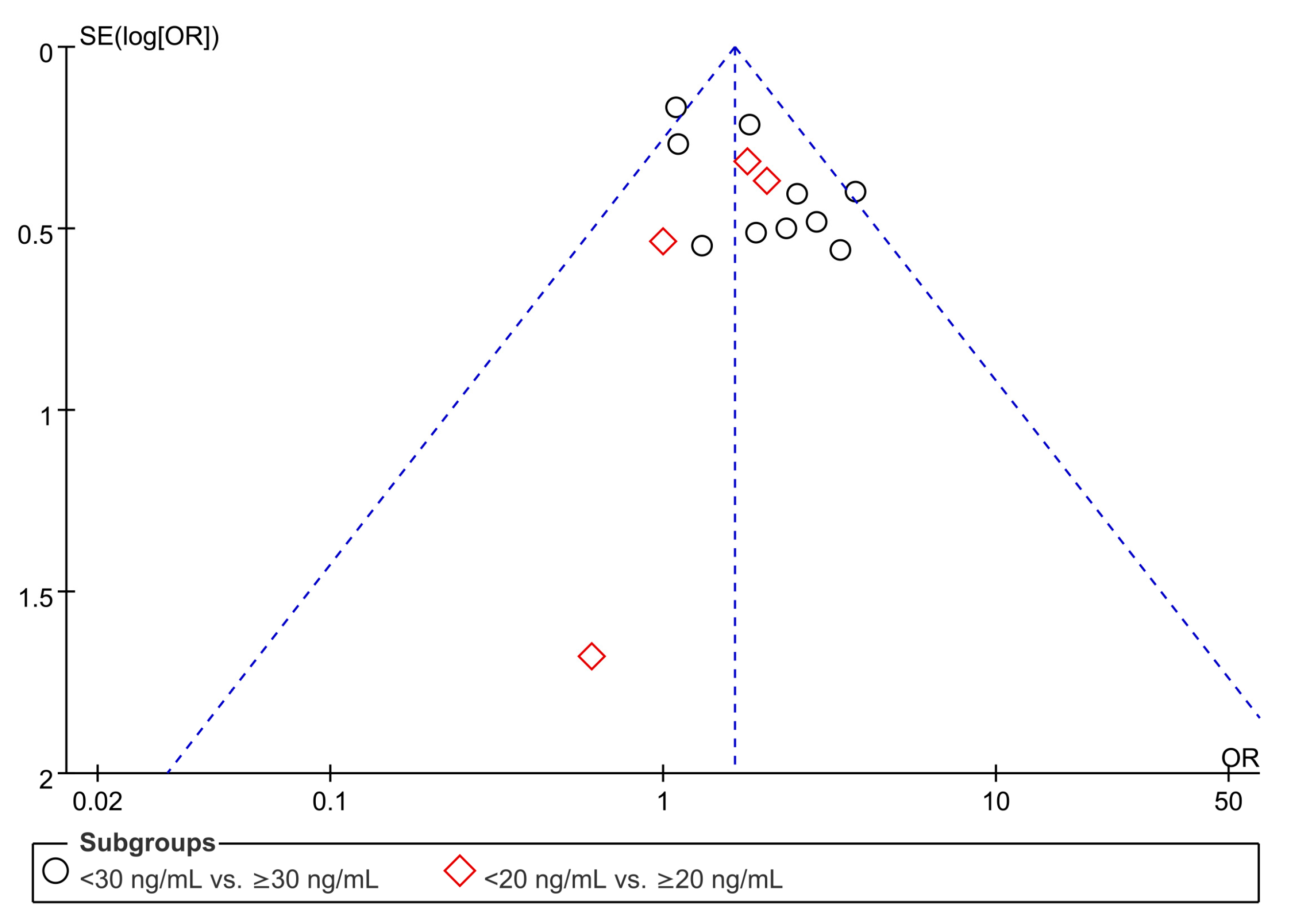
Association of Low Vitamin D with the Risk of VTE Estimated with Odds Ratio
Association of Low Vitamin D with the Risk of VTE Based on a Time-to-Event Analysis
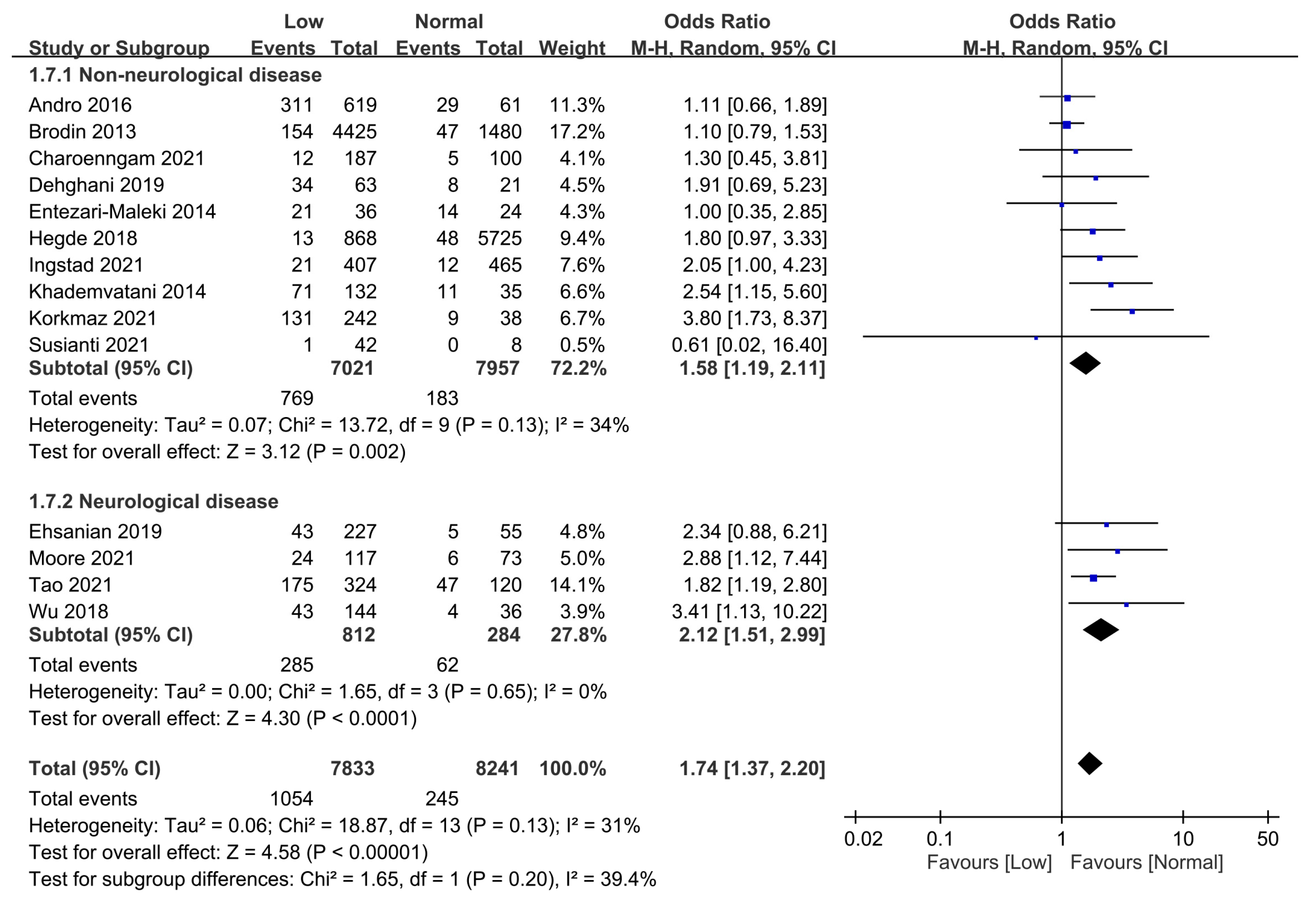
3.2.2. Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Search Strategies for Medline
| Databases | # | Search Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| MEDLINE (Ovid) | 1 | (“Deep vein thrombosis*” or “DVT” or “Thromboembolism” or “Venous thrombosis*” or “Deep-vein thrombosis*” or “Venous thromboembolism” or “Pulmonary embolism*” or “Pulmonary thromboembolism” or “Thromboembolic” or “PE”).mp. |
| 2 | exp “Venous thrombosis”/ OR exp “Pulmonary embolism”/ | |
| 3 | (“Vitamin D” or “25-hydroxyvitamin D” or “Vitamin D deficiency*” or “vitamin D3” or “25OHD” or “25(OH)D” or “vitamin D2” or “Hydroxycholecalciferols” or “hypovitaminosis D”).mp. | |
| 4 | exp “ Vitamin D”/or exp “Vitamin D deficiency”/ | |
| 5 | (1 or 2) and (3 or 4) |
References
- Heit, J.A.; Spencer, F.A.; White, R.H. The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 41, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagot, C.N.; Arya, R. Virchow and his triad: A question of attribution. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 143, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Murin, S.; Harvey, D.; White, R.H. Effect of ethnicity and gender on the incidence of venous thromboembolism in a diverse population in California in 1996. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhaber, S.Z. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lijfering, W.M.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Cannegieter, S.C. Risk factors for venous thrombosis—Current understanding from an epidemiological point of view. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomp, E.R.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Doggen, C.J. Smoking increases the risk of venous thrombosis and acts synergistically with oral contraceptive use. Am. J. Hematol. 2007, 83, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brøndum-Jacobsen, P.; Benn, M.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and risk of venous thromboembolism in the general population with 18,791 participants. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Wang, L.-K.; Hung, K.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Wu, L.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; Chen, J.-Y. Prevalence and Predictors of Insufficient Plasma Vitamin C in a Subtropical Region and Its Associations with Risk Factors of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caprio, M.; Infante, M.; Calanchini, M.; Mammi, C.; Fabbri, A. Vitamin D: Not just the bone. Evidence for beneficial pleiotropic extraskeletal effects. Eat. Weight. Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2017, 22, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, L.K.; Hung, K.C.; Lan, K.M.; Ho, C.H.; Chang, C.Y. Hypovitaminosis D in Postherpetic Neuralgia-High Prevalence and Inverse Association with Pain: A Retrospective Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, K.-C.; Wang, L.-K.; Lin, Y.-T.; Yu, C.-H.; Chang, C.-Y.; Sun, C.-K.; Chen, J.-Y. Association of preoperative vitamin D deficiency with the risk of postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Anesthesia 2022, 79, 110681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Pichiri, I.; Lippi, G. Vitamin D, thrombosis, and hemostasis: More than skin deep. In Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis; Thieme Medical Publishers: Leipzig, Germany, 2012; pp. 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Kong, J.; Duan, Y.; Szeto, F.L.; Liao, A.; Madara, J.L.; Li, Y.C. Increased NF-kappaB activity in fibroblasts lacking the vitamin D receptor. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E315–E322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uberti, F.; Lattuada, D.; Morsanuto, V.; Nava, U.; Bolis, G.; Vacca, G.; Squarzanti, D.F.; Cisari, C.; Molinari, C. Vitamin D protects human endothelial cells from oxidative stress through the autophagic and survival pathways. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mussbacher, M.; Salzmann, M.; Brostjan, C.; Hoesel, B.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Datler, H.; Hohensinner, P.; Basílio, J.; Petzelbauer, P.; Assinger, A.; et al. Cell Type-Specific Roles of NF-kappaB Linking Inflammation and Thrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohsawa, M.; Koyama, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Hirosawa, S.; Kamei, S.; Kamiyama, R. 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) and its potent synthetic analogs downregulate tissue factor and upregulate thrombomodulin expression in monocytic cells, counteracting the effects of tumor necrosis factor and oxidized LDL. Circulation 2000, 102, 2867–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaei, Y.; Vatani, K.K.; Seyyed-Mohammadzad, M.H.; Akbari, M.; Eskandari, R.; Rostamzadeh, A. The relationship between vitamin D status and idiopathic lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2014, 7, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerstad, G.; Grimnes, G.; Brækkan, S.K.; Vik, A.; Brox, J.; Svartberg, J.; Jorde, R.; Hansen, J.-B.; Brodin, E.E. Serum levels of vitamin D are not associated with future risk of venous thromboembolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 109, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folsom, A.R.; Roetker, N.S.; Rosamond, W.D.; Heckbert, S.R.; Basu, S.; Cushman, M.; Lutsey, P.L. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of venous thromboembolism: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, J.; Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Bao, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, Z.; Tan, S.C.; Low, T.Y.; Chu, Y. Association between serum vitamin D levels and venous thromboembolism (VTE): A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 54, 102579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneck, M.J. Venous thromboembolism in neurologic disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 119, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, C.A.; Sun, C.K.; Tsai, I.; Chang, Y.P.; Lin, M.C.; Hung, I.Y.; Chang, Y.J.; Wang, L.K.; Lin, Y.T.; Hung, K.C. Mortality and risk factors associated with pulmonary embolism in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, S.H.; Cheetham, T.D. Diagnosis and management of vitamin D deficiency. BMJ 2010, 340, b5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.Y.; Jee, J.H.; Cho, Y.Y.; Jang, J.Y.; Yu, T.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Hong, Y.J.; Jin, S.-M.; Hur, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D cutoffs for functional bone measures in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delluc, A.; Moineau, M.-P.; Tromeur, C.; Gouillou, M.; Lacut, K.; Carré, J.-L.; Gentric, A.; Le Gal, G.; Andro, M. Serum levels of 25(OH)D are not associated with venous thromboembolism in the elderly population. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenngam, N.; Shirvani, A.; Reddy, N.; Vodopivec, D.M.; Apovian, C.M.; Holick, M.F. Association of vitamin D status with hospital morbidity and mortality in adult hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Endocr. Pract. 2021, 27, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, K.; Nowrouzi, A.; Pourdavood, A.H.; Rahmanian, Z. Effect of Vitamin D deficiency in lower extremity and pulmonary venous thromboembolism. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2019, 6, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanian, R.; Timmerman, M.A.; Wright, J.M.; McKenna, S.; Dirlikov, B.; Crew, J. Venous Thromboembolism is Associated With Lack of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients With Spinal Cord Injury and Low Vitamin D Levels. PM&R 2019, 11, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Entezari-Maleki, T.; Talasaz, A.H.; Salarifar, M.; Hadjibabaie, M.; Javadi, M.R.; Bozorgi, A.; Jenab, Y.; Boroumand, M.A.; Gholami, K. Plasma Vitamin D Status and Its Correlation with Risk Factors of Thrombosis, P-selectin and hs-CRP Level in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism; the First Study of Iranian Population. IJPR 2014, 13, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hegde, V.; Arshi, A.; Wang, C.; Buser, Z.; Wang, J.C.; Jensen, A.R.; Adams, J.S.; Zeegen, E.N.; Bernthal, N.M. Preoperative Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated With Higher Postoperative Complication Rates in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthopedics 2018, 41, e489–e495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingstad, F.; Solberg, L.B.; Nordsletten, L.; Thorsby, P.M.; Hestnes, I.; Frihagen, F. Vitamin D status and complications, readmissions, and mortality after hip fracture. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 32, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, U.T.; Ersoy, S.; Yuksel, A.; Celik, H.; Ucaroglu, E.R.; Velioglu, Y.; Cetinkaya, A.; Demir, D.; Esen, U.; Erdem, K. Association between vitamin D levels and lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis: A case-control study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2021, 139, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.; Goldin, Y.; Patel, H.; Greenwald, B. Low Vitamin D Level Is Associated with Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susianti, H.; Wahono, C.S.; Rahman, P.A.; Pratama, M.Z.; Wulanda, I.A.; Hartanti, K.D.; Dewi, E.S.; Handono, K. Low levels of vitamin D were associated with coagulopathy among hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) patients: A single-centered study in Indonesia. J. Med. Biochem. 2021, 40, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Lou, F.; Liu, Y. The Role of Vitamin D in the Relationship Between Gender and Deep Vein Thrombosis Among Stroke Patients. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 755883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-X.; He, D.-R. Low Vitamin D Levels Are Associated with the Development of Deep Venous Thromboembolic Events in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2018, 24, 69S–75S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Liberto, D.; Scazzone, C.; La Rocca, G.; Cipriani, P.; Pizzo, M.L.; Ruscitti, P.; Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M.; Dieli, F.; Giacomelli, R.; et al. Vitamin D increases the production of IL-10 by regulatory T cells in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 1276. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, D.T.; Sverdlov, A.L.; McNeil, J.J.; Horowitz, J.D. Does vitamin D modulate asymmetric dimethylarginine and C-reactive protein concentrations? Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisada, Y.; Garratt, K.B.; Maqsood, A.; Grover, S.P.; Kawano, T.; Cooley, B.C.; Erlich, J.; Moik, F.; Flick, M.J.; Pabinger, I.; et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and venous thrombosis in pancreatic cancer. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, E.M.; Nonogaki, S.; Katayama, M.L.H.; Folgueira, M.A.A.K.; Alves, V.F.A.; Brentani, M.M. Vitamin D3 modulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in human breast carcinomas under organ culture. Virchows Archiv. 2004, 444, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupuleti, P.; Suchitra, M.; Bitla, A.R.; Sachan, A. Attenuation of Oxidative Stress, Interleukin-6, High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1, and Fibrinogen with Oral Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients with T2DM having Vitamin D Deficiency. J. Lab. Physicians 2022, 14, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondon, M.; Rodabough, R.J.; Budrys, N.; Johnson, K.C.; Berger, J.S.; Shikany, J.M.; Raiesdana, A.; Heckbert, S.R.; Manson, J.E.; LaCroix, A.Z.; et al. The effect of calcium plus vitamin D supplementation on the risk of venous thromboembolism. From the Women’s Health Initiative Randomized Controlled Trial. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jorde, R.; Sneve, M.; Torjesen, P.; Figenschau, Y.; Hansen, J.-B. Parameters of the thrombogram are associated with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels at baseline, but not affected during supplementation with vitamin D. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, e210–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vučković, B.A.; van Rein, N.; Cannegieter, S.C.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Lijfering, W.M. Vitamin supplementation on the risk of venous thrombosis: Results from the MEGA case-control study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.-K.; Hung, K.-C.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chang, Y.-J.; Wu, Z.-F.; Ho, C.-H.; Chen, J.-Y. Age, Gender and Season Are Good Predictors of Vitamin D Status Independent of Body Mass Index in Office Workers in a SubtropicalRegion. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitelzweig, S.B.; Lin, J.; Johnson, B.H.; Schulman, K.L. Venous thromboembolism in the US: Does race matter? J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 2011, 31, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| First Author (Years) | Country | Mean Age (Years) | Male (%) | Population | Sample Size | Study Design | NOS | Vitamin D Threshold (ng/mL) | Measurements of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D | Data for Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brøndum-Jacobsen (2013) [7] | Denmark | 57 | 45 | GP | 18791 | Prospective cohort | 6 | 30 | Plasma—CLIA | HR |
| Brodin (2013) [19] | Norway | 62 | 46 | GP | 6021 | Prospective cohort | 6 | 28 | Serum—ECLIA | OR HR |
| Folsom (2014) [20] | U.S.A. | 56.8 | 24–51 | GP | 12752 | Prospective cohort | 6 | 18 | Serum—LC-MS/MS | HR |
| Entezari-Maleki (2014) [32] | Iran | 54.7 | 53.3 | DVT or PE | 60 | Prospective cross-section | 8 | 20 | Plasma—RIA | OR |
| Khademvatani (2014) [18] | Iran | 47.1 | 48.5 | Idiopathic LE DVT vs. HC | 167 | Case-control | 9 | 30 | Plasma—CLIA | OR |
| Andro (2016) [28] | France | 81.7 | 31.5 | DVT or PE vs. HoC | 680 | Case-control | 7 | 30 | Serum—CLIA | OR |
| Wu (2018) [39] | China | 68 vs. 63 † | 36 | Ischemic stroke | 180 | Prospective cross-section | 8 | 30 | Plasma—CLIA | OR |
| Hegde (2018) [33] | U.S.A. | 65–69 vs. 70–74 ‡ | 24.3 | TKA | 6593 | Retrospective cohort | 8 | 20 | Plasma—Procedure not available | OR |
| Dehghani (2019) [30] | Iran | 47.5 | 61.9 | LE DVT or PE vs. HC | 84 | Case-control | 9 | 30 | Plasma—CLIA | OR |
| Ehsanian (2019) [31] | Canada | 45 | 72 | SCI | 282 | Retrospective cohort | 7 | 30 | Serum—LC-MS/MS | OR |
| Charoenngam (2021) [29] | U.S.A. | 62 | 52.6 | COVID-19 infection | 287 | Retrospective cross-section | 8 | 30 | Serum—CLIA | OR |
| Ingstad (2021) [34] | Norway | 81 | 34 | Hip fracture | 872 | Retrospective cohort | 9 | 20 | Serum—LC-MS/MS | OR |
| Korkmaz (2021) [35] | Turkey | 60 | 49.3 | LE DVT vs. HC | 280 | Case-control | 9 | 30 | Plasma—CLIA | OR |
| Moore (2021) [36] | U.S.A. | 65 | 66 | TBI | 190 | Retrospective cohort | 8 | 30 | Serum—ECLIA | OR |
| Susianti (2021) [37] | Indonesia | 53 vs. 59 | 54 | COVID-19 infection | 50 | Prospective cross-section | 9 | 20 | Serum—ELISA | OR |
| Tao (2021) [38] | China | 70.8 | 59 | Ischemic stroke | 444 | Case-control | 9 | 30 | Serum—ECLIA | OR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, K.-C.; Yang, S.-H.; Chang, C.-Y.; Wang, L.-K.; Lin, Y.-T.; Yu, C.-H.; Chuang, M.-H.; Chen, J.-Y. Is Circulating Vitamin D Status Associated with the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism? A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051113
Hung K-C, Yang S-H, Chang C-Y, Wang L-K, Lin Y-T, Yu C-H, Chuang M-H, Chen J-Y. Is Circulating Vitamin D Status Associated with the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism? A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051113
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Kuo-Chuan, Sheng-Hsiang Yang, Chia-Yu Chang, Li-Kai Wang, Yao-Tsung Lin, Chia-Hung Yu, Min-Hsiang Chuang, and Jen-Yin Chen. 2023. "Is Circulating Vitamin D Status Associated with the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism? A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051113
APA StyleHung, K.-C., Yang, S.-H., Chang, C.-Y., Wang, L.-K., Lin, Y.-T., Yu, C.-H., Chuang, M.-H., & Chen, J.-Y. (2023). Is Circulating Vitamin D Status Associated with the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism? A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients, 15(5), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051113






