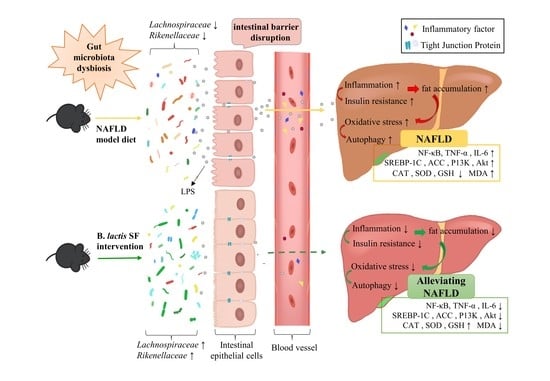
In Vitro Probiotic Properties of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis SF and Its Alleviating Effect on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. B. lactis SF Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Growth Experiments and Endurance Test
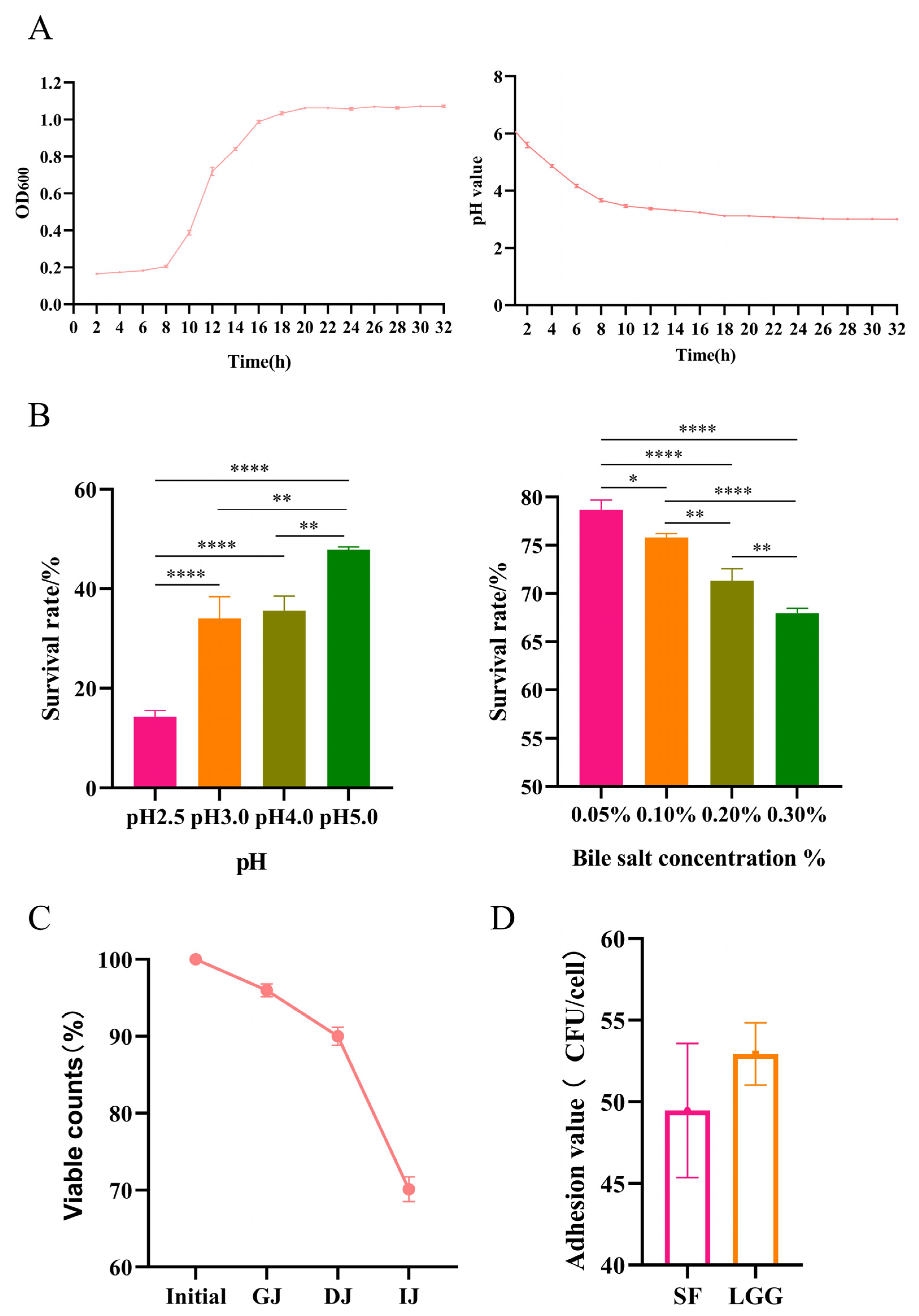
2.2.1. Growth Experiments
2.2.2. Acid and Bile Salt Tolerance Properties
2.2.3. Simulated Gastrointestinal Transit
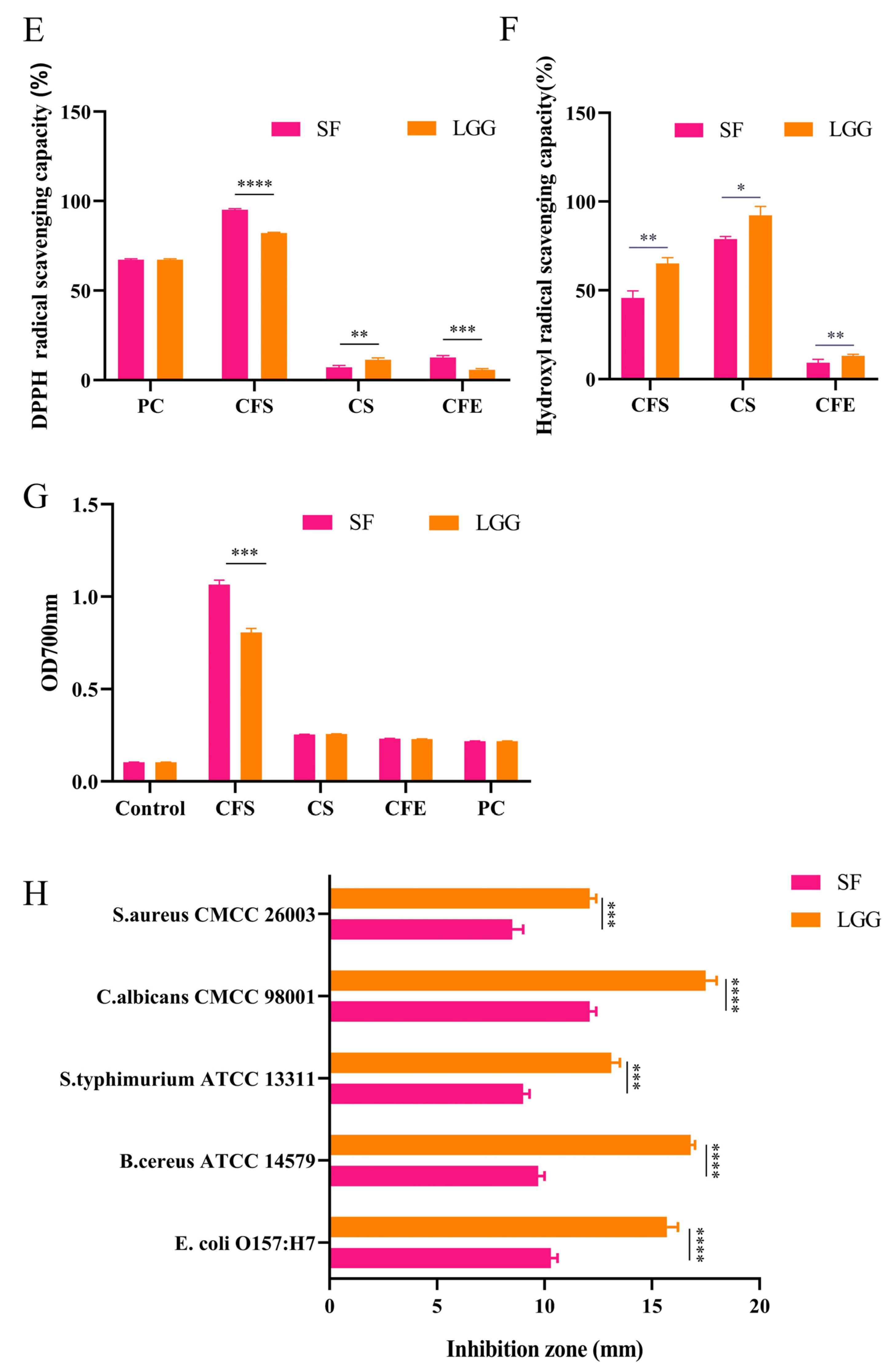
2.3. Antioxidant Ability of B. lactis SF
2.4. Evaluation of Sensitivity to Antibiotics
2.5. Adhesive Determination of Caco-2 Cells
2.6. Antimicrobial Activities of B. lactis SF
2.7. Animals and Experimental Groups
2.8. H&E, Masson’s, and Oil Red O Staining
2.9. Serum- and Liver-Related Index Detection
2.10. Gene Expression Analysis
2.11. DNA Extraction from Mouse Cecal Contents and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.12. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. B. lactis SF Has Good Probiotic Properties
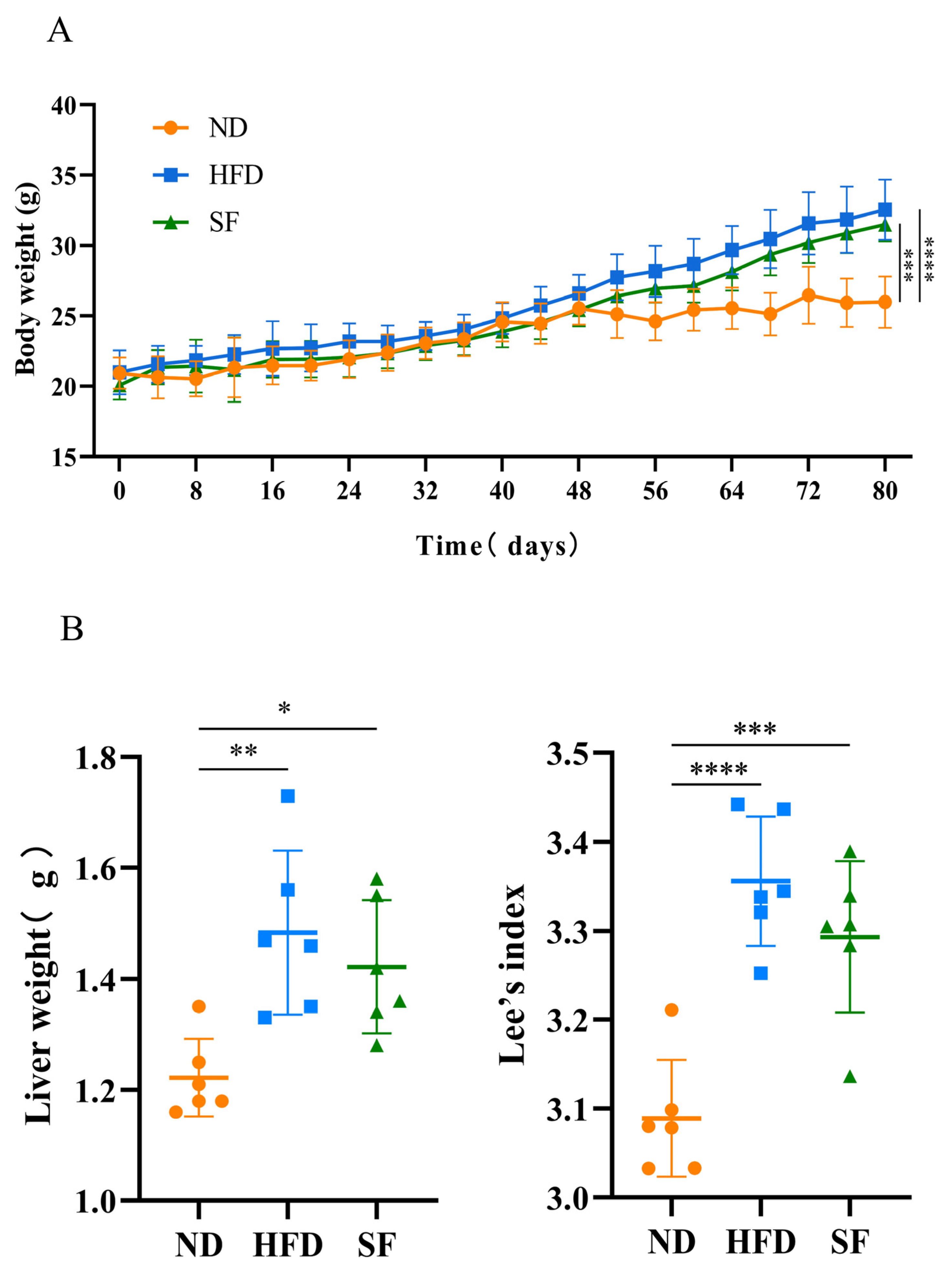
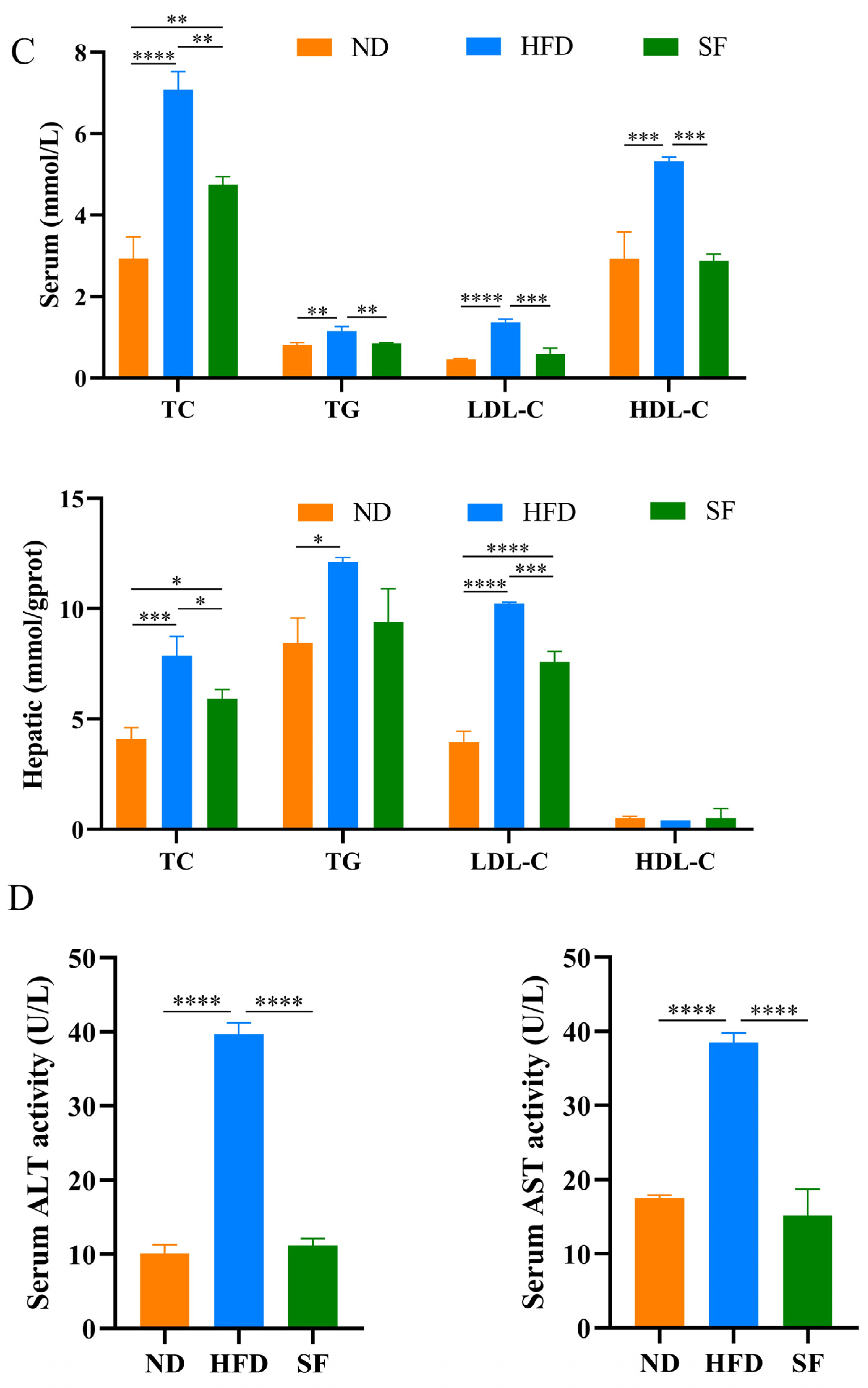
3.2. B. lactis SF Alleviated Diet-Induced Fat Accumulation and Liver Damage in Mice
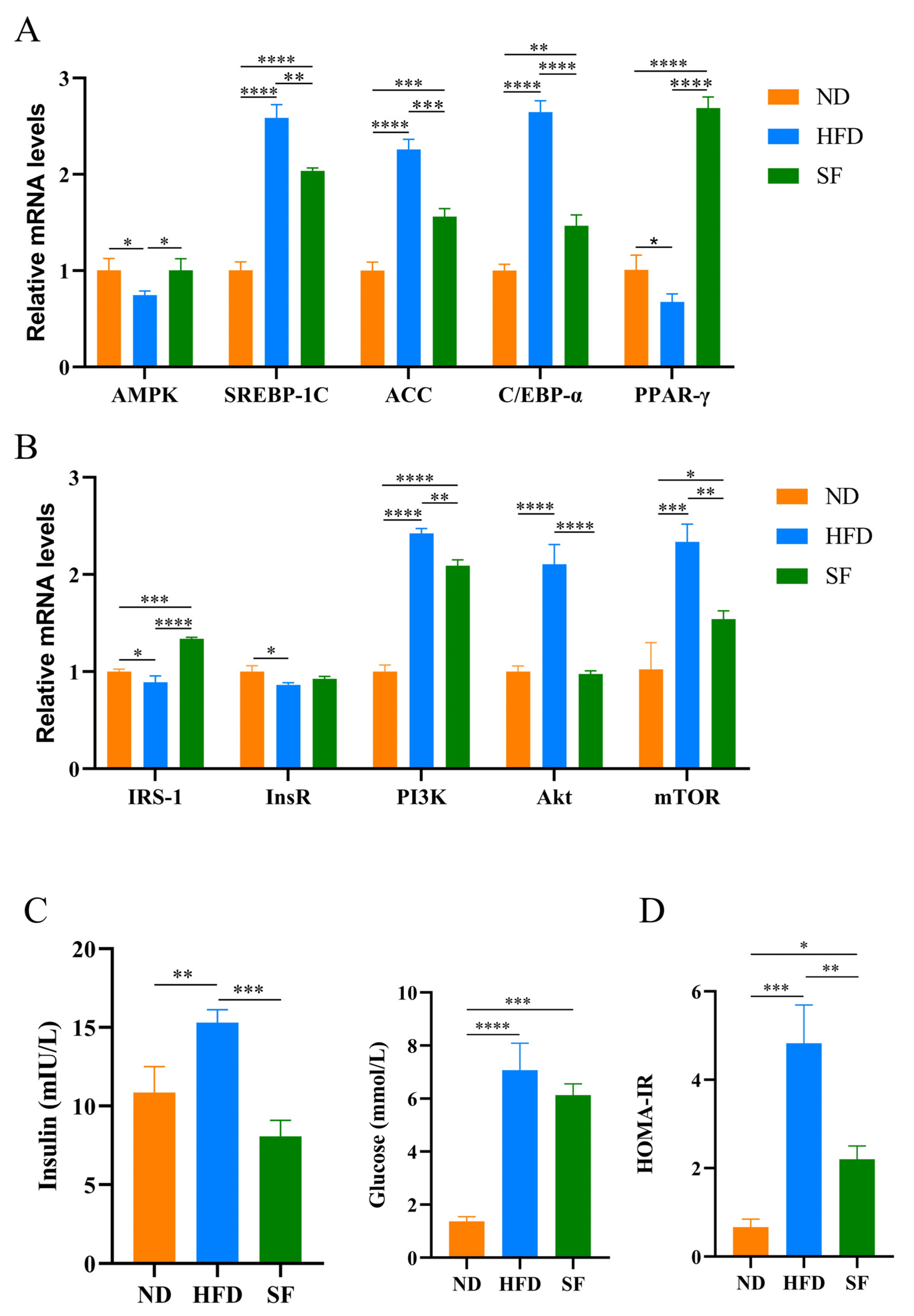
3.3. B. lactis SF Reduced Diet-Induced Lipid Synthesis and Metabolism and Insulin Resistance by Modulating the P13K-Akt/AMPK Signaling Pathway
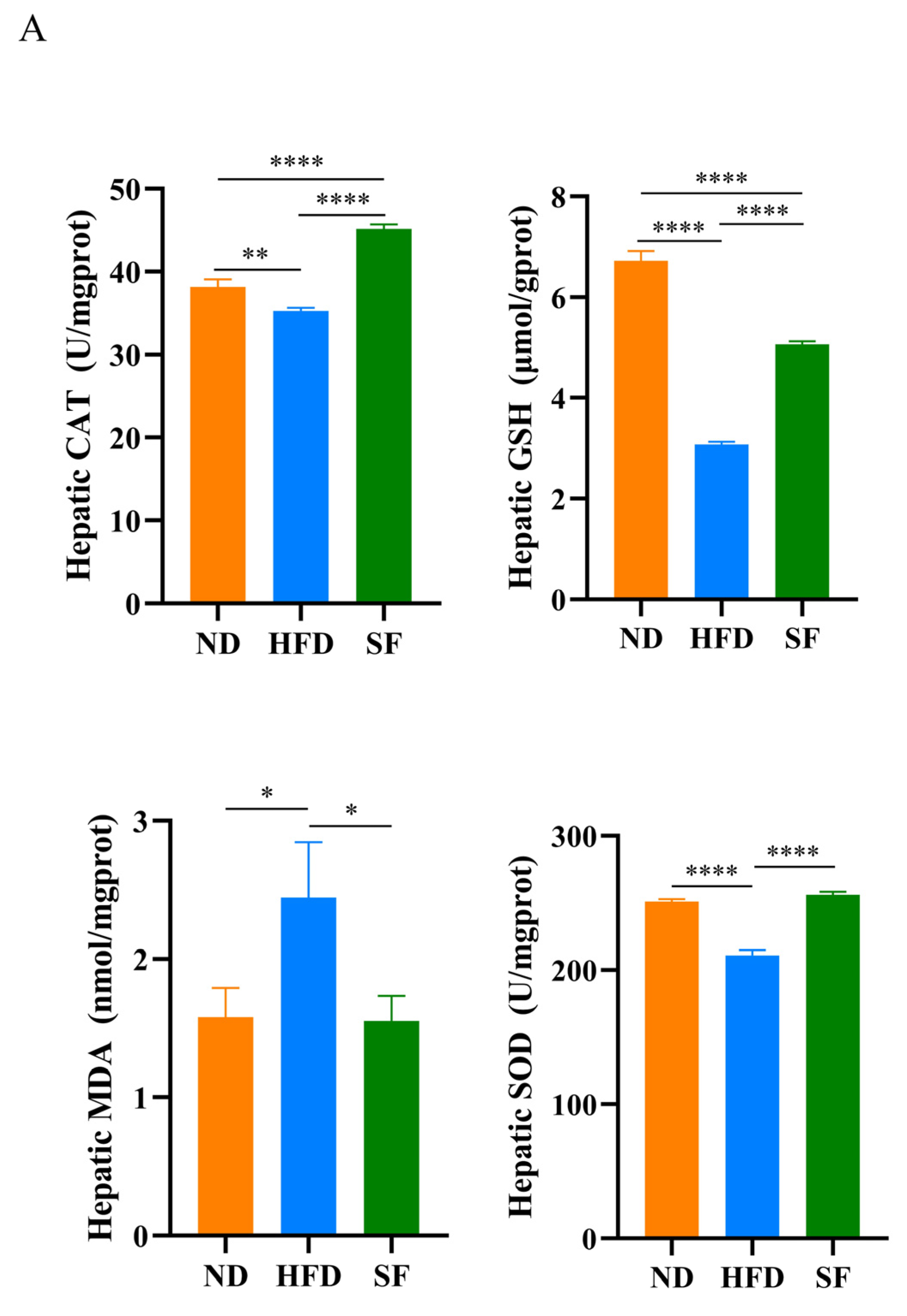
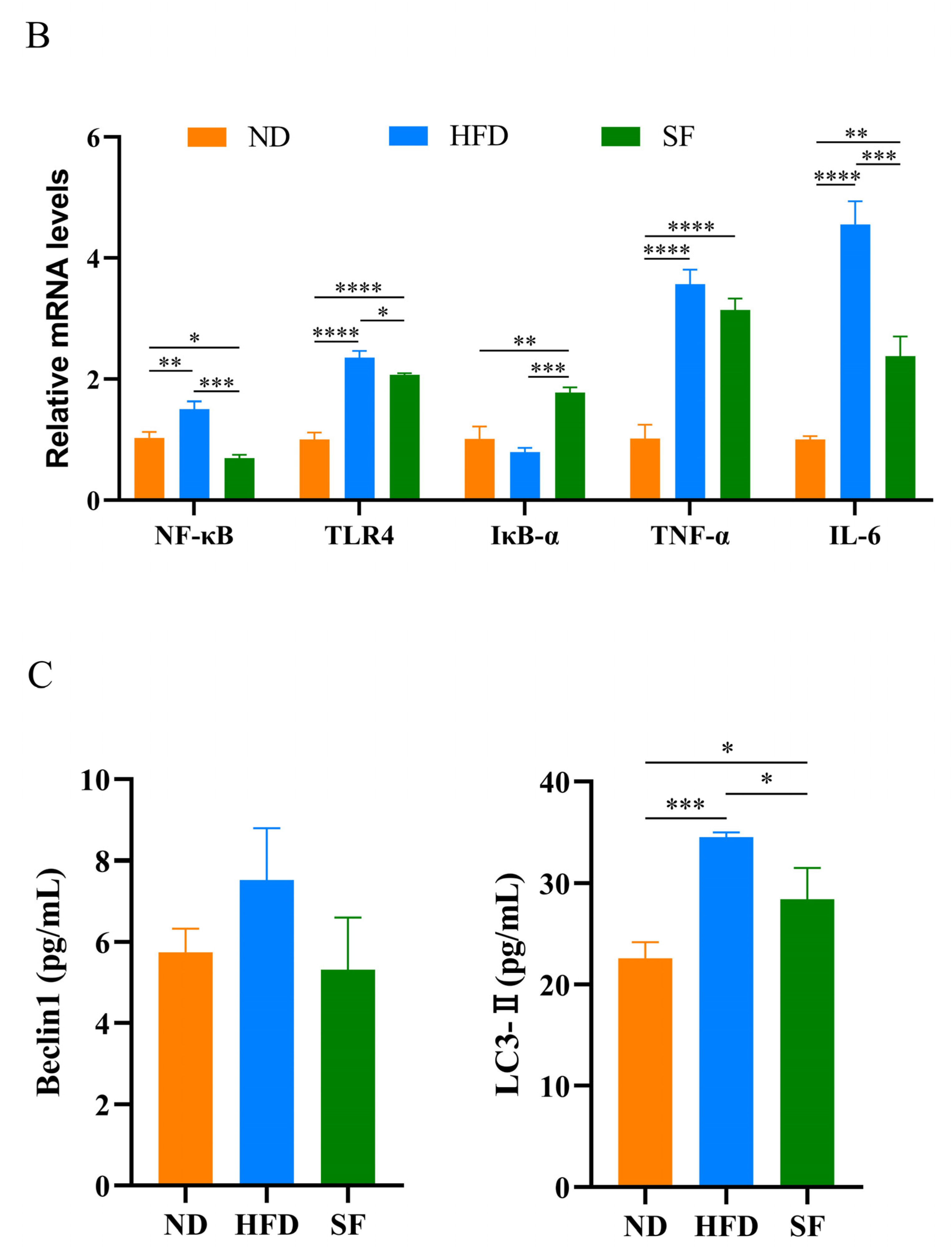
3.4. B. lactis SF Alleviated Diet-Induced Hepatic Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Autophagy
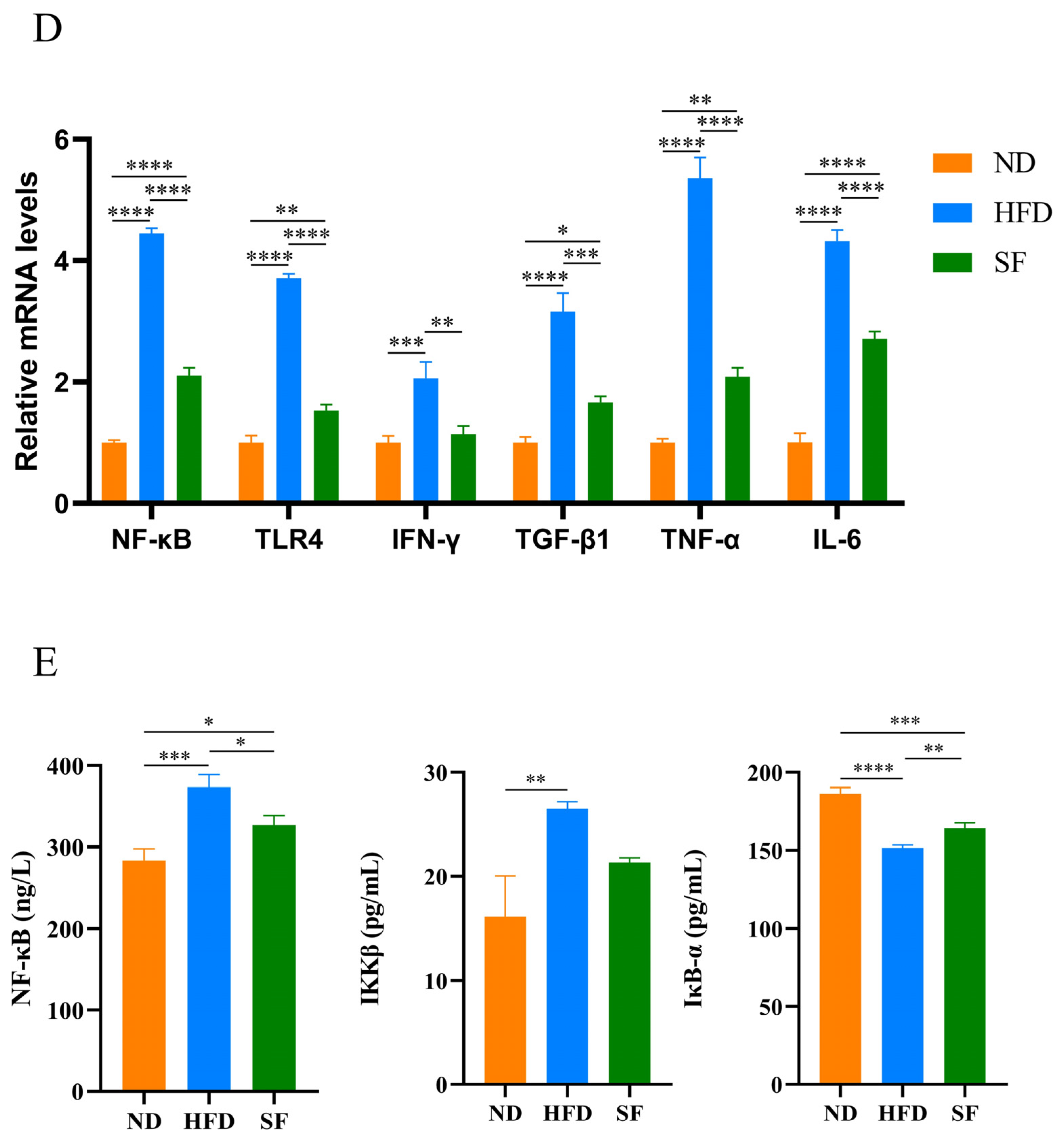
3.5. B. lactis SF Alleviated Diet-Induced Intestinal Barrier Disruption and Intestinal Inflammation by Inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
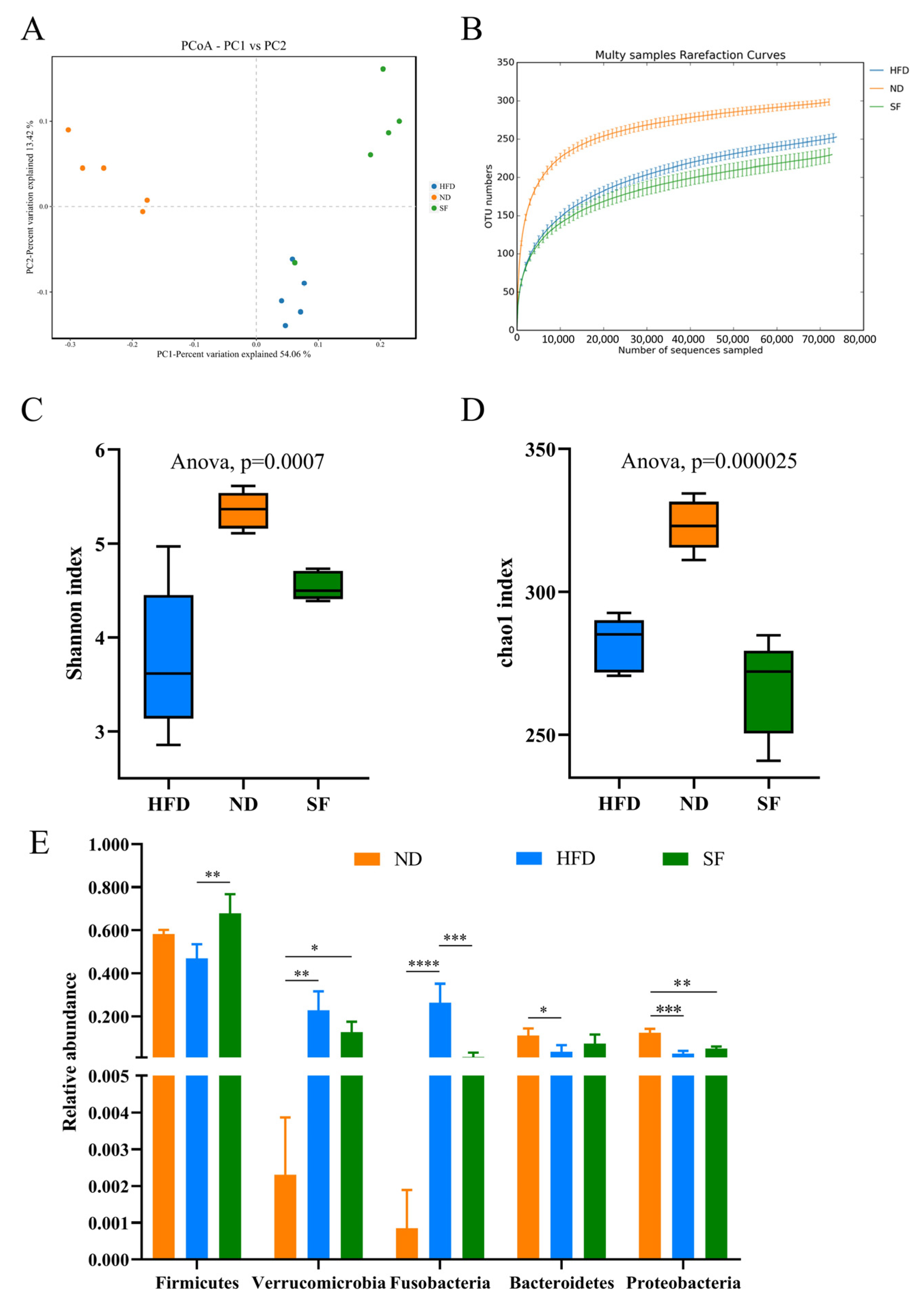
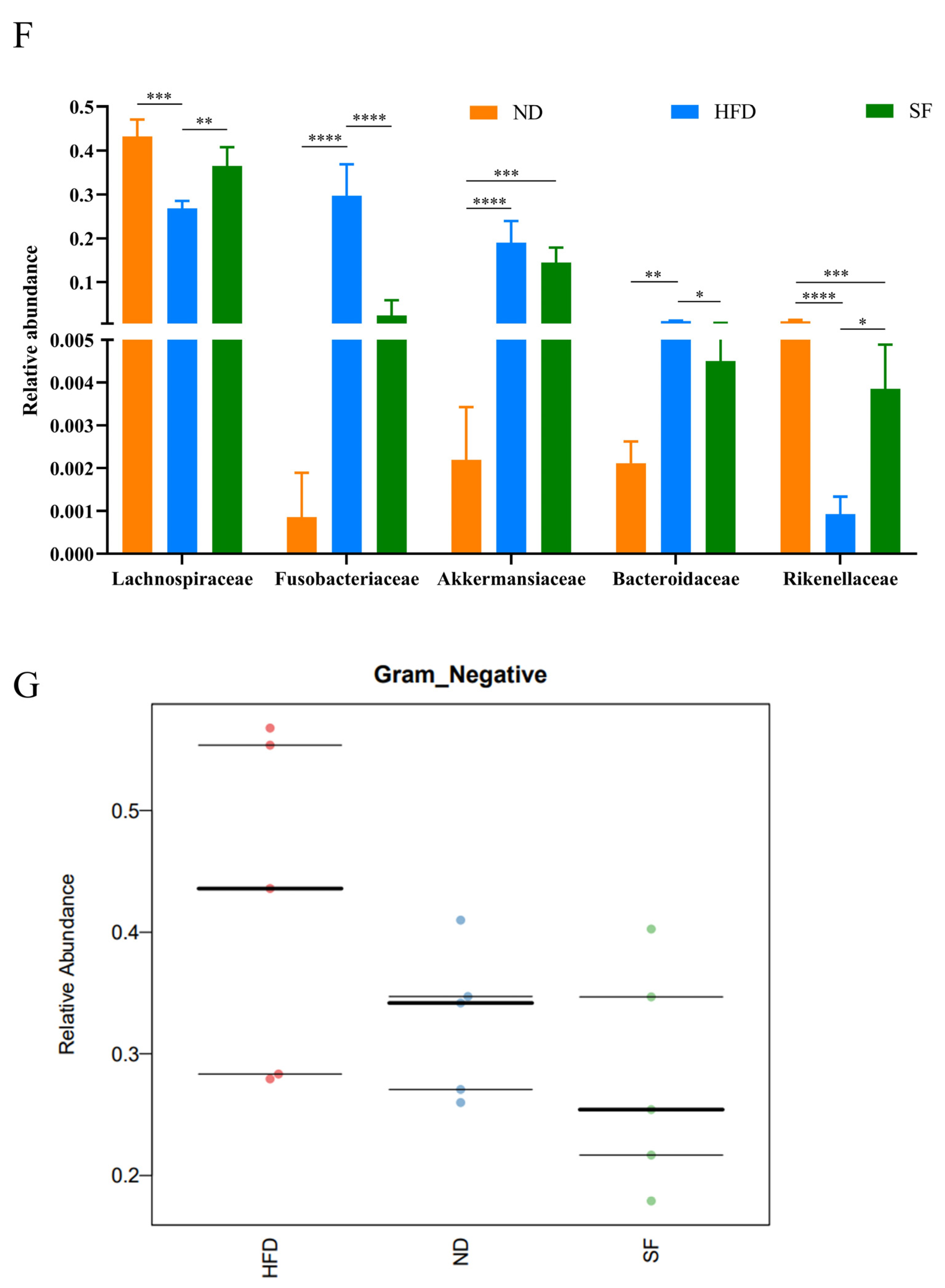
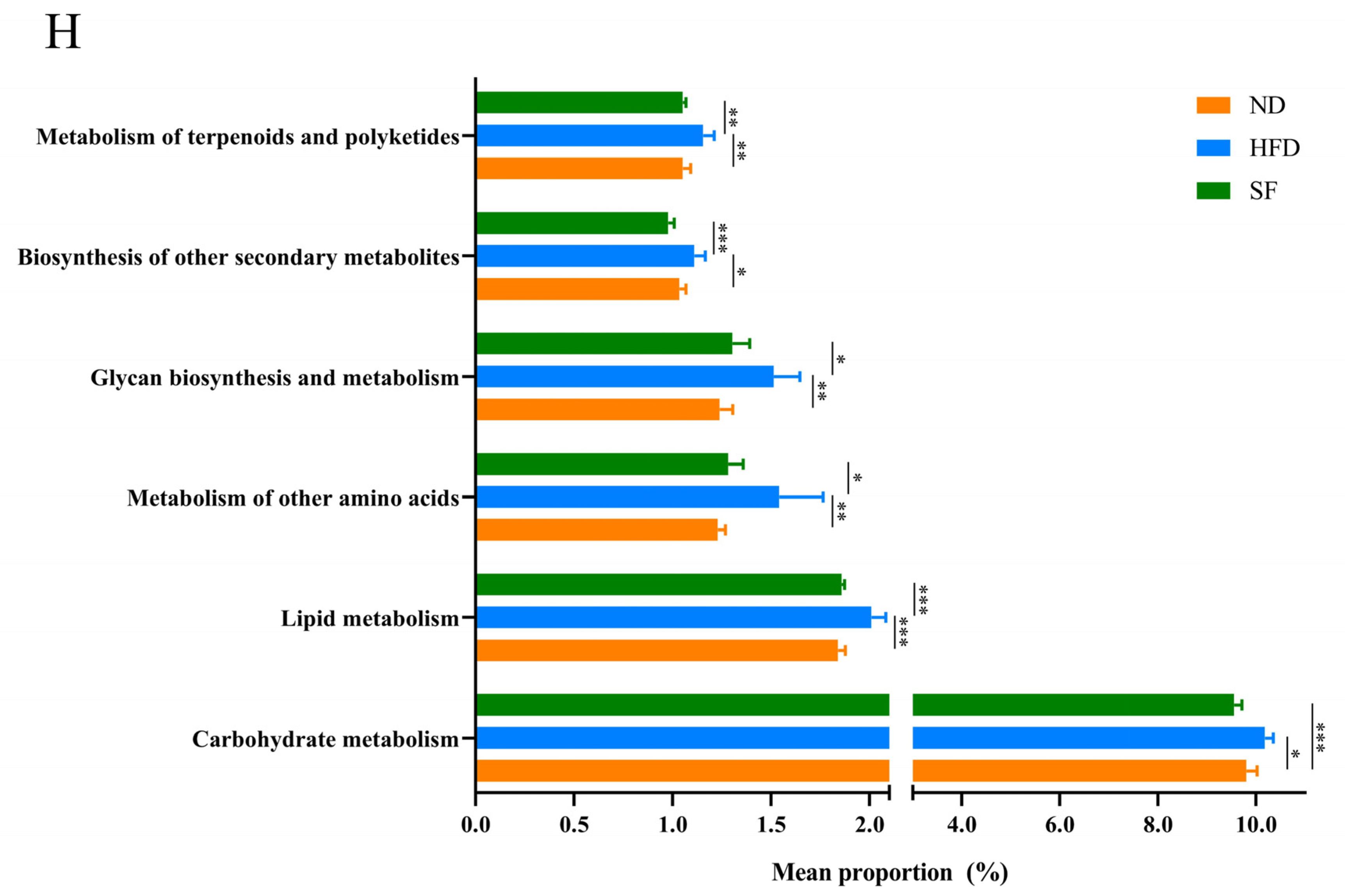
3.6. B. lactis SF Attenuated Diet-Induced Intestinal Dysbiosis in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michelotti, G.A.; Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. NAFLD, NASH and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P.; James, O.J.G. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two ‘Hits’? Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, S.M.B.; Stefano, J.T.; Miele, L.; Ponziani, F.R.; Souza-Basqueira, M.; Okada, L.S.R.R.; de Barros Costa, F.G.; Toda, K.; Mazo, D.F.C.; Sabino, E.C.; et al. Gut microbiome composition in lean patients with NASH is associated with liver damage independent of caloric intake: A prospective pilot study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, N.; Kanwar, P.; Mohanty, S.R. A Comprehensive Updated Review of Pharmaceutical and Nonpharmaceutical Treatment for NAFLD. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 7109270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.T.; Ma, J.L.; Li, H.K. Mechanistic and therapeutic advances in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by targeting the gut microbiota. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria Ghetti, F.; Oliveira, D.G.; de Oliveira, J.M.; de Castro Ferreira, L.; Cesar, D.E.; Moreira, A.P.B. Influence of gut microbiota on the development and progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Diehl, A.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Gut Microbiome. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, A.; Raso, G.M.; Canani, R.B.; Calignano, A.; Meli, R. Probiotics as an emerging therapeutic strategy to treat NAFLD: Focus on molecular and biochemical mechanisms. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, C.; Zhang, X.; Gao, L.; Li, S. Lactobacillus plantarum NA136 improves the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5843–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Yan, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y. Effects of Probiotics V9 on liver function, oxidative stress and lipid metabolism in rats with NAFLD induced by high fat diet and its mechanism. Chin. J. Immunol. 2019, 35, 2822–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Mofidi, F.; Poustchi, H.; Yari, Z.; Nourinayyer, B.; Merat, S.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic supplementation in lean patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Yaqoob, P. Evidence of immunomodulatory effects of a novel probiotic, Bifidobacterium longum bv. infantis CCUG 52486. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, D.; Kansal, V.K. Probiotic Dahi containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum alleviates age-inflicted oxidative stress and improves expression of biomarkers of ageing in mice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhlova, E.V.; Smeianov, V.V.; Efimov, B.A.; Kafarskaia, L.I.; Pavlova, S.I.; Shkoporov, A.N. Anti-inflammatory properties of intestinal Bifidobacterium strains isolated from healthy infants. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 56, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Ma, K.Y.; Liang, Y.; Peng, C.; Zuo, Y. Role and classification of cholesterol-lowering functional foods. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, D.; Kim, D.; Cho, J.; Yang, J.; Chung, M.; Kim, K.; Ha, N. Inhibition of proliferation in colon cancer cell lines and harmful enzyme activity of colon bacteria by Bifidobacterium adolescentis SPM0212. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2008, 31, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerman, M.; Bao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, M. Effects of prebiotic carbohydrates on the growth promotion and cholesterol-lowering abilities of compound probiotics in vitro. LWT 2020, 118, 108703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Tao, X.; Wan, C.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Xu, F.; Shah, N.P.; Wei, H. In vitro probiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY 2013 and its modulatory effect on gut microbiota of mice. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 5850–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Xu, H.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Peng, S.; Dong, S.; Wang, B.; Li, P.; Chen, T.; Xu, F.; Wei, H. Safety Assessment and Probiotic Evaluation of Enterococcus Faecium YF5 Isolated from Sourdough. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.Y.; Huo, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.M.; Chen, S.F.; Lv, H.H.; Peng, L.L.; Wei, H.; Wan, C.X. Protective Effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 1201 Combined with Galactooligosaccharide on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duary, R.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Batish, V.K.; Grover, S. Assessing the adhesion of putative indigenous probiotic lactobacilli to human colonic epithelial cells. Indian J. Med. Res. 2011, 134, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C. Study on Adhesion Ability of Lactic Acid Bacteria to the Colonic Adenocarcinoma Cell Line HT-29. J. China Agric. Univ. 2002, 7, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Guo, B.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z. Preliminary study on the adhesive properties and mechanisms of three probiotic strains. Chin. J. Microecol. 2007, 19, 492–495. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Fan, X.; Hang, X.; Yang, H. An in vitro study of antibacterial activity of 25 strains of probiotics from human gastrointestinal tract. Chin. J. Microecol. 2006, 18, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.F.; Ren, Z.Y.; Huo, Y.L.; Yang, W.Y.; Peng, L.L.; Lv, H.H.; Nie, L.J.; Wei, H.; Wan, C.X. Targeting the gut microbiota to investigate the mechanism of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 1201 in negating colitis aggravated by a high-salt diet. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirjavainen, P.V.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.J. The ability of probiotic bacteria to bind to human intestinal mucus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 167, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsova, M.; Abilev, S.; Poluektova, E.; Danilenko, V. A bioluminescent test system reveals valuable antioxidant properties of lactobacillus strains from human microbiota. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirabunyanon, M. Biotherapy for and protection against gastrointestinal pathogenic infections via action of probiotic bacteria. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 108–128. [Google Scholar]
- Love, S.; Mudasir, M.A.; Bhardwaj, S.C.; Singh, G.; Tasduq, S.A. Long-term administration of tacrolimus and everolimus prevents high cholesterol-high fructose-induced steatosis in C57BL/6J mice by inhibiting de-novo lipogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113403–113417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.S.; Yi, H.A.; Jiang, K.R.; Fakhar, S.H.; Shi, J.; He, Y.S.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.P.; Fan, X.M.; Li, S.D. Transcriptome analysis reveals the efficacy of ginsenoside-Rg1 in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.M.; Yan, J.B.; Wu, L.Y.; Wu, J.T.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, J.P.; Chen, Z.Y.; He, B.H. Probiotics Alleviated Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats via Gut Microbiota/FXR/FGF15 Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 2264737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, K.; Gui, T.; Kan, D.F.; Feng, H.C.; Jin, Y.Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Du, Z.W.; Gai, Z.B.; Wu, J.B.; et al. An Overview of Lipid Metabolism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4020249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Chu, Y.F.; Qin, W.S. IGFBP5 modulates lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity through activating AMPK pathway in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Du, S.S.; Dai, Y.Y.; Yang, F.; Li, X.N. omega 3PUFAs improve hepatic steatosis in postnatal overfed rats and HepG2 cells by inhibiting acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5153–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ore, A.; Akinloye, O.A. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Biomarkers in Clinical and Experimental Models of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Medicina 2019, 55, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.L.; Fuller, C.R.; Dieleman, L.A.; DaCosta, C.M.; Haldeman, K.M.; Sartor, R.B.; Lund, P.K. Enhanced survival and mucosal repair after dextran sodium sulfate–induced colitis in transgenic mice that overexpress growth hormone. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulberis, M.; Kotronis, G.; Gialamprinou, D.; Kountouras, J.; Katsinelos, P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An update with special focus on the role of gut microbiota. Metabolism 2017, 71, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Y.; Xu, L. The interplay between host cellular and gut microbial metabolism in NAFLD development and prevention. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, R.W.; Arhire, L.; Covasa, M. Gut Microbiota: From Microorganisms to Metabolic Organ Influencing Obesity. Obesity 2018, 26, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F.C.; Wasmund, K.; Cobankovic, I.; Jehmlich, N.; Herbold, C.W.; Lee, K.S.; Sziranyi, B.; Vesely, C.; Decker, T.; Stocker, R.; et al. Rational design of a microbial consortium of mucosal sugar utilizers reduces Clostridiodes difficile colonization. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Hold, G.L.; Flint, H.J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Alteration in gut microbiota associated with hepatitis B and non-hepatitis virus related hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, K.; Kumar, V.; Eckmann, L. Gut-liver axis at the frontier of host-microbial interactions. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G413–G419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, F.; Del Ben, M.; Conti, R.; Francioso, S.; Feole, K.; Fiorello, S.; Burattin, M.; Mohanna, M.; Zalunardo, B.; Lirussi, F. Insulin resistance (IR) but not reduced insulin secretion (IS) is associated to non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, A.L.; Li, Z.C.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.F.; Sang, H.C.; Zhi, F. Combination of Probiotics and Salvia miltiorrhiza Polysaccharide Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis via Gut Microbiota Modulation and Insulin Resistance Improvement in High Fat-Induced NAFLD Mice. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Saltiel, A.R. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrih, M.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Inflammation as a potential link between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 218, R25–R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondinone, C.M.; Kramer, D. Proteasome inhibitors regulate tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and insulin signaling in adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 296, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, C.J.; Wei, C.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wang, C.L.; Huang, W.C. Fisetin Protects against Hepatic Steatosis through Regulation of the Sirt1/AMPK and Fatty Acid β-Oxidation Signaling Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 49, 1870–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, L.; Cheng, M. The combination of blueberry juice and probiotics ameliorate non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) by affecting SREBP-1c/PNPLA-3 pathway via PPAR-α. Nutrients 2017, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohjima, M.; Higuchi, N.; Kato, M.; Kotoh, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Fujino, T.; Yada, M.; Yada, R.; Harada, N.; Enjoji, M.; et al. SREBP-1c, regulated by the insulin and AMPK signaling pathways, plays a role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 21, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-M.; Yuan, R.-S.; Zhuang, W.-Y.; Sun, J.-H.; Wu, J.-Y.; Li, H.; Chen, J.-G. Schisandra polysaccharide inhibits hepatic lipid accumulation by downregulating expression of SREBPs in NAFLD mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G.; Pan, D.A. Regulation of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation by the AMP-activated protein kinase. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.K.; Marcinko, K.; Desjardins, E.M.; Lally, J.S.; Ford, R.J.; Steinberg, G.R. Treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Role of AMPK. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2016, 311, E730–E740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.-Q.; Otto, T.; Lane, M. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is required for cycle during adipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3313–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, L.; Madeddu, R.; Palio, E.; Arena, N.; Malaguarnera, M. Heme oxygenase-1 levels and oxidative stress-related parameters in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videla, L.A.; Rodrigo, R.; Orellana, M.; Fernandez, V.; Tapia, G.; Quiñones, L.; Varela, N.; Contreras, J.; Lazarte, R.; Csendes, A.; et al. Oxidative stress-related parameters in the liver of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Clin. Sci. 2004, 106, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowman, J.K.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Newsome, P.N. Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. QJM Int. J. Med. 2009, 103, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, R.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowler, C.; Vanmontagu, M.; Inze, D. Superoxide-dismutase and stress tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 43, 83–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.X.; Xu, C.; Liu, R.T.; Chen, Y.D. Molecular mechanism of catalase activity change under sodium dodecyl sulfate-induced oxidative stress in the mouse primary hepatocytes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 307, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padurariu, M.; Ciobica, A.; Hritcu, L.; Stoica, B.; Bild, W.; Stefanescu, C. Changes of some oxidative stress markers in the serum of patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 469, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, B.Y.; Sun, D.S.; Won, H.S.; Lee, M.A.; Hong, S.U.; Jung, J.H.; Cho, H.M.; Ko, Y.H. Role of autophagy-related protein expression in patients with rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Class | Antibiotic | Content (μg) | Diameter of Inhibition Zone (mm) | Sensitivity 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGG | SF | LGG | SF | |||
| Aminoglycoside | Gentamicin | 10 | 13 | 13 | I | I |
| Streptomycin | 10 | 10 | 9 | R | R | |
| Kanamycin | 30 | 8 | 6 | R | R | |
| Glycopeptide | Bacitracin | 0.04U | 6 | 6 | R | R |
| Polymyxin B | 30 | 6 | 6 | R | R | |
| Vancomycin | 30 | 6 | 6 | R | R | |
| Quinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 5 | 14 | 6 | I | R |
| Beta-lactams | Amoxicillin | 10 | 12 | 10 | R | R |
| Ampicillin | 10 | 13 | 15 | I | I | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | 30 | 22 | 17 | S | S |
| Cephalosporins | Cefoxitin | 30 | 6 | 6 | R | R |
| Amphenicols | Chloramphenicol | 30 | 22 | 20 | S | S |
| Macrolide | Erythromycin | 15 | 21 | 21 | S | S |
| Coumarins | novobiocin | 5 | 17 | 15 | I | I |
| Sulfonamides | Rifampicin | 5 | 23 | 17 | S | I |
| Sulphamethoxazole | 25 | 6 | 26 | R | S | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, H.; Tao, F.; Peng, L.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z.; Chen, J.; Yu, B.; Wei, H.; Wan, C. In Vitro Probiotic Properties of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis SF and Its Alleviating Effect on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061355
Lv H, Tao F, Peng L, Chen S, Ren Z, Chen J, Yu B, Wei H, Wan C. In Vitro Probiotic Properties of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis SF and Its Alleviating Effect on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061355
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Huihui, Feiyue Tao, Lingling Peng, Shufang Chen, Zhongyue Ren, Jiahui Chen, Bo Yu, Hua Wei, and Cuixiang Wan. 2023. "In Vitro Probiotic Properties of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis SF and Its Alleviating Effect on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061355
APA StyleLv, H., Tao, F., Peng, L., Chen, S., Ren, Z., Chen, J., Yu, B., Wei, H., & Wan, C. (2023). In Vitro Probiotic Properties of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis SF and Its Alleviating Effect on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients, 15(6), 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061355