Piceatannol Prevents Obesity and Fat Accumulation Caused by Estrogen Deficiency in Female Mice by Promoting Lipolysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Glucose Tolerance Test
2.4. Biochemical Parameters of Blood
2.5. Micro X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) Analysis of Fat Accumulation
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
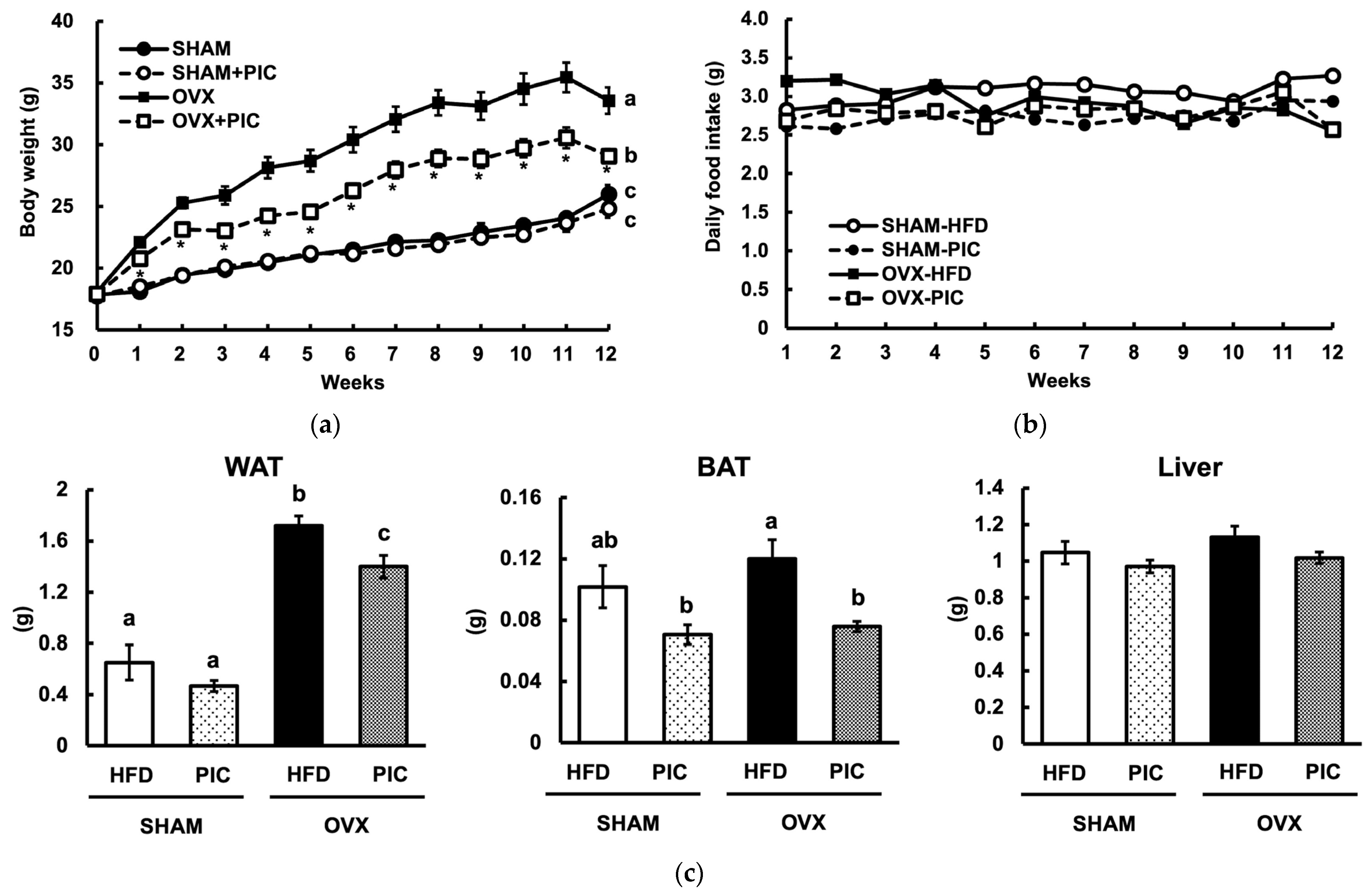
3.1. Effect of Piceatannol on Body and Tissue Weight in HFD-Fed Ovariectomized C57BL/6J Mice
3.2. Effects of PIC on Blood Biochemical Parameters in Ovariectomized Mice
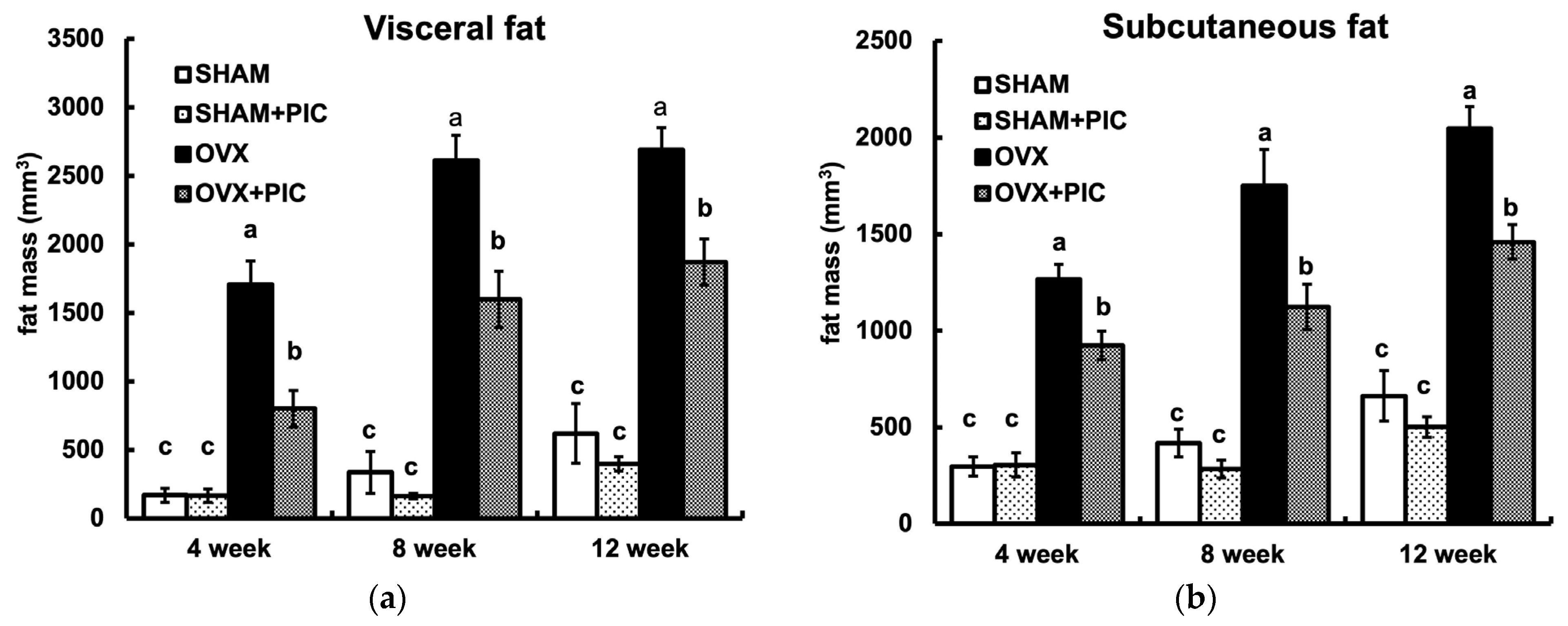
3.3. Effects of PIC on Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat Accumulation HFD-Fed Ovariectomized Mice
3.4. Effects of PIC on the Expression of Proteins Involved in Lipid Metabolism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clegg, D.J. Minireview: The Year in Review of Estrogen Regulation of Metabolism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1957–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leeners, B.; Geary, N.; Tobler, P.N.; Asarian, L. Ovarian Hormones and Obesity. Hum. Reprod. Update 2017, 23, 300–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Menopause-Associated Lipid Metabolic Disorders and Foods Beneficial for Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2020, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. The Sexual Dimorphism of Obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 402, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clegg, D.J.; Brown, L.M.; Woods, S.C.; Benoit, S.C. Gonadal Hormones Determine Sensitivity to Central Leptin and Insulin. Diabetes 2006, 55, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ainslie, D.A.; Morris, M.J.; Wittert, G.; Turnbull, H.; Proietto, J.; Thorburn, A.W. Estrogen Deficiency Causes Central Leptin Insensitivity and Increased Hypothalamic Neuropeptide Y. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Mire, E.; Bouchard, C. Abdominal Obesity and Mortality: The Pennington Center Longitudinal Study. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vega, G.L.; Adams-Huet, B.; Peshock, R.; Willett, D.; Shah, B.; Grundy, S.M. Influence of Body Fat Content and Distribution on Variation in Metabolic Risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4459–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tchernof, A.; Després, J.-P. Pathophysiology of Human Visceral Obesity: An Update. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 359–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, T.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Pan, G.; Höglund, J.; Wadelius, C.; Ek, W.E.; Johansson, Å. Contribution of Genetics to Visceral Adiposity and Its Relation to Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, H.; Kucinska, M.; Murias, M. Biological Activity of Piceatannol: Leaving the Shadow of Resveratrol. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2012, 750, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Seo, S.; Heo, Y.-S.; Yue, S.; Cheng, J.-X.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.-H. Piceatannol, Natural Polyphenolic Stilbene, Inhibits Adipogenesis via Modulation of Mitotic Clonal Expansion and Insulin Receptor-dependent Insulin Signaling in Early Phase of Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11566–11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hijona, E.; Aguirre, L.; Pérez-Matute, P.; Villanueva-Millán, M.J.; Mosqueda-Solis, A.; Hasnaoui, M.; Nepveu, F.; Senard, J.M.; Bujanda, L.; Aldámiz-Echevarría, L.; et al. Limited beneficial effects of piceatannol supplementation on obesity complications in the obese Zucker rat: Gut microbiota, metabolic, endocrine, and cardiac aspects. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 72, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-J.; Chou, S.-C.; Cheng, A.-C.; Kalyanam, N.; Ho, C.-T.; Pan, M.-H. Piceatannol Exerts Anti-Obesity Effects in C57BL/6 Mice through Modulating Adipogenic Proteins and Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2016, 21, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsui, Y.; Sugiyama, K.; Kamei, M.; Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, T.; Katagata, Y.; Ito, T. Extract of Passion Fruit (Passiflora Edulis) Seed Containing High Amounts of Piceatannol Inhibits Melanogenesis and Promotes Collagen Synthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11112–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimando, A.M.; Kalt, W.; Magee, J.B.; Dewey, J.; Ballington, J.R. Resveratrol, Pterostilbene, and Piceatannol in Vaccinium Berries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4713–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viñas, P.; Campillo, N.; Martínez-Castillo, N.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Solid-Phase Microextraction on-Fiber Derivatization for the Analysis of Some Polyphenols in Wine and Grapes Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.M.; Burg, D.L.; Wilson, B.S.; McLaughlin, J.L.; Geahlen, R.L. Inhibition of Mast Cell FceR1-mediated Signaling and Effector Function by the Syk-selective Inhibitor, Piceatannol. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29697–29703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueishi, Y.; Nii, R.; Kakizaki, N. Resveratrol Analogues like Piceatannol Are Potent Antioxidants as Quantitatively Demonstrated through the High Scavenging Ability against Reactive Oxygen Species and Methyl Radical. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 5203–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiolini, M.; Recchia, A.G.; Bonofiglio, D.; Catalano, S.; Vivacqua, A.; Carpino, A.; Rago, V.; Rossi, R.; Andò, S. The Red Wine Phenolics Piceatannol and Myricetin Act as Agonists for Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 35, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, T.; Li, Y.; Hanafusa, Y.; Yeh, Y.; Maruki-Uchida, H.; Kawakami, S.; Sai, M.; Goto, T.; Ito, T.; Kawada, T. Piceatannol Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Macrophages Interacting with Adipocytes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.; Kundu, J.K.; Surh, Y.-J. Piceatannol Inhibits Phorbol Ester-Induced Expression of COX-2 and INOS in HR-1 Hairless Mouse Skin by Blocking the Activation of NF-ΚB and AP-1. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpéné, C.; Pejenaute, H.; del Moral, R.; Boulet, N.; Hijona, E.; Andrade, F.; Villanueva-Millán, M.J.; Aguirre, L.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M. The Dietary Antioxidant Piceatannol Inhibits Adipogenesis of Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Limits Glucose Transport and Lipogenic Activities in Adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, I.S.; Han, Y.; Jo, H.; Lee, K.W.; Song, Y.S. Piceatannol Is Superior to Resveratrol at Suppressing Adipogenesis in Human Visceral Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Plants 2021, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Arnold, A.P.; Reue, K. A Guide for the Design of Pre-Clinical Studies on Sex Differences in Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1216–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casimiro, I.; Stull, N.D.; Tersey, S.A.; Mirmira, R.G. Phenotypic Sexual Dimorphism in Response to Dietary Fat Manipulation in C57BL/6J Mice. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2021, 35, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Miyazaki, H.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; Wu, J.; Ishimi, Y.; Ezaki, O. Ovariectomy in Mice Decreases Lipid Metabolism-Related Gene Expression in Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle with Increased Body Fat. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2005, 51, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, P.A.; Taylor, J.A.; Iwamoto, G.A.; Lubahn, D.B.; Cooke, P.S. Increased Adipose Tissue in Male and Female Estrogen Receptor-α Knockout Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12729–12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.E.; Thorburn, A.W.; Britt, K.L.; Hewitt, K.N.; Wreford, N.G.; Proietto, J.; Oz, O.K.; Leury, B.J.; Robertson, K.M.; Yao, S.; et al. Aromatase-Deficient (ArKO) Mice Have a Phenotype of Increased Adiposity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12735–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayes, J.S.; Watson, G.H. Direct Effects of Sex Steroid Hormones on Adipose Tissues and Obesity. Obes. Rev. 2004, 5, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, G.A.; Patterson, L.H.; Wanogho, E.; Perry, P.J.; Butler, P.C.; Ijaz, T.; Ruparelia, K.C.; Lamb, J.H.; Farmer, P.B.; Stanley, L.A.; et al. The Cancer Preventative Agent Resveratrol Is Converted to the Anticancer Agent Piceatannol by the Cytochrome P450 Enzyme CYP1B1. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setoguchi, Y.; Oritani, Y.; Ito, R.; Inagaki, H.; Maruki-Uchida, H.; Ichiyanagi, T.; Ito, T. Absorption and Metabolism of Piceatannol in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, G.; Qiao, L.; Ge, Q.; Chen, D.; Xu, Z.; Shi, D.; Dai, J.; Qin, J.; Teng, H.; et al. Age-Dependent Variations of Cancellous Bone in Response to Ovariectomy in C57BL/6J Mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luu, Y.K.; Lublinsky, S.; Ozcivici, E.; Capilla, E.; Pessin, J.E.; Rubin, C.T.; Judex, S. In Vivo Quantification of Subcutaneous and Visceral Adiposity by Micro-Computed Tomography in a Small Animal Model. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Judex, S.; Luu, Y.K.; Ozcivici, E.; Adler, B.; Lublinsky, S.; Rubin, C.T. Quantification of Adiposity in Small Rodents Using Micro-CT. Methods 2010, 50, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eguchi, M.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Saitoh, S.; Odawara, Y.; Hirano, T.; Nakata, T.; Miura, T.; Ura, N.; Hareyama, M.; Shimamoto, K. Visceral Obesity in Japanese Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: Reappraisal of Diagnostic Criteria by CT Scan. Hypertens. Res. 2007, 30, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anthonsen, M.W.; Rönnstrand, L.; Wernstedt, C.; Degerman, E.; Holm, C. Identification of Novel Phosphorylation Sites in Hormone-Sensitive Lipase That Are Phosphorylated in Response to Isoproterenol and Govern Activation Properties in Vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, D.G. The Physiological Regulation of Uncoupling Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Bioenerg. 2006, 1757, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagouge, M.; Argmann, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Meziane, H.; Lerin, C.; Daussin, F.; Messadeq, N.; Milne, J.; Lambert, P.; Elliott, P.; et al. Resveratrol Improves Mitochondrial Function and Protects against Metabolic Disease by Activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 2006, 127, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiraby, C.; Tavernier, G.; Lefort, C.; Larrouy, D.; Bouillaud, F.; Ricquier, D.; Langin, D. Acquirement of Brown Fat Cell Features by Human White Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33370–33376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, M.C. The Emergence of the Metabolic Syndrome with Menopause. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2404–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wajchenberg, B.L. Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue: Their Relation to the Metabolic Syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 697–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosano, G.M.C.; Vitale, C.; Marazzi, G.; Volterrani, M. Menopause and Cardiovascular Disease: The Evidence. Climacteric 2007, 10 (Suppl. 1), 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Shimomura, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Futawatari, T.; Ohtani, K.; Sato, N.; Mori, M. Estrogen Increases in Vivo Leptin Production in Rats and Human Subjects. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 154, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Shen, W.J.; Muliro, K.; Patel, S.; Souza, S.C.; Roth, R.A.; Kraemer, F.B. Stimulation of Lipolysis and Hormone-Sensitive Lipase via the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45456–45461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frühbeck, G.; Méndez-Giménez, L.; Fernández-Formoso, J.-A.; Fernández, S.; Rodríguez, A. Regulation of Adipocyte Lipolysis. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2014, 27, 63–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mottillo, E.P.; Granneman, J.G. Intracellular Fatty Acids Suppress β-Adrenergic Induction of PKA-Targeted Gene Expression in White Adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E122–E131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, Y.-T.; Lai, A.C.-Y.; Lin, R.-J.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-T.; Chang, W.-W.; Wu, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chang, W.-Y.; Wu, J.-C.; et al. GPER-Induced Signaling Is Essential for the Survival of Breast Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, G.; Prossnitz, E.R. Estrogen Receptors, Methods and Protocols. In Estrogen Receptors; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1366, pp. 489–502. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Kershaw, J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Komanetsky, S.M.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, X.; Myer, P.R.; Applegate, B.; Kim, K.-H. Piceatannol Antagonizes Lipolysis by Promoting Autophagy-Lysosome-Dependent Degradation of Lipolytic Protein Clusters in Adipocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 105, 108998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, S.; Kinoshita, Y.; Maruki-Uchida, H.; Yanae, K.; Sai, M.; Ito, T. Piceatannol and Its Metabolite, Isorhapontigenin, Induce SIRT1 Expression in THP-1 Human Monocytic Cell Line. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4794–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Ward, W.F. PGC-1alpha: A Key Regulator of Energy Metabolism. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2006, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houten, S.M.; Auwerx, J. PGC-1alpha: Turbocharging Mitochondria. Cell 2004, 119, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, S.B.; Bruun, J.M.; Kristensen, K.; Richelsen, B. Regulation of UCP1, UCP2, and UCP3 mRNA Expression in Brown Adipose Tissue, White Adipose Tissue, and Skeletal Muscle in Rats by Estrogen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, P.; Mehdizadeh, R.; Ansar, M.M.; Damirchi, A. Effects of Ovariectomy and Estrogen Replacement Therapy on Visceral Adipose Tissue and Serum Adiponectin Levels in Rats. Menopause Int. 2010, 16, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, G.E.; Hans, D.; Gonzalez Rodriguez, E.; Vollenweider, P.; Waeber, G.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Lamy, O. Menopausal Hormone Therapy Is Associated With Reduced Total and Visceral Adiposity: The OsteoLaus Cohort. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderle, M.; Pretscher, J.; Brucker, S.Y.; Volz, B.; Hartmann, A.; Fiessler, C.; Hein, A.; Häberle, L.; Jud, S.M.; Lux, M.P.; et al. Association between Breast Cancer Risk Factors and Molecular Type in Postmenopausal Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive Early Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 174, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arisawa, K.; Kaneko, M.; Matsuoka, A.; Ozawa, N.; Kawawa, R.; Ishikawa, T.; Ichi, I.; Fujiwara, Y. Piceatannol Prevents Obesity and Fat Accumulation Caused by Estrogen Deficiency in Female Mice by Promoting Lipolysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061374
Arisawa K, Kaneko M, Matsuoka A, Ozawa N, Kawawa R, Ishikawa T, Ichi I, Fujiwara Y. Piceatannol Prevents Obesity and Fat Accumulation Caused by Estrogen Deficiency in Female Mice by Promoting Lipolysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061374
Chicago/Turabian StyleArisawa, Kotoko, Miyuki Kaneko, Ayumi Matsuoka, Natsuki Ozawa, Rie Kawawa, Tomoko Ishikawa, Ikuyo Ichi, and Yoko Fujiwara. 2023. "Piceatannol Prevents Obesity and Fat Accumulation Caused by Estrogen Deficiency in Female Mice by Promoting Lipolysis" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061374
APA StyleArisawa, K., Kaneko, M., Matsuoka, A., Ozawa, N., Kawawa, R., Ishikawa, T., Ichi, I., & Fujiwara, Y. (2023). Piceatannol Prevents Obesity and Fat Accumulation Caused by Estrogen Deficiency in Female Mice by Promoting Lipolysis. Nutrients, 15(6), 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061374