Construction and Evaluation of a Novel MAP Immunoassay for 9 Nutrition-and-Health-Related Protein Markers Based on Multiplex Liquid Protein Chip Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Main Instruments and Equipment
2.3. Serum Samples
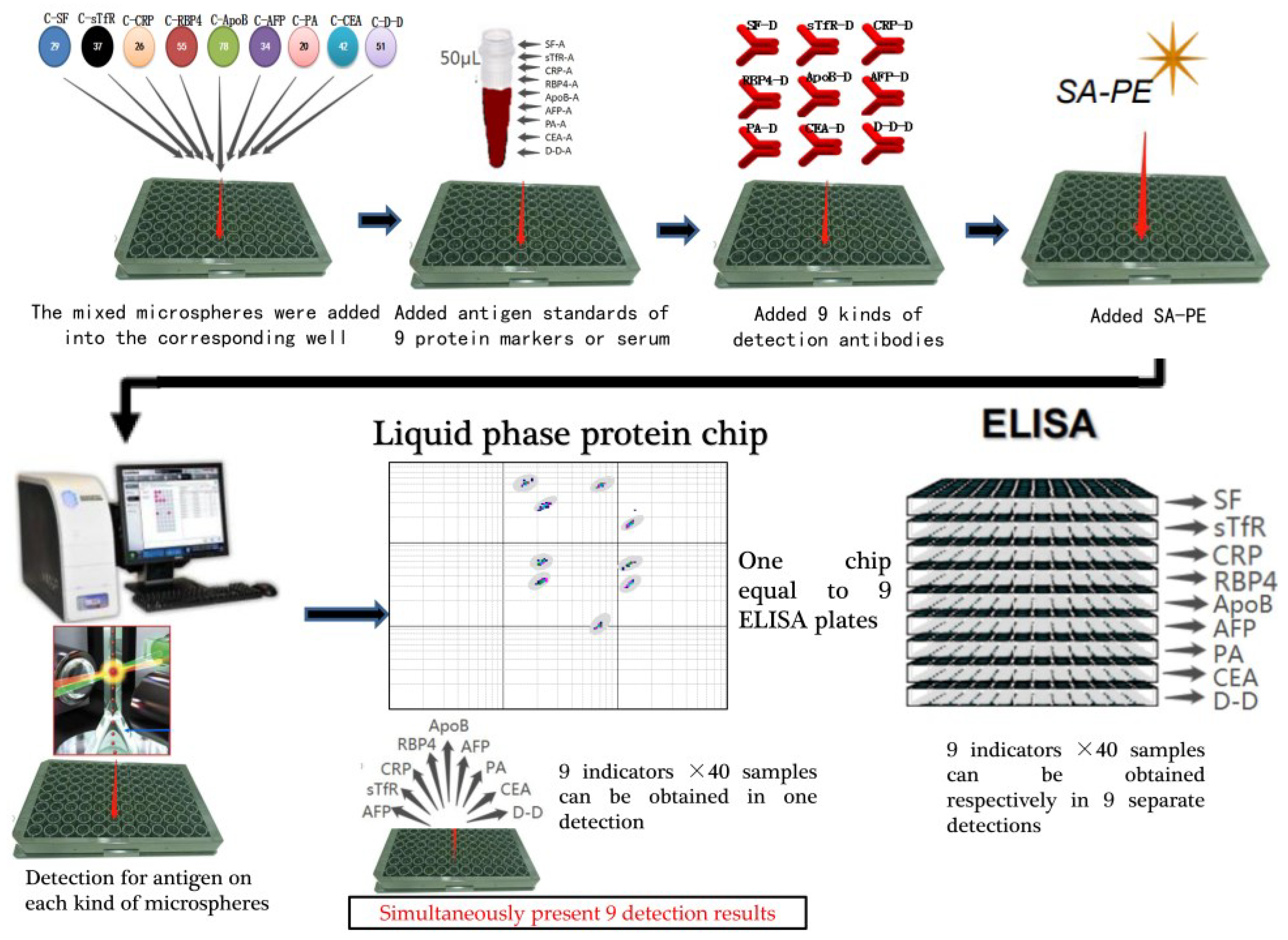
2.4. The Basic Operation Procedure of Liquid Protein Chip
2.5. Optimization of the Combinations of Capture Antibody Concentrations and Detection Antibody Titers of Each Protein Marker
2.6. The Verification of Specific Binding Ability between Antigen and Antibody
- CRR: cross reaction rate,
- Cc: reaction value of cross reaction between an antigen and other antibody,
- C0: blank value of cross reaction between an antigen and other antibody,
- Cp: reaction value of an antigen and its own antibody,
- Cb: blank value of an antigen and its own antibody
2.7. Determinations of Lower Limit of Detection and Biologic Limit of Detection
2.8. The Establishments of S-Curves and the Determination of Regression Equation
2.9. Methodological Evaluation and Verification: Accuracy
2.10. Methodological Evaluation and Verification: Precision
2.11. Methodological Evaluation and Verification: Comparison with Reference Method
2.12. Methodological Evaluation and Verification: Analytical Specificity
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Combination of the Capture Antibody Concentration and the Detection Antibody Titer of Each Protein Marker
3.2. The Verification of Specific Binding Ability between Antigen and Antibody
3.3. Determinations of Lower Limit of Detection and Biologic Limit of Detection
3.4. The Establishments of S-Curves and the Determination of Regression Equation
3.5. Methodological Evaluation and Verification: Accuracy
3.6. Methodological Evaluation and Verification: Precision
3.7. Methodological Evaluation and Verification: Comparison with Reference Method
3.8. Methodological Evaluation and Verification: Analytical Specificity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosalind, S.G. Principles of Nutritional Assessment, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jorg, R.; Albert, S. Proteomics: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Clifton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Report on Chinese Residents’ Chronic Diseases and Nutrition (2020) (English Version); People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Duarte, J.G.; Blackburn, J.M. Advances in the development of human protein microarrays. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.Y.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Li, W.; Huo, J.S. Study on the method of quantitative analysis of serum ferritin and soluble transferrin receptor with protein microarray technology. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.Y.; Huo, J.S.; Ma, X.X.; Sun, J.; Huang, J. Study on the Simultaneously Quantitative Detection for β-Lactoglobulin and Lactoferrin of Cow Milk by Using Protein Chip Technique. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.; Shubhagata, D.; Wilco, G.; Sherry, D. xMAP Cookbook. Available online: https://f.hubspotusercontent30.net/hubfs/128032/Cookbook/BR402139.xMAPCookbook.Ed5.All.Sections.WR.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Syu, G.D.; Dunn, J.; Zhu, H. Development and application of functional protein microarrays. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, J.; Gao, X. Genomic and genechip expression profiling reveals the inhibitory effects of amorphophalli rhizome in TNBC cell. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francois, P.M.; David, J.; Sebastien, B. Precise chip-to chip reagent transfer for cross reactivity-free multiplex sandwich immunoassays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2237, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, E. TNT detection using llama antibodies and a two-step competitive fluid array immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 339, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Jianhua, H.; Jing, L.; Wentao, F.; Zhenwei, B.; Suquan, S.; Liping, Y. Development and application of a novel triplex protein microarray method for rapid detection of antibodies against avian influenza virus, Newcastle disease virus, and avian infectious bronchitis virus. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huanan, W.; Feng, C.; Jianchi, G.; Li, X.; Yujun, Z.; Yuexiao, L.; Ren, H.; Meili, C.; Pengju, G. Establishment of xMAP for the simultaneous detection of antibodies to Newcastle disease virus and avian influenza virus. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitka, M.; Karel, C.; Jiri, P.; Jiri, K.; Pavla, R.; Ondrej, S.; Pavel, T. Simultaneous detection of chicken cytokines in plasma samples using the Bio-Plex assay. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ye, H.; Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Ren, P.; Shi, J.; Dai, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J. Identification of novel autoantibodies based on the protein chip encoded by cancer-driving genes in detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 2020, 9, 1814515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erika, O.H.; Natalia, S.D.; Ivonne, C.B.B.; Monica, V.C.; Andrea, T.C.; Antonio, L.T.; Izabela, G.B.; Lorena, A.V.S.; Daniela, V.F.R.; Aloisio, J.F.R.; et al. Millipore xMap® Luminex (HATMAG-68K): An Accurate and Cost-Effective Method for Evaluating Alzheimer’s Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 716686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, A.; Tamara, R.; Linda, D.; Sandra, B.; Paloma, R.; Patricia, S. Bead-Based Multiplex Assay for the Simultaneous Detection of Antibodies to African Swine Fever Virus and Classical Swine Fever Virus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Xiao, W.; Cheng, Z.; Antonio, F.L.; Mei-hhua, Y. A Review of Current Methods for Analysis of Mycotoxins in Herbal Medicines. Toxins 2018, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, S.A.; Ison, S.H.; Owles, C.; Coe, J.; Sandercock, D.A.; Zanella, A.J. Development and validation of a multiplex fluorescent microsphere immunoassay assay for detection of porcine cytokines. MethodsX 2019, 6, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houman, M.; Walid, M.H.; Yasmine, D.; Emma, G.; Jan, J.D.; Azam, F.T. Rapid, Sensitive, and Selective Quantification of Bacillus cereus Spores Using xMAP Technology. Microorganism 2022, 10, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, J.M.; Schlain, B. Testing claimed minimal detectable concentrations of in vitro medical diagnostic devices. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Wei, L.; Yu, H.; Yang, P. Multiplex profiling of glycoproteins using a novel bead-based lectin array. Proteomics 2014, 14, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.S. Prevalence of anemia among children in India and updated serum ferritin levels. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvi, K.; Cecile, S.; Victor, N.; Leisel, T.; Andre, B.; Christian, R.; Henrik, F.; Pernille, K. Vitamin A and iron status of children before and after treatment of uncomplicated severe acute malnutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, L.F.; Anura, V.K.; Beena, B.; Tinku, T.; Krishnamachari, S.; Christopher, D. Anaemia and iron deficiency in pregnancy and adverse perinatal outcomes in Southern India. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvini, N.R.; Milly, B.; Royce, P.V. Prealbumin: The clinical utility and analytical methodologies. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2022, 59, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasily, M.S.; Baptiste, W.; Marco, N.; Christel, C.; Aline, A.; Camille, A.; Celine, D.; Serge, S.; Jose-Alain, S.; Christina, Z.; et al. Large benefit from simple things: High doe vitamin A improves RBP4-related retinal dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melinda, E.T.; Brigitta, D.; Zsofia, H.; Miklos, S. Cerebrovascular changes and neurodegeneration related to hyperlipidemia: Characteristics of the human ApoB-100 transgenic mice. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, T.; Farhoudi, M.; Bang, O.Y.; Koga, M.; Demchuk, A.M. The emerging value of serum D-dimer measurement in the work-up and management of ischemic stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javier, S.; Anne, L. The heterogeneity of liver cancer metabolism. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1311, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, L.; Alejandro, R.B.; Burt, C. Colon Cancer. In Treasure Island; Statpearls Publishing Press: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Christopher, P.; Thomas, E. Multiplex Immunoassay Techniques for On-Site Detection of Security Sensitive Toxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merck Biomarker Detection Solution Scheme. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.cn/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/marketing/global/documents/417/008/biology-mark-test-solution.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Stine, R.R.; Sakers, A.P.; Teslaa, T.; Kissig, M.; Seale, P. PRDM16 Maintains Homeostasis of the Intestinal Epithelium by Controlling Region-Specific Metabolism. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häussler, R.S.; Bendes, A.; Iglesias, M.J.; Sanchez-rivera, L.; Dodig-crnkovic, T.; Bystrom, S.; Fredolini, C.; Birqersson, E.; Dale, M.; Edfors, F. Systematic development of sandwich immunoassays for the plasma secretome. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1900008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schenk, M.F.; Cordewener, J.H.G.; America, A.H.P.; Peters, J.; Smulders, M.J.M.; Gilissen, L.J.W.J. Proteomic analysis of the major birch allergen Bet v 1 predicts allergenicity for 15 birch species. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.T.; Llewellyn, S.R.; Thorsten, D.; Morgan, I.L.; Marjorie, R.G.; Gildersleeve, J.C.; Shan, L. High-throughput profiling of anti-glycan humoral responses to SIV vaccination and challenge. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirouac, D.C.; Du, J.Y.; Lahdenranta, J.; Overland, R.; Yarar, D.; Paragas, V.; Pace, E.; Mcdonagh, C.F.; Nielsen, U.B.; Onsum, M.D. Computational modeling of ERBB2-amplified breast cancer identifies combined ErbB2/3 blockade as superior to the combination of MEK and AKT inhibitors. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, U12–U30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meimaridou, A.; Haasnoot, W.; Shelver, W.L.; Franek, M.; Nielen, M.W.F. Multiplex immunoassay for persistent organic pollutants in tilapia: Comparison of imaging- and flow cytometry-based platforms using spectrally encoded paramagnetic microspheres. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| The Kind of Reagent | The Name of Product | The Code of Product | Company (City, State, Country) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic reagents | Phosphate buffer (PBS) | KG018279 | Jiangsu KeyGEN BioTECH Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China) |
| SAPE | S866 | Thermo fisher Co., Ltd. (Waltham, MA, USA) | |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | WXBC7961V | Sigma Co., Ltd. (St. Louis, MO, USA) | |
| Coupling reagent | ProteOn Amine Coupling kit | 1762410 | Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (Berkeley, CA, USA) |
| Bio-Plex Amine Coupling kit | 171-406001 | Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (Berkeley, CA, USA) | |
| Antigen standards, capture antibodies and detection antibodies | SF antigen standard | 30-AF15 | Fitzgerald Industries International, Inc. (Acton, MA, USA) |
| SF capture antibody | MAB4062 | R&D Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA) | |
| SF detection antibody | NB110-8384B | Novus Biologicals, Inc. (Centennial, CO, USA) | |
| sTfR antigen standard | 05-52172 | ARP, Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA) | |
| sTfR capture antibody | ab10249 | Abcam, Inc. (Cambridge, UK) | |
| sTfR detection antiboty | NB100-73092B | Novus Biologicals, Inc. (Centennial, CO, USA) | |
| C-reaction protein standard | 30-AC05AF | Fitzgerald Industries International, Inc. (Acton, MA, USA) | |
| C-reaction capture antibody | MAB17071 | R&D Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA) | |
| C-reaction detection antibody | BAM17072 | R&D Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA) | |
| RBP4 antigen standard | 30-1358 | Fitzgerald Industries International, Inc. (Acton, MA, USA) | |
| RBP4 capture antibody | MAB33781 | R&D Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA) | |
| RBP4 detection antibody | BAM33782 | R&D Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA) | |
| Apo B antigen standard | SRP6302-500UG | Sigma Co., Ltd. (St. Louis, MO, USA) | |
| Apo B capture antibody | A2299-38D | USbiological Inc. (Salem, MA, USA) | |
| Apo B detection antibody | A2299-38E | USbiological Inc. (Salem, MA, USA) | |
| PA antigen standard | 30R-AP014 | Fitzgerald Industries International, Inc. (Acton, MA, USA) | |
| PA capture antibody | MAB7505 | R&D Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA) | |
| PA detection antibody | NBP2-90050B | Novus Biologicals, Inc. (Centennial, CO, USA) | |
| AFP antigen standard | PRO-406 | ProSpec-Tany TechnoGene Ltd. (Ness-Ziona, Israel) | |
| AFP capture antibody | NB110-7961 | Novus Biologicals, Inc. (Centennial, CO, USA) | |
| AFP detection antibody | NB120-10072B | Novus Biologicals, Inc. (Centennial, CO, USA) | |
| CEA antigen standard | 30C-CP1001 | Fitzgerald Industries International, Inc. (Acton, MA, USA) | |
| CEA capture antibody | 10-C10F | Fitzgerald Industries International, Inc. (Acton, MA, USA) | |
| CEA detection antibody | orb14352 | Biorbyt, Inc. (Cambridge, UK) | |
| D-D antigen standard | D9321 | Sigma Co., Ltd. (St. Louis, MO, USA) | |
| D-D capture antibody | NB110-8376 | Novus Biologicals, Inc. (Centennial, CO, USA) | |
| D-D detection antibody | NB100-73038B | Novus Biologicals, Inc. (Centennial, CO, USA) | |
| Interference reagents | Direct bilirubin | 14370-250MG | Sigma Co., Ltd. (St. Louis, MO, USA) |
| Indirect bilirubin | F1618-B | FANKE WEI, Inc. (Shanghai, China) | |
| Hemoglobin | H7379 | Sigma Co., Ltd. (St. Louis, MO, USA) | |
| Triglyceride | G107438-5g | Aladdin, Inc. (Shanghai, China) | |
| Comparison Kits | SF immunoturbidimetry kit | FE7002 | Beijing Leadman, Inc. (Beijing, China) |
| sTfR ELISA kit | SEKH-0330 | Beijing Solarbio life science, Inc. (Beijing, China) | |
| C-reaction protein ELISA kit | SEKH-0138 | Beijing Solarbio life science, Inc. (Beijing, China) | |
| Apo B ELISA kit | SEKH-0515 | Beijing Solarbio life science, Inc. (Beijing, China) | |
| PA ELISA kit | EK1684 | Wuhan Boster Biological Technology, Ltd. (Wuhan, China) | |
| RBP4 immunoturbidimetry kit | RB7001 | Beijing Leadman, Inc. (Beijing, China) | |
| D-D immunoturbidimetry kit | DD7680 | Beijing Leadman, Inc. (Beijing, China) | |
| AFP ECLIA kit | 4481798190 | Roche diagnostic product, Inc. (Shanghai, China) | |
| CEA ECLIA kit | 11731629322 | Roche diagnostic product, Inc. (Shanghai, China) |
| Antigen | Detection Antibody | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF-D | sTfR-D | CRP-D | RBP4-D | ApoB-D | AFP-D | PA-D | CEA-D | D-D-D | |
| SF | 100.00 | −0.18 | 0.01 | 1.22 | −0.11 | −0.04 | −0.25 | −7.27 | 0.00 |
| sTfR | −4.87 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 1.61 | −0.14 | −0.04 | 0.04 | 0.17 | −0.10 |
| CRP | −0.59 | 0.09 | 100.00 | −0.66 | 0.03 | 1.09 | 0.00 | −0.99 | 0.00 |
| RBP4 | −1.16 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 100.00 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.02 | −0.25 | 0.00 |
| ApoB | −2.59 | −0.22 | −0.03 | 0.28 | 100.00 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 4.05 | 0.20 |
| AFP | 0.19 | −0.02 | 0.01 | −0.07 | 0.00 | 100.00 | −0.02 | −0.33 | 0.00 |
| PA | 0.74 | 0.00 | −0.04 | 0.13 | −0.09 | −0.03 | 100.00 | 0.74 | 0.03 |
| CEA | −1.99 | 0.02 | 0.00 | −0.02 | 0.00 | 0.05 | −0.08 | 100.00 | −0.39 |
| D-D | 1.09 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 0.00 | −0.08 | 100.00 |
| Antigen | Capture Antibody | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-SF | C-sTfR | C-CRP | C-RBP4 | C-ApoB | C-AFP | C-PA | C-CEA | C-D-D | |
| SF | 100.00 | −14.39 | −0.48 | −5.35 | 0.18 | −0.15 | 0.24 | −1.40 | −1.41 |
| sTfR | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 0.15 | 1.74 | 2.02 |
| CRP | 0.00 | −0.13 | 100.00 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| RBP4 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 100.00 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.10 |
| ApoB | 4.99 | 9.96 | 1.02 | 4.78 | 100.00 | 3.32 | 7.36 | 2.07 | 2.52 |
| AFP | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.40 | 0.49 | −0.31 | 100.00 | 0.89 | 0.33 | 0.20 |
| PA | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 5.17 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 100.00 | 0.08 | 0.20 |
| CEA | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.08 | −0.02 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 4.30 |
| D-D | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| Limit of Detection | SF | sTfR | CRP | RBP4 | ApoB | AFP | PA | CEA | D-D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLD | 12.70 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 45.20 | 134.10 | 5.40 | 21.70 | 6.20 | 214.20 |
| BLD | 25.40 | 2.55 | 12.20 | 55.30 | 1900.00 | 12.50 | 47.70 | 7.30 | 312.50 |
| Protein Marker | Regression Equation | Determination Coefficients (r2) |
|---|---|---|
| SF | y = −0.9106x2 + 63.867x − 40.79 | 0.997 |
| sTfR | y = 0.0012x3 − 0.7202x2 + 139.45x + 433.6 | 0.992 |
| CRP | y = −0.2861x4 + 26.523x3 − 758.02x2 + 7860x − 573.33 | 0.998 |
| RBP4 | y = 619.95ln(x) + 621.12 | 0.996 |
| ApoB | y = 0.467x − 80.259 | 0.995 |
| AFP | y = 119.54x + 0.6148 | 0.997 |
| PA | y = 660.51 ln(x) − 395.57 | 0.981 |
| CEA | y = 30.35x2 + 164.82x + 9.9296 | 0.998 |
| D-D | y = 5.9577x − 6.648 | 0.999 |
| Serum Cases | SF | sTfR | CRP | RBP4 | ApoB | AFP | PA | CEA | D-D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum I + 4% mixed antigen standard | 79.66 | 94.7 | 105.98 | 82.66 | 91.51 | 109.46 | 87.25 | 103.37 | 77.53 |
| Serum II + 5% mixed antigen standard | 70.12 | 74.91 | 121.3 | 85.5 | 72.63 | 122.77 | 127.07 | 85.72 | 86.12 |
| Serum Cases | Evaluation Indicators | Protein Markers | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF | sTfR | CRP | RBP4 | ApoB | AFP | PA | CEA | D-D | ||
| Serum I | (ng/mL) | 0.25 | 64.87 | 10.18 | 152.60 | 29.09 | 0.50 | 134.12 | 0.25 | 51.02 |
| S (ng/mL) | 0.01 | 2.31 | 0.72 | 4.68 | 1.79 | 0.03 | 1.15 | 0.02 | 1.14 | |
| CV (%) | 4.42 | 3.57 | 7.11 | 3.07 | 6.15 | 4.87 | 0.85 | 7.31 | 2.23 | |
| Serum II | (ng/mL) | 0.36 | 52.12 | 8.81 | 155.94 | 61.87 | 2.37 | 130.83 | 1.48 | 226.69 |
| S (ng/mL) | 0.02 | 1.22 | 0.30 | 8.38 | 4.13 | 0.17 | 2.18 | 0.08 | 6.90 | |
| CV (%) | 6.38 | 2.35 | 3.35 | 5.38 | 6.68 | 6.95 | 1.67 | 5.37 | 3.04 | |
| Serum Cases | Evaluation Indicators | Protein Markers | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF | sTfR | CRP | RBP4 | ApoB | AFP | PA | CEA | D-D | ||
| Serum I | (ng/mL) | 0.23 | 21.70 | 1.55 | 13.98 | 50.79 | 0.02 | 144.65 | 0.01 | 7.77 |
| Sb2 | 0.00 | 4.43 | 0.04 | 1.65 | 74.50 | 0.00 | 69.38 | 0.00 | 0.52 | |
| CV (%) | 6.66 | 9.70 | 12.08 | 9.19 | 16.99 | 10.12 | 5.76 | 4.85 | 9.28 | |
| Serum II | (ng/mL) | 0.23 | 20.76 | 3.31 | 13.08 | 31.62 | 0.02 | 122.44 | 0.01 | 18.69 |
| Sb2 | 0.00 | 15.67 | 0.27 | 1.20 | 6.44 | 0.00 | 18.65 | 0.00 | 4.96 | |
| CV (%) | 16.55 | 19.07 | 15.74 | 8.39 | 8.03 | 8.45 | 3.53 | 3.65 | 11.92 | |
| Protein Markers | Between Liquid Protein Chip and Immunoturbidimetry | Between Liquid Protein Chip and ECLIA | Between Liquid Protein Chip and Elisa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| SF | 0.633 | 0.008 | — | — | — | — |
| sTfR | — | — | — | — | 0.504 | 0.047 |
| CRP | — | — | — | — | 0.994 | <0.001 |
| RBP4 | 0.534 | 0.033 | — | — | — | — |
| ApoB | — | — | — | — | 0.682 | 0.004 |
| AFP | — | — | 0.548 | 0.028 | — | — |
| PA | — | — | — | — | 0.689 | 0.003 |
| CEA | — | — | 0.507 | 0.045 | — | — |
| D-D | 0.852 | <0.001 | — | — | — | — |
| Statistic Indicators | Between Liquid Protein Chip and ECLIA | Between Liquid Protein Chip and Immunoturbidimetry | Between Liquid Protein Chip and Elisa | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFP | CEA | SF | RBP4 | D-D | sTfR | CRP | ApoB | PA | |
| t | — | 0.127 | 0.951 | −0.675 | — | −0.943 | — | — | — |
| p | 0.079 | 0.901 | 0.356 | 0.510 | 0.877 | 0.360 | 0.070 | 0.756 | 0.501 |
| Interferent | CRP | SF | AFP | sTfR | D-D | RBP4 | PA | CEA | ApoB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBIL (high) | −17.27 | 34.08 | −10.74 | −18.49 | 86.22 | −10.90 | 1.05 | −3.66 | −10.91 |
| DBIL (low) | 10.76 | 6.58 | 0.20 | −0.38 | 4.76 | −7.21 | −2.78 | 2.88 | −9.32 |
| IBIL (high) | 10.07 | 13.00 | 4.34 | 0.58 | −6.47 | −15.33 | −4.87 | 8.86 | −18.69 |
| IBIL (low) | 16.41 | 4.19 | 15.21 | 2.82 | 8.56 | −17.17 | −6.67 | 13.15 | −18.41 |
| TG (high) | 29.27 | 21.95 | 25.71 | 21.08 | 39.73 | −0.86 | 1.12 | 38.02 | −27.69 |
| TG (low) | 49.84 | 11.84 | 17.25 | 5.79 | 28.81 | −1.94 | −2.59 | 11.80 | −22.90 |
| Hb (high) | −5.96 | 3.90 | −21.38 | −4.06 | −20.75 | −3.23 | 2.55 | −8.92 | −32.09 |
| Hb (low) | 37.07 | 23.10 | 31.53 | 22.23 | 42.87 | 3.48 | −0.53 | 62.06 | −30.67 |
| Protein Markers | Liquid Protein Chip (pg/mL) | Solid Protein Chip (ng/mL) | ELISA (pg/mL) | Immunoturbidimetry (μg/mL) | ECLIA (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF | 12.70 | 1.21 a | — | 0.40 e | |
| sTfR | 1.00 | 1.73 a | 18.00 b | — | — |
| CRP | 0.90 | — | 5.36 b | — | — |
| RBP4 | 45.20 | — | — | 50.00 d | — |
| ApoB | 134.10 | — | 3910.00 b | — | — |
| AFP | 5.40 | — | — | — | 0.50 f |
| PA | 21.70 | — | 6.30 c | — | — |
| CEA | 6.20 | — | — | — | 0.50 f |
| D-D | 214.20 | — | — | 0.50 d | — |
| Detection Methods | Throughput | Volume of Detecting 9 Indicators (μL) | The time of Detecting 9 Indicators (h) | Cost of Single Indicator of Each Sample (CNY) | Whether the Results Can Be Appeared in the Same One Detection | The System Error of Detecting 9 Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid protein chip | 9 | 2 | 5 | 6.75 | Yes | Smaller |
| ELISA a | 1 | 36 | 45 | 100 | No | Larger |
| Immunoturbidimetry b | 1 | 150 | 3 | 50 | No | Larger |
| ECLIA c | 1 | 150 | 3 | 50 | No | Larger |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Niu, J.; Huo, J.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Sun, C. Construction and Evaluation of a Novel MAP Immunoassay for 9 Nutrition-and-Health-Related Protein Markers Based on Multiplex Liquid Protein Chip Technique. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061522
Yin J, Niu J, Huo J, Sun J, Huang J, Sun C. Construction and Evaluation of a Novel MAP Immunoassay for 9 Nutrition-and-Health-Related Protein Markers Based on Multiplex Liquid Protein Chip Technique. Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061522
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jiyong, Jiangping Niu, Junsheng Huo, Jing Sun, Jian Huang, and Chaoqun Sun. 2023. "Construction and Evaluation of a Novel MAP Immunoassay for 9 Nutrition-and-Health-Related Protein Markers Based on Multiplex Liquid Protein Chip Technique" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061522
APA StyleYin, J., Niu, J., Huo, J., Sun, J., Huang, J., & Sun, C. (2023). Construction and Evaluation of a Novel MAP Immunoassay for 9 Nutrition-and-Health-Related Protein Markers Based on Multiplex Liquid Protein Chip Technique. Nutrients, 15(6), 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061522







