Ameliorative Effects of Flavonoids from Platycodon grandiflorus Aerial Parts on Alloxan-Induced Pancreatic Islet Damage in Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Extraction and Isolation
2.4. Chemicals and Reagents
2.5. Zebrafish Care and Embryo Collection
2.6. Evaluation of Pancreatic Islets Recovery and Glucose Uptake
2.7. Action of Diazoxide (DZ) on the Efficacy of Isolated Compounds in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Zebrafish
2.8. Evaluation of mRNA Expression Using RT-qPCR
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy of PgA-EtOH, PgR-EtOH and Their Solvent Fractions in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Zebrafish
3.2. Efficacy of PgA-EtOAc and PgA-BuOH Fractions in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Zebrafish
3.3. Isolation and Identification of Compounds 1–8
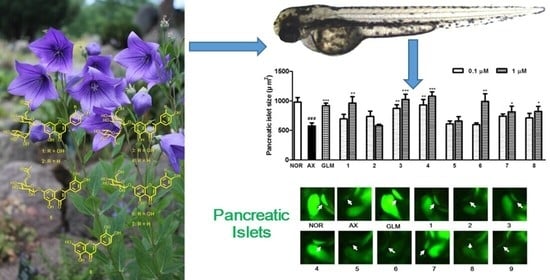
3.4. Effect of Compounds Isolated from the PgA-EtOAc and PgA-BuOH Fractions on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Zebrfish
3.5. Effect of Isolated Compounds on KATP Channels in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Zebrafish
3.6. Effect of Isolated Compounds on mRNA Expression of GCK, GCKR, GLIS3 and CDKN2B in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Zebrafish
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huxley, A.; Griffiths, M.; Levy, M. The New Royal Horticultural Society Dictionary of Gardening; Macmillan Reference Ltd.: London, UK, 1999; Volume 3, p. 651. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.T. Coloured Standard Illustrations of Korean Plants; Academy Book: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1996; p. 342. [Google Scholar]
- Zhonghuabencao Compilation Committee. Zhong Hua Ben Cao; Shanghai Science and Technologic Publisher: Shanghai, China, 1999; Volume 8, pp. 622–627. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Platycodon grandiflorus—An ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethanopharmacol. 2015, 164, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashcroft, F.M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels and disease: From molecule to malady. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E880–E889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sane, R.T.; Menon, S.N.; Inamdar, S.; Mote, M.; Gundi, G. Simultaneous determination of pioglitazone and glimepiride by high-performance liquid chromatography. Chromatographia 2004, 59, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepzig, H.; Kober, G.; Matter, C.; Luus, H.; Schneider, H.; Boedeker, K.H.; Kiowski, W.; Amann, K.W.; Gruber, D.; Harris, S.; et al. Sulfonylureas and ischemic preconditioning; a double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of glimepiride and glibenclamide. Eur. Heart J. 1999, 20, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Bu, S.; Yu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Ghatnekar, G.; Bu, M.; Yang, L.; Lu, B.; Feng, Z.; Lin, S.; et al. Diazoxide prevents diabetes through inhibiting pancreatic β-cells from apoptosis via Bcl-2/Bax rate and p38-β mitogen-activated protein kinase. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, J.; Ji, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Antihyperglycemic effects of Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC. extract on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2007, 62, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgraz, R.; Bonal, C.; Herrera, P.L. β-Cell regeneration: The pancreatic intrinsic faculty. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Li, J.; Wang, N.-L.; Yao, X.-S. Flavonoids and a new polyacetylene from Bidens parviflora Willd. Molecules 2008, 13, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.H.; Hong, B.N.; Rodriguez, I.; Ji, M.G.; Kim, K.; Kim, U.-J.; Kang, T.H. Synergistic potentials of coffee on injured pancreatic islets and insulin action via KATP channel blocking in zebrafish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5612–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djoukeng, J.D.; Arbona, V.; Argamasilla, R.; Gomez-Cadenas, A. Flavonoid profiling in leaves of Citrus genotypes under different environmental situations. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2008, 56, 11087–11097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, G.V.; Rao, P.S. A phytochemical study of Heylandia latebrosa. Fitoterapia 1982, 53, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.K.; Yadav, D.; Shanker, K.; Verma, R.K.; Saxena, A.K.; Gupta, M.M. Flavone glycoside based validated RP-LC method for quality evaluation of Prishniparni (Uraria picta). Chromatographia 2009, 69, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Chang, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Choi, S.W. Antioxidative flavonoids from leaves of Carthamus tinctorius. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2002, 25, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, M.; Kato, M.; Iinuma, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kimura, A.; Ohashi, H.; Sakai, H. Acylated luteolin glucosides from Salix gilgiana. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 2418–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Simon, J.E.; Aviles, I.F.; He, K.; Zheng, Q.-Y.; Tadmor, Y. Analysis of antioxidative phenolic compounds in Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2003, 51, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennini, B.; Chulia, A.J.; Kaouadji, M.; Thomasson, F. Flavonoid glycosides from Erica cinerea. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 2483–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, J.H.; Kang, M.W.; Roh, J.H.; Choi, S.U.; Zee, O.P. Cytotoxic phenolic compounds from Chionanthus retusus. Arch. Pharmcal Res. 2009, 32, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Dushenkov, S.; Ho, C.-T.; Sang, S. Novel acetylated flavonoid glycosides from the leaves of Allium ursinum. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leney, S.E.; Tavaré, J.M. The molecular basis of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake: Signalling, trafficking and potential drug targets. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 203, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchoula, K.; Khatib, A.; Jaffar, A.; Ahamed, Q.U.; Sulaiman, W.M.A.W.; Wahab, R.A.; El-seedi, H.R. The promise of zebrafish as a model of metabolic syndrome. Exp. Anim. 2019, 68, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capiotti, K.M.; Junior, R.A.; Kist, L.W.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D.; Silva, R.S.D. Persistent impaired glucose metabolism in a zebrafish hyperglycemia model. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 171, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.; Maddison, L.A.; Chen, W. Zebrafish as a model for obesity and diabetes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, N.; Duinkerken, B.H.P.; Carroll, E.C.; Giepmans, B.N.G. Microscopic modulation and ananlysis of islets of Langerhans in living zebrafish larvae. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 2497–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, Y.H.; Hong, B.N.; Rodriguez, I.; Park, M.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, Y.-G.; Shim, J.H.; Yasmin, T.; Kim, N.W.; Koo, Y.T.; et al. Steamed ginger may enhance insulin secertion through KATP channel closure in pancreatic β-cells potentially by increasing 1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione content. Nutrients 2020, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, K.; Saito, M.; Oh, K.B.; Nemoto, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Natsume, M.; Abe, H. Intracellular fate of 2-NBDG, a fluorescent probe for glucose uptake activity, in Escherichia coli cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1899–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowl, A.; Alauddin, M.; Rahman, M.; Ahmed, K. Antihyperglycemic effect of Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) seed extract in alloxan-induced diabetic rats and its use in diabetes mellitus: A brief qualitative phytochemical and acute toxicity test on the extract. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 6, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Phadatare, P.D.; Chandrashekhar, V.M. Influence of esomeprazole on hypoglycemic activity of oral antidiabetic agents in rats and rabbits. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 354, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.-H.; Choi, G.N.; Kim, J.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, D.O.; Kim, Y.J.; Heo, H.J. Antioxidant activities from the aerial parts of Platycodon grandiflorum. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazol, I.; Glensk, M.; Cisowski, W. Polyphenolic compounds from Platycodon grandiflorum A. DC. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2004, 61, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess, N.C.; Kozlowski, R.Z.; Carrington, C.A.; Hales, C.N.; Ashford, M.L.J. Effects of sulphonylureas and diazoxide on insulin secretion and nucleotide-sensitive channels in an insulin- secreting cell line. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 95, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Hebrok, M. Intercellular signals regulating pancreas development and function. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Halban, P.A. Decreased beta-cell mass in diabetes: Significance, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, S.C.; Austin, E.; Assouline-Thomas, B.; Kapeluto, J.; Blaichman, J.; Moosavi, M.; Petropavlovskaia, M.; Rosenberg, L. β-Cell mass dynamics and islet cell plasticity in human type 2 diabetes. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1462–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Vega-Monroy, M.L.; Larrieta, E.; German, M.S.; Baez-Saldana, A.; Fernandez-Mejia, C. Effects of biotin supplementation in the diet on insulin secretion, islet gene expression, glucose homeostasis and beta-cell proportion. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tixi-Verdugo, W.; Contreras-Ramos, J.; Sicilia-Argumedo, G.; German, M.S.; Fernandez-Mejia, C. Effects of biotin supplementation during the first week postweaning increases pancreatic islet area, beta-cell proportion, islets number, and beta-cell proliferation. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F.M.; Rorsman, P. KATP channels and islet hormone secretion: New insights and controversies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, R.D.G.; Hales, C.N. The interaction of various inhibitors and stimuli of insulin release studied with rabbit pancreas in vitro. Biochem. J. 1969, 113, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tabachnick, I.I.A.; Gulbenkian, A.; Seidman, F. The effect of a benzothiadiazine, diazoxide, on carbohydrate metabolism. Diabetes 1964, 13, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, L.K.; Florez, J.C. The genetics of type 2 diabetes: What have we learned from GWAS? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1212, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Lu, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, F.; Tang, S.; Bao, Y.; et al. Effects of GCK, GCKR, G6PC2 and MTNR1B variants on glucose metabolism and insulin secretion. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, T.C.; Paula, F.M.; Villate, O.; Colli, M.L.; Moura, R.F.; Cunha, D.A.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Cnop, M.; Julier, C.; et al. GLIS3, a susceptibility gene for type 1 and type 2 diabetes, modulates pancreatic beta cell apoptosis via regulation of a splice variant of the BH3-only protein Bim. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Sharma, R.B.; Nwosu, B.U.; Alonso, L.C. Islet biology, the CDKN2A/B locus and type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| GCK | 5′-ATCCTCATGGTGGACCAA-3′ | 5′-ATCACCAACCTCGGAGC-3′ |
| GCKR | 5′-CTGTGAAAGGGCTCTACTGA-3′ | 5′-AGCAAGAGTACAGCCACACT-3′ |
| GLIS3 | 5′-ATACACTCACACTGCCCTTC-3′ | 5′-GGACAGTGGATTCTGACAAC-3′ |
| CDKN2B | 5′-CGGAGTGAATGCCAATCTG-3′ | 5′-CTGTTCCAGCAGCACAAGAG-3′ |
| β-actin | 5′-CGAGCTGTCTTCCCATCCA-3′ | 5′-TCACCAACGTAGCTGTCTTTCT-3′ |
| C/H | Dorajiside I 1 | Dorajiside II 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | ||
| 2 | - | 167.0 | - | 164.4 | |
| 3 | 6.63s | 104.4 | 6.81 s | 103.2 | |
| 4 | - | 184.2 | - | 182.0 | |
| 5 | - | 163.2 | - | 161.6 | |
| 6 | 6.49 d (2.0) | 101.0 | 6.30 d (2.1) | 99.4 | |
| 7 | - | 164.4 | - | 162.3 | |
| 8 | 6.74 d (1.8) | 96.2 | 6.68 d (2.2) | 94.5 | |
| 9 | - | 159.0 | - | 157.0 | |
| 10 | - | 107.2 | - | 105.5 | |
| 1′ | - | 123.6 | - | 120.9 | |
| 2′ | 7.42 brs | 114.4 | 7.87 d (8.8) | 128.6 | |
| 3′ | - | 147.3 | 6.87 d (8.8) | 116.1 | |
| 4′ | - | 151.4 | 161.2 | ||
| 5′ | 6.93 d (8.1) | 116.9 | 6.87 d (8.8) | 116.1 | |
| 6′ | 7.44 brd (8.1) | 120.6 | 7.87 d (8.8) | 128.6 | |
| Glc | 1″ | 5.20 d (7.7) | 99.8 | 5.20 d (7.7) | 97.6 |
| 2″ | 3.73 t (8.2) | 79.1 | 3.47 dd (9.1, 7.8) | 76.2 | |
| 3″ | 3.67 t (8.8) | 79.1 | 3.72 m | 76.9 | |
| 4″ | 3.40 t (9.4) | 71.9 | 3.13 m | 69.9 | |
| 5″ | 3.79 brt (8.4) | 75.6 | 3.43 brt (8.5) | 73.8 | |
| 6″ | 4.23 dd (11.9, 7.4) | 64.9 | 4.28 dd (11.9, 1.9) | 63.3 | |
| 4.48 brd (11.2) | 3.99 dd (12.0, 7.4) | ||||
| Ac | C=O | 172.9 | 170.2 | ||
| CH3 | 2.09 s | 20.9 | 1.94 s | 20.6 | |
| Rha | 1‴ | 5.32 d (1.2) | 102.7 | 5.05 d (1.5) | 100.6 |
| 2‴ | 3.97 m | 72.3 | 3.63 brs | 70.4 | |
| 3‴ | 3.64 dd (9.5, 2.3) | 72.3 | 3.27 m | 70.5 | |
| 4‴ | 3.45 t (9.6) | 74.1 | 3.15 m | 71.9 | |
| 5‴ | 3.99 m | 70.2 | 3.69 m | 68.4 | |
| 6‴ | 1.38 d (6.2) | 18.4 | 1.14 d (6.2) | 18.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, Y.H.; Kim, E.B.; Kang, J.E.; Kim, J.S.; Jeon, Y.; Shin, S.W.; Kang, T.H.; Kwak, J.H. Ameliorative Effects of Flavonoids from Platycodon grandiflorus Aerial Parts on Alloxan-Induced Pancreatic Islet Damage in Zebrafish. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071798
Nam YH, Kim EB, Kang JE, Kim JS, Jeon Y, Shin SW, Kang TH, Kwak JH. Ameliorative Effects of Flavonoids from Platycodon grandiflorus Aerial Parts on Alloxan-Induced Pancreatic Islet Damage in Zebrafish. Nutrients. 2023; 15(7):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071798
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Youn Hee, Eun Bin Kim, Ji Eun Kang, Ju Su Kim, Yukyoung Jeon, Sung Woo Shin, Tong Ho Kang, and Jong Hwan Kwak. 2023. "Ameliorative Effects of Flavonoids from Platycodon grandiflorus Aerial Parts on Alloxan-Induced Pancreatic Islet Damage in Zebrafish" Nutrients 15, no. 7: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071798
APA StyleNam, Y. H., Kim, E. B., Kang, J. E., Kim, J. S., Jeon, Y., Shin, S. W., Kang, T. H., & Kwak, J. H. (2023). Ameliorative Effects of Flavonoids from Platycodon grandiflorus Aerial Parts on Alloxan-Induced Pancreatic Islet Damage in Zebrafish. Nutrients, 15(7), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071798