The Effect of a Planetary Health Diet on the Human Gut Microbiome: A Descriptive Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.5. Culturing of Bacteria
2.6. Mass-Spectrometry-Based Identification
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
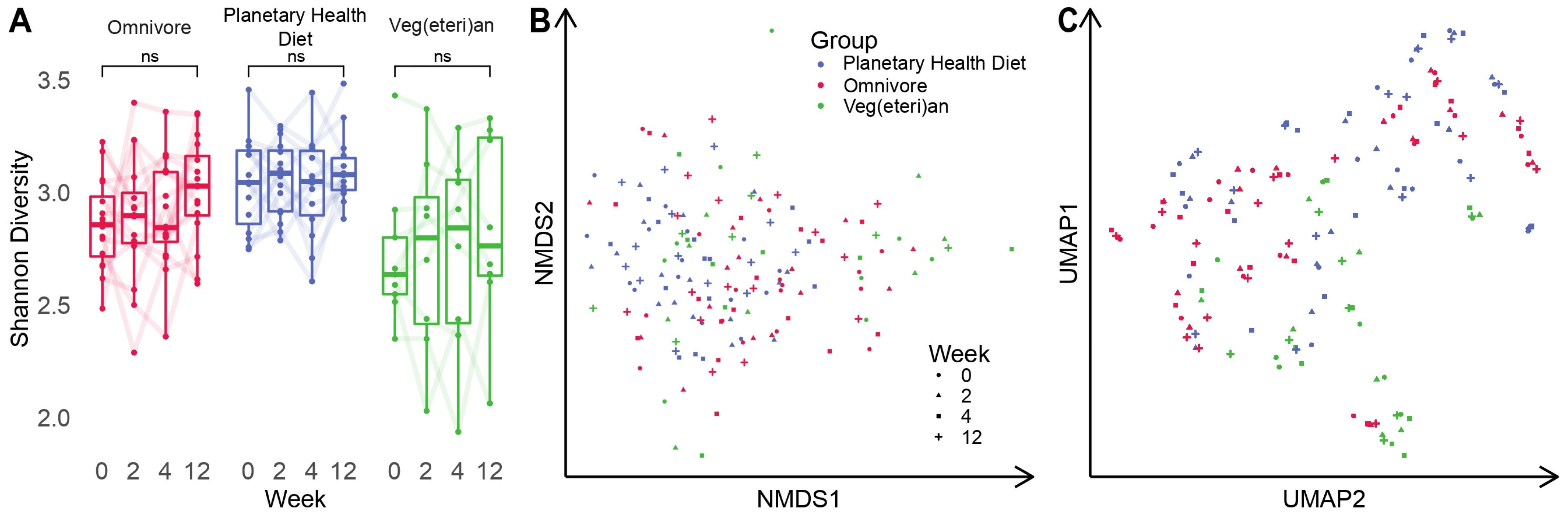
3.1. Intestinal Microbial Diversity Stays Relatively Stable over Time
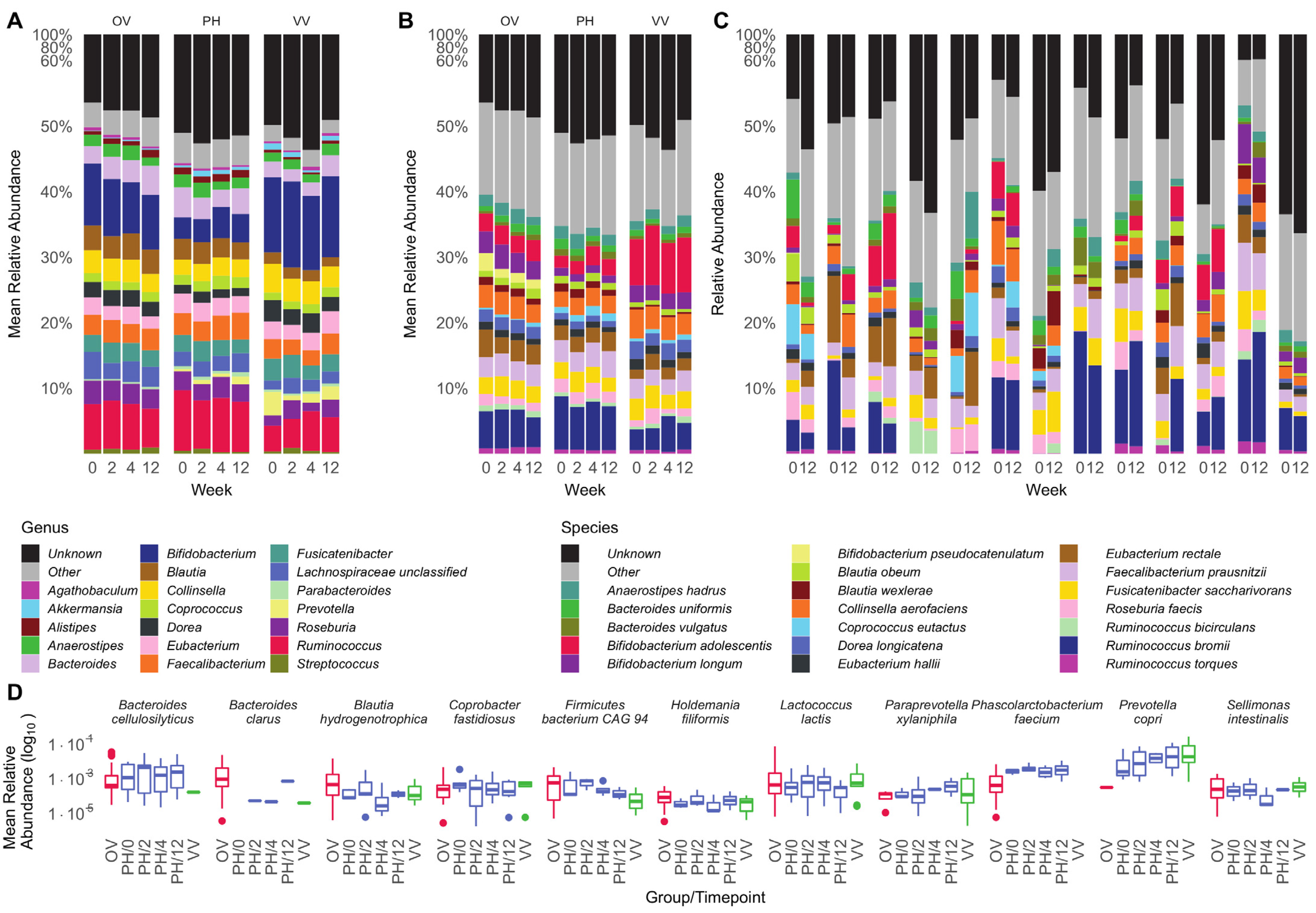
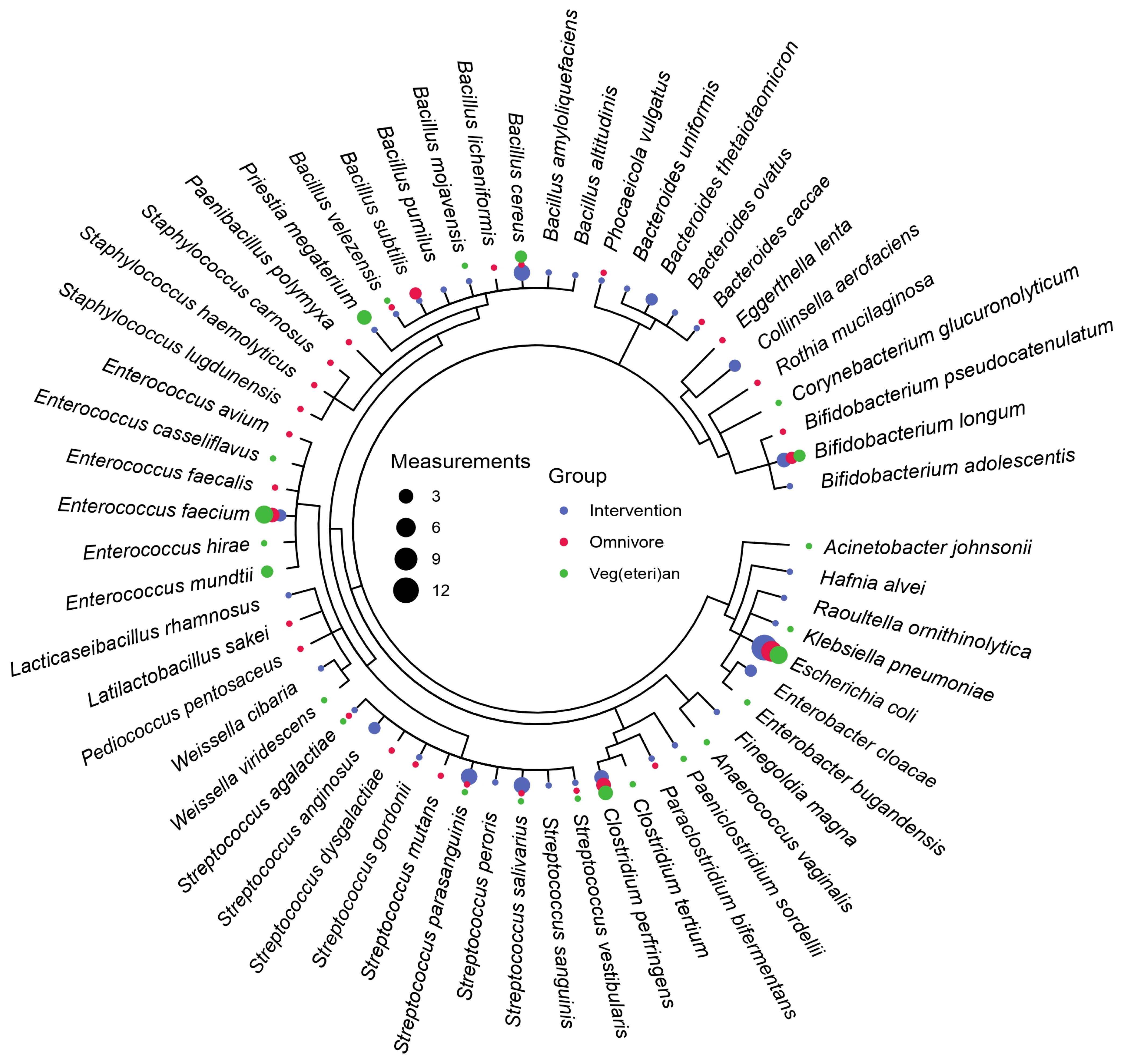
3.2. Microbiota Composition Is Host-Specific and Varies between Diets
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the anthropocene: The EAT-Lancet commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Summary Report of the EAT-Lancet Commission. Available online: https://eatforum.org/eat-lancet-commission/eat-lancet-commission-summary-report/ (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Marchesi, J.R.; Ravel, J. The vocabulary of microbiome research: A proposal. Microbiome 2015, 30, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Chang, H.W.; Yan, D.I.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Wong, K.; Abrouk, M.; Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; et al. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhare, S.V.; Patangia, D.V.; Patil, R.H.; Souche, Y.S.; Patil, N.P. Factors influencing the gut microbiome in children: From infancy to childhood. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.S.; Gupta, A. Influence of early life, diet, and the environment on the microbiome. CGH 2019, 17, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanes, C.; Bittinger, K.; Gao, Y.; Friedman, E.S.; Nessel, L.; Paladhi, U.R.; Chau, L.; Panfen, E.; Fischbach, M.A.; Braun, J.; et al. Role of dietary fiber in the recovery of the human gut microbiome and its metabolome. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 394–407.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, P.; Shen, L.; Niu, L.; Tan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, L.; Hao, X.; Li, X.; et al. Short-chain fatty acids and their association with signalling pathways in inflammation, glucose and lipid metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Stiemsma, L.T.; Dimitriu, P.A.; Thorson, L.; Russell, S.; Yurist-Doutsch, S.; Kuzeljevic, B.; Gold, M.J.; Britton, H.M.; Lefebvre, D.L.; et al. Early infancy microbial and metabolic alterations affect risk of childhood asthma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 307ra152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvin, J. Fiber and prebiotics: Mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslowski, K.M.; Mackay, C.R. Diet, gut microbiota and immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Schmartz, G.P.; Gröger, L.; Grammes, N.; Galata, V.; Philippeit, H.; Weiland, J.; Ludwig, N.; Meese, E.; Tierling, S.; et al. Effects of resistant starch on symptoms, fecal markers, and gut microbiota in Parkinson’s Disease–The RESISTA-PD trial. GPB 2022, 20, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2021, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, A.; Valdes, A.M. Role of the gut microbiome in chronic disease: A narrative review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Shively, C.A.; Register, T.C.; Craft, S.; Yadav, H. Gut microbiome-mediterranean diet intercations in improving host health. F1000research 2019, 8, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, J.; Barthel, B. A look at plant-based diets. Mo. Med. 2021, 118, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery, I.B.; O’Toole, P.W. Diet-microbiota interactions and their implications for healthy living. Nutrients 2013, 5, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watzl, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of plant-based foods and of their constituents. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2008, 78, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorth, M.F.; Blædel, T.; Bendtsen, L.Q.; Lorenzen, J.K.; Holm, J.B.; Kiilerich, P.; Roager, H.M.; Kristiansen, K.; Larsen, L.H.; Astrup, A. Prevotella-to-Bacteroides ratio predicts body weight and fat loss success on 24-week diets varying in macronutrient composition and dietary fiber: Results from a post-hoc analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 43, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, A.; Lahti, L.; Salojärvi, J.; Holtrop, G.; Korpela, K.; Duncan, S.H.; Date, P.; Farquharson, F.; Johnstone, A.M.; Lobley, G.E.; et al. Impact of diet and individual variation on intestinal microbiota composition and fermentation products in obese men. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagmutt, F.J.; Pouzou, J.G.; Costard, S. The EAT-Lancet commission’s dietary composition may not prevent noncommunicable disease mortality. J. Nurt. 2020, 150, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalile, B.; Kim, C.; Challinor, A.; Geurts, L.; Gibney, E.R.; Galdos, M.V.; La Fata, G.; Layé, S.; Mathers, J.C.; Vauzour, D.; et al. The EAT-Lancet reference diet and cognitive function across the life course. Lancet Planet Health 2022, 6, e749–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacau, L.T.; De Carli, E.; de Carvalho, A.M.; Lotufo, P.A.; Moreno, L.A.; Bensenor, I.M.; Marchioni, D.M. Development and validation of an index based on EAT-Lancet recommendations: The Planetary Health Diet Index. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehner, J.; Schmartz, G.P.; Groeger, L.; Dastbaz, J.; Ludwig, N.; Hannig, M.; Rupf, S.; Seitz, B.; Flockerzi, E.; Berger, T.; et al. Systematic cross-biospecimen evaluation of DNA extraction kits for long- and short-read multi-metagenomic sequencing studies. GPB 2022, 20, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, F.; McIver, L.J.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Dubois, L.; Asnicar, F.; Maharjan, S.; Mailyan, A.; Manghi, P.; Scholz, M.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Integrating taxonomic, functional, and strain-level profiling of diverse microbial communities with bioBakery 3. eLife 2021, 10, e65088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.T.; Irber, L. sourmash: A library MinHash sketching of DNA. J. Open Source Softw. 2016, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Rinke, C.; Mussig, A.J.; Chaumeil, P.A.; Hugenholtz, P. GTDB: An ongoing census of bacterial and archaeal diversity through a phylogenetically consistent, rank nonrmalized and complete genome-based taxonomy. Nucl. Acids Res. 2022, 50, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for dimension reduction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar]
- Gloor, G. Alex2: Anova-like differential expression tool for compositional data. ALDEX Man. Modul. 2015, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Das Peddada, S. Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Overmann, J.; Clavel, T. Cultured microbes represent a substantial fraction of the human and mouse gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.M.; Champ, M.M.J.; Cloran, S.J.; Fleith, M.; Van Lieshout, L.; Mejborn, H.; Burley, V.J. Dietary fibre in Europe: Current state of knowledge on definitions, sources, recommendations, intakes and relationships to health. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 149–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.F. A planet based diet benefits personal and planetary health. BMJ 2022, 379, o2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, N.T.; Schmidt, A.W.; Venkataraman, A.; Kim, K.S.; Waldron, C.; Schmidt, T.M. Dynamics of human gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in response to dietary interventions with three fermentable fibers. mBio 2019, 10, e02566-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Solvang, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Walker, A.W.; Mukhopadhya, I. Dietary fibre complexity and its influence on functional groups of the human gut microbiota. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessi, A.M.; Gray, V.; Farquharson, F.M.; Flores-López, A.; Shaw, S.; Stead, D.; Wegmann, U.; Shearman, C.; Gasson, M.; Collie-Duguid, E.S.R.; et al. Β-Glucan is a major growth substrate for human gut bacteria related to Coprococcus eutactus. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 2150–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Sun, Y.; Ip, L.Y.T.; Wang, L.; Chan, F.K.; Miao, Y.; Ng, S.C. Prevotella species in the human gut is primarily comprised of Prevotella copri, Prevotella stercorea and related lineages. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U.; Sczesnak, A.; Longman, R.S.; Segata, N.; Ubeda, C.; Bielski, C.; Rostron, T.; Cerundolo, V.; Pamer, E.G.; Abramson, S.B.; et al. Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. eLife 2013, 2, e01202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Calabrés, E.; Ortega-Hernández, A.; Modrego, J.; Gómez-Gordo, R.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Rodríguez-Bobada, C.; González, P.; Gómez-Garre, D. Gut microbiota profile identifies transition from compensated cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morotomi, M.; Nagai, F.; Sakon, H.; Tanaka, R. Paraprevotella clara gen. Nov.; spo. Nov. and Paraprevotella xylaniphila sp. Nov.; members of the family ‘Prevotellaceae’ isolated from human faeces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenda, T.; Grenda, A.; Domaradzki, P.; Krawczyk, P.; Kwiatek, K. Probiotic potential of Clostridium spp.—Advantages and doubts. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 3118–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
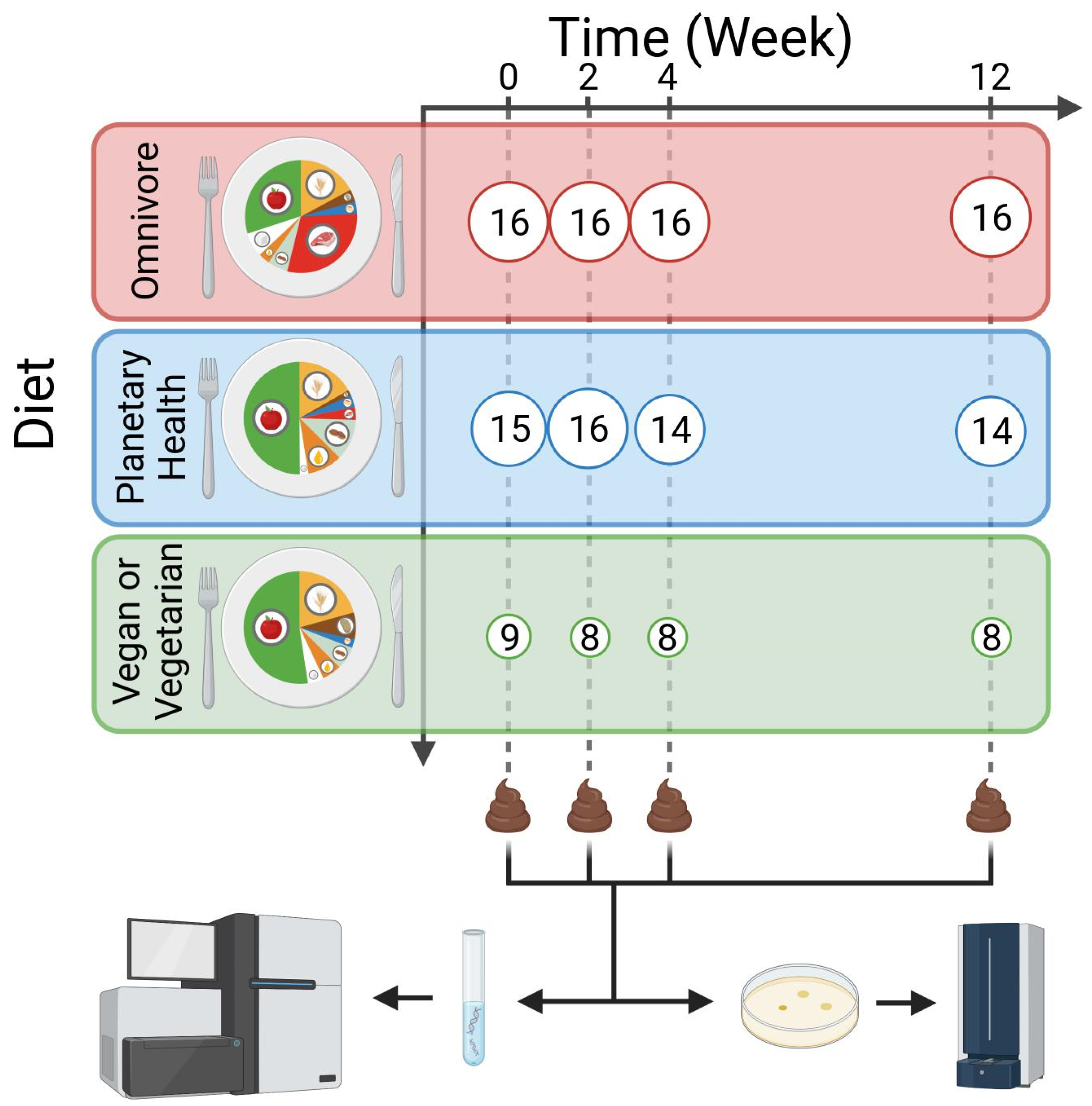
| OV | VV | PH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age ranges | 27–56 | 22–55 | 19–57 |
| BMI ranges | 19.8–32.8 | 19.9–40.1 | 20.0–24.4 |
| Male | 10 | 1 | 4 |
| Female | 6 | 8 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehner, J.; Schmartz, G.P.; Kramer, T.; Keller, V.; Keller, A.; Becker, S.L. The Effect of a Planetary Health Diet on the Human Gut Microbiome: A Descriptive Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081924
Rehner J, Schmartz GP, Kramer T, Keller V, Keller A, Becker SL. The Effect of a Planetary Health Diet on the Human Gut Microbiome: A Descriptive Analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(8):1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081924
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehner, Jacqueline, Georges P. Schmartz, Tabea Kramer, Verena Keller, Andreas Keller, and Sören L. Becker. 2023. "The Effect of a Planetary Health Diet on the Human Gut Microbiome: A Descriptive Analysis" Nutrients 15, no. 8: 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081924
APA StyleRehner, J., Schmartz, G. P., Kramer, T., Keller, V., Keller, A., & Becker, S. L. (2023). The Effect of a Planetary Health Diet on the Human Gut Microbiome: A Descriptive Analysis. Nutrients, 15(8), 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081924







