Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei X12 Strain Induces Apoptosis in HT-29 Cells through Activation of the Mitochondrial Pathway
Highlights
- Whole peptidoglycan (WPG), extracted from L. paracasei subsp. paracasei X12, inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in HT-29 cells in a dose-dependent manner.
- WPG induced apoptosis in HT-29 cells through the activation of the mitochondrial pathway.
- The main finding highlighted the role of WPG in inducing apoptosis in the human colon cancer cell line HT-29.
- The main finding demonstrated the potential application of WPG as a natural agent in the treatment of cancer in the future.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Lactobacillus Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. Preparation of WPG from the Lactobacillus Strain
2.3. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Analysis of Cell Apoptosis
2.6. Morphological Observation of Apoptosis
2.7. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and ROS Levels
2.8. Measurement of Cyto-Crelease
2.9. RNA Extraction and Semi-Quantitative RT-PCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of WPG on Viability of HT-29 Cells and Vero Cells
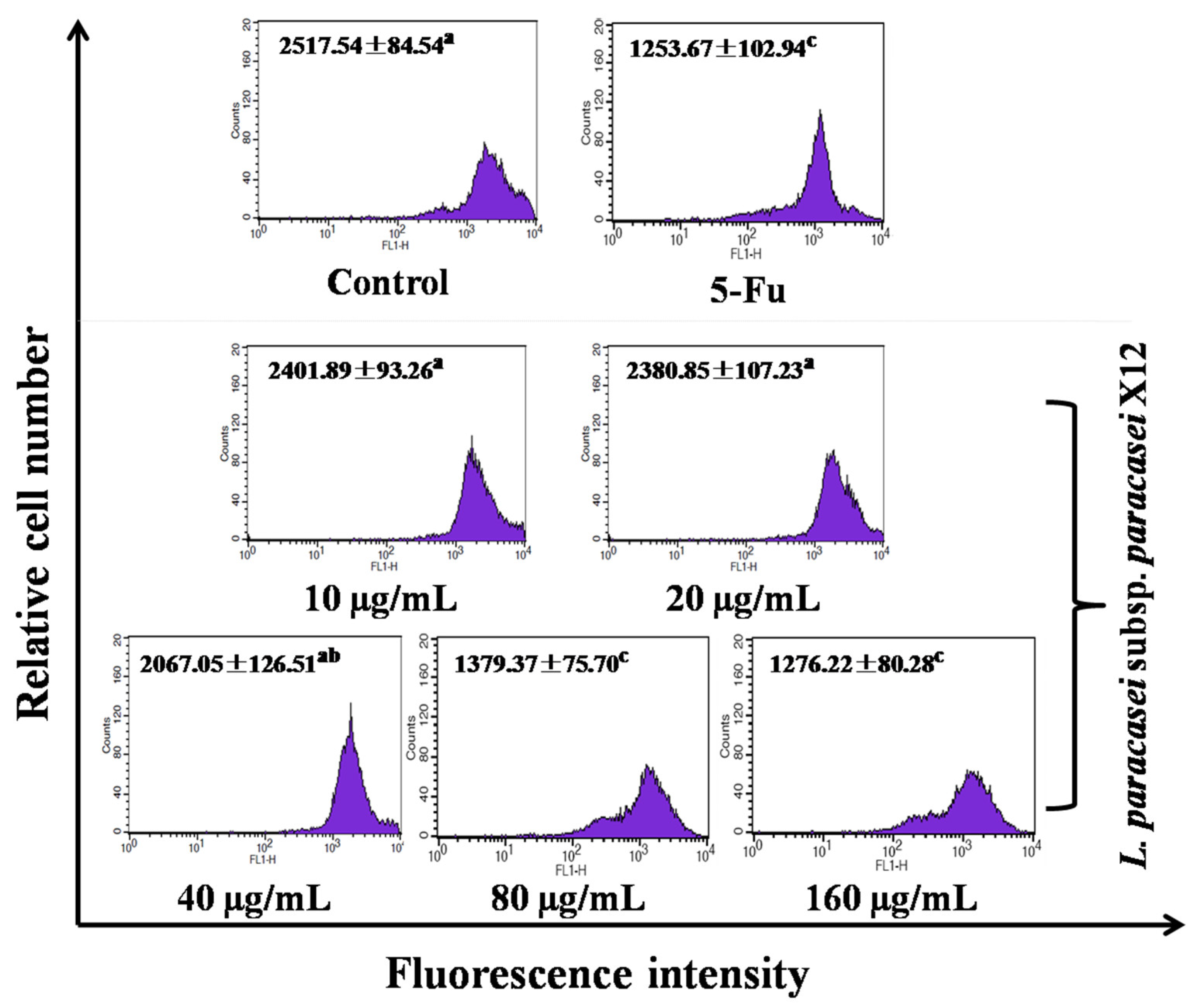
3.2. WPG Induces Apoptosis in HT-29 Cells
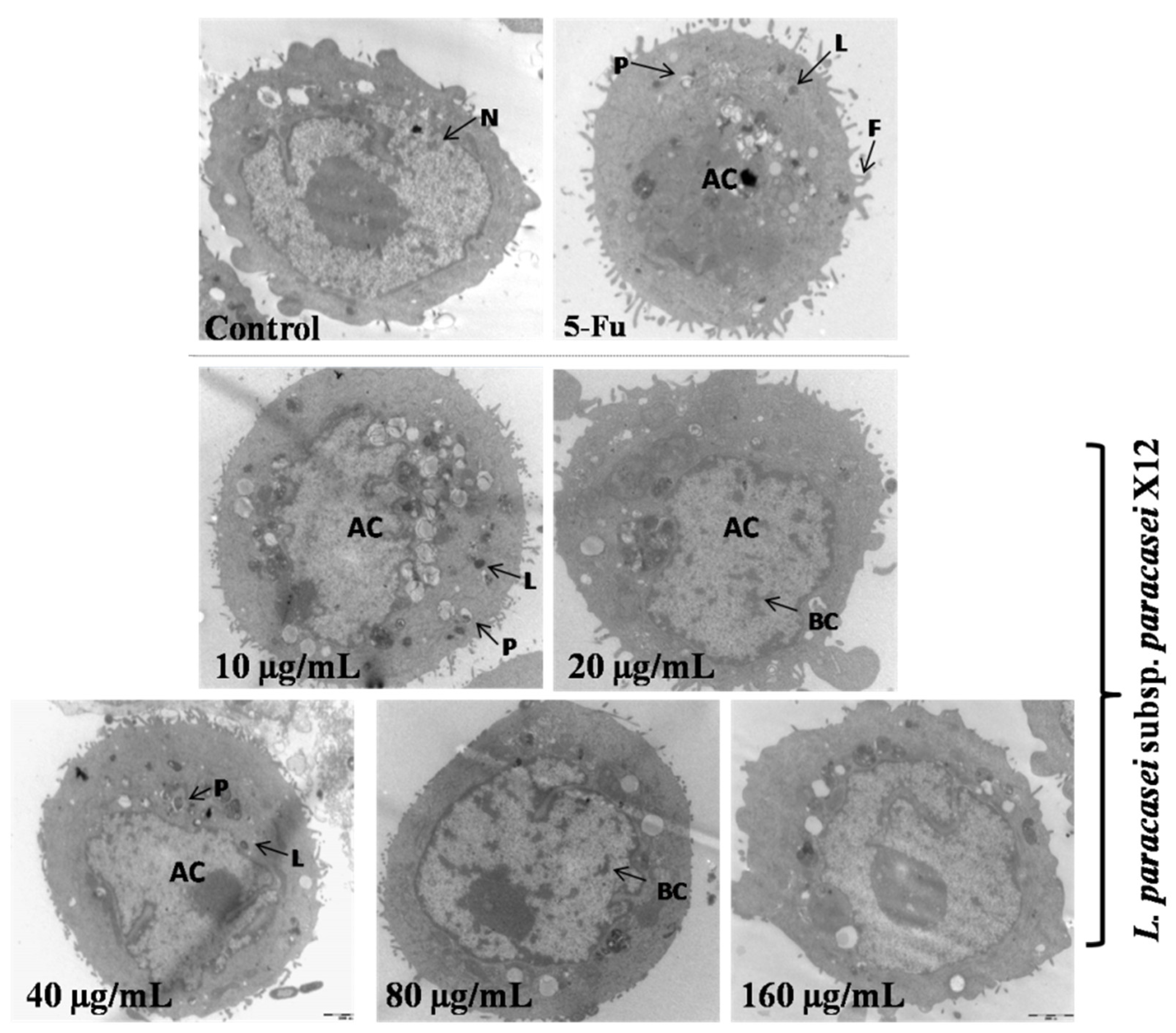
3.3. Effects of WPG on Morphology of HT-29 Cells
3.4. Effect of WPG on Inducing Apoptosis via the Mitochondrial Pathway
3.5. Effects of WPG on Intracellular ROS
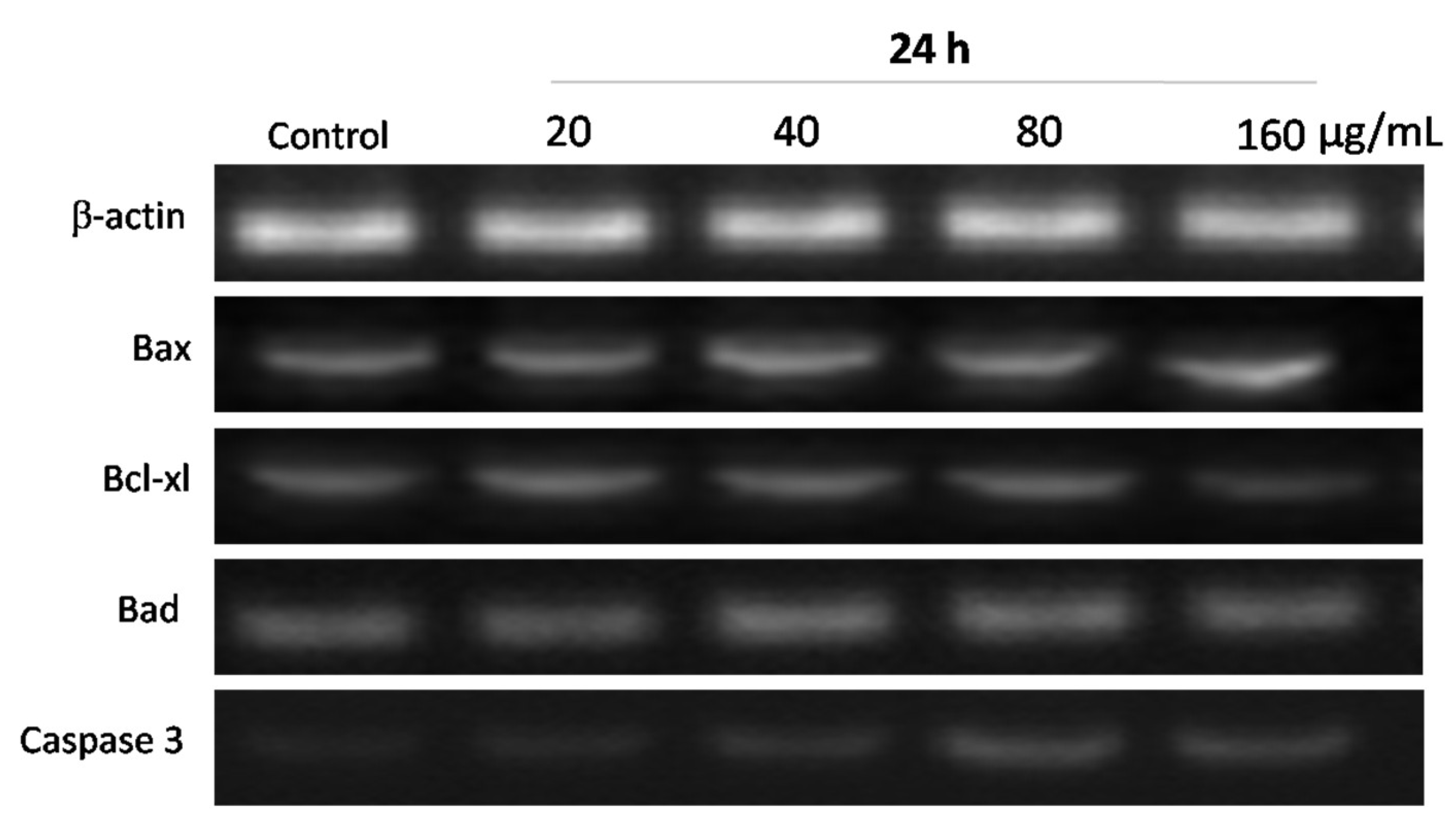
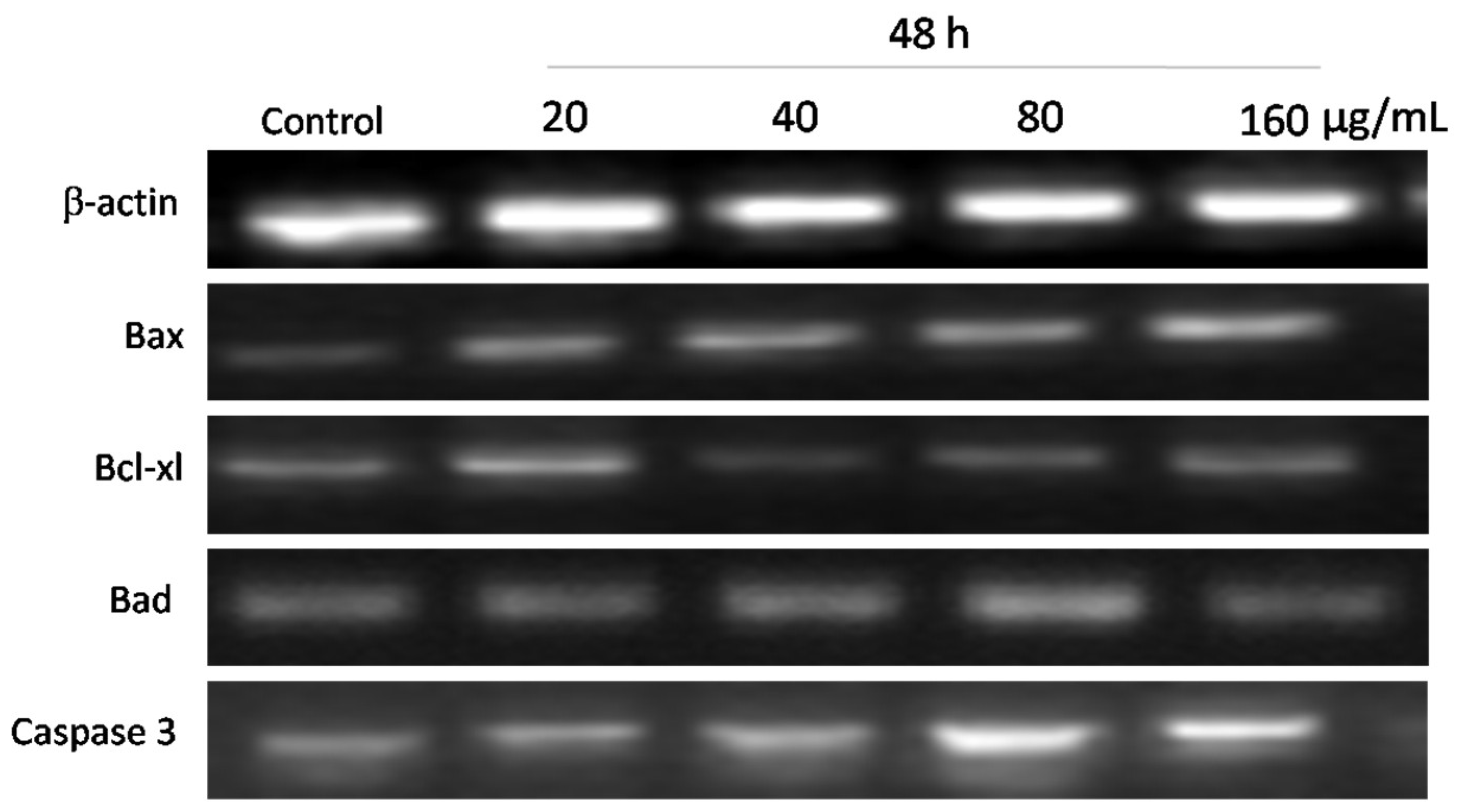
3.6. Effects of WPG on Expression of Apoptosis-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, H.; Chen, C. The colorectal cancer epidemic: Challenges and opportunities for primary, secondary and tertiary prevention. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Xia, J.; Wu, S.; Tu, W.; Pan, Z.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y. Insights into a Possible Influence on Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier Function During Chronic Exposure of Mice to Imazalil. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keku, T.O.; Dulal, S.; Deveaux, A.; Jovov, B.; Han, X. The gastrointestinal microbiota and colorectal cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G351–G363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M. Prebiotics and Probiotics in Digestive Health. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.-Q.; Li, L. The Potential Role of Probiotics in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, A.; Ashtari, S.; Sabet, B.; Davoodi, S.H.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Akbari, M.E.; Niaz, A.; Mortazavian, A.M. Probiotics and their role in gastrointestinal cancers prevention and treatment; an overview. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2018, 11, 284–295. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, C.S. Chapter 21-probiotics and enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract. In Enzymes in Human and Animal Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Shukla, G. Internationally indexed journal. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2015, 6, 529–543. [Google Scholar]
- Shida, K.; Kiyoshima-Shibata, J.; Nagaoka, M.; Watanabe, K.; Nanno, M. Induction of Interleukin-12 by Lactobacillus Strains Having a Rigid Cell Wall Resistant to Intracellular Digestion. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3306–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrouche, T.; Boutin, Y.; Prioult, G.; Fliss, I. Effects of bifidobacterial cytoplasm, cell wall and exopolysaccharide on mouse lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapot-Chartier, M.P.; Kulakauskas, S. Cell wall structure and function in lactic acid bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13 (Suppl. 1), S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-M.; Zhang, L.-W.; Fan, R.-B.; Han, X.; Yi, H.-X.; Zhang, L.-L.; Xue, C.-H.; Li, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Shigwedha, N. Induction of HT-29 cells apoptosis by lactobacilli isolated from fermented products. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, B.; Rodríguez, A.; Kulakauskas, S.; Chapot-Chartier, M.-P. Cell wall homeostasis in lactic acid bacteria: Threats and defences. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 538–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.J.; Reyes, C.N.; Liang, W.; Becker, C.; Shimada, K.; Wheeler, M.L.; Cho, H.C.; Popescu, N.I.; Coggeshall, K.M.; Arditi, M.; et al. Hexokinase Is an Innate Immune Receptor for the Detection of Bacterial Peptidoglycan. Cell 2016, 166, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firtel, M.; Henderson, G.; Sokolov, I. Nanosurgery: Observation of peptidoglycan strands in Lactobacillus helveticus cell walls. Ultramicroscopy 2004, 101, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, W.; Blanot, D.; De Pedro, M.A. Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Mandal, S. Bifidobacteria—Insight into clinical outcomes and mechanisms of its probiotic action. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 192, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, C.M.; Singh, A.T.K. Apoptosis: A Target for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Letai, A.; Sarosiek, K. Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: The balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Kwon, G.T.; Park, J.H.Y. trans-10,cis-12 Conjugated Linoleic Acid Induces Depolarization of Mitochondrial Membranes in HT-29 Human Colon Cancer Cells: A Possible Mechanism for Induction of Apoptosis. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorova, L.D.; Popkov, V.A.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Silachev, D.N.; Pevzner, I.B.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Babenko, V.A.; Zorov, S.D.; Balakireva, A.V.; Juhaszova, M.; et al. Mitochondrial membrane potential. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 552, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.-W.; Wang, X.-M.; Ko, H.; Kwon, H.C.; Cha, J.W.; Yang, H.O. Hyperoside protects primary rat cortical neurons from neurotoxicity induced by amyloid β-protein via the PI3K/Akt/Bad/BclXL-regulated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 672, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Zheng, Q.; Hou, J. Lactobacillus acidophilus S-layer protein-mediated inhibition of PEDV-induced apoptosis of Vero cells. Veter- Microbiol. 2019, 229, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, R.; Kakkar, P. Modulation of Bax/Bcl-2 and caspases by probiotics during acetaminophen induced apoptosis in primary hepatocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiao, Y. Whole Peptidoglycan Extracts from the Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei M5 Strain Exert Anticancer Activity In Vitro. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2871710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Zhang, L.-W.; Tuo, Y.-F.; Guo, C.-F.; Yi, H.-X.; Li, J.-Y.; Han, X.; Du, M. Inhibition of Shigella sonnei adherence to HT-29 cells by lactobacilli from Chinese fermented food and preliminary characterization of S-layer protein involvement. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Song, C.; Shan, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Hu, P.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Guo, S. The antioxidative effects of three lactobacilli on high-fat diet induced obese mice. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65808–65815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Raza, A.; Sethi, V.; Dalal, A.; Ghosh, S.S.; Biswas, G. Understanding flow dynamics, viability and metastatic potency of cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through constricted microchannel. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrani, R.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Kohan, L.; Jafari, B. Saccharomyces cerevisiae inhibits growth and metastasis and stimulates apoptosis in HT-29 colorectal cancer cell line. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 28, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivya, S.; Khandelwal, N.; Abraham, S.K.; Premkumar, K. Impact of anthocyanidins on mitoxantrone-induced cytotoxicity and genotoxicity: An in vitro and in vivo analysis. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Yi, H.; Han, X.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Y. Physicochemical characterization and antitumour activity of exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus casei SB27 from yak milk. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Tang, F.; Lu, M.; Xu, C.; Hu, J.; Mei, M.; Wang, H. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 4027–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, M.; Kumar, A.; Deshidi, R.; Sharma, V.; Singh, R.D.; Singh, J.; Sharma, P.R.; Shah, B.A.; Jaglan, S.; Singh, S. Erratum to: Cladosporol a triggers apoptosis sensitivity by ROS-mediated autophagic flux in human breast cancer cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, P.; Gogoi, S.K.; Sanpui, P.; Paul, A.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Signaling gene cascade in silver nanoparticle induced apoptosis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 77, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, N.; Tafvizi, F.; Jafari, P. Cell cycle arrest and anti-cancer potential of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus against HT-29 cancer cells. Bioimpacts 2021, 11, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamo, Z.; Azrad, M.; Fichtman, B.; Peretz, A. The Cytopathic Effect of Different Toxin Concentrations from Different Clostridioides difficile Sequence Types Strains in Vero Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 763129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucerova, L.; Altanerova, V.; Matuskova, M.; Tyciakova, S.; Altaner, C. Adipose Tissue–Derived Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mediated Prodrug Cancer Gene Therapy. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6304–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Dong, Z.; Lian, W.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, H. Ochratoxin A causes mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptotic and autophagic cell death and also induces mitochondrial biogenesis in human gastric epithelium cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Woo, H.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, H.J. Screening for antiproliferative effects of cellular components from lactic acid bacteria against human cancer cell lines. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Gao, Q.; Min, M.; Zhang, C.; Peng, S.; Shi, Z. Ability of Lactobacillus plantarum lipoteichoic acid to inhibit Vibrio anguillarum-induced inflammation and apoptosis in silvery pomfret (Pampus argenteus) intestinal epithelial cells. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 54, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, X. Effect of selenylation modification on antitumor activity of peptidoglycan from Lactobacillus acidophilus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Zhu, N.; Xiong, X.; Li, G. Peptidoglycan derived from Lactobacillus rhamnosus MLGA up-regulates the expression of chicken β-defensin 9 without triggering an inflammatory response. Innate Immun. 2020, 26, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichera, G.A.; Giese, G. Non-immunologically-mediated cytotoxicity of Lactobacillus casei and its derivative peptidoglycan against tumor cell lines. Cancer Lett. 1994, 85, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damia, G.; Broggini, M. Improving the selectivity of cancer treatments by interfering with cell response pathways. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2550–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kim, Y.; Han, K.; You, S.; Oh, S.; Kim, S. Effects of Lactobacillus strains on cancer cell proliferation and oxidative stress in vitro. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerl, R.; Vaux, D.L. Apoptosis in the development and treatment of cancer. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichera, G.A.; Fichera, M.; Milone, G. Antitumoural activity of a cytotoxic peptide of Lactobacillus casei peptidoglycan and its interaction with mitochondrial-bound hexokinase. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2016, 27, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Limaye, A.; Chang, H.-W.; Liu, J.-R. Screening of Lactic Acid Bacterial Strains with Antiviral Activity Against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 14, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haza, A.I.; Zabala, A.; Morales, P. Protective effect and cytokine production of a Lactobacillus plantarum strain isolated from ewes’ milk cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, J.; Jiang, X.; Tao, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D. Lactobacillus acidophilus CICC 6074 inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in HT-29 cells induced-mouse model. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Orlando, A.; Linsalata, M.; Cavallini, A.; Messa, C. Effects ofLactobacillus Rhamnosus GGon the Cell Growth and Polyamine Metabolism in HGC-27 Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2007, 59, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki-Kakelar, H.; Dehghani, J.; Barzegari, A.; Barar, J.; Shirmohamadi, M.; Sadeghi, J.; Omidi, Y. Lactobacillus plantarum induces apoptosis in gastric cancer cells via modulation of signaling pathways in Helicobacter pylori. Bioimpacts 2020, 10, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.J. Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis Inhibits the Proliferation of SNU-1 Human Stomach Cancer Cells through Induction of G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis via p53 and p21 Expression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1171, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoudeh-Fard, A.; Barzegari, A.; Dehnad, A.; Bastani, S.; Golchin, A.; Omidi, Y. Lactobacillus plantarum induces apoptosis in oral cancer KB cells through upregulation of PTEN and downregulation of MAPK signalling pathways. Bioimpacts 2017, 7, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.J. Cytoplasmic fraction ofLactococcus lactis ssp. lactisinduces apoptosis in SNU-1 stomach adenocarcinoma cells. Biofactors 2004, 22, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.-H.; Xu, Q.; Tong, J.-L.; Xiao, S.-D. Apoptotic effect of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the human gastric cancer cell line MKN45viaactivation of the mitochondrial pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 4255–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Xiong, C.; Wei, A.; Ruan, J. Apoptosis induced by a new flavonoid in human hepatoma HepG2 cells involves reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and MAPK activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 654, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; Kuwana, T.; Bouchier-Hayes, L.; Droin, N.M.; Newmeyer, D.D.; Schuler, M.; Green, D.R. Direct Activation of Bax by p53 Mediates Mitochondrial Membrane Permeabilization and Apoptosis. Science 2004, 303, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Xie, Q.; Li, N.; Guan, J.; Evivie, S.E.; Liu, F.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus KLDS1.0901 on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 788040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-f.; Zhao, G.-w.; Liang, S.-t.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.-h.; Chen, H.-z.; Liu, D.-p. Mitofilin regulates cytochrome c release during apoptosis by controlling mitochondrial cristae remodeling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 428, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Zhou, D.; Xiong, C.; Cai, Y.; Ruan, J. A novel non-aromatic B-ring flavonoid: Isolation, structure elucidation and its induction of apoptosis in human colon HT-29 tumor cell via the reactive oxygen species-mitochondrial dysfunction and MAPK activation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.-H.; Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. The Anti-Cancer Potential of Heat-Killed Lactobacillus brevis KU15176 upon AGS Cell Lines through Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Oh, S.; Yun, H.S.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.H. Cell-bound exopolysaccharide from probiotic bacteria induces autophagic cell death of tumour cells. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Guo, L.; Yan, S.; Lee, R.J.; Yu, S.; Chen, S. Hypocrellin A-based photodynamic action induces apoptosis in A549 cells through ROS-mediated mitochondrial signaling pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponder, K.G.; Boise, L.H. The prodomain of caspase-3 regulates its own removal and caspase activation. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Genes | Primers | |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | Forward | TCACCCTGAAGTACCCCATC |
| Reverse | CCATCTCTTGCTGCAAGTCC | |
| Bax | Forward | TCCACCAAGAAGCTGAGCGA |
| Reverse | GTCCAGCCCATGATGGTTCT | |
| Bad | Forward | CCTTTAAGAAGGGACTTCCTCGCC |
| Reverse | ACTTCCGATGGGACCAAGCCTTCC | |
| Bcl-xl | Forward | ATGGCAGCAGTAAAGCAAGCGC |
| Reverse | TTCTCCTGGTGGCAATGGCG | |
| Caspase 3 | Forward | TTTGTTTGTGTGCTTCTGAGCC |
| Reverse | ATTCTGTTGCCACCTTTCGG | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, Y.; Xue, D.; Zhang, L.; Yi, H. Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei X12 Strain Induces Apoptosis in HT-29 Cells through Activation of the Mitochondrial Pathway. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092123
Wang S, Shan Y, Zhang S, Zhang L, Jiao Y, Xue D, Zhang L, Yi H. Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei X12 Strain Induces Apoptosis in HT-29 Cells through Activation of the Mitochondrial Pathway. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092123
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shumei, Yi Shan, Shuang Zhang, Lanwei Zhang, Yuehua Jiao, Dijia Xue, Lili Zhang, and Huaxi Yi. 2023. "Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei X12 Strain Induces Apoptosis in HT-29 Cells through Activation of the Mitochondrial Pathway" Nutrients 15, no. 9: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092123
APA StyleWang, S., Shan, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, L., Jiao, Y., Xue, D., Zhang, L., & Yi, H. (2023). Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei X12 Strain Induces Apoptosis in HT-29 Cells through Activation of the Mitochondrial Pathway. Nutrients, 15(9), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092123









