Polygenic Risk Score, Lifestyles, and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: A Prospective Chinese Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Outcome Ascertainment
2.3. Definition of the Lifestyle Score
2.4. PRS Construction
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and T2D Risk
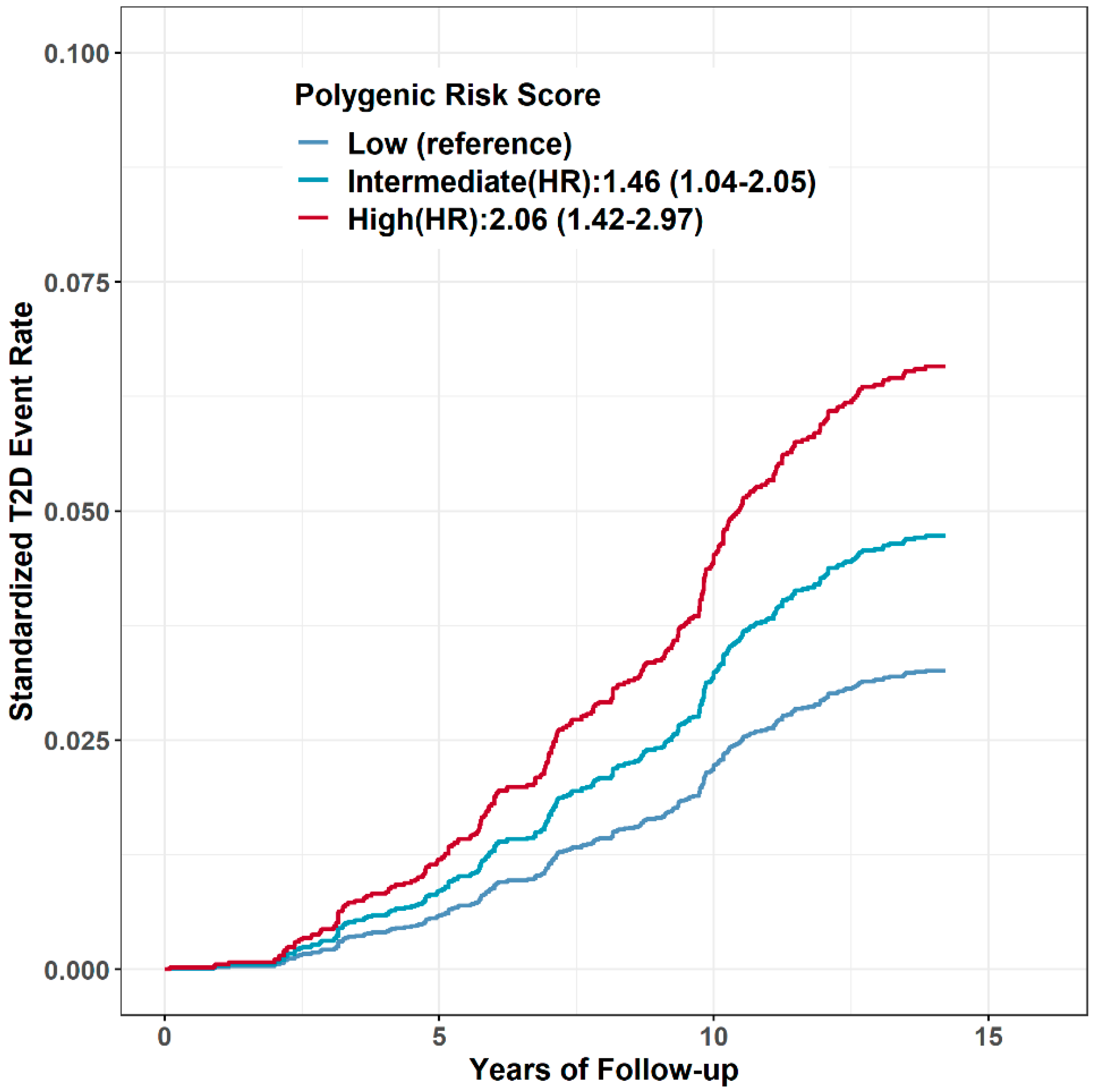
3.2. PRS and T2D Risk
3.3. The Joint Effect of PRS and Lifestyle on T2D Risk
3.4. Benefits of Adhering to Ideal Lifestyle against T2D
3.5. Predicting T2D Risk by PRS and Traditional Clinical Risk Score
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. World Health Statistics 2021. Available online: http://www.who.int/ (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas–11th Edition. Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Ma, R.C.W. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetic complications in China. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisman, A.; Fazli, G.S.; Johns, A.; Booth, G.L. Evolving Trends in the Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes: A Review. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiuto, L.; Patrono, C. Preventing a diabetes pandemic through lifestyle intervention. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, M.; Clark, A.; Bachmann, M.; Garner, N.; Irvine, L.; Howe, A.; Greaves, C.; Auckland, S.; Smith, J.; Turner, J.; et al. Lifestyle Intervention with or Without Lay Volunteers to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes in People with Impaired Fasting Glucose and/or Nondiabetic Hyperglycemia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; An, Y.; Gong, Q.; Gregg, E.W.; Yang, W.; Zhang, B.; Shuai, Y.; Hong, J.; et al. Cardiovascular mortality, all-cause mortality, and diabetes incidence after lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance in the Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study: A 23-year follow-up study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, F.X.; Gao, W.J.; Lyu, J.; Yu, C.Q.; Wang, S.F.; Pang, Z.C.; Cong, L.M.; Dong, Z.; Wu, F.; Wang, H.; et al. Analysis on the heritability of diabetes, based on data from the Chinese adult twins. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2019, 40, 389–393. [Google Scholar]
- Almgren, P.; Lehtovirta, M.; Isomaa, B.; Sarelin, L.; Taskinen, M.R.; Lyssenko, V.; Tuomi, T.; Groop, L.; Botnia Study, G. Heritability and familiality of type 2 diabetes and related quantitative traits in the Botnia Study. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2811–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willemsen, G.; Ward, K.J.; Bell, C.G.; Christensen, K.; Bowden, J.; Dalgard, C.; Harris, J.R.; Kaprio, J.; Lyle, R.; Magnusson, P.K.; et al. The Concordance and Heritability of Type 2 Diabetes in 34,166 Twin Pairs from International Twin Registers: The Discordant Twin (DISCOTWIN) Consortium. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2015, 18, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, M.; Fernandes Silva, L. Genetics of Type 2 Diabetes: Past, Present, and Future. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Lv, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Qin, N.; Ma, H.; He, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.; Tan, W.; Fan, J.; et al. Identification of risk loci and a polygenic risk score for lung cancer: A large-scale prospective cohort study in Chinese populations. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Lv, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.; Zhu, M.; Wang, T.; Yan, C.; Yu, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; et al. Genetic risk, incident gastric cancer, and healthy lifestyle: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies and prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ji, M.; Wang, C.; Dai, J.; Yin, R.; et al. Genetic Risk for Overall Cancer and the Benefit of Adherence to a Healthy Lifestyle. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4618–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, Z.; Cui, Q.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Niu, X.; Shen, C.; Hu, D.; Huang, K.; Chen, J.; et al. A polygenic risk score improves risk stratification of coronary artery disease: A large-scale prospective Chinese cohort study. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Niu, X.; Shen, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Huang, K.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Hu, D.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Development and Validation of a Polygenic Risk Score for Stroke in the Chinese Population. Neurology 2021, 97, e619–e628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Emdin, C.A.; Drake, I.; Natarajan, P.; Bick, A.G.; Cook, N.R.; Chasman, D.I.; Baber, U.; Mehran, R.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Genetic Risk, Adherence to a Healthy Lifestyle, and Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten-Jacobs, L.C.; Larsson, S.C.; Malik, R.; Rannikmae, K.; MEGASTROKE Consortium; International Stroke Genetics Consortium; Sudlow, C.L.; Dichgans, M.; Markus, H.S.; Traylor, M. Genetic risk, incident stroke, and the benefits of adhering to a healthy lifestyle: Cohort study of 306 473 UK Biobank participants. BMJ 2018, 363, k4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lu, J.; Weng, J.; Jia, W.; Ji, L.; Xiao, J.; Shan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Ji, Q.; et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qiao, Q.; Ji, L.; Ning, F.; Yang, W.; Weng, J.; Shan, Z.; Tian, H.; Ji, Q.; Lin, L.; et al. Nonlaboratory-based risk assessment algorithm for undiagnosed type 2 diabetes developed on a nation-wide diabetes survey. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3944–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes branch of Chinese Medicine Association. Chinese Guidelines for Diabetes Prevention and Treatment (2020 edition). Zhonghua Tangniaobing Zazhi 2021, 13, 315–409. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Qian, Y.; Shen, Q.; Yang, M.; Dong, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cui, X.; et al. Metabolic and genetic markers improve prediction of incident type 2 diabetes: A nested case-control study in Chinese. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 3120–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Lopez, A.D.; Wang, L.; Cai, Y.; Page, A.; Yin, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. An integrated national mortality surveillance system for death registration and mortality surveillance, China. Bull. World Health Organ. 2016, 94, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.; Liu, S.; Solomon, C.G.; Willett, W.C. Diet, lifestyle, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Kamineni, A.; Carnethon, M.; Djousse, L.; Mukamal, K.J.; Siscovick, D. Lifestyle risk factors and new-onset diabetes mellitus in older adults: The cardiovascular health study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Long, T.; Yuan, J.; Yao, P.; Wei, S.; et al. Genetic Risk, a Healthy Lifestyle, and Type 2 Diabetes: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 3. Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S34–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.R.; Li, G.W.; Hu, Y.H.; Wang, J.X.; Yang, W.Y.; An, Z.X.; Hu, Z.X.; Lin, J.; Xiao, J.Z.; Cao, H.B.; et al. Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance. The Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, C.H. The bland diet. J. Clin. Nutr. 1954, 2, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lu, F.C.; Department of Disease Control Ministry of Health, P.R.C. The guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Weng, J.; Zhu, D.; Ji, L.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zou, D.; Guo, L.; Ji, Q.; Chen, L.; et al. Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeggini, E.; Scott, L.J.; Saxena, R.; Voight, B.F.; Marchini, J.L.; Hu, T.; de Bakker, P.I.; Abecasis, G.R.; Almgren, P.; Andersen, G.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data and large-scale replication identifies additional susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, F.; Serizawa, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakashima, E.; Ohnaka, K.; Ikegami, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Katsuya, T.; Miyagishi, M.; et al. Confirmation of multiple risk Loci and genetic impacts by a genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, R.; Ng, M.C.; Bao, Y.; Wang, C.; So, W.Y.; Ma, R.C.; Ma, X.; Chan, J.C.; et al. Association of genetic variants of NOS1AP with type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, F.J.; Yang, C.F.; Chen, C.C.; Chuang, L.M.; Lu, C.H.; Chang, C.T.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, R.H.; Shiu, C.F.; Liu, Y.M.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants for type 2 diabetes in Han Chinese. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voight, B.F.; Scott, L.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Morris, A.P.; Dina, C.; Welch, R.P.; Zeggini, E.; Huth, C.; Aulchenko, Y.S.; Thorleifsson, G.; et al. Twelve type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale association analysis. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Hara, K.; Maeda, S.; Yasuda, K.; Takahashi, A.; Horikoshi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Fujita, H.; Grarup, N.; Cauchi, S.; et al. A genome-wide association study in the Japanese population identifies susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes at UBE2E2 and C2CD4A-C2CD4B. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.O.; Long, J.; Cai, Q.; Qi, L.; Xiang, Y.B.; Cho, Y.S.; Tai, E.S.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Chow, W.H.; et al. Identification of new genetic risk variants for type 2 diabetes. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.S.; Chen, C.H.; Hu, C.; Long, J.; Ong, R.T.; Sim, X.; Takeuchi, F.; Wu, Y.; Go, M.J.; Yamauchi, T.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies eight new loci for type 2 diabetes in east Asians. Nat. Genet. 2011, 44, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Qian, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, M.; Lin, Y.; Du, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, C.; Jin, G.; et al. Genetic variants on chromosome 6p21.1 and 6p22.3 are associated with type 2 diabetes risk: A case-control study in Han Chinese. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 57, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Lu, F.; Dong, M.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Shen, C.; Jin, G.; Hu, Z.; Shen, H. Genetic variants of IDE-KIF11-HHEX at 10q23.33 associated with type 2 diabetes risk: A fine-mapping study in Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.P.; Voight, B.F.; Teslovich, T.M.; Ferreira, T.; Segre, A.V.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Khan, H.; Grallert, H.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gan, W.; Lu, L.; Dong, X.; Han, X.; Hu, C.; Yang, Z.; Sun, L.; Bao, W.; Li, P.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies GRK5 and RASGRP1 as type 2 diabetes loci in Chinese Hans. Diabetes 2013, 62, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.C.; Hu, C.; Tam, C.H.; Zhang, R.; Kwan, P.; Leung, T.F.; Thomas, G.N.; Go, M.J.; Hara, K.; Sim, X.; et al. Genome-wide association study in a Chinese population identifies a susceptibility locus for type 2 diabetes at 7q32 near PAX4. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Fujita, H.; Johnson, T.A.; Yamauchi, T.; Yasuda, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Peng, C.; Hu, C.; Ma, R.C.; Imamura, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies three novel loci for type 2 diabetes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, F.; Li, H.; Dong, M.; Lin, Y.; Du, J.; Lin, Y.; Gong, J.; Jin, G.; et al. Genetic variant in fat mass and obesity-associated gene associated with type 2 diabetes risk in Han Chinese. BMC Genet. 2013, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DIAbetes Genetics Replication and Meta-analysis (DIAGRAM) Consortium; Asian Genetic Epidemiology Network Type 2 Diabetes (AGEN-T2D) Consortium; South Asian Type 2 Diabetes (SAT2D) Consortium; Mexican American Type 2 Diabetes (MAT2D) Consortium; Type 2 Diabetes Genetic Exploration by Next-generation sequencing in multi-Ethnic Samples (T2D-GENES) Consortium; Mahajan, A.; Go, M.J.; Zhang, W.; Below, J.E.; Gaulton, K.J.; et al. Genome-wide trans-ancestry meta-analysis provides insight into the genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Takahashi, A.; Yamauchi, T.; Hara, K.; Yasuda, K.; Grarup, N.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Huerta-Chagoya, A.; Hu, C.; et al. Genome-wide association studies in the Japanese population identify seven novel loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.A.; Scott, L.J.; Magi, R.; Marullo, L.; Gaulton, K.J.; Kaakinen, M.; Pervjakova, N.; Pers, T.H.; Johnson, A.D.; Eicher, J.D.; et al. An Expanded Genome-Wide Association Study of Type 2 Diabetes in Europeans. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2888–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Wessel, J.; Willems, S.M.; Zhao, W.; Robertson, N.R.; Chu, A.Y.; Gan, W.; Kitajima, H.; Taliun, D.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. Refining the accuracy of validated target identification through coding variant fine-mapping in type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Taliun, D.; Thurner, M.; Robertson, N.R.; Torres, J.M.; Rayner, N.W.; Payne, A.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Scott, R.A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Akiyama, M.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, M.; Hosoe, J.; Shojima, N.; Hozawa, A.; Kadota, A.; Kuriki, K.; Naito, M.; et al. Identification of 28 new susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spracklen, C.N.; Horikoshi, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Lin, K.; Bragg, F.; Moon, S.; Suzuki, K.; Tam, C.H.T.; Tabara, Y.; Kwak, S.H.; et al. Identification of type 2 diabetes loci in 433,540 East Asian individuals. Nature 2020, 582, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, K.; Akiyama, M.; Kanai, M.; Takahashi, A.; Kawakami, E.; Sugishita, H.; Sakaue, S.; Matoba, N.; Low, S.K.; Okada, Y.; et al. Large-scale genome-wide association study in a Japanese population identifies novel susceptibility loci across different diseases. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.B.; Jang, J.H.; Chung, M.G.; Kim, S.C. Exome Chip Analysis of 14,026 Koreans Reveals Known and Newly Discovered Genetic Loci Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.R.; Kanai, M.; Kamatani, Y.; Okada, Y.; Neale, B.M.; Daly, M.J. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurdasani, D.; Barroso, I.; Zeggini, E.; Sandhu, M.S. Genomics of disease risk in globally diverse populations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragam, K.G.; Dobbyn, A.; Judy, R.; Chaffin, M.; Chaudhary, K.; Hindy, G.; Cagan, A.; Finneran, P.; Weng, L.C.; Loos, R.J.F.; et al. Limitations of Contemporary Guidelines for Managing Patients at High Genetic Risk of Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2769–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics at Baseline | No. (%) in Cohort | No. (%) in T2D Incidence | Log-Rank P | HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age >52 years 1 | 2390 (47.61) | 309 (70.23) | <2.00 × 10−16 | 2.93 (2.39–3.60) |
| Female | 3022 (60.15) | 261 (59.32) | 0.535 | 0.94 (0.78–1.14) |
| Systolic blood pressure >120 mmHg 2 | 2014 (40.14) | 238 (54.21) | 4.25 × 10−11 | 1.88 (1.56–2.27) |
| Diastolic blood pressure >80 mmHg 2 | 1291 (25.74) | 156 (35.54) | 4.48 × 10−7 | 1.65 (1.36–2.01) |
| Fasting blood glucose >4.5 mmol/L 2 | 2169 (43.40) | 324 (73.80) | <2.00 × 10−16 | 3.97 (3.21–4.91) |
| Total cholesterol ≥5.2 mmol/L 2 | 1300 (26.02) | 149 (33.94) | 6.46 × 10−5 | 1.50 (1.23–1.82) |
| Triglycerides ≥1.7 mmol/L 2 | 2128 (42.61) | 284 (64.84) | <2.00 × 10−16 | 2.56 (2.10–3.11) |
| High density lipoprotein cholesterol <1.0 mmol/L 2 | 502 (10.05) | 77 (17.58) | 5.00 × 10−8 | 1.98 (1.55–2.54) |
| Family history of diabetes | 483 (9.72) | 54 (12.27) | 0.088 | 1.28 (0.96–1.74) |
| Overweight/obesity | 1810 (36.10) | 256 (58.32) | <2.00 × 10−16 | 2.60 (2.15–3.15) |
| Central adiposity | 2624 (52.34) | 317 (72.37) | <2.00 × 10−16 | 2.50 (2.03–3.08) |
| Smoking | 1047 (20.94) | 104 (23.64) | 0.121 | 1.19 (0.96–1.48) |
| Drinking | 462 (9.24) | 47 (10.73) | 0.209 | 1.21 (0.90–1.64) |
| No physical exercise | 3236 (65.01) | 294 (67.12) | 0.386 | 1.10 (0.91–1.35) |
| Unhealthy diet | 4004 (80.06) | 364 (82.73) | 0.146 | 1.20 (0.94–1.54) |
| Intermediate lifestyle 3 | 1169 (23.76) | 133 (30.65) | 3.11 × 10−4 | 1.58 (1.23–2.03) |
| Poor lifestyle 3 | 1262 (25.65) | 177 (40.78) | 3.49 × 10−7 | 1.92 (1.49–2.46) |
| HR (95% CI) | P | Ptrend | Absolute Risk over 10 Years (%) | Absolute Risk Reduction over 10 Years (%) | Number of Participants Who Need to Adhere to Healthy Lifestyle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low genetic risk | 0.112 | |||||
| Poor lifestyle | 1 | - | 3.52 (1.30–5.74) | 1 (ref) | ||
| Intermediate lifestyle | 0.55 (0.24–1.24) | 0.151 | 1.93 (0.57–3.30) | 1.58 (−1.07–3.42) | 63 | |
| Ideal lifestyle | 0.52 (0.24–1.14) | 0.103 | 1.83 (0.72–2.95) | 1.68 (−0.88–3.64) | 60 | |
| Intermediate genetic risk | 9.96 × 10−5 | |||||
| Poor lifestyle | 1 | - | 4.73 (3.28–6.19) | 1 (ref) | ||
| Intermediate lifestyle | 0.75 (0.52–1.09) | 0.130 | 3.55 (2.41–4.70) | 1.18 (−0.47–2.75) | 85 | |
| Ideal lifestyle | 0.45 (0.30–0.68) | 1.05 × 10−4 | 2.15 (1.45–2.85) | 2.58 (0.96–4.10) | 39 | |
| High genetic risk | 0.014 | |||||
| Poor lifestyle | 1 | - | 6.77 (3.74–9.80) | 1 (ref) | ||
| Intermediate lifestyle | 0.60 (0.34–1.04) | 0.070 | 4.04 (2.02–6.06) | 2.73 (−0.76–6.06) | 37 | |
| Ideal lifestyle | 0.48 (0.28–0.85) | 0.012 | 3.28 (1.83–4.74) | 3.49 (0.05–6.80) | 29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Cui, X.; Shen, Q.; Wu, D.; Yang, M.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; et al. Polygenic Risk Score, Lifestyles, and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: A Prospective Chinese Cohort Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092144
Liu J, Wang L, Cui X, Shen Q, Wu D, Yang M, Dong Y, Liu Y, Chen H, Yang Z, et al. Polygenic Risk Score, Lifestyles, and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: A Prospective Chinese Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092144
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jia, Lu Wang, Xuan Cui, Qian Shen, Dun Wu, Man Yang, Yunqiu Dong, Yongchao Liu, Hai Chen, Zhijie Yang, and et al. 2023. "Polygenic Risk Score, Lifestyles, and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: A Prospective Chinese Cohort Study" Nutrients 15, no. 9: 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092144
APA StyleLiu, J., Wang, L., Cui, X., Shen, Q., Wu, D., Yang, M., Dong, Y., Liu, Y., Chen, H., Yang, Z., Liu, Y., Zhu, M., Ma, H., Jin, G., & Qian, Y. (2023). Polygenic Risk Score, Lifestyles, and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: A Prospective Chinese Cohort Study. Nutrients, 15(9), 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092144





