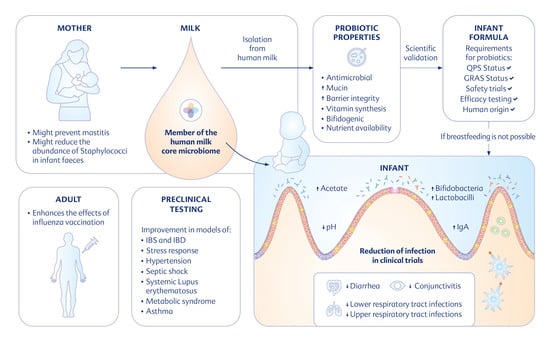
Limosilactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: Clinical Potential of a Probiotic Strain Isolated from Human Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. L. fermentum CECT5716
3. Probiotic Properties and Mechanisms of Action of L. fermentum CECT5716
3.1. Antimicrobial Effect
3.2. Pathogen Exclusion and Barrier Integrity
3.3. Effects on the Gastrointestinal Microbiota
3.4. Effects on Vitamin Synthesis
3.5. Effects on Immune Response
3.6. Secreted Probiotic Factors
3.7. Postbiotic Mechanisms
4. Safety of L. fermentum CECT5716
5. Preclinical Studies
5.1. Gastrointestinal Inflammation
5.2. Psychological Stress
5.3. Hypertension
5.4. Immunity
5.5. Metabolic Disease
5.6. Asthma and Allergy
6. Clinical Trials
6.1. Mastitis
6.2. Influenza Vaccination
6.3. Infections in Infants
6.3.1. Respiratory Tract Infections
6.3.2. Gastroenteritis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ojo-Okunola, A.; Nicol, M.; du Toit, E. Human Breast Milk Bacteriome in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, J.Y.; Noble, L.; Section on Breastfeeding. Policy Statement: Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.D.; França, G.V.A.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salone, L.R.; Vann, W.F., Jr.; Dee, D.L. Breastfeeding: An overview of oral and general health benefits. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2013, 144, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habicht, J.P. Expert consultation on the optimal duration of exclusive breastfeeding: The process, recommendations, and challenges for the future. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2004, 554, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.E.; Ryan, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Breast Milk, a Source of Beneficial Microbes and Associated Benefits for Infant Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, L.; Langa, S.; Martin, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jimenez, E.; Martin, R.; Rodriguez, J.M. The human milk microbiota: Origin and potential roles in health and disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A.; Martin, V.; Jimenez, E.; Mader, I.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Fernandez, L. Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria in human breast milk: Influence of antibiotherapy and other host and clinical factors. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moossavi, S.; Sepehri, S.; Robertson, B.; Bode, L.; Goruk, S.; Field, C.J.; Lix, L.M.; de Souza, R.J.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; et al. Composition and Variation of the Human Milk Microbiota Are Influenced by Maternal and Early-Life Factors. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 324–335.e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.E.; Carrothers, J.M.; Lackey, K.A.; Beatty, N.F.; Brooker, S.L.; Peterson, H.K.; Steinkamp, K.M.; York, M.A.; Shafii, B.; Price, W.J.; et al. Strong Multivariate Relations Exist Among Milk, Oral, and Fecal Microbiomes in Mother-Infant Dyads During the First Six Months Postpartum. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Breast milk microbiota: A review of the factors that influence composition. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boix-Amoros, A.; Puente-Sanchez, F.; du Toit, E.; Linderborg, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E.; Tamames, J.; Mira, A.; et al. Mycobiome Profiles in Breast Milk from Healthy Women Depend on Mode of Delivery, Geographic Location, and Interaction with Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02994-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Ly, M.; Cerini, C.; Saavedra, M.; Aldrovandi, G.M.; Saboory, A.A.; Johnson, K.M.; Pride, D.T. Shared and Distinct Features of Human Milk and Infant Stool Viromes. Front. Microbiol 2018, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumbeck, J.A.; Rasmussen, H.E.; Hutkins, R.W.; Clarke, J.; Shawron, K.; Keshavarzian, A.; Walter, J. Probiotic Bifidobacterium strains and galactooligosaccharides improve intestinal barrier function in obese adults but show no synergism when used together as synbiotics. Microbiome 2018, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Vezza, T.; Garrido-Mesa, N.; Olivares, M.; Comalada, M.; Riccardi, C.; Utrilla, M.P.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Galvez, J. The viability of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 is not essential to exert intestinal anti-inflammatory properties. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodabadi, A.; Soltan Dallal, M.M.; Rahimi Foroushani, A.; Douraghi, M.; Sharifi Yazdi, M.K.; Amin Harati, F. Antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus spp. isolated from the feces of healthy infants against enteropathogenic bacteria. Anaerobe 2015, 34, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Composition at Species Level and Gut Microbiota Diversity in Infants before 6 Weeks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomehzadeh, N.; Javaherizadeh, H.; Amin, M.; Saki, M.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.S.; Hamidi, H.; Seyedmahmoudi, M.; Gorjian, Z. Isolation and identification of potential probiotic Lactobacillus species from feces of infants in southwest Iran. IJID 2020, 96, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kook, S.Y.; Chung, E.C.; Lee, Y.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, S. Isolation and characterization of five novel probiotic strains from Korean infant and children faeces. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, I.; Stegen, J.C.; Maldonado-Gómez, M.X.; Eren, A.M.; Siba, P.M.; Greenhill, A.R.; Walter, J. The Gut Microbiota of Rural Papua New Guineans: Composition, Diversity Patterns, and Ecological Processes. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Langa, S.; Reviriego, C.; Jiminez, E.; Marin, M.L.; Xaus, J.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Human milk is a source of lactic acid bacteria for the infant gut. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Olivares, M.; Marin, M.L.; Fernandez, L.; Xaus, J.; Rodriguez, J.M. Probiotic potential of 3 Lactobacilli strains isolated from breast milk. J. Hum. Lact. 2005, 21, 8–17; quiz 18–21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, N.; Laino, J.E.; Delgado, S.; Jimenez, E.; Juarez del Valle, M.; Savoy de Giori, G.; Sesma, F.; Mayo, B.; Fernandez, L.; LeBlanc, J.G.; et al. Relationships between the genome and some phenotypical properties of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716, a probiotic strain isolated from human milk. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4343–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, E.; Langa, S.; Martin, V.; Arroyo, R.; Martin, R.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716, a probiotic strain isolated from human milk. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bañuelos, O.; Fernández, L.; Corral, J.M.; Valdivieso-Ugarte, M.; Adrio, J.L.; Velasco, J. Metabolism of prebiotic products containing β(2-1) fructan mixtures by two Lactobacillus strains. Anaerobe 2008, 14, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, M.; Diaz-Ropero, M.P.; Martin, R.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Xaus, J. Antimicrobial potential of four Lactobacillus strains isolated from breast milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, R.; Martin, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jimenez, E.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Treatment of infectious mastitis during lactation: Antibiotics versus oral administration of Lactobacilli isolated from breast milk. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; de la Visitacion, N.; Sanchez, M.; Romero, M.; Olivares, M.; Jimenez, R.; Duarte, J. The Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum Prevents Dysbiosis and Vascular Oxidative Stress in Rats with Hypertension Induced by Chronic Nitric Oxide Blockade. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, J.; Canabate, F.; Sempere, L.; Vela, F.; Sanchez, A.R.; Narbona, E.; Lopez-Huertas, E.; Geerlings, A.; Valero, A.D.; Olivares, M.; et al. Human Milk Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 Reduces the Incidence of Gastrointestinal and Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Gálvez, N.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Dominguez-Vera, J.M. Identification of the key excreted molecule by Lactobacillus fermentum related to host iron absorption. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, D.R.; Michail, S.; Wei, S.; McDougall, L.; Hollingsworth, M.A. Probiotics inhibit enteropathogenic E. coliadherence in vitro by inducing intestinal mucin gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. 1999, 276, G941–G950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaecke, T.; Aubert, P.; Grohard, P.A.; Durand, T.; Hulin, P.; Paul-Gilloteaux, P.; Fournier, A.; Docagne, F.; Ligneul, A.; Fressange-Mazda, C.; et al. L. fermentum CECT 5716 prevents stress-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction in newborn rats. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. Off. J. Eur. Gastrointest. Motil. Soc. 2017, 29, e13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Ropero, M.P.; Martin, R.; Sierra, S.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Xaus, J.; Olivares, M. Two Lactobacillus strains, isolated from breast milk, differently modulate the immune response. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Cano, F.J.; Dong, H.; Yaqoob, P. In vitro immunomodulatory activity of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 and Lactobacillus salivarius CECT5713: Two probiotic strains isolated from human breast milk. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazzo, G.; van Best, N.; Bervoets, L.; Dapaah, I.O.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Hornef, M.W.; Lau, S.; Hamelmann, E.; Penders, J. Development of the Microbiota and Associations With Birth Mode, Diet, and Atopic Disorders in a Longitudinal Analysis of Stool Samples, Collected From Infancy Through Early Childhood. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazanella, M.; Maier, T.V.; Clavel, T.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Lucio, M.; Maldonado-Gomez, M.X.; Autran, C.; Walter, J.; Bode, L.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; et al. Randomized controlled trial on the impact of early-life intervention with bifidobacteria on the healthy infant fecal microbiota and metabolome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, D.L.; Craft, K.M.; Townsend, S.D. Infant food applications of complex carbohydrates: Structure, synthesis, and function. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 437, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Delgado Palacio, S.; Arboleya Montes, S.; Mancabelli, L.; et al. The First Microbial Colonizers of the Human Gut: Composition, Activities, and Health Implications of the Infant Gut Microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00036-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Vezza, T.; Utrilla, M.P.; Chueca, N.; Garcia, F.; Olivares, M.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Gálvez, J. Differential intestinal anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus fermentum and Lactobacillus salivarius in DSS mouse colitis: Impact on microRNAs expression and microbiota composition. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, M.; Dou, S.; Cahu, A.; Formal, M.; Le Normand, L.; Romé, V.; Nogret, I.; Ferret-Bernard, S.; Rhimi, M.; Cuinet, I.; et al. Addition of dairy lipids and probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum in infant formula programs gut microbiota and entero-insular axis in adult minipigs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Gutiérrez, B.; Gámez-Belmonte, R.; Suárez, M.D.; Lavín, J.L.; Aransay, A.M.; Olivares, M.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; Sánchez de Medina, F.; Zarzuelo, A. A synbiotic composed of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 and FOS prevents the development of fatty acid liver and glycemic alterations in rats fed a high fructose diet associated with changes in the microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Laino, J.E.; del Valle, M.J.; Vannini, V.; van Sinderen, D.; Taranto, M.P.; de Valdez, G.F.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F. B-group vitamin production by lactic acid bacteria--current knowledge and potential applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrar, F.M.; O’Connor, D.L. Bacterially synthesized folate and supplemental folic acid are absorbed across the large intestine of piglets. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Amaretti, A.; Raimondi, S. Folate production by probiotic bacteria. Nutrients 2011, 3, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, L.J.; Forsberg, C.W.; O’Connor, D.L. Feeding human milk to rats increases Bifidobacterium in the cecum and colon which correlates with enhanced folate status. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, M.; Diaz-Ropero, M.P.; Sierra, S.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Fonolla, J.; Navas, M.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Xaus, J. Oral intake of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 enhances the effects of influenza vaccination. Nutrition 2007, 23, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, E.G.; North, J.; Bakhsh, I.; Marden, C.; Haq, S.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Malayeri, R.; Wickremasinghe, R.G.; Davies, J.K.; Lowdell, M.W. Ligation of CD8alpha on human natural killer cells prevents activation-induced apoptosis and enhances cytolytic activity. Immunology 2005, 116, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Cano, F.J.; Castellote, C.; Gonzalez-Castro, A.M.; Pelegri, C.; Castell, M.; Franch, A. Developmental changes in intraepithelial T lymphocytes and NK cells in the small intestine of neonatal rats. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 58, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleusix, V.; Lacroix, C.; Vollenweider, S.; Duboux, M.; Le Blay, G. Inhibitory activity spectrum of reuterin produced by Lactobacillus reuteri against intestinal bacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Schillde, M.A.; Hormannsperger, G.; Weiher, M.; Alpert, C.A.; Hahne, H.; Bauerl, C.; van Huynegem, K.; Steidler, L.; Hrncir, T.; Perez-Martinez, G.; et al. Lactocepin secreted by Lactobacillus exerts anti-inflammatory effects by selectively degrading proinflammatory chemokines. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peran, L.; Sierra, S.; Comalada, M.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Bailon, E.; Nieto, A.; Concha, A.; Olivares, M.; Zarzuelo, A.; Xaus, J.; et al. A comparative study of the preventative effects exerted by two probiotics, Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus fermentum, in the trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid model of rat colitis. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pophaly, S.D.; Singh, R.; Pophaly, S.D.; Kaushik, J.K.; Tomar, S.K. Current status and emerging role of glutathione in food grade lactic acid bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Fang, Y.Z.; Yang, S.; Lupton, J.R.; Turner, N.D. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pophaly, S.D.; Poonam, S.; Pophaly, S.D.; Kapila, S.; Nanda, D.K.; Tomar, S.K.; Singh, R. Glutathione biosynthesis and activity of dependent enzymes in food-grade lactic acid bacteria harbouring multidomain bifunctional fusion gene (gshF). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, A.; Liu, X.; Miller, M.J. Glutathione Utilization in Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12651–12656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikelsaar, M.; Zilmer, M. Lactobacillus fermentum ME-3—An antimicrobial and antioxidative probiotic. Microb Ecol. Health Dis 2009, 21, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peran, L.; Camuesco, D.; Comalada, M.; Nieto, A.; Concha, A.; Adrio, J.L.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Zarzuelo, A.; Galvez, J. Lactobacillus fermentum, a probiotic capable to release glutathione, prevents colonic inflammation in the TNBS model of rat colitis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2006, 21, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roduit, C.; Frei, R.; Ferstl, R.; Loeliger, S.; Westermann, P.; Rhyner, C.; Schiavi, E.; Barcik, W.; Rodriguez-Perez, N.; Wawrzyniak, M.; et al. High levels of butyrate and propionate in early life are associated with protection against atopy. Allergy 2019, 74, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, C.G.; Christian, P.; Vidaletti, L.P.; Gatica-Domínguez, G.; Menon, P.; Black, R.E. Revisiting maternal and child undernutrition in low-income and middle-income countries: Variable progress towards an unfinished agenda. Lancet 2021, 397, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, M.; Önning, G.; Berggren, A.; Hulthén, L. Probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum 299v increases iron absorption from an iron-supplemented fruit drink: A double-isotope cross-over single-blind study in women of reproductive age. BJN 2015, 114, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavermicocca, P.; Valerio, F.; Evidente, A.; Lazzaroni, S.; Corsetti, A.; Gobbetti, M. Purification and Characterization of Novel Antifungal Compounds from the Sourdough Lactobacillus plantarum Strain 21B. AEM 2000, 66, 4084–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullakhandam, R.; Nair, M.K.; Kasula, S.; Kilari, S.; Thippande, T.G. Ferric reductase activity of low molecular weight human milk fraction is associated with enhanced iron solubility and uptake in Caco-2 cells. BBRC 2008, 374, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, A.; Abreu, Y.; Abreu, A.T.; Gwee, K.A.; Ianiro, G.; Tack, J.; Nguyen, T.V.H.; Hill, C. The clinical evidence for postbiotics as microbial therapeutics. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2117508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Statement on the update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA. 2: Suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until March 2015. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Villoslada, F.; Sierra, S.; Diaz-Ropero, M.P.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Xaus, J.; Olivares, M. Safety assessment of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716, a probiotic strain isolated from human milk. J. Dairy Res. 2009, 76, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefańska, I.; Kwiecień, E.; Jóźwiak-Piasecka, K.; Garbowska, M.; Binek, M.; Rzewuska, M. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains of Potential Use as Feed Additives—The Basic Safety and Usefulness Criterion. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 687071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Technical guidance-Update of the criteria used in the assessment of bacterial resistance to antibiotics of human or veterinary importance. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 732. [Google Scholar]
- Braegger, C.; Chmielewska, A.; Decsi, T.; Kolacek, S.; Mihatsch, W.; Moreno, L.; Piescik, M.; Puntis, J.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. Supplementation of Infant Formula With Probiotics and/or Prebiotics: A Systematic Review and Comment by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maintz, L.; Novak, N. Histamine and histamine intolerance. AJCN 2007, 85, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Z.; Sadiq, F.A.; Han, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Ross, R.P.; Lu, W.; Chen, W. Comprehensive Scanning of Prophages in Lactobacillus: Distribution, Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance Genes, and Linkages with CRISPR-Cas Systems. mSystems 2021, 6, e01211-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Campos, M.; López, M.Á.; Rodriguez-Benítez, M.V.; Romero, J.; Roncero, I.; Linares, M.D.; Maldonado, J.; López-Huertas, E.; Berwind, R.; Ritzenthaler, K.L.; et al. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716 is safe and well tolerated in infants of 1–6 months of age: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pharm. Res. 2012, 65, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Lobón, J.A.; Gil-Campos, M.; Maldonado, J.; López-Huertas, E.; Flores-Rojas, K.; Valero, A.D.; Rodríguez-Benítez, M.V.; Bañuelos, O.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Fonollá, J.; et al. Long-term safety of early consumption of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: A 3-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Pharm. Res. 2015, 95–96, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sojo, M.J.; Garcia-Garcia, J.; Ruiz-Malagón, A.J.; Diez-Echave, P.; Hidalgo-García, L.; Molina-Tijeras, J.A.; González-Lozano, E.; López-Escanez, L.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, M.J.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Limosilactobacillus fermentum in the DCA Experimental Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Rats. Nutrients 2023, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, J.; Loren, V.; Pedrosa, E.; Ojanguren, I.; Xaus, J.; Cabre, E.; Domenech, E.; Gassull, M.A. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716 prevents and reverts intestinal damage on TNBS-induced colitis in mice. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Guzman, M.; Toral, M.; Romero, M.; Jimenez, R.; Galindo, P.; Sanchez, M.; Zarzuelo, M.J.; Olivares, M.; Galvez, J.; Duarte, J. Antihypertensive effects of probiotics Lactobacillus strains in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; de la Visitación, N.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Romero, M.; Yang, T.; Izquierdo-Garcia, J.L.; Jiménez, R.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; et al. Probiotics Prevent Dysbiosis and the Rise in Blood Pressure in Genetic Hypertension: Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1900616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral, M.; Romero, M.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Jiménez, R.; Robles-Vera, I.; Algieri, F.; Chueca-Porcuna, N.; Sánchez, M.; de la Visitación, N.; Olivares, M.; et al. Lactobacillus fermentum Improves Tacrolimus-Induced Hypertension by Restoring Vascular Redox State and Improving eNOS Coupling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Visitación, N.; Robles-Vera, I.; Moleón-Moya, J.; Sánchez, M.; Jiménez, R.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; González-Correa, C.; Olivares, M.; Toral, M.; Romero, M.; et al. Probiotics Prevent Hypertension in a Murine Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Induced by Toll-Like Receptor 7 Activation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arribas, B.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Comalada, M.; Bailón, E.; Camuesco, D.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Zarzuelo, A.; Gálvez, J. Evaluation of the preventative effects exerted by Lactobacillus fermentum in an experimental model of septic shock induced in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azagra-Boronat, I.; Tres, A.; Massot-Cladera, M.; Franch, À.; Castell, M.; Guardiola, F.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 Supplementation in Rats during Pregnancy and Lactation Impacts Maternal and Offspring Lipid Profile, Immune System and Microbiota. Cells 2020, 9, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Han, G.; Li, A.; Kong, X. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 Alleviates the Inflammatory Response in Asthma by Regulating TLR2/TLR4 Expression. Front. Nutr 2022, 9, 931427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, A.R.; Russell, R.K.; Wilson, M.L.; Gilmour, W.H.; Satsangi, J.; Wilson, D.C. Systematic review: The role of breastfeeding in the development of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungor, D.; Nadaud, P.; Dreibelbis, C.; LaPergola, C.C.; Wong, Y.P.; Terry, N.; Abrams, S.A.; Beker, L.; Jacobovits, T.; Jarvinen, K.M.; et al. Infant milk-feeding practices and diagnosed celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease in offspring: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 838s–851s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormannsperger, G.; Schaubeck, M.; Haller, D. Intestinal Microbiota in Animal Models of Inflammatory Diseases. Ilar J. 2015, 56, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; van der Veeken, J.; deRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslowski, K.M.; Vieira, A.T.; Ng, A.; Kranich, J.; Sierro, F.; Yu, D.; Schilter, H.C.; Rolph, M.S.; Mackay, F.; Artis, D.; et al. Regulation of inflammatory responses by gut microbiota and chemoattractant receptor GPR43. Nature 2009, 461, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, B.E.; Mearin, F.; Chang, L.; Chey, W.D.; Lembo, A.J.; Simren, M.; Spiller, R. Bowel Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1393–1407.e1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.C.; Lacy, B.E.; Talley, N.J. Irritable Bowel Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2566–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C. Global burden of irritable bowel syndrome: Trends, predictions and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, K.S. Irritable bowel syndrome: Emerging paradigm in pathophysiology. WJG 2014, 20, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, M.; Alizadeh-Tabari, S.; Zamani, V. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharm. 2019, 50, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, C.; Barau, E.; Molkhou, P.; Raynaud, F.; Barbet, J.P.; Dehennin, L. Food-induced alterations of intestinal permeability in children with cow’s milk-sensitive enteropathy and atopic dermatitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1989, 8, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewiem, M.; Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk, U. Assessment of Selected Intestinal Permeability Markers in Children with Food Allergy Depending on the Type and Severity of Clinical Symptoms. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalesi, S.; Sun, J.; Buys, N.; Jayasinghe, R. Effect of probiotics on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Hypertension 2014, 64, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidl, R.; Garib, V.; Linhart, B.; Haberl, E.M.; Mader, I.; Szépfalusi, Z.; Schmidthaler, K.; Douladiris, N.; Pampura, A.; Varlamov, E.; et al. Extensively Hydrolyzed Hypoallergenic Infant Formula with Retained T Cell Reactivity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Intze, E.; Schaubeck, M.; Rooney, J.P.K.; Hecht, C.; Piloquet, H.; Clavel, T. Early life gut microbiota profiles linked to synbiotic formula effects: A randomized clinical trial in European infants. AJCN 2022, 117, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, J.A.; Maldonado-Lobón, J.A.; Díaz-Ropero, M.P.; Flores-Rojas, K.; Uberos, J.; Leante, J.L.; Affumicato, L.; Couce, M.L.; Garrido, J.M.; Olivares, M. Oral administration to nursing women of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 prevents lactational mastitis development: A randomized controlled trial. Breastfeed. Med. 2017, 12, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Lobón, J.A.; Díaz-López, M.A.; Carputo, R.; Duarte, P.; Díaz-Ropero, M.P.; Valero, A.D.; Sanudo, A.; Sempere, L.; Ruiz-López, M.D.; Banuelos, O. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716 reduces Staphylococcus load in the breastmilk of lactating mothers suffering breast pain: A randomized controlled trial. Breastfeed. Med. 2015, 10, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; He, X.; Ding, S.; Gao, H. Oral Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 in the patients with lactational abscess treated by needle aspiration: The late follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2022, 101, e29761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Maldonado-Lobón, J.A.; Benavides, M.R.; Flores-Rojas, K.; Jaldo, R.; Jiménez del Barco, I.; Bolívar, V.; Valero, A.D.; Prados, E.; et al. Evaluation of the safety, tolerance and efficacy of 1-year consumption of infant formula supplemented with Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 Lc40 or Bifidobacterium breve CECT7263: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; Hurtado, J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Uberos, J.; Maldonado-Lobón, J.; Díaz-Ropero, M.; Bañuelos, O.; Fonollá, J.; Olivares, M.; Group, P. Effects of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 Lc40 on infant growth and health: A randomised clinical trial in nursing women. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, I.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.; Raat, H.; Jaddoe, V.; Franco, O.; Hofman, A.; de Jongste, J.; Moll, H. Breastfeeding and the risk of respiratory tract infections after infancy: The Generation R Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouw, E.; von Gartzen, A.; Weißenborn, A. Bedeutung des Stillens für das Kind. Bundesgesundheitsblatt-Gesundh.-Gesundh. 2018, 61, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, L.A.; Al-Araji, R.A.; McLoughlin, L.M. Guidelines for the management of acute gastroenteritis in children in Europe. Arch. Dis Child. 2015, 100, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; Blanco-Rojo, R.; Olivares, M. Evaluation of the Effect of Limosilactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 on Gastrointestinal Infections in Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Rojo, R.; Maldonado, J.; Schaubeck, M.; Özen, M.; López-Huertas, E.; Olivares, M. Beneficial Effects of Limosilactobacillus fermentum CECT 5716 Administration to Infants Delivered by Cesarean Section. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 906924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Model Disease/Condition | Animal Model | Main Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBS induced by DCA | Rat | Reduction in signs of intestinal hypersensitivity, reduction in inflammation, and improvement in intestinal barrier integrity | Rodriguez-Sojo et al., 2022 [78] |
| Colitis induced by TNBS | Rat | Reduction in histological signs of inflammation | Peran et al., 2006 [61], Peran et al., 2007 [55] |
| Colitis induced by TNBS | Mouse | Reduction in histological signs of inflammation | Mane et al., 2009 [79] |
| Colitis induced by DSS | Mouse | Reduction in histological signs of inflammation | Rodriguez-Nogales et al., 2017 [42] |
| Maternal separation, Water avoidance stress | Rat | Prevention of stress-induced ZO-1 disorganization in epithelial cells and plasma hypercorticosteronaemia; increased exploratory behaviour | Vanhaecke et al., 2016 [35] |
| Hypertension (in SHR) | Rat | Reduction in vascular ROS generation, proinflammatory response, and systolic blood pressure | Gomez-Guzman et al., 2015 [80] |
| Hypertension (in SHR) | Rat | Prevention of hypertension; increase in butyrate-producing bacteria; improved balance of T-helper and T-regulatory cells | Robles-Vera et al., 2020 [81] |
| Hypertension induced by NO blockade | Rat | Reduction in dysbiosis, vascular oxidative stress, and inflammation | Robles-Vera et al., 2018 [31] |
| Hypertension induced by tacrolimus | Mouse | Prevention of hypertension and endothelial dysfunction; improved balance of T-helper and T-regulatory cells | Toral et al., 2018 [82] |
| Hypertension and systemic lupus erythematosus, induced by TLR-7 agonist | Mouse | Prevention of hypertension; reduction in autoantibodies; activation of TLR-9; reduced T-cell activation | Visitación et al., 2021 [83] |
| Septic shock induced by LPS | Mouse | Reduction in LPS-induced changes in organ weight, TNF-α levels, and liver function | Arribas et al., 2008 [84] |
| Immunity in pregnancy and lactation | Rat | Reduction in T-cytotoxic cells and modulation of intestinal cytokines and fatty acid profile; modulation of immunoglobulins and fatty acid profile in pups | Azagra-Boronat et al., 2020 [85] |
| Metabolic syndrome induced by HFD | Rat | Prevention of liver steatosis and systemic inflammation; amelioration of dysbiosis and barrier function (synbiotic treatment with L. fermentum CECT5716 + fructooligosaccharides) | Rivero-Gutiérrez et al., 2017 [45] |
| Overweight induced by HED | Pig | Increase in SCFAs; improvement in endocrine function, e.g., GLP-1 (treatment with L. fermentum CECT5716 + plant/dairy lipids) | Lemaire et al., 2018 [43] |
| Asthma induced by ovalbumin | Mouse | Reduction in inflammatory response and inflammatory cell infiltration in lung | Wang et al., 2022 [86] |
| Condition | Participants | Study Design | Main results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mastitis | 625 lactating mothers | Randomised, double blinded, controlled | 51% reduction in the incidence rate of mastitis in the probiotic group | Hurtado et al., 2017 [103] |
| Mastitis | 352 lactating mothers with mastitis | Randomised, controlled | Lower bacterial count in HM samples of probiotic group, compared to the control group | Arroyo et al., 2010 [30] |
| Mastitis | 148 lactating mothers with breast pain | Randomised, double blinded, controlled | Significant decrease in bacterial load in HM samples of the probiotic group | Maldonado-Lobon et al., 2015 [104] |
| Mastitis | 101 lactating mothers with breast abscess | Multicentre, randomised, double blinded, controlled | Significant decrease in the rate of stopping breastfeeding due to recurrence of mastitis | Zhang et al., 2022 [105] |
| Influenza vaccination | 50 healthy adults (31 male, 19 female) | Randomised, double blinded, placebo controlled | Significantly lower incidence of influenza-like illness; significant increase in antigen-specific IgA in the probiotic group | Olivares et al., 2007 [50] |
| Condition | Participants | Study Design | Main Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal and upper respiratory tract infections | 215 infants | Randomised, double blinded, controlled | Significant reduction in the incidence rate of gastrointestinal and upper respiratory tract infections in the probiotic group | Maldonado et al., 2012 [32] |
| Gastrointestinal infection and safety | 137 infants | Randomised, double blinded, controlled | Significant reduction in gastrointestinal infection; normal growth and weight gain; normal consumption of formula; no symptoms relating to formula | Gil-Campos et al., 2012 [76] |
| Modulation of infant microbiota | 540 infants | Randomised, double blinded, controlled, multicentre | Significant effects on microbiota states: phylogenetic profiles of the infants receiving synbiotic infant formula were closer to reference profiles of those fed with HM | Lagkouvardos et al., 2022 [102] |
| Infection and safety | 236 infants | Randomised, double blinded, controlled | 44% lower incidence of diarrhoea and 2.5 days reduction in duration of diarrhoea; lower incidence of respiratory tract infections among infants born by caesarean section; normal growth | Maldonado et al., 2019 [106] |
| Long-term safety | 110 infants | 3-year follow-up study | No significant difference in growth and incidence of infectious and non-infectious gastrointestinal diseases | Maldonado-Lobon et al., 2015 [77] |
| Infection and growth | 625 mother–infant pairs | Randomised, double blinded, placebo controlled | Lower incidence of conjunctivitis in infants in the probiotic group; higher weight of infants in probiotic group | Pastor-Villaescusa et al., 2020 [107] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozen, M.; Piloquet, H.; Schaubeck, M. Limosilactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: Clinical Potential of a Probiotic Strain Isolated from Human Milk. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092207
Ozen M, Piloquet H, Schaubeck M. Limosilactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: Clinical Potential of a Probiotic Strain Isolated from Human Milk. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092207
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzen, Metehan, Hugues Piloquet, and Monika Schaubeck. 2023. "Limosilactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: Clinical Potential of a Probiotic Strain Isolated from Human Milk" Nutrients 15, no. 9: 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092207
APA StyleOzen, M., Piloquet, H., & Schaubeck, M. (2023). Limosilactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: Clinical Potential of a Probiotic Strain Isolated from Human Milk. Nutrients, 15(9), 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092207