Peripheral Biomarkers of Anorexia Nervosa: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection and Search Strategy
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Appraisal
2.4. Calculating Effect Sizes
2.5. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Search Outcome
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Quality of Studies
3.4. Meta-Analysis Results
3.5. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Galmiche, M.; Déchelotte, P.; Lambert, G.; Tavolacci, M.P. Prevalence of eating disorders over the 2000–2018 period: A systematic literature review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcelus, J.; Mitchell, A.J.; Wales, J.; Nielsen, S. Mortality rates in patients with anorexia nervosa and other eating disorders. A meta-analysis of 36 studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, L.; Weiselberg, E. Anorexia nervosa/atypical anorexia nervosa. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2017, 47, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, A.; Phillipou, A. Current directions in biomarkers and endophenotypes for anorexia nervosa: A scoping review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 137, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, H.R.; Møller, L.; Bartosz, G.; Bast, A.; Bertoni-Freddari, C.; Collins, A.; Cooke, M.; Coolen, S.; Haenen, G.; Hoberg, A.-M. Biomarkers. Mol. Asp. Med. 2002, 23, 101–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.C.; Sundar, R.; Lim, J.S.; Yap, T.A. Towards precision medicine in the clinic: From biomarker discovery to novel therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What are biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, B.; Bartholdy, S.; Robinson, L.; Solmi, M.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Breen, G.; Schmidt, U.; Himmerich, H. A meta-analysis of cytokine concentrations in eating disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 103, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, B.; Leppanen, J.; Campbell, I.C.; Chung, R.; Breen, G.; Schmidt, U.; Himmerich, H. A longitudinal analysis of cytokines in anorexia nervosa. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 85, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Föcker, M.; Timmesfeld, N.; Scherag, S.; Bühren, K.; Langkamp, M.; Dempfle, A.; Sheridan, E.M.; de Zwaan, M.; Fleischhaker, C.; Herzog, W.; et al. Screening for anorexia nervosa via measurement of serum leptin levels. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutigliano, G.; Rocchetti, M.; Paloyelis, Y.; Gilleen, J.; Sardella, A.; Cappucciati, M.; Palombini, E.; Dell’Osso, L.; Caverzasi, E.; Politi, P.; et al. Peripheral oxytocin and vasopressin: Biomarkers of psychiatric disorders? A comprehensive systematic review and preliminary meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 241, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plessow, F.; Eddy, K.T.; Lawson, E.A. The Neuropeptide Hormone Oxytocin in Eating Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Föcker, M.; Timmesfeld, N.; Scherag, S.; Knoll, N.; Singmann, P.; Wang-Sattler, R.; Bühren, K.; Schwarte, R.; Egberts, K.; Fleischhaker, C.; et al. Comparison of metabolic profiles of acutely ill and short-term weight recovered patients with anorexia nervosa reveals alterations of 33 out of 163 metabolites. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, P.; Monteleone, A.M.; Troisi, J.; Dalle Grave, R.; Corrivetti, G.; Calugi, S.; Scala, G.; Patriciello, G.; Zanetti, A.; Maj, M. Metabolomics signatures of acutely ill and short-term weight recovered women with anorexia nervosa. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3980–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Furukawa, T.A.; Tsigkaropoulou, E.; Karavia, A.; Gournellis, R.; Soureti, A.; Bellos, I.; Douzenis, A.; Michopoulos, I. Adipokines in anorexia nervosa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 112, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, M.; Markmann Jensen, S.; Healy, D.; Dureja, A.; Watson, H.J.; Holst, B.; Bulik, C.M.; Sjögren, J.M. A systematic review and meta-analysis finds increased blood levels of all forms of ghrelin in both restricting and binge-eating/purging subtypes of anorexia nervosa. Nutrients 2021, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2009, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feighner, J.P.; Robins, E.; Guze, S.B.; Woodruff, R.A., Jr.; Winokur, G.; Munoz, R. Diagnostic criteria for use in psychiatric research. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1972, 26, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft. Microsoft Excel. Available online: https://office.microsoft.com/excel (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Institute, T.J.B. Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers’ Manual: 2014 Edition; Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Aloe, A.M. Evaluation of various estimators for standardized mean difference in meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 403–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del, A.C.R.; Hoyt, W.T. MAd: Meta-Analysis with Mean Differences (R Package Version 0.8-2). Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MAd (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Raudenbush, S.W.; Bryk, A.S. Hierarchical Linear Models: Applications and Data Analysis Methods; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA:, 2002; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.; Harbord, R.M. Funnel plots in meta-analysis. Stata J. 2004, 4, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, T.D.; Doucouliagos, H. Meta-regression approximations to reduce publication selection bias. Res. Synth. Methods 2014, 5, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McShane, B.B.; Böckenholt, U.; Hansen, K.T. Adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis: An evaluation of selection methods and some cautionary notes. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 11, 730–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Li, T.; Deeks, J.J. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.4; Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: Alberta, ON, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Connan, F.; Lightman, S.L.; Landau, S.; Wheeler, M.; Treasure, J.; Campbell, I.C. An investigation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hyperactivity in anorexia nervosa: The role of CRH and AVP. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, J.; Goodman, L.; Sen Gupta, S.; Mayer, L.; Etu, S.F.; Walsh, B.T.; Wang, J.; Pierson, R.; Warren, M.P. Treatment of anorexia nervosa is associated with increases in bone mineral density, and recovery is a biphasic process involving both nutrition and return of menses. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tortorella, A.; Brambilla, F.; Fabrazzo, M.; Volpe, U.; Monteleone, A.M.; Mastromo, D.; Monteleone, P. Central and peripheral peptides regulating eating behaviour and energy homeostasis in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: A literature review. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. J. Eat. Disord. Assoc. 2014, 22, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butera, P.C. Estradiol and the control of food intake. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 99, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisser, A.-S.; Habbel, P.; Wiedenmann, B.; Klapp, B.F.; Mönnikes, H.; Kobelt, P. Interactions of gastrointestinal peptides: Ghrelin and its anorexigenic antagonists. Int. J. Pept. 2010, 2010, 817457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashi, M.; Asakawa, A.; Harada, T.; Ushikai, M.; Coquerel, Q.; Sinno, M.H.; Déchelotte, P.; Inui, A.; Fetissov, S.O. Ghrelin reactive autoantibodies in restrictive anorexia nervosa. Nutrition 2011, 27, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, M.; Miller, K.K.; Herzog, D.B.; Ramaswamy, K.; Aggarwal, A.; Almazan, C.; Neubauer, G.; Breu, J.; Klibanski, A. Growth hormone and ghrelin responses to an oral glucose load in adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa and controls. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; López, M.; Rahmouni, K. The cellular and molecular bases of leptin and ghrelin resistance in obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, M.; Klibanski, A. Endocrine consequences of anorexia nervosa. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, M.J. Effects of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in human. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 22, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, N.; Fisher, M. Menstrual disorders in adolescents and young adults with eating disorders. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2022, 52, 101240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, M.P. Endocrine manifestations of eating disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, R.L. The endocrinology of the menstrual cycle. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1154, 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tost, M.; Monreal, J.A.; Armario, A.; Barbero, J.D.; Cobo, J.; García-Rizo, C.; Bioque, M.; Usall, J.; Huerta-Ramos, E.; Soria, V.; et al. Targeting hormones for improving cognition in major mood disorders and schizophrenia: Thyroid hormones and prolactin. Clin. Drug Investig. 2020, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wronski, M.L.; Tam, F.I.; Seidel, M.; Mirtschink, P.; Poitz, D.M.; Bahnsen, K.; Steinhäuser, J.L.; Bauer, M.; Roessner, V.; Ehrlich, S. Associations between pituitary-thyroid hormones and depressive symptoms in individuals with anorexia nervosa before and after weight-recovery. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 137, 105630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalvo, I.; Gutiérrez-Zotes, A.; Creus, M.; Monseny, R.; Ortega, L.; Franch, J.; Lawrie, S.M.; Reynolds, R.M.; Vilella, E.; Labad, J. Increased prolactin levels are associated with impaired processing speed in subjects with early psychosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, S.; Tayek, J.A. Cortisol increases gluconeogenesis in humans: Its role in the metabolic syndrome. Clin. Sci. 2001, 101, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, V.; Slettahjell, H.B.; Skavberg Roaldsen, K.; Kostovski, E. Carboxy terminal collagen crosslinks as a prognostic risk factor for fall-related fractures in individuals with established spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2019, 57, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oświęcimska, J.; Ziora, K.; Pluskiewicz, W.; Geisler, G.; Broll-Waśka, K.; Karasek, D.; Dyduch, A. Skeletal status and laboratory investigations in adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa. Bone 2007, 41, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Favaro, A.; Santonastaso, P.; Manzato, E.; Sergi, G.; Correll, C.U. Inflammatory cytokines and anorexia nervosa: A meta-analysis of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 51, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festa, A.; D’Agostino, R., Jr.; Williams, K.; Karter, A.J.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Tracy, R.P.; Haffner, S.M. The relation of body fat mass and distribution to markers of chronic inflammation. Int. J. Obes. 2001, 25, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elegido, A.; Graell, M.; Andrés, P.; Gheorghe, A.; Marcos, A.; Nova, E. Increased naive CD4+ and B lymphocyte subsets are associated with body mass loss and drive relative lymphocytosis in anorexia nervosa patients. Nutr. Res. 2017, 39, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Nomura, K.; Hotta, M.; Takano, K. Malnutrition induces dissociated changes in lymphocyte count and subset proportion in patients with anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2007, 40, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słotwińska, S.M.; Słotwiński, R. Immune disorders in anorexia. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 42, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomeroy, C. Risk of infection and immune function in anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1992, 12, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSarbo, J.R.; DeSarbo, L. Anorexia nervosa and COVID-19. Curr. Psychiatry 2020, 19, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dusseldorp, E.; Su, X.; Meulman, J.J. Multiple moderator meta-analysis using the R-package Meta-CART. Behav. Res. Methods 2020, 52, 2657–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, J.; Hudson, L.D. Anorexia nervosa in adolescents. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2020, 81, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

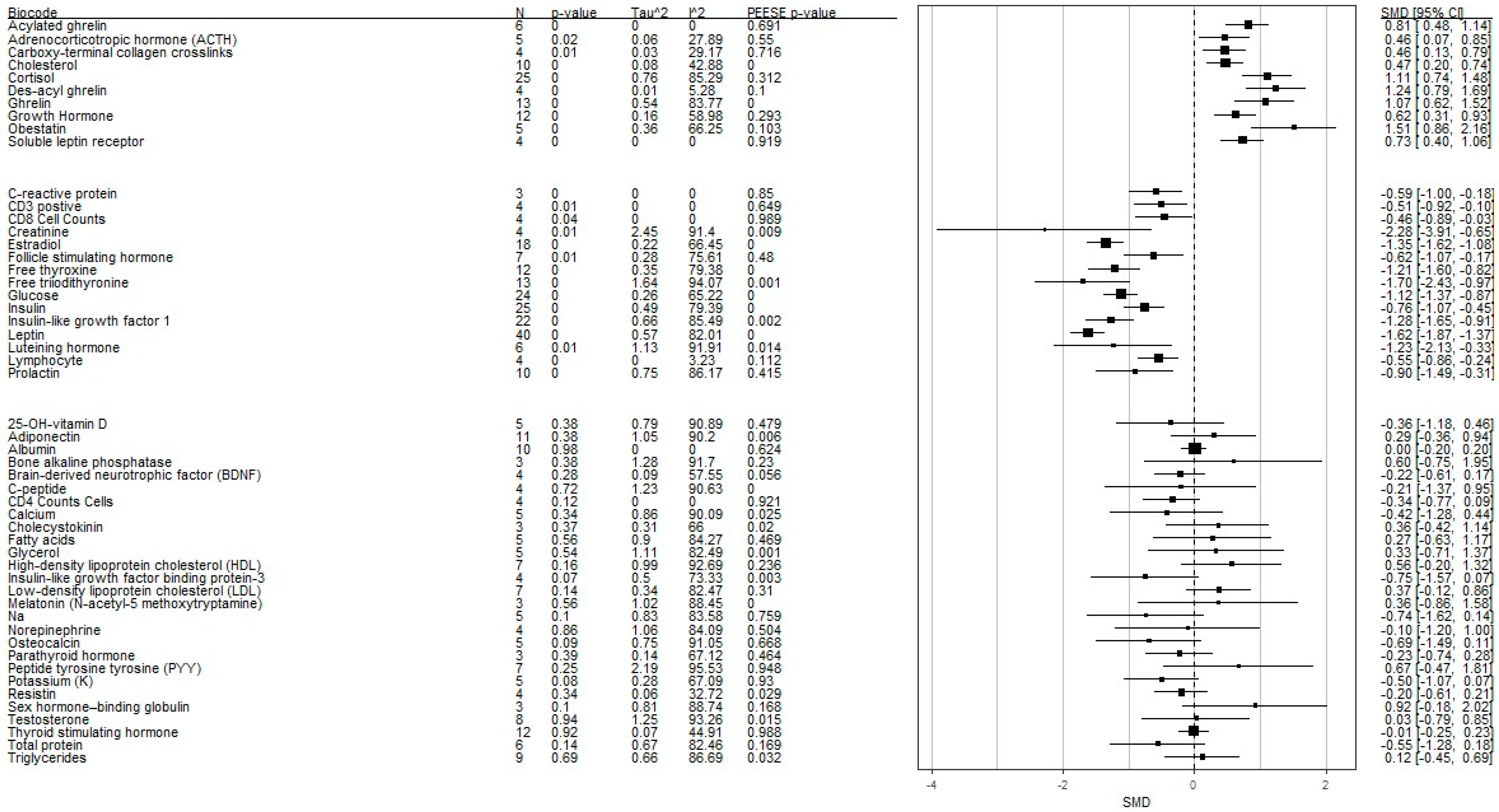
| Peripheral Biomarkers | k | g+ | SE (g+) | CI L | CI U | p | Tau2 | I2 | z (PEESE) | z p (PEESE) | X2 (TPSM) | X2 p (TPSM) | g+ adj | p adj | CI L adj | CI U adj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25-Oh-Vitamin D | 5 | −0.36 | 0.42 | −1.18 | 0.45 | 0.38 | 0.79 | 90.89 | −0.708 | 0.479 | 0.163 | 0.687 | −0.513 | 0.262 | −1.409 | 0.384 |
| Acylated Ghrelin | 6 | 0.81 | 0.17 | 0.48 | 1.14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.398 | 0.691 | 0.135 | 0.713 | 0.735 | 0.006 | 0.212 | 1.258 |
| Adiponectin | 11 | 0.29 | 0.33 | −0.36 | 0.93 | 0.38 | 1.05 | 90.2 | −2.774 | 0.006 | 8.288 | 0.004 | −0.770 | 0.123 | −1.749 | 0.209 |
| Adrenocorticotropic Hormone | 5 | 0.46 | 0.2 | 0.06 | 0.86 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 27.89 | −0.598 | 0.550 | 0.184 | 0.668 | 0.385 | 0.056 | −0.009 | 0.779 |
| Albumin | 10 | 0 | 0.1 | −0.18 | 0.19 | 0.98 | 0 | 0 | 0.490 | 0.624 | 0.528 | 0.467 | −0.036 | 0.732 | −0.245 | 0.172 |
| Bone Alkaline Phosphatase | 3 | 0.6 | 0.69 | −0.74 | 1.95 | 0.38 | 1.28 | 91.7 | 1.201 | 0.230 | 0.893 | 0.345 | −0.113 | 0.906 | −1.974 | 1.749 |
| Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor | 4 | −0.22 | 0.2 | −0.61 | 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.09 | 57.55 | −1.914 | 0.056 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Calcium | 5 | −0.42 | 0.44 | −1.28 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.86 | 90.09 | −4.158 | 0.000 | 5.045 | 0.025 | −1.016 | 0.082 | −2.161 | 0.130 |
| Carboxy-Terminal Collagen Crosslinks | 4 | 0.46 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 29.17 | 0.189 | 0.850 | 0.003 | 0.955 | −0.586 | 0.004 | −0.990 | −0.183 |
| CD3 Positive | 4 | −0.51 | 0.21 | −0.91 | −0.1 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.456 | 0.649 | 0.021 | 0.884 | −0.504 | 0.016 | −0.913 | −0.095 |
| CD4 Cell Counts | 4 | −0.34 | 0.22 | −0.77 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | −0.100 | 0.921 | 0.065 | 0.798 | −0.333 | 0.136 | −0.771 | 0.105 |
| CD8 Cell Counts | 4 | −0.46 | 0.22 | −0.89 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0.013 | 0.989 | 0.032 | 0.858 | −0.454 | 0.041 | −0.891 | −0.018 |
| Cholecystokinin | 3 | 0.36 | 0.4 | −0.42 | 1.13 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 66 | −2.246 | 0.025 | 7.106 | 0.008 | −0.983 | 0.002 | −1.620 | −0.347 |
| Cholesterol | 10 | 0.47 | 0.14 | 0.2 | 0.74 | 0 | 0.08 | 42.88 | −0.363 | 0.716 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Cortisol | 25 | 1.11 | 0.19 | 0.73 | 1.49 | 0 | 0.76 | 85.29 | 2.335 | 0.020 | 2.835 | 0.092 | −0.129 | 0.301 | −0.372 | 0.115 |
| C-Peptide | 4 | −0.21 | 0.59 | −1.37 | 0.95 | 0.72 | 1.23 | 90.63 | 3.524 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.983 | 0.453 | 0.331 | −0.461 | 1.367 |
| C-Reactive Protein | 3 | −0.59 | 0.21 | −0.99 | −0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.011 | 0.312 | 0.780 | 0.377 | −0.586 | 0.004 | −0.990 | −0.183 |
| Creatinine | 4 | −2.28 | 0.83 | −3.9 | −0.65 | 0.01 | 2.45 | 91.4 | −2.614 | 0.009 | 0.156 | 0.693 | −2.174 | 0.008 | −3.781 | −0.566 |
| Des-Acyl Ghrelin | 4 | 1.24 | 0.23 | 0.78 | 1.7 | 0 | 0.01 | 5.28 | −1.644 | 0.100 | 0.603 | 0.437 | 1.395 | 0.000 | 0.825 | 1.966 |
| Estradiol | 18 | −1.35 | 0.14 | −1.62 | −1.08 | 0 | 0.22 | 66.45 | −3.656 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.908 | −1.346 | 0.000 | −1.614 | −1.077 |
| Fatty Acids | 5 | 0.27 | 0.46 | −0.63 | 1.18 | 0.56 | 0.9 | 84.27 | 0.724 | 0.469 | 0.341 | 0.559 | −0.026 | 0.964 | −1.183 | 1.130 |
| Follicle-Stimulating Hormone | 7 | −0.62 | 0.23 | −1.08 | −0.17 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 75.61 | −0.707 | 0.480 | 0.430 | 0.512 | −0.564 | 0.040 | −1.101 | −0.027 |
| Free Thyroxine | 12 | −1.21 | 0.2 | −1.6 | −0.82 | 0 | 0.35 | 79.38 | −3.574 | 0.000 | 0.092 | 0.762 | −1.194 | 0.000 | −1.581 | −0.808 |
| Free Triiodithyronine | 13 | −1.7 | 0.37 | −2.43 | −0.97 | 0 | 1.64 | 94.07 | −3.259 | 0.001 | 1.366 | 0.242 | −1.470 | 0.007 | −2.536 | −0.405 |
| Ghrelin | 13 | 1.07 | 0.23 | 0.62 | 1.52 | 0 | 0.54 | 83.77 | 4.958 | 0.000 | 3.290 | 0.070 | 0.515 | 0.312 | −0.483 | 1.514 |
| Glucose | 24 | −1.12 | 0.13 | −1.38 | −0.86 | 0 | 0.26 | 65.22 | −4.171 | 0.000 | 0.138 | 0.711 | −1.112 | 0.000 | −1.379 | −0.846 |
| Glycerol | 5 | 0.33 | 0.53 | −0.71 | 1.36 | 0.54 | 1.11 | 82.49 | 3.303 | 0.001 | 0.919 | 0.338 | 1.356 | 0.388 | −1.721 | 4.433 |
| Growth Hormone | 12 | 0.62 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.93 | 0 | 0.16 | 58.98 | 1.052 | 0.293 | 0.675 | 0.411 | 0.464 | 0.056 | −0.012 | 0.941 |
| Hdl Cholesterol | 7 | 0.56 | 0.39 | −0.22 | 1.33 | 0.16 | 0.99 | 92.69 | −1.184 | 0.236 | 0.741 | 0.389 | 0.965 | 0.099 | −0.182 | 2.113 |
| Insulin | 25 | −0.76 | 0.16 | −1.08 | −0.45 | 0 | 0.49 | 79.39 | −3.603 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.965 | −0.764 | 0.000 | −1.110 | −0.418 |
| Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 | 22 | −1.28 | 0.19 | −1.66 | −0.91 | 0 | 0.66 | 85.49 | −3.131 | 0.002 | 1.425 | 0.233 | −1.358 | 0.000 | −1.703 | −1.014 |
| Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein−3 | 4 | −0.75 | 0.42 | −1.57 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.5 | 73.33 | −2.959 | 0.003 | 0.196 | 0.658 | −0.680 | 0.099 | −1.488 | 0.128 |
| Ldl Cholesterol | 7 | 0.37 | 0.25 | −0.12 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 0.34 | 82.47 | −3.628 | 0.000 | 3.130 | 0.077 | −1.670 | 0.000 | −1.906 | −1.433 |
| Leptin | 40 | −1.62 | 0.13 | −1.89 | −1.36 | 0 | 0.57 | 82.01 | −1.015 | 0.310 | 7.467 | 0.006 | −1.504 | 0.032 | −0.129 | −2.880 |
| Luteinizing Hormone | 6 | −1.23 | 0.46 | −2.12 | −0.33 | 0.01 | 1.13 | 91.91 | −2.454 | 0.014 | 0.685 | 0.408 | −1.012 | 0.139 | −2.353 | 0.329 |
| Lymphocyte (%) | 4 | −0.55 | 0.16 | −0.87 | −0.23 | 0 | 0 | 3.23 | −1.588 | 0.112 | 0.008 | 0.930 | −0.547 | 0.001 | −0.863 | −0.232 |
| Melatonin (N-Acetyl−5 Methoxytryptamine) | 3 | 0.36 | 0.62 | −0.86 | 1.57 | 0.56 | 1.02 | 88.45 | −4.409 | 0.000 | 0.145 | 0.703 | 0.630 | 0.475 | −1.098 | 2.359 |
| Na | 5 | −0.74 | 0.45 | −1.63 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.83 | 83.58 | −0.306 | 0.759 | 0.903 | 0.342 | −0.397 | 0.673 | −2.242 | 1.448 |
| Norepinephrine | 4 | −0.1 | 0.56 | −1.2 | 1 | 0.86 | 1.06 | 84.09 | 0.669 | 0.504 | 3.691 | 0.055 | 2.132 | 0.468 | −3.628 | 7.892 |
| Obestatin | 5 | 1.51 | 0.33 | 0.86 | 2.16 | 0 | 0.36 | 66.25 | 1.631 | 0.103 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Osteocalcin | 5 | −0.69 | 0.41 | −1.5 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 91.05 | −0.429 | 0.668 | 1.417 | 0.234 | −0.123 | 0.928 | −2.775 | 2.529 |
| Parathyroid Hormone | 3 | −0.23 | 0.26 | −0.75 | 0.29 | 0.39 | 0.14 | 67.12 | −0.733 | 0.464 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Peptide Tyrosine Tyrosine | 7 | 0.67 | 0.58 | −0.46 | 1.8 | 0.25 | 2.19 | 95.53 | 0.065 | 0.948 | 4.655 | 0.031 | 2.226 | 0.022 | 0.319 | 4.132 |
| Potassium | 5 | −0.5 | 0.29 | −1.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 67.09 | −0.088 | 0.930 | 0.351 | 0.554 | −0.430 | 0.228 | −1.130 | 0.270 |
| Prolactin | 10 | −0.9 | 0.3 | −1.49 | −0.3 | 0 | 0.75 | 86.17 | −0.815 | 0.415 | 1.367 | 0.242 | −0.664 | 0.201 | −1.683 | 0.354 |
| Resistin | 4 | −0.2 | 0.21 | −0.61 | 0.21 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 32.72 | 2.186 | 0.029 | 0.092 | 0.762 | −0.208 | 0.431 | −0.724 | 0.309 |
| Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin | 3 | 0.92 | 0.56 | −0.16 | 2.01 | 0.1 | 0.81 | 88.74 | 1.377 | 0.168 | 0.003 | 0.954 | 0.926 | 0.161 | −0.368 | 2.220 |
| Soluble Leptin Receptor | 4 | 0.73 | 0.17 | 0.4 | 1.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.102 | 0.919 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Testosterone | 8 | 0.03 | 0.42 | −0.78 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 1.25 | 93.26 | 2.421 | 0.015 | 4.646 | 0.031 | 1.918 | 0.224 | −1.171 | 5.006 |
| Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone | 12 | −0.01 | 0.12 | −0.24 | 0.22 | 0.92 | 0.07 | 44.91 | 0.015 | 0.988 | 0.140 | 0.708 | −0.035 | 0.700 | −0.214 | 0.144 |
| Total Protein | 6 | −0.55 | 0.37 | −1.28 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.67 | 82.46 | −1.375 | 0.169 | 1.471 | 0.225 | −0.803 | 0.006 | −1.375 | −0.231 |
| Triglycerides | 9 | 0.12 | 0.29 | −0.46 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.66 | 86.69 | 2.143 | 0.032 | 0.162 | 0.687 | −0.033 | 0.938 | −0.863 | 0.797 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.-K.; Watson, H.J.; Del Re, A.C.; Finch, J.E.; Hardin, S.L.; Dumain, A.S.; Brownley, K.A.; Baker, J.H. Peripheral Biomarkers of Anorexia Nervosa: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132095
Wu Y-K, Watson HJ, Del Re AC, Finch JE, Hardin SL, Dumain AS, Brownley KA, Baker JH. Peripheral Biomarkers of Anorexia Nervosa: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2024; 16(13):2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132095
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Ya-Ke, Hunna J. Watson, Aaron C. Del Re, Jody E. Finch, Sabrina L. Hardin, Alexis S. Dumain, Kimberly A. Brownley, and Jessica H. Baker. 2024. "Peripheral Biomarkers of Anorexia Nervosa: A Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 16, no. 13: 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132095
APA StyleWu, Y.-K., Watson, H. J., Del Re, A. C., Finch, J. E., Hardin, S. L., Dumain, A. S., Brownley, K. A., & Baker, J. H. (2024). Peripheral Biomarkers of Anorexia Nervosa: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 16(13), 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132095






