Lactobacillus rhamnosus NKU FL1-8 Isolated from Infant Feces Ameliorates the Alcoholic Liver Damage by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier in C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Culture of L. rhamnosus NKU FL1-8
2.3. Construction of the Developmental Tree of L. rhamnosus NKU FL1-8
2.4. The Determination of Acid Resistant Ability
2.5. The Determination of Bile Salt Resistant Ability
2.6. Animal Model and Experiment Design
2.7. Serum and Liver Biochemical Analysis
2.8. Histopathological Examination
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.11. Assessment of Expression Levels of Relevant Genes by RNA Extraction and q-PCR
2.12. Gut Microbiota
2.13. Statistical Methods and Data Processing
3. Results
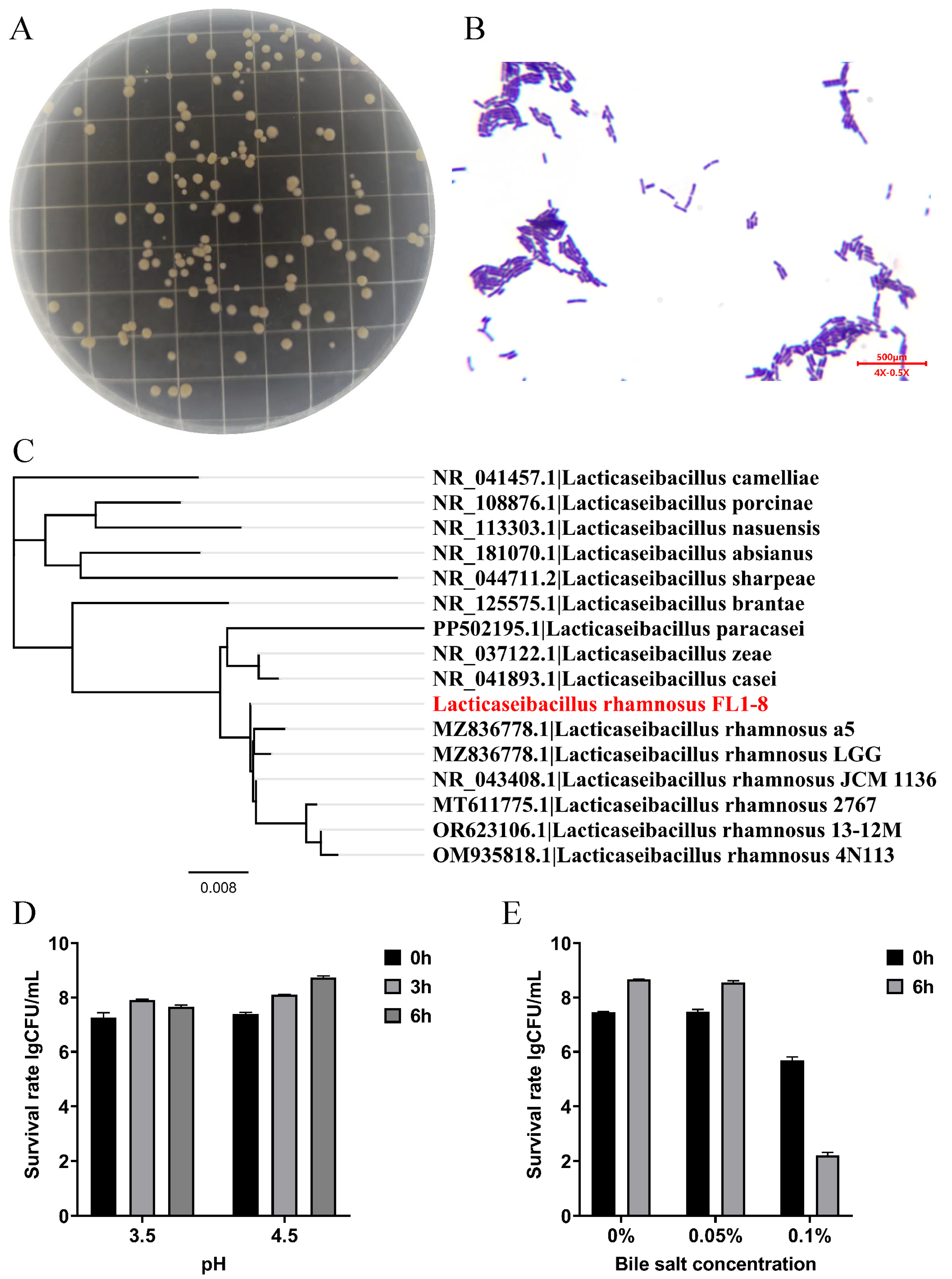
3.1. Colony Morphology and Its Characteristic Parameters
3.2. Body Weight and Serum Indicators
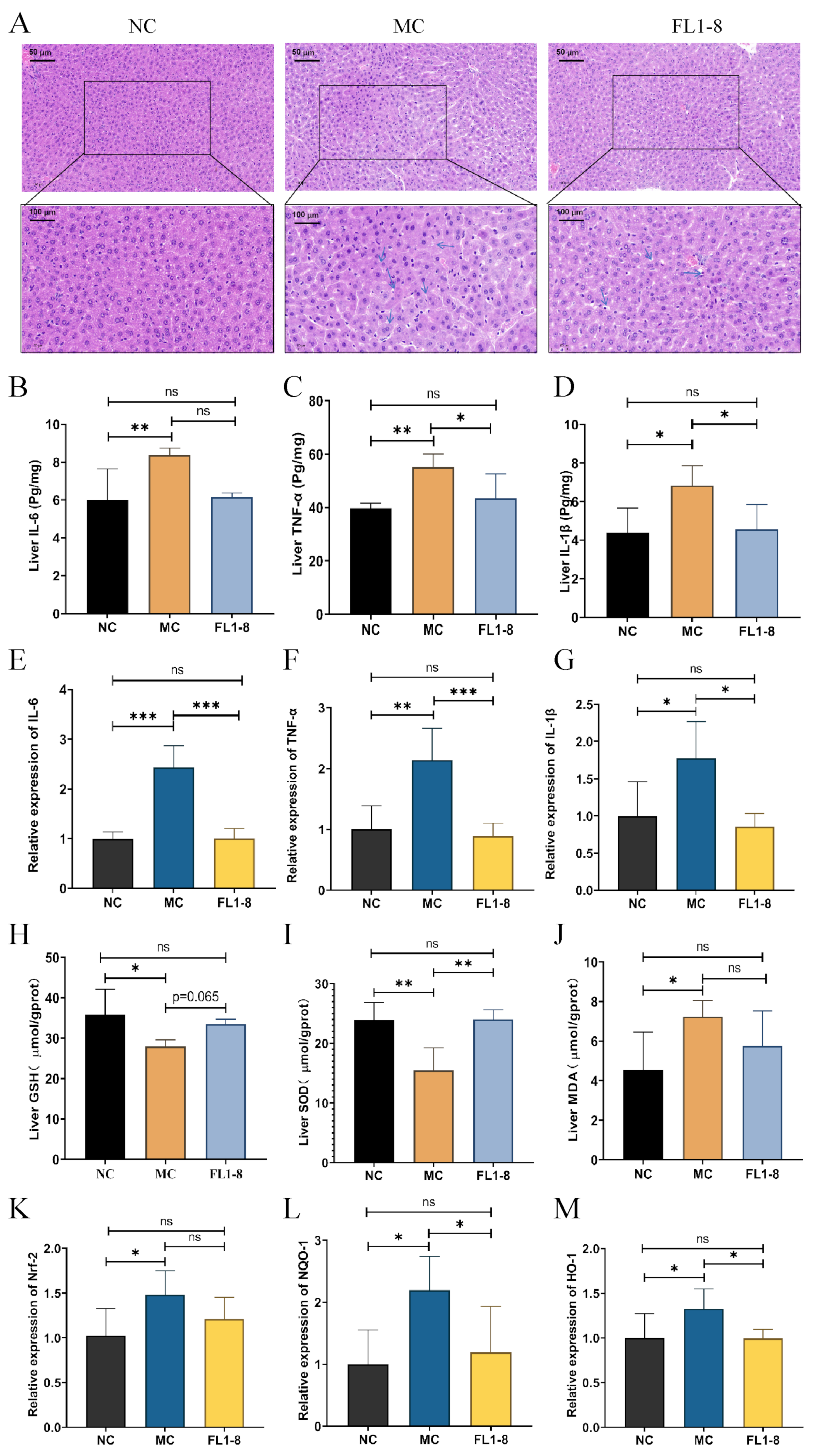
3.3. The Pathology and Oxidative Stress Level in Hepatic
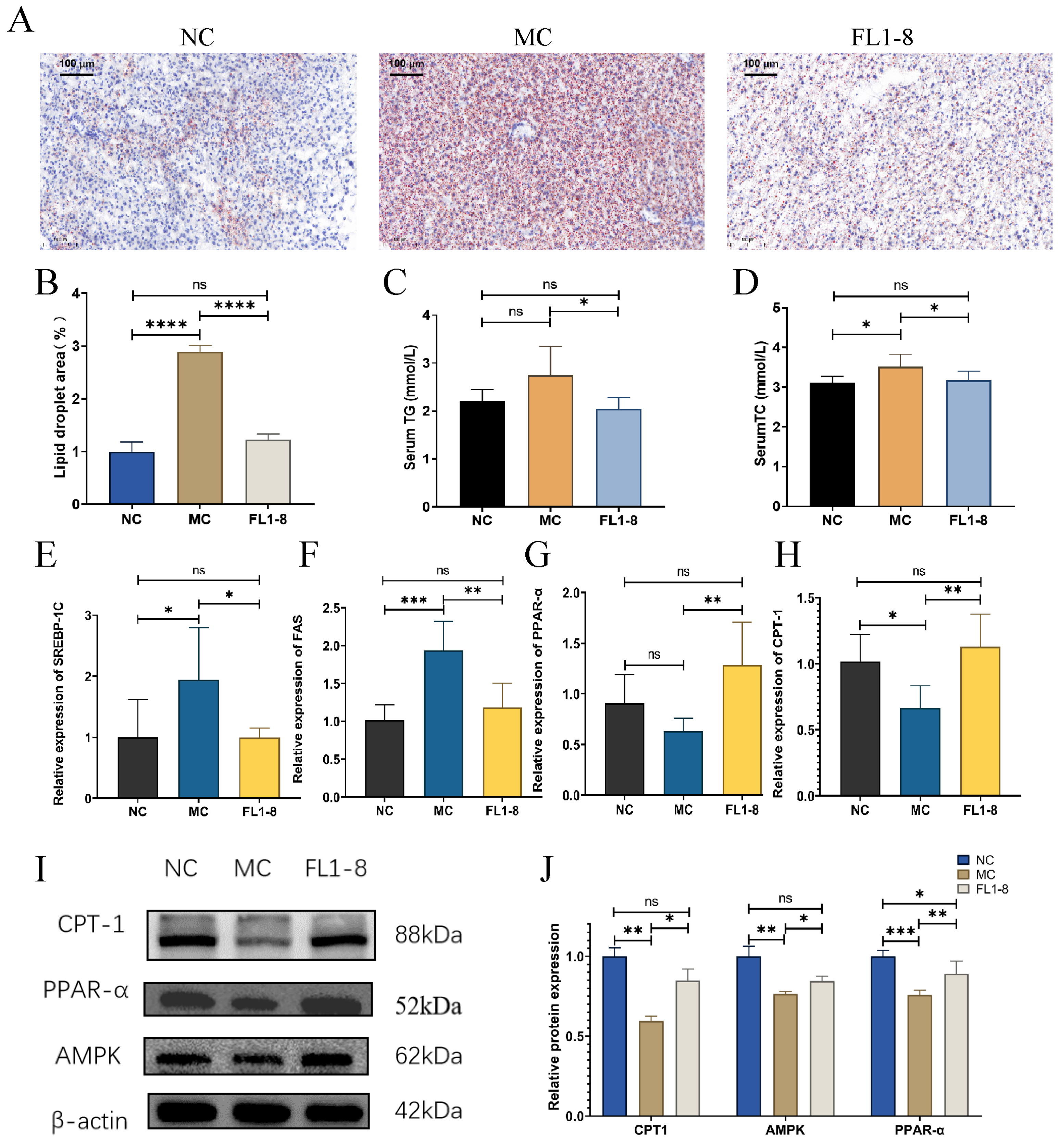
3.4. Levels of Lipid Metabolism
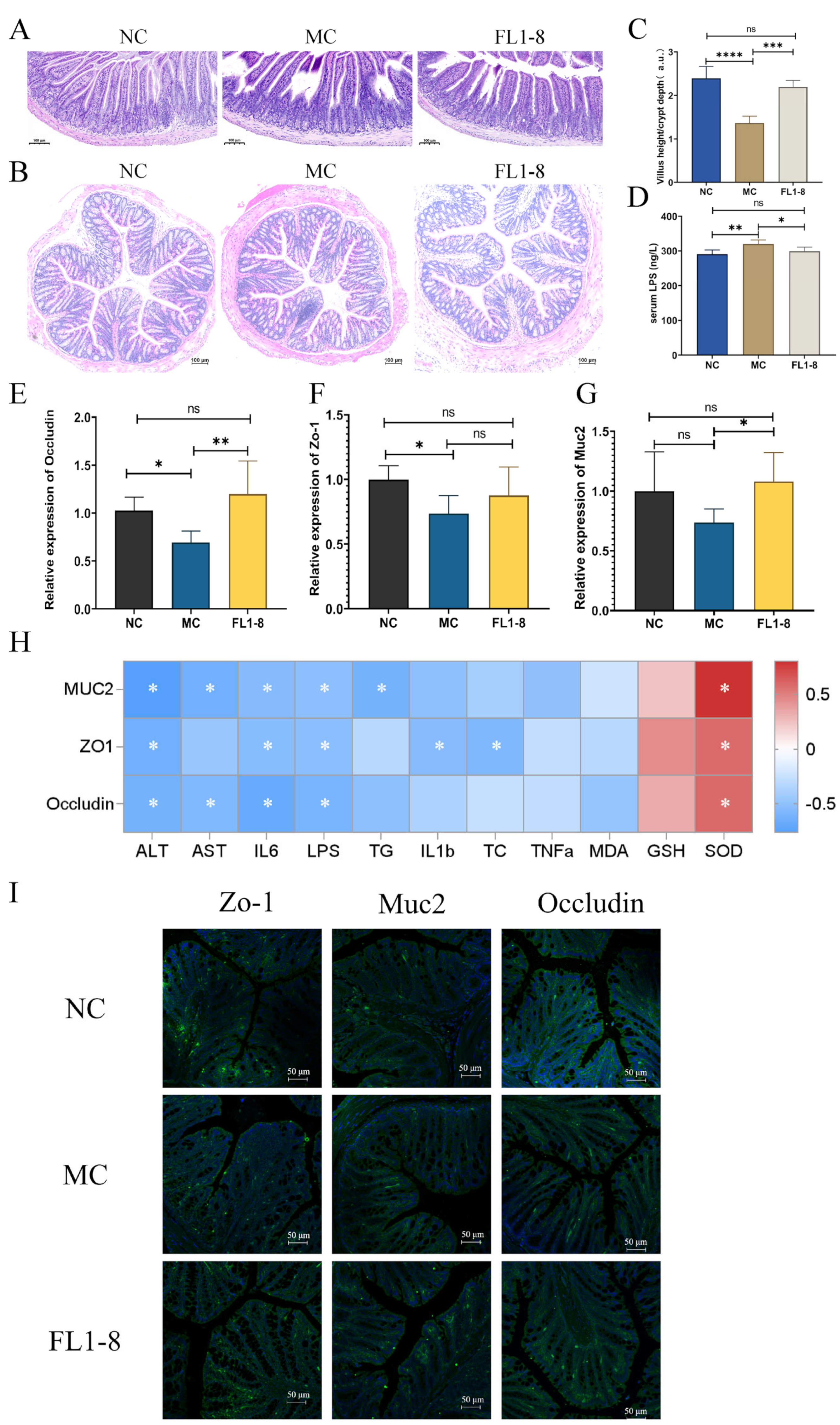
3.5. Intestinal Barrier Integrity
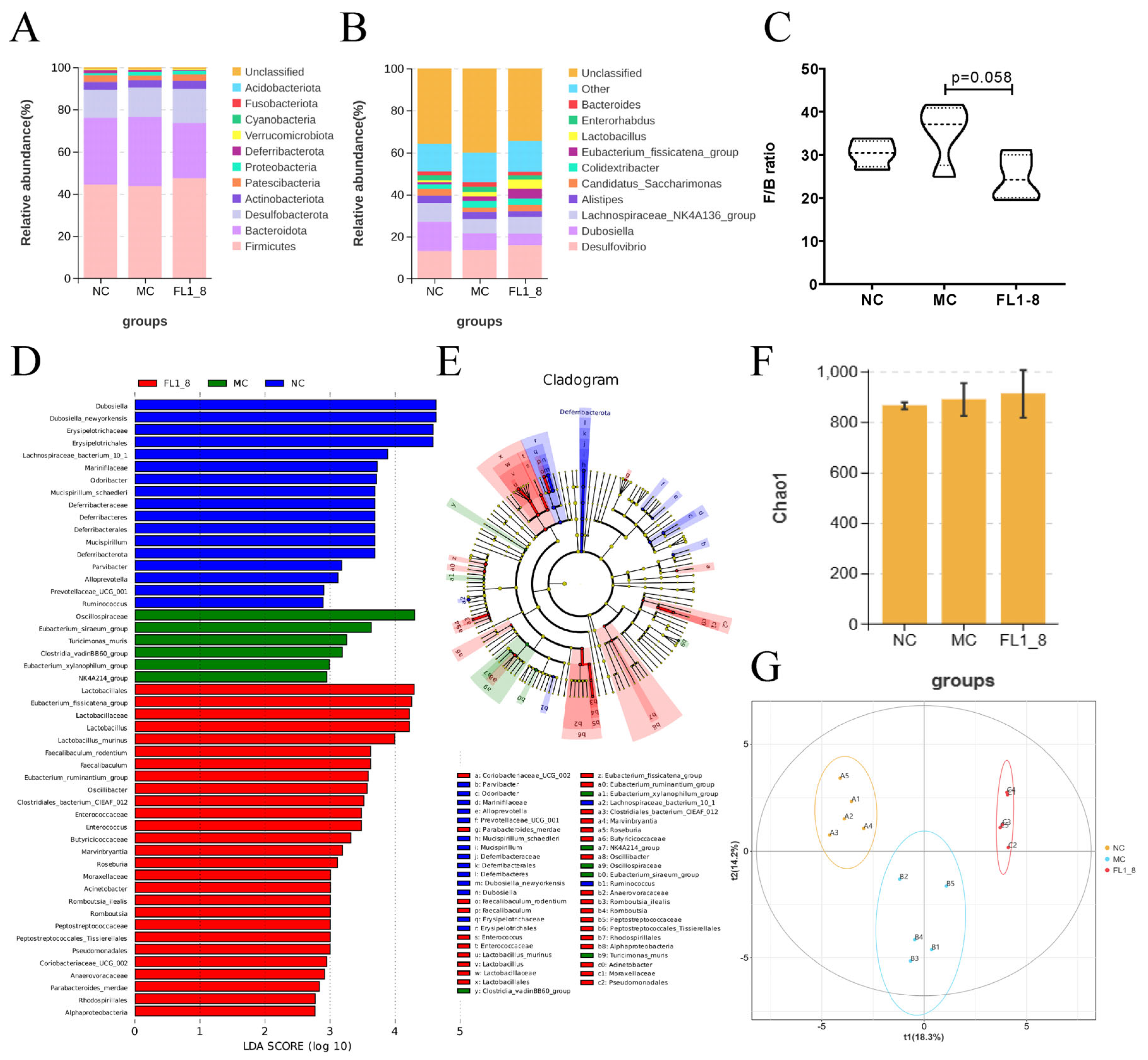
3.6. Gut Microbiota Composition
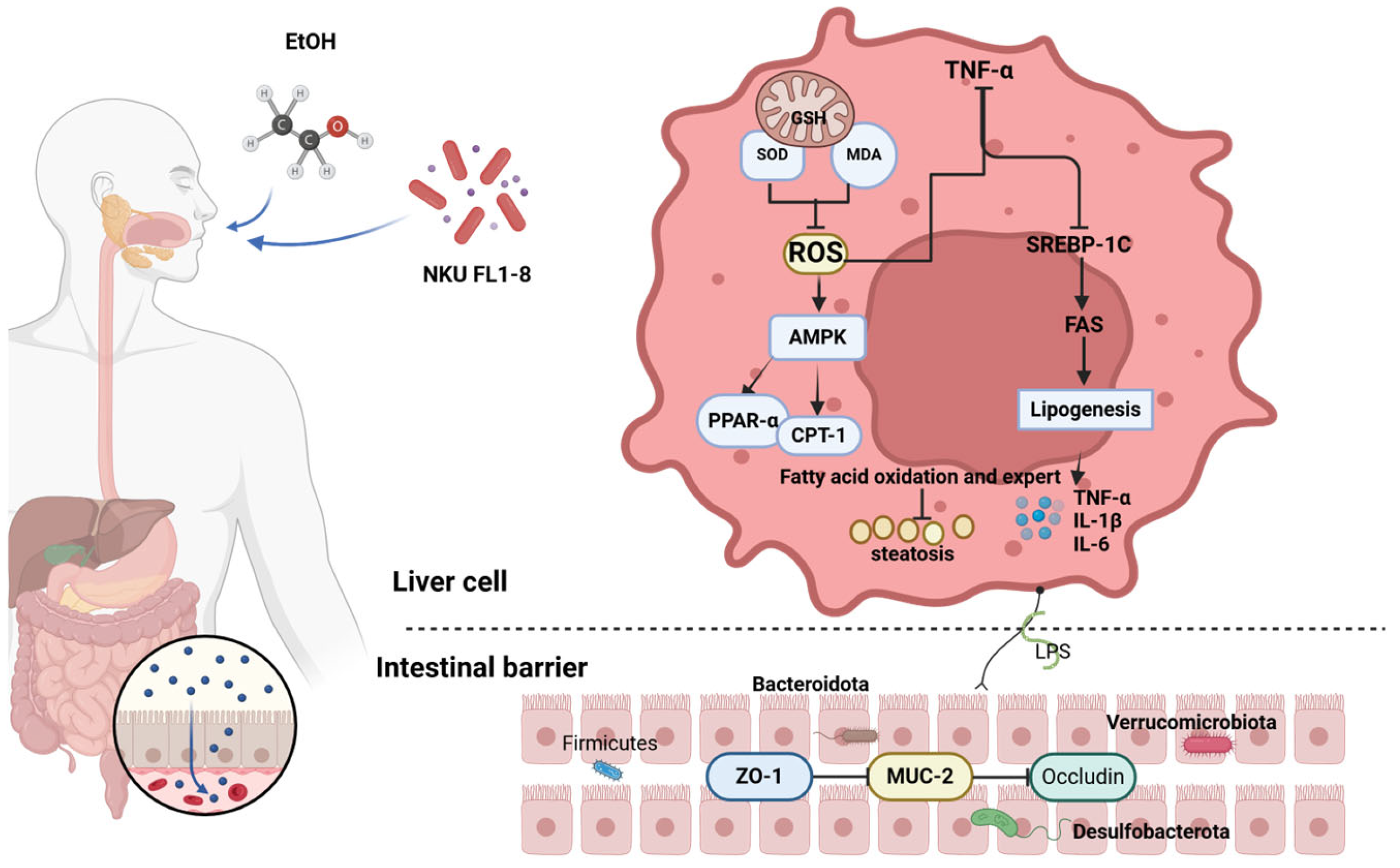
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawental, M.; Kipnis, A.; Rigg, K. Binge drinking among young adults in Israel: Application of the theory of planned behavior. Psychol. Health Med. 2018, 23, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spatz, M.; Ciocan, D.; Merlen, G.; Rainteau, D.; Humbert, L.; Gomes-Rochette, N.; Hugot, C.; Trainel, N.; Mercier-Nome, F.; Domenichini, S.; et al. Bile acid-receptor TGR5 deficiency worsens liver injury in alcohol-fed mice by inducing intestinal microbiota dysbiosis. Jhep. Rep. 2021, 3, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Sethi, B.; Staller, D.W.; Xin, X.; Ma, J.; Dong, Y.; Talmon, G.A.; Mahato, R.I. Anti-miR-96 and Hh pathway inhibitor MDB5 synergistically ameliorate alcohol-associated liver injury in mice. Biomaterials 2023, 295, 122049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, N. A systems biology approach for understanding the collagen regulatory network in alcoholic liver disease. Liver Int 2012, 32, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Fouts, D.E.; Starkel, P.; Hartmann, P.; Chen, P.; Llorente, C.; DePew, J.; Moncera, K.; Ho, S.B.; Brenner, D.A.; et al. Intestinal REG3 Lectins Protect against Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Reducing Mucosa-Associated Microbiota and Preventing Bacterial Translocation. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, S.; Matamoros, S.; Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Jamar, F.; Starkel, P.; Windey, K.; Tremaroli, V.; Backhed, F.; Verbeke, K.; et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4485–E4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, G.; Mirijello, A.; Ferrulli, A.; Antonelli, M.; Landolfi, R.; Gasbarrini, A.; Addolorato, G. Review article: Alcohol and gut microbiota—The possible role of gut microbiota modulation in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, P.A.; Green, S.J.; Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: Alcohol Effects on the Composition of Intestinal Microbiota. Alcohol. Res. 2015, 37, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Galicia-Moreno, M.; Gutierrez-Reyes, G. The role of oxidative stress in the development of alcoholic liver disease. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2014, 79, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Solovieva, N.V.; Leikhter, S.N.; Shidakova, N.A.; Lebedeva, O.V.; Sidorov, P.I.; Bazhukova, T.A.; Soloviev, A.G.; Barve, S.S.; McClain, C.J.; et al. Probiotics restore bowel flora and improve liver enzymes in human alcohol-induced liver injury: A pilot study. Alcohol 2008, 42, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.K.; Lee, I.O.; Tan, P.L.; Eor, J.Y.; Hwang, J.K.; Kim, S.H. Protective Effect of Lactobacillus fermentum LA12 in an Alcohol-Induced Rat Model of Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.G.; Kim, H.I.; Kwon, E.K.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus plantarum LC27 and Bifidobacterium longum LC67 mitigate alcoholic steatosis in mice by inhibiting LPS-mediated NF-kappaB activation through restoration of the disturbed gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4255–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Ye, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Berberine protects acute liver failure in mice through inhibiting inflammation and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 819, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Tao, X.; Liang, S.; Pan, Y.; He, L.; Sun, J.; Wenbo, J.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Protective effect of acidic polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis on acute ethanol-induced liver injury through reducing CYP2E1-dependent oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, A.; Turner, J.R. Cell Biology of Tight Junction Barrier Regulation and Mucosal Disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018, 10, a029314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Jia, Z.; Misra, B.R.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Z.; Yamamoto, M.; Trush, M.A.; Misra, H.P.; Li, Y. Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2-dependent myocardiac cytoprotection against oxidative and electrophilic stress. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2008, 8, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louvet, A.; Mathurin, P. Alcoholic liver disease: Mechanisms of injury and targeted treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Guan, Q.; Duan, W.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Xu, H.Y.; Shi, J.S.; Wang, F.Z.; Lu, R.; Zhang, H.L.; et al. Dietary Goji Shapes the Gut Microbiota to Prevent the Liver Injury Induced by Acute Alcohol Intake. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 929776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, R.G.; Patra, J.K.; Gouda, S.; Park, Y.; Shin, H.S.; Das, G. Benefaction of probiotics for human health: A review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.S.; Lin, S.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, C.C. Effect of probiotics Lactobacillus paracasei GKS6, L. plantarum GKM3, and L. rhamnosus GKLC1 on alleviating alcohol-induced alcoholic liver disease in a mouse model. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2020, 14, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Han, D.H.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.J.; Suk, K.T. Are Probiotics Effective in Targeting Alcoholic Liver Diseases? Probiotics. Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Chen, Z.; Xie, L.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum ST-III culture supernatant protects against acute alcohol-induced liver and intestinal injury. Aging 2023, 16, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugum, M.; McCullough, A. Diagnosis and Management of Alcoholic Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2015, 3, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreelatha, S.; Padma, P.R.; Umadevi, M. Protective effects of Coriandrum sativum extracts on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Jiang, S.; Tang, Y. Hepatoprotective effect of pyrroloquinoline quinone against alcoholic liver injury through activating Nrf2-mediated antioxidant and inhibiting TLR4-mediated inflammation responses. Process Biochem. 2020, 92, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Song, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, M. Mangiferin protects against alcoholic liver injury via suppression of inflammation-induced adipose hyperlipolysis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8837–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ding, W. A small RNA in neutrophils protects against acute-on-chronic alcoholic liver injury. Gut 2017, 66, 565–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Du, Y.Q.; Yuan, L.; Wang, N.N. Protective effect of puerarin on acute alcoholic liver injury. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Mo, C.; Wei, X.; Ma, A. Hepatoprotective Effect of Annulohypoxylon stygium Melanin on Acute Alcoholic Liver Injury in Mice. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, J.; Luo, L.; Zhou, D.; Yin, Z. gamma-Glutamylcysteine alleviates ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity via suppressing oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadeja, R.N.; Upadhyay, K.K.; Devkar, R.V.; Khurana, S. Naturally Occurring Nrf2 Activators: Potential in Treatment of Liver Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 3453926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hu, R.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, Z. Xiaochaihutang attenuates liver fibrosis by activation of Nrf2 pathway in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Jing, X.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L. (-)-Epicatechin attenuates hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome by inhibiting liver oxidative and inflammatory injury. Redox. Biol. 2019, 22, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Insulin induction of SREBP-1c in rodent liver requires LXRalpha-C/EBPbeta complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8182–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdak, Z.; Villegas, K.A.; Harb, R.; Wu, A.M.; Sousa, A.; Wands, J.R. Inhibition of p53 attenuates steatosis and liver injury in a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit, V.A. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1: Central to cell function. Iubmb. Life 2008, 60, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshandehroo, M.; Knoch, B.; Muller, M.; Kersten, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target genes. Ppar. Res. 2010, 2010, 612089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Leij, F.R.; Bloks, V.W.; Grefhorst, A.; Hoekstra, J.; Gerding, A.; Kooi, K.; Gerbens, F.; Te, M.G.; Kuipers, F. Gene expression profiling in livers of mice after acute inhibition of beta-oxidation. Genomics 2007, 90, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Hu, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, H.; Fang, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z. Propionic Acid Targets the TLR4/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway and Inhibits LPS-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 573475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groschwitz, K.R.; Hogan, S.P. Intestinal barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 3–20, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Akinosoglou, K.; de Lastic, A.L.; Skintzi, A.; Mouzaki, A.; Gogos, C.A. The Prognostic Value of Endotoxemia and Intestinal Barrier Biomarker ZO-1 in Bacteremic Sepsis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 359, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, M.; Hosie, S.; Bornstein, J.C.; Franks, A.E.; Hill-Yardin, E.L. The Role of the Gastrointestinal Mucus System in Intestinal Homeostasis: Implications for Neurological Disorders. Front. Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Cheng, D.; Ren, L.; Zheng, L.; Chen, F.; Zeng, T. Bacillus subtilis pretreatment alleviates ethanol-induced acute liver injury by regulating the Gut-liver axis in mice. Toxicology 2023, 488, 153487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama, T.R.; Juritsch, A.F.; Ahmad, R.; Salomon, J.D.; Dhawan, P.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Singh, A.B. The diet-microbiota axis: A key regulator of intestinal permeability in human health and disease. Tissue Barriers 2023, 11, 2077069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J.; et al. Metagenomic analyses of alcohol induced pathogenic alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigor’Eva, I.N. Gallstone Disease, Obesity and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio as a Possible Biomarker of Gut Dysbiosis. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zeng, F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, B. The Positive Effects of Grifola frondosa Heteropolysaccharide on NAFLD and Regulation of the Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kirpich, I.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Barve, S.; McClain, C.J.; Feng, W. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment potentiates intestinal hypoxia-inducible factor, promotes intestinal integrity and ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | Forward | ACAGCAGTTGGTTGGAGCAA |
| Reverse | ACGCGACCATCCTCCTCTTA | |
| Nrf2 | Forward | CTTTAGTCAGCGACAGAAGGAC |
| Reverse | AGGCATCTTGTTTGGGAATGTG | |
| HO-1 | Forward | AGGGCAGAAGGGAATTGCTC |
| Reverse | AAAGAGCTGGAGAGCCAACC | |
| NQO-1 | Forward | GAACCCAGTCTATGCCCCAC |
| Reverse | GGCGTGCAAGGGATGATTTC | |
| PPARα | Forward | TTTCAAGGGTGCCAGTTTCG |
| Reverse | CCATCTTTATTCATCAGGGAGGC | |
| Srebp-1c | Forward | GGAGCCATGGATTGCACATT |
| Reverse | GGCCCGGGAAGTCACTGT | |
| FAS | Forward | TGCTCCCAGCTGCAGGC |
| Reverse | GCCCGGTAGCTCTGGGTGTA | |
| CPT-1 | Forward | GTGACTGGTGGGAGGAATAC |
| Reverse | GAGCATCTCCATGGCGTAG | |
| Zo-1 | Forward | GCCGCTAAGAGCACAGCAA |
| Reverse | GCCCTCCTTTTAACACATCAGA | |
| Muc2 | Forward | ATGCCCACCTCCTCAAAGAC |
| Reverse | GTAGTTTCCGTTGGAACAGTGAA | |
| Occludin | Forward | GCGGAAGAGGTTGACAGTCC |
| Reverse | AGGAGCGAGACCCCACTAA | |
| 16s V3-V4 | Forward | CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG |
| Reverse | GGACTACHVGGGTATTCTAAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Fan, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Wu, S.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus NKU FL1-8 Isolated from Infant Feces Ameliorates the Alcoholic Liver Damage by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier in C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132139
Liu H, Fan D, Wang J, Wang Y, Li A, Wu S, Zhang B, Liu J, Wang S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus NKU FL1-8 Isolated from Infant Feces Ameliorates the Alcoholic Liver Damage by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier in C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients. 2024; 16(13):2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132139
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haiwei, Dancai Fan, Jin Wang, Yuanyifei Wang, Ang Li, Sihao Wu, Bowei Zhang, Jingmin Liu, and Shuo Wang. 2024. "Lactobacillus rhamnosus NKU FL1-8 Isolated from Infant Feces Ameliorates the Alcoholic Liver Damage by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier in C57BL/6J Mice" Nutrients 16, no. 13: 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132139
APA StyleLiu, H., Fan, D., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Li, A., Wu, S., Zhang, B., Liu, J., & Wang, S. (2024). Lactobacillus rhamnosus NKU FL1-8 Isolated from Infant Feces Ameliorates the Alcoholic Liver Damage by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier in C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients, 16(13), 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132139





