The Importance of Vitamin K and the Combination of Vitamins K and D for Calcium Metabolism and Bone Health: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
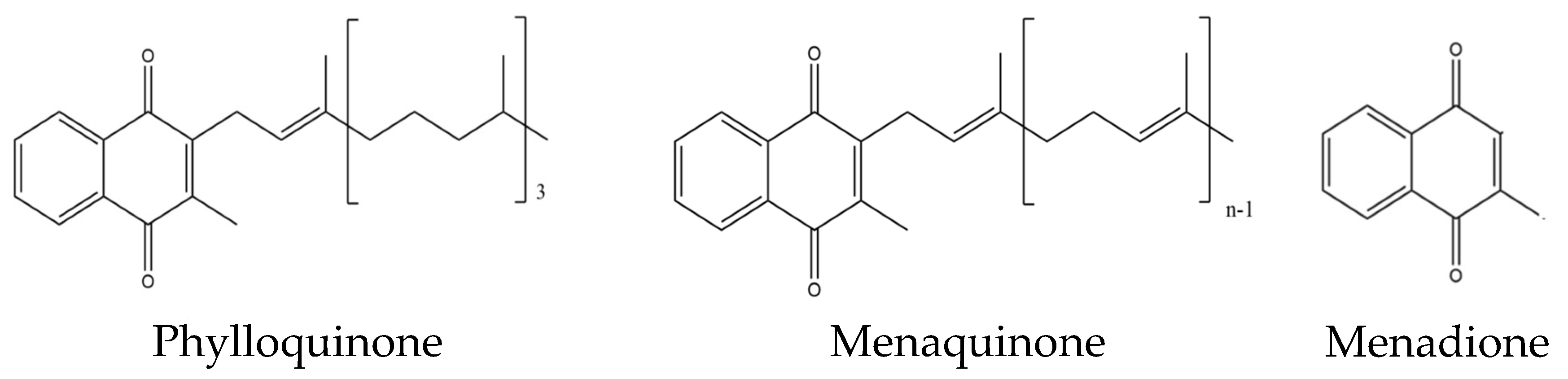
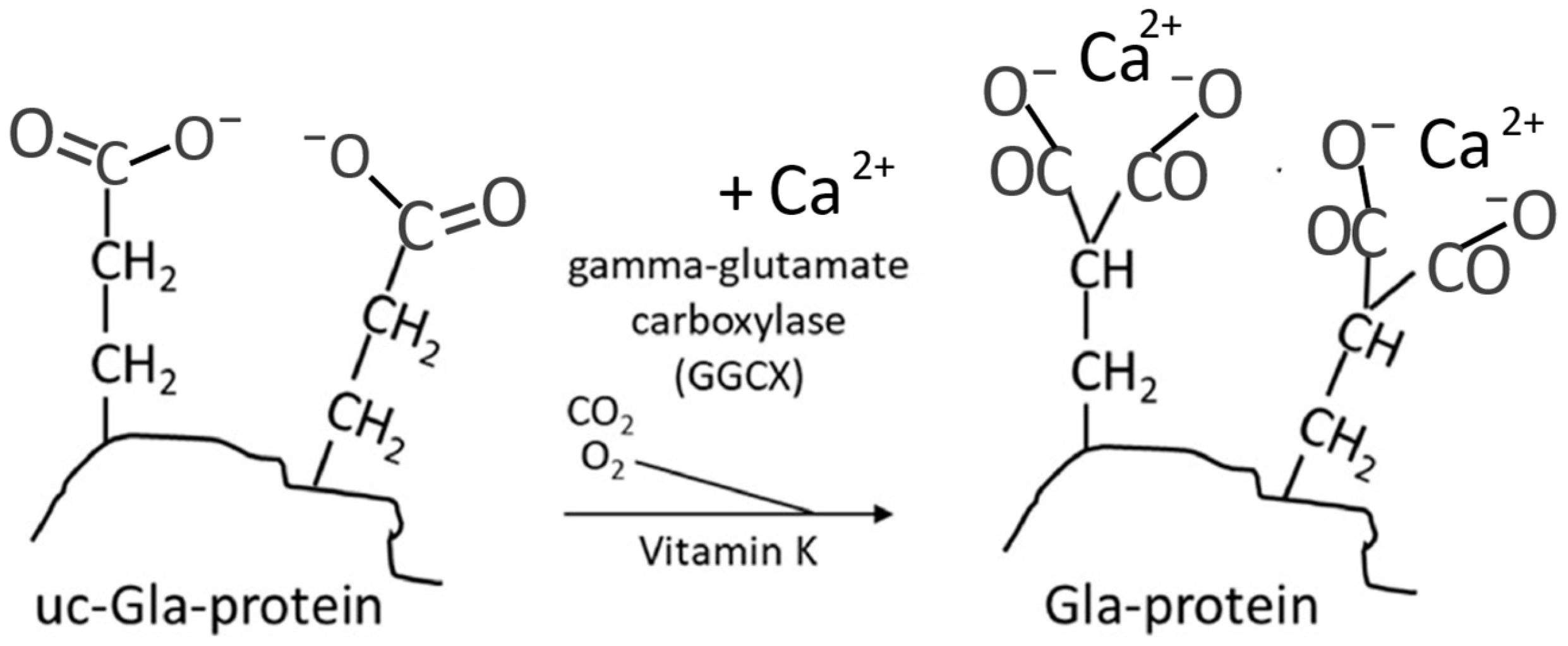
2. Vitamin K as Activator of Osteocalcin and the Bone Health
3. Observational and Interventional and Studies on Vitamin K and Bone
3.1. Observational Studies
3.2. Interventional Studies on Vitamin K and Osteoporosis
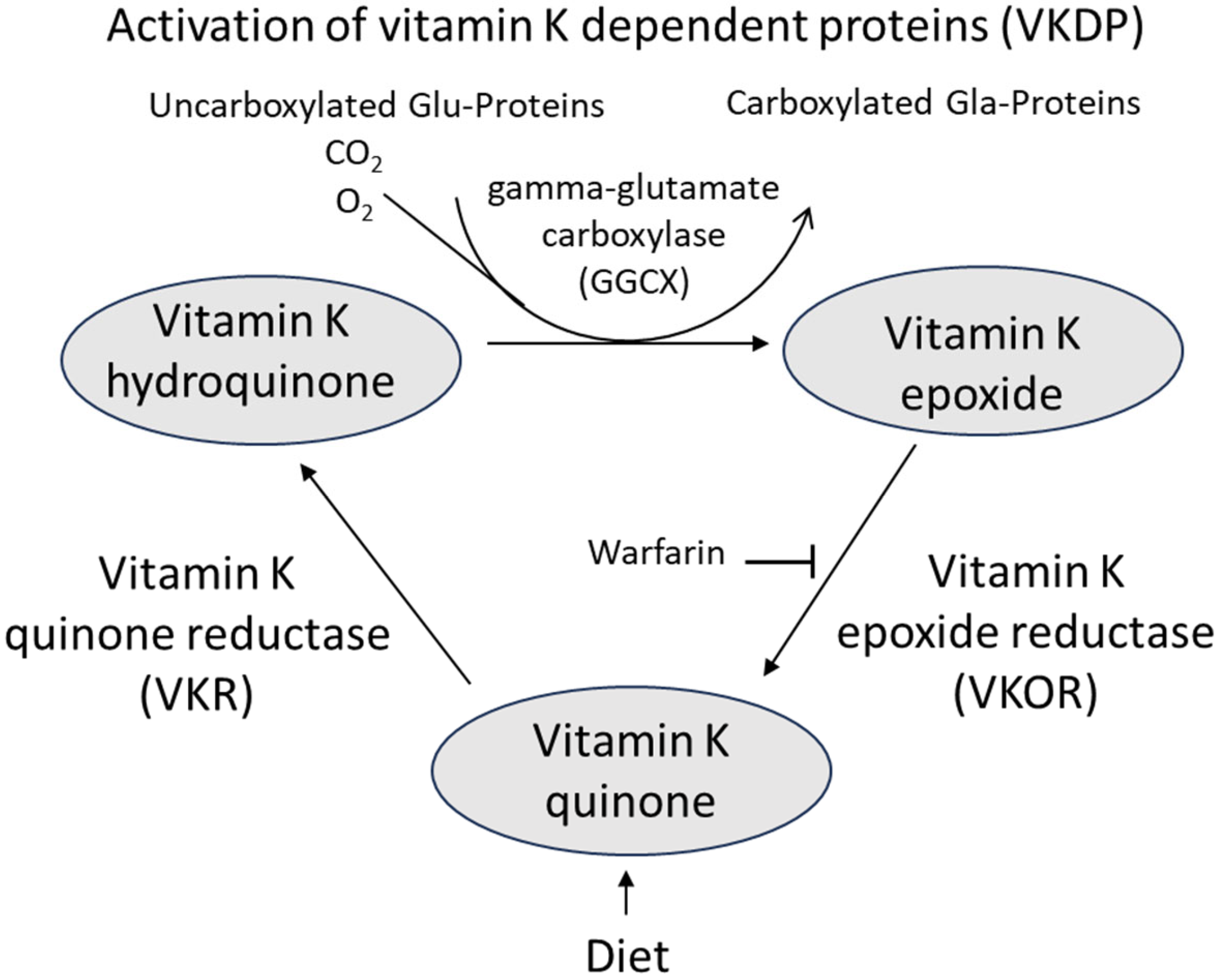
4. Mechanisms of Action of Vitamin K
5. Mechanisms of Action of Vitamin D
6. Clinical Assessment of Pre-Interventional Vitamin Status
7. Vitamin D and Vitamin K Cooperators in Bone Protection?
8. Dietary Sources and Pharmacokinetics of the Vitamins K and D
9. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akkawi, I.; Zmerly, H. Osteoporosis: Current concepts. Joints 2018, 6, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorentzon, M.; Cummings, S.R. Osteoporosis: The evolution of a diagnosis. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 277, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickx, G.; Boudin, E.; Van Hul, W. A look behind the scenes: The risk and pathogenesis of primary osteoporosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangelo, L.; Biamonte, F.; Pepe, J.; Cipriani, C.; Minisola, S. Understanding and managing secondary osteoporosis. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 14, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebeling, P.R.; Nguyen, H.H.; Aleksova, J.; Vincent, A.J.; Wong, P.; Milat, F. Secondary osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 240–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aaseth, J.O.; Alexander, J. Postoperative Osteoporosis in Subjects with Morbid Obesity Undergoing Bariatric Surgery with Gastric Bypass or Sleeve Gastrectomy. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom-Høgestøl, I.K.; Hewitt, S.; Chahal-Kummen, M.; Brunborg, C.; Gulseth, H.L.; Kristinsson, J.A.; Eriksen, E.F.; Mala, T. Bone metabolism, bone mineral density and low-energy fractures 10 years after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Bone 2019, 127, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, N.; Ghasemi, H.; Mohammadi, L.; Rabieenia, E.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dennison, E.; Prieto-Alhambra, D. Osteoporosis epidemiology using international cohorts. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clynes, M.A.; Harvey, N.C.; Curtis, E.M.; Fuggle, N.R.; Dennison, E.M.; Cooper, C. The epidemiology of osteoporosis. Br. Med. Bull. 2020, 133, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, G.; Fassio, A.; Gatti, D.; Viapiana, O.; Benini, C.; Danila, M.I.; Rossini, M. Osteoporosis in 10 years time: A glimpse into the future of osteoporosis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X221083541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouresmaeili, F.; Kamalidehghan, B.; Kamarehei, M.; Goh, Y.M. A comprehensive overview on osteoporosis and its risk factors. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 2029–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Garach, A.; García-Fontana, B.; Muñoz-Torres, M. Nutrients and dietary patterns related to osteoporosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.D.; Tadros, B.J. Bone structure: From cortical to calcium. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 34, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, G.; Dermauw, V.; Bouillon, R. Vitamin D signaling in calcium and bone homeostasis: A delicate balance. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldurthy, V.; Wei, R.; Oz, L.; Dhawan, P.; Jeon, Y.H.; Christakos, S. Vitamin D, calcium homeostasis and aging. Bone Res. 2016, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, V.; Leung, W.; Grey, A.; Reid, I.R.; Bolland, M.J. Calcium intake and bone mineral density: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Brit. Med. J. 2015, 351, h4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brincat, M.; Gambin, J.; Brincat, M.; Calleja-Agius, J. The role of vitamin D in osteoporosis. Maturitas 2015, 80, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemian, E.; Pourali, A.; Sedaghat, F.; Karimi, M.; Basirat, V.; Sajadi Hezaveh, Z.; Holick, M.F. Effect of supplemental vitamin D3 on bone mineral density: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 511–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, M.; Cianciolo, G.; Brandi, M.L.; Ferrari, S.; Nickolas, T.L.; Tripepi, G.; Plebani, M.; Cheung, A. Vitamin K and osteoporosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, K.; Szterk, A. Relationship between structure and biological activity of various vitamin K forms. Foods 2021, 10, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Li, Y. Revisiting the interconnection between lipids and vitamin K metabolism; insights from recent research and potential therapeutic implications: A review. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, V.D.; Mezey, E. Regulation of bone remodeling by vitamin K2. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, M.; Lloyd-Jones, M.; Papaioannou, D. Vitamin K to prevent fractures in older women: Systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. 2009, 13, 1–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, C.; Joyce, R.; van’t Hoofd, C.; Knapen, M.H.J.; Xanthouela, S. Menaquinone content of cheese. Nutrients 2018, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaseth, J.O.; Alehagen, U.; Opstad, T.B.; Alexander, J. Vitamin K and calcium chelation in vascular health. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresz, K. Proper calcium use: Vitamin K2 as a promoter of bone and cardiovascular health. Integr. Med. A Clin. J. 2015, 14, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Zoch, M.L.; Clemens, T.L.; Riddle, R.C. New insights into the biology of osteocalcin. Bone 2016, 82, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinger, I.; Scott, D.; Nicholson, G.C.; Stuart, A.L.; Duque, G.; McCorquodale, T.; Sanders, K.M. Undercarboxylated osteocalcin, muscle strength and indices of bone health in older women. Bone 2014, 64, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.J.; Scott, D.; Ebeling, P.R. Exploring the links between common diseases of ageing—Osteoporosis, sarcopenia and vascular calcification. Clin. Rev. Bone Miner. Metab. 2019, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Fusaro, M.; Ciceri, P.; Gasperoni, L.; Cianciolo, G. The role of vitamin K in vascular calcification. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Feskanich, D.; Weber, P.; Willett, W.C.; Rockett, H.; Booth, S.L.; Colditz, G.A. Vitamin K intake and hip fractures in women: A prospective study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnes, T.E.; Lofthus, C.M.; Meyer, H.E.; Søgaard, A.J.; Tell, G.S.; Apalset, E.M. A combination of low serum concentrations of vitamins K1 and D is associated with increased risk of hip fractures in elderly Norwegians: A NOREPOS study. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 27, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Tsugawa, N.; Kuwabara, A.; Kamao, M.; Tanaka, K.; Okano, T. High prevalence of hypovitaminosis D and K in patients with hip fracture. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 20, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yaegashi, Y.; Onoda, T.; Tanno, K.; Kuribayashi, T.; Sakata, K.; Orimo, H. Association of hip fracture incidence and intake of calcium, magnesium, vitamin D, and vitamin K. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 23, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugawa, N.; Shiraki, M.; Suhara, Y.; Kamao, M.; Ozaki, R.; Tanaka, K. Low plasma phylloquinone concentration is associated with high incidence of vertebral fracture in Japanese women. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2008, 26, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.; Leung, J.; Woo, J. No association between dietary vitamin K intake and fracture risk in chinese community dwelling older men and women: A prospective study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2012, 90, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalset, E.M.; Gjesdal, C.G.; Eide, G.E.; Tell, G.S. Intake of vitamin K1 and K2 and risk of hip fractures: The Hordaland health study. Bone 2011, 49, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beulens, J.W.; Booth, S.L.; van den Heuvel, E.G.; Stoecklin, E.; Baka, A.; Vermeer, C. The role of menaquinones (vitamin K2) in human health. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platonova, K.; Kitamura, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Takachi, R.; Saito, T.; Kabasawa, K.; Takahashi, A.; Kobayashi, R.; Oshiki, R.; Solovev, A.; et al. Dietary calcium and vitamin K are associated with osteoporotic fracture risk in middle-aged and elderly Japanese women, but not men: The Murakami Cohort Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.L.; Ma, Z.J.; He, Y.L.; Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Ruan, B.J.; Wang, Y.X. Efficacy of vitamin K2 in the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasukawa, Y.; Miyakoshi, N.; Ebina, T.; Aizawa, T.; Hongo, M.; Nozaka, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Saito, H.; Chida, S.; Shimada, Y. Effects of risedronate alone or combined with vitamin K2 on serum undercarboxylated osteocalcin and osteocalcin levels in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2014, 32, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirao, M.; Hashimoto, J.; Ando, W.; Ono, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Response of serum carboxylated and undercarboxylated osteocalcin to alendronate monotherapy and combined therapy with vitamin K 2 in postmenopausal women. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2008, 26, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, M.; Gjelstad, I.M.F.; Baksaas, I.; Grande, T.; Aukrust, I.R.; Drevon, C.A.; Tone, G. Bioavailability and chemical/functional aspects of synthetic MK-7 vs. fermentation-derived MK-7 in randomised controlled trials. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2016, 87, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.-B.; Wan, S.-L.; Lu, Y.-J.; Ning, L.; Liu, C.; Fan, S.-W. Does vitamin K2 play a role in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis for postmenopausal women: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos. Int. 2015, 26, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Han, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, D. Efficacy and safety of vitamin K2 for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at a long-term follow-up: Meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2022, 40, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, M.; Petsophonsakul, P.; Akbulut, A.C.; Pavlic, A.; Bohan, F.; Anderson, E.; Schurgers, L. Vitamin K: Double bonds beyond coagulation insights into differences between vitamin K1 and K2 in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurgers, L.J.; Uitto, J.; Reutelingsperger, C.P. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of matrix Gla-protein: A crucial switch to control ectopic mineralization. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oryan, A.; Sahvieh, S. Effects of bisphosphonates on osteoporosis: Focus on zoledronate. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, N.; Nie, F.; Yang, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Vitamin K2 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 124, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, C.M.; Vega, O.A.; Osorio, M.M.; Tapia, J.C.; Antonelli, M.; Stein, G.S.; Galindo, M.A. The cancer-related transcription factor Runx2 modulates cell proliferation in human osteosarcoma cell lines. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, A.C.; Wasilewski, G.B.; Rapp, N.; Forin, F.; Singer, H.; Czogalla-Nitsche, K.J.; Schurgers, L.J. Menaquinone-7 supplementation improves osteogenesis in pluripotent stem cell derived mesenchymal stem cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 618760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Na, W.; Sohn, C. Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and K2 (menaquinone-4) supplementation improves bone formation in a high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2013, 53, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wu, W.J.; Kim, M.S.; Ahn, B.Y. The inhibitory effect of vitamin K on RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, D.A.; Adachi, J.D.; Bell, A.; Brown, V. Denosumab: Mechanism of action and clinical outcomes. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2012, 66, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, N.; Meinitzer, A.; Fritz-Petrin, E.; Enko, D.; Herrmann, M. Role of vitamin K in bone and muscle metabolism. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2023, 112, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabb, M.M.; Sun, A.; Zhou, C.; Grun, F.; Errandi, J.; Romero, K.; Blumberg, B. Vitamin K2 regulation of bone homeostasis is mediated by the steroid and xenobiotic receptor SXR. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43919–43927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, Y.; Suhara, Y. New Aspects of Vitamin K Research with Synthetic Ligands: Transcriptional Activity via SXR and Neural Differentiation Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Azuma, K.; Casey, S.C.; Ito, M.; Urano, T.; Horie, K.; Ouchi, Y.; Kirchner, S.; Blumberg, B.; Inoue, S. Pregnane X receptor knockout mice display osteopenia with reduced bone formation and enhanced bone resorption. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 207, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.H.; Jang, H.N.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, C.S. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on risk of fractures and falls according to dosage and interval: A meta-analysis. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 37, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, P.; Derwin, R.; George, S. What is the impact of daily oral supplementation of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) plus calcium on the incidence of hip fracture in older people? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Older People Nurs. 2023, 18, e12492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi Ghahfarrokhi, S.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A.; Sherwin, C.M.; Heidari-Soureshjani, S. Relationship between serum vitamin D and hip fracture in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2022, 40, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Cong, Q.; Xia, X.; Leong, W.F.; Yeh, J.; Miao, D.; Li, B. Pharmacologic calcitriol inhibits osteoclast lineage commitment via the BMP-Smad1 and IκB-NF-κB pathways. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 1406–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goltzman, D. Functions of vitamin D in bone. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisse, T.S.; Chun, R.F.; Rieger, S.; Adams, J.S.; Hewison, M. Vitamin D activation of functionally distinct regulatory miRNAs in primary human osteoblasts. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Ochiai-Shino, H.; Onodera, S.; Saito, A.; Shibahara, T.; Azuma, T. Promoting effect of 1, 25 (OH) 2 vitamin D3 in osteogenic differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells to osteocyte-like cells. Open Biol. 2015, 5, 140201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borojević, A.; Jauković, A.; Kukolj, T.; Mojsilović, S.; Obradović, H.; Trivanović, D.; Bugarski, D. Vitamin D3 stimulates proliferation capacity, expression of pluripotency markers, and osteogenesis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal/stem cells, partly through sirt1 signaling. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.H. Vitamin D activity and metabolism in bone. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2017, 15, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, A.L.; MacDonald, P.N. Vitamin D: More than a “bone-a-fide” hormone. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.G.; Hanrath, M.A.; Morris, H.A.; Atkins, G.J.; Anderson, P.H. The local production of 1,25(OH)2D3 promotes osteoblast and osteocyte maturation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144 Pt A, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbergsen, A.C.; Watne, L.O.; Wyller, T.B.; Frihagen, F.; Strømsøe, K.; Bøhmer, T.; Mowe, M. Vitamin K1 and 25 (OH) D are independently and synergistically associated with a risk for hip fracture in an elderly population: A case control study. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, X.; Li, K.; Deng, Q.; Li, D. The combination effect of vitamin K and vitamin D on human bone quality: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3280–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rønn, S.H.; Harsløf, T.; Oei, L.; Pedersen, S.B.; Langdahl, B.L. The effect of vitamin MK-7 on bone mineral density and microarchitecture in postmenopausal women with osteopenia, a 3-year randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Osteoporos. Int. 2021, 32, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.E.; Dulnoan, D.; Voong, K.; Ayis, S.; Mangelis, A.; Gorska, R.; Harrington, D.J.; Tang, J.C.Y.; Fraser, W.D.; Hampson, G. The additive effect of vitamin K supplementation and bisphosphonate on fracture risk in post-menopausal osteoporosis: A randomised placebo- controlled trial. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, I.E.; Øyen, J.; Kjellevold, M.; Frøyland, L.; Gjesdal, C.G.; Almås, B.; Rosenlund, G.; Lie, Ø. Reduced bone resorption by intake of dietary vitamin D and K from tailor-made Atlantic salmon: A randomized intervention trial. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 69200–69215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Ballegooijen, A.J.; Pilz, S.; Tomaschitz, A.; Grübler, M.R.; Verheyen, N. The synergistic interplay between vitamins D and K for bone and cardiovascular health: A narrative review. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 7454376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Morsy, A.S.; Beshir, S.R.; Farrag, K.A.E.R.; Mohamed, M.S.; Hamam, G.G. Comparative study on the effect of vitamin K versus combined Ca and vitamin D administration on the prevention of experimentally-induced osteoporosis in adult male albino rats. Egypt. J. Histol. 2011, 34, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N.; Kusano, E.; Takahashi, H.; Ando, Y.; Yano, K.; Tsuda, E.; Asano, Y. Vitamin K2 inhibits glucocorticoid-induced bone loss partly by preventing the reduction of osteoprotegerin (OPG). J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2005, 23, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurgers, L.J.; Vermeer, C. Determination of phylloquinone and menaquinones in food. Hemostasis 2000, 30, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simes, D.C.; Viegas, C.S.; Araújo, N.; Marreiros, C. Vitamin K as a diet supplement with impact in human health: Current evidence in age-related diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.C.; Furlanetto, T.W. Intestinal absorption of vitamin D: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantle, D. Nutritional supplementation for vitamin B12 and vitamin K2 deficiency following ileostomy or colostomy formation. Gastrointest. Nurs. 2020, 18 (Suppl. S4), S12–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Dietary reference values for vitamin K. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 4780. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneki, M.; Stephen, J.; Hosoi, T.; Fujiwara, S. Japanese fermented soybean food as the major determinant of the large geographic difference in circulating levels of vitamin K2: Possible implications for Hip-Fracture risk. Nutrition 2001, 17, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, M.J.; Okano, T. Key Pathways and regulators of vitamin K function and intermediary metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leutner, M.; Matzhold, C.; Bellach, L. Diagnosis of osteoporosis in statin-treated patients is dose-dependent. Ann. Rheum. Dis. Dec. 2019, 78, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.C. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors and the skeleton: A comprehensive review. Osteoporos. Int. 2003, 14, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, T. Risk of osteoporosis in patients treated with direct oral anticoagulants vs. warfarin: An analysis of observational studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1212570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Inaba, N.; Yamashita, T. MK-7 and its effects on bone quality and strength. Nutrients 2020, 12, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. A millenium perspective on Vitamin D. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 88, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aaseth, J.O.; Finnes, T.E.; Askim, M.; Alexander, J. The Importance of Vitamin K and the Combination of Vitamins K and D for Calcium Metabolism and Bone Health: A Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152420
Aaseth JO, Finnes TE, Askim M, Alexander J. The Importance of Vitamin K and the Combination of Vitamins K and D for Calcium Metabolism and Bone Health: A Review. Nutrients. 2024; 16(15):2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152420
Chicago/Turabian StyleAaseth, Jan O., Trine Elisabeth Finnes, Merete Askim, and Jan Alexander. 2024. "The Importance of Vitamin K and the Combination of Vitamins K and D for Calcium Metabolism and Bone Health: A Review" Nutrients 16, no. 15: 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152420
APA StyleAaseth, J. O., Finnes, T. E., Askim, M., & Alexander, J. (2024). The Importance of Vitamin K and the Combination of Vitamins K and D for Calcium Metabolism and Bone Health: A Review. Nutrients, 16(15), 2420. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152420






