Pollen-Food Allergy Syndrome: From Food Avoidance to Deciphering the Potential Cross-Reactivity between Pru p 3 and Ole e 7
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. sIgE nsLTP Profile
2.3. Proteins, Reagents and Antibodies
2.4. Basophil Activation Test
2.5. Epitope Mapping
2.5.1. Enzymatic Digestions
2.5.2. Immunocapturing of Specific Epitope Peptide Fragments
- -
- MON_OLE with 6 μg of Ole e 7 peptides
- -
- MON_PRU with 6 μg of Ole e 7 peptides
- -
- BI with 6 μg of Ole e 7 peptides
- -
- MON_OLE with 6 μg of Pru p 3 peptides
- -
- MON_PRU with 6 μg of Pru p 3 peptides
- -
- BI with 6 μg of Pru p 3 peptides.
- Following three washes with PBS, the immune-specific captured peptides were eluted twice with 0.2% trifluoroacetic acid (100 µL, 15 min, RT). Serum from a non-allergic individual was used as a negative control.
2.5.3. LC-MS Analysis (Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry)
Sample Preparation
Liquid Chromatography
Mass Spectrometry
Data Analysis
2.6. Protein and Peptide Sequence Alignment
2.7. Automated Search for Homologous Sequences
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
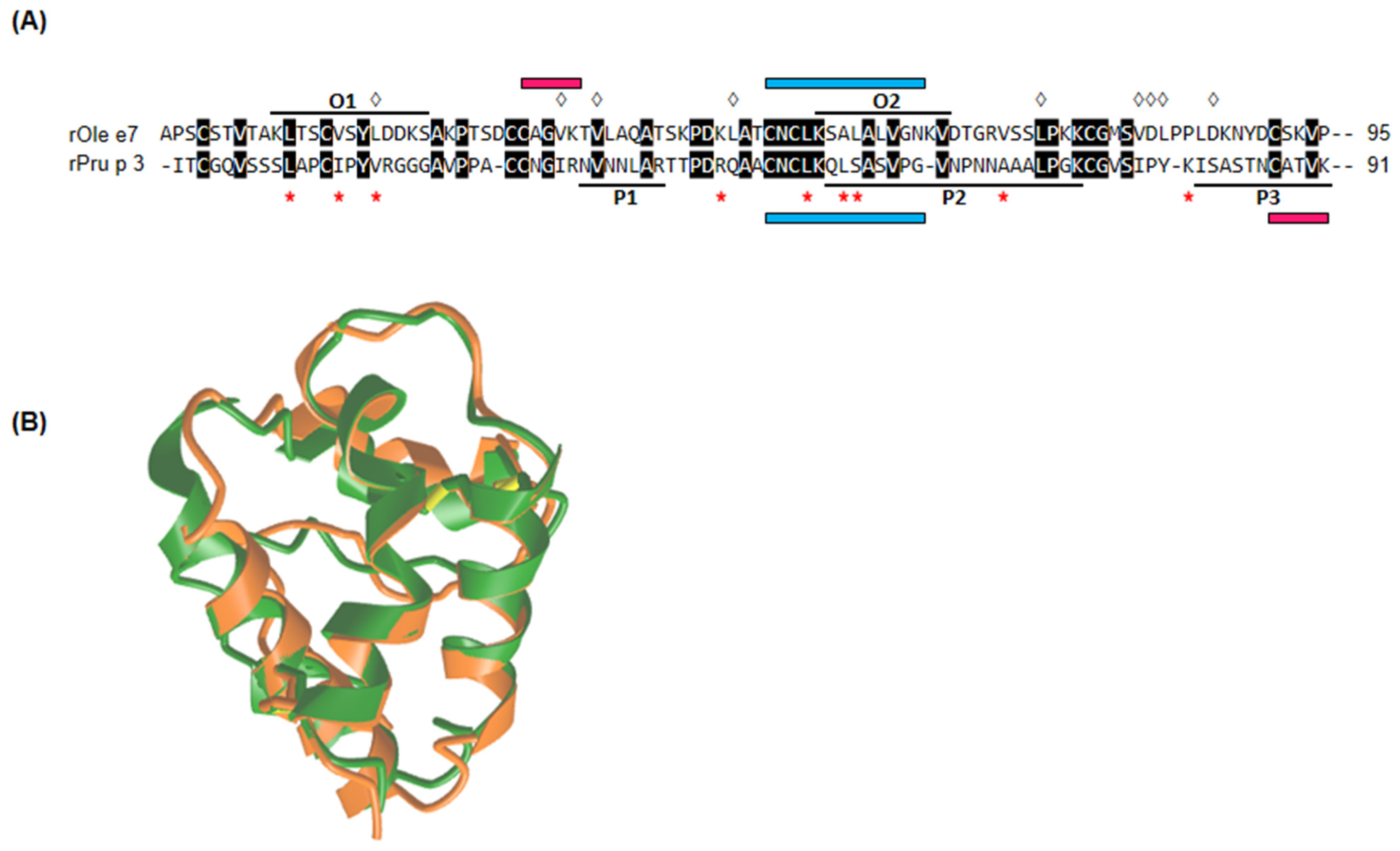
3.2. rOle e 7 and rPru p 3 Epitope Mapping
- O1, residues 10–22: KLTSCVSYLDDKS
- O2, residues 54–64: KSALALVGNKV
- P1, residues 33–39: NVNNLAR
- P2, residues 53–72: QLSASVPGVNPNNAAALPGK
- P3, residues 81–91: ISASTNCATVK
3.3. Sequence and Structural Alignment Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manti, S.; Pecora, G.; Patanè, F.; Giallongo, A.; Parisi, G.F.; Papale, M.; Licari, A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Leonardi, S. Monoclonal Antibodies in Treating Food Allergy: A New Therapeutic Horizon. Nutrients 2021, 5, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomares, F.; Gomez, F.; Bogas, G.; Campo, P.; Perkins, J.R.; Diaz-Perales, A.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Prieto, A.; Barber, D.; Torres, M.J.; et al. Immunological Changes Induced in Peach Allergy Patients with Systemic Reactions by Pru p 3 Sublingual Immunotherapy. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, L.; Muraro, A.; Giovannini, M.; Barni, S.; Liccioli, G.; Paladini, E.; Sarti, L.; Pessina, B.; Skypala, I.; Novembre, E.; et al. Hidden and Rare Food Allergens in Pediatric Age. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębińska, A.; Sozańska, B. Epicutaneous Sensitisation and Food Allergy: Preventive Strategies Targeting Skin Barrier Repair-Facts and Challenges. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poredoš, T.; Vesel Tajnšek, T.; Koren Jeverica, A.; Zajc Avramovič, M.; Markelj, G.; Emeršič, N.; Avčin, T. Comprehensive Care and Education Can Improve Nutritional and Growth Outcomes in Children with Persistent Cow’s Milk, Egg, or Peanut Allergies: A Five-Year Follow-Up Study of Nutritional Status. Nutrients 2023, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skypala, I.J.; Asero, R.; Barber, D.; Cecchi, L.; Diaz Perales, A.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Pastorello, E.A.; Swoboda, I.; Bartra, J.; Ebo, D.G.; et al. Clinical Immunology (EAACI) Task Force. Non-specific Lipid Transfer Protein Allergy across Europe. Nonspecific lipid-transfer proteins: Allergen structure and function, cross-reactivity, sensitisation, and epidemiology. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2021, 11, e12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L.; Bonini, S.; Nunes, C.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Behrendt, H.; Liccardi, G.; Popov, T.; van Cauwenberge, P. Allergenic pollen and pollen allergy in Europe. Allergy 2007, 62, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, M.; Rodríguez, R.; Batanero, E. The spectrum of olive pollen allergens. From structures to diagnosis and treatment. Methods 2014, 66, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.; de la Torre, F.; Feo, F.; Florido, F.; Guardia, P.; Moreno, C.; Quiralte, J.; Lombardero, M.; Villalba, M.; Salcedo, G.; et al. Understanding patient sensitisation profiles in complex pollen areas: A molecular epidemiological study. Allergy 2008, 63, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liccardi, G.; D’Amato, M.; D’Amato, G. Oleaceae pollinosis: A review. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1996, 111, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejera, M.L.; Villalba, M.; Batanero, E.; Rodríguez, R. Identification, isolation, and characterization of Ole e 7, a new allergen of olive tree pollen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florido Lopez, J.F.; Quiralte Enriquez, J.; De Saavedra Alías, J.M.A.; De San Pedro, B.S.; Casañez, E.M. An allergen from Olea europaea pollen (Ole e 7) is associated with plant-derived food anaphylaxis. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 57, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, E.; Abeni, D.; Pomponi, D.; Paganelli, R.; Locanto, M.; Giani, M.; Cecchi, L.; Asero, R. Ole e 1, Ole e 7, and Ole e 9: Identifying distinct clinical subsets of olive tree-allergic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeo-Santos, C.; Navas, A.; Benedé, S.; Ruíz-León, B.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Voge, L.L.; Moreno-Aguilar, C.; Jurado, A.; Villalba, M.; Barderas, R. New insights into the sensitisation to nonspecific lipid transfer proteins from pollen and food: New role of allergen Ole e 7. Allergy 2020, 75, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Hauser, M.; Mari, A.; Ferreira, F.; Gadermaier, G. The role of lipid transfer proteins in allergic diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, J.P.; Barre, A.; Culerrier, R.; Granier, C.; Didier, A.; Rougé, P. Lipid transfer proteins from Rosaceae fruits share consensus epitopes responsible for their IgE-binding cross-reactivity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asero, R.; Brusca, I.; Cecchi, L.; Pignatti, P.; Pravettoni, V.; Scala, E.; Uasuf, C.G.; Villalta, D. Why lipid transfer protein allergy is not a pollen-food syndrome: Novel data and literature review. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 54, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Perales, A.; Lombardero, M.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; García-Selles, F.J.; Pernas, M.; Fernández-Rivas, M.; Barber, D.; Salcedo, G. Lipid-transfer proteins as potential plant panallergens: Cross-reactivity among proteins of Artemisia pollen, Castanea nut and Rosaceae fruits, with different IgE-binding capacities. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, I.; Miguel-Moncin, M.S.; Abel, T.; Foetisch, K.; Hartz, C.; Fortunato, D.; Cistero-Bahima, A.; Vieths, S.; Scheurer, S. Identification of a plane pollen lipid transfer protein (Pla a 3) and its immunological relation to the peach lipid-transfer protein, Pru p 3. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacín, A.; Gómez-Casado, C.; Rivas, L.A.; Aguirre, J.; Tordesillas, L.; Bartra, J.; Blanco, C.; Carrillo, T.; Cuesta-Herranz, J.; de Frutos, C.; et al. Graph based study of allergen crossreactivity of plant lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) using microarray in a multicenter study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, G.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; Barber, D.; Díaz-Perales, A. Plant nonspecific lipid transfer proteins: An interface between plant defence and human allergy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1771, 781. [Google Scholar]
- Asero, R.; Mistrello, G.; Roncarolo, D.; Amato, S.; van Ree, R. A case of allergy to beer showing cross-reactivity between lipid transfer proteins. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001, 87, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorello, E.A.; Ortolani, C.; Farioli, L.; Pravettoni, V.; Ispano, M.; Borga, A.; Bengtsson, A.; Incorvaia, C.; Berti, C.; Zanussi, C. Allergenic cross-reactivity among peach, apricot, plum, and cherry in patients with oral allergy syndrome: An in vivo and in vitro study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asero, R.; Mistrello, G.; Roncarolo, D.; Amato, S.; Caldironi, G.; Barocci, F.; van Ree, R. Immunological cross-reactivity between lipid transfer proteins from botanically unrelated plant-derived foods: A clinical study. Allergy 2002, 57, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardero, M.; García-Sellés, F.J.; Polo, F.; Jimeno, L.; Chamorro, M.J.; García-Casado, G.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Salcedo, G.; Barber, D. Prevalence of sensitisation to Artemisia allergens Art v 1, Art v 3 and Art v 60 kDa. Cross-reactivity among Art v 3 and other relevant lipid-transfer protein allergens. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangorsch, A.; Larsson, H.; Messmer, M.; García-Moral, A.; Lauer, I.; Wolfheimer, S.; Schülke, S.; Bartra, J.; Vieths, S.; Lidholm, J.; et al. Molecular cloning of plane pollen allergen Pla a 3 and its utility as diagnostic marker for peach associated plane pollen allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-López, J.; Tordesillas, L.; Pascal, M.; Muñoz-Cano, R.; Garrido, M.; Rueda, M.; Vilella, R.; Valero, A.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Picado, C.; et al. Role of Art v 3 in pollinosis of patients allergic to Pru p 3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Rivas, M.; González-Mancebo, E.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Benito, C.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; Salcedo, G.; Alonso, M.D.; Rosado, A.; Tejedor, M.A.; Vila, C.; et al. Clinically relevant peach allergy is related to peach lipid transfer protein, Pru p 3, in the Spanish population. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lleonart, R.; Cistero, A.; Carreira, J.; Batista, A.; Del Prado, J.M. Food allergy: Identification of the major IgE-binding component of peach (Prunus persica). Ann. Allergy 1992, 69, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Gamboa, P.M.; Cáceres, O.; Antepara, I.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; Ahrazem, O.; Salcedo, G.; Barber, D.; Lombardero, M.; Sanz, M.L. Two different profiles of peach allergy in the north of Spain. Allergy 2007, 62, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeo-Santos, C.; Mas, S.; Benedé, S.; López-Lucendo, M.; Quiralte, J.; Blanca, M.; Mayorga, C.; Villalba, M.; Barderas, R. A recombinant isoform of the Ole e 7 olive pollen allergen assembled by de novo mass spectrometry retains the allergenic ability of the natural allergen. J. Proteomics 2018, 187, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, M.D.; Smith, A.M.; Vailes, L.D.; Karla, L.; Dhanara, J.V.; Pomés, A. New millennium: The conquest of allergy Recombinant allergens for diagnosis and therapy of allergic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, R.; Villalba, M.; Batanero, E.; Palomares, O.; Quiralte, J.; Salamanca, G.; Sirvent, S.; Castro, L.; Prado, N. Olive Pollen Recombinant Allergens: Value in Diagnosis and Immunotherapy Olive Pollen Allergens: A Brief Overview. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 17, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.; Hoffman, D.R. Expression Systems for Production of Recombinant Allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 128, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Perales, A.; Sanz, M.L.; García-Casado, G.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; García-Selles, F.J.; Lombardero, M.; Polo, F.; Gamboa, P.M.; Barber, D.; Salcedo, G. Recombinant Pru p 3 and natural Pru p 3, a major peach allergen, show equivalent immunologic reactivity: A new tool for the diagnosis of fruit allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, A.; Kringelum, J.V.; Hansen, C.S.; Bøgh, K.L.; Sullivan, E.; Patel, J.; Rigby, N.M.; Eiwegger, T.; Szépfalusi, Z.; de Masi, F.; et al. High-throughput sequencing enhanced phage display enables the identification of patient-specific epitope motifs in serum. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sathe, S.K. Food Allergen Epitope Mapping. J. Agric. Food Chem. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; He, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Advances in epitope mapping technologies for food protein allergens: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Casado, G.; Pacios, L.F.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; Lombardero, M.; García-Selles, F.J.; Polo, F.; Barber, D.; Salcedo, G. Identification of IgE-binding epitopes of the major peach allergen Pru p 3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacios, L.F.; Tordesillas, L.; Cuesta-Herranz, J.; Compes, E.; Sánchez-Monge, R.; Palacín, A.; Salcedo, G.; Díaz-Perales, A. Mimotope mapping as a complementary strategy to define allergen IgE-epitopes: Peach Pru p 3 allergen as a model. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreborg, S.; Frew, A. The European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology. Allergen standardization and skin tests. Allergy 1993, 48, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Perales, A.; Garcia Casado, G.; Sanchez Monge, R.; Garcia Selles, F.J.; Barber, D.; Salcedo, G. cDNA cloning and heterologous expression of the major allergens from peach and apple belonging to the lipid-transfer protein family. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Negi, S.S.; Liao, S.; Gao, V.; Braun, W.; Dreskin, S.C. Conformational IgE epitopes of peanut allergens Ara h 2 and Ara h 6. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evosep Clinical Proteomics. Available online: https://www.evosep.com/ (accessed on 12 September 2021).
- Bache, N.; Geyer, P.E.; Bekker-Jensen, D.B.; Hoerning, O.; Falkenby, L.; Treit, P.V.; Doll, S.; Paron, I.; Müller, J.B.; Meier, F.; et al. A novel LC system embeds analytes in pre-formed gradients for rapid, ultra-robust proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2018, 17, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, F.; Brunner, A.D.; Frank, M.; Ha, A.; Bludau, I.; Voytik, E.; Kaspar-Schoenefeld, S.; Lubeck, M.; Raether, O.; Bache, N.; et al. diaPASEF: Parallel accumulation–serial fragmentation combined with data-independent acquisition. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Teo, G.C.; Polasky, D.A.; Yu, F.; Nesvizhskii, A.I. Fast Deisotoping Algorithm and Its Implementation in the MSFragger Search Engine. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Veiga Leprevost, F.; Haynes, S.E.; Avtonomov, D.M.; Chang, H.Y.; Shanmugam, A.K.; Mellacheruvu, D.; Kong, A.T.; Nesvizhskii, A.I. Philosopher: A versatile toolkit for shotgun proteomics data analysis. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. Empirical statistical model to estimate the accuracy of peptide identifications made by MS/MS and database search. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Keller, A.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. A statistical model for identifying proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvizhskii, A.I. A survey of computational methods and error rate estimation procedures for peptide and protein identification in shotgun proteomics. J. Proteomics 2010, 73, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitski, M.M.; Wilhelm, M.; Hahne, H.; Kuster, B.; Bantscheff, M. A scalable approach for protein false discovery rate estimation in large proteomic data sets. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2015, 14, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bern, M.W.; Kil, Y.J. Two-dimensional target decoy strategy for shotgun proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022 F abio. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expasy SIM Alignment Tool. Available online: https://web.expasy.org/sim/ (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Rial, M.J.; Sastre, J. Food Allergies Caused by Allergenic Lipid Transfer Proteins: What Is behind the Geographic Restriction? Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization and Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. Foods derived from modern biotechnology. In Codex Alimentarius Guidelines, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2009; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, R.A.; Song, P.; Kumpatla, S. Percent amino-acid identity thresholds are not necessarily conservative for predicting allergenic cross-reactivity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 81, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Klein, Z.; Cuevas-Zuviria, B.; Wangorsch, A.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G.; Pazos-Castro, D.; Oeo-Santos, C.; Romero-Sahagun, A.; Pacios, L.F.; Tome-Amat, J.; Scheurer, S.; et al. The key to the allergenicity of lipid transfer protein (LTP) ligands: A structural characterization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeo-Santos, C.; López-Rodríguez, J.C.; García-Mouton, C.; San Segundo-Acosta, P.; Jurado, A.; Moreno-Aguilar, C.; García-Álvarez, B.; Pérez-Gil, J.; Villalba, M.; Barderas, R.; et al. Biophysical and biological impact on the structure and IgE-binding of the interaction of the olive pollen allergen Ole e 7 with lipids. Biochim.Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutert, M.; Barente, A.S.; Fukuda, N.K.; Rodriguez-Mias, R.A.; Villén, J. The regulatory landscape of the yeast phosphoproteome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Klein, Z.; Pazos-Castro, D.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G.; Garrido-Arandia, M.; Diaz-Perales, A.; Tome-Amat, J. Lipid Ligands and Allergenic LTPs: Redefining the Paradigm of the Protein-Centered Vision in Allergy. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 864652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordesillas, L.; Sirvent, S.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Villalba, M.; Cuesta-Herranz, J.; Rodríguez, R.; Salcedo, G. Plant lipid transfer protein allergens: No cross-reactivity between those from foods and olive and Parietaria pollen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 156, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| sIgE 1 | BAT 2 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ole e 1 3 | Ole e 7 4 | Pru p 3 5 | Mal d 3 6 | Art v 3 7 | Tri a 14 8 | Jug r 3 9 | Cor a 8 10 | Ara h 9 11 | Par j 2 12 | rOle e 7 (10 µg/mL) | rPru p 3 (10 µg/mL) | |
| 1. MON_OLE 13 | 0.02 | 149 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 60.6 | 18.6 |
| 2. MON_OLE | 1.26 | 69.7 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 84.7 | 78.8 |
| 3. MON_OLE | 14.3 | 192 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 10.7 | 14.1 |
| 4. MON_PRU 14 | NA 15 | 0.1 | 6.32 | 6.13 | 1.48 | 1.75 | 1.81 | 5.35 | 6.07 | 0.03 | 5.3 | 22.7 |
| 5. MON_PRU | NA | 0.33 | 82.8 | 59.3 | 47 | 6.68 | 50.9 | 29.1 | 30.1 | 0.28 | 3.5 | 69.0 |
| 6. MON_PRU | NA | 0.08 | 10.8 | 11.2 | 0.63 | 0.28 | 5.22 | 3.79 | 5.75 | 0.02 | 4.8 | 46.6 |
| 7. BI 16 | 0 | 39.2 | 29.5 | 26.1 | 17.5 | 17.7 | 19.3 | 6.43 | 26.4 | 0.01 | 36.5 | 48.1 |
| 8. BI | 98.1 | 392 | 202 | 156 | 93.2 | 42.2 | 69.1 | 52 | 135 | 0.12 | 17.5 | 39.6 |
| 9. BI | 10.1 | 30.7 | 23.3 | 20.9 | 31.4 | 6.42 | 18.8 | 7.77 | 20.4 | 0.1 | 69.7 | 49.8 |
| Bound Ole e 7 Epitopes 1 | Bound Pru p 3 Epitopes 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| MON_OLE 3 serum pool | O1: KLTSCVSYLDDKS O2: KSALALVGNKV | P3: ISASTNCATVK |
| MON_PRU 4 serum pool | O2: KSALALVGNKV | P3: ISASTNCATVK |
| BI 5 serum pool | O2: KSALALVGNKV | P1: NVNNLAR P2: QLSASVPGVNPNNAAALPGK P3: ISASTNCATVK |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez, P.; Aguado, R.; Molina, J.; Trujillo-Aguilera, A.; Villalba, M.; Díaz-Perales, A.; Oeo-Santos, C.; Chicano, E.; Blanco, N.; Navas, A.; et al. Pollen-Food Allergy Syndrome: From Food Avoidance to Deciphering the Potential Cross-Reactivity between Pru p 3 and Ole e 7. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172869
Álvarez P, Aguado R, Molina J, Trujillo-Aguilera A, Villalba M, Díaz-Perales A, Oeo-Santos C, Chicano E, Blanco N, Navas A, et al. Pollen-Food Allergy Syndrome: From Food Avoidance to Deciphering the Potential Cross-Reactivity between Pru p 3 and Ole e 7. Nutrients. 2024; 16(17):2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172869
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez, Paula, Rocío Aguado, Juan Molina, Antonio Trujillo-Aguilera, Mayte Villalba, Araceli Díaz-Perales, Carmen Oeo-Santos, Eduardo Chicano, Nadine Blanco, Ana Navas, and et al. 2024. "Pollen-Food Allergy Syndrome: From Food Avoidance to Deciphering the Potential Cross-Reactivity between Pru p 3 and Ole e 7" Nutrients 16, no. 17: 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172869
APA StyleÁlvarez, P., Aguado, R., Molina, J., Trujillo-Aguilera, A., Villalba, M., Díaz-Perales, A., Oeo-Santos, C., Chicano, E., Blanco, N., Navas, A., Ruiz-León, B., & Jurado, A. (2024). Pollen-Food Allergy Syndrome: From Food Avoidance to Deciphering the Potential Cross-Reactivity between Pru p 3 and Ole e 7. Nutrients, 16(17), 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172869









