Abstract
Time-restricted eating (TRE) is a circadian rhythm-based intermittent fasting intervention that has been used to treat obesity. However, the efficacy and safety of TRE for fat loss have not been comprehensively examined and the influences of TRE characteristics on such effects are unknown. This systematic review and meta-analysis comprehensively characterized the efficacy and safety of TRE for fat loss in adults with overweight and obese, and it explored the influence of TRE characteristics on this effect. Methods: A search strategy based on the PICOS principle was used to find relevant publications in seven databases. The outcomes were body composition, anthropometric indicators, and blood lipid metrics. Twenty publications (20 studies) with 1288 participants, covering the period from 2020 to 2024, were included. Results: Compared to the control group, TRE safely and significantly reduced body fat percentage, fat mass, lean mass, body mass, BMI, and waist circumference (MDpooled = −2.14 cm, 95% CI = −2.88~−1.40, p < 0.001), and increased low-density lipoprotein (LDL) (MDpooled = 2.70, 95% CI = 0.17~5.22, p = 0.037), but it did not alter the total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein, and triglycerides (MDpooled = −1.09~1.20 mg/dL, 95% CI −4.31~5.47, p > 0.05). Subgroup analyses showed that TRE only or TRE-caloric restriction with an eating window of 6 to 8 h may be appropriate for losing body fat and overall weight. Conclusions: This work provides moderate to high evidence that TRE is a promising dietary strategy for fat loss. Although it may potentially reduce lean mass and increase LDL, these effects do not pose significant safety concerns. This trial was registered with PROSPERO as CRD42023406329.
1. Introduction
Obesity is a major risk factor for multiple diseases and threatens well-being, life expectancy, and the quality of life in humans [1,2,3]. Eating behaviors, which can alter energy intake, are essential in the etiology of obesity [4,5]. Changing eating behaviors in order to balance energy intake and expenditure is thus one common strategy to prevent or treat obesity [1,6].
The timing of food consumption appears to play a critical role in metabolic health [7]. In recent years, “intermittent fasting,” characterized by shifting mealtimes regardless of meal content, has received much attention for treating obesity. Time-restricted eating (TRE) is one type of intermittent fasting with the goal of improving the regulation of circadian rhythms generated by the endogenous biological clock [8]. Studies have shown that limiting daily food consumption to a 4–12 h period, during which the body is most receptive to food, may improve metabolic health [7,9]. Moreover, TRE is particularly intriguing and well-accepted by many individuals because it is the only dietary intervention that does not directly emphasize caloric restriction or require a prescribed number of fasting days [7].
Multiple studies have examined the benefits of TRE for weight loss [10,11]. However, reports of its efficacy and safety (i.e., adverse events and side effects) are inconsistent. For example, Zhang et al. [12] observed that TRE reduced adiposity but increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) [12]. Lowe et al. showed in another study that TRE did not reduce body fat and instead resulted in a decrease in appendicular lean mass index [13]. A previous systematic review and meta-analyses have also concluded that the impact of TRE was unclear and appears to be nuanced.
The inconsistent results of TRE intervention studies may be due, in part, to the fact that such trials have targeted very different populations and have utilized different TRE designs (e.g., eating windows length). Therefore, in this systematic review and meta-analysis, we aimed to characterize the efficacy and safety of TRE for fat loss, and related blood lipid composition, in adults with overweight and obese by including the most up-to-date peer-reviewed publications. Subgroup analyses were also completed to explicitly compare the influence of TRE intervention characteristics (e.g., eating window length, study duration, participant age, and intervention strategies) on its effectiveness [14,15,16], in the hopes of providing critical knowledge to inform the design of future research using TRE.
2. Methods
2.1. Design
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature were performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [17]. This study was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42023406329) (available online: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?RecordID=406329 URL (accessed on 4 July 2023)).
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
Seven electronic databases (PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Medline, Scopus, and SPORTDiscus) were searched for publications from their inception to June 1, 2024. The search strategy was as follows: (“Time Restricted Eating” or “Eating, Time Restricted” or “Time Restricted Fasting” or “Fasting, Time Restricted,” or “Restricted Fasting, Time” or “Time-Restricted Feeding” or “Feeding, Time Restricted” or “Time Restricted Feedings” or “Time Restricted Meal” or “Time Restricted Diet” or “Early Time-Restricted Eating”) and (“Obesity” OR “Overweight” OR “Excess Weight” OR “Obese Adults” OR “Adult with Obesity” OR “Adult Obesity” OR “Obesity in Adult” OR “Obese” OR “Adiposity”). A manual search of the bibliographic references for extracted articles and existing reviews was conducted to identify studies not captured in the electronic searches. Detailed results can be found in Supplement S2.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Participants: age ≥ 18 years old; BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2; no history of cardiovascular disease, metabolic disease, or gastrointestinal disease; not undergoing other fat loss measures (e.g., medications or surgery); and not pregnant or breastfeeding. (2) Intervention: the experimental group was a TRE that was used for fasting for 12 to 20 h over six weeks, while the control group had unlimited eating time. (3) Outcomes: the primary outcomes were body fat percentage, fat mass, and lean mass; the secondary outcomes were body mass index, waist circumference, and lipid profile (e.g., total cholesterol, (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), and triglycerides (TG)). (4) Study designs: at least one TRE intervention group and one control group were included in the study.
Studies were excluded if they were (1) animal trials, (2) written in a non-English language, (3) without specific data, (4) review and conference articles, and (5) repeated publications.
2.4. Data Extraction
Data extraction was carried out independently by two authors (YX and KZ), and any discrepancies in decisions were resolved through discussions with the other authors (DB and JZ) until a consensus was achieved. Extracted data included author names, year of publication, study design, sample characteristics, TRE protocol, intervention duration, outcomes, and adverse events. We extracted baseline and post-intervention data to calculate the change in outcomes when data on the change in outcomes were not directly available. The formulas [18] were as follows, where the R was set at 0.5 [19,20]:
Mean (change) = Mean (final) − Mean (baseline)
We extracted relevant data using the semi-automated extraction tool WebPlotDigitizer (https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer/, Version 4.6 URL (accessed on 2 June 2024)) for studies when the data could not be obtained by contacting the authors [21,22].
2.5. Quality Assessment
Two investigators (YX and KZ) independently identified the risk of bias for the relevant outcomes using the licensed Excel tool to implement the two revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tools for RCTs. The discrepancies were discussed and determined with a third investigator (DB).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The weighted mean difference (MD) of the outcomes was calculated with a 95% confidence interval (CI) to evaluate the effect of the TRE on primary and secondary outcomes. When the SDs for the outcome indicators were not directly available, the SDs were calculated based on the SE or CI of the group mean according to the procedure described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Review of Interventions (Chapter 6.5.2.3) [23].
A meta-analysis was performed in Stata MP 17.0 (STATA Corp., College Station, TX, USA) using the inverse variance method. Heterogeneity was assessed by measuring the inconsistency (I2 statistic) of intervention effects among the trials. The level of heterogeneity was interpreted according to guidelines from the Cochrane Collaboration: trivial (<25%), low (25~50%), moderate (50~75%), and high (>75%) [24]. A random effects model was employed to estimate pooled effects, anticipating heterogeneity due to variations in participants and interventions across studies. A subgroup analysis was used to analyze potential sources of heterogeneity. The publication bias was assessed by the funnel plot and Egger’s test. If significant asymmetry was detected, the trim-and-fill method was applied for sensitivity analysis [25]. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Additionally, the quality of evidence for outcomes was evaluated using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE), which characterizes the evidence on the study limitations, imprecision, inconsistency, indirectness, and publication bias [26,27].
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
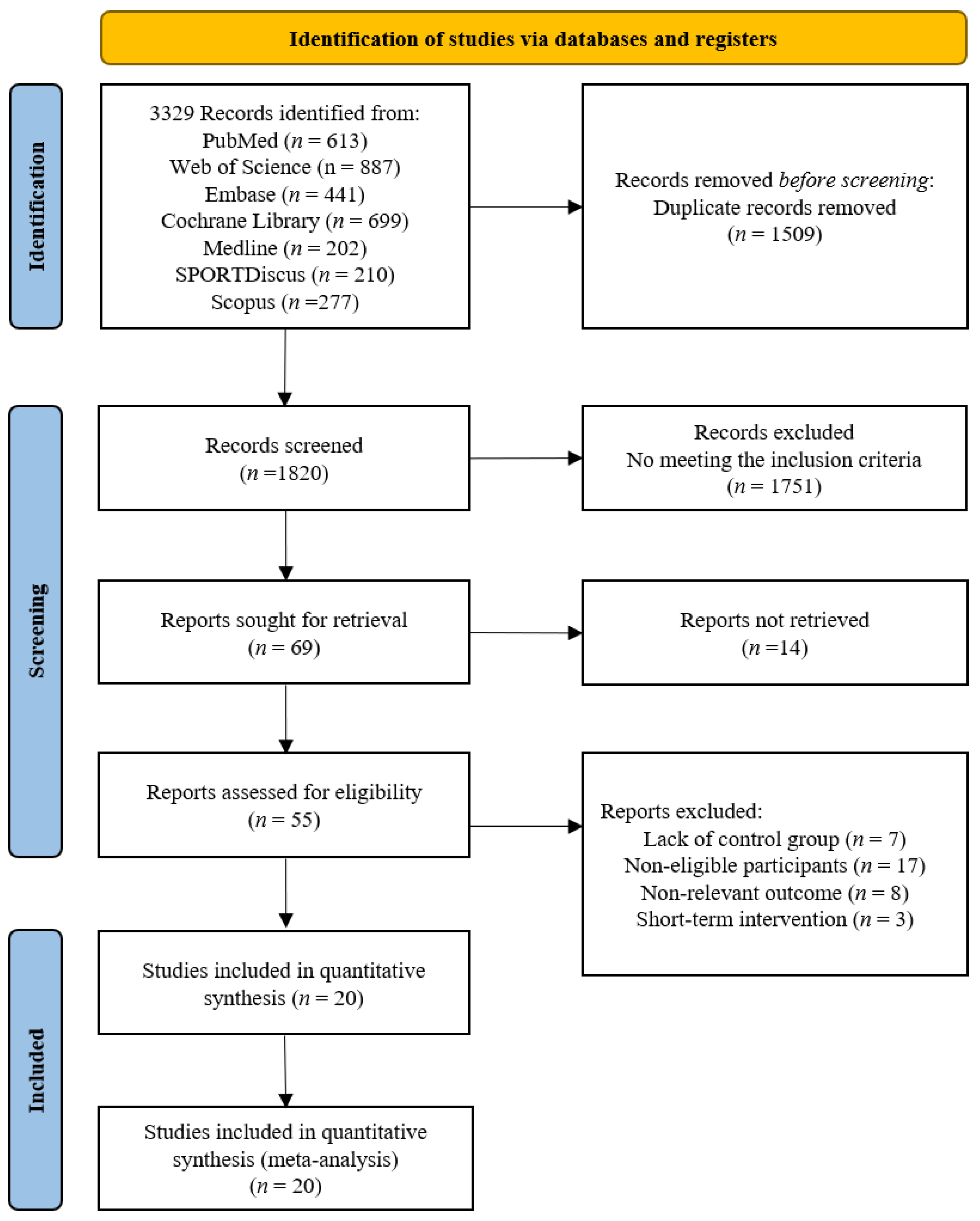
The screening flow diagram is shown in Figure 1. A total of 3329 relevant publications were retrieved (PubMed: n = 613, Web of Science: n = 887, Medline: n = 202, SPORTDiscus: n = 210, EMBASE: n = 441, Cochrane: n = 699, Scopus: n = 277, and Manual search: n = 0), and 3, 260 publications were excluded after reviewing the titles and abstracts. After the evaluation of the full texts, 49 of the 69 publications were removed, and thus, 20 publications consisting of 20 studies were included in the following analyses (Table 1). Uniquely, two publications [10,28] included two randomized controlled trials.
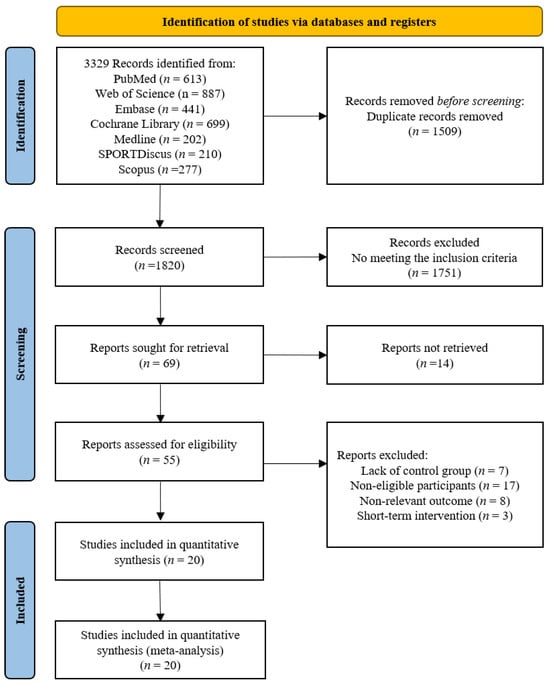
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the publication screening.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the included publications (20).
3.2. Quality Assessment
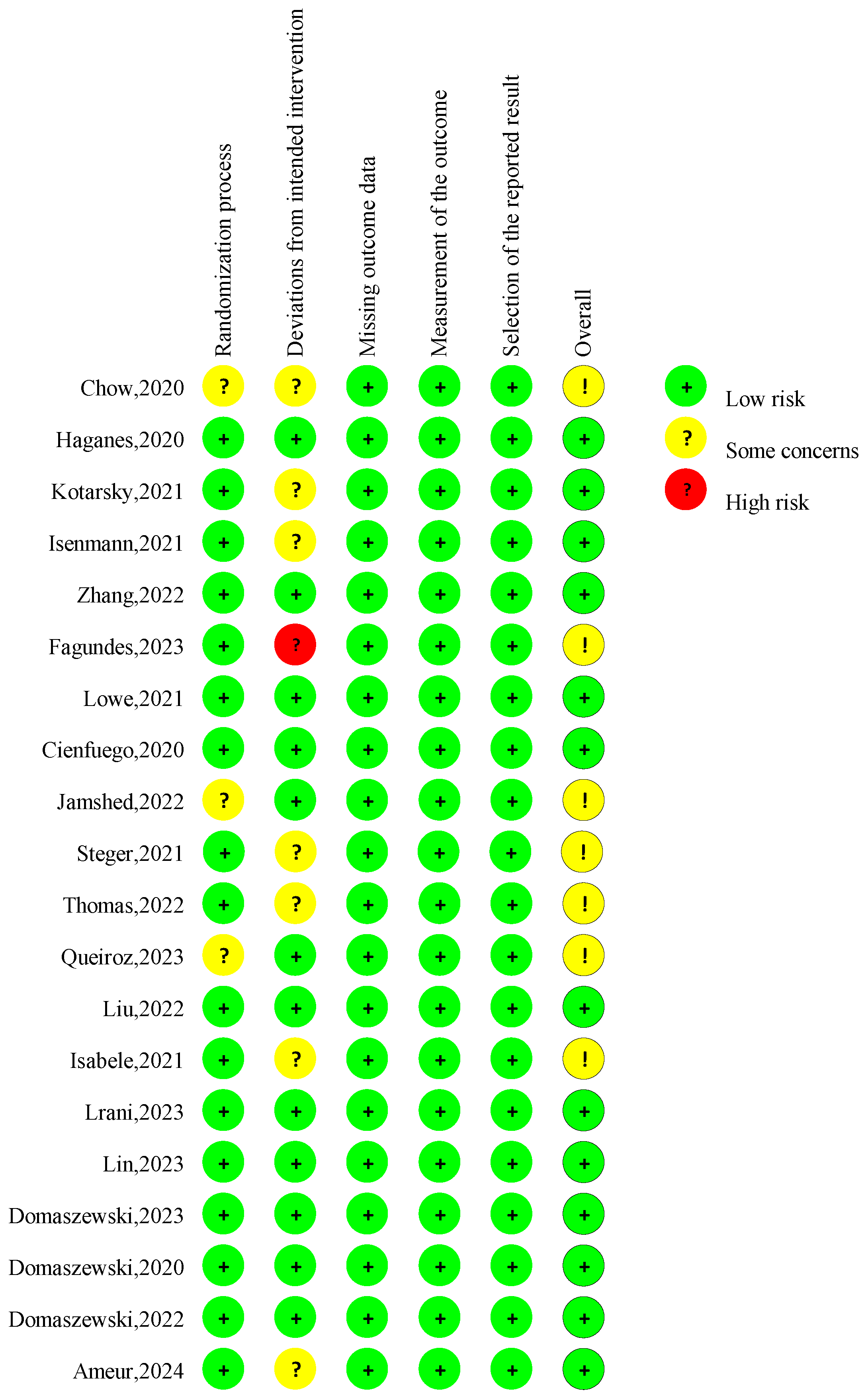
The overall risk of bias judgment was made according to five domain-level assessments (Figure 2). Seven studies had concerns about the overall risk of bias [11,21,29,33,36,37,41]. Four studies lacked specific information about the randomization process, and the allocation sequence’s concealment raised some concerns regarding the randomization process [11,29,37,41]. Seven studies lacked necessary information on analyzing the effect of assignment on intervention [21,29,31,32,33,36,42], raising concerns about the deviations from intended interventions. The risk of bias for missing outcome data, the measurement of the outcome, and the selection of the reported result was considered low for all studies.
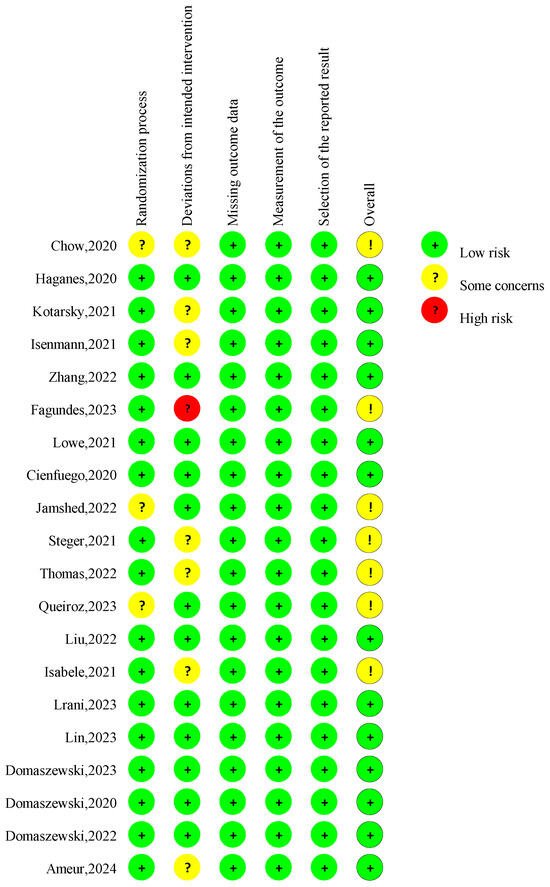
Figure 2.
Risk of bias assessment in the RCTs in the included studies. A total of 20 publications [10,11,12,13,21,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] were incorporated into the review.
3.3. Assessment of Evidence Certainty
We further assessed the meta-results of GRADE certainty evidence. The certainty of the evidence for the overall body composition, anthropometric measures, and blood lipid was considered “high to moderate” (Figure S1).
3.4. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.4.1. Participants
The included publications were conducted in different countries, including the USA [10,11,13,29,31,40,41], Norway [28], Brazil [21,33], Iran [39], Poland [30,34,38], China [12,35], and Germany [32], between 2020 and 2024. Twenty publications included 1288 participants (i.e., 936 women and 352 men) with a mean age range from 23.1 to 69.4 years and a mean BMI from 26 to 40.7 kg/m2. Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of all the included participants.
Participants’ occupational backgrounds included low-income women (n = 1) [33], non-night shift workers (n = 6) [10,13,28,33,36,37], and those with a standardized work schedule (n = 1) [29]. Body mass stabilization consisted of participants with recent stable body mass control (n = 9) [10,11,12,33,36,37,40,41,42]; non-low body fat high-level athletes and individuals specifically training for national and international competitions (n = 1) [32], and participants not taking fat loss medication or enrolled in a weight control or fat loss program (n = 4) [21,28,35,39]. Eight publications reported the physical activity levels of participants at the time of study participation, including physically active (n = 2) [28,32] and sedentary or physically inactive (n = 6) [10,11,31,37,41,42].
3.4.2. Study Design
All the publications consisted of randomized controlled trials. Three publications [10,12,37] utilized a three-arm design of two intervention arms and a control arm. One publication [28] included four experimental groups, that is, TRE (energy intake restricted to 10 h of eating per day), HIIT (supervised treadmill exercise three times per week), combined (TRE + HIIT), and control (no intervention) (Table 1).
3.5. Intervention Characteristics
3.5.1. Diet and Exercise Interventions
Nine publications used TRE [10,12,13,28,29,30,34,38,40] only. The other 11 publications combined TRE with other types of training and/or dietary protocols (i.e., high-intensity interval training (n = 2) [28,42]; concurrent exercise training (n = 1) [31]; caloric restriction (n = 5) [21,33,35,37,39]; and caloric restriction with exercise recommendation (n = 3)).
Participants were either allowed to eat as much as they wanted during the eating time window [10,12,13,28,29,30,34,38,40] or they were required to have similar daily amounts of energy intake and consumption between the TRE and control groups, eliminating the potential influences of the between-group variance of energy exchange on the observations [11,21,31,33,35,36,37,39,42]. In addition, one study used the Macronutrient-Based Diet (MBD) as a control group [32].
3.5.2. TRE Protocol
The duration of the TRE intervention ranged from 6 to 52 weeks (12 months) (i.e., 6 (n = 3) [30,34,38], 7 (n = 1) [28], 8 (n = 6) [10,12,21,31,37,39], 12 (n = 3) [13,29,42], 14 (n = 3) [11,32,41], 39 (n = 1) [36], and 52 (n = 3) [33,35,40] weeks). The eating window length of each TRE was between 4 and 12 h (i.e., 4 (n = 1) [10], 6 (n = 2) [10,12], 8 (n = 13) [11,13,21,29,30,31,32,34,35,37,38,41,42], 10 (n = 3) [28,36,39], and 12 (n = 1) [33] hours). In addition, one publication [40] used an 8-h eating window to reduce the body mass of participants during the first 6-month period, and a 10-h eating window to maintain the body mass during the second 6-month period.
The timing of the eating plan on each day was different across the publications. Only two publications [28,36] provided recommendations on when to start or end eating, thirteen publications recommended the timing of eating, and the other two [29,33] did not. Specifically, in those thirteen publications with designed timing, nine [10,13,30,31,32,34,38,39,40] used delayed time-restricted eating (dTRE; participants ate between 12:00 and 20:00) and four [11,35,41,42] used early time-restricted eating (eTRE; participants ate between 7:00 and 16:00). In addition, two publications [12,37] compared the effects of eTRE and dTRE interventions, and another study allowed participants to choose the protocol of either eTRE or dTRE [21] (Table 1).
3.5.3. Outcome Measurement
The outcomes of body composition included fat mass (n = 18) [10,11,12,13,21,28,29,30,31,32,34,35,36,37,39,40,41,42], lean mass (n = 16) [10,11,12,13,21,29,30,31,32,34,35,36,37,40,41,42], and body fat percentage (n = 11) [12,13,21,29,30,33,34,35,37,38,39], with the addition of body weight estimates based on the total fat mass and body fat percentage (n = 5) [28,31,36,42], as calculated by a formula detailed in Supplement S3. The methods of measuring body composition include dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (n = 10) [10,11,13,29,31,35,36,37,40,41] and bioelectrical impedance measurements (n = 10) [12,21,28,30,32,33,34,38,39,42].
The outcomes of anthropometric measures included body mass (n = 19) [11,12,13,21,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42], BMI (n = 13) [12,13,30,31,32,33,34,35,37,38,39,40,42], and waist circumference (n = 13) [11,12,13,21,31,32,33,34,35,38,39,40,42]. Waist circumference was measured using three methods: at the midpoint between the top of the iliac crest and the base of the lowest ribs (n = 5) [11,13,33,39,42], at the location of the minimum abdominal circumference (n = 2) [21,32] or two finger widths above the umbilicus (n = 1) [31].
The outcomes of the blood sample composition included TC (n = 10) [11,12,13,21,28,31,35,37,40,42]; HDL (n = 11) [10,11,12,13,28,29,31,35,37,40,42]; LDL (n = 10) [10,11,12,13,28,29,35,37,40,42]; and TG (n = 10) [10,11,12,13,28,29,35,37,40,42]. Additionally, most of these publications also examined the effects of TRE on visceral and subcutaneous fat, water, and resting metabolic rate.
3.6. Adverse Events and Side Effects
Thirteen publications [12,13,21,28,29,30,32,34,36,38,39,40,42] did not report information on the reported side effects or adverse events. Seven publications [10,11,31,35,37,40,41] did report the occurrence of adverse events, and several side effects or adverse events were reported, including headaches, nausea, diarrhea, hunger, fatigue, dizziness, decreased appetite, epigastric pain, indigestion, constipation, vertigo, gastric reflux, or stomachache. All reported events were mild, transient, and occurred with a similar frequency across the intervention and control groups.
4. Meta-Analysis
Based on the heterogeneity and the number of studies that were available for grouping, we performed subgroup analyses by comparing the eating window length (i.e., 6 to 8 h and 10 to 12 h), study duration (i.e., ≤39 weeks and ≥39 weeks), participant average age (i.e., 23 to 45-year-old young adults, 45 to 65-year-old middle-aged adults, and ≥65 year-old older adults), and TRE intervention strategies (i.e., TRE-only, TRE combined with CR, TRE combined with exercise, and TRE combined with CR and exercise recommendations) (Table S1). Since the study by Cienfuegos et al. [10] used a 4-h eating time and the study by Isenmann et al. [32] directly compared TRE to MBD, these studies were not included in the meta-analysis.
4.1. Effects of TRE on Body Composition
4.1.1. Body Fat Percentage
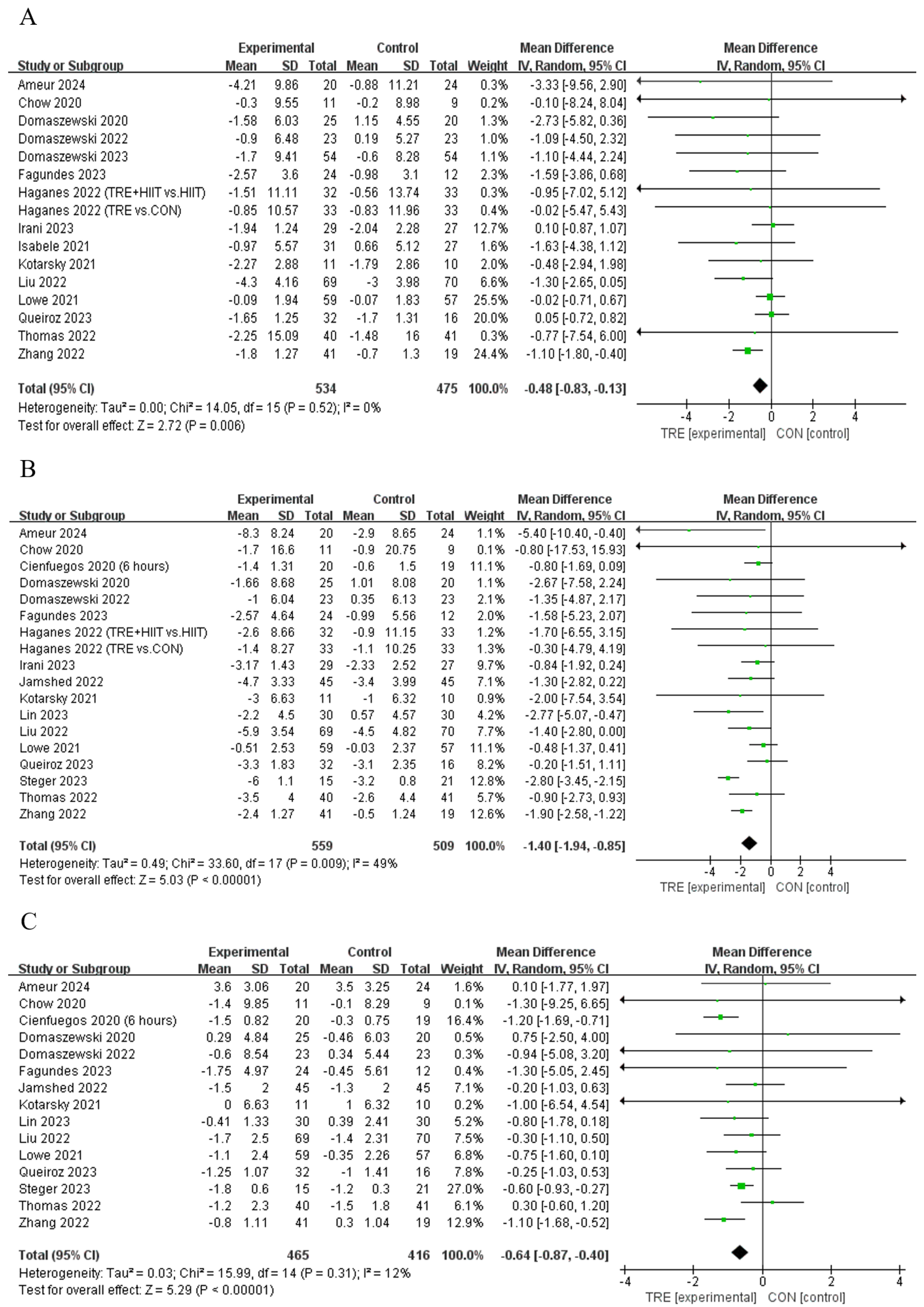
Five studies [12,21,30,33,34] showed that TRE decreased the body fat percentage compared to control, while another six studies [13,29,35,37,38,39] reported that TRE did not alter this outcome (Table 2). Pooled data indicate that TRE decreased the body fat percentage [Fixed: MDpooled = −0.48%, 95% CI (0.83, −0.13), p = 0.007, Figure 3A] with trivial heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, p = 0.522). The funnel plot and Egger’s test (t = −1.61, p = 0.129) indicated no publication bias.

Table 2.
Between-group comparisons of study outcomes (20).
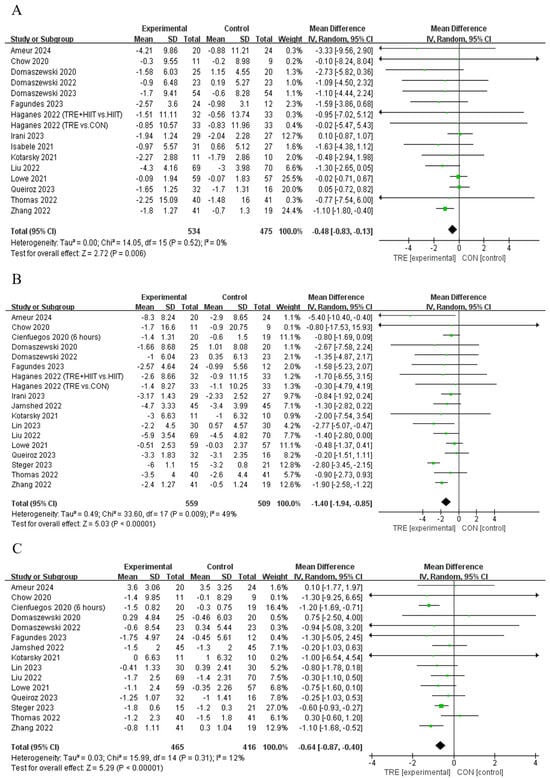
Figure 3.
Meta−analysis results of (A) body fat percentage [12,13,21,28,29,30,31,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,42], (B) fat mass [10,11,12,13,21,28,29,30,31,34,35,36,37,39,40,41,42], and (C) lean mass [10,11,12,13,21,29,30,31,34,35,36,37,40,41,42].
4.1.2. Fat Mass
Twelve studies [10,12,21,28,30,31,34,39,40,41,42] showed that TRE reduced fat mass compared to the control intervention, while another six studies [11,13,29,35,36,37] reported no such effect on this outcome (Table 2). Pooled data indicated that TRE reduced fat mass [Random: MDpooled = −1.40 kg, 95% CI (−1.94, −0.85), p < 0.001, Figure 3B] with trivial heterogeneity (I2 = 49.4%, p = 0.009). The funnel plot and Egger’s test (t = 0.35, p = 0.731) indicated no publication bias.
Subgroup analyses revealed that (1) TRE with an eating window of 6 to 8 h reduced fat mass (MD = −1.66 kg, 95% CI (−2.31, −1.01), p < 0.001), while that with an eating window of 10 to 12 h did not (MD = −0.65 kg, 95% CI (−1.39, 0.90), p = 0.085); (2) the TRE of both ≤ 39 weeks (MD = −1.36 kg, 95% CI (−2.00, −0.72) p < 0.001) and ≥39 weeks study durations reduced fat mass (MD = −1.51 kg, 95% CI (−2.51, −0.51), p = 0.003); (3) the reduction in fat mass was observed in both young adults (MD = −1.61 kg, 95% CI (−2.23, −0.99), p < 0.001) and middle-aged adults (MD = −0.64 kg, 95% CI (−1.27, −0.01), p = 0.045), but not in older adults (MD = −1.80 kg, 95% CI (−4.66, 1.06), p = 0.218); and (4) a decrease in fat mass was observed in the TRE-only group (MD = −1.26 kg, 95% CI (−1.89, −0.62), p < 0.001), TRE combined with CR (MD = −0.83 kg, 95% CI (−1.53, −0.12), p = 0.022), TRE combined with exercise (MD = −3.07 kg, 95% CI (−6.02, −0.12), p = 0.041), and TRE combined with CR and exercise recommendations (MD = −1.87 kg, 95% CI (−3.17, −0.57), p = 0.005, Table S1).
4.1.3. Lean Mass
Four studies [10,12,21,29] reported that TRE reduced lean mass compared to the control intervention, while eleven studies [11,13,30,31,34,35,36,37,40,41,42] did not report a change in this outcome (Table 2). Analyses of pooled data revealed that TRE reduced lean mass [Random: MDpooled = −0.64 kg, 95% CI (−0.87, −0.40), p = < 0.001, Figure 3C] with trivial heterogeneity (I2 = 12.6%, p = 0.314). The funnel plot and Egger’s test (t = 0.83, p = 0.421) indicated no publication bias.
Subgroup analyses demonstrated that (1) TRE with an eating window of 6 to 8 h reduced lean mass (MD = −0.74 kg, 95% CI (−0.95, −0.53), p < 0.001), while eating windows of 10 to 12 h did not (MD = −0.01 kg, 95% CI (−0.60, 0.58), p = 0.968); (2) a TRE duration of ≤ 39 weeks decreased lean mass (MD = −0.73 kg, 95% CI (−0.95, −0.51) p < 0.001), while ≥ 39 weeks did not (MD = −0.25 kg, 95% CI (−0.84, 0.35), p = 0.416); 3) a reduction in lean mass was observed in both young adults (MD = −0.53 kg, 95% CI (−0.77, −0.28), p < 0.001) and middle-aged adults (MD = −1.09 kg, 95% CI (−1.51, −0.66), p < 0.001), but not in older adults (MD = 0.10 kg, 95% CI (−2.45, 2.66), p = 0.936); and 4) a decrease in lean mass was observed in the TRE-only group (MD = −1.04 kg, 95% CI (−1.36, −0.72), p < 0.001), while TRE combined with CR (MD = −0.30 kg, 95% CI (−0.85, 0.26), p= 0.293), TRE combined with exercise (MD = −0.01 kg, 95% CI (−1.78, 1.76), p = 0.989), and TRE combined with CR and exercise recommendations did not (MD = −0.46 kg, 95% CI (−0.75, −0.17), p = 0.002, Table S1).
4.2. Effects of TRE on Anthropometric Measures
4.2.1. Body Mass
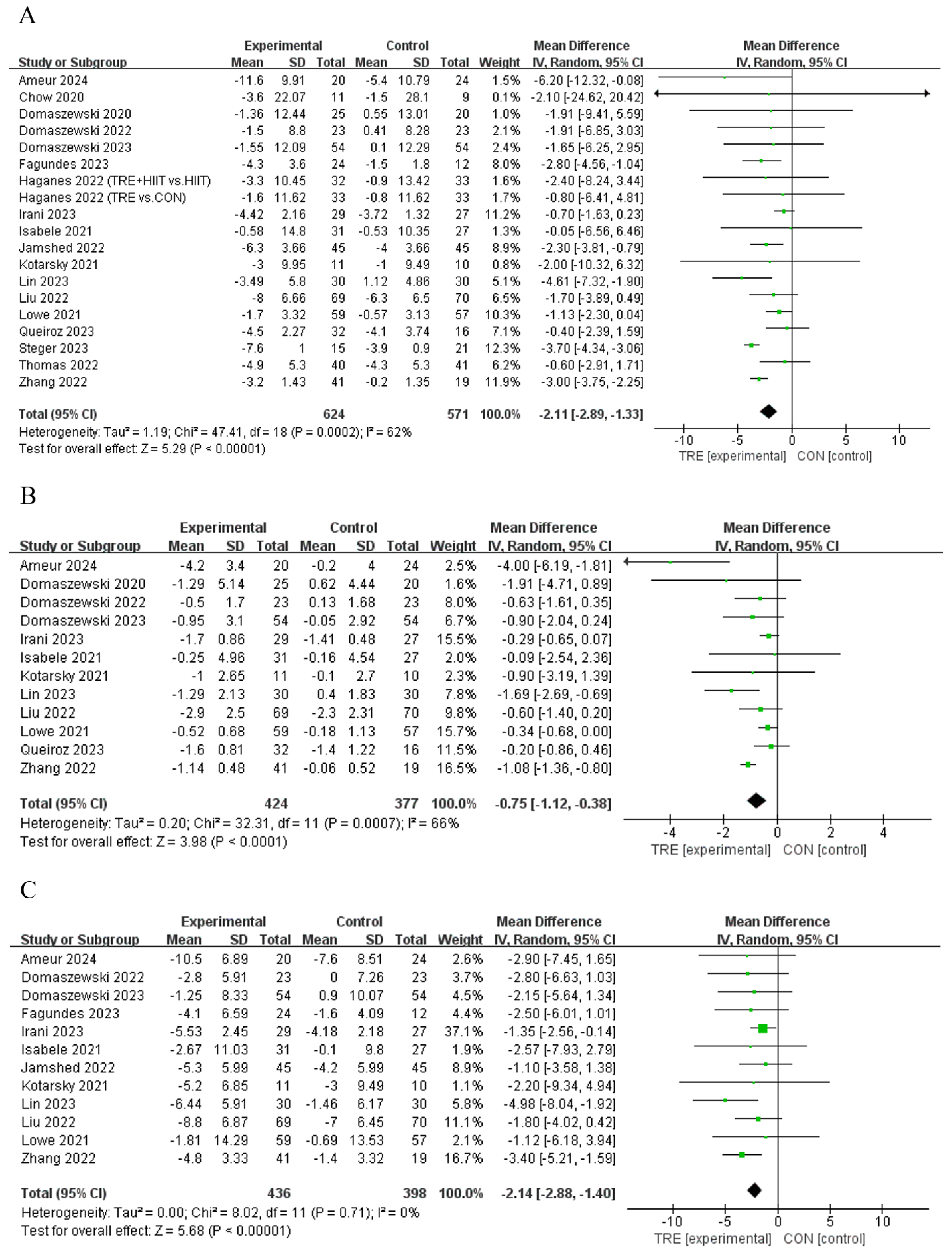
Twelve studies [11,12,21,28,29,31,34,39,40,41,42] reported that TRE reduced body mass compared to control, while another seven studies [13,30,33,35,36,37,38] did not demonstrate this effect (Table 2). An analysis of the pooled data indicated that TRE had no effect on body mass [Random: MDpooled = −2.11 kg, 95% CI (−2.89, −1.33), p < 0.001, Figure 4A] with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 62.0%, p = 0.000). The funnel plot and Egger’s test (t = 1.03, p = 0.318) indicated no publication bias.
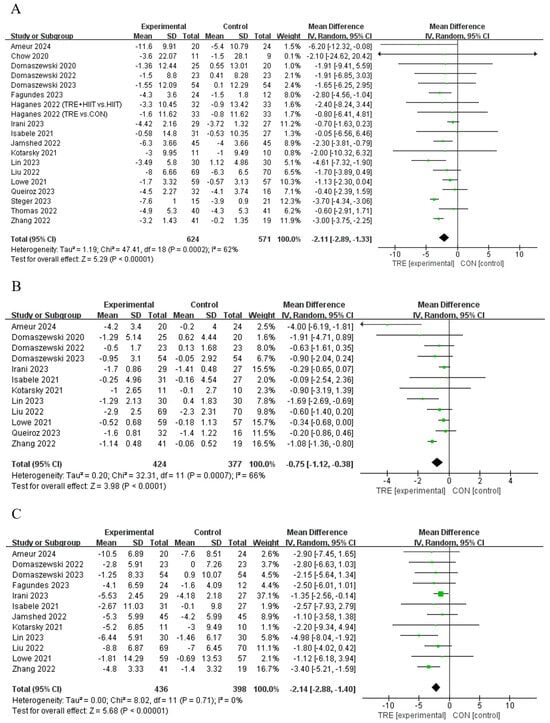
Figure 4.
Meta−analysis results for (A) body mass [11,12,13,21,28,29,30,31,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42], (B) body mass index [12,13,30,31,33,34,35,37,38,39,40,42], and (C) waist circumference [11,12,13,21,31,33,34,35,38,39,40,42].
Subgroup analyses showed that 1) TRE with an eating window of 6 to 8 h reduced body mass (MD = −2.73 kg, 95% CI (3.42, −2.05), p < 0.001), while those with an eating window of 10 to 12 h did not (MD = −0.67 kg, 95% CI (−1.44, −0.11), p = 0.091); 2) the TRE of both ≤ 39 weeks (MD = −2.13 kg, 95% CI (−3.01, −1.25) p < 0.001) and ≥ 39 weeks (MD = −2.02 kg, 95% CI (−3.94, −0.09), p = 0.007) reduced body mass; 3) a reduction in body mass was observed in young adults (MD = −2.24 kg, 95% CI (−3.13, −1.36), p < 0.001), but not in middle-aged adults (MD = −1.13 kg, 95% CI (−2.31, 0.04), p = 0.058) or older adults (MD = −1.79 kg, 95% CI (−4.87, 1.28), p = 0.252); and 4) the TRE-only group (MD = −2.39 kg, 95% CI (−3.42, −1.35), p < 0.001), TRE combined with CR (MD = −1.22 kg, 95% CI (−2.13, −0.30), p = 0.009), and TRE combined with CR and exercise recommendations (MD = 2.48 kg, 95% CI (−4.15, −0.81), p = 0.004) reduced body mass, while TRE combined with exercise did not (MD = −3.76 kg, 95% CI (−7.52, 0.01), p = 0.051, Table S1).
4.2.2. Body Mass Index
Seven studies [12,30,31,34,39,40,42] reported that TRE decreased BMI compared to the control intervention, while another five studies [13,33,35,37,38] did not observe a change in this outcome (Table 2). An analysis of the pooled data indicated that TRE had no effect on BMI [Random: MDpooled = −0.75 kg/m2, 95% CI (−1.12, −0.38), p < 0.001, Figure 4B] with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 66.0%, p = 0.000). The funnel plot and Egger’s test (t = −0.80, p = 0.444) indicated no publication bias.
Subgroup analyses revealed that (1) TRE with an eating window of 6 to 8 h decreased BMI (MD = −0.98 kg/m2, 95% CI (−1.44, −0.52), p < 0.001), while those with an eating window of 10 to 12 h did not (MD = −0.27 kg/m2, 95% CI (−0.58, 0.05) p = 0.097); (2) a TRE duration of both ≤ 39 weeks (MD = −0.70 kg, 95% CI (−1.13, −0.28) p = 0.001) and ≥ 39 weeks (MD = −0.98 kg/m2, 95% CI (−1.85, −0.11), p = 0.027) decreased BMI; (3) a reduction in BMI was observed in both young adults (MD = −0.86 kg/m2, 95% CI (−1.37, −0.34), p < 0.001), and older adults (MD = −0.82 kg/m2, 95% CI (−1.54, −0.11), p = 0.025), but not in middle-aged adults (MD = −0.34 kg/m2, 95% CI (−0.68, 0.00), p = 0.051); and (4) the TRE-only group (MD = −0.89 kg/m2, 95% CI (−1.36, −0.42), p < 0.001) and TRE combined with CR (MD = −0.31 kg/m2, 95% CI (−0.60, −0.57), p = 0.037) decreased BMI, while TRE combined with exercise did not (MD = −2.47 kg/m2, 95% CI (−5.51, 0.57), p = 0.111, Table S1).
4.2.3. Waist Circumference
Seven studies [12,21,30,34,39,40,42] reported that TRE reduced waist circumference compared to the control group, while another five publications [11,13,31,33,35] reported no effect on this outcome (Table 2). An analysis of the pooled data indicated that TRE reduced waist circumference [Random: MDpooled = −2.14 cm, 95% CI (−2.88, −1.40), p < 0.001, Figure 4C] with low heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, p = 0.711). The funnel plot and Egger’s test (t = −1.03, p = 0.328) indicated no publication bias.
4.3. Effects of TRE on Blood Lipid
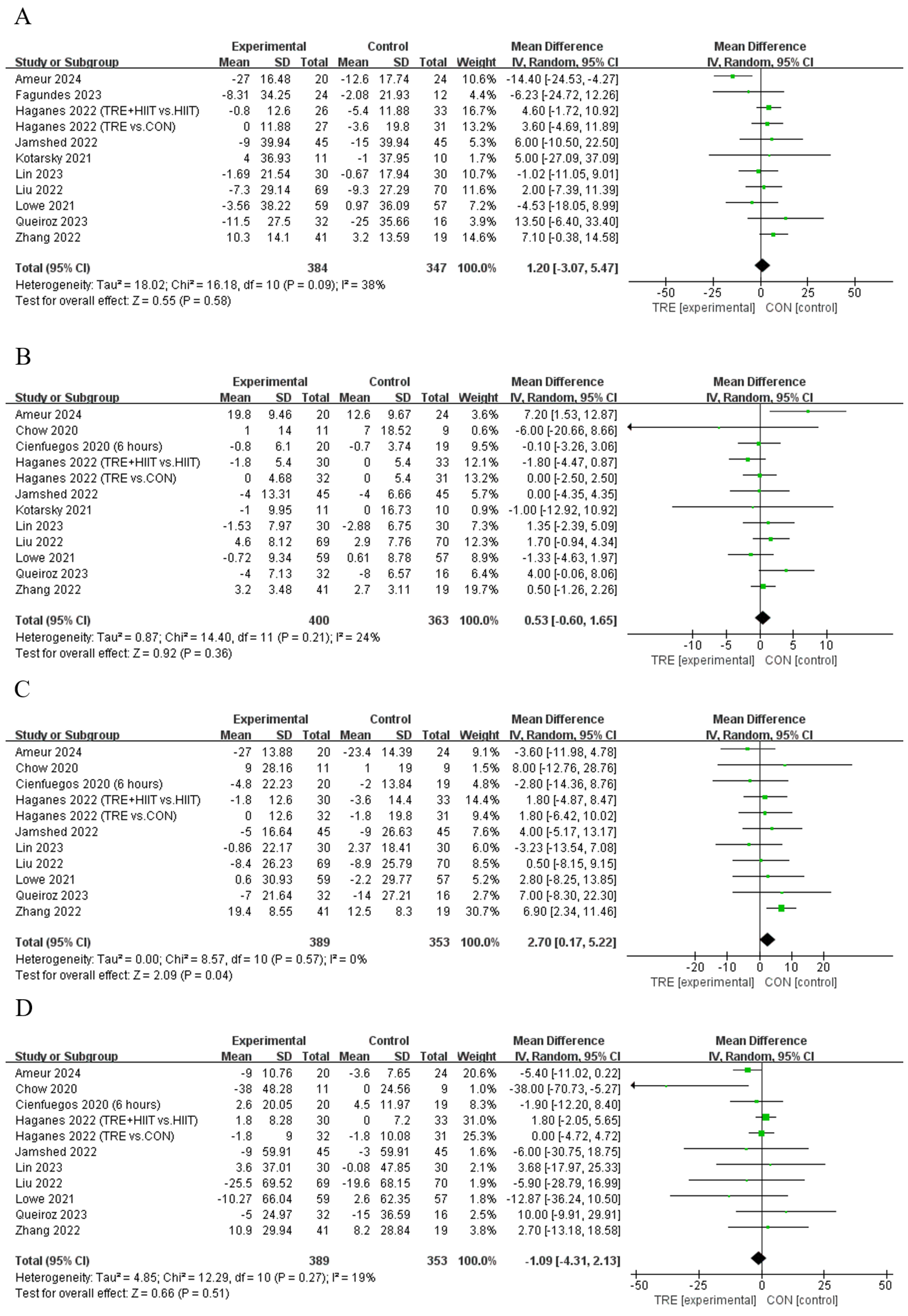
Ten studies [11,13,28,29,35,37,40,42,43] showed that TRE cannot significantly change LDL compared to the control, and only one [12] showed that TRE can significantly increase LDL (Table 2). An analysis of the pooled data indicated that TRE increased LDL [Random: MDpooled = 2.70 mg/dL, 95% CI (0.17, 5.22), p = 0.037, Figure 5C] with low heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, p = 0.573). The funnel plot and Egger’s test (t = −1.24, p = 0.246) indicated no publication bias. For other outcomes of blood lipid, all the studies showed that TER cannot induce significant effects on TC (n = 11, Random: MDpooled = 1.20 mg/dL, 95% CI (−3.07, 5.47), p = 0.582 Figure 5A), HDL (n = 12, Random: MDpooled = 0.53 mg/dL, 95% CI (−0.60, 1.65), p = 0.357, Figure 5B), or TG [n = 11, Random: MDpooled = −1.09 mg/dL, 95% CI (−4.31, 2.13), p = 0.506, Figure 5D] without heterogeneity (I2 = 18.6~38.2%, p = 0.095~0.266). The funnel plots and Egger’s test indicated (t = −1.22~0.4, p = 0.154~0.694) no publication bias.
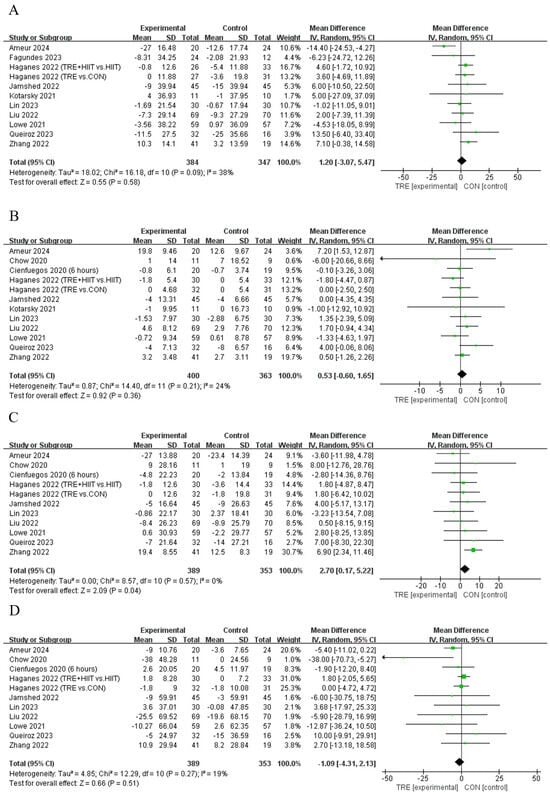
Figure 5.
Meta−analysis results for (A) total cholesterol [11,12,13,21,28,31,35,37,40,42], (B) high−density lipoprotein cholesterol [10,11,12,13,28,29,31,35,37,40,42], (C) low−density lipoprotein cholesterol [10,11,12,13,28,29,35,37,40,42], and (D) triglycerides [10,11,12,13,28,29,35,37,40,42].
There were no significant differences in TC, HDL, and TG between the subgroups, except for HDL, which was significantly increased in TRE combined with CR (MD = 2.38 mg/dL, 95% CI (0.17, 4.60), p = 0.035), and for TG, which was significantly decreased in TRE with an eating window of 6 to 8 h (MD = −4.68 mg/dL, 95% CI (−9.01, −0.36), p = 0.034, Table S1).
5. Discussion
This systematic review and its meta-analysis provide evidence of moderate to high quality that TRE appears safe and effectively reduces body fat, yet also reduces lean mass and does not appear to affect blood lipid levels. Subgroup analyses further indicated that TRE was particularly beneficial for younger and middle-aged adults, and such effect sizes of benefits are pertaining to the design of intervention protocols (e.g., the benefits would be maximized when using a 6 to 8 h eating window length). These results thus provide important knowledge for the appropriate design of TRE protocols, helping the development of weight loss programs using TRE.
Our results indicate that implementing TRE is an effective strategy for body weight, body mass index, and waist circumference in adults with overweight and obese, via a TRE-induced reduction in body fat percentage. These benefits of TRE for fat loss may stem from physiological changes triggered by time-restricted eating, such as synchronization with endogenous circadian rhythms in both central and peripheral biological clocks [44,45]. TRE, as a form of a time-restricted diet aligned with individual circadian rhythms, modulates the eating-fasting cycle to optimize metabolic processes [9,46]. For instance, studies have shown that TRE can increase adiponectin levels during fasting, induce a moderate rise in ketone bodies, and activate AMPK (adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase), which enhances insulin sensitivity, stimulates lipolysis, and promotes the secretion of lipocalin during fasting, thereby aiding in fat reduction [44,47,48]. Additionally, TRE has been observed to reduce caloric intake by about 20% to 30% due to the decreased eating frequency, further contributing to body weight loss [10,12,28,44]. It is observed that TRE with eating windows of 6 to 8 h, either alone or combined with caloric restriction, may be most effective for reducing body fat and overall body mass. Both shorter (e.g., 6 to 14 weeks) and longer (e.g., 39 to 52 weeks) durations of TRE resulted in fat loss. Combining TRE with exercise led to a significant decrease in body fat, but no change in overall body mass, likely due to the retention of lean mass, which will be further discussed in the next section. Another reason could be the “ceiling effect,” where the inherent ability of exercise therapy (e.g., HIIT) to reduce body weight [49] limits the additional benefits of TRE. Only a few studies (n = 3) have explored the effects of TRE combined with exercise, with differing outcomes, indicating the need for more research to fully understand these interactions. Remarkably, no significant weight loss benefits of TRE were observed in older cohorts, possibly due to insufficient statistical power from the small number of studies (n = 3) with limited sample sizes. It is thus worthwhile to perform studies with the focus on older adults and explore the effects of TRE on body weight and composition, as well as its potential benefits for sarcopenic obesity [50] in this population.
Interestingly, we observed that TRE reduced lean mass, which also contributed to the observed weight loss induced by TRE. Such a loss of lean mass may be attributed primarily to inadequate protein intake and changes in protein turnover (decreased muscle protein synthesis, increased catabolism, or both) [51,52,53]. Furthermore, a loss of body water may contribute, as weight loss often reduces circulation and body fluids in adults with overweight and obese [12,54]. However, this does not appear to raise safety concerns [55], as studies indicate that in adults with obese and overweight, lean mass typically accounts for only 20 to 30% of the total weight lost during weight reduction. The observed lean mass loss with TRE in this study was relatively small (about 17.1%), suggesting it is within a reasonable range [12,13,52]. Significant lean mass reduction was observed with shorter TRE durations, suggesting that muscle protein loss may occur early in the process and could decrease as ketogenesis increases [56]. Only one study, Lowe et al. [13], observed that 65% of the weight loss during a 12-week, 8-h restricted eating on TRE was lean mass. While the exact cause remains unclear, such a high percentage of lean mass loss has been linked to weight rebound and an increased risk of sarcopenia, particularly when the lean mass loss exceeds fat loss [52,57,58]. Given the limited attention to this issue [28,31,47], we still recommend combining TRE with strength training and appropriate protein supplementation to prevent lean mass loss, despite the absence of serious adverse events or sarcopenia reports [59]. Future studies are warranted to explicitly characterize the effects of TRE on muscle mass and hydration, and the related long-term influences on sarcopenia risk, providing more comprehensive knowledge to optimize TRE protocols for weight reduction without compromising health.
No significant effects of TRE on blood lipids were observed, except for an unexpected increase in LDL [12]. This increase could represent a short-term adverse reaction to dietary changes, possibly attributed to prolonged fasting and the resulting increased reliance on fat oxidation during the TRE intervention [11,12,60]. In addition, the effect of TRE on most blood lipids is negligible because we mainly focused on adults with overweight and obese without metabolic diseases, and the results of this study were mainly influenced by those observed in younger adults, such as in Zhang et al. [12], who observed that blood lipid levels in young adults with overweight (23 ± 1 years) were all within the normal range (TC 164~178, HDL 40~46, LDL 96~105, TG 84~93 mg/dL). Therefore, this suggests that the regulatory effect of TRE on lipid metabolism in this group of people is minimal and is unrelated to any safety concerns. Remarkably, TG levels were significantly lower with a 6 to 8-h eating window diet, likely due to the extended fasting period that accelerates the body’s transition into a fat-metabolizing state. During this fasting period, insulin levels decrease, which enhances lipolysis and consequently reduces TG levels [61,62,63]. However, one study demonstrated that over a 12-month period, an 8-hour time-restricted eating regimen combined with daily caloric restriction provided no additional benefits compared to daily caloric restriction alone [35]. Despite this, the present study observed an association between TRE combined with CR and an increase in HDL, which might be due to the reduction in body fat and overall weight [64]. Overall, the potential of combining TRE with CR remains promising, though further research is required to confirm its benefits. It is important to note that blood lipid metabolism is regulated by circadian rhythms, which differ among individuals [65]. To optimize the effects of TRE on blood lipids, it may be necessary to tailor the TRE protocol to align with individual circadian rhythms, potentially improving cardiovascular health [62,65].
Some limitations should be noted when interpreting the observations in this work. First, a relatively small number (n = 20) of studies were included in the meta-analysis and the study protocols varied. For instance, the duration of TRE interventions ranged from 6 to 52 weeks, which may potentially limit the strength of the evidence. Second, this analysis focused primarily on adults with overweight and obese without metabolic abnormalities, and most of the included studies concentrated on young and middle-aged women (i.e., 72.8% of the included participants). As a result, the findings may not be generalizable to patients with metabolic disorders such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or polycystic ovary syndrome. Further studies are necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of TRE interventions in other populations, such as in older men and individuals with metabolic diseases, to establish the generalizability of TRE to public health. Third, due to the limited number of publications, several sub-group analyses cannot be performed (e.g., the level of baseline physical activity in participants, which may contribute to the effects of TRE) [66]. Additionally, future studies should more explicitly evaluate and track side effects and adverse events, while also considering the quantification of protein intake and the incorporation of regular physical exercise.
This work provides moderate to high amounts of evidence that TRE is a promising dietary strategy for fat loss. Although it may potentially reduce lean mass and increase LDL, these effects do not pose significant safety concerns.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu16193390/s1. (1) Supplement S1: Table S1 Subgroup analysis results; Figure S1: Certainty of the evidence; (2) Supplement S2: Search query history for Seven electronic databases; and (3) Supplement S3: Body Fat Percentage Calculation.
Author Contributions
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows—Y.X., K.Z. and Z.S. analyzed and interpreted the data; Y.X., K.Z. and J.Z. drafted the manuscript; J.Z. and D.B. critically reviewed the manuscript; and D.B. had primary responsibility for the final content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors reported no funding received for this study.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The database supporting the conclusions of this systematic review will be available from the corresponding author upon request, pending application and approval.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
References
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolotkin, R.L.; Meter, K.; Williams, G.R. Quality of Life and Obesity. Obes. Rev. 2001, 2, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2022: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- McDowell, A.; Caughman, R.; Bischo, L. Total Energy Intake of the US Population: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1991. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 1072S–1080S. [Google Scholar]
- Gallant, A.R.; Lundgren, J.; Drapeau, V. The Night-Eating Syndrome and Obesity: NES and Obesity. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.O. Understanding and Addressing the Epidemic of Obesity: An Energy Balance Perspective. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.C.; Gallop, M.R.; Flores Ramos, S.; Zarrinpar, A.; Broussard, J.L.; Chondronikola, M.; Chaix, A.; Klein, S. Complex Physiology and Clinical Implications of Time-Restricted Eating. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1991–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaix, A.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Melkani, G.C.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Eating to Prevent and Manage Chronic Metabolic Diseases. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2019, 39, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, J.D.N.; Macedo, R.C.O.; Tinsley, G.M.; Reischak-Oliveira, A. Time-Restricted Eating and Circadian Rhythms: The Biological Clock Is Ticking. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2863–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cienfuegos, S.; Gabel, K.; Kalam, F.; Ezpeleta, M.; Wiseman, E.; Pavlou, V.; Lin, S.; Oliveira, M.L.; Varady, K.A. Effects of 4- and 6-h Time-Restricted Feeding on Weight and Cardiometabolic Health: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Adults with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 366–378.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshed, H.; Steger, F.L.; Bryan, D.R.; Richman, J.S.; Warriner, A.H.; Hanick, C.J.; Martin, C.K.; Salvy, S.J.; Peterson, C.M. Effectiveness of Early Time-Restricted Eating for Weight Loss, Fat Loss, and Cardiometabolic Health in Adults with Obesity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Ren, J.; Gao, X.; Lv, S.; Liang, L.; Zhang, F.; Yin, B.; et al. Randomized Controlled Trial for Time-Restricted Eating in Overweight and Obese Young Adults. Iscience 2022, 25, 104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, D.A.; Wu, N.; Rohdin-Bibby, L.; Moore, A.H.; Kelly, N.; Liu, Y.E.; Philip, E.; Vittinghoff, E.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Olgin, J.E.; et al. Effects of Time-Restricted Eating on Weight Loss and Other Metabolic Parameters in Women and Men With Overweight and Obesity: The TREAT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-H.; Lu, L.W.; Ge, Q.; Feng, D.; Yu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, C.; Chen, F. Missing Puzzle Pieces of Time-Restricted-Eating (TRE) as a Long-Term Weight-Loss Strategy in Overweight and Obese People? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Hu, F. Metabolic Efficacy of Time-Restricted Eating in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 3428–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wen, S.; Lu, D.; Shen, X.; Deng, H.; Xu, L. Is Time-Restricted Eating (8/16) Beneficial for Body Weight and Metabolism of Obese and Overweight Adults? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Collaboration, C. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, 2nd ed.; Cochrane Book Series; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, T. Effects of Chronic Exercise Interventions on Executive Function among Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagundes, G.B.P.; Tibães, J.R.B.; Silva, M.L.; Braga, M.M.; Silveira, A.L.M.; Teixeira, A.L.; Ferreira, A.V.M. Metabolic and Behavioral Effects of Time-Restricted Eating in Women with Overweight or Obesity: Preliminary Findings from a Randomized Study. Nutrition 2023, 107, 111909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Steeb, T.; Wessely, A.; Koch, E.A.T.; Vera, J.; Berking, C.; Heppt, M.V. Is Tebentafusp Superior to Combined Immune Checkpoint Blockade and Other Systemic Treatments in Metastatic Uveal Melanoma? A Comparative Efficacy Analysis with Population Adjustment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 115, 102543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Higgins, J.P.T. Measuring Inconsistency in Meta-Analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and Fill: A Simple Funnel-Plot-Based Method of Testing and Adjusting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balshem, H.; Helfand, M.; Schünemann, H.J.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Vist, G.E.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Meerpohl, J.; Norris, S. GRADE Guidelines: 3. Rating the Quality of Evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meader, N.; King, K.; Llewellyn, A.; Norman, G.; Brown, J.; Rodgers, M.; Moe-Byrne, T.; Higgins, J.P.; Sowden, A.; Stewart, G. A Checklist Designed to Aid Consistency and Reproducibility of GRADE Assessments: Development and Pilot Validation. Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haganes, K.L.; Silva, C.P.; Eyjólfsdóttir, S.K.; Steen, S.; Grindberg, M.; Lydersen, S.; Hawley, J.A.; Moholdt, T. Time-Restricted Eating and Exercise Training Improve HbA1c and Body Composition in Women with Overweight/Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1457–1471.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.S.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Alvear, A.; Fleischer, J.G.; Thor, H.; Dietsche, K.; Wang, Q.; Hodges, J.S.; Esch, N.; Malaeb, S.; et al. Time-Restricted Eating Effects on Body Composition and Metabolic Measures in Humans Who Are Overweight: A Feasibility Study. Obesity 2020, 28, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewski, P.; Konieczny, M.; Pakosz, P.; Bączkowicz, D.; Sadowska-Krępa, E. Effect of a Six-Week Intermittent Fasting Intervention Program on the Composition of the Human Body in Women over 60 Years of Age. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotarsky, C.J.; Johnson, N.R.; Mahoney, S.J.; Mitchell, S.L.; Schimek, R.L.; Stastny, S.N.; Hackney, K.J. Time-Restricted Eating and Concurrent Exercise Training Reduces Fat Mass and Increases Lean Mass in Overweight and Obese Adults. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenmann, E.; Dissemond, J.; Geisler, S. The Effects of a Macronutrient-Based Diet and Time-Restricted Feeding (16:8) on Body Composition in Physically Active Individuals—A 14-Week Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Maranhão Pureza, I.R.; da Silva, A.E., Jr.; Silva Praxedes, D.R.; Lessa Vasconcelos, L.G.; de Lima Macena, M.; Vieira de Melo, I.S.; de Menezes Toledo Florêncio, T.M.; Bueno, N.B. Effects of Time-Restricted Feeding on Body Weight, Body Composition and Vital Signs in Low-Income Women with Obesity: A 12-Month Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewski, P.; Konieczny, M.; Pakosz, P.; Łukaniszyn-Domaszewska, K.; Mikuláková, W.; Sadowska-Krępa, E.; Anton, S. Effect of a Six-Week Times Restricted Eating Intervention on the Body Composition in Early Elderly Men with Overweight. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, P.; Guo, D.; Lin, J.; Xu, B.; Li, C.; et al. Calorie Restriction with or without Time-Restricted Eating in Weight Loss. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.A.; Zaman, A.; Sloggett, K.J.; Steinke, S.; Grau, L.; Catenacci, V.A.; Cornier, M.; Rynders, C.A. Early Time-restricted Eating Compared with Daily Caloric Restriction: A Randomized Trial in Adults with Obesity. Obesity 2022, 30, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, J.d.N.; Macedo, R.C.O.; dos Santos, G.C.; Munhoz, S.V.; Machado, C.L.F.; de Menezes, R.L.; Menzem, E.N.; Moritz, C.E.J.; Pinto, R.S.; Tinsley, G.M.; et al. Cardiometabolic Effects of Early v. Delayed Time-Restricted Eating plus Energetic Restriction in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: An Exploratory Randomised Clinical Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 129, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewski, P.; Konieczny, M.; Dybek, T.; Łukaniszyn-Domaszewska, K.; Anton, S.; Sadowska-Krępa, E.; Skorupska, E. Comparison of the Effects of Six-Week Time-Restricted Eating on Weight Loss, Body Composition, and Visceral Fat in Overweight Older Men and Women. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 174, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, H.; Abiri, B.; Khodami, B.; Yari, Z.; Lafzi Ghazi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, N.; Saidpour, A. Effect of Time Restricted Feeding on Anthropometric Measures, Eating Behavior, Stress, Serum Levels of BDNF and LBP in Overweight/Obese Women with Food Addiction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Cienfuegos, S.; Ezpeleta, M.; Gabel, K.; Pavlou, V.; Mulas, A.; Chakos, K.; McStay, M.; Wu, J.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; et al. Time-Restricted Eating Without Calorie Counting for Weight Loss in a Racially Diverse Population: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steger, F.L.; Jamshed, H.; Bryan, D.R.; Richman, J.S.; Warriner, A.H.; Hanick, C.J.; Martin, C.K.; Salvy, S.-J.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Eating Affects Weight, Metabolic Health, Mood, and Sleep in Adherent Completers: A Secondary Analysis. Obesity 2023, 31 (Suppl. S1), 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, R.; Maaloul, R.; Tagougui, S.; Neffati, F.; Hadj Kacem, F.; Najjar, M.F.; Ammar, A.; Hammouda, O. Unlocking the Power of Synergy: High-Intensity Functional Training and Early Time-Restricted Eating for Transformative Changes in Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Health in Inactive Women with Obesity. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cienfuegos, S.; Gabel, K.; Kalam, F.; Ezpeleta, M.; Pavlou, V.; Lin, S.; Wiseman, E.; Varady, K.A. The Effect of 4-h versus 6-h Time Restricted Feeding on Sleep Quality, Duration, Insomnia Severity and Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults with Obesity. Nutr. Health Berkhamsted Herts. 2022, 28, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adafer, R.; Messaadi, W.; Meddahi, M.; Patey, A.; Haderbache, A.; Bayen, S.; Messaadi, N. Food Timing, Circadian Rhythm and Chrononutrition: A Systematic Review of Time-Restricted Eating’s Effects on Human Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.D.; Panda, S. Fasting, Circadian Rhythms, and Time-Restricted Feeding in Healthy Lifespan. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arble, D.M.; Bass, J.; Laposky, A.D.; Vitaterna, M.H.; Turek, F.W. Circadian Timing of Food Intake Contributes to Weight Gain. Obesity 2009, 17, 2100–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoogian, E.N.C.; Chow, L.S.; Taub, P.R.; Laferrère, B.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Eating for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Diseases. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 405–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantranupong, L.; Wolfson, R.L.; Sabatini, D.M. Nutrient-Sensing Mechanisms across Evolution. Cell 2015, 161, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrow, J.S.; Summerbell, C.D. Meta-Analysis: Effect of Exercise, with or without Dieting, on the Body Composition of Overweight Subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic Obesity in Older Adults: Aetiology, Epidemiology and Treatment Strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Nieuwenhuizen, A.; Tomé, D.; Soenen, S.; Westerterp, K.R. Dietary Protein, Weight Loss, and Weight Maintenance. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cava, E.; Yeat, N.C.; Mittendorfer, B. Preserving Healthy Muscle during Weight Loss. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, M.J.; Wackerhage, H.; Spangenburg, E.E.; Booth, F.W. Control of the Size of the Human Muscle Mass. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 799–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, J.W.; Sitren, H.S.; Daniels, M.J.; Langkamp-Henken, B. Effects of Variation in Protein and Carbohydrate Intake on Body Mass and Composition during Energy Restriction: A Meta-Regression. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varady, K.A.; Lin, S.; Oddo, V.M.; Cienfuegos, S. Debunking the Myths of Intermittent Fasting. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 503–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurens, C.; Grundler, F.; Damiot, A.; Chery, I.; Le Maho, A.; Zahariev, A.; Le Maho, Y.; Bergouignan, A.; Gauquelin-Koch, G.; Simon, C.; et al. Is Muscle and Protein Loss Relevant in Long-Term Fasting in Healthy Men? A Prospective Trial on Physiological Adaptations. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.D.; Sen, A.; Gordon, P.M. Influence of Resistance Exercise on Lean Body Mass in Aging Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasiakos, S.M.; Cao, J.J.; Margolis, L.M.; Sauter, E.R.; Whigham, L.D.; McClung, J.P.; Rood, J.C.; Carbone, J.W.; Combs, G.F.; Young, A.J. Effects of High-Protein Diets on Fat-Free Mass and Muscle Protein Synthesis Following Weight Loss: A Randomized Controlled Trial. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3837–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Wan, K.; Miyashita, M.; Ho, R.S.; Zheng, C.; Poon, E.T.; Wong, S.H. The Effect of Time-Restricted Eating Combined with Exercise on Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, E.; Beyl, R.A.; Poggiogalle, E.; Hsia, D.S.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Reduces Appetite and Increases Fat Oxidation But Does Not Affect Energy Expenditure in Humans. Obesity 2019, 27, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Kang, J.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yu, J.M.; Cho, S.T.; Oh, C.-M.; Kim, T. Beneficial Effects of Time-Restricted Eating on Metabolic Diseases: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaix, A.; Zarrinpar, A.; Miu, P.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Feeding Is a Preventative and Therapeutic Intervention against Diverse Nutritional Challenges. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.H.; Yockey, S.R. Weight Loss and Improvement in Comorbidity: Differences at 5%, 10%, 15%, and Over. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooley, J.J. Circadian Regulation of Lipid Metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiegler, P.; Cunliffe, A. The Role of Diet and Exercise for the Maintenance of Fat-Free Mass and Resting Metabolic Rate during Weight Loss. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).