GFRAL Is Widely Distributed in the Brain and Peripheral Tissues of Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Immunofluorescence Labeling and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.3. Antibody Validation with HFF-1 and HEK293 Cells
3. Results
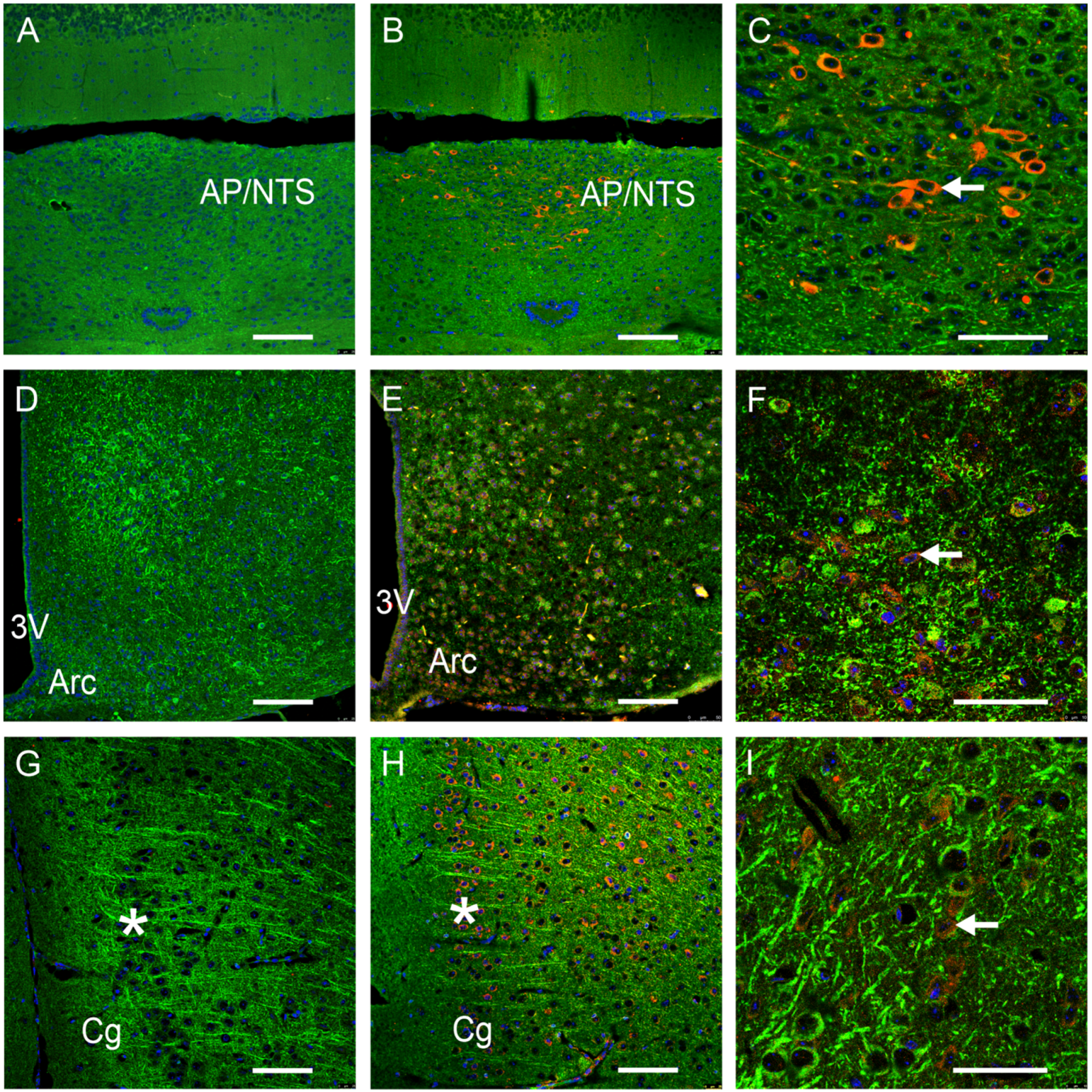
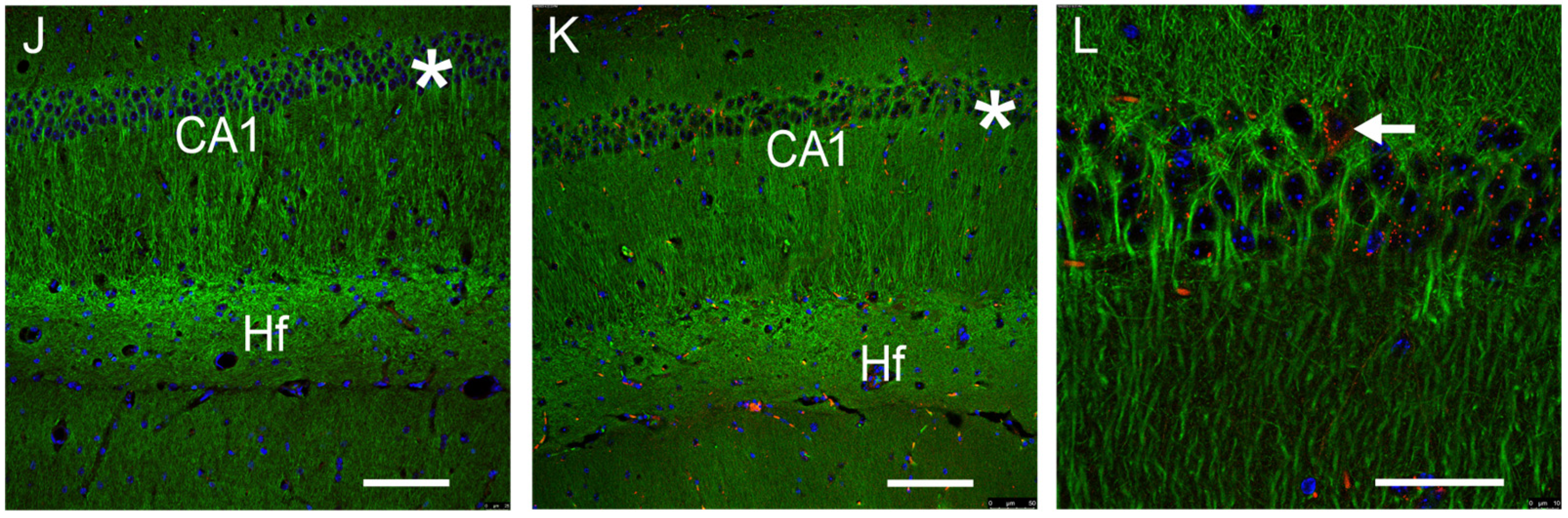
3.1. GFRAL-IR Is Expressed in Various Mouse Brain Areas
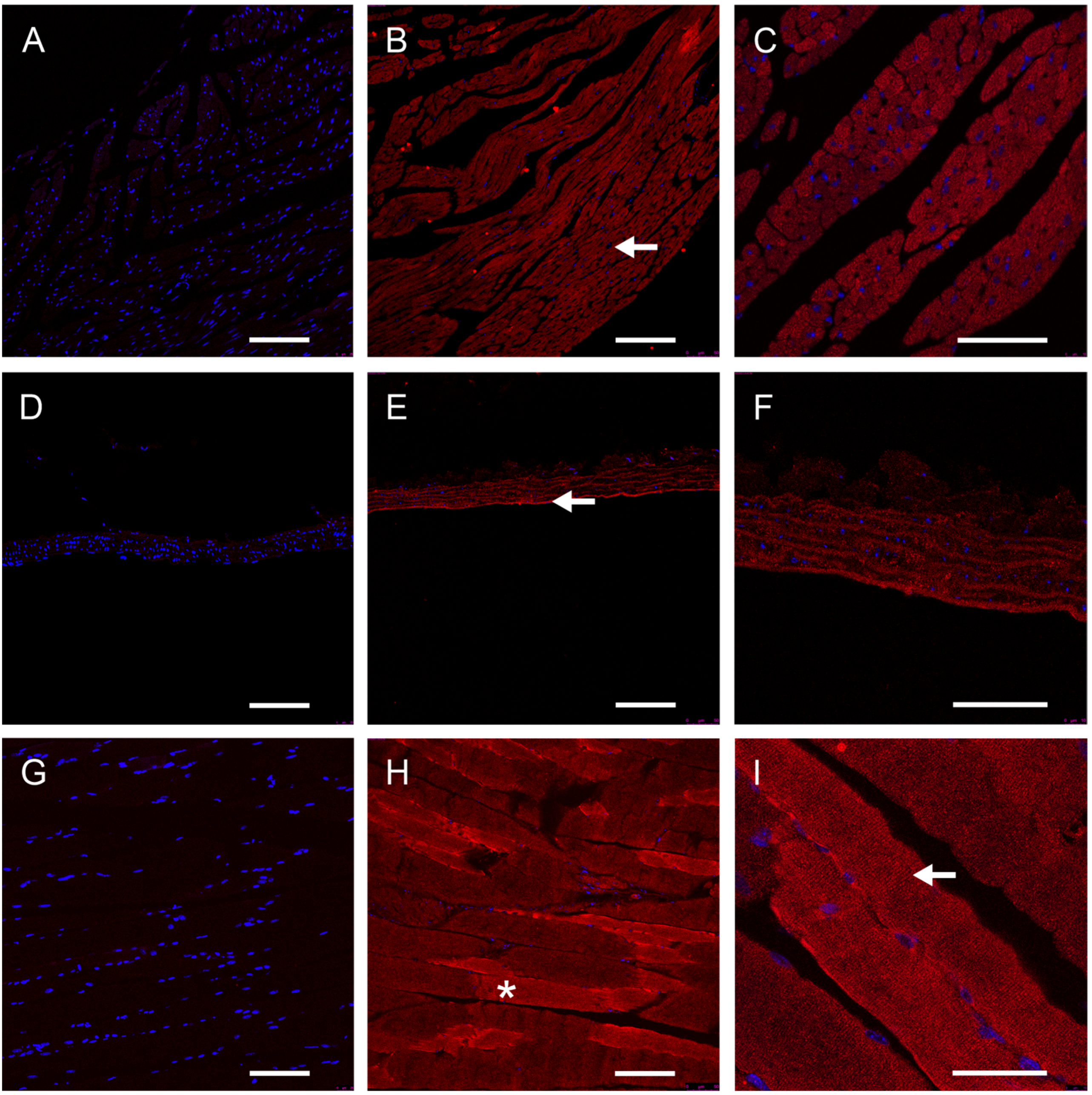
3.2. Peripheral Tissues of Mice Express GFRAL-IR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, J.-Y.; Crawley, S.; Chen, M.; Ayupova, D.A.; Lindhout, D.A.; Higbee, J.; Kutach, A.; Joo, W.; Gao, Z.; Fu, D.; et al. Non-homeostatic body weight regulation through a brainstem-restricted receptor for GDF15. Nature 2017, 550, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullican, S.E.; Lin-Schmidt, X.; Chin, C.-N.; Chavez, J.A.; Furman, J.L.; Armstrong, A.A.; Beck, S.C.; South, V.J.; Dinh, T.Q.; Cash-Mason, T.D.; et al. GFRAL is the receptor for GDF15 and the ligand promotes weight loss in mice and nonhuman primates. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, V.W.W.; Husaini, Y.; Sainsbury, A.; Brown, D.A.; Breit, S.N. The MIC-1/GDF15-GFRAL Pathway in Energy Homeostasis: Implications for Obesity, Cachexia, and Other Associated Diseases. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johann, K.; Kleinert, M.; Klaus, S. The Role of GDF15 as a Myomitokine. Cells 2021, 10, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostálová, I.; Roubícek, T.; Bártlová, M.; Mráz, M.; Lacinová, Z.; Haluzíková, D.; Kaválková, P.; Matoulek, M.; Kasalicky, M.; Haluzík, M. Increased serum concentrations of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The influence of very low calorie diet. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, V.W.; Zhang, H.P.; Manandhar, R.; Lee-Ng, K.K.M.; Lebhar, H.; Marquis, C.P.; Husaini, Y.; Sainsbury, A.; Brown, D.A.; Breit, S.N. Treatment with the TGF-b superfamily cytokine MIC-1/GDF15 reduces the adiposity and corrects the metabolic dysfunction of mice with diet-induced obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, A.P.; Chen, M.; Taskar, P.; Rimmington, D.; Patel, S.; Tadross, J.A.; Cimino, I.; Yang, M.; Welsh, P.; Virtue, S.; et al. GDF15 mediates the effects of metformin on body weight and energy balance. Nature 2020, 578, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Day, E.A.; Townsend, L.K.; Djordjevic, D.; Jørgensen, S.B.; Steinberg, G.R. GDF15: Emerging biology and therapeutic applications for obesity and cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostálová, I.; Kaválková, P.; Papežová, H.; Domluvilová, D.; Zikán, V.; Haluzík, M. Association of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 with nutritional status, body composition and bone mineral density in patients with anorexia nervosa: The influence of partial realimentation. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewska-Kupczewska, M.; Kowalska, I.; Nikolajuk, A.; Adamska, A.; Otziomek, E.; Gorska, M.; Straczkowski, M. Hyperinsulinemia acutely increases serum macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 concentration in anorexia nervosa and obesity. Clin. Endocrinol. 2012, 76, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomgaard, P.; Hansen, J.S.; Townsend, L.K.; Gudiksen, A.; Secher, N.H.; Clemmesen, J.O.; Støving, R.K.; Goetze, J.P.; Wright, D.C.; Pilegaard, H. GDF15 is an exercise-induced hepatokine regulated by glucagon and insulin in humans. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1037948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bootcov, M.R.; Bauskin, A.R.; Valenzuela, S.M.; Moore, A.G.; Bansal, M.; He, X.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Donnellan, M.; Mahler, S.; Pryor, K.; et al. MIC-1, a novel macrophage inhibitory cytokine, is a divergent member of the TGF-beta superfamily. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11514–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttner, M.; Laaff, M.; Schechinger, B.; Rappold, G.; Unsicker, K.; Suter-Crazzolara, C. Characterization of the rat, mouse, and human genes of growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage inhibiting cytokine-1 (GDF-15/MIC-1). Gene 1999, 237, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strelau, J.; Sullivan, A.; Böttner, M.; Lingor, P.; Falkenstein, E.; Suter-Crazzolara, C.; Galter, D.; Jaszai, J.; Krieglstein, K.; Unsicker, K. Growth/differentiation factor-15/macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 is a novel trophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons in vivo. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8597–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Portal. Available online: https://www.gtexportal.org/home/gene/GDF15 (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Breit, S.N.; Brown, D.A.; Tsai, V.W.-W. The GDF15-GFRAL Pathway in Health and Metabolic Disease: Friend or Foe? Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chang, C.-C.; Sun, Z.; Madsen, D.; Zhu, H.; Padkjær, S.B.; Wu, X.; Huang, T.; Hultman, K.; Paulsen, S.J.; et al. GFRAL is the receptor for GDF15 and is required for the anti-obesity effects of the ligand. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerson, P.J.; Wang, F.; Du, Y.; Liu, Q.; Pickard, R.T.; Gonciarz, M.D.; Coskun, T.; Hamang, M.J.; Sindelar, D.K.; Ballman, K.K.; et al. The metabolic effects of GDF15 are mediated by the orphan receptor GFRAL. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Wu, X.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Paraoan, L.; Zhou, J. Identification, expression and functional characterization of the GRAL gene. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Clark, M.S.; Palmiter, R.D. Deciphering a neuronal circuit that mediates appetite. Nature 2012, 483, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, V.W.-W.; Manandhar, R.; Jørgensen, S.B.; Lee-Ng, K.K.M.; Zhang, H.P.; Marquis, C.P.; Jiang, L.; Husaini, Y.; Lin, S.; Sainsbury, A.; et al. The anorectic actions of the TGFβ cytokine MIC-1/GDF15 require an intact brainstem area postrema and nucleus of the solitary tract. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriben, R.; Chen, M.; Higbee, J.; Oeffinger, J.; Ventura, R.; Li, B.; Mondal, K.; Gao, Z.; Ayupova, D.; Taskar, P.; et al. Antibody-mediated inhibition of GDF15-GFRAL activity reverses cancer cachexia in mice. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, S.M.; Saudek, V.; O’Rahilly, S. GDF15: A Hormone Conveying Somatic Distress to the Brain. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnaa007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Townsend, L.K.; DesOrmeaux, G.J.; Frangos, S.M.; Batchuluun, B.; Dumont, L.; Kuhre, R.E.; Ahmadi, E.; Hu, S.; Rebalka, I.A.; et al. GDF15 promotes weight loss by enhancing energy expenditure in muscle. Nature 2023, 619, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, P.; Silvestre, R.A.; Díez, J.J. Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) in endocrinology. Endocrine 2023, 81, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimeault, M.; Batra, S.K. Divergent molecular mechanisms underlying the pleiotropic functions of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 224, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Portal. Available online: https://www.gtexportal.org/home/gene/GFRAL (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Fairlie, W.D.; Moore, A.G.; Bauskin, A.R.; Russell, P.K.; Zhang, H.P.; Breit, S.N. MIC-1 is a novel TGF-beta superfamily cytokine associated with macrophage activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.M.; Blázquez, J.L.; Guerra, M. The design of barriers in the hypothalamus allows the median eminence and the arcuate nucleus to enjoy private milieus: The former opens to the portal blood and the latter to the cerebrospinal fluid. Peptides 2010, 31, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korf, H.-W.; Møller, M. Arcuate nucleus, median eminence, and hypophysial pars tuberalis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 180, 227–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindowski, K.; von Bohlen und Halbach, O.; Strelau, J.; Ridder, D.A.; Herrmann, O.; Schober, A.; Schwaninger, M.; Unsicker, K. Regulation of GDF-15, a distant TGF-β superfamily member, in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiariello, A.; Valente, S.; Pasquinelli, G.; Baracca, A.; Sgarbi, G.; Solaini, G.; Medici, V.; Fantini, V.; Poloni, T.E.; Tognocchi, M.; et al. The expression pattern of GDF15 in human brain changes during aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1058665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.; Martucci, M.; Mosconi, G.; Chiariello, A.; Cappuccilli, M.; Totti, V.; Santoro, A.; Franceschi, C.; Salvioli, S. GDF15 Plasma Level Is Inversely Associated With Level of Physical Activity and Correlates With Markers of Inflammation and Muscle Weakness. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Biancotto, A.; Moaddel, R.; Moore, A.Z.; Gonzalez-Freire, M.; Aon, M.A.; Candia, J.; Zhang, P.; Cheung, F.; Fantoni, G.; et al. Plasma proteomic signature of age in healthy humans. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.S.; Goeminne, L.J.E.; Kim, J.T.; Tian, J.W.; Kim, S.-H.; Nga, H.T.; Kang, S.G.; Kang, B.E.; Byun, J.-S.; Lee, Y.-S.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 protects against the aging-mediated systemic inflammatory response in humans and mice. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccitelli, C.; Selbach, M. mRNAs, proteins and the emerging principles of gene expression control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, T.C.; Gorse, K.; Herrmann, J.R.; Kochanek, P.M. Hippocampal and Prefrontal Cortical Brain Tissue Levels of Irisin and GDF15 Receptor Subunits in Children. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldarelli, R.M.; Smith, C.M.; Finger, J.H.; Hayamizu, T.F.; McCright, I.J.; Xu, J.; Shaw, D.R.; Beal, J.S.; Blodgett, O.; Campbell, J.; et al. The mouse Gene Expression Database (GXD): 2021 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D924–D931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, K.; Antosik, P.; Grzanka, D.; Gagat, M.; Smolińska, M.; Grzanka, A.; Gzil, A.; Kasperska, A.; Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska, A. Expression of the Body-Weight Signaling Players: GDF15, GFRAL and RET and their clinical relevance in Gastric Cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4698–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ni, B.; Wang, H. Upregulated GDF-15 expression facilitates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through orphan receptor GFRAL. Aging 2020, 12, 22564–22581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, C.; Parmar, A.; Murphy, E.; Carper, D.; Lair, B.; Maes, P.; Vion, J.; Boulet, N.; Fontaine, C.; Marquès, M.; et al. Growth and differentiation factor 15 is secreted by skeletal muscle during exercise and promotes lipolysis in humans. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e131870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yin, C.; Lan, X.; Wu, L.; Du, X.; Griffiths, H.R.; Gao, D. Adipokines, Hepatokines and Myokines: Focus on Their Role and Molecular Mechanisms in Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 873699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcot, V.; Lu, Y.; Highland, H.M.; Schurmann, C.; Justice, A.E.; Fine, R.S.; Bradfield, J.P.; Esko, T.; Giri, A.; Graff, M.; et al. Protein-altering variants associated with body mass index implicate pathways that control energy intake and expenditure in obesity. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittekind, D.A.; Scholz, M.; Kratzsch, J.; Löffler, M.; Horn, K.; Kirsten, H.; Witte, V.; Villringer, A.; Kluge, M. Genome-wide association and transcriptome analysis suggests total serum ghrelin to be linked with GFRAL. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, K.; Medori, M.C.; Macchia, A.; Cecchin, S.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Beccari, T.; Gatta, V.; Stuppia, L.; Benfatti, V.; Dalla Ragione, L.; et al. Genetic variants identified in novel candidate genes for anorexia nervosa and analysis of molecular pathways for diagnostic applications. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fichtner, K.; Kalwa, H.; Lin, M.-M.; Gong, Y.; Müglitz, A.; Kluge, M.; Krügel, U. GFRAL Is Widely Distributed in the Brain and Peripheral Tissues of Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050734
Fichtner K, Kalwa H, Lin M-M, Gong Y, Müglitz A, Kluge M, Krügel U. GFRAL Is Widely Distributed in the Brain and Peripheral Tissues of Mice. Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):734. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050734
Chicago/Turabian StyleFichtner, Karoline, Hermann Kalwa, Miao-Miao Lin, Yuanyuan Gong, Anne Müglitz, Michael Kluge, and Ute Krügel. 2024. "GFRAL Is Widely Distributed in the Brain and Peripheral Tissues of Mice" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050734
APA StyleFichtner, K., Kalwa, H., Lin, M.-M., Gong, Y., Müglitz, A., Kluge, M., & Krügel, U. (2024). GFRAL Is Widely Distributed in the Brain and Peripheral Tissues of Mice. Nutrients, 16(5), 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050734




