Biotechnological, Nutritional, and Therapeutic Applications of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Its By-Products: A Review of the Past Five-Year Findings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Botanic and Agronomic Features
3. Nutritive Features
| Cultivar | RBQ | - | Quinoa Preta | - | BRS Piabiru | Ames 13.727 | - | Jessie | - |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | Bolivia | USA | Peru; Spain | China | Brazil | Asia | - | Europe | Ecuador |
| Nutrients 1 (%) | |||||||||
| Energy (kcal) | - | - | 424.0 | - | 389 | 345.9 | 359 | 340.7 | - |
| Protein | 12.52 | 10.82 | 14.6 | 71.76 | 17.0 | 14.24 | 13.5 | 15.96 | 16.70 |
| Fat | 6.48 | 4.65 | 6.8 | 1.4 | 6.0 | 10.6 | 6.48 | 5.10 | - |
| Carbohydrate | - | 74.10 | 76.1 | - | 66.5 | - | 57.2 | 50.07 | - |
| Fiber | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.53 | 15.33 | 11.10 |
| Ash | 2.43 | 2.08 | 2.7 | 1.66 | 2.1 | - | 2.44 | 3.33 | 1.96 |
| Sugars | 2.36 | - | 3.1 | - | 1.17 | - | 4.31 | 2.81 | - |
| Amide | - | - | - | 22.04 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Minerals 2 | |||||||||
| Calcium | - | 43.98 | - | - | - | 1.7 | - | 87.9 | 0.18 |
| Iron | - | 4.80 | - | - | - | 0.15 | - | 7.9 | 7.8 |
| Magnesium | - | 195.07 | - | - | - | 2.9 | - | 205.5 | 0.16 |
| Potassium | - | 387.28 | - | - | - | 16 | - | 908.8 | 0.33 |
| Sodium | - | 16.18 | - | - | - | 2.95 | - | 11.7 | 0.02 |
| Phosphorus | - | 599.43 | - | - | - | - | - | 550.3 | 0.32 |
| Amino acids 2 | |||||||||
| EAAs | |||||||||
| Histidine | - | 2.98 | - | 3.51 | - | - | 0.36 | 7.54 | 2.31 |
| Isoleucine | - | 3.86 | - | 3.2 | - | - | 0.49 | 4.46 | 2.87 |
| Leucine | - | 7.01 | - | 5.91 | - | - | 0.79 | 5.43 | - |
| Lysine | - | 6.28 | - | 5.45 | - | - | 0.78 | 13.55 | 3.81 |
| Valine | - | 4.65 | - | 3.01 | - | - | 0.61 | 5.66 | 3.81 |
| Threonine | - | 4.21 | - | 2.01 | - | - | 0.49 | 7.82 | 2.62 |
| Methionine + Cystine | - | - | - | 1.88 | - | - | 0.46 | 1.57 | - |
| Tryptophan | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.48 | - |
| NEAAs | |||||||||
| Phenylalanine + Tyrosine | - | 7.30 | - | 4.97 | - | - | 1.24 | 6.8 | 3.31 |
| Glutamic acid | - | 15.66 | - | 13.39 | - | - | 1.77 | 14.39 | 13.44 |
| Aspartic acid | - | 9.06 | - | 7.88 | - | - | 1.07 | 11.39 | 7.68 |
| Alanine | - | 4.80 | - | 2.68 | - | - | 0.55 | 3.51 | 2.87 |
| Glycine | - | 5.68 | - | 4.02 | - | - | 1.13 | 4.22 | 11.00 |
| Arginine | - | 9.32 | - | 7.64 | - | - | 0.68 | 7.79 | 6.50 |
| Proline | - | 3.93 | - | 2.70 | - | - | 0.49 | - | 2.87 |
| Serine | - | 4.98 | - | 3.12 | - | - | 0.61 | 3.95 | 8.19 |
| Fatty acids 1 (relative %) | |||||||||
| C14:0 | 0.14 | - | - | - | 0.277 | 0.48 | - | 0.19 | - |
| C16:0 | 8.86 | - | 20 | - | 11.09 | 12.06 | - | 9.02 | - |
| C16:1 | 0.09 | - | - | - | 0.088 | 0.30 | - | 0.13 | - |
| C17:0 | 0.18 | - | - | - | 0.058 | - | - | 0.06 | - |
| C18:0 | 0.78 | - | - | - | 0.786 | 1.62 | - | 0.47 | - |
| C18:1 | 29.84 | - | 32 | - | 22.67 | 21.9 | - | 17.93 | - |
| C18:2 | 50.16 | - | 31 | - | 56.70 | 54.38 | - | 61.40 | - |
| C18:3n3 | 6.52 | - | - | - | 2.74 | 9.11 | - | 7.17 | - |
| C20:1 | 1.35 | - | - | - | 1.50 | - | - | 0.32 | - |
| C20:4 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.40 | - | 0.28 | - |
| C22:1 | 1.16 | - | - | - | 1.78 | - | - | 1.31 | - |
| References | [36] | [37] | [38] | [39] | [40] | [41] | [42] | [43] | [44] |
| Vitamins (100 mg g−1) | Quinoa A | Quinoa A | Quinoa B | Corn C | Sorghum D | Rice E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascorbic acid | - | - | - | 6.8 | - | 1.66 |
| α tocopherol | 1.39 | 0.919 | 2.44 | 0.07 | 0.32 | 4.91 |
| β tocopherol | 0.063 | - | 0.08 | - | 0.012 | - |
| γ tocopherol | 0.053 | 2.67 | 4.55 | - | 0.092 | - |
| δ tocopherol | - | - | 0.35 | - | 0 | - |
| Thiamine | 0.13 | - | 0.36 | 0.155 | 0.79 | 4.30 |
| Riboflavin | 0.03 | - | 0.32 | 0.055 | 0.05 | 1.66 |
| Niacin | 12.35 | - | 1.52 | 1.77 | - | 6.63 |
| References | [45] | [40] | [30] | [46] | [47] | [48] |
4. Phytocomponents from Quinoa with Potential to Benefit Human Health
4.1. Phenolic Compounds
| Cultivar/Origin | Part of the Plant/Extract or Isolated Compounds | Investigated | Experimental Model | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White quinoa, United Arab Emirates | Water-soluble extract of whole grain fermented by Bifidobacterium spp. | Cytotoxic, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, and antioxidant activities | In vitro enzymatic and antioxidant assays, tumor cell lines | Solid-state fermentation improved the biological activities of quinoa; fermented grains showed significant antihypertensive and antioxidant activities. | [57] |
| White quinoa, Spain; white, black, and red quinoas, Bolivia; white quinoa, Peru | Grain flour ultrasonically extracted using 80% methanol → 70% acetone; extracts combined at the end | Antioxidant capacity | DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging tests; ferric ion reducing assay potential (FRAP) and ferrous ion chelation capacity | Peruvian white and Bolivian black quinoa samples showed the best antioxidant activities in all assays, with good correlations with total phenolic and flavonoid contents. | [36] |
| Ecuador | Quinoa protein concentrate obtained from grain flour → peptides released in digestion collected by ultrafiltration | Antioxidant and chemopreventive activities | Static in vitro gastrointestinal digestion; colon cancer cell culture; ORAC assay | Peptides < 5 kDa showed the highest antioxidant activity and peptides > 5 kDa promoted the greatest anticancer effects. | [35] |
| 28 varieties from Bolivia, Chile, Denmark, USA, and Peru | Quinoa oil extracted with n-hexane → 3 mL methanol/water solution (4:1, v/v) | Antioxidant capacity | DPPH and FRAP chemical assays | Variability in total phenolic and carotenoid contents, which is reflected in different antioxidant capacities. Conspicuous amounts of phytosterols and squalene were detected in the samples. | [58] |
| Spain | Grain extracts obtained via ultrasound-assisted extraction with ethanol → concentration with butanol | Pancreatic lipase and alpha-glucosidase inhibition effects | In vitro enzymatic assays, intestinal simulatedconditions | The extracts (saponins + phenolics) had inhibitory effects on pancreatic lipase and alpha-glucosidase. While intestinal conditions worsened the inhibition of lipase, it slightly catalyzed the α-amylase. | [59] |
| Bolivia | Methanol extracts from whole grains and industrial by-products (mixed quinoa and amaranth flakes) | Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities | ABTS, FRAP, and CUPRAC antioxidant assays; human cervical carcinoma cell lines | The evaluated material is a significant source of antioxidant compounds and has demonstrated inhibitory activity against cancer cells at different stages. | [60] |
| Cultivars MengLi 1 and MengLi 2, China | Aqueous extracts of sprouted and non-sprouted quinoa seed yogurts | Antioxidant capacity in vitro | ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC antioxidant assays | Germinated quinoa yogurts had good antioxidant capacities in all tests, with high levels of flavonoids and total phenolics. | [61] |
| USA | Soluble phenolic compounds obtained by sequential hydrolysis (alkaline and acid) from quinoa seeds, sprouts, and flakes | Antioxidant activity | Static in vitro gastrointestinal digestion; ORAC and DPPH assay | The results indicate that quinoa flavonoids (mainly quercetin and kaempferol glycosides) are bioaccessible and that their release in the gastrointestinal tract may have strong antioxidant activity against free radicals. | [56] |
| 38 colorful cultivars from the Altiplano region of Puno, Peru | Free phenolics extracted from grains with acid (HCl)-methanol/water (50:50, v/v); grain betalains extracted with a water/methanol solution (80:20, v/v) | Antioxidant activity | DPPH assay; Vis-NIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy | The study demonstrated that the total antioxidant capacity of colored quinoa seeds, including non-extractable and extractable antioxidants, can be predicted by Vis-NIR spectra coupled with chemometrics. | [55] |
| BRS Piabiru, Brazil | Ethanol/water extract (80:20, v/v) of the grain | Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities, hepatotoxicity | Oxidative hemolysis inhibition assay (OxHLIA) and inhibition of the production of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) (cell-based methods); plate microdilution and INT assay; pig liver cell culture | In this pioneering study of Brazilian quinoa, four organic acids (quinic acid as the main one), and α- and γ-tocopherols as isoforms of vitamin E were detected. Quercetin and kaempferol glycosides were the principal phenolics of the extract that presented antioxidant and antimicrobial activities, without toxic effects. | [40] |
| Red quinoa, Peru | Phenolic fraction obtained by extraction with hexane in Soxhlet, followed by extraction of the residue with ethanol | Neuroprotective effect | Mice with scopolamine-induced memory deficits; memory test; ex vivo acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, CAT and SOD activities; ROS and TBARS assays | The extract prevented induced declarative memory deficit and restored antioxidant indicators and AChE activity. | [54] |
| Cultivar MengLi 2, China | Oleanolic acid (OA) extracted from sprouted quinoa yogurts | Antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antiangiogenic activities | DPPH and ABTS chemical assays, in vitro inhibition of dipeptidyl dipeptidase DPP-4; human umbilical endothelial cells | Quinoa OA had its concentration optimized by the germination process and showed antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antiangiogenic activities. Sprouted quinoa can be exploited to obtain OA nutraceuticals or consumed as a food/functional ingredient. | [62] |
| White quinoa, China | Soluble (SDF) and insoluble (IDF) dietary fiber extracted from grain | Antioxidant and hypoglycemic capabilities | DPPH, FRAP, hydroxyl radical assays; in vitro inhibition of alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase; glucose adsorption capacity and glucose dialysis delay index | Polyphenols bound to insoluble fiber were responsible for the superior DPPH radical scavenging activity and α-amylase inhibitory activity compared with insoluble fiber. | [63] |
| Red quinoa, Spain | Saponin-rich methanolic extracts by ultrasound-assisted extraction → acid hydrolysis | Pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity and hypocholesterolemic effect | In vitro enzymatic assays; in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of cholesterol | The hydrolysis of saponin-rich extracts enhanced compounds’ bioactivities and can be used to obtain multifunctional products to inhibit pancreatic lipase and cholesterol absorption at the same time. | [64] |
| Argentina | Hydroalcoholic extracts of germinated quinoa grain obtained under subcritical conditions | Antioxidant activity | TEAC, FRAP, and ORAC chemical tests; Rancimat accelerated oxidation test | The authors found excellentantioxidant capabilities for extracts rich in bioactives obtained from germinated quinoa, which revealed the potential for application in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products. | [65] |
| China | Polysaccharides isolated by membrane technology from the aqueous extract of the grain | Antioxidant, antidiabetic, and immunoregulatory potential | DPPH and ABTS tests; in vitro inhibition of alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase; RAW 264.7 cell cultures, and instrumental analysis | Three fractions of polysaccharides, formed mainly by glucose, galactose, and arabinose, exertedimmunoregulatory activity in RAW264.7 cells and dose-dependent in vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic activities. | [66] |
| MengLi, China | Polysaccharide isolated from the grain by alkaline extraction and purified with column chromatography | Antioxidant capacity in vitro | DPPH, ABTS, hydroxyl radical, superoxide radical, and ferric-reducing capacity assays | The authors obtained and characterized the structure of the polysaccharide, which showed promising radical scavenging activities in all assays performed. | [67] |
| Altiplano, Peru | Bioactive peptides (BP) obtained from quinoa protein → hydrolysis with alcalase and trypsin | Antioxidant activity and alpha-glucosidase inhibition effect | ABTS+ radical scavenging activity; inhibitory measurement of alpha-glucosidase enzyme in vitro | BP showed the highest antioxidant activity; the best α-glucosidase inhibitor was generated by trypsin. These preparations could be used to produce nutraceuticals or food ingredients. | [68] |
| Red quinoa, Peru | Grain ethanolic extract | Neuroprotective effect | Drosophila melanogaster with rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease (PD); behavioral tests; dopamine dosage, AChE, CAT, and SOD tyrosine activities; ROS and TBARS assays | Quinoa extract protected against rotenone toxicity, indicating potential as an adjunct in the treatment of PD. This effect may be related to the phenolics in the extract, which showed antioxidant action and the ability to modulate some enzymes. | [69] |
| Canada | Bioactive peptides (BP) isolated from hulled grain protein concentrate via electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes | Antihypertensive and antidiabetic properties | In vitro glucose uptake;animal model of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) | PB were able to modulate L6 cell glucose with a potential antidiabetic effect. A decrease in systolic blood pressure was observed in the presence of fractionated peptides, with 100 mg/kg as a dose comparable to captopril (positive control) | [70] |
| China | Water-soluble polysaccharides (QP) obtained by a successive extraction and purification protocol developed by the authors | Antioxidant activity; antiaging effects | ABTS and DPPH chemical tests; male Kunming mice submitted to the Morris water maze test, biochemical analysis, and histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis | QP demonstrated antiaging effects in vivo, restoring the cognitive impairment of aging induced by D-galactose. Administration of 800 mg·kg−1 for 10 weeks decreased oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation, improved organ function, and restored lipid metabolism and SIRT1 pathway regulation. | [71] |
| Egypt | Whole seeds | Hypoglycemic and antidiabetic effects | Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats | Quinoa ingestion had a hypoglycemic and improvement effect on cholesterol, HDL, and LDL levels. | [72] |
4.2. Saponins
4.3. Peptides
4.4. Polysaccharides and Dietary Fiber
5. Biotechnological Potential of Quinoa Grains and Quinoa Biowastes
5.1. Food Technology
5.2. Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Industries
5.3. Other Biotechnological Potentialities
6. Attention Points: Antinutritional Substances in Quinoa Raw Seeds and Their Use in Human and Animal Nourishment
7. Final Considerations and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, A. Shaping a sustainable food future by rediscovering long-forgotten ancient grains. Plant Sci. 2018, 269, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alandia, G.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Kyvsgaard, N.C.; Condori, B.; Liu, F. Nitrogen sustains seed yield of quinoa under intermediate drought. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2016, 202, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, I.D.L.; Chantelle, L.; Magnani, M.; Cordeiro, A.M.T.D.M. Nutritional, therapeutic, and technological perspectives of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): A review. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, F.; Bazile, D.; Biaggi, C.; Callo-Concha, D.; Jacquet, J.; Jemal, O.M.; King, O.I.; Mbosso, C.; Padulosi, S.; Speelman, E.N.; et al. When neglected species gain global interest: Lessons learned from quinoa’s boom and bust for teff and minor millet. Glob. Food Sec. 2022, 32, 100613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrosan, M.; Tan, T.C.; Easa, A.M.; Gammoh, S.; Alu’datt, M.H. Recent updates on lentil and quinoa protein-based dairy protein alternatives: Nutrition, technologies, and challenges. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, A.C.; Sanlier, N. A new generation plant for the conventional cuisine: Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhai, Q.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Hou, Z.; Cao, Y.; Feng, J.; Xue, P. Safety assessment of crude saponins from Chenopodium quinoa willd. husks: 90-day oral toxicity and gut microbiota & metabonomics study in rats. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alandia, G.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Bazile, D.; Condori, B. Global expansion of quinoa and challenges for the Andean region. Glob. Food Sec. 2020, 26, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrali, D.; Giupponi, L.; De la Peña-Armada, R.; Villanueva-Suárez, M.J.; Mateos-Aparicio, I. The quinoa variety influences the nutritional and antioxidant profile rather than the geographic factors. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 133531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Peñas, E.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Pseudocereal grains: Nutritional value, health benefits and current applications for the development of gluten-free foods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzai, H. Trends in Quinoa Adoption in Marginal Areas: An Assessment of Economic Viability and Policy Outlook. J. Agribus. Rural Dev. 2020, 3, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, B.; Goyal, A.; Irshaan, S.; Kumar, V.; Sihag, M.K.; Patel, A.; Kaur, I. Quinoa. In Whole Grains and Their Bioactives: Composition and Health, 1st ed.; Johnson, J., Wallace, T.C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 269–305. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, É.G.F.; Barbosa, J.C.; de Oliveira Penna, L.; Neves, E.O.; Pereira, P.A.P.; da Cunha, S.F.V.; Vasconcelos, C.M. Maceração de grãos de Chenopodium quinoa Willd: Efeito do tempo e temperatura. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e399119483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaikishun, S.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Song, S. Quinoa: In perspective of global challenges. Agronomy 2019, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.I.; Farooq, M.; Syed, Q.A.; Ishaq, A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Hatamleh, A.A. Botany, nutritional value, phytochemical composition and biological activities of quinoa. Plants 2021, 10, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manaa, A.; Goussi, R.; Derbali, W.; Cantamessa, S.; Abdelly, C.; Barbato, R. Salinity tolerance of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) as assessed by chloroplast ultrastructure and photosynthetic performance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 162, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, M.W.; Trinh, M.D.L.; Nørrevang, A.F.; Bendtsen, A.K.; Wang, C.; Østerberg, J.T.; Shabala, S.; Hedrich, R.; Wendt, T.; Palmgren, M. The epidermal bladder cell-free mutant of the salt-tolerant quinoa challenges our understanding of halophyte crop salinity tolerance. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K.; Gatti, R.C.; Mitra, A. Climate change-induced salinity variation impacts on a stenoecious mangrove species in the Indian Sundarbans. Ambio 2017, 46, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, R.C.; Di Gioia, F.; Ferreira, I.C.; Petropoulos, S.A. Halophytes for future horticulture: The case of small-scale farming in the mediterranean basin. In Handbook of Halophytes, 1st ed.; Grigore, M.N., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, D.E.; Ho, Y.S.; Lightfoot, D.J.; Schmöckel, S.M.; Li, B.; Borm, T.J.; Ohyanagi, H.; Mineta, K.; Michell, C.T.; Saber, N.; et al. The genome of Chenopodium quinoa. Nature 2017, 542, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazile, D. Quinoa, A Model Crop for Tomorrow’s Agriculture. In Biology and Biotechnology of Quinoa, 1st ed.; Varma, A., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, R.C.; Di Gioia, F.; Ferreira, I.C.; Petropoulos, S.A. Wild greens used in the Mediterranean diet. In The Mediterranean Diet, 2nd ed.; Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, V.I.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Shabala, S. Salt tolerance mechanisms in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcios, A.E.; Weichgrebe, D.; Papenbrock, J. Potential use of the facultative halophyte Chenopodium quinoa Willd. as substrate for biogas production cultivated with different concentrations of sodium chloride under hydroponic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, G.; D’Ambrosio, T.; Rinaldi, M.; Rascio, A. Heritabilities of morphological and quality traits and interrelationships with yield in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) genotypes in the Mediterranean environment. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 70, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifacio, A. Quinoa breeding and modern variety development. In State of the Art Report on Quinoa Around the World in 2013, 1st ed.; Bazile, D., Bertero, D., Nieto, C., Eds.; FAO and CIRAD: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 172–191. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i4042e.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Buckland, K.; Rasmussen, A.; Smith, E. Quinoa Production for the Willamette Valley, 1st ed.; Oregon State University Extension Service: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2020; Available online: https://catalog.extension.oregonstate.edu/em9300/html (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Ahmadi, S.H.; Solgi, S.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Quinoa: A super or pseudo-super crop? Evidences from evapotranspiration, root growth, crop coefficients, and water productivity in a hot and semi-arid area under three planting densities. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 225, 105784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Walia, S.; Kumar, R. Functional composition, physiological effect and agronomy of future food quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): A review. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 118, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) as source of bioactive compounds: A review. Bioact. Compd. Health Dis. 2019, 2, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, E.E.; Uslu, N.; Ghafoor, K.; AL-Juhaimi, F.; Özcan, M.M.; Ahmed, I.A.M. Variations in bioactive properties, fatty acid compositions, and phenolic compounds of quinoa grain and oils roasted in a pan. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Verruma-Bernardi, M.R.; Forti, V.A.; Borges, M.T.M.R. Quinoa and amaranth as functional foods: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 2277–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, V.; Miguel Silva, P.; Crispim Massuela, D.; Khan, M.W.; Hamar, A.; Khajehei, F.; Graeff-Hönninger, S.; Piatti, C. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): An overview of the potentials of the “golden grain” and socio-economic and environmental aspects of its cultivation and marketization. Foods 2020, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navruz-Varli, S.; Sanlier, N. Nutritional and health benefits of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcacundo, R.; Miralles, B.; Carrillo, W.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. In vitro chemopreventive properties of peptides released from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) protein under simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Lucas-Gonzales, R.; Ricci, A.; Fontecha, J.; Fernandez-Lopez, J.; Perez-Alvarez, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M. Chemical, fatty acid, polyphenolic profile, techno-functional and antioxidant properties of flours obtained from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Sim, K.H. Nutritional value and the kaempferol and quercetin contents of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) from different regions. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 50, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Encina-Zelada, C.; Barros, L.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Cadavez, V.; Ferreira, I.C. Chemical and nutritional characterization of Chenopodium quinoa Willd (quinoa) grains: A good alternative to nutritious food. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, R.; Yuan, W. Composition and secondary structure of proteins isolated from six different quinoa varieties from China. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.L.; Fernandes, Â.; Pereira, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Sokovic, M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Nutritional value, physicochemical characterization and bioactive properties of the Brazilian quinoa BRS Piabiru. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2969–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaitov, B.; Karimov, A.A.; Toderich, K.; Sultanova, Z.; Mamadrahimov, A.; Allanov, K.; Islamov, S. Adaptation, grain yield and nutritional characteristics of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) genotypes in marginal environments of the Aral Sea basin. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 44, 1365–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lietz, G.; Seal, C.J. Phenolic, apparent antioxidant and nutritional composition of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seeds. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3245–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.J.R.; Prieto, J.M.; Sobrado, V.C.; Magro, P.C. Nutritional characterization of six quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) varieties cultivated in Southern Europe. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 99, 103876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacrés, E.; Quelal, M.; Galarza, S.; Iza, D.; Silva, E. Nutritional value and bioactive compounds of leaves and grains from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Plants 2022, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradini Filho, A.M.; Borges, J.T.D.S.; Sant’ana, H.M.P.; Chaves, J.B.P.; Medeiros, E.A.A.; Pirozi, M.R. Nutritional characterization of Quinoa from brazilian variety BRs Piabiru. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 93299–93304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyuan, S.; Tong, L.; Liu, R. Corn phytochemicals and their health benefits. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, S.S.; Anunciação, P.C.; de Morais Cardoso, L.; Della Lucia, C.M.; de Carvalho, C.W.P.; Queiroz, V.A.V.; Sant’Ana, H.M.P. Stability of B vitamins, vitamin E, xanthophylls and flavonoids during germination and maceration of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.). Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.; Eleazu, C.; Igweibor, N.; Ugwu, C.; Enwefa, G.; Nwigboji, N. Comparative study on the nutrients, heavy metals and pesticide composition of some locally produced and marketed rice varieties in Nigeria. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, M.; Roberto, M.; Dmitriev, B. Determination of physiological maturity of four quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) varieties for introduction in the Russian Federation. Res. Crop. 2022, 23, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshahidi, L.K.; Caballero, E.; Osses, A.; Hyland, B.W.; Ternan, N.G.; Gill, C.I. Modest improvement in CVD risk markers in older adults following quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) consumption: A randomized-controlled crossover study with a novel food product. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3313–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lietz, G.; Bal, W.; Watson, A.; Morfey, B.; Seal, C. Effects of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) consumption on markers of CVD risk. Nutrients 2018, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choque Delgado, G.T.; Carlos Tapia, K.V.; Pacco Huamani, M.C.; Hamaker, B.R. Peruvian Andean grains: Nutritional, functional properties and industrial uses. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 9634–9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, R.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Garg, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Fiorino, M.; Ameen, S.M.; Haddad, M.A.; Al-Hiary, M. Natural polyphenols: Chemical classification, definition of classes, subcategories, and structures. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, S.P.; Roos, A.A.; Gindri, A.L.; Domingues, V.O.; Ascari, J.; Guerra, G.P. Neuroprotective effect of red quinoa seeds extract on scopolamine-induced declarative memory deficits in mice: The role of acetylcholinesterase and oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 69, 103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macavilca, E.A.; Condezo-Hoyos, L. Assessment of total antioxidant capacity of altiplano colored quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) by visible and near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and chemometrics. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 134, 110182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Schneider, R.G. Quinoa flavonoids and their bioaccessibility during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Johnson, S.K.; Liu, S.Q.; Al-Mheiri, A.; Abushelaibi, A. Cytotoxicity, antihypertensive, antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of solid-state fermented lupin, quinoa and wheat by Bifidobacterium species: In-vitro investigations. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 95, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Aluwi, N.A.; Saunders, S.R.; Ganjyal, G.M.; Medina-Meza, I.G. Metabolic fingerprinting unveils quinoa oil as a source of bioactive phytochemicals. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, T.; Del Hierro, J.N.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Inhibitory effect of quinoa and fenugreek extracts on pancreatic lipase and α-amylase under in vitro traditional conditions or intestinal simulated conditions. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paśko, P.; Tyszka-Czochara, M.; Namieśnik, J.; Jastrzębski, Z.; Leontowicz, H.; Drzewiecki, J.; Martinez-Ayala, A.L.; Nemirovski, A.; Barasch, D.; Gorinstein, S. Cytotoxic, antioxidant and binding properties of polyphenols from the selected gluten-free pseudocereals and their by-products: In vitro model. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 87, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiroghene, O.J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Zhang, C.; Lv, J.; Pang, X.; Zhang, M. Antioxidant capacity of germinated quinoa-based yoghurt and concomitant effect of sprouting on its functional properties. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 116, 108592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiroghene, O.J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Jing, L.; Liu, L.; Pang, X.; Lv, J. Bioactive assessment of the antioxidative and antidiabetic activities of oleanane triterpenoid isolates of sprouted quinoa yoghurt beverages and their anti-angiogenic effects on HUVECS line. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xiong, M.; Bai, T.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Huang, Z.; Qin, W. Comparative study on the structure, physicochemical, and functional properties of dietary fiber extracts from quinoa and wheat. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 111816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Hierro, J.N.; Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The hydrolysis of saponin-rich extracts from fenugreek and quinoa improves their pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity and hypocholesterolemic effect. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufari, J.R.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, A.C.; Bergesse, A.E.; Miranda-Villa, P.P.; Nepote, V.; Velez, A.R. Bioactive compounds extraction from malted quinoa using water-ethanol mixtures under subcritical conditions. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 138, 110574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, B. Physicochemical properties, structural characterization and biological activities of polysaccharides from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seeds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Qin, P.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Yao, Y.; Ren, G. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of alkali-extracted polysaccharides from quinoa. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Moslehishad, M.; Salami, M. Antioxidant and alpha-glucosidase enzyme inhibitory properties of hydrolyzed protein and bioactive peptides of quinoa. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrientos, M.S. Effect of Quinoa Extract on an Experimental Model of Parkinson’s Disease in Drosophila Melanogast. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Pampa, Uruguaiana, Brazil, 28 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- González-Muñoz, A.; Valle, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Bazinet, L.; Enrione, J. Production of antihypertensive and antidiabetic peptide fractions from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Hu, J.L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, X.; Guo, Z.-B.; Zou, L.; Wu, D.T. Physicochemical characteristics and biological activities of soluble dietary fibers isolated from the leaves of different quinoa cultivars. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamri, E.; Amany, B.; Bayomy, H. Quinoa seeds (Chenopodium Quinoa): Nutritional value and potential biological effects on hyperglycemic rats. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, E.; Savarino, P.; JS Claereboudt, E.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Deleu, M.; Lins, L.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Enhancing the membranolytic activity of chenopodium quinoa saponins by fast microwave hydrolysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigo, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Dovale, G.; Pastén, A.; Vega-Gálvez, A.; Aubourg, S.P. The effect of glazing based on saponin-free quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) extract on the lipid quality of frozen fatty fish. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Li, J.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Cao, J.; Chi, X.; Dong, Q. Screening for α-Glucosidase-Inhibiting Saponins from Pressurized Hot Water Extracts of Quinoa Husks. Foods 2022, 11, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Chemical characterization and bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds from saponin-rich extracts and their acid-hydrolysates obtained from fenugreek and quinoa. Foods 2020, 9, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taco, V.; Savarino, P.; Benali, S.; Villacrés, E.; Raquez, J.M.; Gerbaux, P.; Duez, P.; Nachtergael, A. Deep eutectic solvents for the extraction and stabilization of Ecuadorian quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) saponins. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Liu, R.; Cao, S.; Zhang, W.; Guanghong, Z. Meat protein based bioactive peptides and their potential functional activity: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1956–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanabria, R.O.G.; Merino, G.E.D.; Rivera, A.C.R. Uso de paja de quinua como alimento suplementario de ganado de leche. Pol. Con 2021, 6, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Xue, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, G. Improved antibacterial effects of alkali-transformed saponin from quinoa husks against halitosis-related bacteria. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, S.P.; Prado-Guerra, A.; Pérez, A.I.G.; Prieto, L.F.C. Study of quinoa plant residues as a way to produce energy through thermogravimetric analysis and indexes estimation. Renew. Energ. 2020, 146, 2224–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Teng, C.; Fan, X.; Guo, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Qin, P. Nutrient composition, functional activity and industrial applications of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, R.; Vásquez, G.; Colson, E.; Gerbaux, P.; Frischmon, C.; Nesic, A.; García, D.E.; Cabrera-Barjas, G. Phytostimulant properties of highly stable silver nanoparticles obtained with saponin extract from Chenopodium quinoa. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4987–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cássia Spacki, K.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Uber, T.M.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.; Peralta, R.A.; Moreira, R.d.F.P.M.; Helm, C.V.; de Lima, E.A.; Bracht, A.; et al. Full Exploitation of Peach Palm (Bactris gasipaes Kunth): State of the Art and Perspectives. Plants 2022, 11, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedi, M.A.; di Bari, V.; Ibbett, R.; Darwish, R.; Nwaiwu, O.; Umar, Z.; Agarwal, D.; Worrall, R.; Gray, D.; Foster, T. Upcycling and valorisation of food waste. In Routledge Handbook of Food Waste, 1st ed.; Reynolds, C., Soma, T., Spring, C., Lazell, J., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 413–427. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez Torres, O.P.; Barros Rodriguez, M.; Sanchez, D.; Guishca-Cunuhay, C. Comportamiento productivo, degradación ruminal y producción de gas in vitro en ovinos alimentados con dietas a base de residuos pos-cosecha de Chenopodium quinoa. Rev. Investig. Vet. Peru 2018, 29, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Ruiz, M.; Cañon-Jones, H.; Schlotterbeck, T.; Lopez, M.A.; Tomas, Á.; San Martín, R. Safety and efficacy of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) saponins derived molluscicide to control of Pomacea maculata in rice fields in the Ebro Delta, Spain. Crop Prot. 2018, 111, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tang, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, G. Preparation of a highly porous carbon material based on quinoa husk and its application for removal of dyes by adsorption. Materials 2018, 11, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Ramirez, A.; Salas-Veizaga, D.M.; Grey, C.; Karlsson, E.N.; Rodriguez-Meizoso, I.; Linares-Pastén, J.A. Integrated process for sequential extraction of saponins, xylan and cellulose from quinoa stalks (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 121, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laqui-Vilca, C.; Aguilar-Tuesta, S.; Mamani-Navarro, W.; Montaño-Bustamante, J.; Condezo-Hoyos, L. Ultrasound-assisted optimal extraction and thermal stability of betalains from colored quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) hulls. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurek, I.; Góral, I.; Gęsiński, K.; Wojciechowski, K. Effect of saponins from quinoa on a skin-mimetic lipid monolayer containing cholesterol. Steroids 2019, 147, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, K.G.; Durval, I.J.; Silva, I.A.; Fabiola, C.G. Emulsifying capacity of biosurfactants from Chenopodium quinoa and Pseudomonas aeruginosa UCP 0992 with focus of application in the cosmetic industry. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2020, 79, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.; Hou, Z.; Xue, P. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. husks against foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 149, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, G. Biodegradability of quinoa stalks: The potential of quinoa stalks as a forage source or as biomass for energy production. Fuel 2020, 266, 117064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghumman, A.; Mudgal, S.; Singh, N.; Ranjan, B.; Kaur, A.; Rana, J.C. Physicochemical, functional and structural characteristics of grains, flour and protein isolates of Indian quinoa lines. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 09982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariaeenejad, S.; Kavousi, K.; Jahanshahi, D.A.; Mamaghani, A.S.A.; Ghasemitabesh, R.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Salekdeh, G.H. Enzymatically triggered delignification through a novel stable laccase: A mixed in-silico/in-vitro exploration of a complex environmental microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 211, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariaeenejad, S.; Motamedi, E.; Salekdeh, G.H. Highly efficient removal of dyes from wastewater using nanocellulose from quinoa husk as a carrier for immobilization of laccase. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 349, 126833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester-Sánchez, J.; Fernández-Espinar, M.T.; Haros, C.M. Isolation of red quinoa fibre by wet and dry milling and application as a potential functional bakery ingredient. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zou, L. Anti-aging effects of polysaccharides from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) in improving memory and cognitive function. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 94, 105097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.E.; Builes, S.; Heredia Salgado, M.A.; Tarelho, L.A.; Arroyave, C.; Aristizábal, A.; Chavez, E. Adsorption of cadmium using biochars produced from agro-residues. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 14592–14602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.E.; Arroyave, C.; Aristizábal, A.; Almeida, B.; Builes, S.; Chavez, E. Reducing cadmium bioaccumulation in Theobroma cacao using biochar: Basis for scaling-up to field. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayibi, S.; Monlau, F.; Marias, F.; Thevenin, N.; Jimenez, R.; Oukarroum, A.; Alboulkas, A.; Zeroual, Y.; Barakat, A. Industrial symbiosis of anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis: Performances and agricultural interest of coupling biochar and liquid digestate. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeimi, A.; Khoshkam, S.; Eslaminejad, T. Natural cellulose fibers from Quinoa wastes reinforced carbon nanotube/ZnO bio-nanocomposite as a novel recyclable catalyst for oxidation reaction. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 7795–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Tian, S.; Chen, H.; Gao, S.; Dong, X.; Du, K. Advances in xylooligosaccharides from grain byproducts: Extraction and prebiotic effects. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawof, W. Ethical and Sustainable Cosmetics and Their Importance on Consumer Purchase Behavior. Undergraduate Honors Thesis, East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN, USA, 2021. Available online: https://dc.etsu.edu/honors/746 (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Vecino, X.; Rodríguez-López, L.; Ferreira, D.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B.; Rodrigues, L.R. Bioactivity of glycolipopeptide cell-bound biosurfactants against skin pathogens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, C.B.B.; Almeida, F.C.; Silva, I.A.; Souza, T.C.; Meira, H.M.; Rita de Cássia, F.; Luna, J.M.; Santos, V.A.; Converti, A.; Banat, I.M.; et al. Production of green surfactants: Market prospects. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 51, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Strobel, B.W.; Cedergreen, N. What is the aquatic toxicity of saponin-rich plant extracts used as biopesticides? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melini, V.; Melini, F. Functional components and anti-nutritional factors in gluten-free grains: A focus on quinoa seeds. Foods 2021, 10, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maridini Filho, A.M.; Pirozi, M.R.; Borges, J.T.D.S.; Pinheiro Sant’Ana, H.M.; Chaves, J.B.P.; Coimbra, J.S.D.R. Quinoa: Nutritional, functional, and antinutritional aspects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1618–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Mishra, V.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, S.; Vaishnav, A.; Singh, S.V. Industrial and Environmental Applications of Plant-Derived Saponins: An Overview and Future Prospective. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, B.L.; Rojas-Silva, P.; Rojo, L.E.; Delatorre-Herrera, J.; Baldeón, M.E.; Raskin, I. Innovations in health value and functional food development of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kataria, A.; Singh, B. Effect of thermal processing on the bioactive compounds, antioxidative, antinutritional and functional characteristics of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 160, 113256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
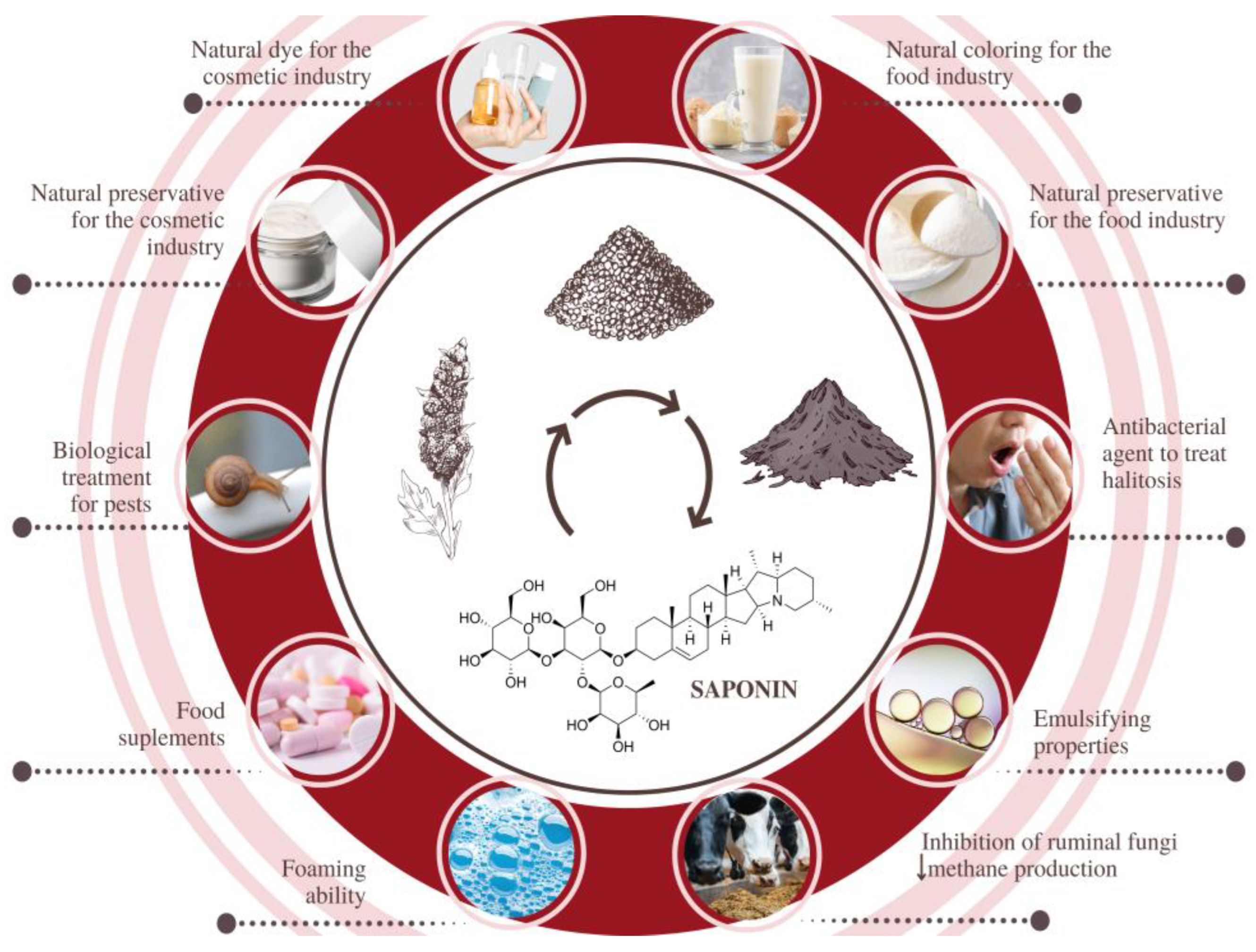

| Cultivar/Origin | Part of the Plant/Extract | Potential Application and Justification | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quinoa Real, Bolivia | Husk saponins, extracted with distilled water and modified by alkali treatment | Biological treatment of pests. Due to the toxicological properties and field effectiveness of the modified saponins, this molluscicide is a good candidate for the control of Pomacea maculata, without causing environmental damage. | [87] |
| China | Grain husks subjected to carbonization and chemical activation with KOH to produce porous carbon material | Removal of industrial dyes by adsorption. The biomaterial showed high adsorption rates for malachite green, rhodamine B, methyl violet, methylene blue, and methyl orange, dyes present in dyeing wastewater. | [88] |
| Real Blanca, Bolivia | Saponins, xylan, and cellulose from quinoa stalks | Valuable molecules for the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. Within the biorefinery approach, integrated processing to separate saponins, xylan, and cellulose is possible. | [89] |
| Five colorful cultivars, Peru | Quinoa husks extracted with ultrasound for the recovery of betalains and saponins | Natural and bifunctional ingredients (coloring function + preservative function) for the food and cosmetic industries. | [90] |
| Ancovinto ecotype, Chile | A saponin-free extract obtained from the grain | Food preservation. An innovative glazing system based on the inclusion of hydroethanolic extracts of saponin-free quinoa promoted the quality enhancement of frozen Atlantic mackerel. | [74] |
| Faro variety, Poland | Aqueous husk extracts rich in saponins | Cosmetic ingredients. Saponin-rich quinoa extracts can enhance skin penetration for cosmetic or pharmaceutical purposes. | [91] |
| No. Jingli-1, China | Quinoa husk saponins modified by alkali treatment | Antibacterial agent to treat halitosis. Interesting due to its excellent cost-effectiveness and notorious activity against three bacteria related to halitosis. | [80] |
| Ecuador | Post-harvest and threshing residues submitted to the drying | Sheep feeding. The use of 20% of quinoa residue in the diet of sheep can improve the productive parameters, possibly due to an improvement in the ruminal environment. | [86] |
| Spain | Aerial plant parts and seed husks | Both biomaterials showed potential for energy purposes. Aerial parts were shown to be a better fuel due to their calorific value (17.33 MJ/kg) and volatile matter (73.3%). | [81] |
| Brazil | Grain hydroethanolic extract | Emulsifying agents for the formulation of cosmetics. | [92] |
| China | Quinoa husks submitted to ultrasonic extractions with 75% anhydrous ethanol | Food preservative. Due to their great cost-effectiveness and antimicrobial potential, these saponins can be used against foodborne pathogenic bacteria. | [93] |
| Turkey | Dried stalks/stems | Quinoa stalks could be used for energy production; the authors found an energy value of 18.27 MJ/kg for the biowaste. | [94] |
| Various cultivars, India | Grains, flour and protein isolates | Enriching and functional food ingredients. One of the protein isolates demonstrated excellent foaming and emulsification properties. | [95] |
| Iran | Quinoa rusks | Substrate for the production of bioethanol via hydrolysis with laccase (isolated from a complex environment) and subsequent fermentation with S. cerevisiae. | [96] |
| Iran | Quinoa husk nanocellulose as a carrier for laccase immobilization | Removal of dyes from wastewater. Nanocellulose was tested as a nanocarrier for laccase immobilization and provided an efficient nanobiocatalyst for the removal of malachite green and congo red from water. | [97] |
| Red quinoa Real, Bolivia | Fractions of polyphenols and dietary fiber extracted from grains | Functional ingredients for baking. The incorporation of 5% of dietary fiber in bread allowed for increases in total fiber content, nutritional value, and antioxidant potential. | [98] |
| Nine different cultivars, China | Soluble dietary fiber isolated from leaves | Functionalizing or nutraceutical food ingredients. Dietary fibers had a remarkable effect on in vitro antioxidant activities, lipid and bile acid binding capacity, immunoregulatory activities, and prebiotic effects. | [99] |
| Ecuador | Quinoa straw transformed into biochar (for soil correction) | Biochar was efficient in reducing cadmium bioaccumulation in leaves and provided minerals to increase productivity. | [100,101] |
| Morocco | Quinoa waste, dried at 40 °C for three days and then ground | Substrate for biochar production via anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis. The simultaneous use of bioproducts promoted a substantial increase in tomato production. | [102] |
| Ecuador | Quinoa straw and stubble (waste from the threshing process) | Supplementary feed for dairy cattle. Partial replacement of commercial feed supplementation by a combination of silage-containing quinoa straw (20%) did not affect production indicators. | [79] |
| Iran | Cellulose fibers recovered from quinoa waste incorporated with multi-walled carbon/ZnO nanotubes (bio-nanocomposite) | Polymer for manufacturing a new recyclable biocatalyst for oxidation reactions. High conversions and excellent selectivity were verified for the oxidation of alcohols; the biocomposite can be applied in high-performance fabrics and smart materials. | [103] |
| China | Saponins recovered from quinoa husks by hot pressurized water extraction | Dietary supplements to control postprandial hyperglycemia and drug potential. The in vitro inhibition of alpha-glucosidase by saponins was higher than the value recorded for acarbose; molecular docking indicated triterpenoid saponins as the most bioactive. | [75] |
| White Real, Bolivia | Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) from quinoa stalks | Prebiotic and nutraceutical food ingredients. | [104] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casalvara, R.F.A.; Ferreira, B.M.R.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Yamaguchi, N.U.; Bracht, A.; Bracht, L.; Comar, J.F.; de Sá-Nakanishi, A.B.; de Souza, C.G.M.; Castoldi, R.; et al. Biotechnological, Nutritional, and Therapeutic Applications of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Its By-Products: A Review of the Past Five-Year Findings. Nutrients 2024, 16, 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060840
Casalvara RFA, Ferreira BMR, Gonçalves JE, Yamaguchi NU, Bracht A, Bracht L, Comar JF, de Sá-Nakanishi AB, de Souza CGM, Castoldi R, et al. Biotechnological, Nutritional, and Therapeutic Applications of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Its By-Products: A Review of the Past Five-Year Findings. Nutrients. 2024; 16(6):840. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060840
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasalvara, Rhaira Fernanda Ayoub, Bruna Mayara Roldão Ferreira, José Eduardo Gonçalves, Natália Ueda Yamaguchi, Adelar Bracht, Lívia Bracht, Jurandir Fernando Comar, Anacharis Babeto de Sá-Nakanishi, Cristina Giatti Marques de Souza, Rafael Castoldi, and et al. 2024. "Biotechnological, Nutritional, and Therapeutic Applications of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Its By-Products: A Review of the Past Five-Year Findings" Nutrients 16, no. 6: 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060840
APA StyleCasalvara, R. F. A., Ferreira, B. M. R., Gonçalves, J. E., Yamaguchi, N. U., Bracht, A., Bracht, L., Comar, J. F., de Sá-Nakanishi, A. B., de Souza, C. G. M., Castoldi, R., Corrêa, R. C. G., & Peralta, R. M. (2024). Biotechnological, Nutritional, and Therapeutic Applications of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and Its By-Products: A Review of the Past Five-Year Findings. Nutrients, 16(6), 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060840












