Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan Rice Bran, Exerts Anti-COVID-19 Effects and Boosts Immunity in Human Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Donors
2.2. Biobran
2.3. Antibodies and Reagents
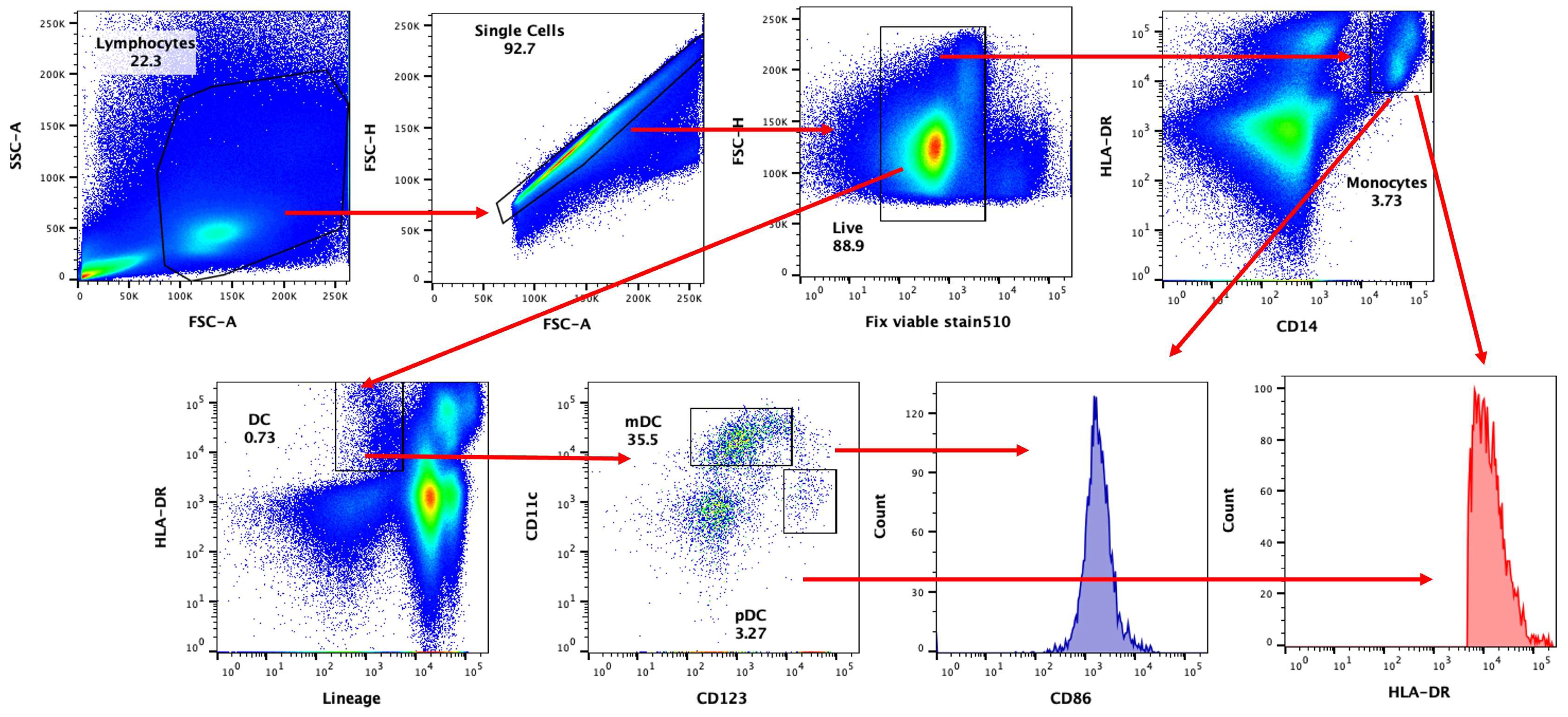
2.4. Immuno-Phenotyping (Flow Cytometry)
2.5. Multiplex Cytokine/Chemokine Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DCs and Monocytes Are Activated by SARS-CoV-2 in PBMCs
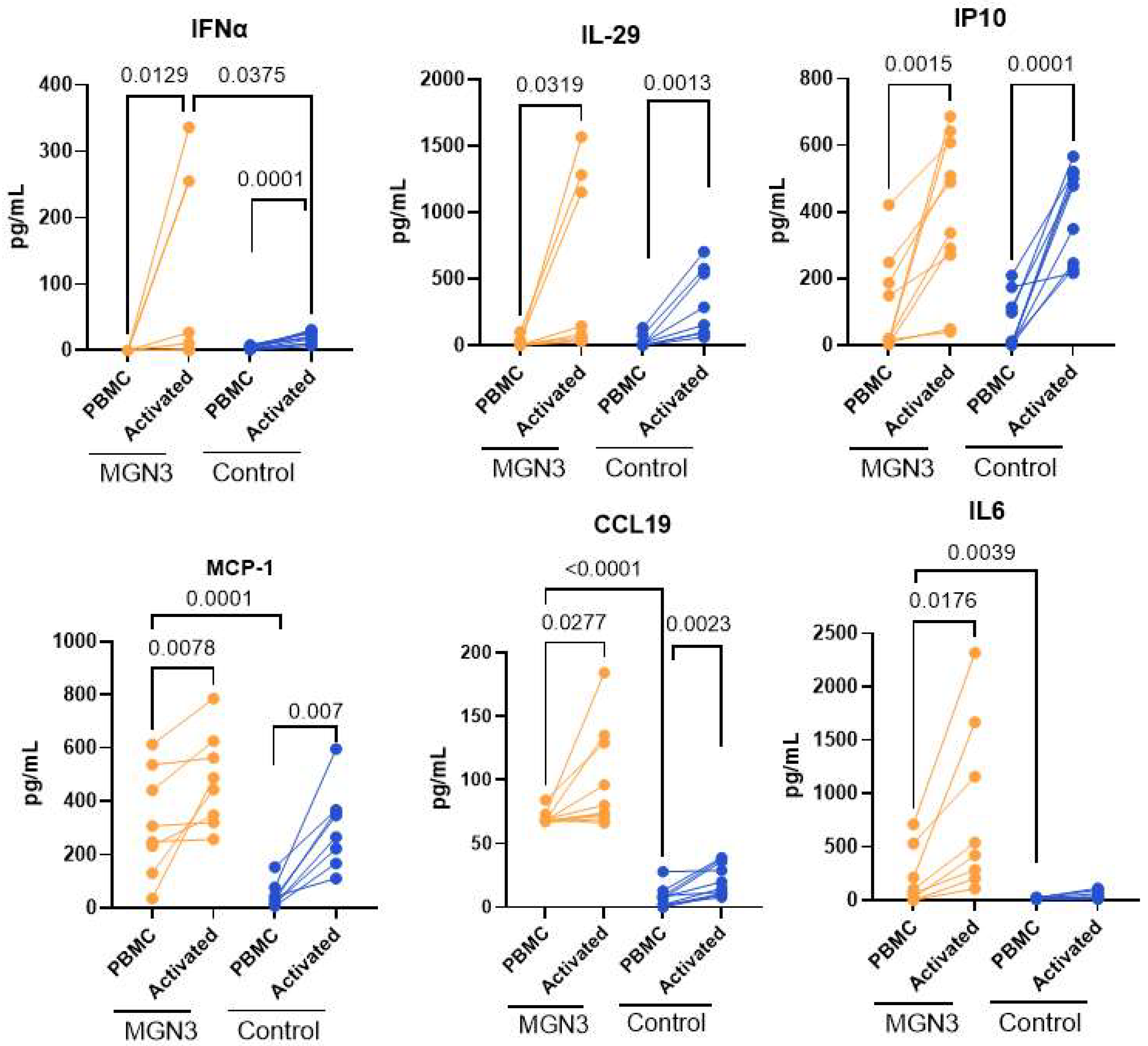
3.2. Secretion of Soluble Mediators from SARS-CoV-2-Stimulated PBMCs at 24 h
3.3. IFN-α Secretion at Day 7
3.4. T Cell Responses in the Biobran/MGN-3-Supplemented Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.-L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipman, M.; Chambers, R.C.; Singer, M.; Brow, J.S. SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: Clinical picture of COVID-19 and implications for research. Thorax 2020, 75, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rha, M.S.; Shin, E.C. Activation or exhaustion of CD8(+) T cells in patients with COVID-19. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, J.; Kalinke, U.; Oxenius, A. Regulation of antiviral T cell responses by type I interferons. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Innate immunity to virus infection. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 227, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza-Cabrerizo, M.; Cardoso, A.; Minutti, C.M.; Costa, M.P.d.; Sousa, C.R.e. Dendritic Cells Revisited. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 39, 131–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, R.M.; Banchereau, J. Taking dendritic cells into medicine. Nature 2007, 449, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marongiu, L.; Valache, M.; Facchini, F.A.; Granucci, F. How dendritic cells sense and respond to viral infections. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 2217–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.A.; Gálvez, N.M.S.; Andrade, C.A.; Pacheco, G.A.; Bohmwald, K.; Berrios, R.V.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M. The Role of Dendritic Cells During Infections Caused by Highly Prevalent Viruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Agrawal, S.; Cao, J.; Gupta, S.; Agrawal, A. Impaired secretion of interferons by dendritic cells from aged subjects to influenza: Role of histone modifications. Age 2013, 35, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, W.; Wang, T.; Ran, D.; Davalos, V.; Planas-Serra, L.; Pujol, A.; Esteller, M.; Wang, X.; Yu, H. Accelerated biological aging in COVID-19 patients. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, B.; Kwon, E.B.; Chung, H.S.; Choi, J.G. Mulberrofuran G, a mulberry component, prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection by blocking the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 receptor-binding domain and human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Natural products, alone or in combination with FDA-approved drugs, to treat COVID-19 and lung cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Horbanczuk, J.O.; Willschke, H.; Gai, Z.; Atanasov, A.G. The significance of natural product derivatives and traditional medicine for COVID-19. Processes 2020, 8, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Song, X.Q. Oral GS-441524 derivatives: Next-generation inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1015355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmi, F.; Vejux, A.; Ghzaiel, I.; Ksila, M.; Zarrouk, A.; Ghrairi, T.; Essadek, S.; Mandard, S.; Leoni, V.; Poli, G.; et al. Role of diet and nutrients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Incidence on oxidative stress, inflammatory status and viral production. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, J.S.; Johnson, J.B.; Steel, J.C.; Broszczak, D.A.; Neilsen, P.M.; Walsh, K.B.; Naiker, M. Natural product-derived phytochemicals as potential agents against coronaviruses: A review. Virus Res. 2020, 284, 197989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.E.; Senol Deniz, F.S. Natural products as potential leads against coronaviruses: Could they be encouraging structural models against SARS-CoV-2? Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2020, 10, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Moccia, S.; Spagnuolo, C.; Tedesco, I.; Russo, G.L. Roles of flavonoids against coronavirus infection. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 328, 109211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraiso, I.L.; Revel, J.S.; Stevens, J.F. Potential use of polyphenols in the battle against COVID-19. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.E.; Tawfeek, N.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Fikry, E. Agathis robusta Bark Essential Oil Effectiveness against COVID-19: Chemical Composition, In Silico and In Vitro Approaches. Plants 2022, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Propolis, Bee Honey, and Their Components Protect against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review of In Silico, In Vitro, and Clinical Studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.R.; Lin, C.S.; Lai, H.C.; Lin, Y.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.C.; Wu, K.C.; Huang, S.H.; Lin, C.W. Antiviral activity of Sambucus Formosan Nakai ethanol extract and related phenolic acid constituents against human coronavirus NL63. Virus Res. 2019, 273, 197767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zuckerman, D.M.; Brantley, S.; Sharpe, M.; Childress, K.; Hoiczyk, E.; Pendleton, A.R. Sambucus nigra extracts inhibit infectious bronchitis virus at an early point during replication. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroduske, A.; Jekabsons, K.; Riekstina, U.; Muceniece, R.; Rostoks, N.; Nakurte, I. Wild Sambucus nigra L. from north-east edge of the species range: A valuable germplasm with inhibitory capacity against SARS-CoV2 S-protein RBD and hACE2 binding in vitro. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 165, 113438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wei, J.; Huang, T.; Lei, L.; Shen, C.; Lai, J.; Yang, M.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits the replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in cultured Vero cells. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-H. Anti–SARS-CoV-2 Natural Products as Potentially Therapeutic Agents. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 590509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzoca, M.E.; Leuci, S.; Mignogna, M.D.; Muzio, E.L.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Muzio, L.L. Natural compounds may contribute in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection: A narrative review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemilä, H.; Chalker, E. Vitamin C may reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients: A meta-regression analysis. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemilä, H.; Chalker, E. Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: A meta-analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Abdulmalek, S.; Fadel, H.H. Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan Rice Bran, Protects against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): An In Vitro and In Silico Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.L.; Micalos, P.S.; Pak, S.C. Modified rice bran arabinoxylan as a nutraceutical in health and disease-A scoping review with bibliometric analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Agrawal, S. Activation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells in vitro by the biological response modifier arabinoxylan rice bran (MGN-3/Biobran). Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Agrawal, S. Mgn-3/biobran enhances generation of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells via upregulation of dec-205 expression on dendritic cells. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2014, 27, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Matsuura, M. Augmentation of macrophage phagocytosis by modified arabinoxylan rice bran (MGN-3/biobran). Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2004, 17, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaid, A.F.; Shaheen, M.; Ghoneum, M. Biobran/MGN-3, an arabinoxylan rice bran, enhances NK cell activity in geriatric subjects: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaid, A.F.; Agrawal, S.; Agrawal, A.; Ghoneum, M. Dietary Supplementation with Biobran/MGN-3 Increases Innate Resistance and Reduces the Incidence of Influenza-like Illnesses in Elderly Subjects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneum, M. Anti-HIV activity in vitro of MGN-3, an activated arabinoxylane from rice bran. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 243, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, H.; Medhat, E.; Shaheen, M.; Zekri, A.-R.N.; Darwish, T.; Ghoneum, M. Arabinoxylan rice bran (Biobran) suppresses the viremia level in patients with chronic HCV infection: A randomized trial. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaid, A.F.; Fahmi, R.M.; Shaheen, M.; Ghoneum, M. The enhancing effects of Biobran/MGN-3, an arabinoxylan rice bran, on healthy old adults’ health-related quality of life: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Qual. Life Res. 2020, 29, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Salazar, J.; Tran, T.M.; Agrawal, A. Sex-Related Differences in Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 739757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guan, F.; Miller, H.; Byazrova, M.G.; Cndotti, F.; Benlagha, K.; Camara, N.O.S.; Lei, J.; Filatov, A.; Liu, C. The role of dendritic cells in COVID-19 infection. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2195019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshbafnadi, M.; Zonouzi, S.K.; Sabahi, M.; Dolatshahi, M.; Aarabi, M.H. Aging & COVID-19 susceptibility, disease severity, and clinical outcomes: The role of entangled risk factors. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 154, 111507. [Google Scholar]
- Starke, K.R.; Reissig, D.; Petereit-Haack, G.; Schmauder, S.; Nienhaus, A.; Seidler, A. The isolated effect of age on the risk of COVID-19 severe outcomes: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, L. Aging of the Immune System: Research Challenges to Enhance the Health Span of Older Adults. Front. Aging 2020, 1, 602108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Aging of the Immune System. Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13 (Suppl. 5), S422–S428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueggeman, J.M.; Zhao, J.; Schank, M.; Yao, Z.Q.; Moorman, J.P. Trained Immunity: An Overview and the Impact on COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 837524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagovkina, N.V.; Zheleznov, L.M.; Subbotina, K.A.; Tsaan, A.A.; Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Gordeychuk, I.V.; Korduban, A.K.; Ivin, Y.Y.; Kovpak, A.A.; Piniaeva, A.N.; et al. accination with Oral Polio Vaccine Reduces COVID-19 Incidence. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 907341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.I.; Remington, S.J. Structure of wheat serine carboxypeptidase II at 3.5-A resolution. A new class of serine proteinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 6528–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Encinas, M.A.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Rascon-Chu, A.; Astiazaran-Garcia, H.F.; Valencia-Rivera, D.E. Ferulated Arabinoxylans and Their Gels: Functional Properties and Potential Application as Antioxidant and Anticancer Agent. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 2314759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, C.; Cheung, A.; Stark, Z.; Choo, S.; Downie, L.; White, S.; Conyers, R.; Cole, T. A novel presentation of homozygous loss-of-function STAT-1 mutation in an infant with hyperinflammation-A case report and review of the literature. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, H.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Chi, L.; Zhang, L.; Su, L. Type I interferons suppress viral replication but contribute to T cell depletion and dysfunction during chronic HIV-1 infection. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e94366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Hu, K.; Huang, L.; Lu, M.; Hu, Q. CCL19 and CCR7 Expression, Signaling Pathways, and Adjuvant Functions in Viral Infection and Prevention. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasagni, L.; Francalanci, M.; Annunziato, F.; Lazzeri, E.; Giannini, S.; Cosmi, L.; Sagrinati, C.; Mazzinghi, B.; Orlando, C.; Maggi, E.; et al. An alternatively spliced variant of CXCR3 mediates the inhibition of endothelial cell growth induced by IP-10, Mig, and I-TAC, and acts as functional receptor for platelet factor 4. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsen, S.G.; Aksoy, M.O.; Yang, Y.; Shahabuddin, S.; Litvin, J.; Safadi, F.; Rogers, T.J. The chemokine receptor CXCR3 and its splice variant are expressed in human airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, L584–L591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazirinejad, R.; Ahmadi, Z.; Arababadi, M.K.; Hassanshahi, G.; Kennedy, D. The biological functions, structure and sources of CXCL10 and its outstanding part in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Sanada, H.; Dohi, H.; Hirai, S.; Egashira, Y. Suppressive effect of modified arabinoxylan from rice Bran (MGN-3) on D-Galactosamine-induced IL-18 expression and hepatitis in rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Sugita, S.; Hirai, S.; Egashira, Y. Protective effect of low molecular fraction of MGN-3, a modified arabinoxylan from rice bran, on acute liver injury by inhibition of NF-kB and JNK/MAPK expression. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Hui, P.; Yarovinsky, T.O.; Badeti, S.; Pham, K.; Liu, C. Potential role of IFN-α in COVID-19 patients and its underlying treatment options. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4005–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Cui, C.; Tu, L.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Diversity of locally produced IFN-α subtypes in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells and mouse lung tissues during influenza virus infection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6351–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Han, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, D.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Luo, F.; Liu, Y. Subcutaneous injection of IFN alpha-2b for COVID-19: An observational study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, R.; González, D.; Rivero, H.B.; Rivero, J.C.; Pérez, A.; López, L.D.R.; Mezquia, N.; Venegas, R.; Betancourt, J.R.; Domínguez, R.E. Therapeutic effectiveness of interferon-α2b against COVID-19: The Cuban experience. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2020, 40, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herberman, R.B. Possible role of NK cells in host resistance against tumors and diseases. Clin. Immunol. Allergy 1983, 3, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, L.; Bottino, C.; Pende, D.; Mingari, M.C.; Biassoni, R.; Moretta, A. Human natural killer cells: Their origin, receptors and function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneum, M. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by modified arabinoxylan from rice bran (MGN-3). Int. J. Immunother. 1998, 14, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoneum, M.; Jewett, A. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma from human peripheral blood lymphocytes by MGN-3, arabinoxylan from rice bran, and its synergy with interleukin-2 in vitro. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2000, 24, 314–324. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoneum, M.; Abedi, S. Enhancement of natural killer cell activity of aged mice by modified arabinoxylan rice bran (MGN-3/Biobran). J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Martinez, A.; Valentín, J.; Fernández, L.; Hernández-Jiménez, E.; López-Collazo, E.; Zerbes, P.; Schwörer, E.; Nuñéz, F.; Martín, I.G.; Sallis, H.; et al. Arabinoxylan rice bran (MGN-3/Biobran) enhances natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity against neuroblastoma in vitro and in vivo. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Brown, J. NK immunorestoration of cancer patients by MGN-3, a modified arabinoxylan rice bran (study of 32 patients followed for up to 4 years). In Anti-Aging Medical Therapeutics, Vol. III; Klatz, R., Goldman, R., Eds.; Health Quest Publications: Marina del Rey, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Cholujova, D.; Jakubikova, J.; Czako, B.; Martisova, M.; Hunakova, L.; Duraj, J.; Mistrik, M.; Sedlak, J. MGN-3 arabinoxylan rice bran modulates innate immunity in multiple myeloma patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, S.P.; Martin, S.J. Mechanisms of granule-dependent killing. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzacco, L.; Trumpfheller, C.; Siegal, F.P.; Mehandru, S.; Markowitz, M.; Carrington, M.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Piperno, A.G.; Steinman, R.M. DEC-205 receptor on dendritic cells mediates presentation of HIV gag protein to CD8+ T cells in a spectrum of human MHC I haplotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, M.; Faridi, R.M.; Sligl, W.; Shabani-Rad, M.-T.; Dharmani-Khan, P.; Parker, A.; Kalra, A.; Tripathi, M.B.; Storek, J.; Tervaert, J.W.C.; et al. Impaired natural killer cell counts and cytolytic activity in patients with severe COVID-19. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5035–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, A.J.; Rustagi, A.; Zhao, N.Q.; Roque, J.; Martínez-Colón, G.J.; McKechnie, J.L.; Ivison, G.T.; Ranganath, T.; Vergara, R.; Hollis, T.; et al. A single-cell atlas of the peripheral immune response in patients with severe COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, B.; Knoll, R.; Bonaguro, L.; ToVinh, M.; Raabe, J.; Astaburuaga-García, R.; Schulte-Schrepping, J.; Kaiser, K.M.; Rieke, G.J.; Bischoff, J.; et al. Early IFN-α signatures and persistent dysfunction are distinguishing features of NK cells in severe COVID-19. Immunity 2021, 54, 2650–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Tizian, C.; Ferreira-Gomes, M.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Heinrich, F.; Frischbutter, S.; Angermair, S.; Hohnstein, T.; Mattiola, I.; et al. Untimely TGFβ responses in COVID-19 limit antiviral functions of NK cells. Nature 2021, 600, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Blish, C.A. Defining the role of natural killer cells in COVID-19. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agrawal, S.; Agrawal, A.; Ghoneum, M. Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan Rice Bran, Exerts Anti-COVID-19 Effects and Boosts Immunity in Human Subjects. Nutrients 2024, 16, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060881
Agrawal S, Agrawal A, Ghoneum M. Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan Rice Bran, Exerts Anti-COVID-19 Effects and Boosts Immunity in Human Subjects. Nutrients. 2024; 16(6):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060881
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgrawal, Sudhanshu, Anshu Agrawal, and Mamdooh Ghoneum. 2024. "Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan Rice Bran, Exerts Anti-COVID-19 Effects and Boosts Immunity in Human Subjects" Nutrients 16, no. 6: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060881
APA StyleAgrawal, S., Agrawal, A., & Ghoneum, M. (2024). Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan Rice Bran, Exerts Anti-COVID-19 Effects and Boosts Immunity in Human Subjects. Nutrients, 16(6), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060881






