Platycodi Radix Extract Prevents Hepatic Steatosis by Enhancing Bile Acid Synthesis in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Fatty Liver Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Platycodi Radix Extract
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Glucose and Insulin Tolerance Test
2.4. Histology
2.5. Serum Biochemistry and Liver Lipids Analysis
2.6. Protein Identification through LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.7. Bio-Informatic Analysis
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
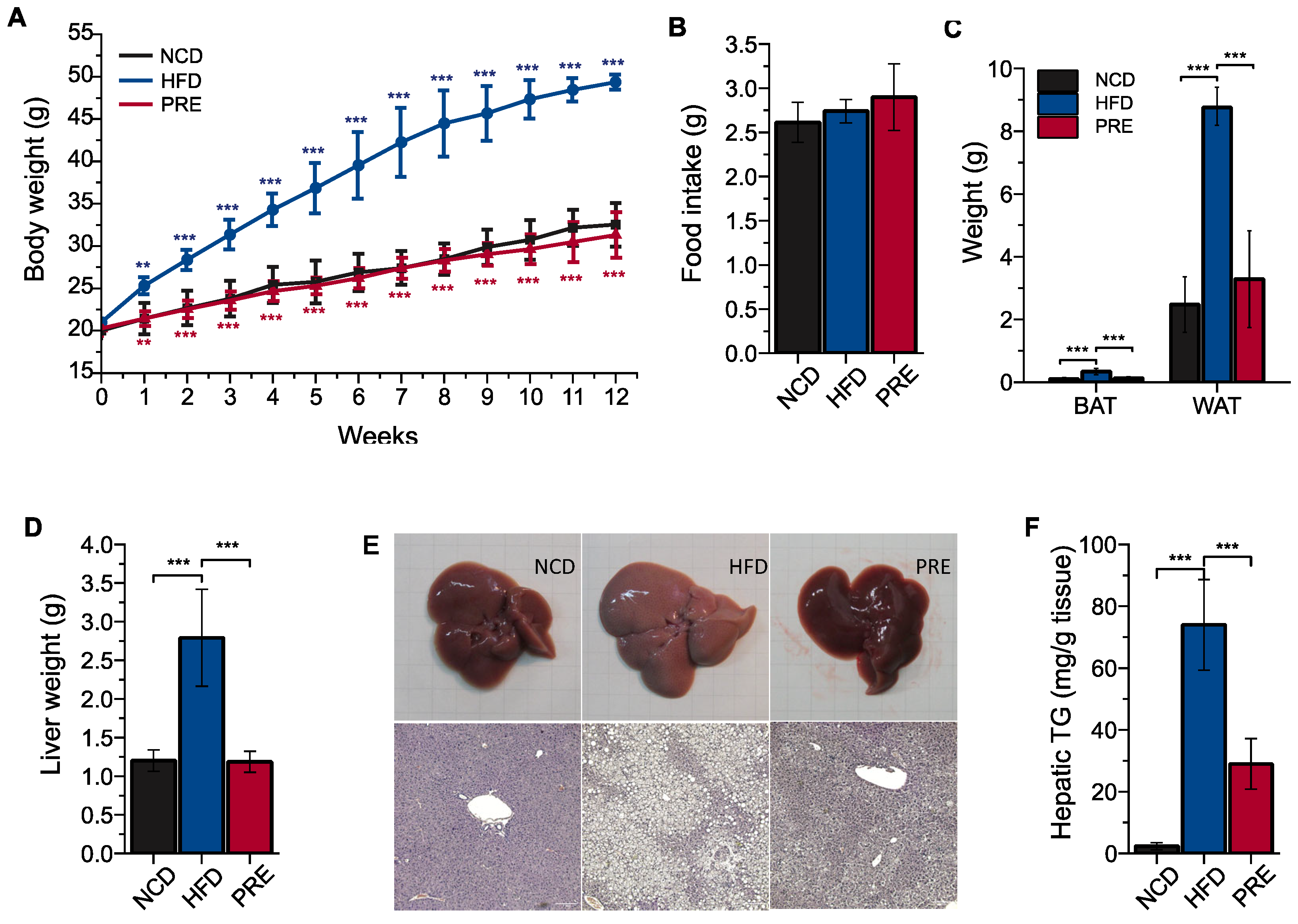
3.1. Preventive Effects of PRE on Obesity and Fatty Liver in an HFD-Induced NAFLD Mouse Model
3.2. Preventive Effects of PRE on Metabolic Disorders in an HFD-Induced NAFLD Mouse Model
3.3. Proteomic Analysis of the Biological Pathways Underlying PRE Effects in An HFD-Induced NAFLD Mouse Model
3.4. Experimental Validation of the Effect of PRE on Cholesterol and Bile Acid Metabolism in an HFD-Induced NAFLD Mouse Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buschemeyer, W.C., 3rd; Freedland, S.J. Obesity and prostate cancer: Epidemiology and clinical implications. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D.; Curtin, L.R.; McDowell, M.A.; Tabak, C.J.; Flegal, K.M. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 2006, 295, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; Kim, S.; Rusev, E.R.; Du, S.; Zizza, C. Measuring the full economic costs of diet, physical activity and obesity-related chronic diseases. Obes. Rev. 2006, 7, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagiri, S.; Naito, Y.; Ichikawa, H.; Mizushima, K.; Takagi, T.; Handa, O.; Kokura, S.; Yoshikawa, T. Bofutsushosan, an Oriental Herbal Medicine, Attenuates the Weight Gain of White Adipose Tissue and the Increased Size of Adipocytes Associated with the Increase in Their Expression of Uncoupling Protein 1 in High-Fat Diet-Fed Male KK/Ta mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2008, 42, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Patil, I.Y.; Jiang, T.; Sancheti, H.; Walsh, J.P.; Stiles, B.L.; Yin, F.; Cadenas, E. High-fat diet induces hepatic insulin resistance and impairment of synaptic plasticity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arguello, G.; Balboa, E.; Arrese, M.; Zanlungo, S. Recent insights on the role of cholesterol in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enjoji, M.; Yasutake, K.; Kohjima, M.; Nakamuta, M. Nutrition and nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease: The significance of cholesterol. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 925807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 2019, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluchowski, N.L.; Becuwe, M.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and liver disease: From basic biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechmann, L.P.; Hannivoort, R.A.; Gerken, G.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Trauner, M.; Canbay, A. The interaction of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firenzuoli, F.; Gori, L. Herbal Medicine Today: Clinical and Research Issues. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2007, 4, 594728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.M.; Ye, J.M. Strategies for the discovery and development of anti-diabetic drugs from the natural products of traditional medicines. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 16, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofowora, A.; Ogunbodede, E.; Onayade, A. The role and place of medicinal plants in the strategies for disease prevention. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Yao, Y.; Yin, W.; Ye, T. The role of natural products in the prevention and treatment of pulmonary fibrosis: A review. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroel-Vicente, C.; Gutiérrez-Palomo, S.; Ferri, J.; Cortes, D.; Cabedo, N. Natural products and analogs as preventive agents for metabolic syndrome via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: An overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 221, 113535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.d.L.; Teixeira, S.S.; Monteiro, M.H.D.; De-Oliveira, A.C.A.X.; Paumgartten, F.J.R. Traditional use and safety of herbal medicines. Rev. Bras. De Farmacogn. 2014, 24, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumpail, B.J.; Li, A.A.; Iqbal, U.; Sallam, S.; Shah, N.D.; Kwong, W.; Cholankeril, G.; Kim, D.; Ahmed, A. Potential Therapeutic Benefits of Herbs and Supplements in Patients with NAFLD. Diseases 2018, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakudya, E.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, N.K.; Jeong, Y.S. Platycosides from the Roots of Platycodon grandiflorum and Their Health Benefits. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 19, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhao, J.; Lu, G.; Qi, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. A humanized neutralizing antibody against MERS-CoV targeting the receptor-binding domain of the spike protein. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.J.; Kim, H.K.; Han, M.H.; Oh, Y.N.; Yoon, H.M.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, G.; Hwang, H.; Kim, B.; Choi, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorus in lipopolysaccharidestimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Noh, E.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Jung, S.H.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, Y.S. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase II by Platycodon grandiflorum saponins via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 2315–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, W.I.; Lim, S.T. Antioxidant and anticancer activities of organic extracts from Platycodon grandiflorum A. De Candolle roots. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 93, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, H.G.; Han, E.H.; Hwang, Y.P.; Lee, Y.C.; Chung, Y.C.; Jeong, H.G. Protective effect of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum against carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Li, W.; Choi, B.T.; Kim, N.D.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, Y.H. Implication of intracellular ROS formation, caspase-3 activation and Egr-1 induction in platycodon D-induced apoptosis of U937 human leukemia cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2009, 63, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.K.; Kimura, Y.; Okuda, H.; Xu, B.J.; Zheng, Y.N. Platycodi radix affects lipid metabolism in mice with high fat diet-induced obesity. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2760–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Seo, E.K.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, T.K.; Cho, Y.W.; Ezaki, O.; Kim, C.H. Effect of dietary Platycodon grandiflorum on the improvement of insulin resistance in obese Zucker rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2000, 11, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Harding, S.V.; Marinangeli, C.P.; Kim, Y.S.; Jones, P.J. Hypocholesterolemic and anti-obesity effects of saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum in hamsters fed atherogenic diets. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, H195–H200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Kang, M.; Kim, Y.S. Platycodin D inhibits lipogenesis through AMPKalpha-PPARgamma2 in 3T3-L1 cells and modulates fat accumulation in obese mice. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.J.; Han, L.K.; Zheng, Y.N.; Lee, J.H.; Sung, C.K. In vitro inhibitory effect of triterpenoidal saponins from Platycodi Radix on pancreatic lipase. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.M.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, B.C. Platycodon grandiflorum modifies adipokines and the glucose uptake in high-fat diet in mice and L6 muscle cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, J.; Ji, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Antihyperglycemic effects of Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC. extract on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2007, 62, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; You, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Chung, Y.C.; Jeong, T.C.; Jeong, H.G. Hepatoprotective effects of Platycodon grandiflorum on acetaminophen-induced liver damage in mice. Cancer Lett. 2001, 174, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, D.S.; Cho, H.Y. Protective effects of Platycodi radix on alcohol-induced fatty liver. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.D.; Han, S.B.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, C.W.; Park, S.K.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, H.M. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of macrophages by polysaccharide isolated from the radix of Platycodon grandiflorum. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Pan, H.; Sun, H.; Li, D. A promising balanced Th1 and Th2 directing immunological adjuvant, saponins from the root of Platycodon grandiflorum. Vaccine 2008, 26, 3937–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Ryu, R.; Lee, J.; Cho, S.J.; Kwon, E.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Liu, K.H.; Rina, Y.; Sung, M.K.; et al. Platycodon grandiflorus Root Extract Attenuates Body Fat Mass, Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance through the Interplay between the Liver and Adipose Tissue. Nutrients 2016, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.M.; Park, K.-T.; Park, E.C.; Kim, S.I.; Choi, M.S.; Liu, K.-H.; Lee, C.H. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomic and Lipidomic Analyses of the Effects of Dietary Platycodon grandiflorum on Liver and Serum of Obese Mice under a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2017, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahashi, M.; Yuza, K.; Hirose, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Ramanathan, R.; Hait, N.C.; Hylemon, P.B.; Zhou, H.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. The roles of bile acids and sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in the hepatobiliary diseases. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Sun, X. Cholesterol metabolism: A double-edged sword in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 762828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, R. Dysregulation of bile acids in patients with NAFLD. In Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-An Update; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Reilly, S.M.; Yu, E.; Osborn, O.; Lackey, D.; Yoshihara, E.; Perino, A.; Jacinto, S.; Lukasheva, Y. Intestinal FXR agonism promotes adipose tissue browning and reduces obesity and insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.-X.; Niu, W.-X.; Ren, J.-F.; Cai, S.-Y.; Yu, D.-K.; Liu, H.-T.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.-C.; Shao, R.-G.; et al. A novel ASBT inhibitor, IMB17-15, repressed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development in high-fat diet-fed Syrian golden hamsters. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stofan, M.; Guo, G.L. Bile Acids and FXR: Novel Targets for Liver Diseases. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.-Y. Farnesoid X receptor: A master regulator of hepatic triglyceride and glucose homeostasis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S. Bile Acid Receptor Farnesoid X Receptor: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2017, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.L. Bile acids: Regulation of synthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Peppel, I.P.; Rao, A.; Dommerholt, M.B.; Bongiovanni, L.; Thomas, R.; de Bruin, A.; Karpen, S.J.; Dawson, P.A.; Verkade, H.J.; Jonker, J.W. The Beneficial Effects of Apical Sodium-Dependent Bile Acid Transporter Inactivation Depend on Dietary Fat Composition. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 2000750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Kosters, A.; Mells, J.E.; Zhang, W.; Setchell, K.D.R.; Amanso, A.M.; Wynn, G.M.; Xu, T.; Keller, B.T.; Yin, H.; et al. Inhibition of ileal bile acid uptake protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet–fed mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 357ra122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matye, D.J.; Wang, H.; Luo, W.; Sharp, R.R.; Chen, C.; Gu, L.; Jones, K.L.; Ding, W.-X.; Friedman, J.E.; Li, T. Combined ASBT inhibitor and FGF15 treatment improves therapeutic efficacy in experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, B.L.; Sedgeman, L.R.; Williams, K.J.; Morand, P.; Cheng, A.; Jarrett, K.E.; Chan, A.P.; Brearley-Sholto, M.C.; Wahlström, A.; Ashby, J.W.; et al. FXR activation protects against NAFLD via bile-acid-dependent reductions in lipid absorption. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1671–1684.e1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, R.M.; Reid, A.E. FXR Agonists as Therapeutic Agents for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2015, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppel, I.P.v.d.; Verkade, H.J.; Jonker, J.W. Metabolic consequences of ileal interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G619–G625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, C.; Smith, C.D.; Sundseth, S.S.; Pink, H.M.; Wilson, J.G.; Lewis, M.C. Ileal bile acid transporter inhibition, CYP7A1 induction, and antilipemic action of 264W94. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F. Bile Acids: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Physiology 1999, 14, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, B.; Jones, S.A.; Price, R.R.; Watson, M.A.; McKee, D.D.; Moore, L.B.; Galardi, C.; Wilson, J.G.; Lewis, M.C.; Roth, M.E.; et al. A Regulatory Cascade of the Nuclear Receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 Represses Bile Acid Biosynthesis. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.T.; Makishima, M.; Repa, J.J.; Schoonjans, K.; Kerr, T.A.; Auwerx, J.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Molecular basis for feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdasaryan, A.; Fuchs, C.D.; Österreicher, C.H.; Lemberger, U.J.; Halilbasic, E.; Påhlman, I.; Graffner, H.; Krones, E.; Fickert, P.; Wahlström, A.; et al. Inhibition of intestinal bile acid absorption improves cholestatic liver and bile duct injury in a mouse model of sclerosing cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matye, D.J.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Chao, X.; Wang, H.; Ni, H.; Ding, W.-X.; Li, T. Gut-restricted apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter inhibitor attenuates alcohol-induced liver steatosis and injury in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Log2 (Fold Change) | Number of Proteins | |
|---|---|---|
| Only PRE | 245 | |
| Log ratio ≧ 1 | 22 | |
| −1 < Log ratio < 1 | 719 | |
| Log ratio ≦ −1 | 227 | |
| Only HFD | 147 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.; Baek, W.H.; Yun, S.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, G.-H.; Kim, S.I.; Jeong, H.G.; Park, E.C. Platycodi Radix Extract Prevents Hepatic Steatosis by Enhancing Bile Acid Synthesis in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Fatty Liver Mouse Model. Nutrients 2024, 16, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060893
Kim W, Baek WH, Yun SH, Lee H, Kim MJ, Lee S-Y, Kim G-H, Kim SI, Jeong HG, Park EC. Platycodi Radix Extract Prevents Hepatic Steatosis by Enhancing Bile Acid Synthesis in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Fatty Liver Mouse Model. Nutrients. 2024; 16(6):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060893
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Wooyoung, Woon Hee Baek, Sung Ho Yun, Hayoung Lee, Mi Jeong Kim, Sang-Yeop Lee, Gun-Hwa Kim, Seung Il Kim, Hye Gwang Jeong, and Edmond Changkyun Park. 2024. "Platycodi Radix Extract Prevents Hepatic Steatosis by Enhancing Bile Acid Synthesis in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Fatty Liver Mouse Model" Nutrients 16, no. 6: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060893
APA StyleKim, W., Baek, W. H., Yun, S. H., Lee, H., Kim, M. J., Lee, S.-Y., Kim, G.-H., Kim, S. I., Jeong, H. G., & Park, E. C. (2024). Platycodi Radix Extract Prevents Hepatic Steatosis by Enhancing Bile Acid Synthesis in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Fatty Liver Mouse Model. Nutrients, 16(6), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060893








