Food Cravings and Obesity in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Considerations
Abstract
1. Introduction
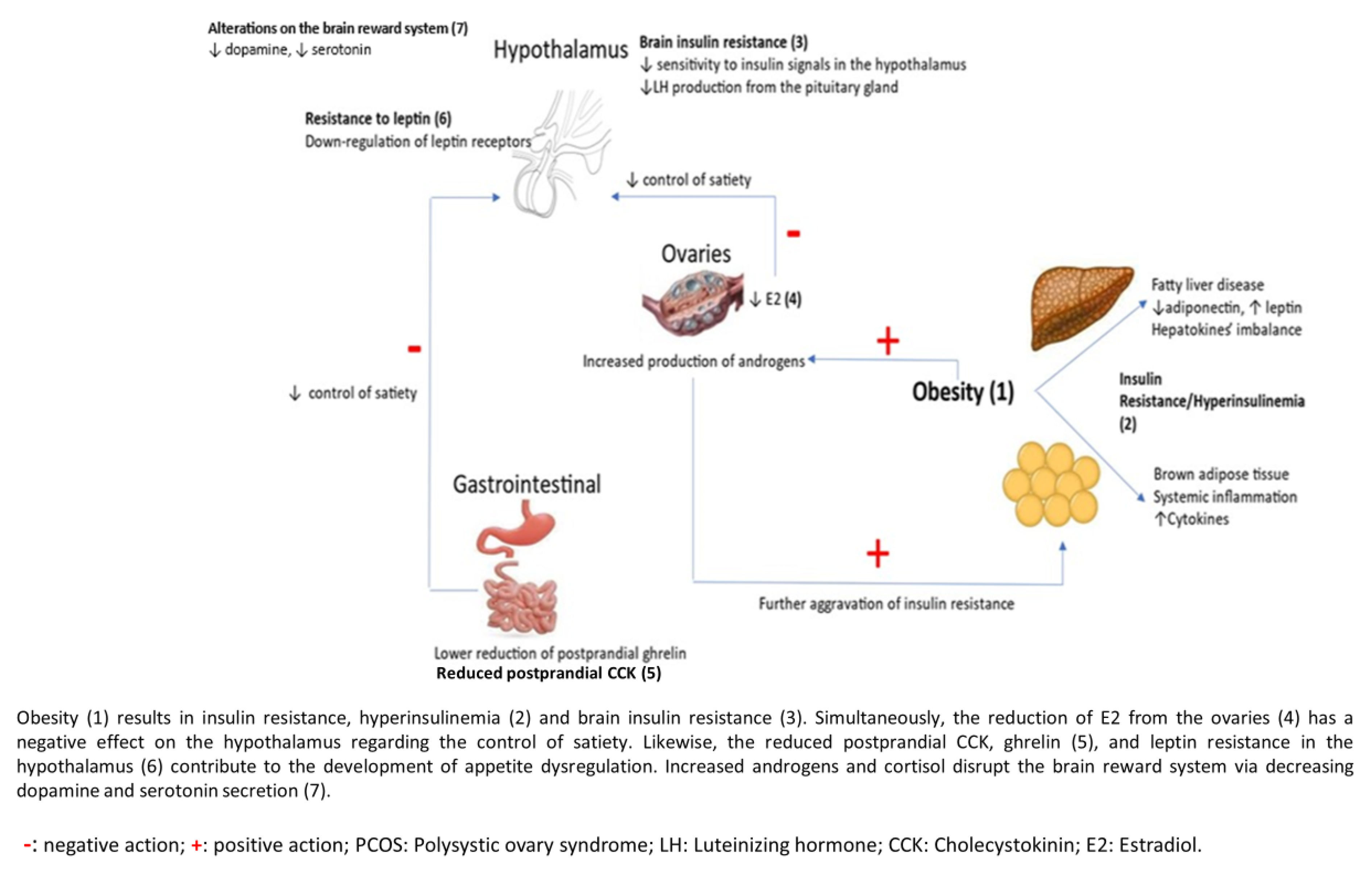
2. Metabolic and Hormonal Derangements Predisposing to Food Disorders in Women with PCOS
2.1. Obesity
2.2. Insulin Resistance (IR)
2.3. Gastrointestinal Hormones
2.4. Brain Reward System
2.5. Hyperandrogenism
3. Eating Disorders in PCOS: Pathogenetic Mechanism
4. Eating Disorders: Prevalence and Clinical Aspects
4.1. Binge Eating
4.2. Mood Disorders—Anxiety—Depression
5. Nutritional and Lifestyle Modifications to Improve Food Cravings
6. Medical Interventions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azziz, R. PCOS in 2015: New insights into the genetics of polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balen, A.H.; Morley, L.C.; Misso, M.; Franks, S.; Legro, R.S.; Wijeyaratne, C.N.; Stener-Victorin, E.; Fauser, B.C.; Norman, R.J.; Teede, H. The management of anovulatory infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: An analysis of the evidence to support the development of global WHO guidance. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2016, 22, 687–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teede, H.; Deeks, A.; Moran, L. Polycystic ovary syndrome: A complex condition with psychological, reproductive, and metabolic manifestations that impacts on health across the lifespan. BMC Med. 2010, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Kakoly, N.S.; Tan, J.W.J.; Fitzgerald, G.; Bahri Khomami, M.; Joham, A.E.; Cooray, S.D.; Misso, M.L.; Norman, R.J.; Harrison, C.L.; et al. Metabolic syndrome in polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoly, N.S.; Khomami, M.B.; Joham, A.E.; Cooray, S.D.; Misso, M.L.; Norman, R.J.; Harrison, C.L.; Ranasinha, S.; Teede, H.J.; Moran, L.J. Ethnicity, obesity and the prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes in PCOS: A systematic review and meta-regression. Hum. Reprod. Update 2018, 24, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirmans, S.M.; Parish, R.C.; Blake, S.; Wang, X. Epidemiology and comorbidities of polycystic ovary syndrome in an indigent population. J. Investig. Med. 2014, 62, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soydinc, E.; Soydinc, S.; Arıturk, Z.; Tekbas, E.; Cakici, M.; Islamoglu, Y.; Ercan, S.; Sari, I.; Davutoglu, V. Increased epicardial fat thickness is related with body mass index in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 2111–2113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Halagappa, V.K.; Riazi, S.; Hu, X.; Ecelbarger, C.A. Reduced expression of insulin receptors in the kidneys of insulin-resistant rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2661–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanaki, K.; Karagiannakis, D.S.; Raftopoulou, M.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Paschou, S.A.; Ilias, I. Obesity and hyperandrogenism are implicated with anxiety, depression, and food cravings in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrine 2023, 82, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoban, Ö.G.; Tulacı, Ö.D.; Adanır, A.S.; Önder, A. Psychiatric Disorders, Self-Esteem, and Quality of Life in Adolescents with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2019, 32, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanes, Y.M.; Reeves, S.; Gibson, E.L.; Piggott, C.; May, V.A.; Hart, K.H. Binge eating behaviors and food cravings in women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Appetite 2017, 109, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhija, N.; Tayade, S.; Toshniwal, S.; Tilva, H. Clinico-Metabolic Profile in Lean Versus Obese Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Women. Cureus 2023, 15, e37809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, F.; Wu, Q.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Hua, K. Life Modifications and PCOS: Old Story But New Tales. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 808898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glueck, C.J.; Morrison, J.A.; Daniels, S.; Wang, P.; Stroop, D. Sex hormone-binding globulin, oligomenorrhea, polycystic ovary syndrome, and childhood insulin at age 14 years predict the metabolic syndrome and class III obesity at age 24 years. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 308–313.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, M.; Doherty, D.A.; Atkinson, H.; Sloboda, D.M.; Franks, S.; Norman, R.J.; Hart, R. Clinical, ultrasound and biochemical features of polycystic ovary syndrome in adolescents: Implications for diagnosis. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.; Chávez, M.; Olivar, L.; Rojas, M.; Morillo, J.; Mejías, J.; Calvo, M.; Bermúdez, V. Polycystic ovary syndrome, insulin resistance, and obesity: Navigating the pathophysiologic labyrinth. Int. J. Reprod. Med. 2014, 2014, 719050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cena, H.; Chiovato, L.; Nappi, R.E. Obesity, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, and Infertility: A New Avenue for GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e2695–e2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkey, B.E. Diabetes: Have we got it all wrong? Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2432–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehart, H.; Kumpf, S.; Ittner, A.; Ricci, R. MAPK signaling in cellular metabolism: Stress or wellness? EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeusler, R.A.; McGraw, T.E.; Accili, D. Biochemical and cellular properties of insulin receptor signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, V.; Uchida, T.; Yenush, L.; Davis, R.; White, M.F. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser (307). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9047–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, M.; Duncan, R.E.; Varady, K.A.; Frasson, D.; Hellerstein, M.K.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I.; Wang, Y.; Kang, C.; et al. Adipose overexpression of desnutrin promotes fatty acid use and attenuates diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2009, 58, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckardt, K.; Taube, A.; Eckel, J. Obesity-associated insulin resistance in skeletal muscle: Role of lipid accumulation and physical inactivity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2011, 12, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Nie, X.; He, B. Insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome across various tissues: An updated review of pathogenesis, evaluation, and treatment. J. Ovarian Res. 2023, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, K.L.; Smith, A.C.; Junkin, K.A.; Dyck, D.J. Globular adiponectin resistance develops independently of impaired insulin-stimulated glucose transport in soleus muscle from high-fat-fed rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E83–E90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasova, B.A.; Ivanova, P.D.; Ivanovska, B.Z. Adiponectin as a Serum Marker of Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Correlation with Indicators of Metabolic Disturbances. Acta Endo 2018, 14, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meex, R.C.R.; Watt, M.J. Hepatokines: Linking nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2007, 13, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanaki, K.; Ilias, I.; Paschou, S.A.; Karagiannakis, D.S. Hepatokines: The missing link in the development of insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism in PCOS? Hormones 2023, 22, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannouli, A.; Stefanaki, C.; Kouskoutis, C.; Konidari, M.; Mani, I.; Konidari, K.; Markantonis, S.L.; Mantzou, A.; Dourakis, S.P.; Deligeoroglou, E.; et al. Hepatokine Profile in Adolescents with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inci Coskun, E.; Omma, T.; Taskaldiran, I.; Firat, S.N.; Culha, C. Metabolic role of hepassocin in polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 5175–5183. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, G.C.; Castañer, O.; Warnberg, J.; Subirana, I.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Serra-Majem, L.; Romaguera, D.; Estruch, R.; et al. Prospective association of physical activity and inflammatory biomarkers in older adults from the PREDIMED-Plus study with overweight or obesity and metabolic syndrome. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3092–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimobayashi, M.; Albert, V.; Woelnerhanssen, B.; Frei, I.C.; Weissenberger, D.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Clement, N.; Moes, S.; Colombi, M.; Meier, J.A.; et al. Insulin resistance causes inflammation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, D.; Tal, R. Inositol Treatment and ART Outcomes in Women With PCOS. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 2016, 1979654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Qiao, J. Association of Insulin Resistance and Elevated Androgen Levels with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): A Review of Literature. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9240569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coviello, A.D.; Legro, R.S.; Dunaif, A. Adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome have an increased risk of the metabolic syndrome associated with increasing androgen levels independent of obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apridonidze, T.; Essah, P.A.; Iuorno, M.J.; Nestler, J.E. Prevalence and characteristics of the metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovejoy, J.C.; Bray, G.A.; Bourgeois, M.O.; Macchiavelli, R.; Rood, J.C.; Greeson, C.; Partington, C. Exogenous androgens influence body composition and regional body fat distribution in obese postmenopausal women—A clinical research center study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 2198–2203. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.R.; Walker, K.Z.; Strauss, B.J.G. Effects of estradiol with and without testosterone on body composition and relationships with lipids in postmenopausal women. Menopause 2000, 7, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.R. Metabolic and hedonic drives in the neural control of appetite: Who is the boss? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautron, L.; Elmquist, J.K.; Williams, K.W. Neural control of energy balance: Translatin circuits to therapies. Cell 2015, 161, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, G.S.; Heisler, L.K. Unraveling the brain regulation of appetite: Lessons from genetics. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.W.; Elmquist, J.K. From neuroanatomy to behavior: Central integration of peripheral signals regulating feeding behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, M.; Alvarez, C.V.; Nogueiras, R.; Diéguez, C. Energy balance regulation by thyroid hormones at central level. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, J.W.; Elmquist, J.K.; Williams, K.W. Neuronal circuits that regulate feeding behavior and metabolism. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullmann, S.; Kleinridders, A.; Small, D.M.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.U.; Preissl, H.; Heni, M. Central nervous pathways of insulin action in the control of metabolism and food intake. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruud, J.; Steculorum, S.M.; Brüning, J.C. Neuronal control of peripheral insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Polotsky, A.J.; Rochester, D.; Berga, S.L.; Loucks, T.; Zeitlian, G.; Gibbs, K.; Polotsky, H.N.; Feng, S.; Isaac, B.; et al. Pulsatile luteinizing hormone amplitude and progesterone metabolite excretion are reduced in obese women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vall, S.A.; Herrera, D.; Sklar, B.; Wu, S.; Wondisford, F.; Radovick, S.; Wolfe, A. Insulin receptor signaling in the GnRH neuron plays a role in the abnormal GnRH pulsatility of obese female mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119995. [Google Scholar]
- Valdearcos, M.; Douglass, J.D.; Robblee, M.M.; Dorfman, M.D.; Stifler, D.R.; Bennett, M.L.; Gerritse, I.; Fasnacht, R.; Barres, B.A.; Thaler, J.P.; et al. Microglial inflammatory signaling orchestrates the hypothalamic immune response to dietary excess and mediates obesity susceptibility. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainez, N.M.; Jonak, C.R.; Nair, M.G.; Ethell, I.M.; Wilson, E.H.; Carson, M.J.; Coss, D. Diet-induced obesity elicits macrophage infiltration and reduction in spine density in the hypothalamus of male but not female mice. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, J.C.; Gautam, D.; Burks, D.J.; Gillette, J.; Schubert, M.; Orban, P.C.; Klein, R.; Krone, W.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Kahn, C.R. Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction. Science 2000, 289, 2122–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávalos, Y.; Kerr, B.; Maliqueo, M.; Dorfman, M. Cell and molecular mechanisms behind diet-induced hypothalamic inflammation and obesity. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, S.; Haselhorst, U.; Quadbeck, B.; Tan, S.; Kimmig, R.; Mann, K.; Janssen, O.E. Decreased soluble leptin receptor levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 154, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jahromi, B.N.; Dabaghmanesh, M.H.; Parsanezhad, M.E.; Fatehpoor, F. Association of leptin and insulin resistance in PCOS: A case-controlled study. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2017, 15, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.I.; Hsu, M.I.; Lin, S.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Hsu, C.S.; Tzeng, C.R. Adiponectin and leptin in overweight/obese and lean women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2015, 31, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghestani, M.H.; Daghestani, M.; Daghistani, M.; El-Mazny, A.; Bjørklund, G.; Chirumbolo, S.; Al Saggaf, S.H.; Warsy, A. A study of ghrelin and leptin levels and their relationship to metabolic profiles in obese and lean Saudi women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainz, N.; Barrenetxe, J.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Martinez, J.A. Leptin Resistance and Diet-Induced Obesity: Central and Peripheral Actions of Leptin. Metabolism 2015, 64, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, D.E.; Purnell, J.Q.; Frayo, R.S.; Schmidova, K.; Wisse, B.E.; Weigle, D.S. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koleva, D.I.; Orbetzova, M.M.; Atanassova, P.K. Adipose tissue hormones and appetite and body weight regulators in insulin resistance. Folia Med. 2013, 55, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale-Gurbuz, T.; Akhan, S.E.; Bastu, E.; Telci, A.; Iyibozkurt, A.C.; Topuz, S. Adiponectin, leptin, and ghrelin levels in obese adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Gynecol. 2013, 26, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, L.J.; Noakes, M.; Clifton, P.M.; Wittert, G.A.; Tomlinson, L.; Galletly, C.; Luscombe, N.D.; Norman, R.J. Ghrelin and measures of satiety are altered in polycystic ovary syndrome but not differentially affected by diet composition. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3337–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, P.J.; Ghatei, M.A.; Malik, I.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Wilding, J.P. Food fails to suppress ghrelin levels in obese humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2984–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, C.W.; Patterson, M.; Vincent, R.P.; Hunt, C.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Postprandial plasma ghrelin is suppressed proportional to meal calorie content in normal-weight but not obese subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saydam, B.O.; Yildiz, B.O. Gut-Brain Axis and Metabolism in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5572–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asarian, L.; Geary, N. Estradiol enhances cholecystokinin-dependent lipid-induced satiation and activates estrogen receptor alpha-expressing cells in the nucleus tractus solitarius of ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5656–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammacharoen, S.; Lutz, T.A.; Geary, N.; Asarian, L. Hindbrain administration of estradiol inhibits feeding and activates estrogen receptor-alpha-expressing cells in the nucleus tractus solitarius of ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschberg, A.L.; Naessén, S.; Stridsberg, M.; Byström, B.; Holtet, J. Impaired cholecystokinin secretion and disturbed appetite regulation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2004, 19, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xu, P.; Oyola, M.G.; Xia, Y.; Yan, X.; Saito, K.; Zou, F.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Hinton, A., Jr.; et al. Estrogens stimulate serotonin neurons to inhibit binge-like eating in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4351–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.G.; Florio, E.; Punzo, D.; Borrelli, E. The Brain’s Reward System in Health and Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1344, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, K.Z.; Cheer, J.F.; Tonini, R. Modulating the Neuromodulators: Dopamine, Serotonin, and the Endocannabinoid System. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, T.C.; Epel, E.S. Stress, eating and the reward system. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Météreau, E.; Déchaud, H.; Pugeat, M.; Dreher, J.C. Hormonal treatment increases the response of the reward system at the menopause transition: A counterbalanced randomized placebo-controlled fMRI study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 50, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasa, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Yano, K.; Yiliyasi, M.; Kuwahara, A.; Matsui, S.; Irahara, M. Effects of chronic testosterone administration on the degree of preference for a high-fat diet and body weight in gonadal-intact and ovariectomized female rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 349, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, C.A.; Berent-Spillson, A.; Love, T.; Persad, C.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zubieta, J.K.; Smith, Y.R. Functional neuroimaging of emotional processing in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A case-control pilot study. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 100, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinridders, A.; Cai, W.; Cappellucci, L.; Ghazarian, A.; Collins, W.R.; Vienberg, S.G.; Pothos, E.N.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin resistance in brain alters dopamine turnover and causes behavioral disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3463–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Yan, L.Y.; Qiao, J. Increased expression of P450scc and CYP17 in development of endogenous hyperandrogenism in a rat model of PCOS. Endocrine 2013, 43, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Garmey, J.C.; Veldhuis, J.D. Interactive stimulation by luteinizing hormone and insulin of the steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein and 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (CYP17) genes in porcine theca cells. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkel, L.; Sorva, R.; Voutilainen, R. Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin in obese children. J. Pediatr. 1985, 107, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milutinović, D.V.; Nikolić, M.; Veličković, N.; Djordjevic, A.; Bursać, B.; Nestorov, J.; Teofilović, A.; Antić, I.B.; Macut, J.B.; Zidane, A.S.; et al. Enhanced Inflammation without Impairment of Insulin Signaling in the Visceral Adipose Tissue of 5α-Dihydrotestosterone-Induced Animal Model of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2017, 125, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbould, A. Chronic testosterone treatment induces selective insulin resistance in subcutaneous adipocytes of women. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 192, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortón, M.; Botella-Carretero, J.I.; Benguría, A.; Villuendas, G.; Zaballos, A.; San Millán, J.L.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Peral, B. Differential gene expression profile in omental adipose tissue in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, C.T.; Teede, H.J.; Hill, B.; Loxton, D.; Joham, A.E. Increased prevalence of eating disorders, low self-esteem, and psychological distress in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A community-based cohort study. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 112, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tresure, J.; Duarte, T.A.; Schmidt, U. Eating disorders. Lancet 2020, 395, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.H.; Girdler, S.S.; Bulik, C.M. The role of reproductive hormones in the development and maintenance of eating disorders. Expert Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 7, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J.; Scholtz, S.; Lacey, H.; Conway, G. The prevalence of eating disorders in women with facial hirsutism: An epidemiological cohort study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2008, 41, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, I.; Giles, S.; Paganini, C. Binge eating in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: Prevalence, causes, and management strategies. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghetti, P.; Tosi, F. Insulin resistance and PCOS: Chicken or egg? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroshko, I.; Brennan, L.; O’Brien, P. Predictors of dropout in weight loss interventions: A systematic review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 912–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCluskey, S.; Evans, C.; Hubert Lacey, J.; Malcolm Pearce, J.; Jacobs, H. Polycystic ovary syndrome and bulimia. Fertil. Steril. 1991, 55, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, J.; Barr, S.; Jeanes, Y. Eating frequency and snacking habits in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2009, 22, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giuseppe, R.; Braschi, V.; Bosoni, D.; Biino, G.; Stanford, F.C.; Nappi, R.E.; Cena, H. Dietary underreporting in women affected by polycystic ovary syndrome: A pilot study. Nutr. Diet 2019, 76, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernadett, M. Prevalence of eating disorders among women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Psychiatr. Hung 2016, 31, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Asdaq, S.M.B.; Jomah, S.; Hasan, R.; Al-Baroudi, D.; Alharbi, M.; Alsubaie, S.; Buhamad, M.H.; Alyahya, B.; Al-Yamani, M.J. Impact of polycystic ovary syndrome on eating behavior, depression and health-related quality of life: A cross-sectional study in Riyadh. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3342–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Cooney, L.G.; Saini, S.; Smith, M.E.; Sammel, M.D.; Allison, K.C.; Dokras, A. Increased risk of disordered eating in polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juli, R.; Juli, M.R.; Juli, G.; Juli, L. Eating Disorders and Psychiatric Comorbidity. Psychiatr. Danub. 2023, 35 (Suppl. 2), 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hollinrake, E.; Abreu, A.; Maifeld, M.; Van Voorhis, B.J.; Dokras, A. Increased risk of depressive disorders in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2007, 87, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annagόr, B.B.; Kerimoglu, F.S.; Tazegόl, A.; Gόndόz, Έ.S.; Genηoglu, B.B. Psychiatric comorbidity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2015, 41, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesta, C.E.; Månsson, M.; Palm, C.; Lichtenstein, P.; Iliadou, A.N.; Landén, M. Polycystic ovary syndrome and psychiatric disorders: Co-morbidity and heritability in a nationwide Swedish cohort. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 73, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blay, S.L.; Aguiar, J.V.A.; Passos, I.C. Polycystic ovary syndrome and mental disorders: A systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, Z.; Li, K. The prevalence of anxiety and depression of different severity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A meta-analysis. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2021, 37, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummen, M.; Tischmann, L.; Gatta-Cherifi, B.; Adam, T.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M. Dietary Protein and Energy Balance in relation to Obesity and Co-morbidities. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q. Control of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes without weight loss by modification of diet composition. Nutr. Metab. 2006, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leidy, H.J.; Clifton, P.M.; Astrup, A.; Wycherley, T.P.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.D.; Woods, S.C.; Mattes, R.D. The role of protein in weight loss and maintenance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 1320S–1329S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromentin, G.; Darcel, N.; Chaumontet, C.; Marsset-Baglieri, A.; Nadkarni, N.; Tomé, D. Peripheral and central mechanisms involved in the control of food intake by dietary amino acids and proteins. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2012, 25, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombarolli, M.S.; de Oliveira, J.; Cordás, T.A. Craving for carbs: Food craving and disordered eating in low-carb dieters and its association with intermittent fasting. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, N.A.; Dyer, K.A.; Buckley, J.D.; Brinkworth, G.D.; Coates, A.M.; Parfitt, G.; Howe, P.R.C.; Noakes, M.; Murphy, K.J. Reductions in food cravings are similar with low-fat weight loss diets differing in protein and carbohydrate in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomized clinical trial. Nutr. Res. 2018, 57, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovski, E.; Mazhar, N.; Komishon, A.; Khayyat, R.; Li, D.; Mejia, S.B.; Khan, T.; Jenkins, A.L.; Smircic-Duvnjak, L.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; et al. Effect of viscous fiber supplementation on obesity indicators in individuals consuming calorie-restricted diets: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InterAct Consortium. Dietary fibre and incidence of type 2 diabetes in eight European countries: The EPIC-InterAct Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zong, A.; An, R.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; et al. Effects of whole grain intake on glycemic traits: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 4351–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teede, H.J.; Misso, M.L.; Costello, M.F.; Dokras, A.; Laven, J.; Moran, L.; Piltonen, T.; Norman, R.J.; International PCOS Network. Recommendations from the international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1602–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shele, G.; Genkil, J.; Speelman, D. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Exercise on Hormones in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, R.K.; Boyle, R.A.; Moholdt, T.; Kiel, I.; Hopkins, W.G.; Harrison, C.L.; Stepto, N.K. Exercise Interventions in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, I.K.; Ashe, M.C.; Cobucci, R.N.; Soares, G.M.; de Oliveira Maranhão, T.M.; Dantas, P.M.S. The effect of exercise as an intervention for women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, I.K.; Nunes, F.; Queiros, V.S.; Cobucci, R.N.; Dantas, P.B.; Soares, G.M.; Cabral, B.G.A.T.; Maranhão, T.M.O.; Dantas, P.M.S. Effect of high-intensity interval training on metabolic parameters in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilbert, A.; Petroff, D.; Herpertz, S.; Pietrowsky, R.; Tuschen-Caffier, B.; Vocks, S.; Schmidt, R. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of psychological and medical treatments for binge-eating disorder. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2019, 87, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Odeberg, J.; Gustafsson, S.; Råstam, M.; Brolund, A.; Pettersson, A.; Parling, T. Psychological, pharmacological, and combined treatments for binge eating disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ 2018, 21, e5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathisen, T.F.; Rosenvinge, J.H.; Friborg, O.; Vrabel, K.; Bratland-Sanda, S.; Pettersen, G.; Sundgot-Borgen, J. Is physical exercise and dietary therapy a feasible alternative to cognitive behavior therapy in treatment of eating disorders? A randomized controlled trial of two group therapies. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, O.M.; Sofopoulos, M.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Dincer, F.; Thakkar, B.; Sahin-Efe, A.; Filippaios, A.; Bowers, J.; Srnka, A.; Gavrieli, A.; et al. GLP-1 receptors exist in the parietal cortex, hypothalamus and medulla of human brains and the GLP-1 analogue liraglutide alters brain activity related to highly desirable food cues in individuals with diabetes: A crossover, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tronieri, J.S.; Wadden, T.A.; Walsh, O.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Alamuddin, N.; Gruber, K.; Leonard, S.; Bakizada, Z.M.; Chao, A.M. Effects of liraglutide on appetite, food preoccupation, and food liking: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichsen, M.; Breitschaft, A.; Tadayon, S.; Wizert, A.; Skovgaard, D. The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating, and gastric emptying in adults with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.; Bang, N.; Ratliff, E.L.; Paszkowiak, M.A.; Khorgami, Z.; Khalsa, S.S.; Simmons, W.K. Successful treatment of binge eating disorder with the GLP-1 agonist semaglutide: A retrospective cohort study. Obes. Pillars. 2023, 7, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, E.A.; Caroleo, M.; Rania, M.; Calabrò, G.; Staltari, F.A.; de Filippis, R.; Aloi, M.; Condoleo, F.; Arturi, F.; Segura-Garcia, C. An open-label trial on the efficacy and tolerability of naltrexone/bupropion SR for treating altered eating behaviors and weight loss in binge eating disorder. Eat. Weight Disord. 2021, 26, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, C.M.; Lydecker, J.A.; Fineberg, S.K.; Moreno, J.O.; Ivezaj, V.; Gueorguieva, R. Naltrexone-Bupropion and Behavior Therapy, Alone and Combined, for Binge-Eating Disorder: Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2022, 179, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, C.M.; Lydecker, J.A.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Pittman, B.; McKee, S.A. Naltrexone/bupropion for binge-eating disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Obesity 2023, 31, 2762–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, C.M.; Lydecker, J.A.; Gueorguieva, R. Naltrexone plus bupropion combination medication maintenance treatment for binge-eating disorder following successful acute treatments: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 7775–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Jin, B.; Pan, Y.; Han, Y.; You, T.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. The Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine-Associated Complementary and Alternative Medicine on Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 6619597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.N.; Yang, H.; Chen, F.; Li, S.Y. Clinical observation on therapy of strengthening spleen and tonifying kidney combined with clomiphene in improving the pregnancy rate of infertile patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Acad. J. Shanghai Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 33, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Zhu, G.L.; Wang, N.M. Study on the curative effect of Kaiyu Erchen decoction and Guizhi Fuling wan in treating Infertility caused by mutual knot of phlegm and blood stasis. Shanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 40, 341–343. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, S.; Lim, S.; Alycia, C.; Pirotta, S.; Thomson, R.; Gibson-Helm, M.; Blackmore, R.; Naderpoor, N.; Bennett, C.; Ee, C.; et al. Lifestyle management in polycystic ovary syndrome–beyond diet and physical activity. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, N.M.; Machado, J.; Lopes, L.; Criado, M.B. A Review on Acupuncture Efficiency in Human Polycystic Ovary/Ovarian Syndrome. J. Pharmacopunct. 2023, 26, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefanaki, K.; Karagiannakis, D.S.; Peppa, M.; Vryonidou, A.; Kalantaridou, S.; Goulis, D.G.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Paschou, S.A. Food Cravings and Obesity in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Considerations. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071049
Stefanaki K, Karagiannakis DS, Peppa M, Vryonidou A, Kalantaridou S, Goulis DG, Psaltopoulou T, Paschou SA. Food Cravings and Obesity in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Considerations. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071049
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefanaki, Katerina, Dimitrios S. Karagiannakis, Melpomeni Peppa, Andromachi Vryonidou, Sophia Kalantaridou, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Theodora Psaltopoulou, and Stavroula A. Paschou. 2024. "Food Cravings and Obesity in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Considerations" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071049
APA StyleStefanaki, K., Karagiannakis, D. S., Peppa, M., Vryonidou, A., Kalantaridou, S., Goulis, D. G., Psaltopoulou, T., & Paschou, S. A. (2024). Food Cravings and Obesity in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Considerations. Nutrients, 16(7), 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071049








