Water Intake and Adiposity Outcomes among Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Abstraction
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Certainty of Evidence Assessment
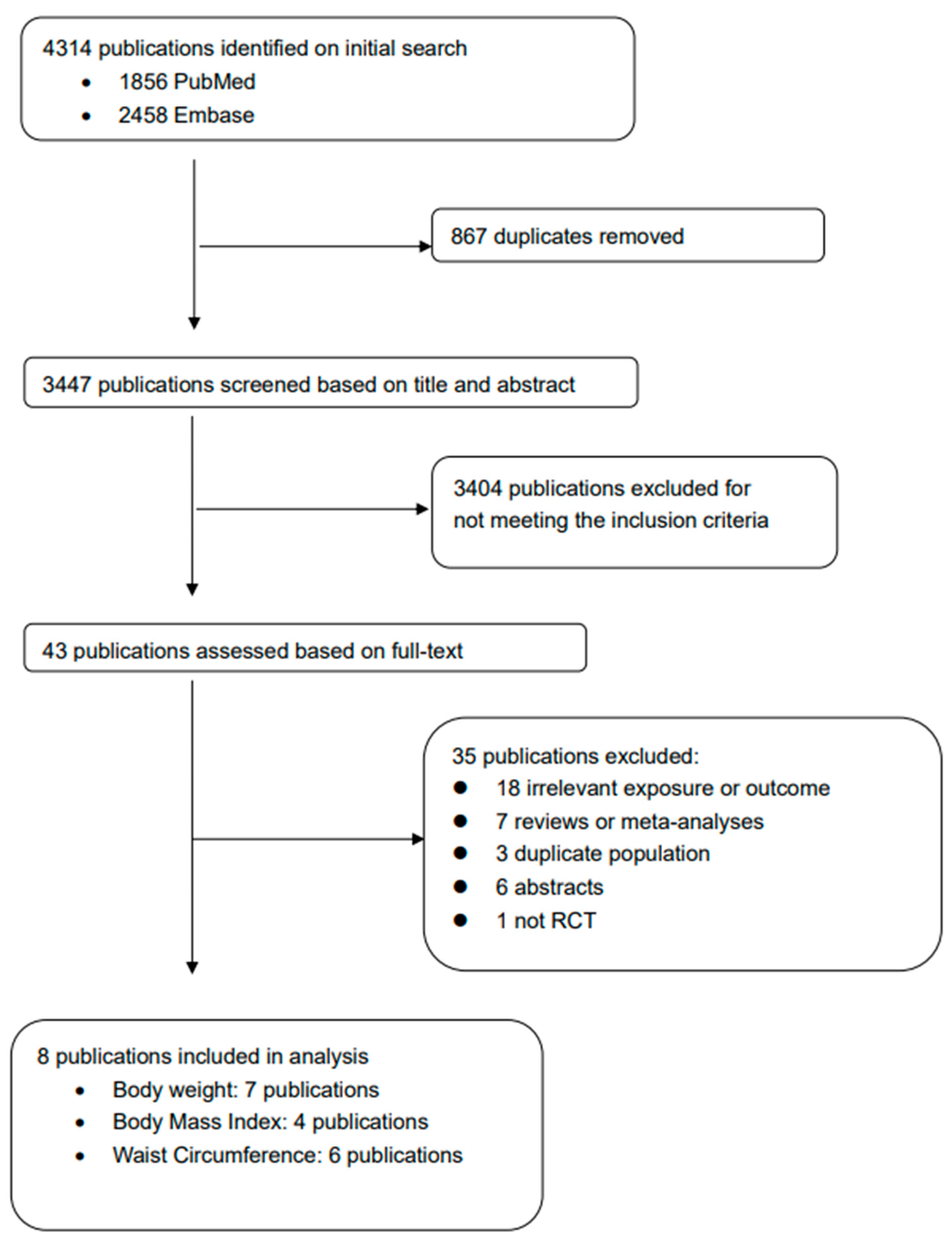
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included RCTs
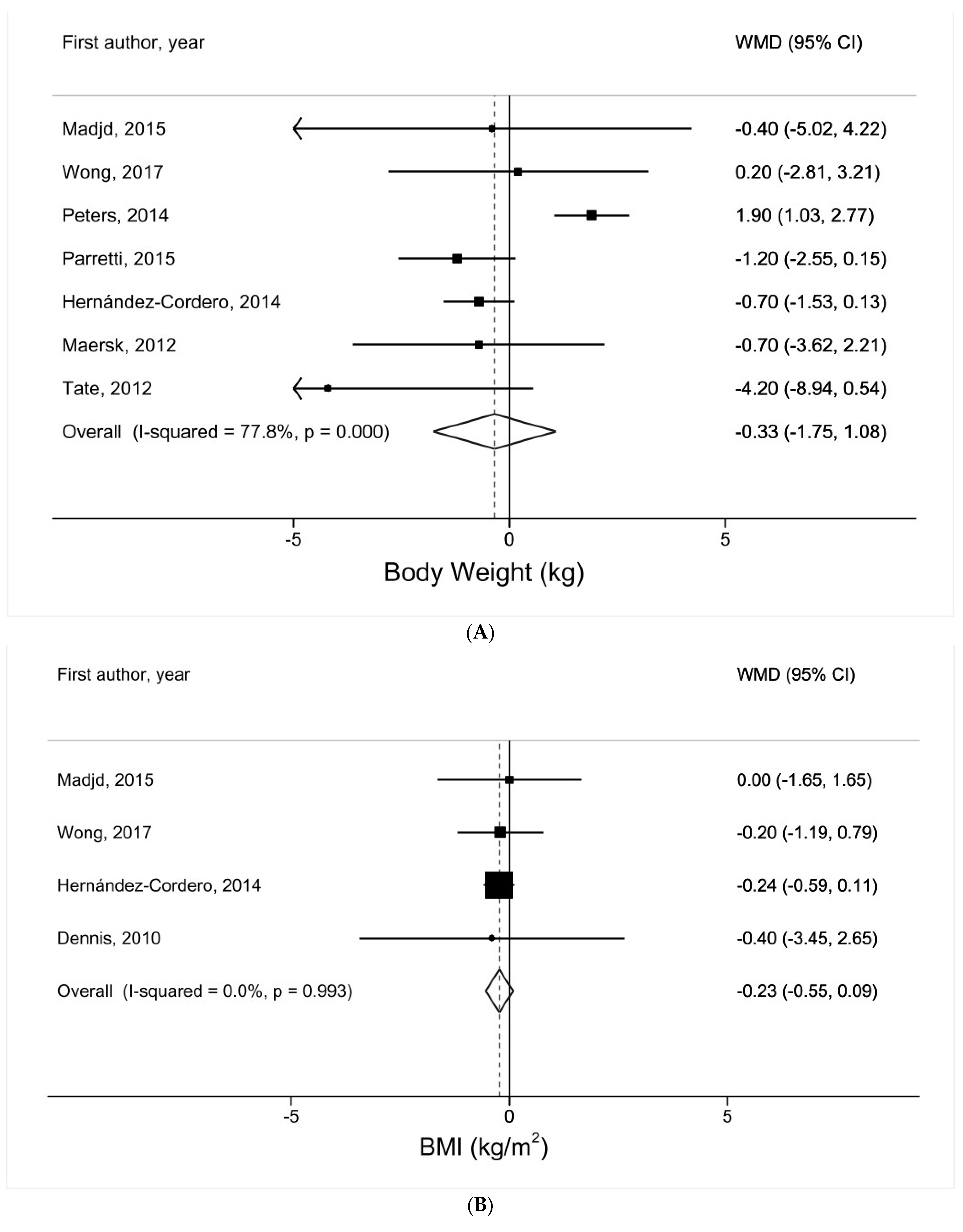
3.2. Water Intake and Body Weight
3.3. Water Intake and BMI
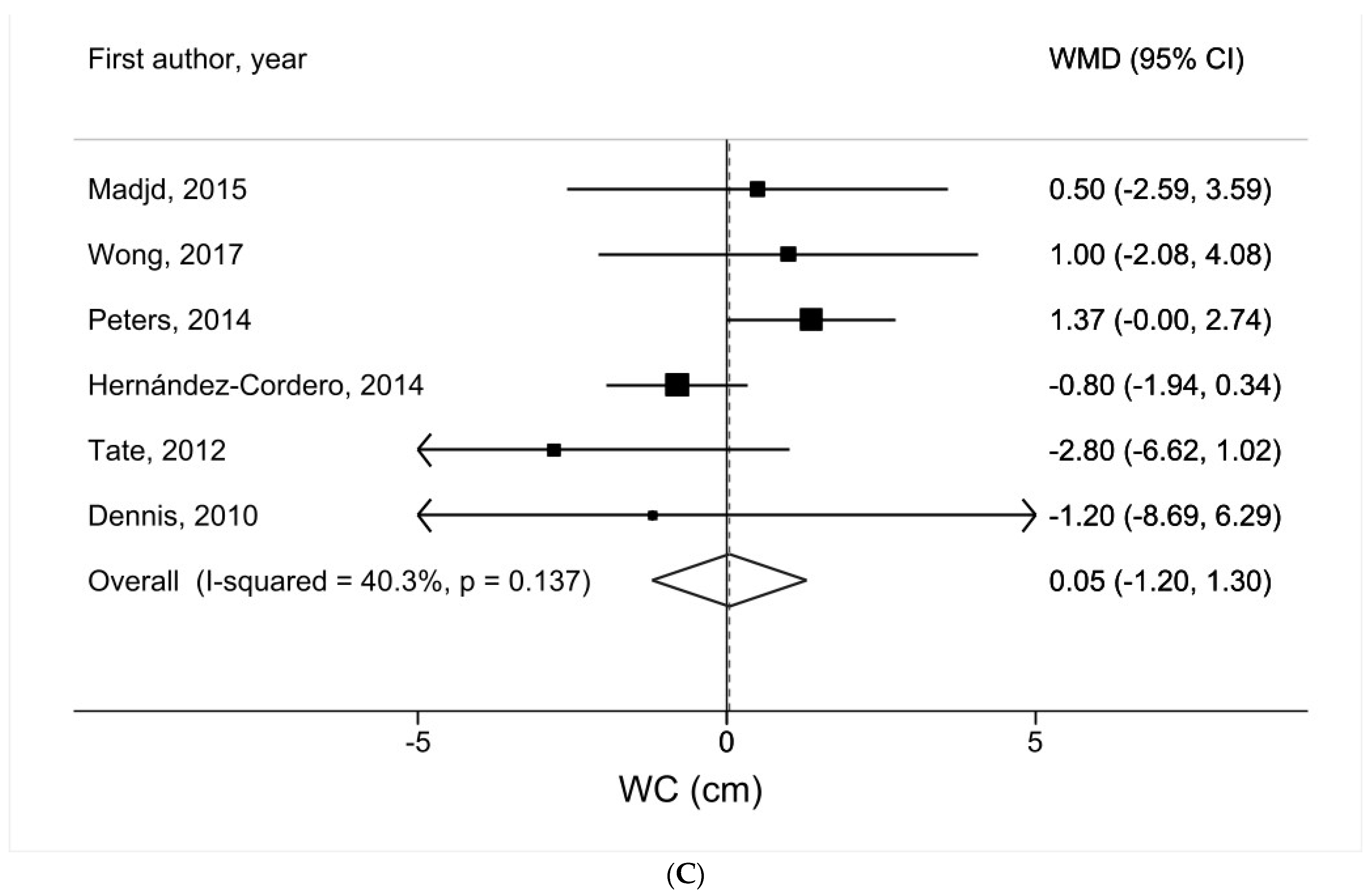
3.4. Water Intake and WC
3.5. Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Jayedi, A.; Soltani, S.; Motlagh, S.Z.; Emadi, A.; Shahinfar, H.; Moosavi, H.; Shab-Bidar, S. Anthropometric and adiposity indicators and risk of type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ 2022, 376, e067516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, W.J.; Khera, A.V.; Kim, J.Y.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, S.W.; Shin, J.I.; Won, H.H. Association between adiposity and cardiovascular outcomes: An umbrella review and meta-analysis of observational and Mendelian randomization studies. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3388–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, S.; Irfan, W.; Jameel, A.; Ahmed, S.; Shahid, R.K. Obesity and Cancer: A Current Overview of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Outcomes, and Management. Cancers 2023, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.D.; Kahan, S. Maintenance of Lost Weight and Long-Term Management of Obesity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeras, K.; Acho, R.J.; Lopez, P.P. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Chronic Complications; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seeras, K.; Philip, K.; Baldwin, D.; Prakash, S. Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, E.A.; Dengo, A.L.; Comber, D.L.; Flack, K.D.; Savla, J.; Davy, K.P.; Davy, B.M. Water consumption increases weight loss during a hypocaloric diet intervention in middle-aged and older adults. Obesity 2010, 18, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Walleghen, E.L.; Orr, J.S.; Gentile, C.L.; Davy, B.M. Pre-meal water consumption reduces meal energy intake in older but not younger subjects. Obesity 2007, 15, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappalainen, R.; Mennen, L.; van Weert, L.; Mykkänen, H. Drinking water with a meal: A simple method of coping with feelings of hunger, satiety and desire to eat. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1993, 47, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Çıtar Dazıroğlu, M.E.; Acar Tek, N. Water Consumption: Effect on Energy Expenditure and Body Weight Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, K.; Parker, B.; Wishart, J.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Jones, K.L.; Chapman, I.; Horowitz, M. Energy intake and appetite are related to antral area in healthy young and older subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delzenne, N.; Blundell, J.; Brouns, F.; Cunningham, K.; De Graaf, K.; Erkner, A.; Lluch, A.; Mars, M.; Peters, H.P.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M. Gastrointestinal targets of appetite regulation in humans. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, L.; Young, J.B. Sympathoadrenal activity and obesity: Physiological rationale for the use of adrenergic thermogenic drugs. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1993, 17 (Suppl. 1), S29–S34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.M.; Dulloo, A.G.; Montani, J.P. Water-induced thermogenesis reconsidered: The effects of osmolality and water temperature on energy expenditure after drinking. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3598–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Cordero, S.; Barquera, S.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Villanueva-Borbolla, M.A.; González de Cossio, T.; Dommarco, J.R.; Popkin, B. Substituting water for sugar-sweetened beverages reduces circulating triglycerides and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in obese but not in overweight Mexican women in a randomized controlled trial. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1742–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madjd, A.; Taylor, M.A.; Delavari, A.; Malekzadeh, R.; Macdonald, I.A.; Farshchi, H.R. Effects on weight loss in adults of replacing diet beverages with water during a hypoenergetic diet: A randomized, 24-wk clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maersk, M.; Belza, A.; Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Ringgaard, S.; Chabanova, E.; Thomsen, H.; Pedersen, S.B.; Astrup, A.; Richelsen, B. Sucrose-sweetened beverages increase fat storage in the liver, muscle, and visceral fat depot: A 6-mo randomized intervention study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parretti, H.M.; Aveyard, P.; Blannin, A.; Clifford, S.J.; Coleman, S.J.; Roalfe, A.; Daley, A.J. Efficacy of water preloading before main meals as a strategy for weight loss in primary care patients with obesity: RCT. Obesity 2015, 23, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.C.; Wyatt, H.R.; Foster, G.D.; Pan, Z.; Wojtanowski, A.C.; Vander Veur, S.S.; Herring, S.J.; Brill, C.; Hill, J.O. The effects of water and non-nutritive sweetened beverages on weight loss during a 12-week weight loss treatment program. Obesity 2014, 22, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, D.F.; Turner-McGrievy, G.; Lyons, E.; Stevens, J.; Erickson, K.; Polzien, K.; Diamond, M.; Wang, X.; Popkin, B. Replacing caloric beverages with water or diet beverages for weight loss in adults: Main results of the Choose Healthy Options Consciously Everyday (CHOICE) randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.M.W.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Robinson, L.; Feldman, H.A.; Ludwig, D.S. Effects of Advice to Drink 8 Cups of Water per Day in Adolescents with Overweight or Obesity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, e170012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.; Polisena, J.; Husereau, D.; Moulton, K.; Clark, M.; Fiander, M.; Mierzwinski-Urban, M.; Clifford, T.; Hutton, B.; Rabb, D. The effect of English-language restriction on systematic review-based meta-analyses: A systematic review of empirical studies. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2012, 28, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, J.D.; Cornett, R.A.; Savla, J.S.; Davy, K.P.; Davy, B.M. Daily self-monitoring of body weight, step count, fruit/vegetable intake, and water consumption: A feasible and effective long-term weight loss maintenance approach. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 685–692.e682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, E.; George Davey, S.; Martin, S.; Christoph, M. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chu, H. Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2018, 74, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, B.M.; Dennis, E.A.; Dengo, A.L.; Wilson, K.L.; Davy, K.P. Water consumption reduces energy intake at a breakfast meal in obese older adults. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 1236–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, T.V.; Allison, D.B.; Birch, L.L.; Stallings, V.A.; Moore, R.H.; Faith, M.S. Caloric compensation and eating in the absence of hunger in 5- to 12-y-old weight-discordant siblings. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piernas, C.; Popkin, B.M. Snacking increased among U.S. adults between 1977 and 2006. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, D.; Nóbrega, C.; Manco, L.; Padez, C. The contribution of genetics and environment to obesity. Br. Med. Bull. 2017, 123, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, J.; Shannon, J.R.; Grogan, E.; Biaggioni, I.; Robertson, D. A potent pressor response elicited by drinking water. Lancet 1999, 353, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, A.D.; Brechtel, G.; Johnson, A.; Fineberg, N.; Henry, D.P.; Steinberg, H.O. Interactions between insulin and norepinephrine on blood pressure and insulin sensitivity. Studies in lean and obese men. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straznicky, N.E.; Lambert, E.A.; Lambert, G.W.; Masuo, K.; Esler, M.D.; Nestel, P.J. Effects of dietary weight loss on sympathetic activity and cardiac risk factors associated with the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 5998–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari-Moghaddam, A.; Aslani, N.; Saneei, P.; Keshteli, A.H.; Daneshpajouhnejad, P.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Adibi, P. Water intake and intra-meal fluid consumption in relation to general and abdominal obesity of Iranian adults. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichieri, R.; Yokoo, E.M.; Pereira, R.A.; Veiga, G.V. Water and sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and changes in BMI among Brazilian fourth graders after 1-year follow-up. Public. Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.-B.; Wang, H.-J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.-L.; Qi, S.-F.; Tian, Q.-B. Plain water intake and association with the risk of overweight in the Chinese adult population: China health and nutrition survey 2006–2011. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderete, E.; Bejarano, I.; Rodríguez, A. Beverage intake and obesity in early childhood: Evidence form primary health care clients in Northwest Argentina. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2016, 7, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Graniel, I.; Becerra-Tomás, N.; Babio, N.; Serra-Majem, L.; Vioque, J.; Zomeño, M.D.; Corella, D.; Pintó, X.; Bueno-Cavanillas, A.; Tur, J.A. Baseline drinking water consumption and changes in body weight and waist circumference at 2-years of follow-up in a senior Mediterranean population. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3982–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, J.; O’Connor, L.; Flynn, A. Cross-sectional association of dietary water intakes and sources, and adiposity: National Adult Nutrition Survey, the Republic of Ireland. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhan, S.; Tian, Z.; Li, N.; Li, T.; Wu, D.; Zeng, Z.; Zhuang, X. Food Additives Associated with Gut Microbiota Alterations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Friends or Enemies? Nutrients 2022, 14, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento-Andrade, Y.; Suárez, R.; Quintero, B.; Garrochamba, K.; Chapela, S.P. Gut microbiota and obesity: New insights. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1018212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamoorthi, A.; LeDuc, C.A.; Thaker, V.V. The metabolic conditioning of obesity: A review of the pathogenesis of obesity and the epigenetic pathways that “program” obesity from conception. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1032491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, J.; Swithers, S.E. Artificial sweeteners and metabolic dysregulation: Lessons learned from agriculture and the laboratory. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, A.M.; Ashwell, M.; Halford, J.C.G.; Hardman, C.A.; Maloney, N.G.; Raben, A. Low-calorie sweeteners in the human diet: Scientific evidence, recommendations, challenges and future needs. A symposium report from the FENS 2019 conference. J. Nutr. Sci. 2021, 10, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, V.S.; Popkin, B.M.; Bray, G.A.; Després, J.P.; Hu, F.B. Sugar-sweetened beverages, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease risk. Circulation 2010, 121, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nseir, W.; Nassar, F.; Assy, N. Soft drinks consumption and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collison, K.S.; Saleh, S.M.; Bakheet, R.H.; Al-Rabiah, R.K.; Inglis, A.L.; Makhoul, N.J.; Maqbool, Z.M.; Zaidi, M.Z.; Al-Johi, M.A.; Al-Mohanna, F.A. Diabetes of the liver: The link between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and HFCS-55. Obesity 2009, 17, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.S.; Lin, W.T.; Gonzalez, G.V.; Kao, Y.H.; Chen, L.S.; Lin, H.Y. Sugar intake from sweetened beverages and diabetes: A narrative review. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, G.M.; Giang, H.T.N.; Ghozy, S.; Altibi, A.M.; Kandil, H.; Le, H.H.; Eid, P.S.; Radwan, I.; Makram, O.M.; Hien, T.T.T.; et al. Protocol registration issues of systematic review and meta-analysis studies: A survey of global researchers. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2020, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Population | Overweight and/or obese individuals |
| Intervention | Water intake intervention |
| Comparator | Any other beverages, placebo |
| Outcome | Body weight, body mass index, waist circumference |
| Study design | Randomized controlled trials |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.-Y.; Khil, J.; Keum, N. Water Intake and Adiposity Outcomes among Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070963
Chen Q-Y, Khil J, Keum N. Water Intake and Adiposity Outcomes among Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070963
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qiao-Yi, Jaewon Khil, and NaNa Keum. 2024. "Water Intake and Adiposity Outcomes among Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070963
APA StyleChen, Q.-Y., Khil, J., & Keum, N. (2024). Water Intake and Adiposity Outcomes among Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 16(7), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070963





