Electron Microscopy for the Stability Assessment of Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures: Focus on Precipitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Electron Microscopy
3. Results
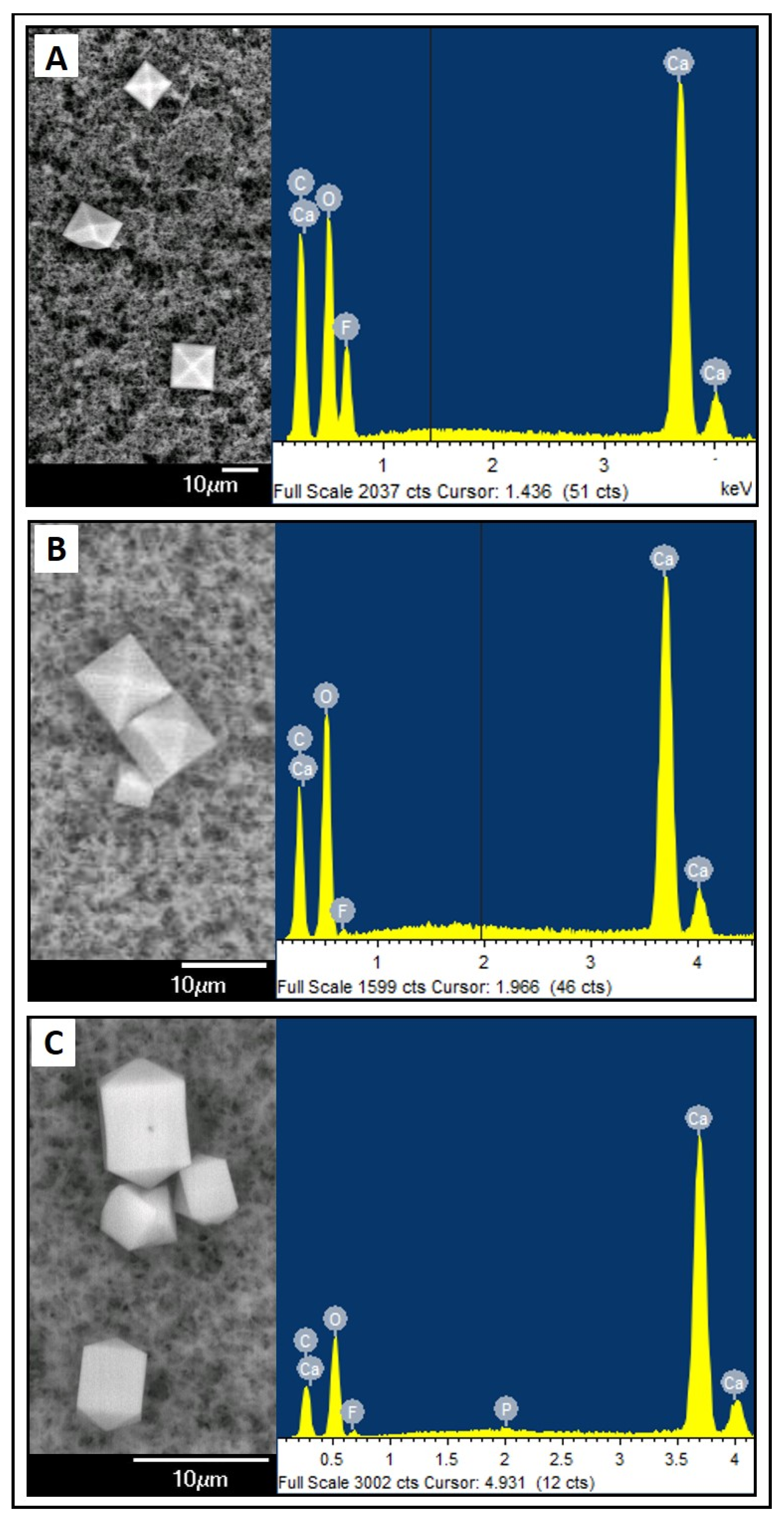
3.1. Crystalline precipitates
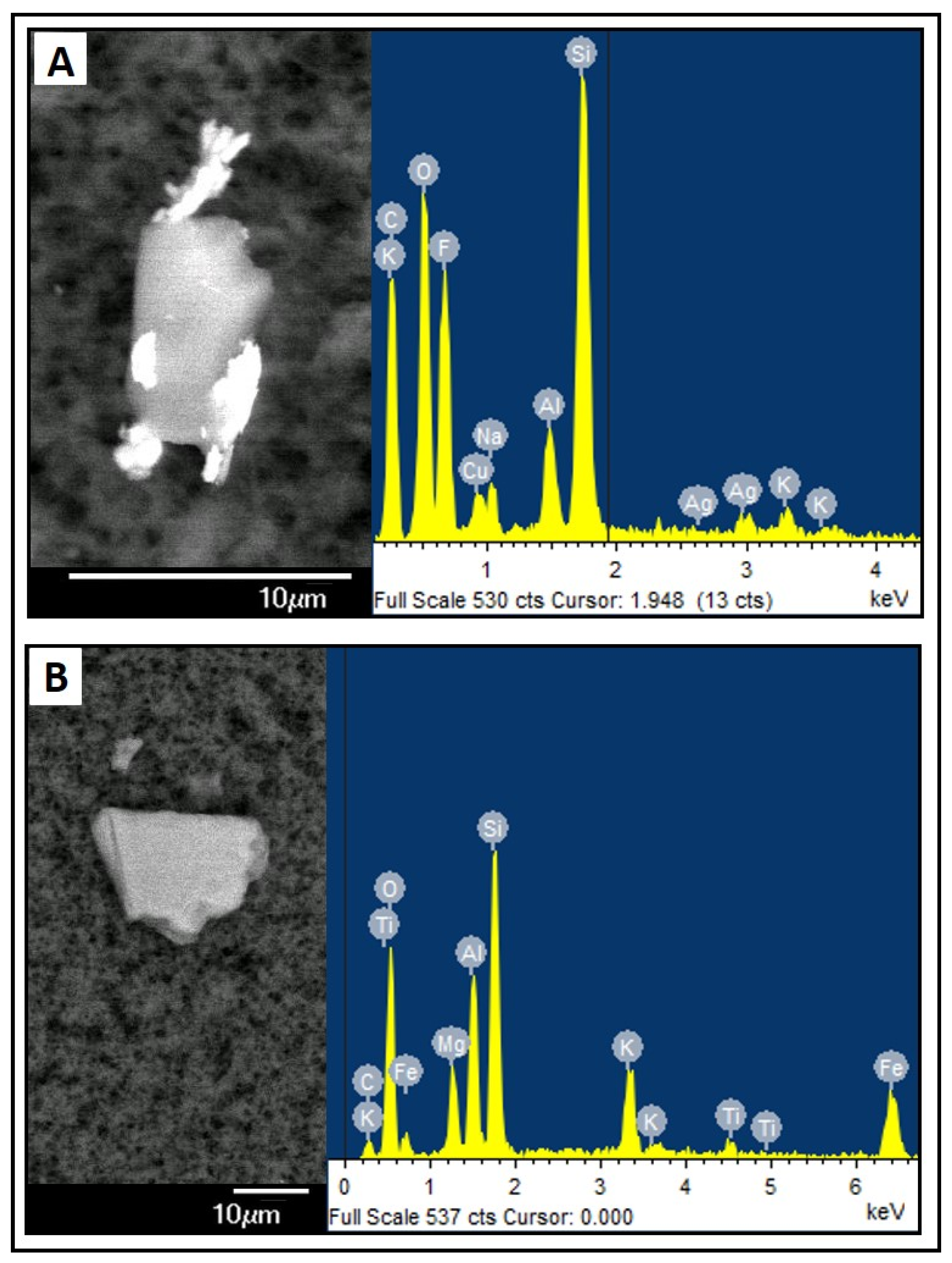
3.2. Amorphous Precipitates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mihatsch, W.A.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Desci, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2303–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, P.; Blaser, A.R.; Berger, M.M.; Alhazzani, W.; Calder, P.C.; Casaer, M.P.; Hiesmayr, M.; Mayer, K.; Montejo, J.C.; Pichard, C.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 48–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonyon, T.; Tomaso, A.E.; Kotha, P.; Owen, H.; Patel, D.; Carter, P.W.; Cronin, J.; Green, J.-B.D. Interactions between Parenteral Lipid Emulsions and Container Surfaces. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborie, S.; Denis, A.; Dassieu, G.; Bedu, A.; Tourneux, P.; Pinquier, D.; Kermorvant, E.; Millet, V.; Klosowski, S.; Patural, H.; et al. Shielding Parenteral Nutrition Solutions From Light: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L.; Guidetti, M.; Zolezzi, C.; Fasano, M.C.; Paganelli, F.; Merli, C.; Bersani, G.; Pizzoferrato, A.; Miglioli, M. Peroxidation Potential of Lipid Emulsions after Compounding in All-in-One Solutions. Nutrition 2003, 19, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero-Millán, L.; Lago Rivero, N.; Blanco Rodicio, A.; García Beloso, N.; Legido Soto, J.L.; Piñeiro-Corrales, G. Stability of Lipid Emulsion in Total Parenteral Nutrition: An Overview of Literature. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 45, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, J.; Silvestri, A.P.; Franke, R.; Bistrian, B.R.; Nehne, J.; Newton, D.W.; Driscoll, D.F. Calcium and Phosphate Compatibility in Low-Osmolarity Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures Intended for Peripheral Vein Administration. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.D.O.; Lobo, B.W.; Volpato, N.M.; da Veiga, V.F.; Cabral, L.M.; de Sousa, V.P. Influence of the Calcium Concentration in the Presence of Organic Phosphorus on the Physicochemical Compatibility and Stability of All-in-One Admixtures for Neonatal Use. Nutr. J. 2009, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, M.J.; Dumas, G.; Silvestri, A.; Bistrian, B.R.; Driscoll, D.F. Physical Compatibility of Neonatal Total Parenteral Nutrient Admixtures Containing Organic Calcium and Inorganic Phosphate Salts. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2005, 62, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H.; Saito, J.; Nagai, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; Ito, Y. Maximization of Calcium and Phosphate in Neonatal Total Parenteral Nutrition. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Dumas, G.J.; Silvestri, A.P.; Young, S.; Martin, C.R.; Bistrian, B.R.; Driscoll, D.F. Physical Compatibility of Neonatal Total Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures Containing Organic Calcium and Inorganic Phosphate Salts in a Simulated Infusion at 37 °C. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 10, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allwood, M.C.; Kearney, M.C.J. Compatibility and Stability of Additives in Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures. Nutrition 1998, 14, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKay, M.; Anderson, C. Physical Compatibility of Sodium Glycerophosphate and Calcium Gluconate in Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Solutions. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.; MacKay, M. Physical Compatibility of Calcium Chloride and Sodium Glycerophosphate in Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Solutions. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raupp, P.; Kries, R.V.; Pfahl, H.-G.; Manz, F. Glycero- vs Glucose-Phosphate in Parenteral Nutrition of Premature Infants: A Comparative in Vitro Evaluation of Calcium/Phosphorus Compatibility. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1991, 15, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchoud, L.; Fonzo-Christe, C.; Sadeghipour, F.; Bonnabry, P. Maximizing Calcium and Phosphate Content in Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Solutions Using Organic Calcium and Phosphate Salts. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foinard, A.; Perez, M.; Barthélémy, C.; Lannoy, D.; Flamein, F.; Storme, L.; Addad, A.; Bout, M.-A.; Décaudin, B.; Odou, P. In Vitro Assessment of Interaction Between Amino Acids and Copper in Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pera, D.C.; Peris, M.C.; Arévalo, M.F.; Muñoz, P.G.; Tutor, M.M.; Corrales, G.P.; Penín, I.R.; de Mallorca, D.P.; de Pontevedra, H. Consenso Español Sobre La Preparación de Mezclas Nutrientes Parenterales. Farm. Hosp. 2009, 33, 81–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mckinnon, B.T. FDA Safety Alert: Hazards of Precipitation Associated With Parenteral Nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 1996, 11, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P.A. Methods of Assessing Stability of Parenteral Nutrition Regimens. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2001, 4, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Pharmacopeia. General Chapter, (788) Particulate Matter in Injections. USP-NF; [Revised 2023]; Pharmacopeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, D.F. Stability and Compatibility Assessment Techniques for Total Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures: Setting the Bar According to Pharmacopeial Standards. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2005, 8, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaieb, D.S.; Chaumeil, J.C.; Jebnoun, S.; Khrouf, N.; Hedhili, A.; Sfar, S. Effect of the Intravenous Lipid Emulsions on the Availability of Calcium When Using Organic Phosphate in TPN Admixtures. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, M.J.; Schrank, G.D.; Russell, S. Particulate Evaluation of Parenteral Nutrition Solutions by Electronic Particle Counting and Scanning Electron Microscopy. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1981, 38, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liviskie, C.J.; Lange, S.A.; McPherson, C.C. Precipitation of Heparin Products With Calcium Gluconate: The Activity of Inactive Ingredients. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 22, 314–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero-Millán, L.; Bea-Mascato, B.; Legido Soto, J.L.; Martínez-López-De-Castro, N.; Lago-Rivero, N. Evaluation of the Stability of Newborn Hospital Parenteral Nutrition Solutions. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lázaro Cebas, A.; Pablos Bravo, S.; Gomis Muñoz, P.; Orbaneja, M.Á.; Spiers, S.; Shinn, M.; Ferrari Piquero, J.M. Límites de precipitación en nutriciones parenterales pediátricas con fuentes de calcio y fosfato orgánicas. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambados, F.; Brealey, J. Incompatibilities with Trace Elements During TPN Solution Admixture. Aust. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1998, 28, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, C.; Hatziantoniou, S.; Skouroliakou, M.; Markantonis-Kyroudis, S. Assessment of the Physicochemical Stability of All-in-One Parenteral Emulsions for Neonates According to USP Specifications. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P.A.; Bethune, K.; Fox, J.; Ledger, R.; Barnett, M. Particulate Contamination in Parenteral Nutrition Solutions: Still a Cause for Concern? Nutrition 2001, 17, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlabed, M.; Martin Mena, A.; Gaudy, R.; Perez, M.; Genay, S.; Hecq, J.-D.; Odou, P.; Lebuffe, G.; Décaudin, B. Analysis of Particulate Exposure during Continuous Drug Infusion in Critically Ill Adult Patients: A Preliminary Proof-of-Concept in Vitro Study. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2018, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, S.R.; Bohrer, D.; Garcia, S.C.; do Nascimento, P.C.; Noremberg, S. Aluminum Content in Intravenous Solutions for Administration to Neonates. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.S.; Kothari, H.; Hayes, B.D.; Tataronis, G.; Hudlin, M.; Doole, J.; Hartman, C. Effect of Addiivet Selection on Calculated Aluminum Content of Parenteral Nutrient Solutions. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2007, 64, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Sánchez, A.; Tejada-González, P.; Arteta-Jiménez, M. Aluminium in Parenteral Nutrition: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtney-Martin, G.; Kosar, C.; Campbell, A.; Avitzur, Y.; Wales, P.W.; Steinberg, K.; Harrison, D.; Chambers, K. Plasma Aluminum Concentrations in Pediatric Patients Receiving Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watrobska-Swietlikowska, D.; Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz, A.; MacLoughlin, R. The Presence of Inorganic Calcium in Pediatric Parenteral Admixtures. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | N (g/L) | Prot (g/L) | Gluc (g/L) | Lip (g/L) | Na (mMol/L) | K (mMol/L) | Mg (mMol/L) | Ca (mMol/L) | P (mMol/L) | OSM (mOsm/L) | CAN (mMol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN1 | 3.14 | 19.64 | 71.43 | 7.14 | 20.00 | 10.00 | 1.25 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 743.33 | 750 |
| PN2 | 3.38 | 21.10 | 80.25 | 11.38 | 30.00 | 15.00 | 2.25 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 878.62 | 1149 |
| PN3 | 3.56 | 22.22 | 87.11 | 14.78 | 35.00 | 20.00 | 2.60 | 17.50 | 17.50 | 969.77 | 1341 |
| PN4 | 3.70 | 23.13 | 92.60 | 17.50 | 40.00 | 30.00 | 3.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 1054.23 | 1542 |
| PN5 | 4.20 | 26.25 | 106.80 | 21.60 | 40.00 | 30.00 | 3.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 1178.95 | 1542 |
| PN6 | 4.70 | 29.38 | 121.00 | 25.80 | 50.00 | 35.00 | 3.50 | 22.50 | 25.00 | 1350.08 | 1749 |
| PN7 | 5.20 | 32.50 | 135.20 | 29.90 | 60.00 | 40.00 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 30.00 | 1520.80 | 1956 |
| PN8 | 3.14 | 19.64 | 71.43 | 40.00 | 80.00 | 50.00 | 5.00 | 30.00 | 40.00 | 1150.91 | 2370 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otero-Millán, L.; Bea-Mascato, B.; Legido Soto, J.L.; Martínez-López-De-Castro, N.; Lago Rivero, N. Electron Microscopy for the Stability Assessment of Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures: Focus on Precipitation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091390
Otero-Millán L, Bea-Mascato B, Legido Soto JL, Martínez-López-De-Castro N, Lago Rivero N. Electron Microscopy for the Stability Assessment of Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures: Focus on Precipitation. Nutrients. 2024; 16(9):1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091390
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtero-Millán, Luis, Brais Bea-Mascato, Jose Luis Legido Soto, Noemi Martínez-López-De-Castro, and Natividad Lago Rivero. 2024. "Electron Microscopy for the Stability Assessment of Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures: Focus on Precipitation" Nutrients 16, no. 9: 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091390
APA StyleOtero-Millán, L., Bea-Mascato, B., Legido Soto, J. L., Martínez-López-De-Castro, N., & Lago Rivero, N. (2024). Electron Microscopy for the Stability Assessment of Parenteral Nutrition Admixtures: Focus on Precipitation. Nutrients, 16(9), 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091390





