Impact of Time-Restricted Eating and High-Intensity Exercise on Nutrient Intake in Women with Overweight/Obesity: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Highlights
- A daily 10 h time-restricted eating (TRE) window with ad libitum energy intake reduced intakes of several micronutrients in women with overweight/obesity.
- TRE induced inadequate intakes for more micronutrients compared with a control group and a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) group.
- HIIT did not have any negative impacts on micronutrient intake.
- Inadequate intakes of micronutrients are common in individuals with overweight or obesity and may exacerbate metabolic health impairments. TRE is a feasible dietary strategy for weight loss but may induce micronutrient inadequacy in individuals with a poor baseline diet.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Interventions
2.3. Dietary Intake Outcomes
2.4. Nutrient Intake Adequacy in Relation to the 2023 Nordic Nutrition Recommendations
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Participants and Adherence to Interventions
3.2. Total Energy and Macronutrients
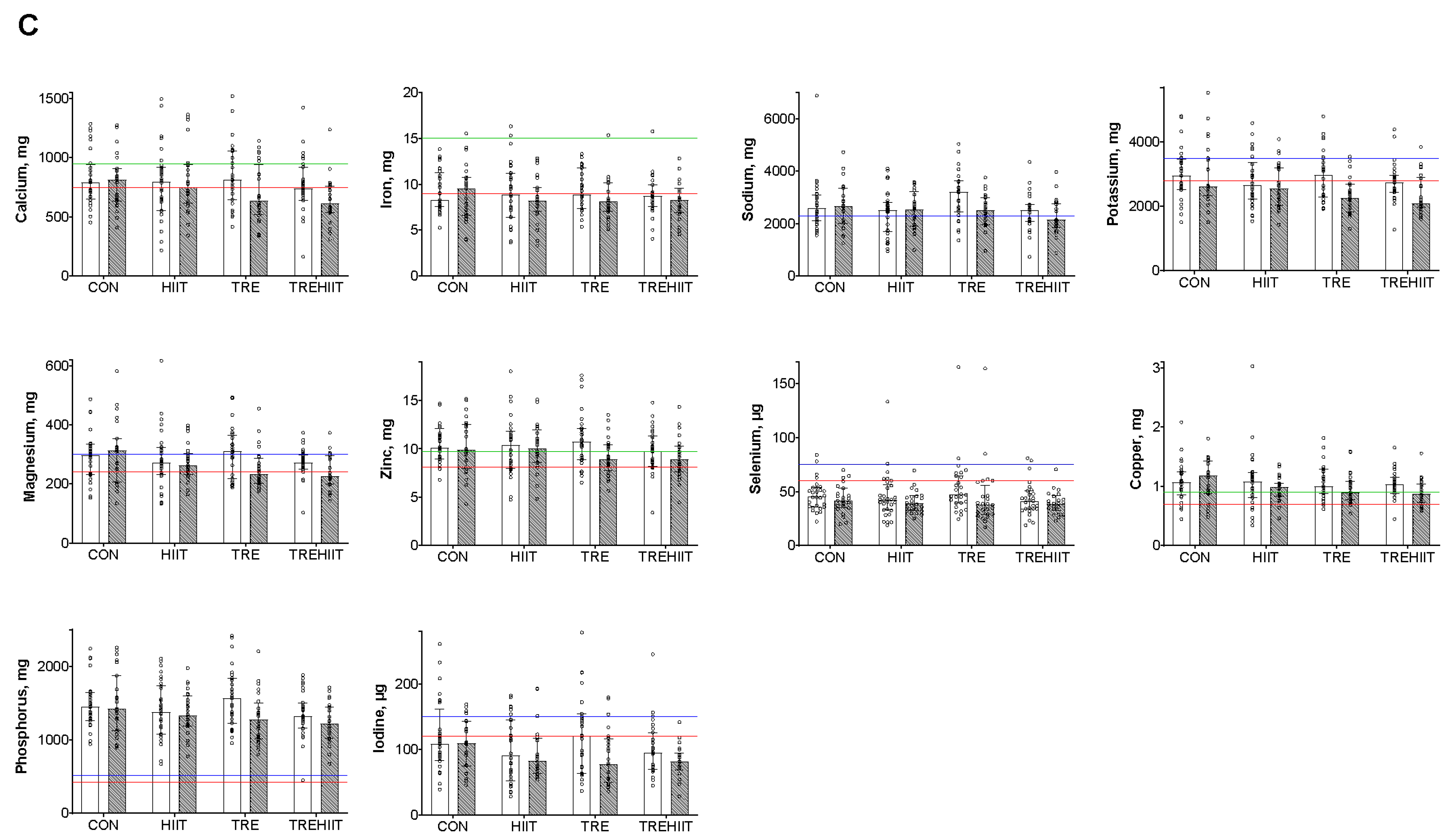
3.3. Micronutrient Intakes
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Implications
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, A.K. Reported consumption of low-nutrient-density foods by American children and adolescents: Nutritional and health correlates, NHANES III, 1988 to 1994. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2003, 157, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Reider, C.; Brooks, J.R.; Fulgoni, V.L., 3rd. Comparison of prevalence of inadequate nutrient intake based on body weight status of adults in the United States: An analysis of NHANES 2001–2008. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrup, A.; Bügel, S. Overfed but undernourished: Recognizing nutritional inadequacies/deficiencies in patients with overweight or obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.; Melchor, J.; Carr, R.; Karjoo, S. Obesity and malnutrition in children and adults: A clinical review. Obes. Pillars 2023, 8, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piuri, G.; Zocchi, M.; Della Porta, M.; Ficara, V.; Manoni, M.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Pinotti, L.; Maier, J.A.; Cazzola, R. Magnesium in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimalawansa, S.J. Associations of vitamin D with insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 175, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakharova, I.; Klimov, L.; Kuryaninova, V.; Nikitina, I.; Malyavskaya, S.; Dolbnya, S.; Kasyanova, A.; Atanesyan, R.; Stoyan, M.; Todieva, A.; et al. Vitamin D Insufficiency in Overweight and Obese Children and Adolescents. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoogian, E.N.C.; Chow, L.S.; Taub, P.R.; Laferrère, B.; Panda, S. Time-restricted Eating for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Diseases. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 405–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, E.B.; Devlin, B.L.; Hawley, J.A. Perspective: Time-Restricted Eating-Integrating the What with the When. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezpeleta, M.; Cienfuegos, S.; Lin, S.; Pavlou, V.; Gabel, K.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Varady, K.A. Time-restricted eating: Watching the clock to treat obesity. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varady, K.A.; Cienfuegos, S.; Ezpeleta, M.; Gabel, K. Clinical application of intermittent fasting for weight loss: Progress and future directions. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.W.; Kraus, W.E.; Powell, K.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Janz, K.F.; Jakicic, J.M.; Troiano, R.P.; Sprow, K.; Torres, A.; Piercy, K.L.; et al. High-Intensity Interval Training for Cardiometabolic Disease Prevention. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; van Baak, M.A.; Battista, F.; Busetto, L.; Carraça, E.V.; Dicker, D.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; Farpour-Lambert, N.; et al. Effect of exercise training interventions on energy intake and appetite control in adults with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Kong, Z.; Shi, Q.; Nie, J. Acute effect of high-intensity interval training versus moderate-intensity continuous training on appetite-regulating gut hormones in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati Zeppa, S.; Sisti, D.; Amatori, S.; Gervasi, M.; Agostini, D.; Piccoli, G.; Bertuccioli, A.; Rocchi, M.B.L.; Stocchi, V.; Sestili, P. High-intensity Interval Training Promotes the Shift to a Health-Supporting Dietary Pattern in Young Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Amaro-Gahete, F.J.; De-la-O, A.; Castillo, M.J. Impact of different exercise training modalities on energy and nutrient intake and food consumption in sedentary middle-aged adults: A randomised controlled trial. J. Human. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 33, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haganes, K.L.; Silva, C.P.; Eyjólfsdóttir, S.K.; Steen, S.; Grindberg, M.; Lydersen, S.; Hawley, J.A.; Moholdt, T. Time-restricted eating and exercise training improve HbA1c and body composition in women with overweight/obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1457–1471.e1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moholdt, T.; Silva, C.; Lydersen, S.; Hawley, J. Isolated and combined effects of high-intensity interval training and time-restricted eating on glycaemic control in reproductive-aged women with overweight or obesity: Study protocol for a four-armed randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e040020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomhoff, R.; Andersen, R.; Arnesen, E.K.; Christensen, J.J.; Eneroth, H.; Erkkola, M.; Gudanaviciene, I.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Høyer-Lund, A.; Lemming, E.W.; et al. Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Twisk, J.; Bosman, L.; Hoekstra, T.; Rijnhart, J.; Welten, M.; Heymans, M. Different ways to estimate treatment effects in randomised controlled trials. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2018, 10, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.D.; Kim, S.; Bersamin, A.; Dopler-Nelson, M.; Otten, J.; Oelrich, B.; Cherin, R. Micronutrient Quality of Weight-loss Diets That Focus on Macronutrients: Results From the A TO Z Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampl, J.S.; Betts, N.M. Comparisons of dietary intake and sources of fat in low- and high-fat diets of 18- to 24-year-olds. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1995, 95, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xanthakos, S.A. Nutritional deficiencies in obesity and after bariatric surgery. Pediatr. Clin. North. Am. 2009, 56, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouns, F. Overweight and diabetes prevention: Is a low-carbohydrate-high-fat diet recommendable? Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundblad, M.W.; Andersen, L.F.; Jacobsen, B.K.; Carlsen, M.H.; Hjartåker, A.; Grimsgaard, S.; Hopstock, L.A. Energy and nutrient intakes in relation to National Nutrition Recommendations in a Norwegian population-based sample: The Tromsø Study 2015–16. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, T.C. Safety of low-carbohydrate diets. Obes. Rev. 2005, 6, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.; Panda, S. A Smartphone App Reveals Erratic Diurnal Eating Patterns in Humans that Can Be Modulated for Health Benefits. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, E.B.; Devlin, B.L.; Lim, K.H.C.; Moresi, L.N.Z.; Geils, C.; Brennan, L.; Hawley, J.A. Time-Restricted Eating as a Nutrition Strategy for Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Feasibility Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engeset, D.; Hofoss, D.; Nilsson, L.M.; Olsen, A.; Tjønneland, A.; Skeie, G. Dietary patterns and whole grain cereals in the Scandinavian countries--differences and similarities. The HELGA project. Public. Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengi Çelik, Ö.; Köksal, E.; Aktürk, M. Time-restricted eating (16/8) and energy-restricted diet: Effects on diet quality, body composition and biochemical parameters in healthy overweight females. BMC Nutr. 2023, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhsh, J.A.; Vu, M.H.; Salvy, S.J.; Goran, M.I.; Vidmar, A.P. Effects of 8-h time-restricted eating on energy intake, dietary composition and quality in adolescents with obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2024, 19, e13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, E.; Vu, M.H.; Salvy, S.J.; Bakhsh, J.; Goran, M.I.; Raymond, J.K.; Espinoza, J.C.; Vidmar, A.P. Randomized Controlled Feasibility Trial of Late 8-h Time-Restricted Eating for Adolescents with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2024, 124, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, A.K.; Graubard, B.I. 40-Year Trends in Meal and Snack Eating Behaviors of American Adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huseinovic, E.; Winkvist, A.; Slimani, N.; Park, M.K.; Freisling, H.; Boeing, H.; Buckland, G.; Schwingshackl, L.; Weiderpass, E.; Rostgaard-Hansen, A.L.; et al. Meal patterns across ten European countries—Results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) calibration study. Public. Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2769–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.; Bryant, E.; Blundell, J.E.; King, N.A. Acute compensatory eating following exercise is associated with implicit hedonic wanting for food. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 97, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, N.A.; Horner, K.; Hills, A.P.; Byrne, N.M.; Wood, R.E.; Bryant, E.; Caudwell, P.; Finlayson, G.; Gibbons, C.; Hopkins, M.; et al. Exercise, appetite and weight management: Understanding the compensatory responses in eating behaviour and how they contribute to variability in exercise-induced weight loss. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Keating, S.E.; Holland, D.J.; Coombes, J.S.; Leveritt, M.D. The Chronic Effect of Interval Training on Energy Intake: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Obes. 2018, 2018, 6903208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, S.G.; Boyd, P.; Bailey, C.P.; Shams-White, M.M.; Agurs-Collins, T.; Hall, K.; Reedy, J.; Sauter, E.R.; Czajkowski, S.M. Perspective: Time-Restricted Eating Compared with Caloric Restriction: Potential Facilitators and Barriers of Long-Term Weight Loss Maintenance. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapela, S.; Martinuzzi, A.; Llobera, N.D.; Ceriani, F.; González, V.; Montalván, M.; Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E. Obesity and micronutrients deficit, when and how to suplement. Food Agric. Immunol. 2024, 35, 2381725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.E.; Mareschal, J.; Schwab, N.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Borloz, S.; Ostinelli, G.; Gauthier-Jaques, A.; Umwali, S.; Gonzalez Rodriguez, E.; Aeberli, D.; et al. The Effects of Time-Restricted Eating versus Standard Dietary Advice on Weight, Metabolic Health and the Consumption of Processed Food: A Pragmatic Randomised Controlled Trial in Community-Based Adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlou, V.; Cienfuegos, S.; Lin, S.; Ezpeleta, M.; Ready, K.; Corapi, S.; Wu, J.; Lopez, J.; Gabel, K.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; et al. Effect of Time-Restricted Eating on Weight Loss in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2339337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.L. Overview of dietary assessment methods for measuring intakes of foods, beverages, and dietary supplements in research studies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
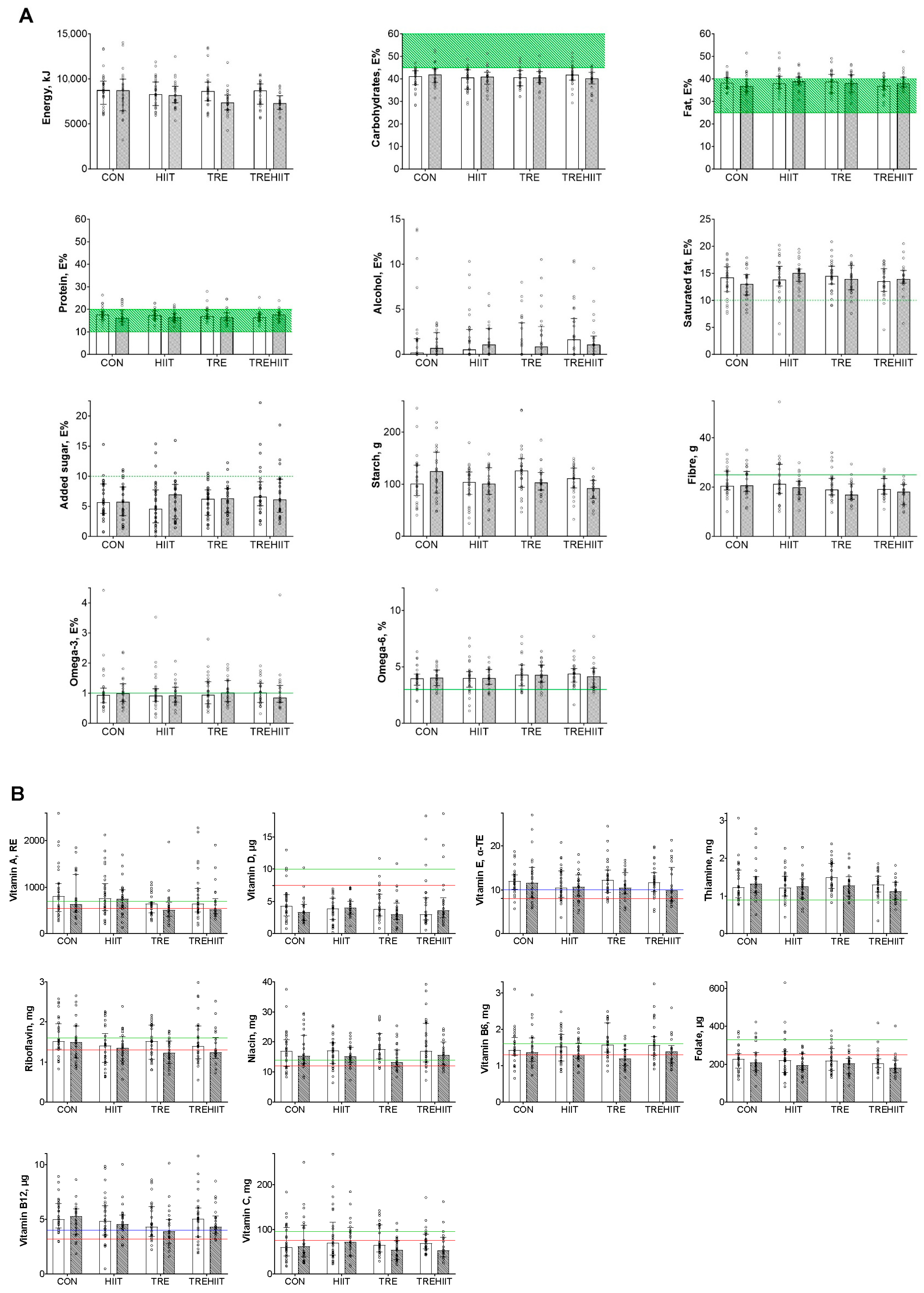

| CON (n = 33) | TRE (n = 33) | HIIT (n = 33) | TREHIIT (n = 32) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean (SD) | n | Mean (SD) | n | Mean (SD) | n | Mean (SD) | |
| Age, years | 33 | 36.4 (6.2) | 33 | 36.2 (5.9) | 33 | 34.9 (7.0) | 32 | 37.3 (5.7) |
| Weight, kg | 33 | 95.0 (11.2) | 33 | 91.0 (10.8) | 33 | 91.3 (13.0) | 32 | 88.2 (10.3) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 33 | 33.1 (4.2) | 33 | 31.8 (3.3) | 33 | 32.5 (4.5) | 32 | 31.4 (4.0) |
| Total energy intake, kJ/day | 28 | 8776.5 (1938.3) | 27 | 8683.9 (2002.0) | 30 | 8444.8 (1571.2) | 27 | 8222.5 (1430.6) |
| Carbohydrates, E% | 28 | 39.8 (4.9) | 27 | 40.4 (20.4) | 30 | 39.6 (5.0) | 27 | 41.6 (4.7) |
| Fat, E% | 28 | 38.0 (3.8) | 27 | 38.0 (5.4) | 30 | 38.6 (5.1) | 27 | 37.0 (3.6) |
| Protein, E% | 28 | 17.7 (3.1) | 27 | 17.9 (3.0) | 30 | 17.4 (2.6) | 27 | 16.7 (2.6) |
| Alcohol, E% | 28 | 2.2 (4.1) | 27 | 1.6 (2.4) | 30 | 1.9 (2.8) | 27 | 2.5 (3.1) |
| Baseline (Week 0) | End of Intervention (Week 6 + 7) | Difference (Group × Time) Compared with CON | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Estimated Effect | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Energy and macronutrients | |||||
| Total energy intake, kJ/day | |||||
| CON | 8776.5 (1938.3) | 8503.9 (2523.8) | |||
| TRE | 8683.9 (2002.0) | 7456.3 (1451.1) | −540.7 | −1260.0 to 178.4 | 0.139 |
| HIIT | 8444.8 (1571.2) | 8280.9 (1521.5) | 153.5 | −561.9 to 868.9 | 0.672 |
| TREHIIT | 8222.5 (1430.6) | 7262.6 (1181.5) | −727.3 | −1458.4 to 3.9 | 0.051 |
| Total energy intake, kcal/day | |||||
| CON | 2093.6 (465.5) | 2028.6 (602.5) | |||
| TRE | 2072.5 (478.8) | 1779.6 (346.7) | −127.3 | −299.0 to 44.5 | 0.145 |
| HIIT | 2016.1 (374.5) | 1977.7 (363.2) | 39.4 | −131.5 to 210.3 | 0.649 |
| TREHIIT | 1962.1 (341.2) | 1733.3 (281.5) | −172.1 | −346.7 to 2.6 | 0.053 |
| Carbohydrates, g/day | |||||
| CON | 210.9 (61.0) | 213.1 (70.0) | |||
| TRE | 210.1 (53.5) | 179.5 (37.5) | −21.6 | −43.0 to −0.1 | 0.049 |
| HIIT | 200.6 (50.6) | 200.7 (46.4) | −1.2 | −22.5 to 20.2 | 0.913 |
| TREHIIT | 204.1 (42.6) | 172.5 (37.3) | −28.9 | −50.7 to −7.0 | 0.010 |
| Carbohydrates, E% | |||||
| CON | 39.8 (4.9) | 41.8 (5.8) | |||
| TRE | 40.4 (20.4) | 41.0 (4.4) | −1.5 | −4.1 to 1.0 | 0.228 |
| HIIT | 39.6 (5.0) | 40.8 (4.3) | −1.3 | −3.9 to 1.2 | 0.291 |
| TREHIIT | 41.6 (4.7) | 40.1 (4.5) | −2.5 | −5.1 to 0.1 | 0.056 |
| Fibre, g/day | |||||
| CON | 22.1 (5.3) | 22.3 (6.1) | |||
| TRE | 20.6 (5.8) | 18.1 (4.4) | −2.0 | −4.3 to 0.3 | 0.085 |
| HIIT | 22.6 (8.8) | 20.0 (4.4) | −0.9 | −3.1 to 1.4 | 0.459 |
| TREHIIT | 19.7 (3.9) | 17.4 (4.3) | −2.6 | −5.0 to −0.3 | 0.027 |
| Starch, g/day | |||||
| CON | 109.2 (46.3) | 120.9 (48.0) | |||
| TRE | 126.3 (46.4) | 107.2 (27.0) | −13.2 | −28.1 to 1.8 | 0.083 |
| HIIT | 99.2 (35.0) | 100.2 (32.1) | −7.5 | −22.3 to 7.4 | 0.322 |
| TREHIIT | 107.0 (28.2) | 89.4 (22.6) | −26.0 | −41.2 to −10.8 | <0.001 |
| Added sugar, g/day | |||||
| CON | 33.2 (20.4) | 30.6 (20.1) | |||
| TRE | 30.7 (15.7) | 28.4 (16.0) | −1.9 | −10.2 to 6.4 | 0.652 |
| HIIT | 28.0 (23.0) | 31.9 (18.3) | 4.2 | −4.0 to 12.5 | 0.312 |
| TREHIIT | 38.8 (27.4) | 31.3 (21.1) | −1.8 | −10.2 to 6.7 | 0.677 |
| Added sugar, E% | |||||
| CON | 6.1 (3.2) | 5.9 (3.1) | |||
| TRE | 5.9 (2.6) | 6.2 (2.7) | −0.0 | −1.5 to 1.5 | 0.994 |
| HIIT | 5.3 (3.4) | 6.4 (3.4) | 0.9 | −0.6 to 2.3 | 0.247 |
| TREHIIT | 7.6 (4.3) | 7.0 (4.0) | 0.3 | −1.2 to 1.8 | 0.671 |
| Fat, g/day | |||||
| CON | 88.1 (19.3) | 85.0 (28.9) | |||
| TRE | 88.1 (17.4) | 76.2 (18.8) | −4.5 | −12.9 to 3.9 | 0.292 |
| HIIT | 86.1 (17.4) | 85.2 (15.6) | 1.8 | −6.7 to 10.1 | 0.673 |
| TREHIIT | 81.3 (18.1) | 75.0 (13.2) | −4.9 | −13.4 to 3.7 | 0.260 |
| Fat, E% | |||||
| CON | 38.0 (3.8) | 37.3 (5.4) | |||
| TRE | 38.0 (5.4) | 38.3 (4.7) | 0.8 | −1.5 to 3.0 | 0.496 |
| HIIT | 38.6 (5.1) | 39.0 (3.6) | 0.9 | −1.4 to 3.1 | 0.438 |
| TREHIIT | 37.0 (3.6) | 39.0 (4.0) | 1.8 | −0.5 to 4.0 | 0.117 |
| Saturated fat, g/day | |||||
| CON | 32.0 (11.7) | 29.9 (12.0) | |||
| TRE | 33.5 (10.4) | 27.5 (9.0) | −2.2 | −6.1 to 1.7 | 0.261 |
| HIIT | 31.4 (10.1) | 32.4 (7.5) | 3.0 | −0.9 to 6.8 | 0.133 |
| TREHIIT | 30.0 (9.4) | 27.3 (7.3) | −0.5 | −4.5 to 3.4 | 0.788 |
| Saturated fat, E% | |||||
| CON | 13.6 (3.2) | 13.1 (2.8) | |||
| TRE | 14.5 (2.9) | 13.7 (2.6) | 0.0 | −1.4 to 1.4 | 0.992 |
| HIIT | 14.0 (3.7) | 14.8 (2.5) | 1.3 | −0.1 to 2.7 | 0.068 |
| TREHIIT | 13.6 (2.9) | 14.2 (2.9) | 1.2 | −0.2 to 2.6 | 0.103 |
| Cholesterol, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 292.0 (102.5) | 241.2 (90.5) | |||
| TRE | 292.0 (110.6) | 241.3 (98.6) | 3.1 | −48.4 to 54.7 | 0.905 |
| HIIT | 276.7 (147.8) | 260.1 (85.0) | 37.6 | −13.8 to 89.0 | 0.150 |
| TREHIIT | 278.8 (126.0) | 282.7 (126.4) | 44.2 | −8.3 to 96.7 | 0.098 |
| Omega-3, g/day * | |||||
| CON | 2.4 (1.4) | 2.4 (1.2) | |||
| TRE | 2.5 (1.2) | 2.2 (0.9) | −0.1 | −0.6 to 0.3 | 0.583 |
| HIIT | 2.3 (1.4) | 2.1 (0.9) | −0.1 | −0.6 to 0.4 | 0.736 |
| TREHIIT | 2.2 (0.9) | 2.0 (1.4) | −0.2 | −0.9 to 0.4 | 0.483 |
| Omega-3, E% * | |||||
| CON | 1.1 (0.8) | 1.1 (0.5) | |||
| TRE | 1.1 (0.5) | 1.1 (0.4) | 0.0 | −0.2 to 0.2 | 0.844 |
| HIIT | 1.0 (0.6) | 1.0 (0.4) | 0.0 | −0.3 to 0.2 | 0.749 |
| TREHIIT | 1.0 (0.4) | 1.1 (0.8) | 0.0 | −0.3 to 0.4 | 0.878 |
| Omega-6, g/day * | |||||
| CON | 9.1 (2.5) | 9.8 (4.6) | |||
| TRE | 10.1 (3.9) | 8.8 (2.7) | −1.3 | −3.0 to 0.5 | 0.162 |
| HIIT | 8.9 (3.3) | 8.8 (2.3) | −0.7 | −2.5 to 1.1 | 0.456 |
| TREHIIT | 9.4 (2.8) | 7.9 (2.2) | −2.1 | −3.9 to −0.2 | 0.029 |
| Omega-6, E% * | |||||
| CON | 4.0 (1.0) | 4.4 (1.8) | |||
| TRE | 4.4 (1.3) | 4.4 (1.0) | −0.1 | −0.9 to 0.6 | 0.752 |
| HIIT | 4.0 (1.4) | 4.0 (0.9) | −0.3 | −1.1 to 0.5 | 0.448 |
| TREHIIT | 4.3 (1.0) | 4.2 (1.2) | −0.3 | −1.2 to 0.5 | 0.413 |
| Protein, g/day | |||||
| CON | 90.4 (15.8) | 85.5 (22.7) | |||
| TRE | 91.4 (19.4) | 75.4 (16.4) | −7.3 | −15.1 to 0.5 | 0.068 |
| HIIT | 87.1 (18.4) | 82.7 (16.1) | 0.6 | −7.2 to 8.4 | 0.875 |
| TREHIIT | 81.5 (16.7) | 75.7 (15.5) | −4.7 | −12.6 to 3.3 | 0.248 |
| Protein, E% | |||||
| CON | 17.7 (3.1) | 17.4 (3.6) | |||
| TRE | 17.9 (3.0) | 17.1 (3.1) | −0.5 | −1.7 to 0.7 | 0.371 |
| HIIT | 17.4 (2.6) | 16.9 (2.3) | −0.4 | −1.6 to 0.8 | 0.529 |
| TREHIIT | 16.7 (2.6) | 17.5 (2.4) | 0.4 | −0.8 to 1.6 | 0.522 |
| Alcohol, g/day * | |||||
| CON | 6.8 (13.8) | 3.6 (4.5) | |||
| TRE | 4.7 (6.9) | 5.5 (8.5) | 2.7 | −1.2 to 6.5 | 0.172 |
| HIIT | 5.7 (8.8) | 5.2 (6.8) | 2.4 | −1.1 to 5.8 | 0.183 |
| TREHIIT | 6.6 (8.4) | 4.3 (5.1) | 0.9 | −2.2 to 3.9 | 0.573 |
| Alcohol, E% * | |||||
| CON | 2.2 (4.1) | 1.2 (1.3) | |||
| TRE | 1.6 (2.4) | 2.0 (2.9) | 1.1 | −0.1 to 2.4 | 0.069 |
| HIIT | 1.9 (2.8) | 1.7 (2.0) | 0.9 | −0.1 to 1.9 | 0.075 |
| TREHIIT | 2.5 (3.1) | 1.8 (2.3) | 0.6 | −0.5 to 1.7 | 0.309 |
| Fat soluble vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RAE/day * | |||||
| CON | 904.4 (564.0) | 789.2 (469.4) | |||
| TRE | 629.2 (220.1) | 572.9 (349.2) | −104.8 | −295.2 to 85.6 | 0.281 |
| HIIT | 845.0 (484.2) | 761.6 (362.5) | 40.0 | −166.4 to 246.3 | 0.704 |
| TREHIIT | 814.1 (541.5) | 662.3 (389.0) | −95.1 | −316.5 to 126.3 | 0.400 |
| Vitamin D, µg/day* ᵃ | |||||
| CON | 4.8 (2.9) | 3.8 (2.0) | |||
| TRE | 4.6 (2.5) | 3.7 (2.4) | 0.3 | −0.7 to 1.2 | 0.583 |
| HIIT | 3.8 (2.0) | 4.2 (1.6) | 1.3 | 0.4 to 2.2 | 0.004 |
| TREHIIT | 4.7 (4.1) | 5.1 (4.4) | 1.3 | −0.1 to 2.5 | 0.038 |
| Vitamin E, α-TE/day | |||||
| CON | 12.0 (3.0) | 12.5 (5.7) | |||
| TRE | 12.5 (4.3) | 10.9 (3.2) | −1.4 | −3.2 to 0.4 | 0.127 |
| HIIT | 11.5 (3.9) | 10.8 (3.4) | −1.1 | −2.9 to 0.7 | 0.222 |
| TREHIIT | 12.1 (3.7) | 11.3 (4.5) | −1.3 | −3.2 to 0.5 | 0.158 |
| Water soluble vitamins | |||||
| Thiamine, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 1.4 (0.5) | 1.4 (0.5) | |||
| TRE | 1.6 (0.4) | 1.3 (0.4) | −0.2 | −0.4 to 0.1 | 0.043 |
| HIIT | 1.3 (0.4) | 1.2 (0.4) | −0.1 | −0.2 to 0.1 | 0.375 |
| TREHIIT | 1.3 (0.3) | 1.2 (0.3) | −0.2 | −0.4 to 0.0 | 0.025 |
| Riboflavin, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 1.6 (0.5) | 1.5 (0.5) | |||
| TRE | 1.5 (0.4) | 1.2 (0.3) | −0.1 | −0.3 to 0.1 | 0.193 |
| HIIT | 1.4 (0.5) | 1.3 (0.4) | 0.1 | −0.1 to 0.3 | 0.416 |
| TREHIIT | 1.5 (0.6) | 1.4 (0.4) | −0.1 | −0.3 to 0.1 | 0.525 |
| Niacin, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 17.5 (6.7) | 17.3 (6.3) | |||
| TRE | 18.6 (5.5) | 14.8 (4.4) | −2.2 | −4.8 to 0.5 | 0.109 |
| HIIT | 16.5 (4.7) | 15.7 (3.8) | −0.5 | −3.1 to 2.2 | 0.724 |
| TREHIIT | 19.4 (8.2) | 16.2 (4.4) | −1.7 | −4.4 to 1.0 | 0.207 |
| Vitamin B6, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 1.5 (0.5) | 1.5 (0.5) | |||
| TRE | 1.7 (0.5) | 1.2 (0.3) | −0.3 | −0.5 to −0.1 | 0.015 |
| HIIT | 1.5 (0.4) | 1.4 (0.3) | −0.1 | −0.3 to 0.1 | 0.551 |
| TREHIIT | 1.7 (0.6) | 1.4 (0.4) | −0.1 | −0.4 to 0.1 | 0.190 |
| Folate, µg/day | |||||
| CON | 228.0 (65.5) | 230.9 (81.5) | |||
| TRE | 226.8 (68.0) | 197.7 (51.7) | −19.5 | −47.2 to 8.2 | 0.165 |
| HIIT | 232.7 (109.7) | 206.3 (54.4) | 2.9 | −24.6 to 30.4 | 0.832 |
| TREHIIT | 214.4 (57.9) | 193.6 (58.7) | −20.1 | −48.2 to 18.1 | 0.160 |
| Vitamin B12, µg/day | |||||
| CON | 5.4 (1.5) | 5.0 (1.6) | |||
| TRE | 4.9 (1.9) | 4.2 (1.9) | −0.3 | −1.2 to 0.6 | 0.520 |
| HIIT | 5.0 (2.1) | 4.9 (1.5) | 0.2 | −0.7 to 1.0 | 0.736 |
| TREHIIT | 5.0 (2.2) | 4.8 (1.4) | −0.1 | −1.0 to 0.8 | 0.893 |
| Vitamin C, mg/day * | |||||
| CON | 70.8 (39.8) | 78.1 (55.2) | |||
| TRE | 77.4 (33.5) | 55.9 (24.5) | −22.3 | −43.0 to −1.7 | 0.034 |
| HIIT | 86.5 (59.4) | 78.4 (42.9) | 1.1 | −22.9 to 25.2 | 0.926 |
| TREHIIT | 74.3 (27.7) | 62.9 (33.7) | −15.3 | −36.3 to 5.7 | 0.154 |
| Minerals | |||||
| Calcium, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 819.3 (235.3) | 801.8 (231.5) | |||
| TRE | 849.9 (267.6) | 701.4 (248.8) | −75.1 | −185.8 to 35.6 | 0.182 |
| HIIT | 781.6 (302.0) | 810.1 (277.6) | 39.4 | −70.8 to 149.6 | 0.481 |
| TREHIIT | 762.0 (241.6) | 640.9 (201.9) | −112.8 | −225.4 to −0.1 | 0.050 |
| Iron, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 9.2 (2.3) | 9.1 (3.1) | |||
| TRE | 9.4 (2.2) | 8.4 (2.3) | −0.4 | −1.5 to 0.6 | 0.442 |
| HIIT | 9.1 (3.2) | 8.3 (2.5) | −0.0 | −1.1 to 1.0 | 0.979 |
| TREHIIT | 8.8 (2.2) | 8.2 (2.1) | −0.5 | −1.6 to 0.5 | 0.331 |
| Sodium, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 2711.0 (1005.0) | 2691.5 (865.9) | |||
| TRE | 3099.3 (922.0) | 2457.7 (703.7) | −320.2 | −675.1 to 34.6 | 0.076 |
| HIIT | 2384.4 (872.1) | 2509.7 (712.1) | 63.3 | −289.8 to 416.4 | 0.723 |
| TREHIIT | 2468.4 (720.0) | 2271.6 (679.5) | −181.9 | −542.8 to 178.9 | 0.320 |
| Potassium, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 3007.7 (816.1) | 2996.0 (1002.2) | |||
| TRE | 2995.0 (788.1) | 2362.7 (585.7) | −391.7 | −661.9 to −121.6 | 0.005 |
| HIIT | 2803.7 (794.5) | 2634.7 (690.0) | 15.6 | −252.8 to 284.0 | 0.909 |
| TREHIIT | 2740.9 (621.1) | 2381.4 (617.5) | −326.0 | −600.3 to −51.7 | 0.020 |
| Magnesium, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 295.1 (80.8) | 306.8 (108.6) | |||
| TRE | 306.6 (86.5) | 250.4 (69.6) | −45.2 | −75.0 to −15.5 | 0.003 |
| HIIT | 282.5 (101.8) | 270.9 (60.9) | −0.2 | −29.7 to 29.3 | 0.989 |
| TREHIIT | 272.5 (50.5) | 242.4 (59.4) | −37.6 | −67.8 to −7.4 | 0.015 |
| Zinc, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 10.5 (2.0) | 10.4 (2.9) | |||
| TRE | 11.0 (2.9) | 9.2 (2.0) | −1.0 | −2.2 to 0.2 | 0.093 |
| HIIT | 10.5 (3.3) | 10.2 (2.4) | 0.1 | −1.1 to 1.3 | 0.913 |
| TREHIIT | 9.8 (2.3) | 9.1 (2.3) | −0.8 | −2.1 to 0.4 | 0.180 |
| Selenium, µg/day * | |||||
| CON | 46.8 (14.1) | 43.2 (13.3) | |||
| TRE | 53.6 (26.9) | 45.3 (29.7) | 1.0 | −9.3 to 11.2 | 0.851 |
| HIIT | 45.7 (21.9) | 53.4 (64.6) | 10.6 | −16.1 to 37.3 | 0.437 |
| TREHIIT | 43.0 (15.7) | 39.7 (10.70) | −3.1 | −9.4 to 3.3 | 0.343 |
| Copper, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 1.1 (0.3) | 1.1 (0.4) | |||
| TRE | 1.1 (0.3) | 1.0 (0.3) | −0.1 | −0.2 to 0.0 | 0.161 |
| HIIT | 1.1 (0.5) | 1.0 (0.2) | −0.1 | −0.2 to 0.1 | 0.440 |
| TREHIIT | 1.0 (0.2) | 0.9 (0.2) | −0.2 | −0.3 to 0.0 | 0.026 |
| Phosphorus, mg/day | |||||
| CON | 1484.0 (329.1) | 1510.2 (430.0) | |||
| TRE | 1571.9 (406.2) | 1296.3 (344.8) | −197.7 | −326.8 to −68.7 | 0.003 |
| HIIT | 1414.1 (386.8) | 1363.2 (296.1) | −34.7 | −162.9 to 93.6 | 0.593 |
| TREHIIT | 1351.1 (312.1) | 1224.1 (279.0) | −169.6 | −300.7 to −38.6 | 0.012 |
| Iodine, µg/day | |||||
| CON | 119.7 (55.2) | 107.6 (38.4) | |||
| TRE | 121.9 (60.3) | 87.2 (43.1) | −21.0 | −43.6 to 1.7 | 0.069 |
| HIIT | 98.4 (48.5) | 97.0 (41.1) | −0.7 | −23.3 to 21.9 | 0.953 |
| TREHIIT | 102.0 (41.9) | 81.5 (25.0) | −19.7 | −42.8 to 3.4 | 0.094 |
| Vitamins | EAR | No Change/Intake Increased Above EAR, No. (%) | Intake Decreased Below EAR, No. (%) | p-Value Fisher’s Exact Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A, RAE/day | 540.0 | 0.006 | ||
| CON | 21 (91.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | ||
| HIIT | 22 (91.7%) | 2 (8.3%) | ||
| TRE | 13 (56.5%) | 10 (43.5%) | 0.043 vs. CON 0.034 vs. HIIT | |
| TREHIIT | 14 (63.6%) | 8 (36.4%) | ||
| Vitamin D, µg/day | 7.5 | 0.112 | ||
| CON | 20 (87.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| HIIT | 24 (100%) | 0 | ||
| TRE | 21 (91.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 22 (100%) | 0 | ||
| Vitamin E, α-TE/day | 8.0 | 0.695 | ||
| CON | 21 (91.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | ||
| HIIT | 22 (91.7%) | 2 (8.3%) | ||
| TRE | 20 (87.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 18 (81.8%) | 4 (18.2%) | ||
| Thiamine, mg/day | 0.65 | 0.740 | ||
| CON | 22 (95.7%) | 1 (4.3%) | ||
| HIIT | 24 (100.0%) | 0 | ||
| TRE | 23 (100.0%) | 0 | ||
| TREHIIT | 22 (100.0%) | 0 | ||
| Riboflavin, mg/day | 1.3 | 0.393 | ||
| CON | 19 (82.6%) | 4 (17.4%) | ||
| HIIT | 22 (91.7%) | 2 (8.3%) | ||
| TRE | 17 (73.9%) | 6 (26.1%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 17 (77.3%) | 5 (22.7%) | ||
| Niacin, mg/day | 12.0 | 0.213 | ||
| CON | 22 (95.7%) | 1 (4.3%) | ||
| HIIT | 23 (95.8%) | 1 (4.2%) | ||
| TRE | 18 (78.3%) | 5 (21.7%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 19 (86.4%) | 3 (13.6%) | ||
| Vitamin B6, mg/day | 1.3 | 0.128 | ||
| CON | 16 (69.6%) | 7 (30.4%) | ||
| HIIT | 19 (79.2%) | 5 (20.8%) | ||
| TRE | 12 (52.2%) | 11 (47.8%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 18 (81.8%) | 4 (18.2%) | ||
| Folate, µg/day | 250.0 | 0.887 | ||
| CON | 21 (91.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | ||
| HIIT | 22 (91.7%) | 2 (8.3%) | ||
| TRE | 20 (87.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 19 (86.4%) | 3 (13.6%) | ||
| Vitamin B12, µg/day | 3.2 | 0.221 | ||
| CON | 20 (87.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| HIIT | 23 (95.8%) | 1 (4.2%) | ||
| TRE | 18 (78.3%) | 5 (21.7%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 21 (95.5%) | 1 (4.5%) | ||
| Vitamin C, mg/day | 75.0 | 0.420 | ||
| CON | 21 (91.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | ||
| HIIT | 21 (87.5%) | 3 (12.5%) | ||
| TRE | 17 (73.9%) | 6 (26.1%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 18 (81.8%) | 4 (18.2%) | ||
| Minerals | ||||
| Calcium, mg/day | 750.0 | 0.651 | ||
| CON | 19 (82.6%) | 4 (17.4%) | ||
| HIIT | 21 (87.5%) | 3 (12.5%) | ||
| TRE | 17 (73.9%) | 6 (26.1%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 17 (77.3%) | 5 (22.7%) | ||
| Iron, mg/day | 9.0 | 0.596 | ||
| CON | 20 (87.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| HIIT | 22 (91.7%) | 2 (8.3%) | ||
| TRE | 20 (87.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 17 (77.3%) | 5 (22.7%) | ||
| Potassium, mg/day | 2800.0 | 0.501 | ||
| CON | 19 (82.6%) | 4 (17.4%) | ||
| HIIT | 21 (87.5%) | 3 (12.5%) | ||
| TRE | 16 (69.6%) | 7 (30.4%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 17 (77.3%) | 5 (22.7%) | ||
| Magnesium, mg/day | 240.0 | 0.015 | ||
| CON | 20 (78.3%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| HIIT | 22 (79.2%) | 2 (8.3%) | ||
| TRE | 17 (69.6%) | 6 (26.1%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 12 (54.5%) | 10 (45.5%) | ||
| Zinc, mg/day | 8.1 | 0.638 | ||
| CON | 18 (78.3%) | 5 (21.7%) | ||
| HIIT | 22 (91.7%) | 2 (8.3%) | ||
| TRE | 20 (87.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 19 (86.4%) | 3 (13.6%) | ||
| Selenium, µg/day | 60.0 | 0.929 | ||
| CON | 22 (95.7%) | 1 (4.3%) | ||
| HIIT | 21 (87.5%) | 3 (12.5%) | ||
| TRE | 21 (91.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 20 (90.9%) | 2 (9.1%) | ||
| Copper, mg/day | 0.7 | 0.402 | ||
| CON | 20 (87.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | ||
| HIIT | 23 (95.8%) | 1 (4.2%) | ||
| TRE | 21 (91.3%) | 2 (8.7%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 18 (81.8%) | 4 (18.2%) | ||
| Phosphorus, mg/day | 420.0 | - | ||
| CON | 23 (100%) | 0 | ||
| HIIT | 24 (100%) | 0 | ||
| TRE | 23 (100%) | 0 | ||
| TREHIIT | 22 (100%) | 0 | ||
| Iodine, µg/day | 120.0 | 0.568 | ||
| CON | 19 (82.6%) | 4 (17.4%) | ||
| HIIT | 18 (75.0%) | 6 (25.0%) | ||
| TRE | 15 (65.2%) | 8 (34.8%) | ||
| TREHIIT | 15 (68.2%) | 7 (31.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haganes, K.L.; Devlin, B.L.; Orr, R.K.; Moholdt, T. Impact of Time-Restricted Eating and High-Intensity Exercise on Nutrient Intake in Women with Overweight/Obesity: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020218
Haganes KL, Devlin BL, Orr RK, Moholdt T. Impact of Time-Restricted Eating and High-Intensity Exercise on Nutrient Intake in Women with Overweight/Obesity: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2025; 17(2):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020218
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaganes, Kamilla L., Brooke L. Devlin, Rosalie K. Orr, and Trine Moholdt. 2025. "Impact of Time-Restricted Eating and High-Intensity Exercise on Nutrient Intake in Women with Overweight/Obesity: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 17, no. 2: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020218
APA StyleHaganes, K. L., Devlin, B. L., Orr, R. K., & Moholdt, T. (2025). Impact of Time-Restricted Eating and High-Intensity Exercise on Nutrient Intake in Women with Overweight/Obesity: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 17(2), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020218






