Maternal Folate and Vitamin B 12 Concentrations During Pregnancy Influence Neonatal Nutritional Status and Adiposity: Results from the OBESO Cohort
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Maternal Assessment
2.3. Newborn Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Maternal Analysis
3.2. Maternal Folate, Vitamin B12 and Homocysteine Status
3.3. Neonatal Description
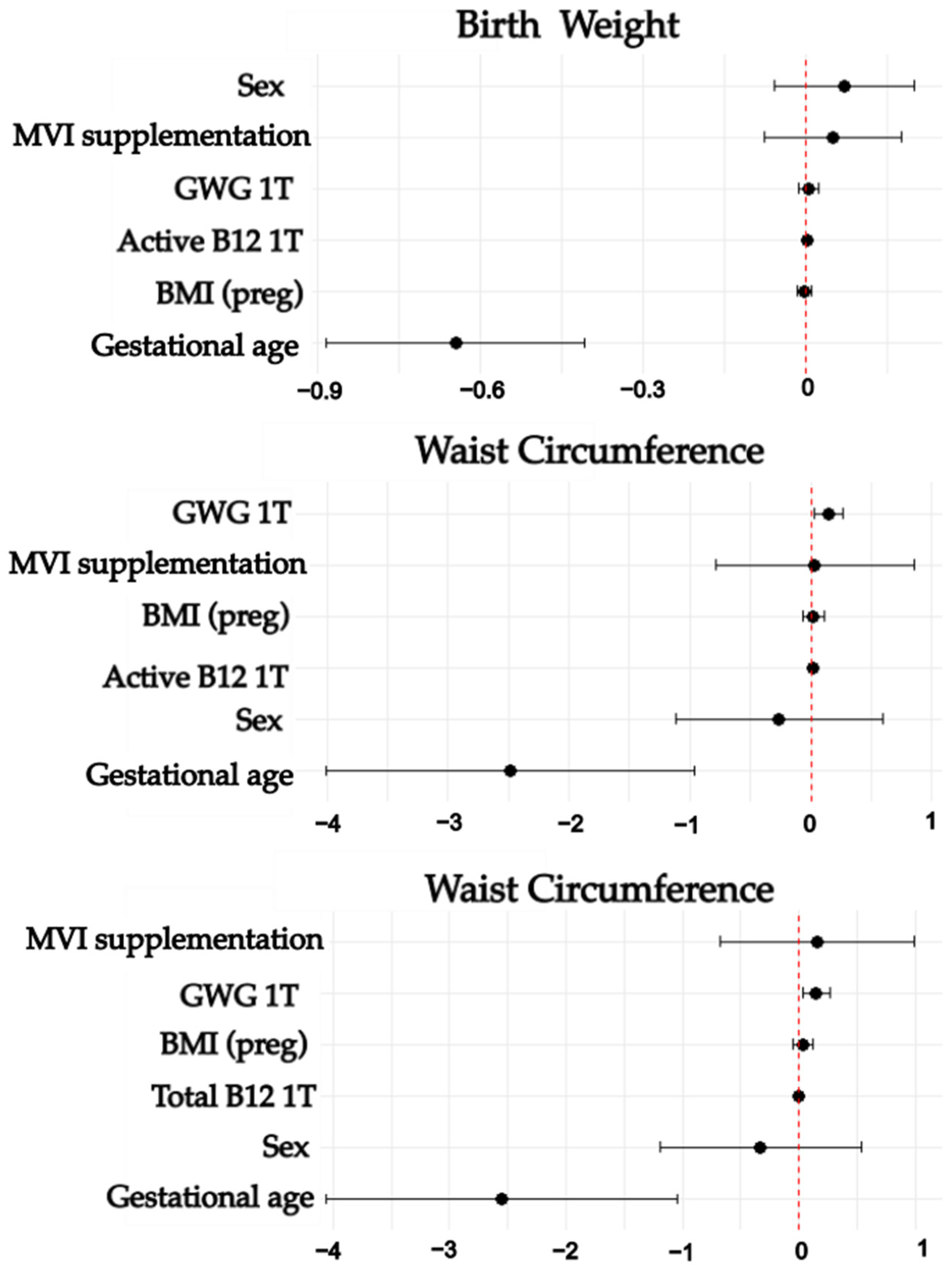
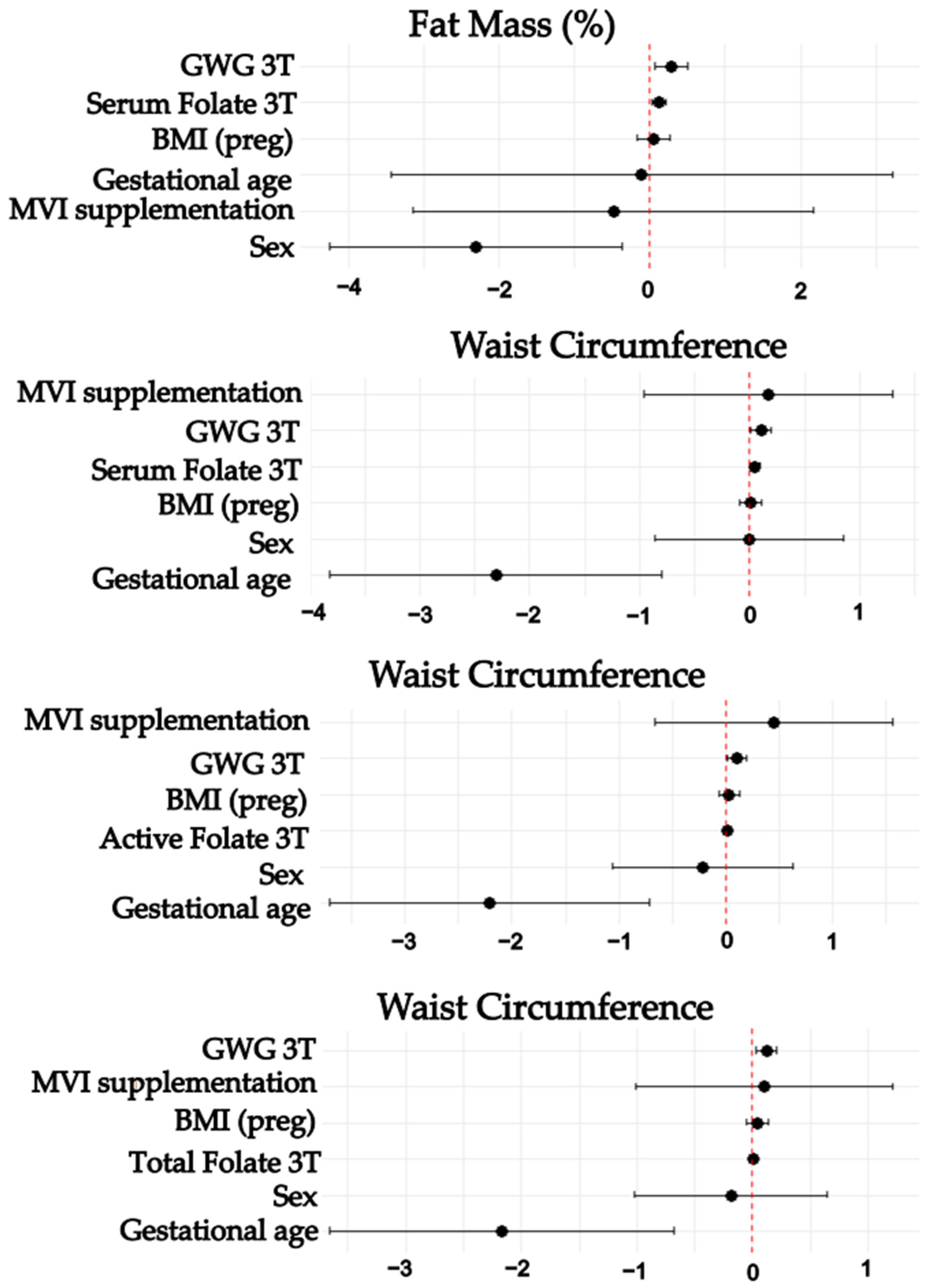
3.4. Associations Between Maternal Folate, Vitamin B12, Homocysteine Status, and Neonatal Nutrition Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanson, M.A.; Bardsley, A.; De-Regil, L.M.; Moore, S.E.; Oken, E.; Poston, L.; Ma, R.C.; McAuliffe, F.M.; Maleta, K.; Purandare, C.N.; et al. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) recommendations on adolescent, preconception, and maternal nutrition: “Think Nutrition First”. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2015, 131 (Suppl. S4), S213–S253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muktabhant, B.; Lawrie, T.A.; Lumbiganon, P.; Laopaiboon, M. Diet or exercise, or both, for preventing excessive weight gain in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 6, CD007145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moreno, J.; Juárez-López, J.S.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.L. Obesidad y embarazo. Rev. Med. MD 2013, 4, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Xu, X.; Yan, Y. Estimated global overweight and obesity burden in pregnant women based on panel data model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, E.J.; Kim, Y.J. What is fetal programming?: A lifetime health is under the control of in utero health. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2017, 60, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, J.E.; Ohuma, E.O.; Bradley, E.; Idueta, L.S.; Hazel, E.; Okwaraji, Y.B.; Erchick, D.J.; Yargawa, J.; Katz, J.; Lee, A.C.C.; et al. Small babies, big risks: Global estimates of prevalence and mortality for vulnerable newborns to accelerate change and improve counting. Lancet 2023, 401, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamaluddine, Z.; Sharara, E.; Helou, V.; El Rashidi, N.; Safadi, G.; El-Helou, N.; Ghattas, H.; Sato, M.; Blencowe, H.; Campbell, O.M.R. Effects of size at birth on health, growth and developmental outcomes in children up to age 18: An umbrella review. Arch. Dis. Child. 2023, 108, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezo, Y.; Elder, K.; Clement, A.; Clement, P. Folic Acid, Folinic Acid, 5 Methyl TetraHydroFolate Supplementation for Mutations That Affect Epigenesis through the Folate and One-Carbon Cycles. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, C.E.; Brassington, A.H.; Kwong, W.Y.; Sinclair, K.D. One-Carbon Metabolism: Linking Nutritional Biochemistry to Epigenetic Programming of Long-Term Development. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 7, 263–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamah-Levy, T.; Villalpando, S.; Mejía-Rodríguez, F.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Rangel-Baltazar, E.; Zambrano-Mujica, N. Prevalence of iron, folate, and vitamin B12 deficiencies in 20 to 49 years old women: Ensanut 2012. Salud Publica Mex. 2015, 57, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz-Góngora, V.; García-Guerra, A.; Shamah-Levy, T.; Villalpando, S.; Valdez-Echeverría, R.; Mejía-Rodríguez, F. Estado de micronutrimentos en niños, niñas y mujeres mexicanas: Análisis de la Ensanut Continua 2022. Salud Publica Mex. 2023, 65, s231–s237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, S.; Meier, V.; Patrick, H. Review of Vitamin B12 deficiency in pregnancy: A diagnosis not to miss as veganism and vegetarianism become more prevalent. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, M.; Urrutia, R.P.; Hudson, K.N.; Middleton, J.C.; Kahwati, L.C. Folic Acid Supplementation to Prevent Neural Tube Defects. JAMA 2023, 330, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.D.; O’Connor, D.L. Guideline No. 427: Folic Acid and Multivitamin Supplementation for Prevention of Folic Acid–Sensitive Congenital Anomalies. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2022, 44, 707–719.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS). WHO Recommendations on Antenatal Care for a Positive Pregnancy Expirience; Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS): Ginebra, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Behere, R.V.; Deshmukh, A.S.; Otiv, S.; Gupte, M.D.; Yajnik, C.S. Maternal Vitamin B12 Status During Pregnancy and Its Association with Outcomes of Pregnancy and Health of the Offspring: A Systematic Review and Implications for Policy in India. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 619176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, U.; Katre, P.; Yajnik, C.S. Maternal and Child Nutrition: The First 1,000 Days: 74th Nestlé Nutrition Institute Workshop; Bhatia, J., Bhutta, Z.A., Kalhan, S.C., Eds.; Nestlé Nutrition Institute Workshop Series; S. Karger: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic: Report of a WHO Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; 253p. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lohman, T.; Roche, A.; Martorell, R. Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual; Human Kinetics Books; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broeck, J.; Willie, D.; Younger, N. The World Health Organization child growth standards: Expected implications for clinical and epidemiological research. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Ismail, L.C.; Victora, C.G.; Ohuma, E.O.; Bertino, E.; Altman, D.G.; Lambert, A.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Carvalho, M.; Jaffer, Y.A.; et al. International standards for newborn weight, length, and head circumference by gestational age and sex: The Newborn Cross-Sectional Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project. Lancet 2014, 384, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Giuliani, F.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Bertino, E.; Ohuma, E.O.; Ismail, L.C.; Barros, F.C.; Altman, D.G.; Victora, C.; Noble, J.A.; et al. Postnatal growth standards for preterm infants: The Preterm Postnatal Follow-up Study of the INTERGROWTH-21 st Project. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e681–e691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirthensohn, M.; Wehrli, S.; Ljungblad, U.W.; Huemer, M. Biochemical, Nutritional, and Clinical Parameters of Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Infants: A Systematic Review and Analysis of 292 Cases Published between 1962 and 2022. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, P.L.; Florindo, C.; Janeiro, P.; Santos, R.L.; Mexia, S.; Rocha, H.; de Almeida, I.T.; Vilarinho, L.; Gaspar, A. Acquired Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Newborns: Positive Impact on Newborn Health through Early Detection. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Cano, A.M.; Perichart-Perera, O.; Gutiérrez-Castrellón, P. Importancia de la vitamina B12 y el folato en la salud perinatal. Gac. Med. Mex. 2023, 156, S27–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Rodríguez, J.; Díaz-López, A.; Canals-Sans, J.; Arija, V. Maternal Vitamin B12 Status during Pregnancy and Early Infant Neurodevelopment: The ECLIPSES Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, L.E.; Miller, E.E.; Mendez, M.A.; Murtha, A.P.; Murphy, S.K.; Hoyo, C. Maternal B vitamins: Effects on offspring weight and DNA methylation at genomically imprinted domains. Clin. Epigenetics 2016, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergen, N.E.; Schalekamp-Timmermans, S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Lindemans, J.; Russcher, H.; Tiemeier, H.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Steegers, E.A. Maternal and Neonatal Markers of the Homocysteine Pathway and Fetal Growth: The Generation R Study. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2016, 30, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildizdas, H.Y.; Erdogan, B.G.; Tepe, T.; Goruroglu, O.; Ozlu, F.; Satar, M.; Narli, N. Birth weight, head circumference, and length of newborns are unaffected by maternal levels of vitamin B12 and folate. Nutr. Res. 2022, 104, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajnik, C.S.; Deshpande, S.S.; Jackson, A.A.; Refsum, H.; Rao, S.; Fisher, D.J.; Bhat, D.S.; Naik, S.S.; Coyaji, K.J.; Joglekar, C.V.; et al. Vitamin B12 and folate concentrations during pregnancy and insulin resistance in the offspring: The Pune Maternal Nutrition Study. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadgil, M.; Joshi, K.; Pandit, A.; Otiv, S.; Joshi, R.; Brenna, J.T.; Patwardhan, B. Imbalance of folic acid and vitamin B12 is associated with birth outcome: An Indian pregnant women study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X. Maternal methyl donor supplementation: A potential therapy for metabolic disorder in offspring. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 124, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, D.J.; Conway, M.; O’keeffe, L.M.; McDonnell, C.M.; Bartels, H.C.; Yelverton, C.; Segurado, R.; Mehegan, J.; McAuliffe, F.M. Dietary intakes of iron, folate, and vitamin B12 during pregnancy and correlation with maternal hemoglobin and fetal growth: Findings from the ROLO longitudinal birth cohort study. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2023, 309, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sámano, R.; Martínez-Rojano, H.; Chico-Barba, G.; Gamboa, R.; Tolentino, M.; Toledo-Barrera, A.X.; Ramírez-González, C.; Mendoza-Flores, M.E.; Hernández-Trejo, M.; Godínez-Martínez, E. Serum Folate, Red Blood Cell Folate, and Zinc Serum Levels Are Related with Gestational Weight Gain and Offspring’s Birth-Weight of Adolescent Mothers. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Hao, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, J.; Tao, F.; Huang, K. Peri-Conceptional Folic Acid Supplementation and Children’s Physical Development: A Birth Cohort Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Yan, S.; Tao, F.; Huang, K. Birth outcomes and early growth patterns associated with age at adiposity rebound: The Ma’anshan birth cohort (MABC) study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.S.; Muldoon, K.A.; Sheyholislami, H.; Behan, N.; Lamers, Y.; Rybak, N.; White, R.R.; Harvey, A.L.; Gaudet, L.M.; Smith, G.N.; et al. Impact of high-dose folic acid supplementation in pregnancy on biomarkers of folate status and 1-carbon metabolism: An ancillary study of the Folic Acid Clinical Trial (FACT). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilsner, J.R.; Hu, H.; Wright, R.O.; Kordas, K.; Ettinger, A.S.; Sanchez, B.N.; Cantonwine, D.; Lazarus, A.L.; Cantoral, A.; Schnaas, L.; et al. Maternal MTHFR genotype and haplotype predict deficits in early cognitive development in a lead-exposed birth cohort in Mexico City. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carboni, L. Active Folate Versus Folic Acid: The Role of 5-MTHF (Methylfolate) in Human Health. Integr. Med. 2022, 21, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Fardous, A.M.; Heydari, A.R. Uncovering the Hidden Dangers and Molecular Mechanisms of Excess Folate: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Xie, H. Risk of Excess Maternal Folic Acid Supplementation in Offspring. Nutrients 2024, 16, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramijinni, R.R.; Mahajan, A.; Sapehia, D.; Singh, P.; Suri, V.; Kaur, J. Association of Altered Ratio of Maternal Folic Acid and Vitamin B12 during Pregnancy with Newborn Birth Weight, Head Circumference, and Chest Circumference. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2024, 43, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boachie, J.; Adaikalakoteswari, A.; Samavat, J.; Saravanan, P. Low Vitamin B12 and Lipid Metabolism: Evidence from Pre-Clinical and Clinical Studies. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, E.G.; Reynolds, C.M.E.; Cawley, S.; Woodside, J.V.; Molloy, A.M.; Turner, M.J. Folate and vitamin B12 levels in early pregnancy and maternal obesity. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 231, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, P.; Bhalerao, A. High Homocysteine Levels During Pregnancy and Its Association with Placenta-Mediated Complications: A Scoping Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e35244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katre, P.; Bhat, D.; Lubree, H.; Otiv, S.; Joshi, S.; Joglekar, C.; Rush, E.; Yajnik, C. Vitamin B12 and folic acid supplementation and plasma total homocysteine concentrations in pregnant Indian women with low B12 and high folate status. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 19, 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Sukumar, N.; Rafnsson, S.B.; Kandala, N.B.; Bhopal, R.; Yajnik, C.S.; Saravanan, P. Prevalence of vitamin B-12 insufficiency during pregnancy and its effect on offspring birth weight: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1232–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, P.; Bhalerao, A. Raised Maternal Homocysteine Levels in Antenatal Women at 10 to 14 Weeks of Gestation and Placenta-Mediated Complications: A Cohort Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e40423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, C.G.; Villar, J.; Barros, F.C.; Ismail, L.C.; Chumlea, C.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Bertino, E.; Ohuma, E.O.; Lambert, A.; Carvalho, M.; et al. Anthropometric Characterization of Impaired Fetal Growth. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, e151431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatte, K.; Farias, D.R.; Normando, P.; Berti, T.L.; de Castro, I.R.R.; Kac, G. High Serum Folate Concentration, Vitamin B12 Deficiency, and Anthropometric Nutritional Status in Brazilian Children Aged 6–59 Months: Data from the Brazilian National Survey of Child Nutrition. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J. The effect of prepregnancy body mass index on maternal micronutrient status: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, B.; Du, Y.; Rong, S.; Xu, G.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Bao, W. Inverse Association Between Serum Vitamin B12 Concentration and Obesity Among Adults in the United States. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. The Methyl Folate Trap a physiological response in man to prevent methyl group deficiency in kwashiorkor (methionine deficiency) and an explanation for folic-acid-induced exacerbation of subacute combined degeneration in pernicious anaemia. Lancet 1981, 318, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Nonato, I.; Galván-Valencia, Ó.; Hernández-Barrera, L.; Oviedo-Solís, C.; Barquera, S. Prevalencia de obesidad y factores de riesgo asociados en adultos mexicanos: Resultados de la Ensanut 2022. Salud Publica Mex. 2023, 65, s238–s247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamah-Levy, T.; Gaona-Pineda, E.B.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Morales-Ruan, C.; Valenzuela-Bravo, D.G.; Humarán IM, G.; Ávila-Arcos, M.A. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in Mexican school-aged children and adolescents. Ensanut 2020–2022. Salud Publica Mex. 2023, 65, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Molloy, A.M. Should vitamin B 12 status be considered in assessing risk of neural tube defects? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1414, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Selhub, J. Folate and vitamin B-12 status in relation to anemia, macrocytosis, and cognitive impairment in older Americans in the age of folic acid fortification. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetley, E.A.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Phinney, K.W.; Fazili, Z.; Lacher, D.A.; Bailey, R.L.; Blackmore, S.; Bock, J.L.; Brody, L.C.; Carmel, R.; et al. Biomarkers of folate status in NHANES: A roundtable summary. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 303S–312S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, L.B.; Stover, P.J.; McNulty, H.; Fenech, M.F.; Gregory, J.F., III; Mills, J.L.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Fazili, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ueland, P.M.; et al. Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development—Folate Review. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1636S–1680S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R. Indicators for assessing folate and vitamin B-12 status and for monitoring the efficacy of intervention strategies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 666S–672S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
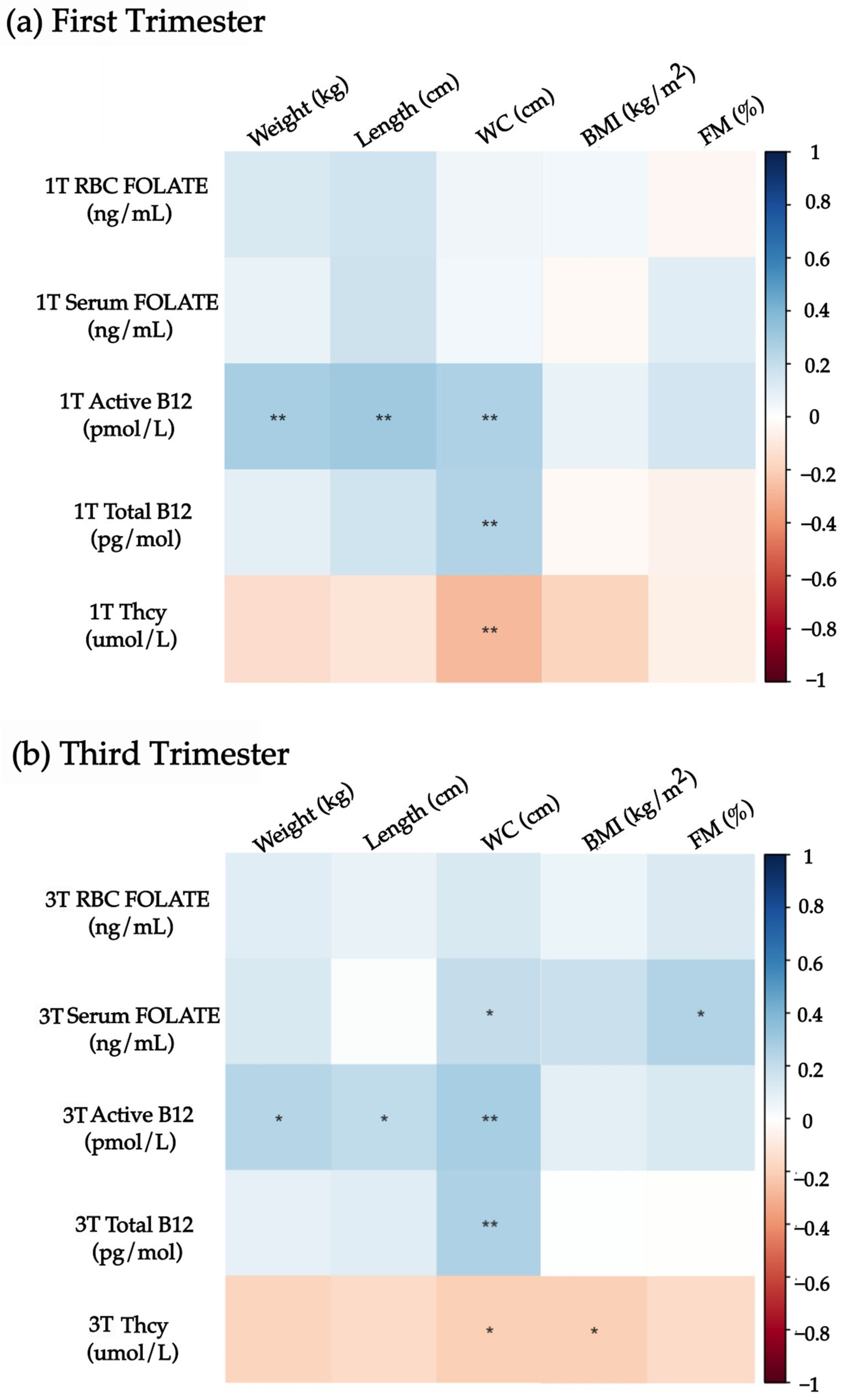
| First Trimester | Third Trimester | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal Characteristics (n = 90) | All (%, n) | Total Vitamin B12 (pg/mol) | Serum Folate (ng/mL) | Homocysteine (µmol/L) | Total Vitamin B12 (pg/mol) | Serum Folate (ng/mL) | Homocysteine (µmol/L) |
| All | 402.02 ± 313.11 | 25.40 ± 9.51 | 5.25 ± 1.11 | 296.21 ± 209.57 | 22.04 ± 9.38 | 4.78 ± 1.17 | |
| Maternal BMIpreg Normal Ow/Ob | 46.6% (42) 53.3% (48) | 477.26 ± 419.75 331.19 ± 142.63 | 24.39 ± 8.42 26.29 ± 10.38 | 5.08 ± 0.98 5.43 ± 1.21 | 321.76 ± 240.87 272.39 ± 177.50 | 20.41 ± 7.27 23.45 ± 10.78 | 4.81 ± 1.08 4.74 ± 1.24 |
| Parity Nulliparous Multiparous | 56.6% (51) 43.3% (39) | 400.88 ± 309.38 399.05 ± 322.80 | 26.63 ± 10.72 23.72 ± 7.36 | 5.24 ± 1.05 5.30 ± 1.21 | 287.50 ± 176.90 307.58 ± 247.90 | 21.37 ± 6.51 22.92 ± 12.21 | 4.89 ± 1.22 4.61 ± 1.09 |
| Education Basic Middle Higher | 21.1% (19) 32.2% (29) 46.6% (42) | 386.94 ± 172.65 334.03 ± 164.94 452.97 ± 421.01 | 24.61 ± 8.09 22.72 ± 10.17 27.72 ± 10.17 | 5.05 ± 0.89 5.46 ± 1.14 5.22 ± 1.18 | 265.94 ± 118.35 244.20 ± 85.97 345.80 ± 281.57 | 20.54 ± 6.65 19.20 ± 6.78 * 24.68 ± 11.25 * | 4.81 ± 1.30 5.02 ± 1.09 4.57 ± 1.16 |
| Socioeconomic status Low Medium/high | 61.1% (55) 38.9% (35) | 391.54 ± 322.43 421.17 ± 303.31 | 25.43 ± 9.34 25.70 ± 9.81 | 5.38 ± 1.22 5.02 ± 0.82 | 275.35 ± 177.18 335-76 ± 253.60 | 22.22 ± 7.13 22.21 ± 12.18 | 4.10 ± 1.26 4.68 ± 1.00 |
| First Trimester | Third Trimester | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Folate (ng/mL) | 25.40 ± 9.57 | 22.04 ± 9.38 | 0.037 |
| RBC Folate (ng/mL) | 666.32 ± 263.34 | 728.58 ± 369.86 | <0.001 |
| Total Vitamin B12 (pg/mol) | 402.02 ± 313.11 | 296.21 ± 209.57 | <0.001 |
| Active Vitamin B12 (pmol/L) | 76.30 ± 35.10 | 72.99 ± 32.48 | <0.001 |
| Homocysteine (µmol/L) | 5.26 ± 1.11 | 4.78 ± 1.17 | <0.001 |
| Newborn Characteristics (n = 90) | All (%, n) | First Trimester | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Vitamin B12 (pg/mol) | Active Vitamin B12 (pmol/L) | RBC Folate (ng/mL) | Serum Folate (ng/mL) | Homocysteine (µmol/L) | ||
| All | 402.02 ± 313.11 | 76.30 ± 35.10 | 666.32 ± 263.34 | 25.40 ± 9.57 | 5.26 ± 1.11 | |
| Sex Male Female | 43.3% (39) 56.7% (51) | 458.29 ± 360.89 * 358.73 ± 270.43 * | 78.72 ± 34.59 73.19 ± 34.93 | 686.36 ± 278.12 651.37 ± 253.51 | 26.54 ± 10.86 24.57 ± 8.40 | 5.10 ± 1.19 5.39 ± 1.04 |
| Resolution Vaginal birth Cesarean section | 44.4% (40) 55.6% (50) | 390.24 ± 349.63 408.56 ± 281.93 | 73.29 ± 35.17 77.39 ± 34.77 | 646.57 ± 234.96 682.42 ± 285.80 | 23.86 ± 10.51 26.69 ± 8.49 | 5.20 ± 1.25 5.32 ± 1.00 |
| Gestational age Preterm Term | 8.9% (8) 91.1% (82) | 310.57 ± 96.89 407.76 ± 324.24 | 60.12 ± 25.15 76.82 ± 35.19 | 669.85 ± 335.19 666.01 ± 258.86 | 20.35 ± 4.89 * 25.83 ± 9.70 * | 6.04 ± 0.89 * 5.20 ± 1.11 * |
| Stunting Yes No | 13.2% (12) 86.8% (78) | 301.75 ± 111.12 416.24 ± 336.02 | 68.07 ± 31.17 76.17 ± 35.58 | 673.08 ± 265.69 661.72 ± 263.90 | 20.15 ± 5.30 ** 26.31 ± 9.89 ** | 5.21 ± 1.11 ** 5.17 ± 1.05 ** |
| Low birth weight Yes No | 13.2% (12) 86.8% (78) | 301.54 ± 141.71 414.02 ± 328.51 | 48.13 ± 26.77 ** 79.74 ± 33.98 ** | 640.54 ± 231.17 669.94 ± 268.70 | 24.79 ± 7.27 25.50 ± 9.85 | 5.61 ± 1.42 5.21 ± 1.06 |
| BMI for age Wasting Normal Ow risk | 2.2% (2) 93.3% (84) 4.4% (4) | 282.50 ± 104.94 408.66 ± 326.39 293.00 ± 67.60 | 34.00 ± 15.83 76.21 ± 34.90 72.22 ± 36.00 | 363.50 ± 51.61 672.16 ± 265.60 633.50 ± 178.62 | 23.75 ± 7.14 25.55 ± 9.86 24.72 ± 5.69 | 5.73 ± 2.65 5.26 ± 1.11 5.45 ± 0.70 |
| Small for gestational age Yes No | 15.5% (14) 84.5% (76) | 430.90 ± 526.59 395.78 ± 275.58 | 68.47 ± 39.90 76.61 ± 33.99 | 626.58 ± 232.71 672.50 ± 268.63 | 24.11 ± 8.40 25.60 ± 9.71 | 5.66 ± 1.07 5.20 ± 1.11 |
| Newborn Characteristics (n = 90) | All (%, n) | Third Trimester | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Vitamin B12 (pg/mol) | Active Vitamin B12 (pmol/L) | RBC Folate (ng/mL) | Serum Folate (ng/mL) | Homocysteine (µmol/L) | ||
| All | 296.21 ± 209.57 | 72.99 ± 32.48 | 728.58 ± 369.86 | 22.04 ± 9.38 | 4.78 ± 1.17 | |
| Sex Male Female | 43.3% (39) 56.7% (51) | 317.923 ± 197.99 282.43 ± 217.702 | 81.26 ± 30.08 * 69.15 ± 33.71 * | 748.02 ± 373.00 726.74 ± 375.78 | 21.33 ± 7.89 22.48 ± 10.48 | 4.76 ± 1.2 4.78 ± 1.15 |
| Resolution Vaginal birth Cesarean section | 44.4% (40) 55.6% (50) | 274.25 ± 199.13 316.66 ± 216.69 | 70.46 ± 34.28 77.54 ± 31.13 | 716.525 ± 340.73 752.020 ± 399.505 | 20.366 ± 8.252 23.317 ± 10.188 | 4.79 ± 1.20 4.75 ± 1.15 |
| Gestational age Preterm Term | 8.9% (8) 91.1% (82) | 230.37 ± 83.02 304.39 ± 216.56 | 62.65 ± 23.53 75.54 ± 33.21 | 857.75 ± 556.00 724.04 ± 362.18 | 19.83 ± 7.02 22.20 ± 9.64 | 5.43 ± 1.25 * 4.70 ± 1.14 * |
| Stunting Yes No | 13.2% (12) 86.8% (78) | 221.50 ± 78.14 307.46 ± 224.02 | 65.87 ± 20.39 73.65 ± 34.27 | 751.08 ± 450.20 724.54 ± 361.61 | 18.72 ± 4.88 22.52 ± 9.95 | 5.21 ± 1.11 4.73 ± 1.17 |
| Low birth weight Yes No | 13.2% (12) 86.8% (78) | 210.00 ± 78.76 * 310.37 ± 220.03 * | 51.19 ± 25.89 ** 77.39 ± 32.36 ** | 749.45 ± 377.18 612.81 ± 334.36 | 18.14 ± 4.48 22.52 ± 9.89 | 4.66 ± 0.99 5.51 ± 1.95 |
| BMI for age Wasting Normal Ow risk | 2.2% (2) 93.3% (84) 4.4% (4) | 210.55 ± 75.66 304.09 ± 216.76 261.23 ± 110.50 | 47.95 ± 22.55 72.43 ± 32.68 78.11 ± 32.71 | 249.50 ± 53.03 737.16 ± 375.88 573.00 ± 294.84 | 14.12 ± 8.88 21.99 ± 9.60 23.08 ± 7.54 | 6.38 ± 2.12 4.76 ± 1.14 4.51 ± 1.02 |
| Small for gestational age Yes No | 15.5% (14) 84.5% (76) | 210.26 ± 66.82 ** 329.72 ± 234.47 ** | 75.37 ± 32.40 68.59 ± 34.31 | 615.69 ± 295.60 726.65 ± 382.05 | 21.94 ± 9.65 21.99 ± 9.46 | 4.66 ± 1.07 5.43 ± 1.05 |
| First Trimester | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | B | Standard Error | p | 95%CI | R2 | |
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Birth Weight | 0.001 | 0.342 | ||||
| Active B12 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.021 | 0.000 | 0.004 | |
| Gestational age | −0.646 | 0.12 | <0.001 | −0.884 | −0.407 | |
| Waist circumference | <0.001 | 0.162 | ||||
| Active B12 | 0.012 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.024 | |
| Gestational age | −2.487 | 0.763 | 0.002 | −4.007 | −0.967 | |
| Waist circumference | <0.001 | 0.173 | ||||
| Total B12 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.024 | 0 | 0.003 | |
| Gestational age | −2.551 | 0.757 | 0.001 | −4.059 | −1.044 | |
| Third Trimester | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | B | Standard Error | p | 95% CI | R2 | |
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Waist circumference | <0.001 | 0.174 | ||||
| Active B12 | 0.016 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.028 | |
| Gestational age | −2.212 | 0.75 | 0.004 | −3.706 | −0.717 | |
| GWG 3T | 0.103 | 0.046 | 0.027 | 0.012 | 0.194 | |
| Waist circumference | <0.001 | 0.244 | ||||
| Total B12 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.001 | 0.005 | |
| Gestational age | −2.172 | 0.747 | 0.005 | −3.659 | −0.685 | |
| GWG 3T | 0.121 | 0.046 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.213 | |
| Waist circumference | <0.001 | 0.15 | ||||
| Serum folate | 0.048 | 0.023 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.093 | |
| Gestational age | −2.309 | 0.759 | 0.003 | −3.82 | −0.797 | |
| GWG 3T | 0.103 | 0.046 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.195 | |
| Fat Mass (%) ** | <0.001 | 0.245 | ||||
| Serum folate | 0.127 | 0.047 | 0.009 | 0.033 | 0.220 | |
| Sex | −2.304 | 0.972 | 0.021 | −4.247 | −0.361 | |
| GWG 3T | 0.289 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.509 | |
| Variable | p | Odds Ratio | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| Low birth weight | ||||
| Active B12 1T | 0.007 | 0.959 | 0.93 | 0.989 |
| Active B12 3T | 0.026 | 0.967 | 0.939 | 0.996 |
| Stunting | ||||
| Thcy 1T | 0.005 | 2.320 | 1.172 | 4.590 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Ludlow, I.; Rodríguez-Cano, A.M.; Mendoza-Ortega, J.A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, C.; Suárez-Rico, B.V.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G.; Tolentino-Dolores, M.; Parra-Hernández, S.B.; Sánchez-Martínez, M.; Acevedo-Gallegos, S.; et al. Maternal Folate and Vitamin B 12 Concentrations During Pregnancy Influence Neonatal Nutritional Status and Adiposity: Results from the OBESO Cohort. Nutrients 2025, 17, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030372
González-Ludlow I, Rodríguez-Cano AM, Mendoza-Ortega JA, Rodríguez-Hernández C, Suárez-Rico BV, Estrada-Gutierrez G, Tolentino-Dolores M, Parra-Hernández SB, Sánchez-Martínez M, Acevedo-Gallegos S, et al. Maternal Folate and Vitamin B 12 Concentrations During Pregnancy Influence Neonatal Nutritional Status and Adiposity: Results from the OBESO Cohort. Nutrients. 2025; 17(3):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030372
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Ludlow, Isabel, Ameyalli M. Rodríguez-Cano, Jonatan A. Mendoza-Ortega, Carolina Rodríguez-Hernández, Blanca V. Suárez-Rico, Guadalupe Estrada-Gutierrez, Maricruz Tolentino-Dolores, Sandra B. Parra-Hernández, Maribel Sánchez-Martínez, Sandra Acevedo-Gallegos, and et al. 2025. "Maternal Folate and Vitamin B 12 Concentrations During Pregnancy Influence Neonatal Nutritional Status and Adiposity: Results from the OBESO Cohort" Nutrients 17, no. 3: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030372
APA StyleGonzález-Ludlow, I., Rodríguez-Cano, A. M., Mendoza-Ortega, J. A., Rodríguez-Hernández, C., Suárez-Rico, B. V., Estrada-Gutierrez, G., Tolentino-Dolores, M., Parra-Hernández, S. B., Sánchez-Martínez, M., Acevedo-Gallegos, S., & Perichart-Perera, O. (2025). Maternal Folate and Vitamin B 12 Concentrations During Pregnancy Influence Neonatal Nutritional Status and Adiposity: Results from the OBESO Cohort. Nutrients, 17(3), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030372






