Unraveling the Connections: Eating Issues, Microbiome, and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Eating Disorders Associated ASD
4. Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID)
4.1. ARFID Subtypes
4.2. ARFID Impact on Gut Microbiome
5. Impact of Sensory Processing Issues, Behavioral Rigidity, and Anxiety on Food Preferences
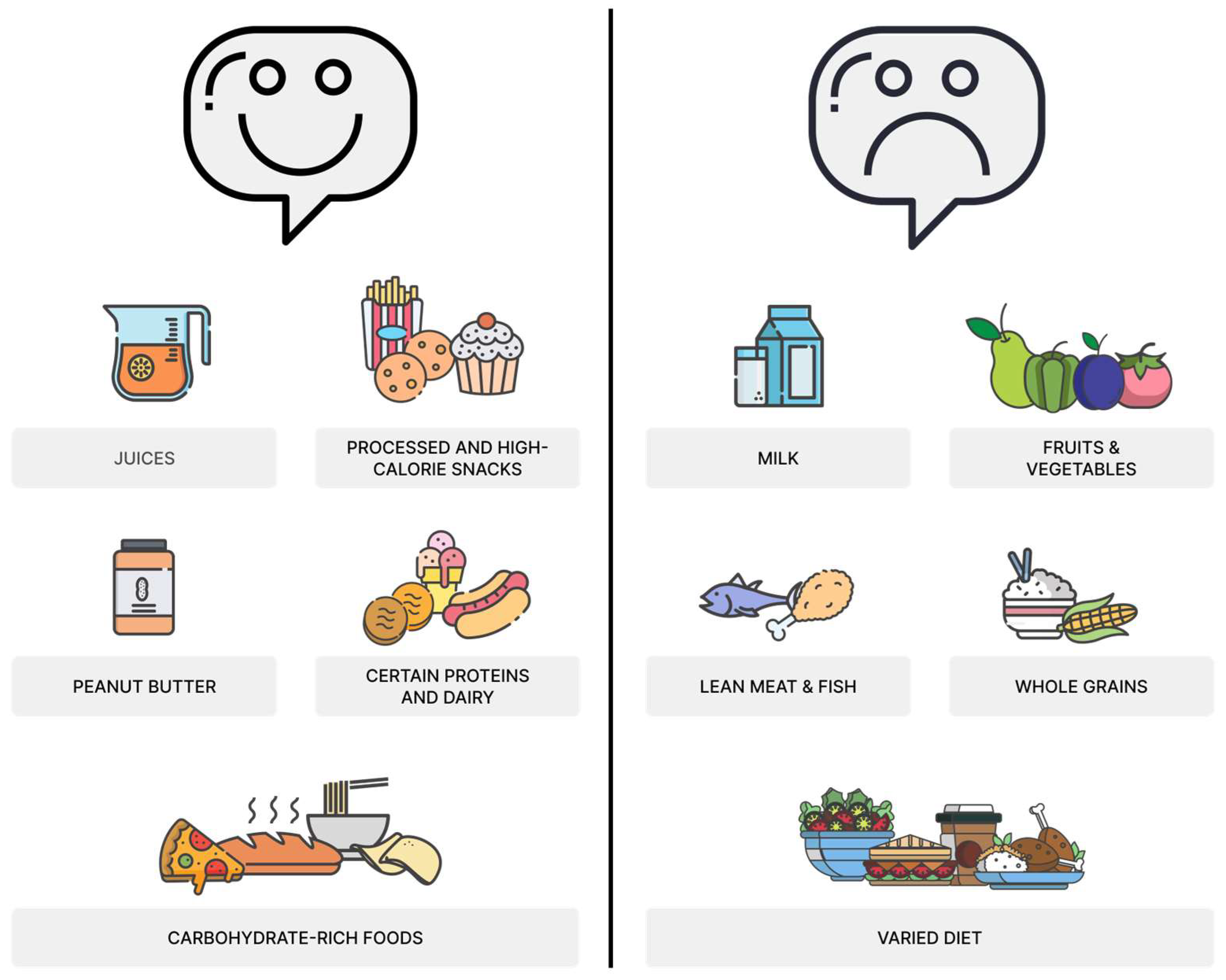
6. Dietary Patterns in Children with ASD
7. Diet Quality of Patients with ASD
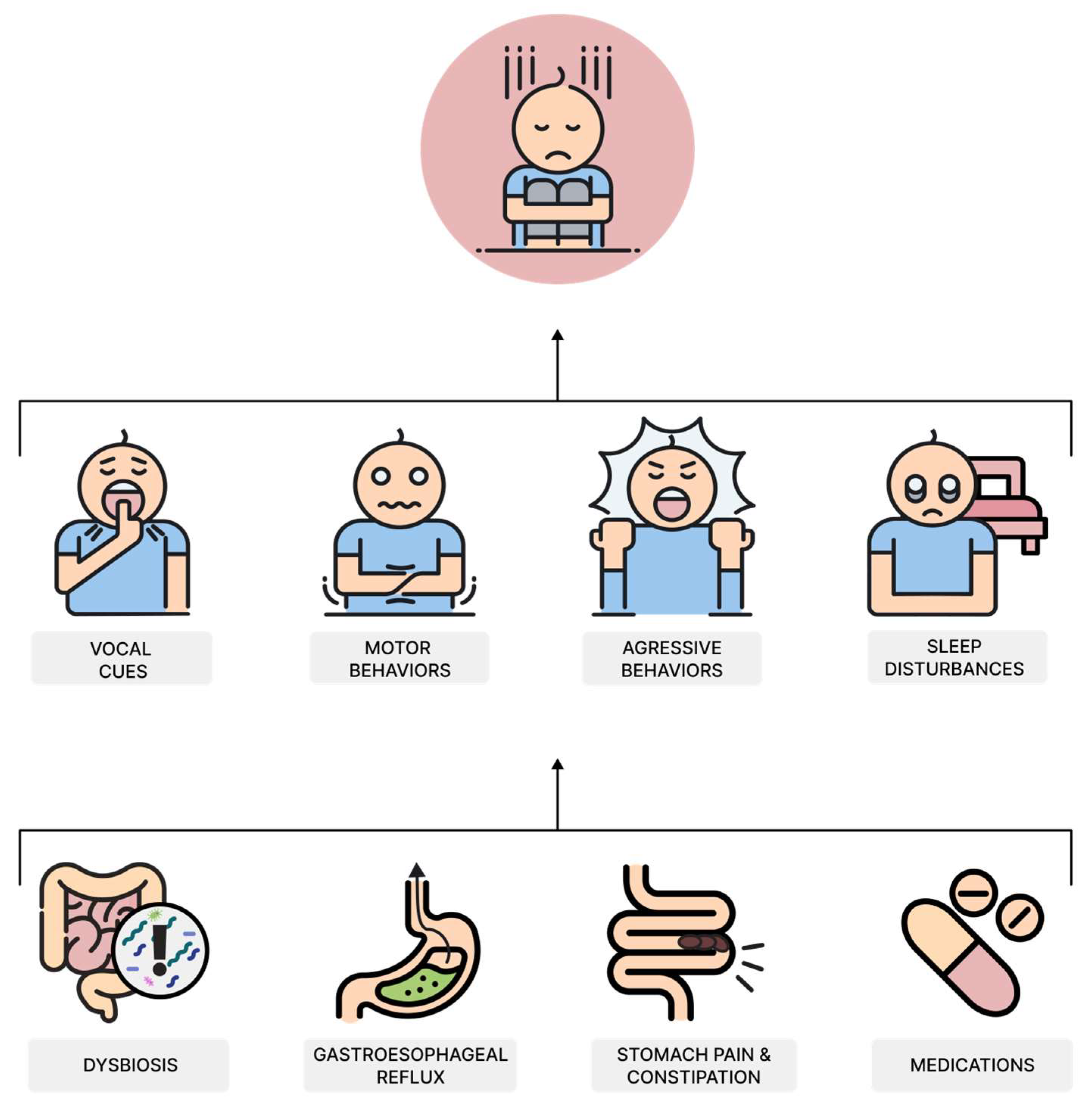
8. Characteristic of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Children with ASD
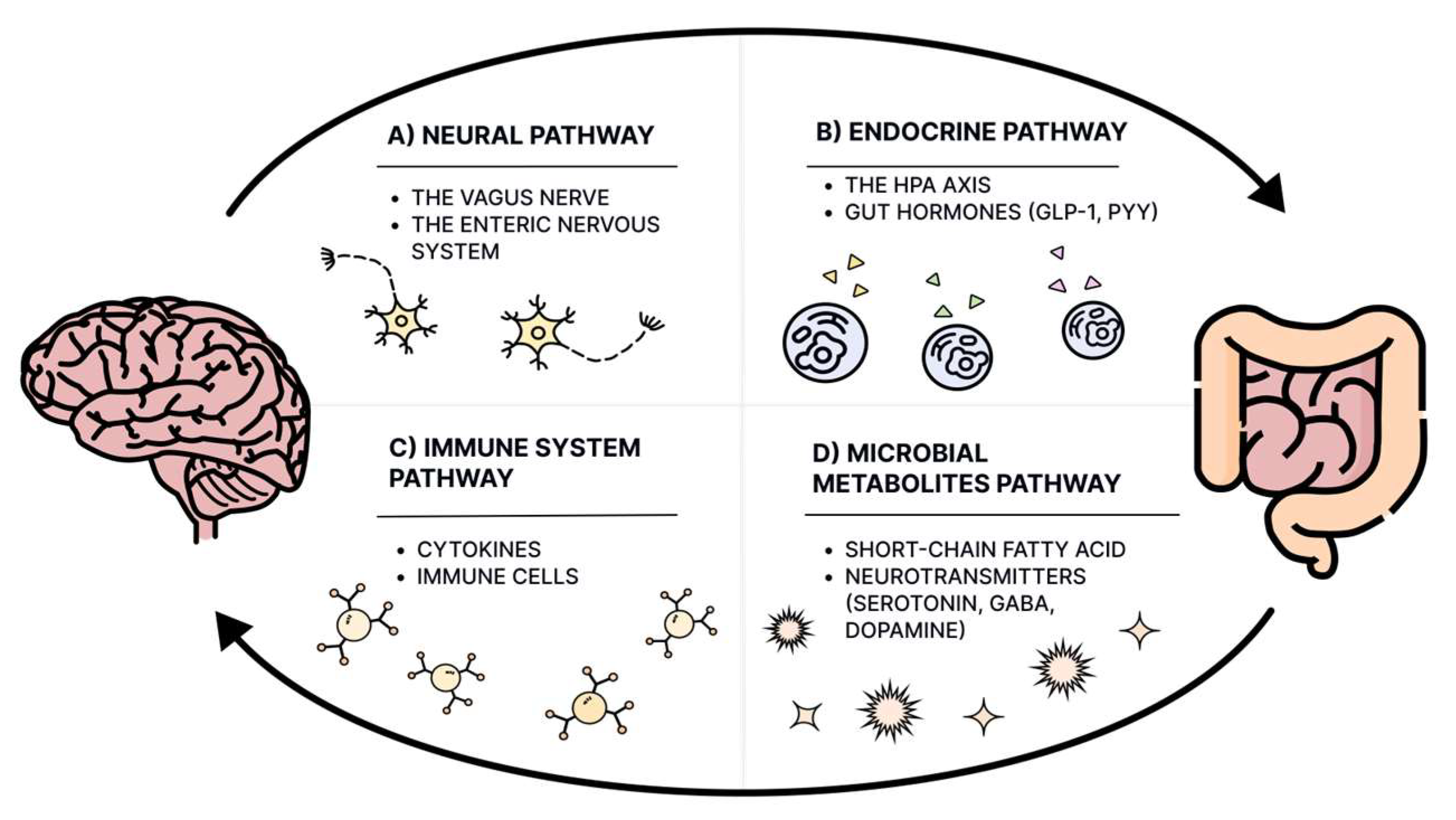
9. The Gut–Brain Axis and Gut Microbiota in ASD
10. How ARFID, Dietary Selectivity, and Dietary Neophobia Can Affect the Gut Microbiome?
11. The Gut–Brain–Behavior Cascade: A Self-Perpetuating Model in Autism Spectrum Disorder
12. Clinical Implications and Future Research Directions
13. Limitations and Strengths
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamp-Becker, I. Autism Spectrum Disorder in ICD-11-a Critical Reflection of Its Possible Impact on Clinical Practice and Research. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talantseva, O.I.; Romanova, R.S.; Shurdova, E.M.; Dolgorukova, T.A.; Sologub, P.S.; Titova, O.S.; Kleeva, D.F.; Grigorenko, E.L. The Global Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Three-Level Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1071181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidan, J.; Fombonne, E.; Scorah, J.; Ibrahim, A.; Durkin, M.S.; Saxena, S.; Yusuf, A.; Shih, A.; Elsabbagh, M. Global Prevalence of Autism: A Systematic Review Update. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviers, M.; Jongh, M.; Dickonson, L.; Malan, R.; Pike, T. Parent-Reported Feeding and Swallowing Difficulties of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (Aged 3 to 5 Years) Compared to Typically Developing Peers: A South African Study. Afr. Health Sci. 2020, 20, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; Wang, F.; Xing, Y.P.; Li, Y.; Lv, Y.; Ke, H.; Li, Z.; Lv, P.J.; et al. Gastrointestinal Symptoms Have a Minor Impact on Autism Spectrum Disorder and Associations with Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1000419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, W.G.; Berry, R.C.; McCracken, C.; Nuhu, N.N.; Marvel, E.; Saulnier, C.A.; Klin, A.; Jones, W.; Jaquess, D.L. Feeding Problems and Nutrient Intake in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review of the Literature. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2013, 43, 2159–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayes, S.D.; Zickgraf, H. Atypical Eating Behaviors in Children and Adolescents with Autism, ADHD, Other Disorders, and Typical Development. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2019, 64, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, G.; Linnsand, P.; Hermansson, J.; Dinkler, L.; Johansson, M.; Gillberg, C. Feeding Problems Including Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in a Multiethnic Population. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 780680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljac, E.; Hoofs, V.; Princen, M.M.; Poljac, E. Understanding Behavioural Rigidity in Autism Spectrum Conditions: The Role of Intentional Control. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraskewich, J.; von Ranson, K.M.; McCrimmon, A.; McMorris, C.A. Feeding and Eating Problems in Children and Adolescents with Autism: A Scoping Review. Autism 2021, 25, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, R.F.; Cutler, A. Dysregulated Breastfeeding Behaviors in Children Later Diagnosed with Autism. J. Perinat. Educ. 2015, 24, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provost, B.; Crowe, T.K.; Osbourn, P.L.; McClain, C.; Skipper, B.J. Mealtime Behaviors of Preschool Children: Comparison of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Children with Typical Development. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2010, 30, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnhill, K.; Tami, A.; Schutte, C.; Hewitson, L.; Olive, M.L. Targeted Nutritional and Behavioral Feeding Intervention for a Child with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2016, 2016, 1420549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, S.D.; Souders, M.C.; Kral, T.V.E.; Chao, A.M.; Pinto-Martin, J. Correlates of Feeding Difficulties Among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 52, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, W.G.; Postorino, V.; McCracken, C.E.; Berry, R.C.; Criado, K.K.; Burrell, T.L.; Scahill, L. Dietary Intake, Nutrient Status, and Growth Parameters in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Severe Food Selectivity: An Electronic Medical Record Review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-López, J.; Leiva-García, B.; Planells, E.; Planells, P. Food Selectivity, Nutritional Inadequacies, and Mealtime Behavioral Problems in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Compared to Neurotypical Children. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 2155–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandini, L.G.; Anderson, S.E.; Curtin, C.; Cermak, S.; Evans, E.W.; Scampini, R.; Maslin, M.; Must, A. Food Selectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Typically Developing Children. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łoboś, P.; Januszewicz, A. Food Neophobia in Children. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 25, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela-Zamora, A.F.; Ramírez-Valenzuela, D.G.; Ramos-Jiménez, A. Food Selectivity and Its Implications Associated with Gastrointestinal Disorders in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, G.L.; Llewellyn, C.; Fildes, A.; Ronald, A. Autism Spectrum Disorder and Food Neophobia: Clinical and Subclinical Links. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, T.V.E.; Souders, M.C.; Tompkins, V.H.; Remiker, A.M.; Eriksen, W.T.; Pinto-Martin, J.A. Child Eating Behaviors and Caregiver Feeding Practices in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Public Health Nurs. 2015, 32, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse/2024-01/mms/en#1242188600 (accessed on 7 December 2024).
- Kennedy, H.L.; Dinkler, L.; Kennedy, M.A.; Bulik, C.M.; Jordan, J. How Genetic Analysis May Contribute to the Understanding of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID). J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicely, T.A.; Lane-Loney, S.; Masciulli, E.; Hollenbeak, C.S.; Ornstein, R.M. Prevalence and Characteristics of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in a Cohort of Young Patients in Day Treatment for Eating Disorders. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkler, L.; Wronski, M.-L.; Lichtenstein, P.; Lundström, S.; Larsson, H.; Micali, N.; Taylor, M.J.; Bulik, C.M. Etiology of the Broad Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder Phenotype in Swedish Twins Aged 6 to 12 Years. JAMA Psychiatry 2023, 80, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koomar, T.; Thomas, T.R.; Pottschmidt, N.R.; Lutter, M.; Michaelson, J.J. Estimating the Prevalence and Genetic Risk Mechanisms of ARFID in a Large Autism Cohort. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 668297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keski-Rahkonen, A.; Ruusunen, A. Avoidant-Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Autism: Epidemiology, Etiology, Complications, Treatment, and Outcome. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2023, 36, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, S.; van Dyck, Z.; Dremmel, D.; Munsch, S.; Hilbert, A. Early-Onset Restrictive Eating Disturbances in Primary School Boys and Girls. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 24, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders|Psychiatry Online. Available online: https://psychiatryonline.org/doi/book/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 (accessed on 7 December 2024).
- ICD-11. Available online: https://icd.who.int/en (accessed on 7 December 2024).
- Fonseca, N.K.O.; Curtarelli, V.D.; Bertoletti, J.; Azevedo, K.; Cardinal, T.M.; Moreira, J.D.; Antunes, L.C. Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder: Recent Advances in Neurobiology and Treatment. J. Eat. Disord. 2024, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Cerezo, J.; Neale, J.; Julius, N.; Croudace, T.; Lynn, R.M.; Hudson, L.D.; Nicholls, D. Subtypes of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Children and Adolescents: A Latent Class Analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 68, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, K.T.; Thomas, J.J.; Hastings, E.; Edkins, K.; Lamont, E.; Nevins, C.M.; Patterson, R.M.; Murray, H.B.; Bryant-Waugh, R.; Becker, A.E. Prevalence of DSM-5 Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in a Pediatric Gastroenterology Healthcare Network. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, L.; Mandy, W.; Bryant-Waugh, R. Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Severe Food Selectivity in Children and Young People with Autism: A Scoping Review. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2022, 64, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.; Archibald, T.; Hembry, P.; Howard, M.; Kelly, C.; Loomes, R.; Markham, L.; Moss, H.; Munuve, A.; Oros, A.; et al. The Clinical Presentation of Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder Is Largely Independent of Sex, Autism Spectrum Disorder and Anxiety Traits. medRxiv 2023, 63, 102190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Sun, S.; Deng, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Du, H.; Gao, J.; Zou, X.; Lin, X.; et al. Using 16S rDNA and Metagenomic Sequencing Technology to Analyze the Fecal Microbiome of Children with Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.-C.; Lombardo, M.V.; Baron-Cohen, S. Autism. Lancet 2014, 383, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, O.; Kaple, M. Sensory Processing Differences in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Narrative Review of Underlying Mechanisms and Sensory-Based Interventions. Cureus 2023, 15, e48020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistol, L.T.; Bandini, L.G.; Must, A.; Phillips, S.; Cermak, S.A.; Curtin, C. Sensory Sensitivity and Food Selectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 48, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrska, A.; Błażejczyk, I.; Faruga, A.; Potaczek, M.; Wilczyński, K.M.; Janas-Kozik, M. Patterns of Food Selectivity among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, K.L.; Anderson, S.E.; Curtin, C.; Must, A.; Bandini, L.G. A Comparison of Food Refusal Related to Characteristics of Food in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Typically Developing Children. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.L.; Stern, K. Co-Occurring Behavioral Difficulties in Children with Severe Feeding Problems: A Descriptive Study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 58, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, M.A.; Nelson, N.W.; Curtis, A.B. Longitudinal Follow-up of Factors Associated with Food Selectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism 2014, 18, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, M.A.; Nelson, N.W.; Curtis, A.B. Associations of Physiological Factors, Age, and Sensory Over-Responsivity with Food Selectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Open J. Occup. Ther. 2012, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandini, L.; Curtin, C.; Phillips, S.; Anderson, S.E.; Maslin, M.; Must, A. Changes in Food Selectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.S.; Tovar, A.; Jayasuriya, A.T.; Welker, E.; Schober, D.J.; Copeland, K.; Dev, D.A.; Murriel, A.L.; Amso, D.; Ward, D.S. The Relationship between Physical Activity and Diet and Young Children’s Cognitive Development: A Systematic Review. Prev. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daelmans, B.; Darmstadt, G.L.; Lombardi, J.; Black, M.M.; Britto, P.R.; Lye, S.; Dua, T.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Richter, L.M. Lancet Early Childhood Development Series Steering Committee Early Childhood Development: The Foundation of Sustainable Development. Lancet 2017, 389, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Yang, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Jia, F.; Wu, L.; Hao, Y.; et al. Association of Feeding Patterns in Infancy with Later Autism Symptoms and Neurodevelopment: A National Multicentre Survey. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emond, A.; Emmett, P.; Steer, C.; Golding, J. Feeding Symptoms, Dietary Patterns, and Growth in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Pediatrics 2010, 126, e337–e342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, E.W.; Must, A.; Anderson, S.E.; Curtin, C.; Scampini, R.; Maslin, M.; Bandini, L. Dietary Patterns and Body Mass Index in Children with Autism and Typically Developing Children. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2012, 6, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Flores-Rojas, K.; de la Torre-Aguilar, M.J.; Gomez-Fernández, A.R.; Martín-Borreguero, P.; Perez-Navero, J.L.; Gil, A.; Gil-Campos, M. Dietary Patterns, Eating Behavior, and Nutrient Intakes of Spanish Preschool Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspini, B.; Prosperi, M.; Guiducci, L.; Santocchi, E.; Tancredi, R.; Calderoni, S.; Morales, M.A.; Morelli, M.; Simione, M.; Fiechtner, L.; et al. Dietary Patterns and Weight Status in Italian Preschoolers with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Typically Developing Children. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, P.; Venkatesh, L.; Bharti, B.; Singhi, P. Feeding Problems and Nutrient Intake in Children with and without Autism: A Comparative Study. Indian. J. Pediatr. 2017, 84, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diolordi, L.; del Balzo, V.; Bernabei, P.; Vitiello, V.; Donini, L.M. Eating Habits and Dietary Patterns in Children with Autism. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2014, 19, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, K.A.; Williams, K. Food Preferences and Factors Influencing Food Selectivity for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2006, 27, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, C.; Hubbard, K.; Anderson, S.E.; Mick, E.; Must, A.; Bandini, L.G. Food Selectivity, Mealtime Behavior Problems, Spousal Stress, and Family Food Choices in Children with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 3308–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margari, L.; Marzulli, L.; Gabellone, A.; de Giambattista, C. Eating and Mealtime Behaviors in Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Current Perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 2083–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguid, N.; Anwar, M.; Zaki, S.; Kandeel, W.; Ahmed, N.; Tewfik, I. Dietary Patterns of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Study Based in Egypt. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 3, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicer, A.H.; Alsaffar, A.A. Body Mass Index, Dietary Intake and Feeding Problems of Turkish Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 3978–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meguid, N.A.; Anwar, M.; Bjørklund, G.; Hashish, A.; Chirumbolo, S.; Hemimi, M.; Sultan, E. Dietary Adequacy of Egyptian Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Compared to Healthy Developing Children. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cermak, S.A.; Curtin, C.; Bandini, L.G. Food Selectivity and Sensory Sensitivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinlin, L.M.; Weinstein, M. Scurvy: Old Disease, New Lessons. Paediatr. Int. Child. Health 2023, 43, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumeyer, A.M.; Gates, A.; Ferrone, C.; Lee, H.; Misra, M. Bone Density in Peripubertal Boys with Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2013, 43, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittana, M.; Ahmadani, A.; Williams, K.E.; Attlee, A. Nutritional Status and Feeding Behavior of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Middle East and North Africa Region: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahathuduwa, C.N.; West, B.D.; Blume, J.; Dharavath, N.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Mastergeorge, A. The Risk of Overweight and Obesity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, C.; Anderson, S.E.; Must, A.; Bandini, L. The Prevalence of Obesity in Children with Autism: A Secondary Data Analysis Using Nationally Representative Data from the National Survey of Children’s Health. BMC Pediatr. 2010, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shedlock, K.; Susi, A.; Gorman, G.H.; Hisle-Gorman, E.; Erdie-Lalena, C.R.; Nylund, C.M. Autism Spectrum Disorders and Metabolic Complications of Obesity. J. Pediatr. 2016, 178, 183–187.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, A.Ç.; Özcan, Ö. The Nutritional Behavior of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder, Parental Feeding Styles, and Anthropometric Measurements. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2022, 76, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, S.; Nasser, J.A. Nutritional Status of Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Do We Know Enough? Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewska, J.; Klukowski, M. Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Links and Risks—A Possible New Overlap Syndrome. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2015, 6, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holingue, C.; Newill, C.; Lee, L.-C.; Pasricha, P.J.; Daniele Fallin, M. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review of the Literature on Ascertainment and Prevalence. Autism Res. 2018, 11, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Jing, J.; Liu, B.; Strathearn, L.; Bao, W. Association of Food Allergy and Other Allergic Conditions with Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e180279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristori, M.V.; Quagliariello, A.; Reddel, S.; Ianiro, G.; Vicari, S.; Gasbarrini, A.; Putignani, L. Autism, Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Nutritional Interventions. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feillet, F.; Bocquet, A.; Briend, A.; Chouraqui, J.-P.; Darmaun, D.; Frelut, M.-L.; Girardet, J.-P.; Guimber, D.; Hankard, R.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Nutritional Risks of ARFID (Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorders) and Related Behavior. Arch. Pediatr. 2019, 26, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofei, S.Y.; Fuchs, G.J. Constipation Burden in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Emergency Department and Healthcare Use. J. Pediatr. 2018, 202, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Rosenbaum, J. Chronic Diarrhoea in Children: A Practical Algorithm-Based Approach. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2020, 56, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, V.L.; Soke, G.N.; Reynolds, A.; Tian, L.H.; Wiggins, L.; Maenner, M.; DiGuiseppi, C.; Kral, T.V.E.; Hightshoe, K.; Ladd-Acosta, C.; et al. Association between Pica and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Preschoolers with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder: Study to Explore Early Development. Disabil. Health J. 2021, 14, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Beltagi, M.; Saeed, N.K.; Bediwy, A.S.; Elbeltagi, R.; Alhawamdeh, R. Role of Gastrointestinal Health in Managing Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2023, 12, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriacou, C.; Forrester-Jones, R.; Triantafyllopoulou, P. Clothes, Sensory Experiences and Autism: Is Wearing the Right Fabric Important? J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 53, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, K.; Li, H.; Huo, R. Propranolol Treatment for Infantile Hemangiomas: Short-Term Adverse Effects and Follow-Up to Age Two. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2728952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.; Coghill, D. Adverse Effects of Pharmacotherapies for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Epidemiology, Prevention and Management. CNS Drugs 2008, 22, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfageh, B.H.; Wang, Z.; Mongkhon, P.; Besag, F.M.C.; Alhawassi, T.M.; Brauer, R.; Wong, I.C.K. Safety and Tolerability of Antipsychotic Medication in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Paediatr. Drugs 2019, 21, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madra, M.; Ringel, R.; Margolis, K.G. Gastrointestinal Issues and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 44, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosperi, M.; Santocchi, E.; Muratori, F.; Narducci, C.; Calderoni, S.; Tancredi, R.; Morales, M.A.; Guiducci, L. Vocal and Motor Behaviors as a Possible Expression of Gastrointestinal Problems in Preschoolers with Autism Spectrum Disorder. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leader, G.; Abberton, C.; Cunningham, S.; Gilmartin, K.; Grudzien, M.; Higgins, E.; Joshi, L.; Whelan, S.; Mannion, A. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, C.; Card, B. A Pilot Study to Evaluate Nutritional Influences on Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Behavior Patterns in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Complement. Ther. Med. 2012, 20, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The Gut-Brain Axis: Interactions between Enteric Microbiota, Central and Enteric Nervous Systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fülling, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut Microbe to Brain Signaling: What Happens in Vagus…. Neuron 2019, 101, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, A.; Bloom, S.R. Gut Hormones and Appetite Control: A Focus on PYY and GLP-1 as Therapeutic Targets in Obesity. Gut Liver 2012, 6, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, P.; Parker, H.E.; Adriaenssens, A.E.; Hodgson, J.M.; Cork, S.C.; Trapp, S.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Identification and Characterization of GLP-1 Receptor-Expressing Cells Using a New Transgenic Mouse Model. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut Microbiota, Metabolites and Host Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis in Behaviour and Brain Disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, N.; Morris, M.E. Role of Monocarboxylate Transporters in Drug Delivery to the Brain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.W.; On, N.H.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Miller, D.W.; Hatch, G.M. Fatty Acid Transport Protein Expression in Human Brain and Potential Role in Fatty Acid Transport across Human Brain Microvessel Endothelial Cells. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braniste, V.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Kowal, C.; Anuar, F.; Abbaspour, A.; Tóth, M.; Korecka, A.; Bakocevic, N.; Ng, L.G.; Kundu, P.; et al. The Gut Microbiota Influences Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 263ra158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, G.; Sleeth, M.L.; Sahuri-Arisoylu, M.; Lizarbe, B.; Cerdan, S.; Brody, L.; Anastasovska, J.; Ghourab, S.; Hankir, M.; Zhang, S.; et al. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate Reduces Appetite via a Central Homeostatic Mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, N.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, C. Inflammation-Related Biomarkers in Major Psychiatric Disorders: A Cross-Disorder Assessment of Reproducibility and Specificity in 43 Meta-Analyses. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minter, M.R.; Zhang, C.; Leone, V.; Ringus, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Oyler-Castrillo, P.; Musch, M.W.; Liao, F.; Ward, J.F.; Holtzman, D.M.; et al. Antibiotic-Induced Perturbations in Gut Microbial Diversity Influences Neuro-Inflammation and Amyloidosis in a Murine Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaidez, V.; Hansen, R.L.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Gastrointestinal Problems in Children with Autism, Developmental Delays or Typical Development. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.B.; Johansen, L.J.; Powell, L.D.; Quig, D.; Rubin, R.A. Gastrointestinal Flora and Gastrointestinal Status in Children with Autism--Comparisons to Typical Children and Correlation with Autism Severity. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrindo, P.; Williams, K.C.; Lee, E.B.; Walker, L.S.; McGrew, S.G.; Levitt, P. Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Autism: Parental Report, Clinical Evaluation, and Associated Factors. Autism Res. 2012, 5, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petra, A.I.; Panagiotidou, S.; Hatziagelaki, E.; Stewart, J.M.; Conti, P.; Theoharides, T.C. Gut-Microbiota-Brain Axis and Its Effect on Neuropsychiatric Disorders with Suspected Immune Dysregulation. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudadio, I.; Fulci, V.; Palone, F.; Stronati, L.; Cucchiara, S.; Carissimi, C. Quantitative Assessment of Shotgun Metagenomics and 16S rDNA Amplicon Sequencing in the Study of Human Gut Microbiome. OMICS 2018, 22, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.W. Studying the Human Microbiota. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 902, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Li, F. Association Between Gut Microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Vázquez, L.; Van Ginkel Riba, G.; Arija, V.; Canals, J. Composition of Gut Microbiota in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbonnet, L.; Clarke, G.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota Is Essential for Social Development in the Mouse. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, S.; Mian, F.M.; Stanisz, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; Cambier, E.; Ben-Amram, H.; Koren, O.; Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J. Low-Dose Penicillin in Early Life Induces Long-Term Changes in Murine Gut Microbiota, Brain Cytokines and Behavior. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffington, S.A.; Di Prisco, G.V.; Auchtung, T.A.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Costa-Mattioli, M. Microbial Reconstitution Reverses Maternal Diet-Induced Social and Synaptic Deficits in Offspring. Cell 2016, 165, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, Z.R.; Young, L.J. Oxytocin, Vasopressin, and the Neurogenetics of Sociality. Science 2008, 322, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgritta, M.; Dooling, S.W.; Buffington, S.A.; Momin, E.N.; Francis, M.B.; Britton, R.A.; Costa-Mattioli, M. Mechanisms Underlying Microbial-Mediated Changes in Social Behavior in Mouse Models of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neuron 2019, 101, 246–259.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bove, M.; Palmieri, M.A.; Santoro, M.; Agosti, L.P.; Gaetani, S.; Romano, A.; Dimonte, S.; Costantino, G.; Sikora, V.; Tucci, P.; et al. Amygdalar Neurotransmission Alterations in the BTBR Mice Model of Idiopathic Autism. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, G.; Cruz, N.J.; Kang, D.-W.; Gandal, M.J.; Wang, B.; Kim, Y.-M.; Zink, E.M.; Casey, C.P.; Taylor, B.C.; Lane, C.J.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota from Autism Spectrum Disorder Promote Behavioral Symptoms in Mice. Cell 2019, 177, 1600–1618.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota Modulate Behavioral and Physiological Abnormalities Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, A.R.; Park, H.; Mulhern, T.J.; Jackson, G.R.; Comolli, J.C.; Borenstein, J.T.; Hayden, P.J.; Prantil-Baun, R. Comprehensive Evaluation of Poly(I:C) Induced Inflammatory Response in an Airway Epithelial Model. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, V.X.; Patel, S.; Jones, H.F.; Dale, R.C. Maternal Immune Activation and Neuroinflammation in Human Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The Changing Face of the Family Enterobacteriaceae (Order: “Enterobacterales”): New Members, Taxonomic Issues, Geographic Expansion, and New Diseases and Disease Syndromes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00174-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, C.; Mou, H.; Kong, Q. Nondigestible Carbohydrates, Butyrate, and Butyrate-Producing Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, S130–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waidmann, M.; Bechtold, O.; Frick, J.-S.; Lehr, H.-A.; Schubert, S.; Dobrindt, U.; Loeffler, J.; Bohn, E.; Autenrieth, I.B. Bacteroides Vulgatus Protects against Escherichia Coli-Induced Colitis in Gnotobiotic Interleukin-2-Deficient Mice. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkusa, T.; Yoshida, T.; Sato, N.; Watanabe, S.; Tajiri, H.; Okayasu, I. Commensal Bacteria Can Enter Colonic Epithelial Cells and Induce Proinflammatory Cytokine Secretion: A Possible Pathogenic Mechanism of Ulcerative Colitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Xie, J.; Gao, L.; Liu, L.; Ou, S.; Chen, L.; Peng, X. The Primary Biological Network of Bifidobacterium in the Gut. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, F.; Sims, A.; Strudwick, K.; Carrasco, J.; Waters, A.; Ford, V.; Hopkins, J.; Whitlingum, G.; Absoud, M.; Kelly, V.B. Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Clinical Implications for Assessment and Management. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2022, 64, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.L.; Doifode, T.; Rezende, V.L.; Costa, M.A.; Rhoads, J.M.; Soutullo, C.A. The Many Faces of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Life Sci. 2024, 337, 122357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, N.; Chida, Y.; Aiba, Y.; Sonoda, J.; Oyama, N.; Yu, X.-N.; Kubo, C.; Koga, Y. Postnatal Microbial Colonization Programs the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal System for Stress Response in Mice. J. Physiol. 2004, 558, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankova, B.B.; Agarwal, R.; MacFabe, D.F.; La Gamma, E.F. Enteric Bacterial Metabolites Propionic and Butyric Acid Modulate Gene Expression, Including CREB-Dependent Catecholaminergic Neurotransmission, in PC12 Cells--Possible Relevance to Autism Spectrum Disorders. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Stilling, R.M.; Kennedy, P.J.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Minireview: Gut Microbiota: The Neglected Endocrine Organ. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, L.Y.; Margolis, K.G. Autism Spectrum Disorders and the Gastrointestinal Tract: Insights into Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avetisyan, M.; Schill, E.M.; Heuckeroth, R.O. Building a Second Brain in the Bowel. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 125, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B. The Enteric Nervous System and Neurogastroenterology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, N.J.; Hu, H. Enteric Nervous System: Sensory Transduction, Neural Circuits and Gastrointestinal Motility. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, M.A.; Ehsan, L.; Moore, S.R.; Levin, D.E. The Enteric Nervous System and Its Emerging Role as a Therapeutic Target. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 8024171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.B.; de Lartigue, G.; Page, A.J. Dissecting the Role of Subtypes of Gastrointestinal Vagal Afferents. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternini, C.; Anselmi, L.; Rozengurt, E. Enteroendocrine Cells: A Site of “taste” in Gastrointestinal Chemosensing. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2008, 15, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Enteroendocrine Cells: Chemosensors in the Intestinal Epithelium. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, M.H.; Tecott, L.H. Serotonin and the Regulation of Mammalian Energy Balance. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reigstad, C.S.; Salmonson, C.E.; Rainey, J.F.; Szurszewski, J.H.; Linden, D.R.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Farrugia, G.; Kashyap, P.C. Gut Microbes Promote Colonic Serotonin Production through an Effect of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Enterochromaffin Cells. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous Bacteria from the Gut Microbiota Regulate Host Serotonin Biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Theije, C.G.M.; Wopereis, H.; Ramadan, M.; van Eijndthoven, T.; Lambert, J.; Knol, J.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Oozeer, R. Altered Gut Microbiota and Activity in a Murine Model of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misiak, B.; Łoniewski, I.; Marlicz, W.; Frydecka, D.; Szulc, A.; Rudzki, L.; Samochowiec, J. The HPA Axis Dysregulation in Severe Mental Illness: Can We Shift the Blame to Gut Microbiota? Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 102, 109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.P.; McKlveen, J.M.; Ghosal, S.; Kopp, B.; Wulsin, A.; Makinson, R.; Scheimann, J.; Myers, B. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Stress Response. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zeng, B.; Zeng, L.; Du, X.; Li, B.; Huo, R.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Dong, M.; Pan, J.; et al. Gut Microbiota Regulates Mouse Behaviors through Glucocorticoid Receptor Pathway Genes in the Hippocampus. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thion, M.S.; Low, D.; Silvin, A.; Chen, J.; Grisel, P.; Schulte-Schrepping, J.; Blecher, R.; Ulas, T.; Squarzoni, P.; Hoeffel, G.; et al. Microbiome Influences Prenatal and Adult Microglia in a Sex-Specific Manner. Cell 2018, 172, 500–516.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Lee, S.; Won, J.; Jin, Y.; Hong, Y.; Hur, T.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-R.; Hong, Y. Pathophysiological and Neurobehavioral Characteristics of a Propionic Acid-Mediated Autism-like Rat Model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratsman, N.; Getselter, D.; Elliott, E. Sodium Butyrate Attenuates Social Behavior Deficits and Modifies the Transcription of Inhibitory/Excitatory Genes in the Frontal Cortex of an Autism Model. Neuropharmacology 2016, 102, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamawaki, Y.; Yoshioka, N.; Nozaki, K.; Ito, H.; Oda, K.; Harada, K.; Shirawachi, S.; Asano, S.; Aizawa, H.; Yamawaki, S.; et al. Sodium Butyrate Abolishes Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-like Behaviors and Hippocampal Microglial Activation in Mice. Brain Res. 2018, 1680, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnala, R.; Arumugam, T.V.; Gupta, N.; Dheen, S.T. HDAC Inhibitor Sodium Butyrate-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation Enhances Neuroprotective Function of Microglia During Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6391–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, R.B.; Valvassori, S.S.; Lopes-Borges, J.; Mariot, E.; Dal-Pont, G.C.; Amboni, R.T.; Bianchini, G.; Quevedo, J. Sodium Butyrate and Mood Stabilizers Block Ouabain-Induced Hyperlocomotion and Increase BDNF, NGF and GDNF Levels in Brain of Wistar Rats. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 61, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barichello, T.; Generoso, J.S.; Simões, L.R.; Faller, C.J.; Ceretta, R.A.; Petronilho, F.; Lopes-Borges, J.; Valvassori, S.S.; Quevedo, J. Sodium Butyrate Prevents Memory Impairment by Re-Establishing BDNF and GDNF Expression in Experimental Pneumococcal Meningitis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yan, J.; Yang, T.; Zhu, J.; Li, T.; Wei, H.; Chen, J. Fecal Microbiome Transplantation from Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Modulates Tryptophan and Serotonergic Synapse Metabolism and Induces Altered Behaviors in Germ-Free Mice. mSystems 2021, 6, e01343-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, S.; Sacco, R.; Persico, A.M. Blood Serotonin Levels in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marler, S.; Ferguson, B.J.; Lee, E.B.; Peters, B.; Williams, K.C.; McDonnell, E.; Macklin, E.A.; Levitt, P.; Gillespie, C.H.; Anderson, G.M.; et al. Brief Report: Whole Blood Serotonin Levels and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Mirizzi, P.; Fadda, R.; Pirollo, C.; Ricciardi, O.; Mazza, M.; Valenti, M. Food Selectivity in Children with Autism: Guidelines for Assessment and Clinical Interventions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, T.; Mirowska-Guzel, D. The Role of Serotonin Neurotransmission in Gastrointestinal Tract and Pharmacotherapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelyan, N.; Del Colle, A.; Li, Z.; Park, Y.; Xing, A.; Jacobsen, J.P.R.; Luna, R.A.; Jensen, D.D.; Madra, M.; Saurman, V.; et al. Effects of Serotonin and Slow-Release 5-Hydroxytryptophan on Gastrointestinal Motility in a Mouse Model of Depression. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 507–521.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.X.; Henders, A.K.; Alvares, G.A.; Wood, D.L.A.; Krause, L.; Tyson, G.W.; Restuadi, R.; Wallace, L.; McLaren, T.; Hansell, N.K.; et al. Autism-Related Dietary Preferences Mediate Autism-Gut Microbiome Associations. Cell 2021, 184, 5916–5931.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.D.; Funabashi, M.; Adame, M.D.; Wang, Z.; Boktor, J.C.; Haney, J.; Wu, W.-L.; Rabut, C.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Hwang, S.-J.; et al. A Gut-Derived Metabolite Alters Brain Activity and Anxiety Behaviour in Mice. Nature 2022, 602, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Needham, B.D.; Adame, M.D.; Serena, G.; Rose, D.R.; Preston, G.M.; Conrad, M.C.; Campbell, A.S.; Donabedian, D.H.; Fasano, A.; Ashwood, P.; et al. Plasma and Fecal Metabolite Profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.J.; Marler, S.; Altstein, L.L.; Lee, E.B.; Akers, J.; Sohl, K.; McLaughlin, A.; Hartnett, K.; Kille, B.; Mazurek, M.; et al. Psychophysiological Associations with Gastrointestinal Symptomatology in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2017, 10, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P.; Carpenter, K.L.H.; Major, S.; Deaver, M.; Vermeer, S.; Herold, B.; Franz, L.; Howard, J.; Dawson, G. Gastrointestinal Problems Are Associated with Increased Repetitive Behaviors but Not Social Communication Difficulties in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism 2021, 25, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, R.N.; Bearss, K.E.; Lettinga, J.; Erickson, C.; Rodowski, M.; Aman, M.G.; McCracken, J.T.; McDougle, C.J.; Tierney, E.; Vitiello, B.; et al. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in a Sample of Children with Pervasive Developmental Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2009, 39, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, R.A.; Oezguen, N.; Balderas, M.; Venkatachalam, A.; Runge, J.K.; Versalovic, J.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J.; Anderson, G.M.; Savidge, T.; Williams, K.C. Distinct Microbiome-Neuroimmune Signatures Correlate with Functional Abdominal Pain in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.M.; Antony, K.M.; Ma, J.; Prince, A.L.; Showalter, L.; Moller, M.; Aagaard, K.M. The Early Infant Gut Microbiome Varies in Association with a Maternal High-Fat Diet. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, M.; Feng, X.; Song, M.; Shao, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Lv, L.; Su, X. Maternal Immune Activation Alters Adult Behavior, Intestinal Integrity, Gut Microbiota and the Gut Inflammation. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, A.H. Behavioral Management of Feeding Disorders of Childhood. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. S5), 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, N.A.S.; Ramli, N.S.; Hamzaid, N.H.; Hassan, N.I. Exploring Eating and Nutritional Challenges for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Parents’ and Special Educators’ Perceptions. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.Y.; Hamzaid, N.H.; Ibrahim, N. Parental Perceptions on the Importance of Nutrients for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and the Coping Strategies: A Qualitative Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Shimada, S. Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cabral, I.D.; Bernal-Mercado, A.T.; Islas-Rubio, A.R.; Suárez-Jiménez, G.M.; Robles-García, M.Á.; Puebla-Duarte, A.L.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L. Exploring Dietary Interventions in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Foods 2024, 13, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, N.P.; Yamamoto, B.Y.; Kunihiro, B.P.; Nunokawa, C.K.L.; Rubas, N.C.; Wells, R.K.; Umeda, L.; Phankitnirundorn, K.; Torres, A.; Peres, R.; et al. Ketogenic Diet Induced Shifts in the Gut Microbiome Associate with Changes to Inflammatory Cytokines and Brain-Related miRNAs in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, A.; Corsello, A.; Spolidoro, G.C.; Trovato, C.M.; Agostoni, C.; Orsini, A.; Milani, G.P.; Peroni, D.G. The Influence of Ketogenic Diet on Gut Microbiota: Potential Benefits, Risks and Indications. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Suganthy, N.; Kesika, P.; Chaiyasut, C. The Role of Microbiome, Dietary Supplements, and Probiotics in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Q.X.; Loke, W.; Venkatanarayanan, N.; Lim, D.Y.; Soh, A.Y.S.; Yeo, W.S. A Systematic Review of the Role of Prebiotics and Probiotics in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Medicina 2019, 55, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, M.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.H.; Tanpure, R.; Kim, J.I.; Jeon, B.-H.; Park, H.-K. Psychobiotics and Fecal Microbial Transplantation for Autism and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Microbiome Modulation and Therapeutic Mechanisms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1238005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-W.; Liong, M.T.; Chung, Y.-C.E.; Huang, H.-Y.; Peng, W.-S.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Lin, Y.-S.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-C. Effects of Lactobacillus Plantarum PS128 on Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in Taiwan: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.H. Analyzing the Influence of Physical Exercise Interventions on Social Skills in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Insights from Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1399902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Guo, C.; Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. The Effect of Physical Exercise on Disordered Social Communication in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1193648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, A.; Mennitti, C.; Falcone, N.; La Monica, I.; Di Iorio, M.R.; Tripodi, L.; Gentile, A.; Vitale, M.; Pero, R.; Pastore, L.; et al. Positive Effects of Physical Activity in Autism Spectrum Disorder: How Influences Behavior, Metabolic Disorder and Gut Microbiota. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1238797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-K.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.-H.; Lee, Y.-H. Effect of Acute Exercise on Executive Function in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2012, 27, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, C.V.A.; Ferreira, J.P.; Quinaud, R.T.; Silva, K.M.N.; Carvalho, H.M.; Gaspar, J.M. Exercise Improves the Social and Behavioral Skills of Children and Adolescent with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1027799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.; Schmidt, R.; Cryan, J.F.; Hilbert, A. A Role for the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder: A New Conceptual Model. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2024, 57, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ARFID Subtype | Description | Key Characteristics | General Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lack of Interest | Characterized by a lack of appetite or interest in eating or food. | Small bites Slow eating Prolonged mealtimes Chronic low appetite No significant comorbidity with ASD | 25.1% [32] 57.6% [33] |
| Sensory Sensitivity | Avoidance of foods due to sensory issues, such as taste, smell, texture, or appearance. | Rigid eating behaviors Food selectivity and neophobia High comorbidity with ASD [34] | 29.5% [32] 21.2% [33] |
| Fear/Aversive | Avoidance of food due to fear of aversive consequences, such as choking, vomiting, or pain. | High anxiety levels Often triggered by traumatic events (e.g., choking episode) Shorter symptoms duration High comorbidity with anxiety disorders | 7.2% [32] 9.1% [33] |
| Combined Presentation | Avoidance of food due to fear of aversive consequences, such as choking, vomiting, or pain. | High probability of all symptoms except fear-based avoidance Younger age at diagnosis High comorbidity with ASD and learning disabilities | 38.2% [32] |
| Mechanism | Impact of Gut Microbiota on Eating Behavior/ASD Symptoms | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Social behavior and communication modulation | Microbiota influences social interactions and communication behaviors through neural pathways | Behavioral improvements were seen through microbiota modulation [110,112] Lactobacillus reuteri supplementation improved social behaviors via vagal signaling [112] It also affects oxytocin-dopamine pathways in the brain [110,112] |
| Serotonin regulation | Microbiota affects appetite and satiety Influences mood and behavior | ASD patients show hyperserotonemia [152,153,154] Altered serotonin metabolism in both the gut and brain affects gastrointestinal motility and mood [153,155,156] |
| Dietary diversity impact | Microbiota affects food preferences | A less diverse diet correlates with lower microbiota diversity [157] Altered gut microbiota in ASD patients may simply result from dietary preferences and not ASD itself [157] |
| Metabolite production | Bacterial metabolites affect behavior They can influence anxiety and irritability | 4-EPS linked to anxiety [158,159] Clinical improvements are seen when targeting these metabolites [158] |
| Gastrointestinal function | Microbiota affects gastrointestinal system functions | GI symptoms are common in ASD (constipation, diarrhea) [160,161,162] |
| Inflammation and immune response | Inflammatory state affects appetite, influences gut–brain communication, and impacts behavior | Specific bacteria linked to inflammatory markers [163] Correlation of ASD with pro-inflammatory cytokines [163] |
| Early development | Microbiota shapes future eating patterns, influences neurodevelopment, and affects long-term behavior | Maternal microbiome affects offspring development [110,112,164] Early-life disruption has lasting effects [110,112,164] |
| Intestinal epithelium barrier function | Microbiota affects nutrient absorption, influences gut–brain communication, and impacts food tolerance | Altered intestinal barrier integrity in ASD, also known as “Leaky gut” [115,165] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomaszek, N.; Urbaniak, A.D.; Bałdyga, D.; Chwesiuk, K.; Modzelewski, S.; Waszkiewicz, N. Unraveling the Connections: Eating Issues, Microbiome, and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients 2025, 17, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030486
Tomaszek N, Urbaniak AD, Bałdyga D, Chwesiuk K, Modzelewski S, Waszkiewicz N. Unraveling the Connections: Eating Issues, Microbiome, and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients. 2025; 17(3):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030486
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomaszek, Natalia, Agata Dominika Urbaniak, Daniel Bałdyga, Kamila Chwesiuk, Stefan Modzelewski, and Napoleon Waszkiewicz. 2025. "Unraveling the Connections: Eating Issues, Microbiome, and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder" Nutrients 17, no. 3: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030486
APA StyleTomaszek, N., Urbaniak, A. D., Bałdyga, D., Chwesiuk, K., Modzelewski, S., & Waszkiewicz, N. (2025). Unraveling the Connections: Eating Issues, Microbiome, and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients, 17(3), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030486








