Effects of Kefir Consumption on Gut Microbiota and Athletic Performance in Professional Female Soccer Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
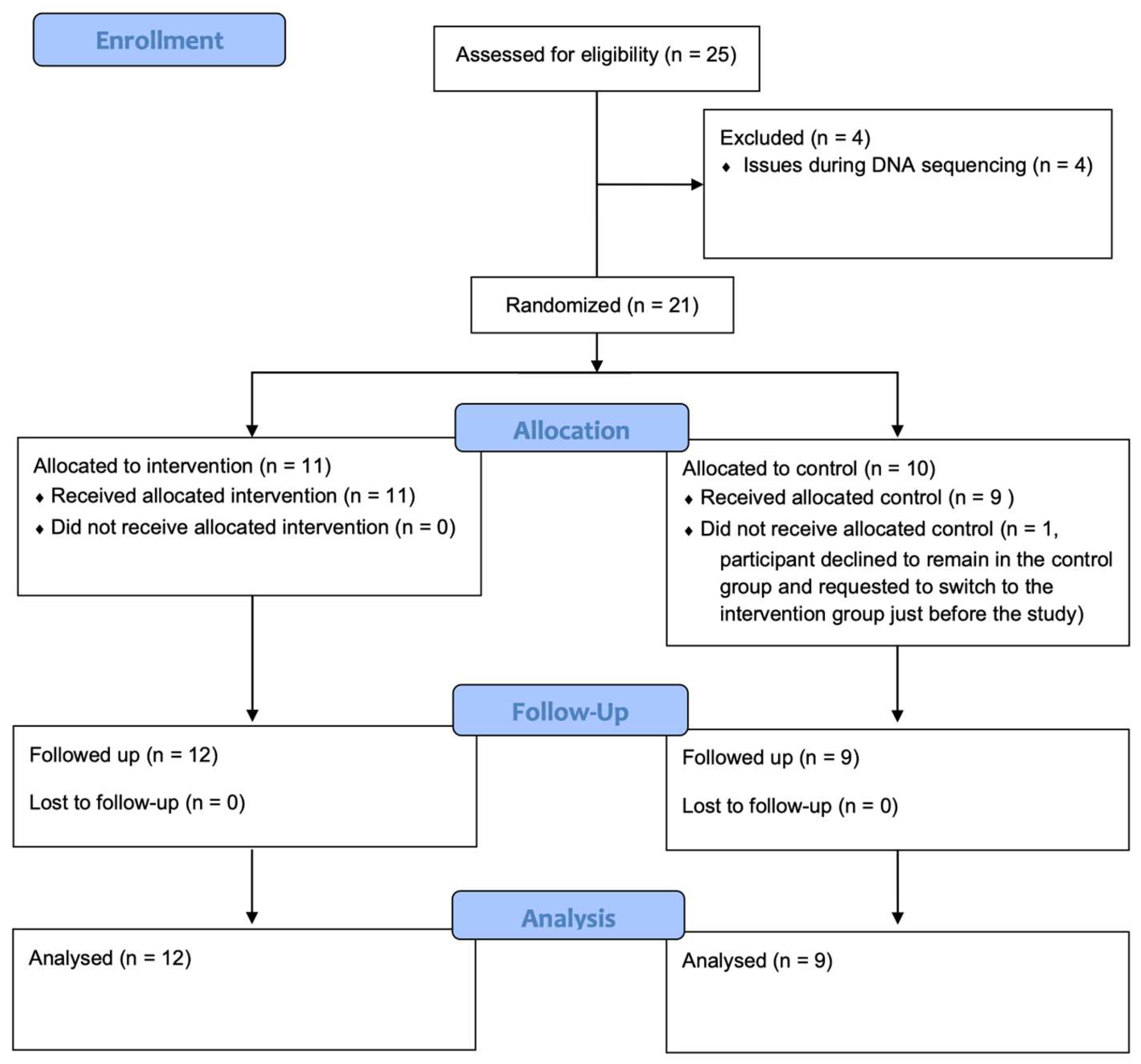
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants and Kefir Supplementation
2.3. Anthropometry and Body Composition
2.4. Dietary Assessment
2.5. Athletic Performance Assessment
2.6. DNA Extraction from Stool Samples (DiaRex)
2.7. 16S Amplicon Sequencing
2.8. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Effects of Regular Kefir Consumption on Microbial Diversity and Composition
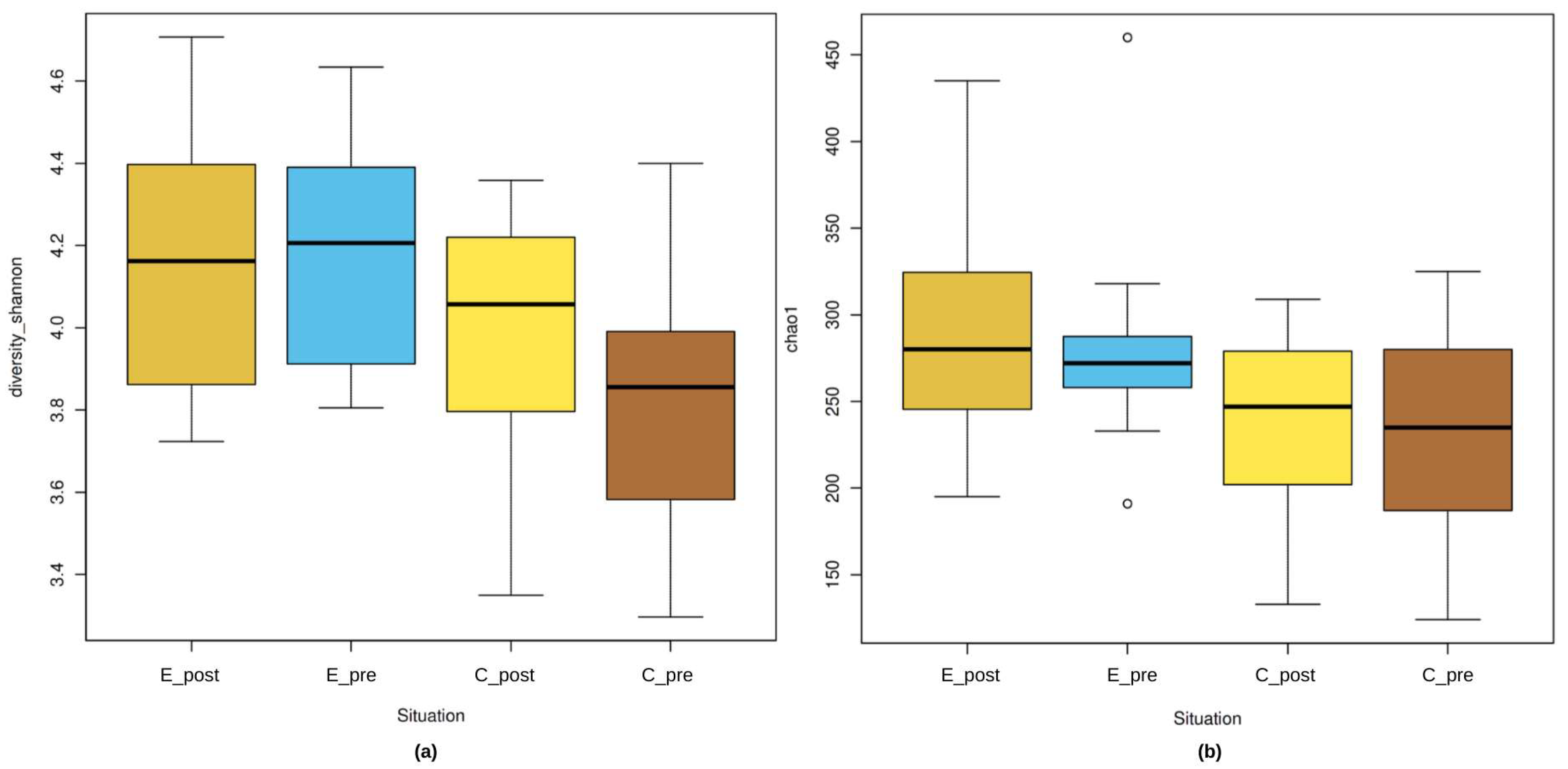
3.2.1. Alpha Diversity
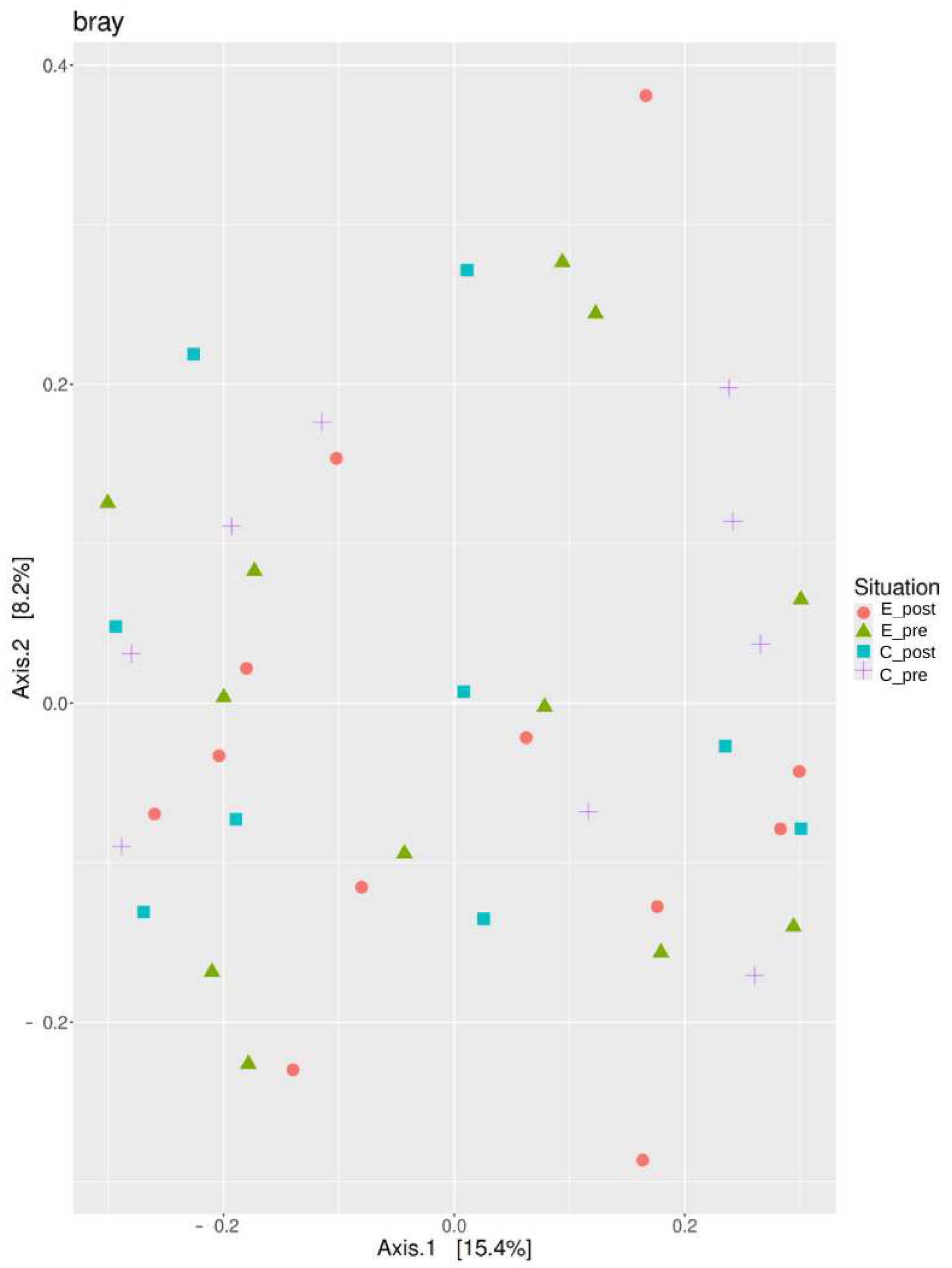
3.2.2. Beta Diversity
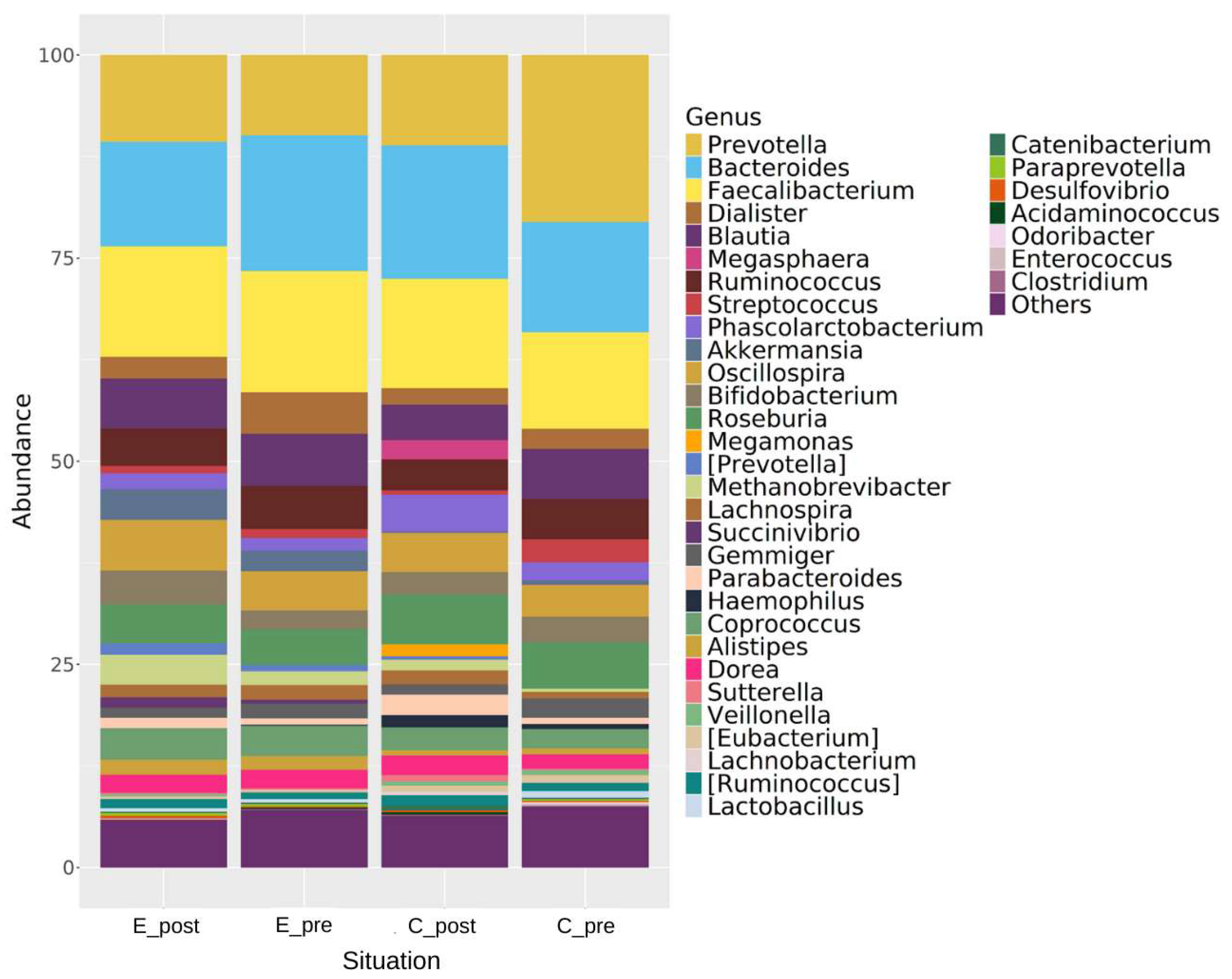
3.3. Changes in Genus, Phylum, and Species Levels Associated with Regular Kefir Consumption
3.3.1. Phylum Level Taxonomic Changes
3.3.2. Genus- and Species-Level Changes
3.4. Association Between Gut Microbiota Composition and Athletic Performance in Kefir-Consuming Athletes
3.5. Interplay Between Gut Microbiota, Dietary Intake, and Athletic Performance Metrics in Kefir-Consuming Athletes
3.5.1. Gut Microbiota and Athletic Performance Correlations
- Finishing speed (km/h)
- VO2max (mL.kg−1.min−1)
3.5.2. Gut Microbiota and Body Composition Correlations
- Fat Mass (kg)
- Fat-Free Mass (kg)
- Body Fat (%)
3.5.3. Gut Microbiota and Dietary Intake Correlations
- Dietary Fiber Intake (g)
- Protein Intake (g, %)
- Fat Intake (g)
4. Discussion
4.1. Dietary Intake as a Gut Microbiota Modulator
4.2. Gut Microbiota and Body Composition
4.3. Role of the Gut Microbiota in Athletic Performance
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, X.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Mao, Y.-H. Dietary Patterns, Gut Microbiota and Sports Performance in Athletes: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Dietary Strategies to Improve Exercise Performance by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Foods 2024, 13, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, D.D.; Dias, M.M.S.; Grześkowiak, Ł.M.; Reis, S.A.; Conceição, L.L.; Maria do Carmo, G.P. Milk kefir: Nutritional, Microbiological and Health Benefits. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourrie, B.C.T.; Willing, B.P.; Cotter, P.D. The Microbiota and Health Promoting Characteristics of the Fermented Beverage Kefir. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, C.; Cotter, P.D.; O’toole, P.W. Analysis of Health Benefits Conferred by Lactobacillus Species from Kefir. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X. Plant-Derived Bioactive Components Regulate Gut Microbiota to Prevent Depression and Depressive-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: Focus on Neurotransmitters. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, P.; Shen, L.; Niu, L.; Tan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, L.; Hao, X.; Li, X.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Their Association with Signalling Pathways in Inflammation, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-J.; Huang, W.-C.; Lin, J.-S.; Chen, Y.-M.; Ho, S.-T.; Huang, C.-C.; Tung, Y.-T. Kefir Supplementation Modifies Gut Microbiota Composition, Reduces Physical Fatigue, and Improves Exercise Performance in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-C.; Jhang, W.-L.; Lee, C.-C.; Kan, N.-W.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Ho, C.-S.; Chang, C.-H.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Lin, J.-S.; Huang, C.-C. The Effect of Kefir Supplementation on Improving Human Endurance Exercise Performance and Anti-Fatigue. Metabolites 2021, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J.; Lazinica, B.; Pedisic, Z. Test–retest reliability of the 30-15 Intermittent Fitness Test: A systematic review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čović, N.; Jelešković, E.; Alić, H.; Rađo, I.; Kafedžić, E.; Sporiš, G.; McMaster, D.T.; Milanović, Z. Reliability, Validity and Usefulness of 30-15 Intermittent Fitness Test in Female Soccer Players. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D. Amplicon Sequence Variants Artificially Split Bacterial Genomes into Separate Clusters. mSphere 2021, 6, e0019121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.J.; Koren, O.; Hugenholtz, P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Walters, W.A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Angenent, L.T.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.E. Impact of Training Sets on Classification of High-Throughput Bacterial 16s rRNA Gene Surveys. ISME J. 2012, 6, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet Rapidly and Reproducibly Alters the Human Gut Microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaki, M.; Pither, J.; Baumeister, P.; Little, J.P.; Gill, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Ahmadi-Vand, Z.; Marsden, K.R.; Gibson, D.L. Cardiorespiratory Fitness as a Predictor of Intestinal Microbial Diversity and Distinct Metagenomic Functions. Microbiome 2016, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caesar, R.; Tremaroli, V.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Cani, P.D.; Bäckhed, F. Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and Dietary Lipids Aggravates WAT Inflammation through TLR Signaling. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, M. Immune Function in Sport and Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tap, J.; Furet, J.; Bensaada, M.; Philippe, C.; Roth, H.; Rabot, S.; Lakhdari, O.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Corthier, G.; et al. Gut Microbiota Richness Promotes Its Stability upon Increased Dietary Fibre Intake in Healthy Adults. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4954–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.M.; Bautista, E.J.; Nguyen, H.; Hanson, B.M.; Chen, L.; Lek, S.H.; Sodergren, E.; Weinstock, G.M. Community Characteristics of the Gut Microbiomes of Competitive Cyclists. Microbiome 2017, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramp, T.; Broad, E.; Martin, D.; Meyer, B.J. Effects of Preexercise Carbohydrate Ingestion on Mountain Bike Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient Metabolism by the Human Gut Microbiome: Major Fermentation By-Products and Their Impact on Host Health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Yang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Guan, L.; Zhu, W. The Colonic Microbiome and Epithelial Transcriptome Are Altered in Rats Fed a High-Protein Diet Compared with a Normal-Protein Diet. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Yang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, W. Temporal Microbiota Changes of High-Protein Diet Intake in a Rat Model. Anaerobe 2017, 47, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, L.-G.; Choi, G.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, B.-Y.; Lee, S.; Park, H. The Combination of Sport and Sport-Specific Diet Is Associated with Characteristics of Gut Microbiota: An Observational Study. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2019, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, W.; Meng, L.; Huang, H. Oscillospira—A Candidate for the Next-Generation Probiotics. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1987783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, D.; Jiang, R.; Ge, L.; Tong, C.; Xu, K. Associations among Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, the Gut Microbiota, and Intestinal Immunity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 8879227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.; Jeong, D.; Kang, I.-B.; Chon, J.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Song, K.-Y.; Seo, K.-H. Kefir Alleviates Obesity and Hepatic Steatosis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice by Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Mycobiota: Targeted and Untargeted Community Analysis with Correlation of Biomarkers. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 44, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, N.T.; Schmidt, A.W.; Venkataraman, A.; Kim, K.S.; Waldron, C.; Schmidt, T.M. Dynamics of Human Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Response to Dietary Interventions with Three Fermentable Fibers. mBio 2019, 10, e02566-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yun, J.M.; Kim, M.K.; Kwon, O.; Cho, B. Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 Supplementation Reduces the Visceral Fat Accumulation and Waist Circumference in Obese Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Darimont, C.; Drapeau, V.; Emady-Azar, S.; Lepage, M.; Rezzonico, E.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Berger, B.; Philippe, L.; Ammon-Zuffrey, C.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus CGMCC1.3724 Supplementation on Weight Loss and Maintenance in Obese Men and Women. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.E.; Jäger, R.; Carpenter, K.C.; Kerksick, C.M.; Purpura, M.; Townsend, J.R.; West, N.P.; Black, K.; Gleeson, M.; Pyne, D.B.; et al. The Athletic Gut Microbiota. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchomel, T.J.; Nimphius, S.; Stone, M.H. The Importance of Muscular Strength in Athletic Performance. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1419–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.L.; Holscher, H.D. Fueling Gut Microbes: A Review of the Interaction between Diet, Exercise, and the Gut Microbiota in Athletes. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2021, 12, 2190–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Jung, S.-C.; Kwak, K.; Kim, J.-S. The Role of Prebiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota: Implications for Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; de Vos, W.M. Next-Generation Beneficial Microbes: The Case of Akkermansia muciniphila. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiman, J.; Luber, J.M.; Chavkin, T.A.; MacDonald, T.; Tung, A.; Pham, L.-D.; Wibowo, M.C.; Wurth, R.C.; Punthambaker, S.; Tierney, B.T.; et al. Meta-Omics Analysis of Elite Athletes Identifies a Performance-Enhancing Microbe That Functions via Lactate Metabolism. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P. Influence of Foods and Nutrition on the Gut Microbiome and Implications for Intestinal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Experimental (Mean ± SD) | Control (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 24.42 ± 2.52 | 22.14 ± 3.61 |
| Weight (kg) | 60.32 ± 5.44 | 58.03 ± 7.64 |
| Fat mass (kg) | 10.58 ± 2.37 | 10.63 ± 3.43 |
| Fat-free mass (kg) | 48.16 ± 3.58 | 46.88 ± 5.49 |
| Body fat (%) | 17.02 ± 2.49 | 16.43 ± 2.80 |
| Species | Low (%) | Medium (%) | High (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faecalibacterium prausnitzii | - | 0.73 | 27.19 |
| Prevotella copri | 7.87 | - | 17.48 |
| Akkermansia muciniphila | 0.83 | 12.67 | 6.12 |
| Dorea formicigenerans | 28.43 | - | - |
| Oxalobacter formigenes | 25.89 | - | - |
| Coprococcus catus | 0.52 | 31.00 | 0.38 |
| Species | Low (%) | Medium (%) | High (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faecalibacterium prausnitzii | 28.43 | 31.00 | 27.18 |
| Prevotella copri | 25.89 | 5.36 | 17.47 |
| Roseburia faecis | 7.86 | 6.62 | 6.36 |
| Ruminococcus bromii | 5.37 | 9.52 | 3.21 |
| Akkermansia muciniphila | 0.82 | 12.67 | 6.11 |
| Gemmiger formicilis | 2.65 | 4.22 | 4.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Öneş, E.; Zavotçu, M.; Nisan, N.; Baş, M.; Sağlam, D. Effects of Kefir Consumption on Gut Microbiota and Athletic Performance in Professional Female Soccer Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030512
Öneş E, Zavotçu M, Nisan N, Baş M, Sağlam D. Effects of Kefir Consumption on Gut Microbiota and Athletic Performance in Professional Female Soccer Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2025; 17(3):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030512
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖneş, Ece, Mutlucan Zavotçu, Nida Nisan, Murat Baş, and Duygu Sağlam. 2025. "Effects of Kefir Consumption on Gut Microbiota and Athletic Performance in Professional Female Soccer Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 17, no. 3: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030512
APA StyleÖneş, E., Zavotçu, M., Nisan, N., Baş, M., & Sağlam, D. (2025). Effects of Kefir Consumption on Gut Microbiota and Athletic Performance in Professional Female Soccer Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 17(3), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030512








