The Impact of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Lipid Absorption and Lymphatic Transport in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. CBD Treatment Study
2.3. Lipid Infusate Preparation
2.4. Lymph Collection
2.5. Calculations of Absorptive and Transport Index
2.6. Quantification of TG, Cholesterol, Phospholipids, and Non-Esterified Fatty Acid
2.7. Measurements of Apolipoproteins
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) for the Expression of Target Genes
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight and Lymph Flow Change
3.2. Lymphatic Isotope Labeled TG and CHOL Output
3.3. Distribution of Labeled TG and CHOL in the Small Intestine
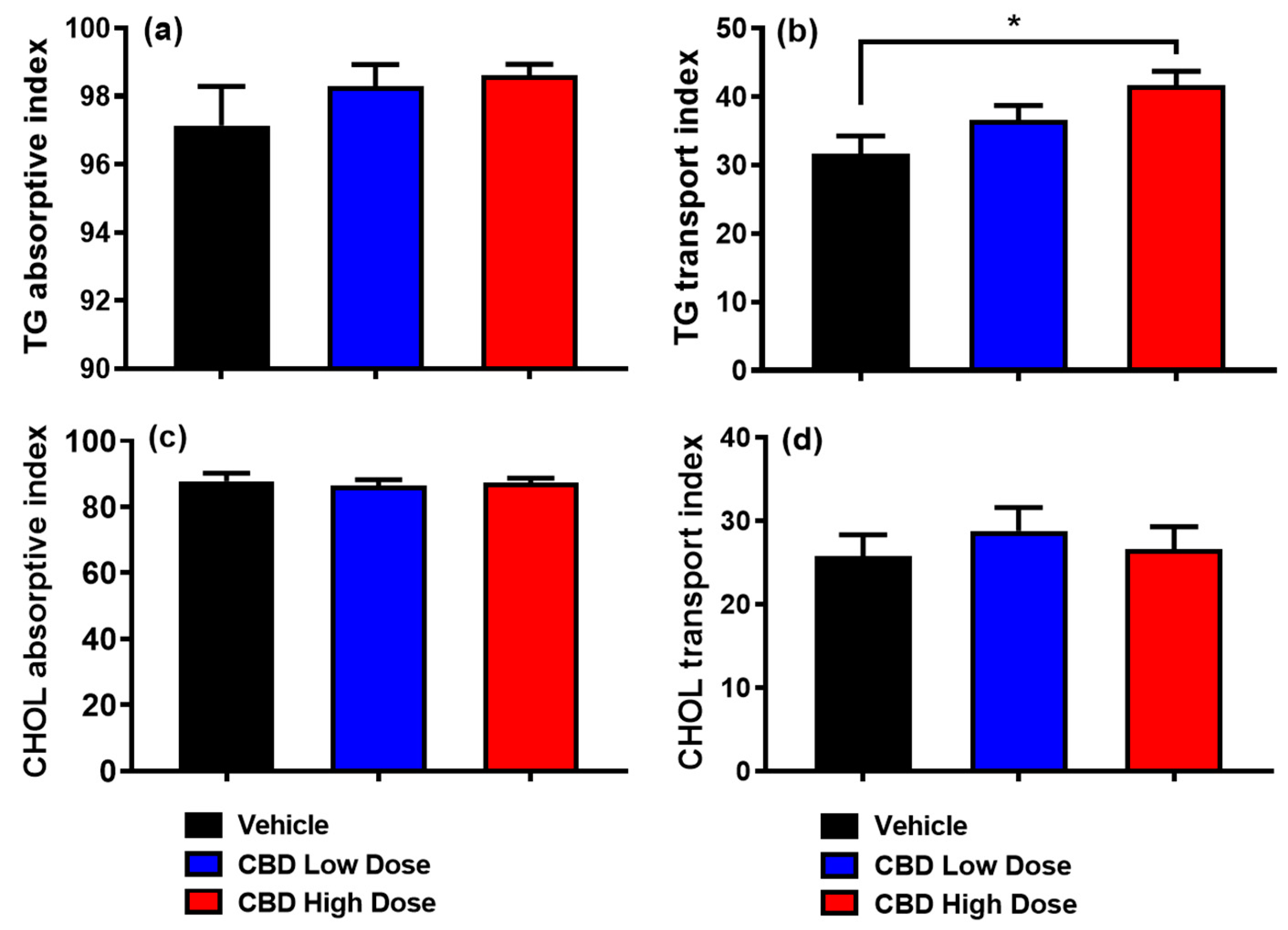
3.4. Absorptive and Transport Index
3.5. Output of Total TG, CHOL, PL, and NEFA in the Lymph
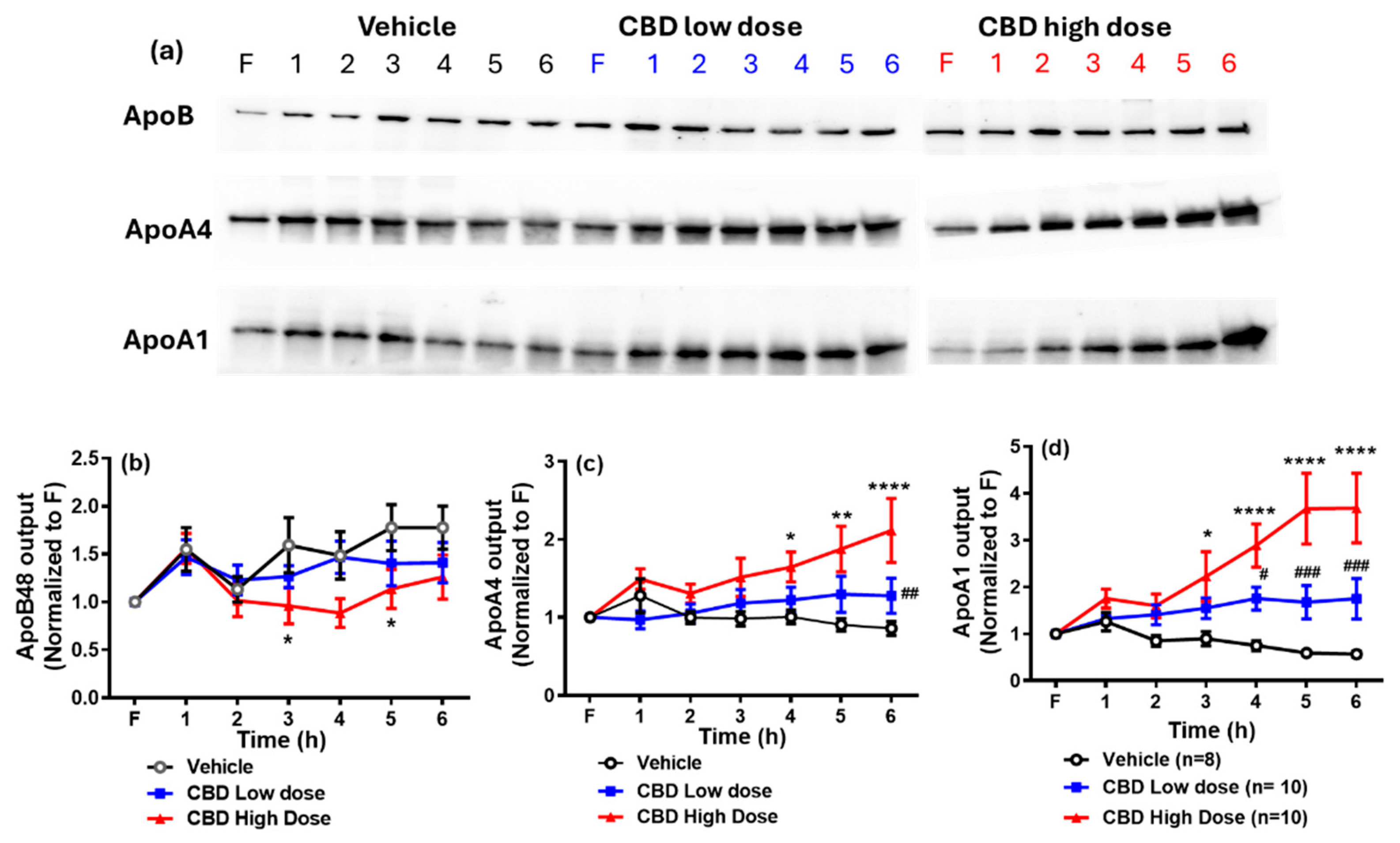
3.6. Lymphatic Output of Apolipoproteins
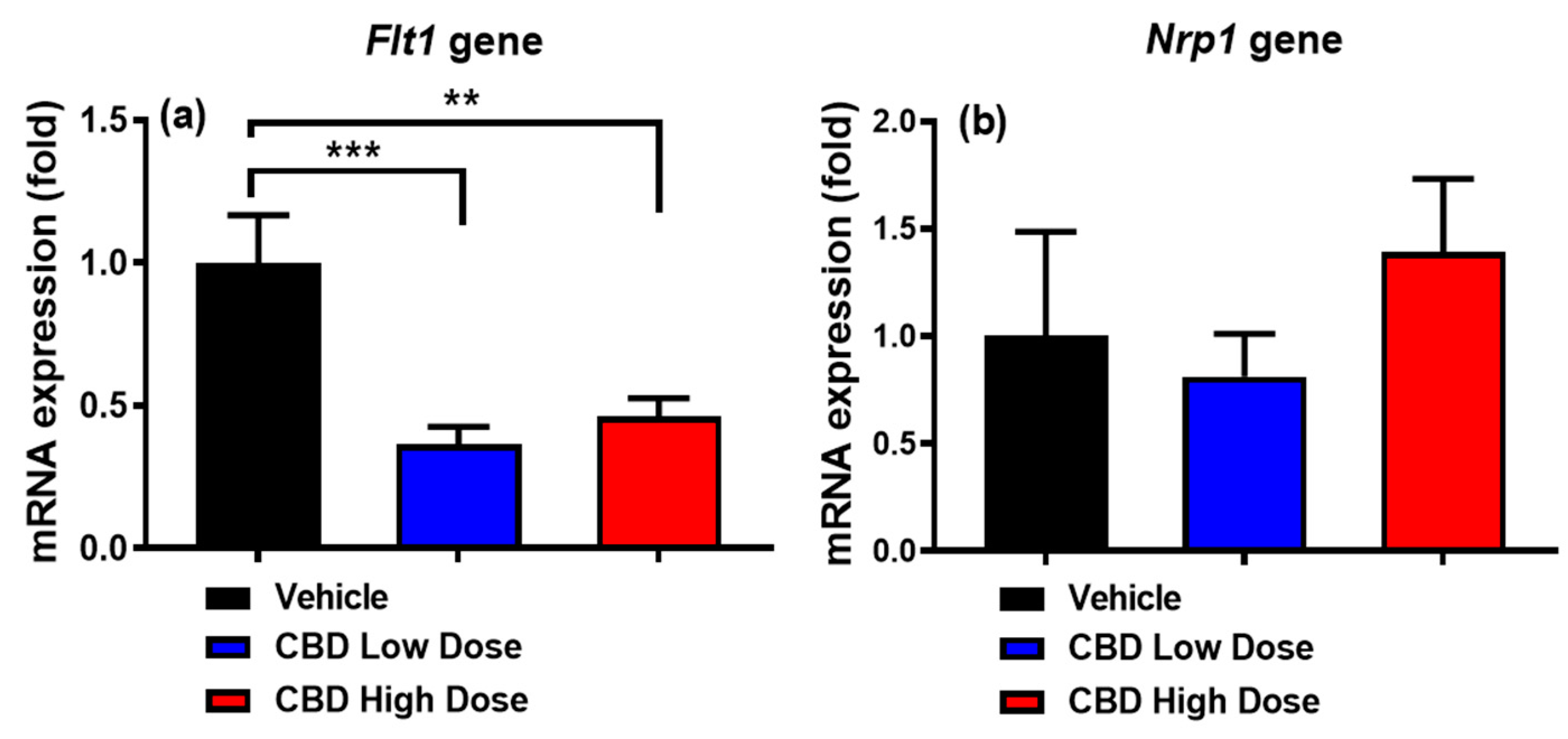
3.7. Expression of Genes Regulating Intestinal Lacteal Structure and Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lowe, H.; Toyang, N.; Steele, B.; Bryant, J.; Ngwa, W. The Endocannabinoid System: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Various Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogan, N.M.; Mechoulam, R. Cannabinoids in Health and Disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 9, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoon, K.A.; Ratcliffe, S.H.; Barrett, D.A.; Thomas, E.L.; Stott, C.; Bell, J.D.; O’Sullivan, S.E.; Tan, G.D. Efficacy and Safety of Cannabidiol and Tetrahydrocannabivarin on Glycemic and Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Group Pilot Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parray, H.A.; Yun, J.W. Cannabidiol Promotes Browning in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 416, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatowska-Jankowska, B.; Jankowski, M.M.; Swiergiel, A.H. Cannabidiol Decreases Body Weight Gain in Rats: Involvement of CB2 Receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 490, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.; Funk, K.; Figueroa Barrientos, A.; Bailey, A.; Shrader, S.; Feng, W.; McClain, C.J.; Song, Z.-H. The Modulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol in the Gut. Cells 2024, 13, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, C.; Paris, D.; Martella, A.; Melck, D.; Guadagnino, I.; Cawthorne, M.; Motta, A.; Di Marzo, V. Two Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoids Reduce Intracellular Lipid Levels and Inhibit Hepatosteatosis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Qin, C.; Chu, Y.J.; Berton, M.; Lee, J.B.; Zgair, A.; Bettonte, S.; Stocks, M.J.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Barrett, D.A.; et al. Natural Sesame Oil Is Superior to Pre-Digested Lipid Formulations and Purified Triglycerides in Promoting the Intestinal Lymphatic Transport and Systemic Bioavailability of Cannabidiol. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 162, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Qin, C.; Cipolla, E.; Lee, J.B.; Zgair, A.; Chu, Y.; Ortori, C.A.; Stocks, M.J.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Barrett, D.A.; et al. Inclusion of Medium-Chain Triglyceride in Lipid-Based Formulation of Cannabidiol Facilitates Micellar Solubilization in Vitro, but in Vivo Performance Remains Superior with Pure Sesame Oil Vehicle. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zarkada, G.; Han, J.; Li, J.; Dubrac, A.; Ola, R.; Genet, G.; Boyé, K.; Michon, P.; Künzel, S.E.; et al. Lacteal Junction Zippering Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity. Science 2018, 361, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calapai, F.; Cardia, L.; Calapai, G.; Di Mauro, D.; Trimarchi, F.; Ammendolia, I.; Mannucci, C. Effects of Cannabidiol on Locomotor Activity. Life 2022, 12, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitan, A.; Gover, O.; Sulimani, L.; Meiri, D.; Schwartz, B. The Effect of Orally Administered Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) on Obesity Parameters in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shen, L.; Yang, Q.; Nauli, A.M.; Bingamon, M.; Wang, D.Q.H.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Tso, P. Sexual Dimorphism in Intestinal Absorption and Lymphatic Transport of Dietary Lipids. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 5015–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A Simple Method for the Isolation and Purification of Total Lipides from Animal Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstedt, S.E.; Hayashi, H.; Kritchevsky, D.; Tso, P. A Comparison of Absorption of Glycerol Tristearate and Glycerol Trioleate by Rat Small Intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259, G386–G393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockner, R.K.; Hughes, F.B.; Isselbacher, K.J. Very Low Density Lipoproteins in Intestinal Lymph: Role in Triglyceride and Cholesterol Transport during Fat Absorption. J. Clin. Investig. 1969, 48, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.M.; Nordskog, B.K.; Nauli, A.M.; Zheng, S.; Vonlehmden, S.B.; Yang, Q.; Lee, D.; Swift, L.L.; Davidson, N.O.; Tso, P. Why Does the Gut Choose Apolipoprotein B48 but Not B100 for Chylomicron Formation? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G344–G352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.L.; Pullinger, C.; Kroes, I.; Kroes, J.; Hardman, D.A.; Chen, G.; Curtiss, L.K.; Gutierrez, M.M.; Kane, J.P.; Schumaker, V.N. A Single Copy of Apolipoprotein B-48 Is Present on the Human Chylomicron Remnant. J. Lipid Res. 1997, 38, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Cardelli, J.A.; Nutting, D.F.; Bergstedt, S.; Tso, P. Fat Feeding Increases Size, but Not Number, of Chylomicrons Produced by Small Intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 259, G709–G719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahel, P.; Xiao, C.; Davis, X.; Tso, P.; Lewis, G.F. Glucose and GLP-2 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-2) Mobilize Intestinal Triglyceride by Distinct Mechanisms. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Nutting, D.F.; Fujimoto, K.; Cardelli, J.A.; Black, D.; Tso, P. Transport of Lipid and Apolipoproteins A-I and A-IV in Intestinal Lymph of the Rat. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 1613–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Mitchell, S.; Leng, S.; Meng, S.; Gallagher, J.W.; Shelness, G.S.; Morris, G.S.; Mahan, J.; et al. Overexpression of Apolipoprotein A-IV Enhances Lipid Secretion in IPEC-1 Cells by Increasing Chylomicron Size. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 3473–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vowinkel, T.; Mori, M.; Krieglstein, C.F.; Russell, J.; Saijo, F.; Bharwani, S.; Turnage, R.H.; Davidson, W.S.; Tso, P.; Granger, D.N.; et al. Apolipoprotein A-IV Inhibits Experimental Colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearston, K.; Tan, J.T.M.; Cochran, B.J.; Rye, K.A. Inhibition of Vascular Inflammation by Apolipoprotein A-IV. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 901408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recalde, D.; Ostos, M.A.; Badell, E.; Garcia-Otin, A.L.; Pidoux, J.; Castro, G.; Zakin, M.M.; Scott-Algara, D. Human Apolipoprotein A-IV Reduces Secretion of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Atherosclerotic Effects of a Chronic Infection Mimicked by Lipopolysaccharide. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.D.; Castellani, L.W.; Qiao, J.H.; Van Lenten, B.J.; Lusis, A.J.; Reue, K. Reduced Aortic Lesions and Elevated High Density Lipoprotein Levels in Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Mouse Apolipoprotein A-IV. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duverger, N.; Tremp, G.; Caillaud, J.M.; Emmanuel, F.; Castro, G.; Fruchart, J.C.; Steinmetz, A.; Denèfle, P. Protection against Atherogenesis in Mice Mediated by Human Apolipoprotein A-IV. Science 1996, 273, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Lo, C.C.; Woollett, L.A.; Liu, M. Apolipoprotein A-IV Exerts Its Anorectic Action through a PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in the Hypothalamus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Pearson, K.J.; Xiong, Y.; Lo, C.M.; Tso, P.; Woods, S.C.; Davidson, W.S.; Liu, M. Characterization of Apolipoprotein A-IV in Brain Areas Involved in Energy Homeostasis. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 95, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, D.H.; Lancaster, N.; Schonfeld, G. The Effects of Fat Feeding on Apolipoprotein AI Secretion from Rat Small Intestinal Epithelium. Metabolism 1982, 31, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasan, K.M.; Brocks, D.R.; Lee, S.D.; Sachs-Barrable, K.; Thornton, S.J. Impact of Lipoproteins on the Biological Activity and Disposition of Hydrophobic Drugs: Implications for Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glickman, R.M.; Green, P.H. The Intestine as a Source of Apolipoprotein A1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 2569–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgila, K.; Vyrla, D.; Drakos, E. Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), Immunity, Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soran, H.; Schofield, J.D.; Durrington, P.N. Antioxidant Properties of HDL. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K.Y.Y.; Ho, T.W.W.; Xu, Z.; Neculai, D.; Beauchemin, C.A.A.; Lee, W.L.; Fairn, G.D. Apolipoprotein A1 and High-Density Lipoprotein Limit Low-Density Lipoprotein Transcytosis by Binding SR-B1. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.L.; Clark, S.B.; Holt, P.R. Transmucosal Triglyceride Transport Rates in Proximal and Distal Rat Intestine in Vivo. J. Lipid Res. 1975, 16, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiratsuka, S.; Nakao, K.; Nakamura, K.; Katsuki, M.; Maru, Y.; Shibuya, M. Membrane Fixation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 Ligand-Binding Domain Is Important for Vasculogenesis and Angiogenesis in Mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, S.; Takashima, S.; Miao, H.Q.; Neufeld, G.; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilin-1 Is Expressed by Endothelial and Tumor Cells as an Isoform- Specific Receptor for Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Cell 1998, 92, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkada, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Lange, M.; Zeng, L.; Lv, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, K.; et al. Chylomicrons Regulate Lacteal Permeability and Intestinal Lipid Absorption. Circ. Res. 2023, 133, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Massena, S.; Kutschera, S.; Padhan, N.; Gualandi, L.; Sundvold-Gjerstad, V.; Gustafsson, K.; Choy, W.W.; Zang, G.; et al. VEGFR2 Induces C-Src Signaling and Vascular Permeability in Vivo via the Adaptor Protein TSAD. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Shen, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, M. The Impact of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Lipid Absorption and Lymphatic Transport in Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061034
Zhu Q, Yang Q, Shen L, Xu M, Liu M. The Impact of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Lipid Absorption and Lymphatic Transport in Rats. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061034
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Qi, Qing Yang, Ling Shen, Meifeng Xu, and Min Liu. 2025. "The Impact of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Lipid Absorption and Lymphatic Transport in Rats" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061034
APA StyleZhu, Q., Yang, Q., Shen, L., Xu, M., & Liu, M. (2025). The Impact of Cannabidiol (CBD) on Lipid Absorption and Lymphatic Transport in Rats. Nutrients, 17(6), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061034




