Tryptophan Attenuates Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Intestinal Injury Through Modulation of Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Gut Microbiota Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Analysis of Tryptophan Concentration in Serum
2.4. Histological Analysis
2.5. ELISA
2.6. Intestinal Permeability
2.7. Tunnel Staining
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.9. 16S Sequencing Analysis
2.10. Measurement of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
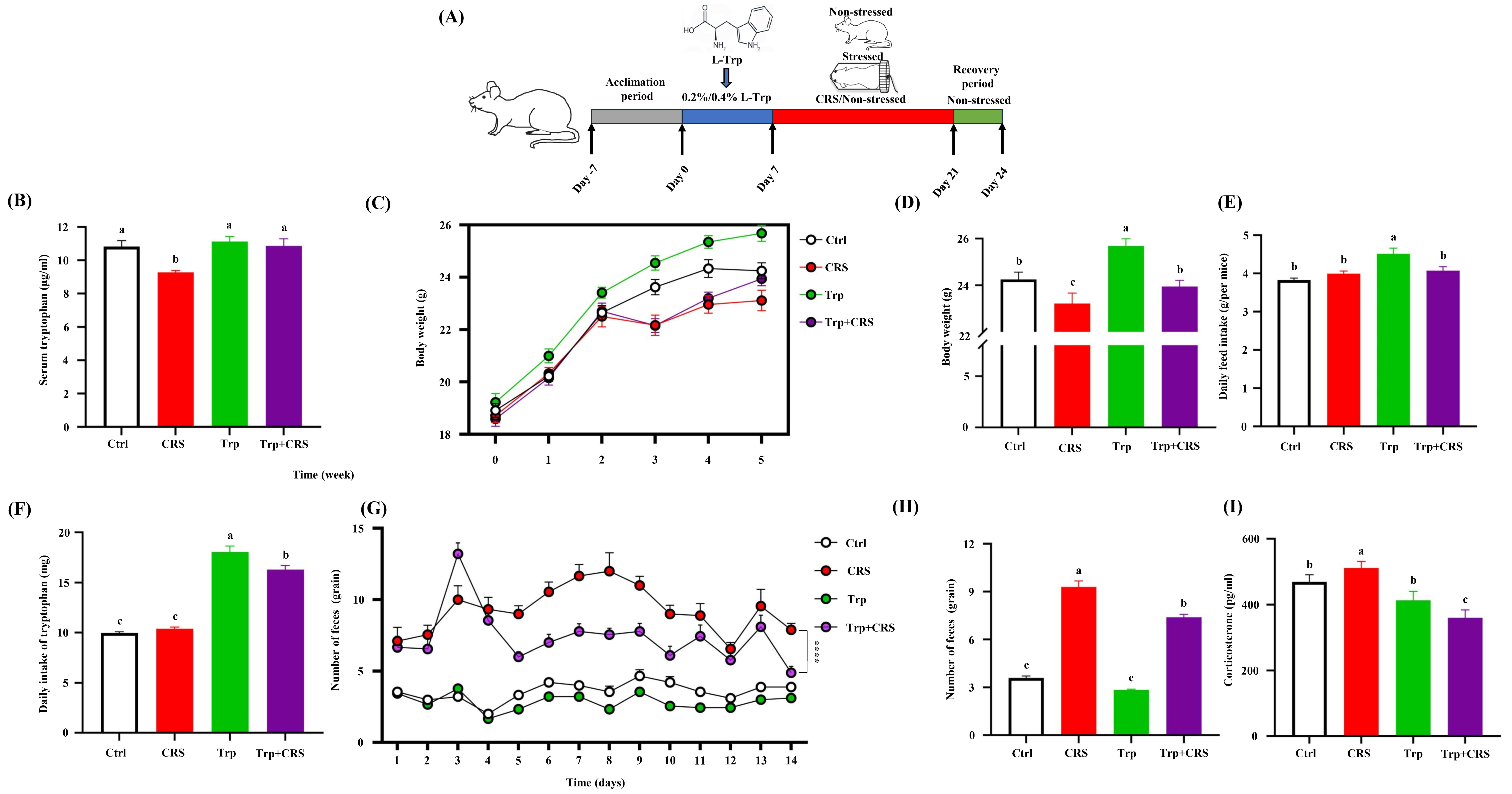
3.1. Tryptophan Restored CRS-Induced Stress Responses in the Body
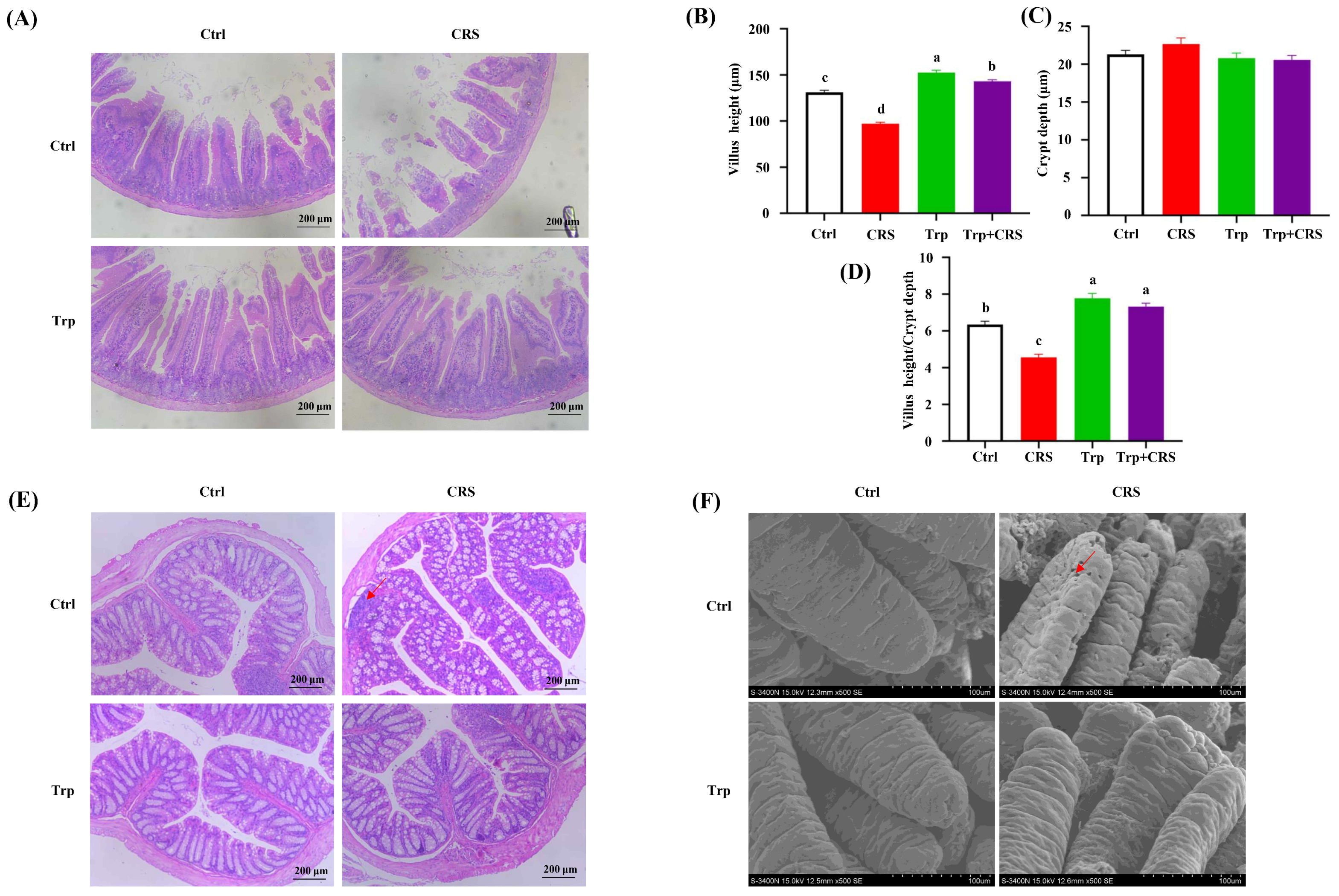
3.2. Tryptophan Attenuates CRS-Induced Intestinal Injury
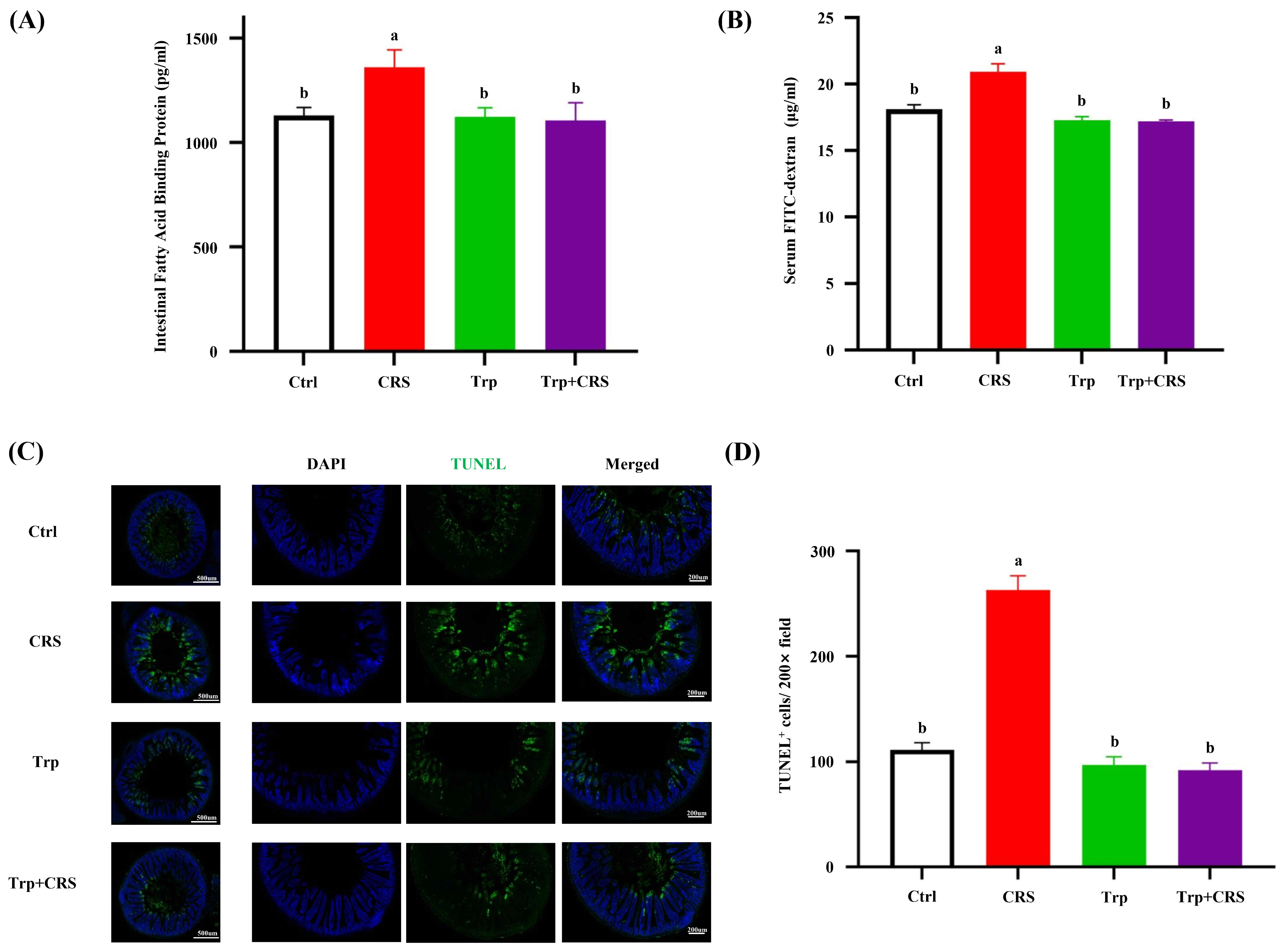
3.3. Tryptophan Attenuates CRS-Induced Intestine Leakage and Epithelial Apoptosis
3.4. Tryptophan Activates the Expression of Intestinal Kyn and 5-HT Metabolism-Related Enzyme Genes
3.5. Tryptophan Inhibits CRS-Induced Gut Microbiota Dysfunction
3.6. Prediction Analysis of Tryptophan for the Metabolic Pathways of CRS-Induced Microbiota
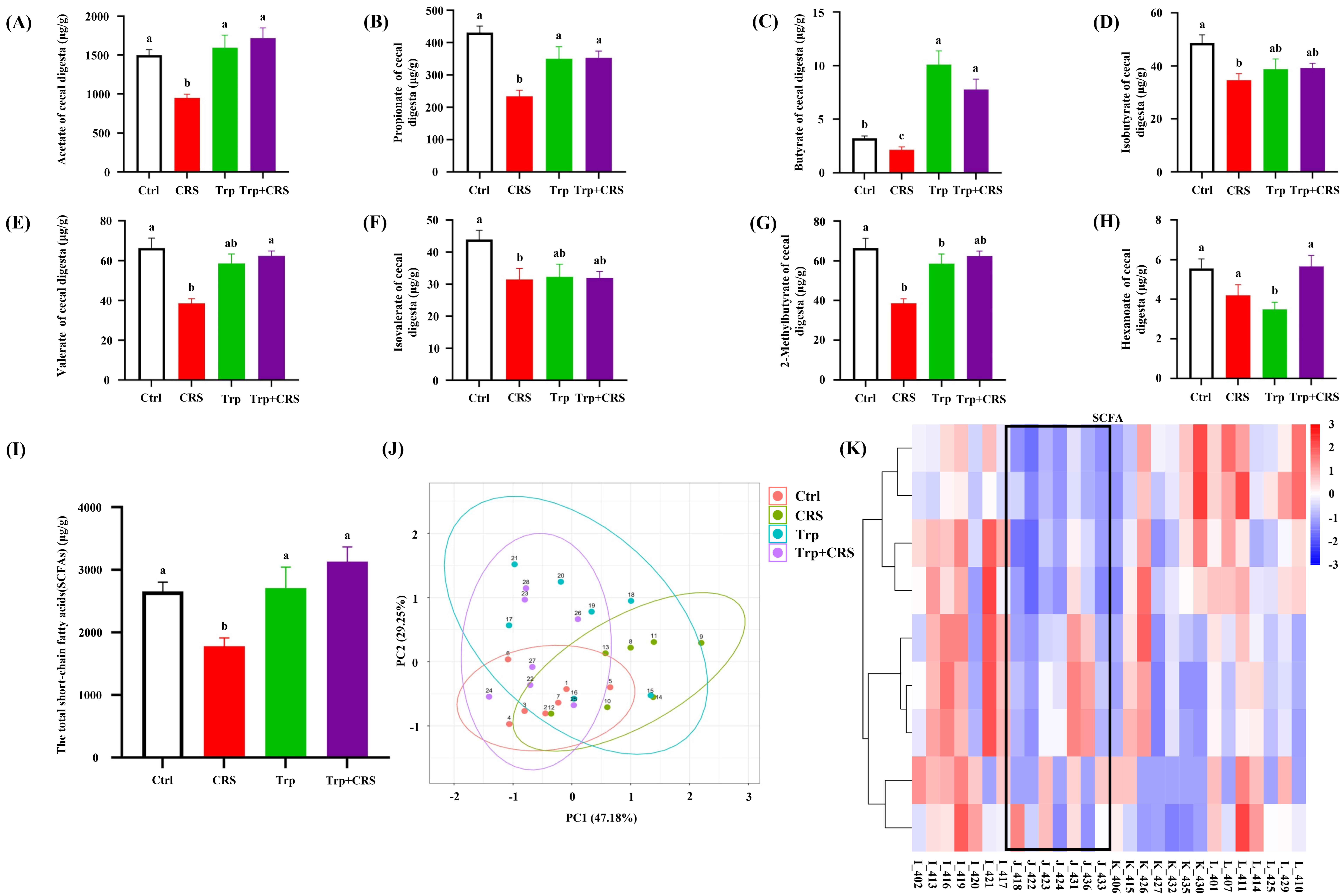
3.7. Tryptophan Inhibits CRS-Induced Decrease in SCFAs
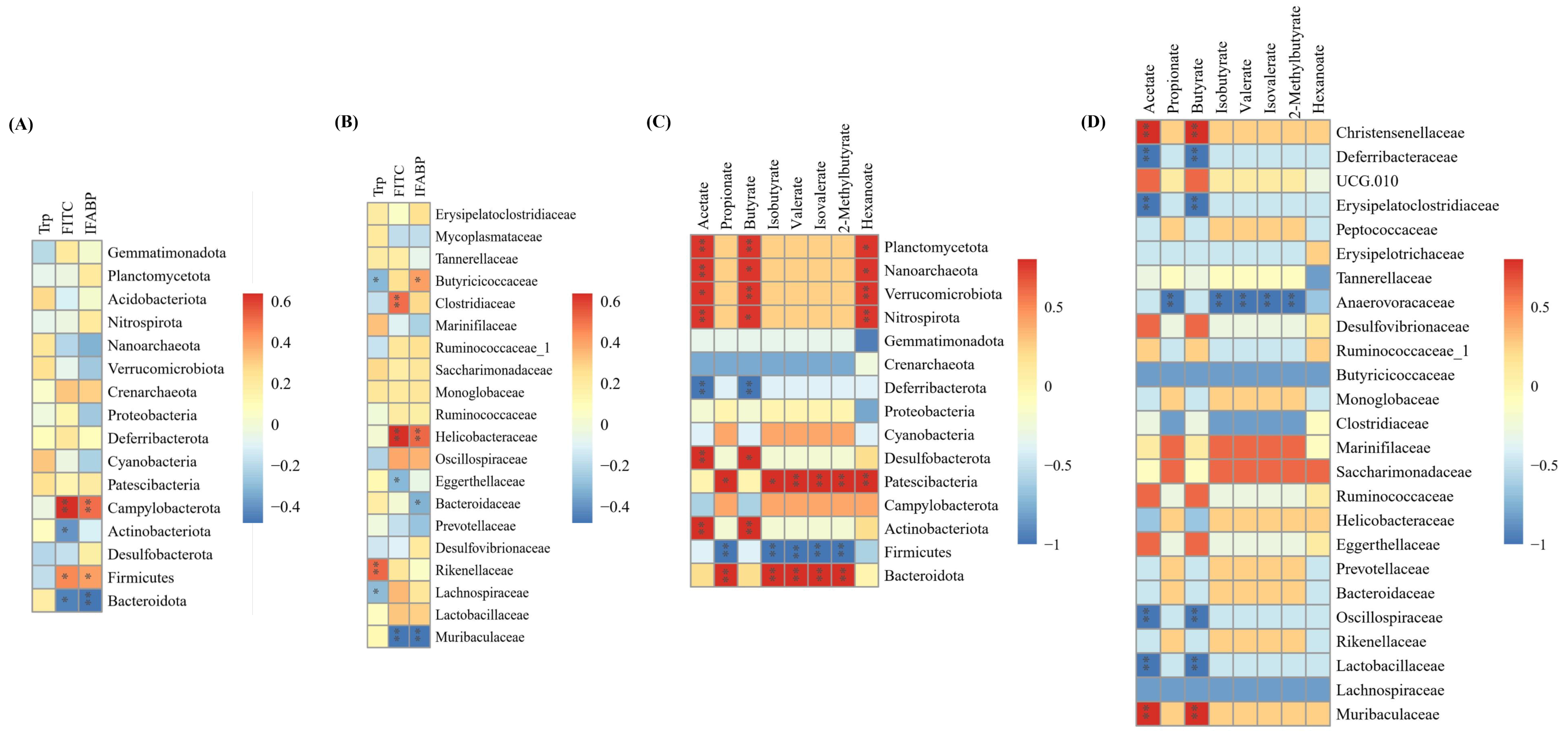
3.8. Correlations Between Tryptophan, Intestinal Permeability, SCFAs and Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Amino Acid Content and Gene Expression Analysis
Appendix A.1. Amino Acid Content in Diets with Varying Tryptophan Levels
| Ingredient | Basic Feeds | Supplemental Tryptophan Feeds |
|---|---|---|
| Glycine | 0.96% | 0.90% |
| Alanine | 0.96% | 0.92% |
| Serine | 0.87% | 0.82% |
| Proline | 1.38% | 1.28% |
| Valine | 0.90% | 0.85% |
| Serine | 0.74% | 0.70% |
| Isoleucine | 0.75% | 0.70% |
| Leucine | 1.49% | 1.41% |
| Asparagine | 1.83% | 1.71% |
| Lysine | 1.06% | 0.96% |
| Glutamate | 3.70% | 3.46% |
| Methionine | 0.20% | 0.23% |
| Histidine | 0.57% | 0.51% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.93% | 0.87% |
| Arginine | 1.37% | 1.21% |
| Serine | 0.61% | 0.54% |
| Cysteine | 0.25% | 0.26% |
| Total 17 amino acids | 18.57% | 17.33% |
| Tryptophan | 0.20% | 0.40% |
Appendix A.2. Sequence List of qRT-PCR Primers
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′ → 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| SLC3A1 | ATGAAGGGATGCCGAACCAAT | CAGGGATACTCACGGCGTTG |
| IDO1 | GCCTCCTATTCTGTCTTATGCAG | ATACAGTGGGGATTGCTTTGATT |
| TDO | ATGAGTGGGTGCCCGTTTG | GGCTCTGTTTACACCAGTTTGAG |
| TPH2 | GGTTGTCCTTGGATTCTGCTG | GCCTGGATTCGATATGAAGCAT |
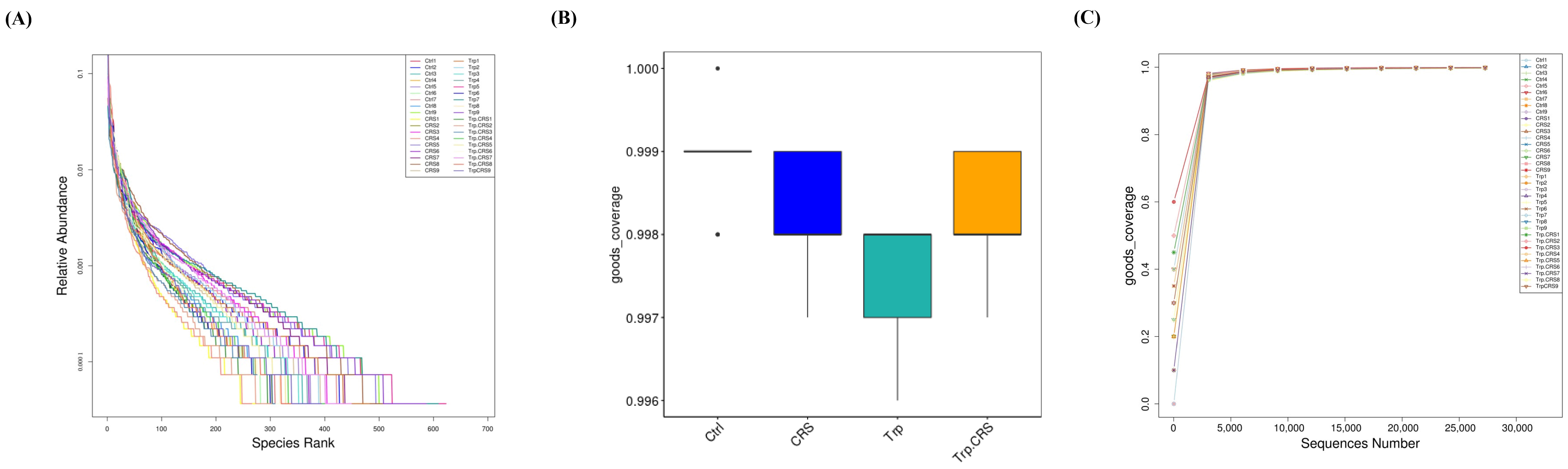
Appendix B. Analysis of Microbial Diversity and Community Structure
References
- Xu, W.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y. Impairment of CRH in the intestinal mucosal epithelial barrier of pregnant Bama miniature pig induced by restraint stress. Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Torres, G.; Rodriguez-Arrastia, M.; Roman, P.; Sanchez-Labraca, N.; Cardona, D. Stress and the gut microbiota-brain axis. Behav. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, I.C.; Shanahan, M.L.; Hirsh, A.T.; Stewart, J.C.; Rand, K.L. The relationship between meaning in life and post-traumatic stress symptoms in US military personnel: A meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-C.; Ye, F.; Xu, C.-X.; Chang, Q.; Liu, X.-M.; Pan, R.-L. Effect of Radix Polygalae extract on the colonic dysfunction in rats induced by chronic restraint stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 294, 115349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, D.-J.; Pethaperumal, S.; Siwakoti, B.; Chien, H.-J.; Cheng, C.-F.; Hung, S.-C.; Lien, T.-S.; Sun, D.-S.; Chang, H.-H. Activating Transcription Factor 3 Protects against Restraint Stress-Induced Gastrointestinal Injury in Mice. Cells 2021, 10, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, K.L.; Kim, J.S. Restraint stress induces and exacerbates intestinal inflammation in interleukin-10 deficient mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8580–8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Gao, T.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Role of melatonin in murine “restraint stress”-induced dysfunction of colonic microbiota. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, K.; Zhuang, R. Acute cold water-immersion restraint stress induces intestinal injury and reduces the diversity of gut microbiota in mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 706849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Peng, S.; Lin, K.; Zhao, B.; Wei, L.; Tuo, Q.; Liao, D.; Yuan, T.; Shi, Z. Chronic stress-induced depression requires the recruitment of peripheral Th17 cells into the brain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, R.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, M.; Zhang, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Xiaoyaosan slows cancer progression and ameliorates gut dysbiosis in mice with chronic restraint stress and colorectal cancer xenografts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, S.A.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Ardizzone, A.; Pantaleo, L.; Campolo, M.; Paterniti, I.; Cucinotta, L.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Efficacy of a product containing xyloglucan and pea protein on intestinal barrier function in a partial restraint stress animal model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järbrink-Sehgal, E.; Andreasson, A. The gut microbiota and mental health in adults. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 62, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Cao, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; You, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Chronic stress promotes colitis by disturbing the gut microbiota and triggering immune system response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2960–E2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, X. Fecal microbiota transplantation from chronic unpredictable mild stress mice donors affects anxiety-like and depression-like behavior in recipient mice via the gut microbiota-inflammation-brain axis. Stress 2019, 22, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Impact of the gut microbiota on intestinal immunity mediated by tryptophan metabolism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L.; Henson, J.D.; Hall, S. Intestinal dysbiosis, the tryptophan pathway and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2022, 15, 11786469211070533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, R. Involvement of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in chronic restraint stress: Disturbances of the kynurenine metabolic pathway in both the gut and brain. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Meininger, C.J. Analysis of citrulline, arginine, and methylarginines using high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 440, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 30987-2020; Determination of Free Amino Acids in Plants. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, K.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Diao, H. Phospholipid metabolites of the gut microbiota promote hypoxia-induced intestinal injury via CD1d-dependent γδ T cells. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2096994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Mitra, S.; Crowe, S.E. Oxidative stress: An essential factor in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal mucosal diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israeli, E.; Hershcovici, T.; Berenshtein, E.; Zannineli, G.; Wengrower, D.; Weiss, O.; Chevion, M.; Goldin, E. The effect of restraint stress on the normal colon and on intestinal inflammation in a model of experimental colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 53, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-C.; Gan, L.; Tan, Y.; Yan, M.-Z.; Liu, X.-M.; Chang, Q.; Pan, R.-L. Chronic restraint stress induced changes in colonic homeostasis-related indexes and tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism in rats. J. Proteom. 2021, 240, 104190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.-Y. Impact of psychological stress on irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14126–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.-Y.; He, Q.-Y.; Zhang, R.-R.; Luo, B.-F.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Chen, X.-F. Evaluation of two laboratory model methods for diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.F.; Kim, H.-M.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.-J.; Lim, C.-Y.; Koo, B.-S.; Kang, S.-S. Effect of probiotic administration on gut microbiota and depressive behaviors in mice. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 28, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roager, H.M.; Licht, T.R. Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Li, G.; Zheng, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Su, Y.; Chu, Q.; Yuan, X.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1304–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.-D.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J.M. Intestinal permeability—A new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Lv, M.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, D. The effect of dietary tryptophan levels on oxidative stress of liver induced by diquat in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.-S.; Zhang, W.; Jiao, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Shi, H.N. The effect of exposure to high altitude and low oxygen on intestinal microbial communities in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, S.J.; Guzik, A.C.; van der Meulen, J.; Dekker, R.; Kogut, J.; Kerr, B.J.; Southern, L.L. Effects of supplemental L-tryptophan on serotonin, cortisol, intestinal integrity, and behavior in weanling piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, T.; Feng, G.; Tan, H.; Piao, X.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Chlorogenic acid alleviates chronic stress-induced intestinal damage by inhibiting the P38MAPK/NF-κB pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 9381–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liang, L.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. Extracellular vesicles of Fusobacterium nucleatum compromise intestinal barrier through targeting RIPK1-mediated cell death pathway. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1902718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tao, J.; Lu, J.; Jia, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Tian, G.; Cai, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J. Dietary Tryptophan supplementation improves antioxidant status and alleviates inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis, and pyroptosis in the intestine of piglets after lipopolysaccharide challenge. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Feng, H.Y.; Guo, Z.Y.; Li, X.; Nie, X.L.; Zhao, Y.Y. Host/microbiota interactions-derived tryptophan metabolites modulate oxidative stress and inflammation via aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 184, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, M.; Su, Y.; Pan, Z.; Liang, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; et al. Gegen Qinlian decoction activates AhR/IL-22 to repair intestinal barrier by modulating gut microbiota-related tryptophan metabolism in ulcerative colitis mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 302, 115919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, H.; Yan, Z.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Influence of Xiaoyaosan on depressive-like behaviors in chronic stress-depressed rats through regulating tryptophan metabolism in hippocampus. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Dai, Z.; Liu, N.; Ji, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, G. Dietary L-tryptophan modulates the structural and functional composition of the intestinal microbiome in weaned piglets. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, D.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; Costas, B.; Azeredo, R.; Mancera, J.M. Tryptophan-supplemented diet modulates the metabolic response of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles reared under space-confined conditions and submitted to acute inflammation. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 51, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Robusto, B.; Morel, L. Intestinal dysbiosis and tryptophan metabolism in autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Fang, C.; Dou, X.; Zhang, L.; Shan, A. Gut-Derived metabolites from dietary tryptophan supplementation quench intestinal inflammation through the AMPK-SIRT1-autophagy pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 16080–16095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Schoones, T.; Wells, J.M.; Fogliano, V.; Capuano, E. Substrate-driven differences in tryptophan catabolism by gut microbiota and aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, K.; Li, N.; Zhang, L.; Qin, L.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Qu, C.; Miao, J. Soluble dietary fiber and cellulose from Saccharina japonica by-product ameliorate Loperamide-induced constipation via modulating enteric neurotransmitters, short-chain fatty acids and gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, E.; Corr, S.C. Lactobacillus spp. for gastrointestinal health: Current and future perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 840245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, D.; Khater, S.I.; Sherkawy, H.S.; Elgamal, A.; Hasan, A.A.; Muhammed, A.A.; Farag, M.F.M.; Eissa, S.A.; Ismail, T.A.; Eissa, H.M.; et al. Protective role of nano-encapsulated bifidobacterium breve, bacilllus coagulans, and lactobacillus plantarum in colitis model: Insights toward propagation of short-chain fatty acids and reduction of exaggerated inflammatory and oxidative response. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, A.; Pasolli, E.; Masetti, G.; Ercolini, D.; Segata, N. Prevotella diversity, niches and interactions with the human host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, W. New insights into the mechanisms of high-fat diet mediated gut microbiota in chronic diseases. iMeta 2023, 2, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, J.; Sun, T.; Qin, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, J. Tryptophan Attenuates Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Intestinal Injury Through Modulation of Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Gut Microbiota Homeostasis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060975
Zheng J, Sun T, Qin T, Wu Y, Zhang W, Qiu Y, Chen J. Tryptophan Attenuates Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Intestinal Injury Through Modulation of Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Gut Microbiota Homeostasis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060975
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Jianhua, Tianqi Sun, Tongtong Qin, Yunpeng Wu, Wensheng Zhang, Yefeng Qiu, and Jingqing Chen. 2025. "Tryptophan Attenuates Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Intestinal Injury Through Modulation of Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Gut Microbiota Homeostasis" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060975
APA StyleZheng, J., Sun, T., Qin, T., Wu, Y., Zhang, W., Qiu, Y., & Chen, J. (2025). Tryptophan Attenuates Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Intestinal Injury Through Modulation of Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Gut Microbiota Homeostasis. Nutrients, 17(6), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060975






