Influence of Intermittent Fasting on Body Composition, Physical Performance, and the Orexinergic System in Postmenopausal Women: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Body-Composition Assessment
2.3. Orexin-A Analysis
2.4. Performance Evaluations
2.5. Nutritional Intervention
2.6. High-Intensity Interval Training Intervention
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Cabo, R.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifflin, M.D.; St Jeor, S.T. A practical approach to calorie intake estimation and the prediction of weight loss. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1990, 90, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, R.E.; Sears, D.D.; Chavin, K.D. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Varady, K.A. Intermittent versus daily calorie restriction: Which diet regimen is more effective for weight loss? Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 338–346. [Google Scholar]
- Tinsley, G.M.; La Bounty, P.M. Effects of intermittent fasting on body composition and clinical health markers in humans. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 661–674. [Google Scholar]
- Stockman, M.C.; Thomas, D.; Burke, J.; Apovian, C.M. Intermittent Fasting: Is the Wait Worth the Weight? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 172–185. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, L.; Hamilton, S.; Azevedo, L.B.; Olajide, J.; De Brún, C.; Waller, G.; Whittaker, V.; Sharp, T.; Lean, M.; Hankey, C.; et al. Intermittent fasting interventions for treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JBI Database Syst. Rev. Implement Rep. 2018, 16, 507–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, I.; La Marra, M.; Di Maio, G.; Monda, V.; Chieffi, S.; Guatteo, E.; Messina, G.; Moscatelli, F.; Monda, M.; Messina, A. Physiological Role of Orexinergic System for Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Biswas, D.A. Physiological Role of Orexin/Hypocretin in the Human Body in Motivated Behavior: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e34009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.D. Appetite Regulation: Hormones, Peptides, and Neurotransmitters and Their Role in Obesity. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2017, 13, 586–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.H.; Small, C.J.; Dakin, C.L.; Abbott, C.R.; Morgan, D.G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. The central effects of orexin-A in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in vivo and in vitro in male rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2001, 13, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavanji, V.; Pomonis, B.; Kotz, C.M. Orexin, serotonin, and energy balance. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2022, 14, e1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, M.L.; Oliveira, M.N.; Vieira-Potter, V.J. Adipocyte Metabolism and Health after the Menopause: The Role of Exercise. Nutrients 2023, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuit, M.; Maillard, F.; Pereira, B.; Marquezi, M.L.; Lancha Jr, A.H.; Boisseau, N. Effect of high intensity interval training on body composition in women before and after menopause: A meta-analysis. Exp. Physiol. 2020, 105, 1470–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batitucci, G.; Faria Junior, E.V.; Nogueira, J.E.; Brandão, C.F.; Abud, G.F.; Ortiz, G.U.; Marchini, J.S.; Freitas, E.C. Impact of Intermittent Fasting Combined With High-Intensity Interval Training on Body Composition, Metabolic Biomarkers, and Physical Fitness in Women With Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 884305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Moehl, K.; Ghena, N.; Schmaedick, M.; Cheng, A. Intermittent metabolic switching, neuroplasticity and brain health. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, A.; Gámez-Nava, J.I.; Díaz-de la Cruz, E.N.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.G.; Becerra-Alvarado, I.N.; Aceves-Aceves, J.A.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.N.; Mir a-Díaz, A.G. The Effect of Visceral Abdominal Fat Volume on Oxidative Stress and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Subjects with Normal Weight, Overweight and Obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baimel, C.; Bartlett, S.E.; Chiou, L.C.; Lawrence, A.J.; Muschamp, J.W.; Patkar, O.; Tung, L.W.; Borgl, S.L. Orexin/hypocretin role in reward: Implications for opioid and other addictions. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg-Martin, E.S.; Matsumoto, M.; Hikosaka, O. Dopamine in motivational control: Rewarding, aversive, and alerting. Neuron 2010, 68, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataky, M.W.; Young, W.F.; Nair, K.S. Hormonal and Metabolic Changes of Aging and the Influence of Lifestyle Modifications. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 788–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordevic, A.L.; Bonham, M.; Ghasem-Zadeh, A.; Evans, A.; Barber, E.; Day, K.; Kwok, A.; Truby, H. Reliability of compartmental body composition measures in weight-stable adults using ge iDXA: Implications for research and practice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfell-Jones, M.; Olds, T.; Stew, A.; Carter, L. Recent advances in body composition methodologies in two population groups: An updated narrative review. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscatelli, F.; Monda, A.; Messina, A.; Monda, M.; Monda, V.; Villano, I.; De Maria, A.; Nicola, M.; Marsala, G.; de Stefano, M.I.; et al. Evaluation of Orexin-A Salivary Levels and Its Correlation with Attention after Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation in Female Volleyball Players. Sport. Med.-Open 2024, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.E.; Spruit, M.A.; Troosters, T.; Puhan, M.A.; Pepin, V.; Saey, D.; McCormack, M.C.; Carlin, B.W.; Sciurba, F.C.; Pitta, F.; et al. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society technical standard: Field walking tests in chronic respiratory disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901534. [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon, R.W. Handgrip strength: A summary of studies comparing dominant and non-dominant limb measurements. Percept. Mot. Skills 2003, 96, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga-Vega, D.; Merino-Marban, R.; Viciana, J. Criterion-Related Validity of Sit-and-Reach Tests for Estimating Hamstring and Lumbar Extensibility: A Meta-Analysis. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2014, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tanaka, H.; Monahan, K.D.; Seals, D.R. Age-predicted maximal heart rate revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblat, M.A.; Lin, E.; da Costa, B.R.; Thomas, S.G. Programming Interval Training to Optimize Time-Trial Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sport. Med. 2021, 51, 1687–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.D.; Moehl, K.; Donahoo, W.T.; Marosi, K.; Lee, S.A.; Mainous, A.G., 3rd; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Mattson, M.P. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting. Obesity 2018, 26, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, N.; Beaulieu, K.; Finlayson, G.; Hopkins, M. Metabolic adaptations during negative energy balance and their potential impact on appetite and food intake. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, S.; Klempel, M.C.; Kroeger, C.M.; Trepanowski, J.F.; Varady, K.A. Alternate day fasting and endurance exercise combine to reduce body weight and favorably alter plasma lipids in obese humans. Obesity 2020, 28, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, S.C.; Yang, R.S.; Yang, R.J.; Chang, S.F. Effects of resistance training on body composition and functional capacity among sarcopenic obese residents in long-term care facilities: A preliminary study. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, M.; Capodaglio, P.; Ferrario, C.; Tarabini, M.; Galli, M.; Cerri, C.G. Effects of resistance training in women with severe obesity: A preliminary study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 759–766. [Google Scholar]
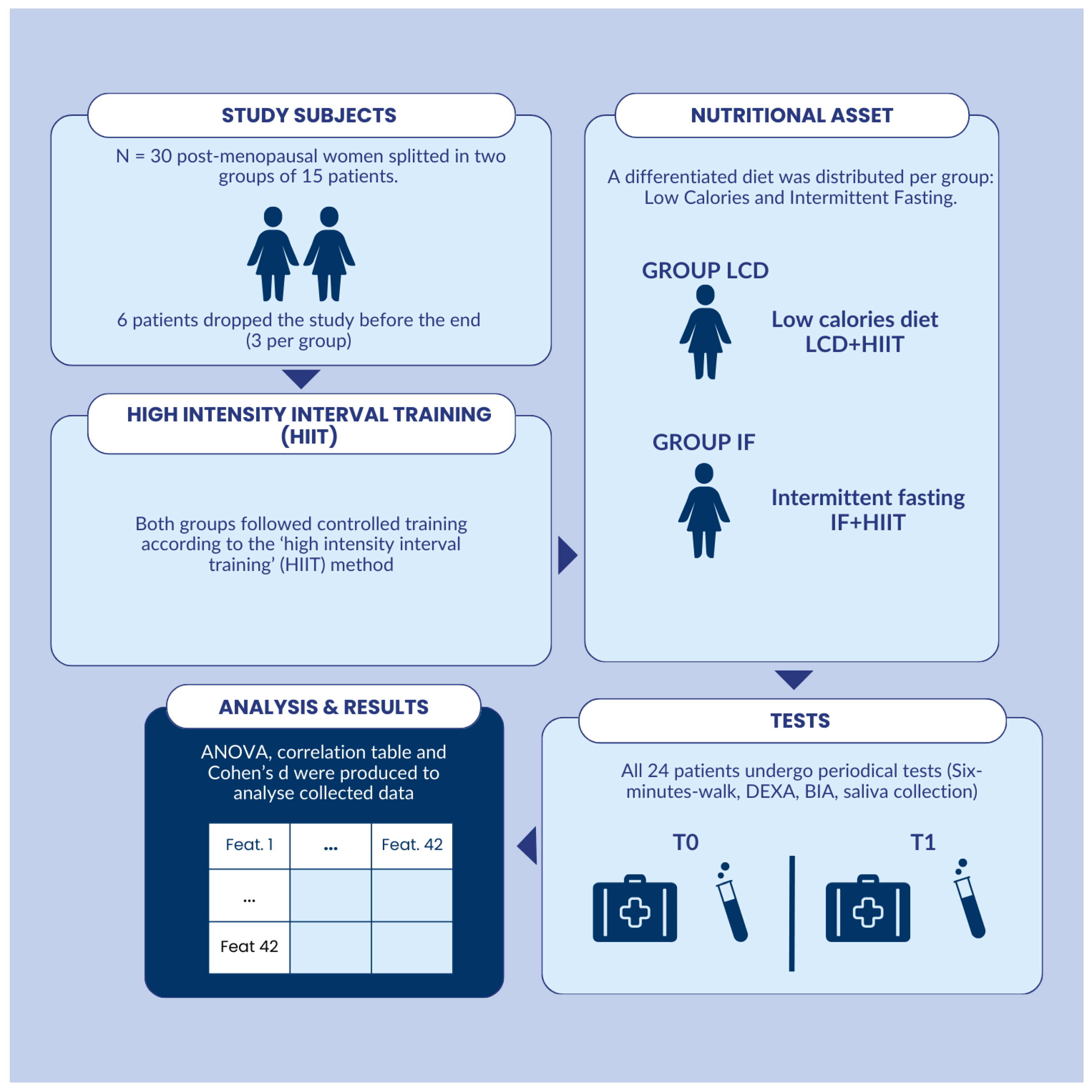
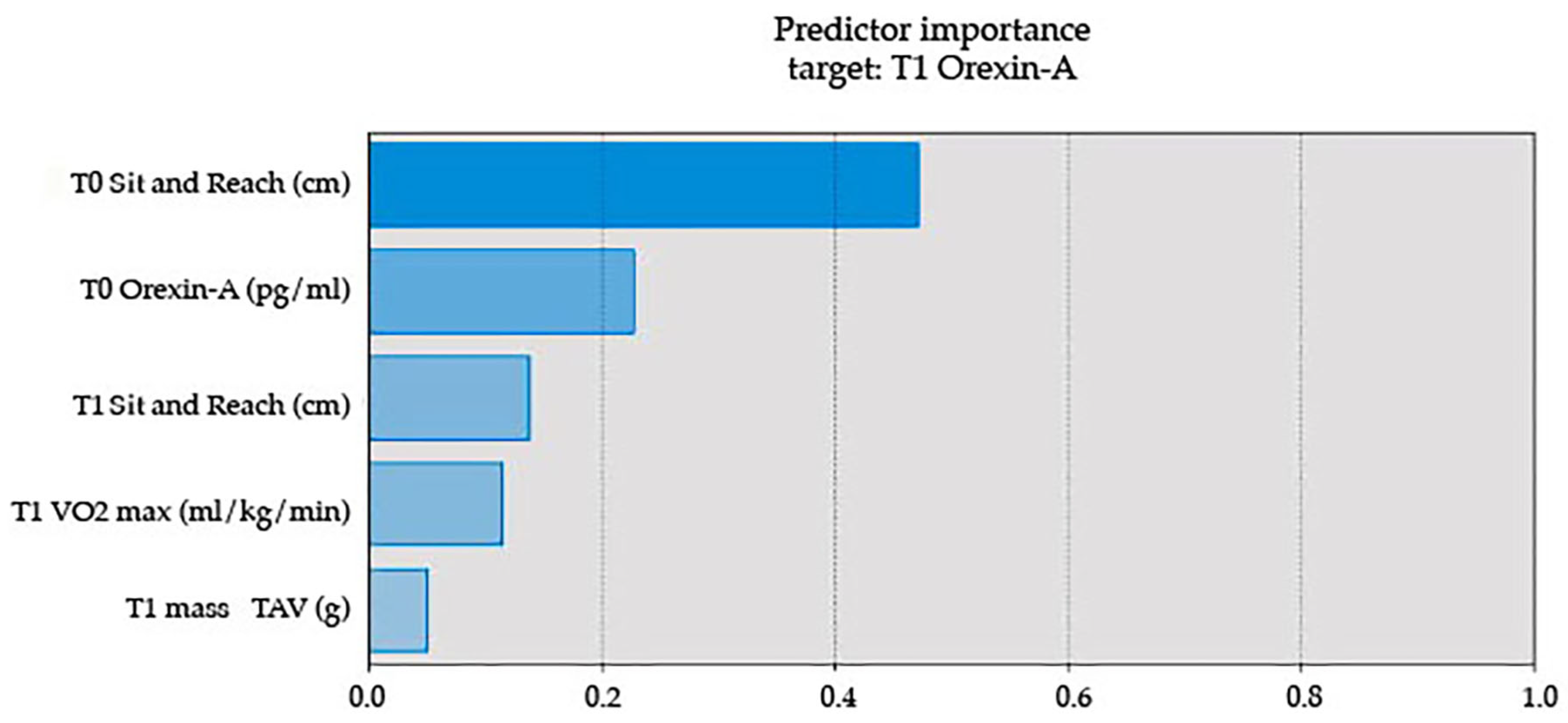

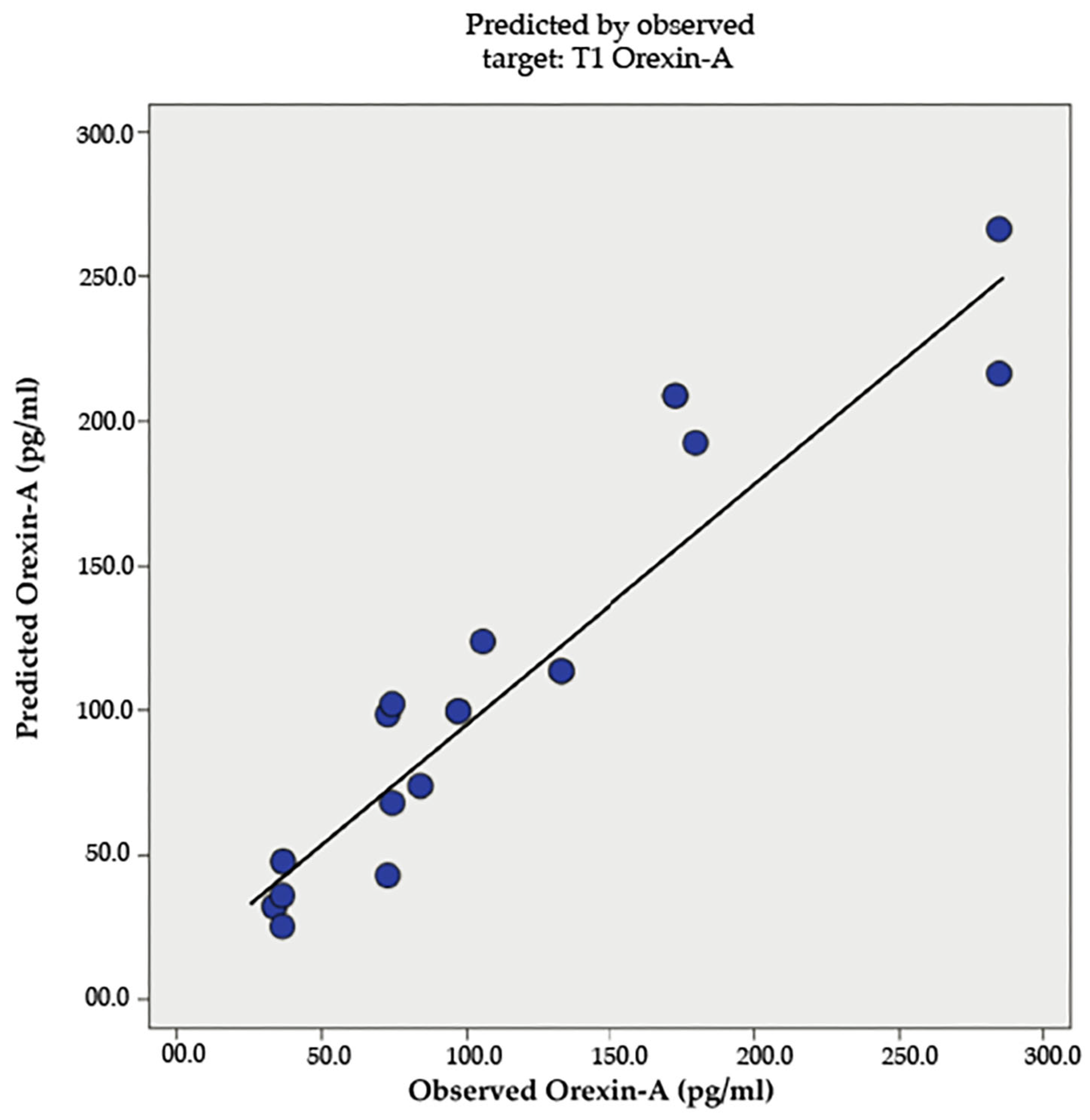
| Measure | IF Mean | IF St. Dev. | LCD Mean | LCD St. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 Distance (m) | 480.17 | 96.68 | 553.33 | 63.14 |
| T1 Distance (m) | 610.08 | 36.13 | 603.50 | 33.81 |
| T0 Evaluation (%) | 79.67 | 18.78 | 83.50 | 15.11 |
| T1 Evaluation (%) | 101.08 | 10.10 | 90.58 | 12.75 |
| T0 max (mL/kg/min) | 27.07 | 2.85 | 25.70 | 4.56 |
| T1 Max (mL/kg/min) | 32.77 | 3.51 | 29.87 | 2.78 |
| T0 HR mean (bpm) | 109.33 | 21.12 | 127.67 | 15.25 |
| T1 HR mean (bpm) | 117.25 | 15.62 | 121.25 | 10.50 |
| T0 Orexin-A (pg/mL) | 53.26 | 30.73 | 35.18 | 16.75 |
| T1 Orexin-A (pg/mL) | 143.89 | 81.47 | 63.68 | 20.63 |
| T0 Sit and Reach (cm) | 8.42 | 3.15 | 14.42 | 4.17 |
| T1 Sit and Reach (cm) | 16.92 | 6.33 | 15.25 | 3.96 |
| T0 Weight (kg) | 66.29 | 4.28 | 63.92 | 9.37 |
| T1 Weight (kg) | 64.08 | 5.97 | 63.54 | 9.05 |
| Test Group | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 Distance (m) | |||||
| Between Groups | 32,120.17 | 1 | 32,120.17 | 4.82 | 0.033 |
| Within Groups | 146,674.33 | 22 | 6667.01 | ||
| Total | 178,794.50 | 23 | |||
| T0 HR mean (bpm) | |||||
| Between Groups | 2016.67 | 1 | 2016.67 | 5.94 | 0.023 |
| Within Groups | 7465.33 | 22 | 339.33 | ||
| Total | 3482.00 | 23 | |||
| T0 Sit and Reach (cm) | |||||
| Between Groups | 216.00 | 1 | 216 | 15.85 | 0.001 |
| Within Groups | 299.83 | 22 | 13.63 | ||
| Total | 515.83 | 23 | |||
| T1 Evaluation (%) | |||||
| Between Groups | 661.50 | 1 | 661.50 | 4.99 | 0.036 |
| Within Groups | 2311.83 | 22 | 132.85 | ||
| Total | 313.02 | 23 | |||
| T1 Max (mL/kg/min) | |||||
| Between Groups | 50.46 | 1 | 50.46 | 5.03 | 0.035 |
| Within Groups | 220.81 | 22 | 10.04 | ||
| Total | 271.27 | 23 | |||
| T1 Orexin-A (pg/mL) | |||||
| Between Groups | 38,607.48 | 1 | 38,607.48 | 10.93 | 0.003 |
| Within Groups | 77,700.51 | 22 | 3531.84 | ||
| Total | 116,307.99 | 23 | |||
| T1 Resistance () | |||||
| Between Groups | 10,045.04 | 1 | 10,045.04 | 6.73 | 0.017 |
| Within Groups | 32,846.92 | 22 | 1493.04 | ||
| Total | 1633.96 | 23 | |||
| Test Pair | Statistic | Value |
|---|---|---|
| T0 Distance (m)—T0 HR mean (bpm) | Pearson Correlation | 0.611 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.002 | |
| T0 Distance (m)—T0 Sit and Reach (cm) | Pearson Correlation | 0.426 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.038 | |
| T0 Distance (m)—T1 Orexin-A (pg/mL) | Pearson Correlation | −0.667 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.000 | |
| T0 HR Mean (bpm)—T0 Sit and Reach (cm) | Pearson Correlation | 0.612 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.001 | |
| T0 HR Mean (bpm)—T1 Orexin-A (pg/mL) | Pearson Correlation | −0.573 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.003 | |
| T0 Sit and Reach (cm)—T1 Orexin-A (pg/mL) | Pearson Correlation | −0.492 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.015 | |
| T1 Evaluation (%)—T1 Max (mL/kg/min) | Pearson Correlation | 0.668 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.000 | |
| T1 Evaluation (%)—T1 RPE | Pearson Correlation | 0.422 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.400 | |
| T1 Evaluation (%)—T1 Resistance () | Pearson Correlation | −0.805 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.000 | |
| T1 RPE—T1 Resistance () | Pearson Correlation | −0.511 |
| p-value (2-tailed) | 0.011 |
| Variables | T0 | T1 | ΔT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance (m) | −0.90 | 0.19 | 1.09 |
| Evaluation (%) | −0.22 | 0.91 | 1.13 |
| max (mL/kg/min) | 0.36 | 0.92 | 0.56 |
| RPE | 0.77 | 1.72 | 0.95 |
| Sit and Reach (cm) | −1.63 | 0.32 | 1.95 |
| Orexin-A (pg/mL) | 0.73 | 1.35 | 0.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valenzano, A.A.; Vasco, P.; D’Orsi, G.; Marzovillo, R.R.R.; Torquato, M.; Messina, G.; Polito, R.; Cibelli, G. Influence of Intermittent Fasting on Body Composition, Physical Performance, and the Orexinergic System in Postmenopausal Women: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071121
Valenzano AA, Vasco P, D’Orsi G, Marzovillo RRR, Torquato M, Messina G, Polito R, Cibelli G. Influence of Intermittent Fasting on Body Composition, Physical Performance, and the Orexinergic System in Postmenopausal Women: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071121
Chicago/Turabian StyleValenzano, Anna A., Paride Vasco, Gabriella D’Orsi, Raffaella R. R. Marzovillo, Maria Torquato, Giovanni Messina, Rita Polito, and Giuseppe Cibelli. 2025. "Influence of Intermittent Fasting on Body Composition, Physical Performance, and the Orexinergic System in Postmenopausal Women: A Pilot Study" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071121
APA StyleValenzano, A. A., Vasco, P., D’Orsi, G., Marzovillo, R. R. R., Torquato, M., Messina, G., Polito, R., & Cibelli, G. (2025). Influence of Intermittent Fasting on Body Composition, Physical Performance, and the Orexinergic System in Postmenopausal Women: A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 17(7), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071121






