The Link Between Oxysterols and Gut Microbiota in the Co-Dysfunction of Cognition and Muscle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
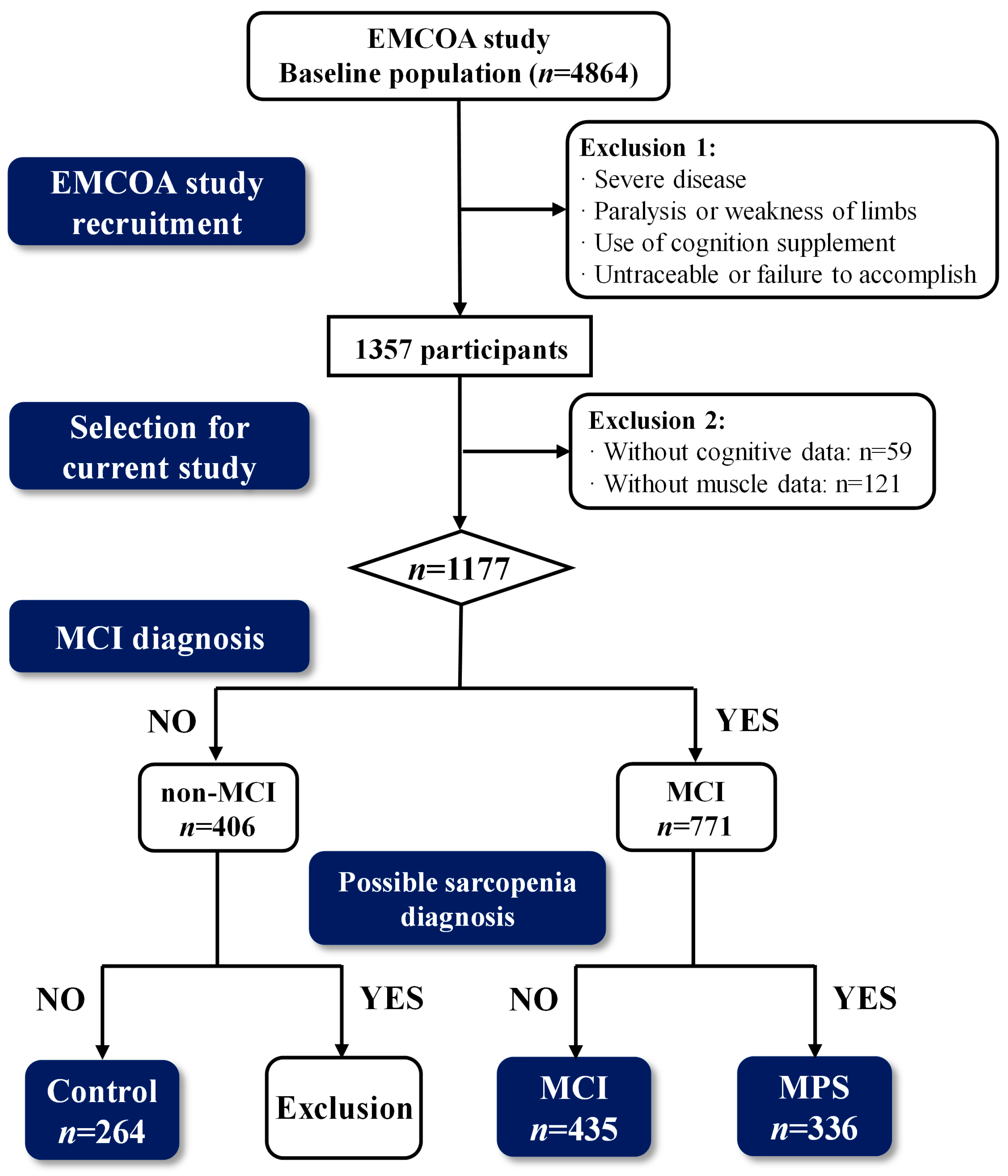
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Diagnostic Criteria of MCI and MPS
2.3. Dietary Survey and Assessment
2.4. Cognitive Function Assessment
2.5. Body Composition Test
2.6. Calf Circumference Measurement
2.7. Handgrip Strength Test
2.8. The Five-Time Chair Stand Test
2.9. Serum Lipids, Oxysterols, and Biomarkers Detection
2.10. Fecal Gut Microbiota
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants Characteristics
3.2. Cognitive Test Scores
3.3. Muscle Mass and Function
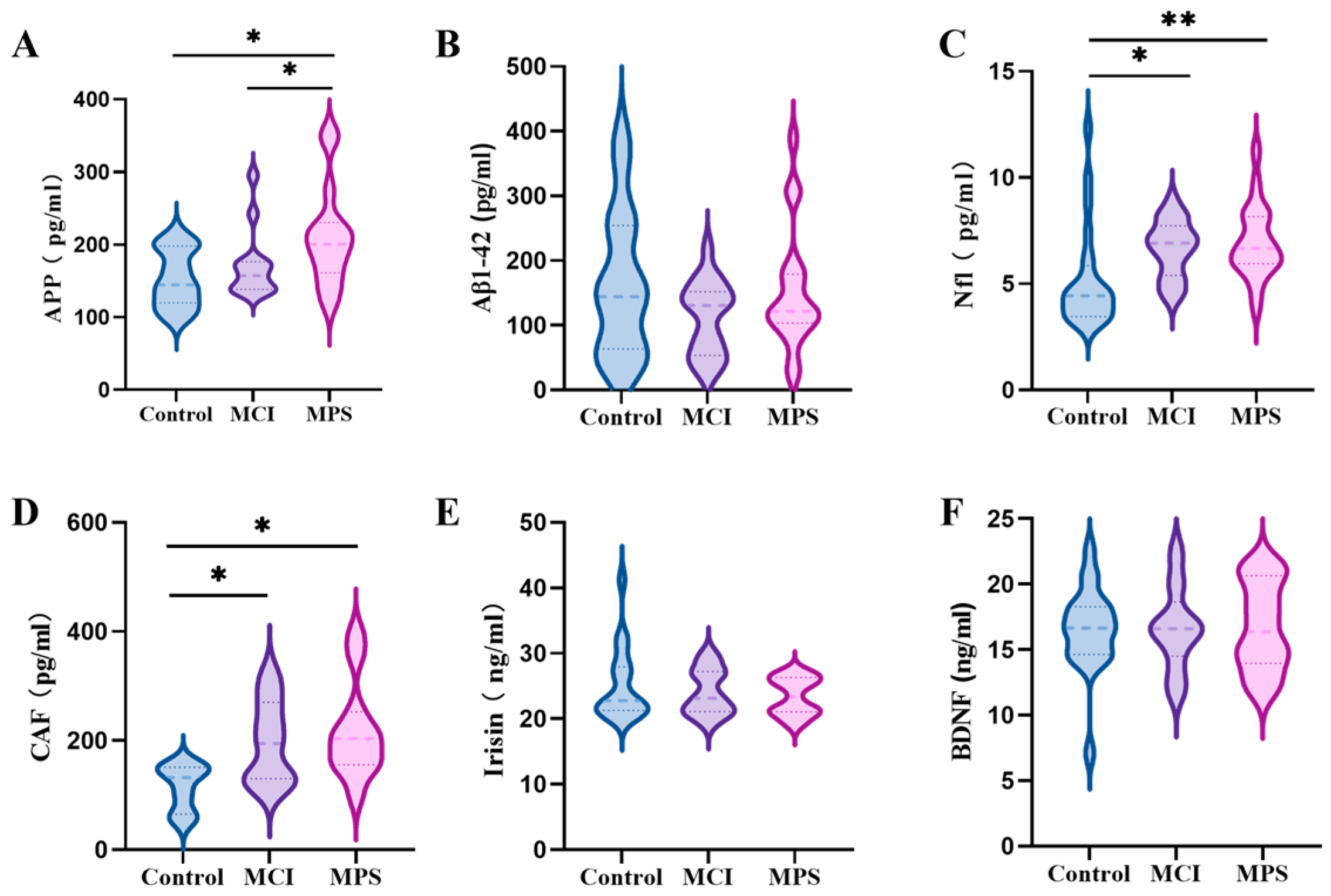
3.4. Serum Biomarkers
3.5. Serum Oxysterols Concentrations
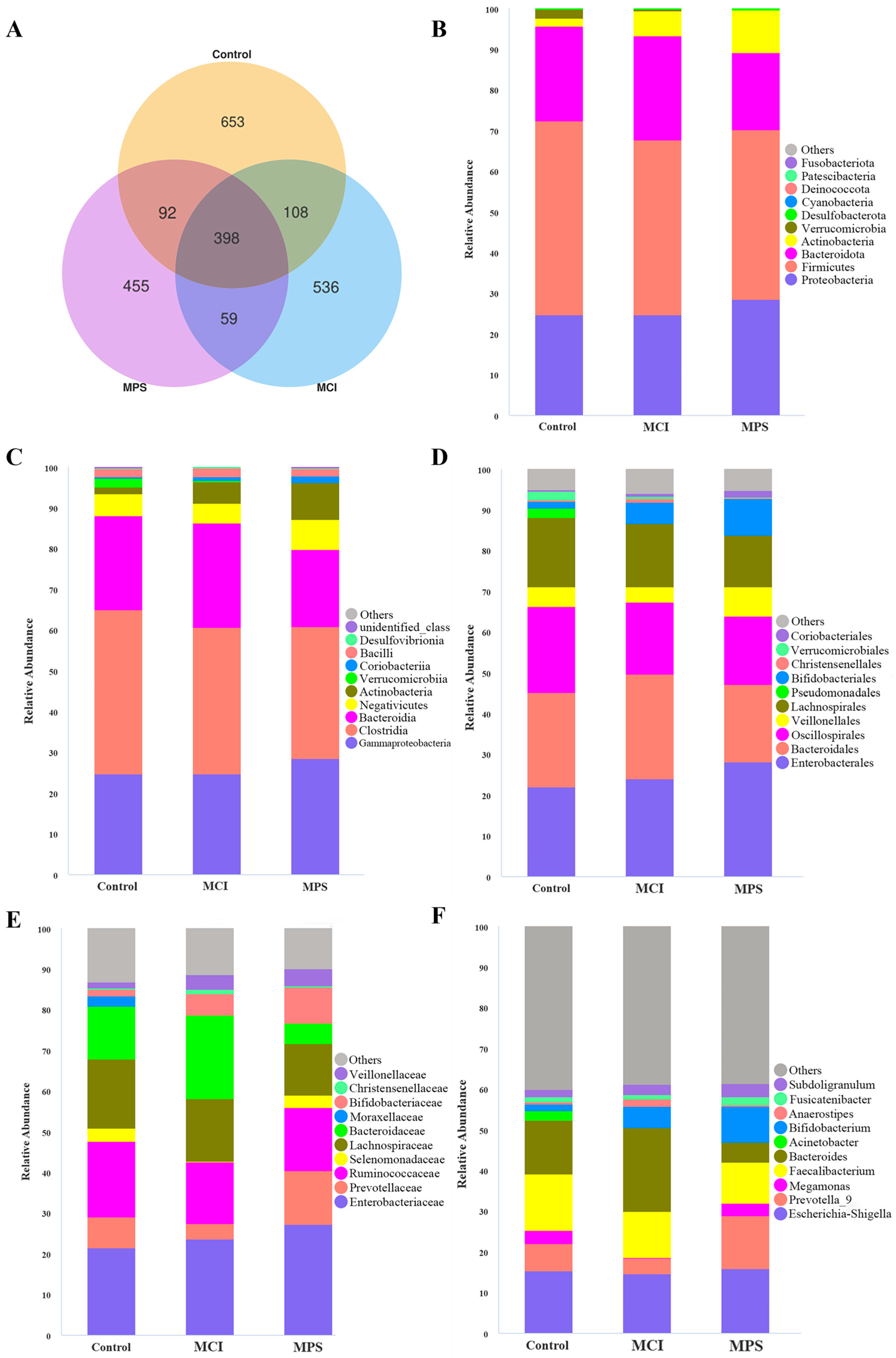
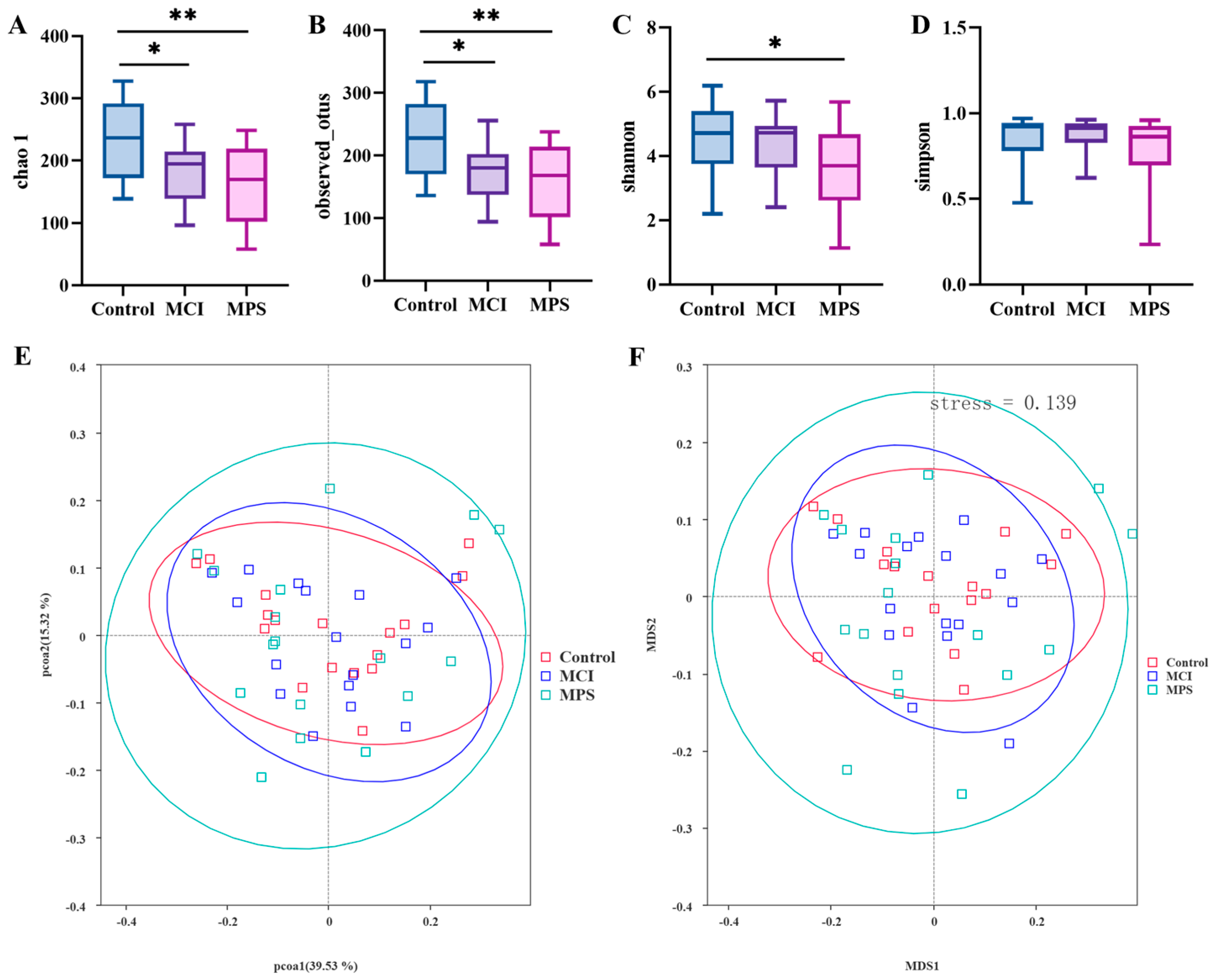
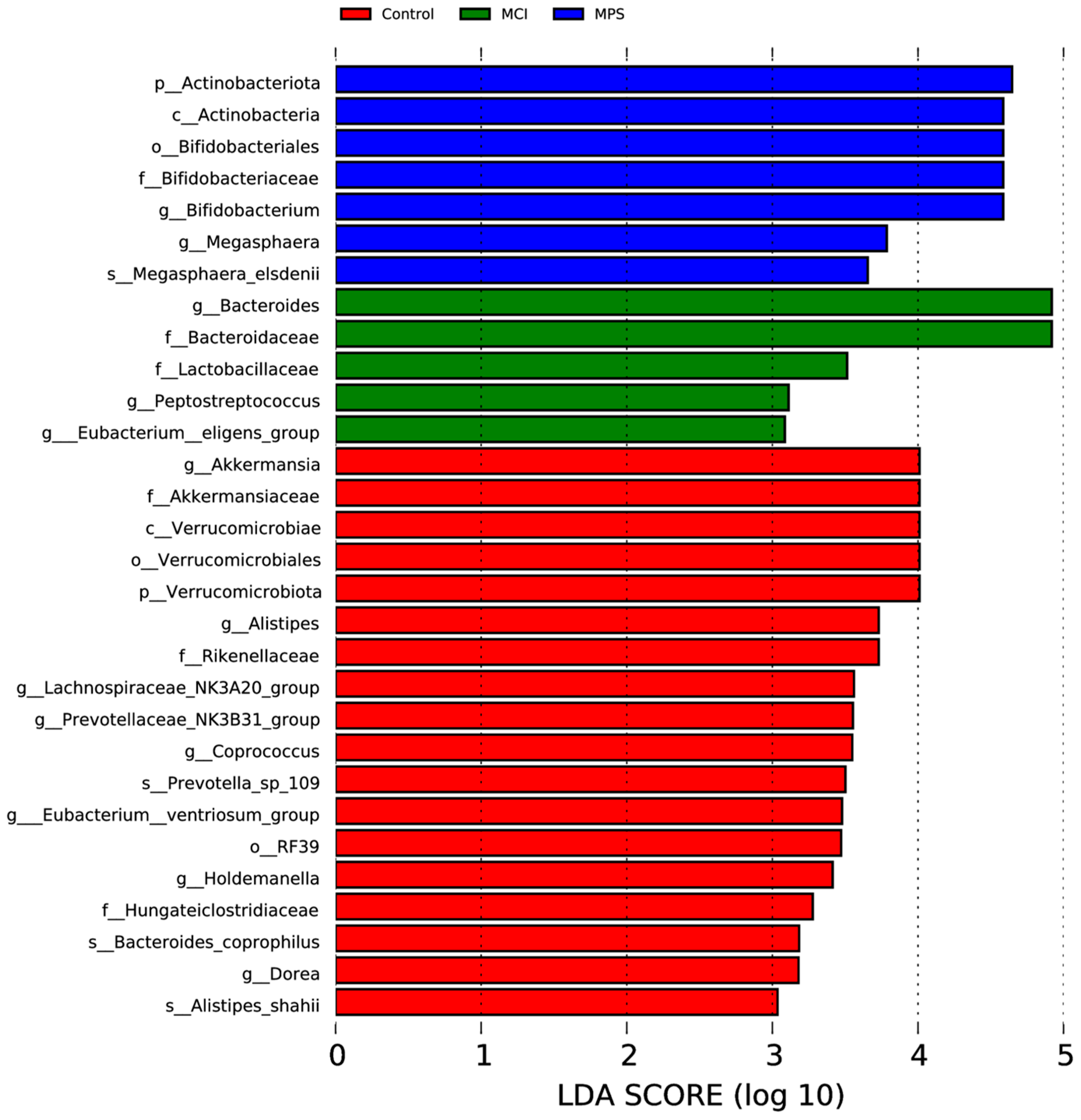
3.6. Gut Microbiota
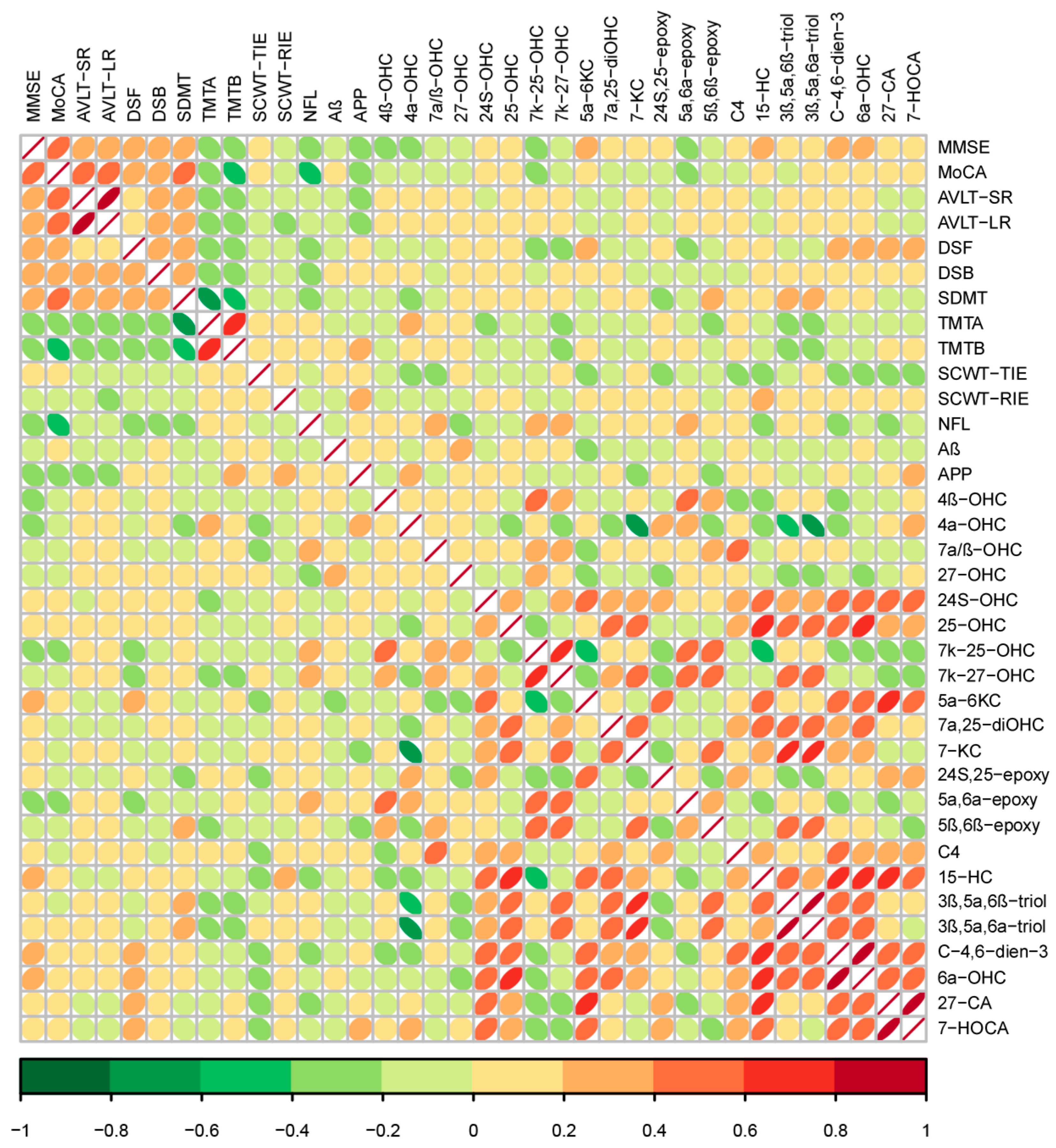
3.7. Association of Cognition and Muscle Indexes
3.8. Association of Oxysterols with Cognition Indexes
3.9. Association of Oxysterols with Muscle Indexes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahami Monfared, A.A.; Byrnes, M.J.; White, L.A.; Zhang, Q. Alzheimer’s disease: Epidemiology and clinical progression. Neurol. Ther. 2022, 11, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Peng, W.; Ren, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Sarcopenia and mild cognitive impairment among elderly adults: The first longitudinal evidence from CHARLS. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2944–2952. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Jia, X.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Q. The longitudinal bidirectional association between sarcopenia and cognitive function in community-dwelling older adults: Findings from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. J. Glob. Health 2023, 13, 04182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Han, P.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, P.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, Z.; Shen, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Relationships between sarcopenia, depressive symptoms, and mild cognitive impairment in Chinese community-dwelling older adults. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 286, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amini, N.; Ibn Hach, M.; Lapauw, L.; Dupont, J.; Vercauteren, L.; Verschueren, S.; Tournoy, J.; Gielen, E. Meta-analysis on the interrelationship between sarcopenia and mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2024, 15, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Sugimoto, T.; Niida, S.; Toba, K.; Sakurai, T. Association between appetite and sarcopenia in patients with mild cognitive impairment and early-stage alzheimer’s disease: A case-control study. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho-Júnior, H.J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Panza, F. Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between adherence to Mediterranean diet with physical performance and cognitive function in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Qin, Z.; Xiao, R. Longitudinal and nonlinear relations of dietary and Serum cholesterol in midlife with cognitive decline: Results from EMCOA study. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, R.; Li, H.; Li, T.; Guan, L.; Ding, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, H.; Yu, K.; Zhao, A.; et al. Correlation between mild cognitive impairment and Sarcopenia: The prospective role of lipids and basal metabolic rate in the link. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, I.H.K.; Shokr, H.; Shephard, F.; Chakrabarti, L. Oxysterols and oxysterol sulfates in alzheimer’s disease brain and cerebrospinal fluid. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 87, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; An, Y.; Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, C.; Xiao, R. Relationship between oxysterols and mild cognitive impairment in the elderly: A case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghzaiel, I.; Zarrouk, A.; Pires, V.; de Barros, J.-P.P.; Hammami, S.; Ksila, M.; Hammami, M.; Ghrairi, T.; Jouanny, P.; Vejux, A.; et al. 7β-Hydroxycholesterol and 7-ketocholesterol: New oxidative stress biomarkers of sarcopenia inducing cytotoxic effects on myoblasts and myotubes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 232, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, M.; Fu, Y.; Zhong, H.-L.; Gou, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Xu, J.-J.; Huynh, T.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; et al. Mapping the human gut mycobiome in middle-aged and elderly adults: Multiomics insights and implications for host metabolic health. Gut 2022, 71, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.M.; Cho, J.; Lee, C. Gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease: How to study and apply their relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Zou, G.; Zou, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, Z. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease: From pathogenesis to treatment. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cheng, J.-K.; Hu, Y.-M. Gut microbiota as a promising therapeutic target for age-related sarcopenia. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 81, 101739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, L.; Ju, M.; Feng, W.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Xiao, R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol impairs learning and memory ability via decreasing brain glucose uptake mediated by the gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, F.; Su, C.; Du, W.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Su, W.; et al. A comparison of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) for mild cognitive impairment screening in Chinese middle-aged and older population: A cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, L.; Kostev, K.; Smith, L.; Oh, H.; López-Sánchez, G.F.; Shin, J.I.; Abduljabbar, A.S.; Haro, J.M.; Koyanagi, A. Sarcopenia and mild cognitive impairment in older adults from six low- and middle-income countries. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 82, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.; Xu, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Deng, X.; Wu, L.; Zou, X.; Zuo, J.; Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Associations of sarcopenia and its defining components with cognitive function in community-dwelling oldest old. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 292. [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Uchida, K.; Kishino, Y.; Saji, N.; Niida, S.; Sakurai, T. Cross-Sectional associations of Sarcopenia and its components with neuropsychological performance among memory clinic patients with mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer’s disease. J. Frailty Aging 2022, 11, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, S.H.; Lim, S.; Park, K.S.; Kim, K.W.; Jang, H.C. Sarcopenia as a predictor of future cognitive impairment in older adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 496–502. [Google Scholar]
- Machii, N.; Kudo, A.; Saito, H.; Tanabe, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Hirai, H.; Masuzaki, H.; Shimabukuro, M. Walking speed is the sole determinant criterion of sarcopenia of mild cognitive impairment in japanese elderly patients with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Studenski, S.A.; An, Y.; Kuo, P.-L.; Schrack, J.A.; Wanigatunga, A.A.; Simonsick, E.M.; Resnick, S.M.; Ferrucci, L. Association of combined slow gait and low activity fragmentation with later onset of cognitive impairment. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2135168. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someya, Y.; Tamura, Y.; Kaga, H.; Sugimoto, D.; Kadowaki, S.; Suzuki, R.; Aoki, S.; Hattori, N.; Motoi, Y.; Shimada, K.; et al. Sarcopenic obesity is associated with cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older adults: The Bunkyo Health Study. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, L.; Leung, B.P.; Wee, S.; Tay, K.S.; Ali, N.; Chan, M.; Lim, W.S. Association of nutrition and immune-endocrine dysfunction with muscle mass and performance in cognitively impaired older adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2018, 75, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, L.E.; Wang, R.; Cederholm, T.; Wiggenraad, F.; Rydén, M.; Hagman, G.; Hellénius, M.-L.; Kivipelto, M.; Thunborg, C. Association of Sarcopenia and its defining components with the degree of cognitive impairment in a memory clinic population. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 96, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verberk, I.M.W.; Misdorp, E.O.; Koelewijn, J.; Ball, A.J.; Blennow, K.; Dage, J.L.; Fandos, N.; Hansson, O.; Hirtz, C.; Janelidze, S.; et al. Characterization of pre-analytical sample handling effects on a panel of Alzheimer’s disease-related blood-based biomarkers: Results from the Standardization of Alzheimer’s Blood Biomarkers (SABB) working group. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 1484–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, P.; Pedrini, S.; Doecke, J.D.; Thota, R.; Villemagne, V.L.; Doré, V.; Singh, A.K.; Wang, P.; Rainey-Smith, S.; Fowler, C.; et al. Plasma Aβ42/40 ratio, p-tau181, GFAP, and NfL across the Alzheimer’s disease continuum: A cross-sectional and longitudinal study in the AIBL cohort. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, J.; De Vito, G.; Segurado, R.; Pessanha, L.; Dolan, J.; Narici, M.; Boreham, C. Plasma neurofilament light levels associate with muscle mass and strength in middle-aged and older adults: Findings from GenoFit. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.-X.; Lee, D.; Sun, D.; Zhao, K.; Xiong, L.; Guo, H.-H.; Ren, X.; Chen, P.; Lopez de Boer, R.; Lu, Y.; et al. Muscular Swedish mutant APP-to-Brain axis in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.; Iqbal, M.S.; Muhammad, T.; Ahmad, F.; Qaisar, R. Elevated plasma zonulin and CAF22 are correlated with sarcopenia and functional dependency at various stages of Alzheimer’s diseases. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 184, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Alsaawi, T.A.; Aldisi, D.; Abulmeaty, M.M.A.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Alnaami, A.M.; Sabico, S.; Al-Daghri, N.M. Screening for sarcopenia among elderly arab females: Influence of body composition, lifestyle, Irisin, and Vitamin D. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.Y.; Jang, I.-Y.; Jung, H.-W.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, E.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, E.; Kim, B.-J. Serum irisin level is independent of sarcopenia and related muscle parameters in older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 162, 111744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, W.D.; Clark, B.C. Neuromuscular junction transmission failure in aging and sarcopenia: The nexus of the neurological and muscular systems. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 89, 101966. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, R.; Kim, Y.; Baek, S.; Suram, R.P.; An, S.-J.L.; Hong, Y. C-Terminal agrin fragment as a biomarker for sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2025, 16, e13707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, E.; Sarto, F.; Sartori, R.; Zanchettin, G.; Löfler, S.; Kern, H.; Narici, M.V.; Zampieri, S. C-terminal agrin fragment as a biomarker of muscle wasting and weakness: A narrative review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cui, S.; Hao, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Ju, M.; Feng, W.; Xiao, R. Regulation of Th17/Treg balance by 27-hydroxycholesterol and 24s-hydroxycholesterol correlates with learning and memory ability in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.Y.; Lewis, M.; Doherty, J.J.; Shi, Y.; Cashikar, A.G.; Amelianchik, A.; Tymchuk, S.; Sullivan, P.M.; Qian, M.; Covey, D.F.; et al. 25-Hydroxycholesterol amplifies microglial IL-1β production in an apoE isoform-dependent manner. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, G.; Staurenghi, E.; Zerbinati, C.; Gargiulo, S.; Iuliano, L.; Giaccone, G.; Fantò, F.; Poli, G.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Gamba, P. Changes in brain oxysterols at different stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Their involvement in neuroinflammation. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, L. Exploring the Intricate Nexus of Sarcopenia and Cognitive Impairment. Aging Dis. 2023, 15, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Huang, C.-W.; Nouchi, R.; Cheng, C.-H. Gut microbiota in patients with Alzheimer’s disease spectrum: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging 2022, 14, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cheung, W.-H.; Li, J.; Chow, S.K.-H.; Yu, J.; Wong, S.H.; Ip, M.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Wong, R.M.Y. Understanding the gut microbiota and sarcopenia: A systematic review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Hao, L.; Ju, M.; Xiao, R. Diet quality, gut microbiota, and microRNAs associated with mild cognitive impairment in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticinesi, A.; Mancabelli, L.; Tagliaferri, S.; Nouvenne, A.; Milani, C.; Del Rio, D.; Lauretani, F.; Maggio, M.G.; Ventura, M.; Meschi, T. The gut-muscle axis in older subjects with low muscle mass and performance: A proof of concept study exploring fecal microbiota composition and function with shotgun metagenomics sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2020, 21, 8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Index | Control | MCI | MPS | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General characteristics (n = 1035) | ||||
| Male, n (%) | 105 (39.7) | 170 (39.1) | 141 (42.0) | 0.711 |
| Age (years) | 62 ± 7 | 61.5 ± 8 | 65 ± 8 | <0.001 * |
| Education year (n) | <0.001 * | |||
| <9 | 136 | 254 | 228 | |
| 9~12 | 93 | 147 | 91 | |
| >12 | 33 | 34 | 17 | |
| Height (cm) | 163.00 ± 11.00 | 163.00 ± 11.00 | 162.00 ± 11.00 | 0.035 * |
| Weight (kg) | 64.40 ± 12.30 | 64.70 ± 11.80 | 63.80 ± 15.10 | 0.592 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.10 ± 0.16 | 24.26 ± 0.14 | 24.42 ± 0.17 | 0.412 |
| Smoker, n (%) | 46 (18.6) | 87 (20.4) | 63 (19.1) | 0.825 |
| Drinker, n (%) | 28 (11.3) | 56 (13.1) | 51 (15.5) | 0.346 |
| Serum lipids (n = 1032) | ||||
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.87 ± 1.42 | 4.82 ± 1.50 | 4.80 ± 1.50 | 0.282 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.48 ± 0.89 | 1.58 ± 0.94 | 1.49 ± 0.91 | 0.258 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.37 ± 0.41 | 1.34 ± 0.41 | 1.28 ± 0.45 | 0.001 * |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.57 ± 0.99 | 2.58 ± 1.16 | 2.57 ± 1.18 | 0.522 |
| Dietary nutrients intake (n = 957) | ||||
| Energy (kcal/day) | 1623.72 ± 702.25 | 1577.89 ± 773.45 | 1597.46 ± 777.08 | 0.477 |
| Protein (g/day) | 61.03 ± 36.02 | 59.40 ± 35.45 | 60.55 ± 34.59 | 0.638 |
| Fat (g/day) | 70.54 ± 43.63 | 68.70 ± 47.06 | 70.06 ± 44.06 | 0.844 |
| Cholesterol (mg/day) | 439.50 ± 226.35 | 448.50 ± 183.19 | 453.50 ± 114.55 | 0.296 |
| Index | Control | MCI | MPS | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global cognition (n = 1035) | ||||
| MMSE | 29 ± 2 | 27 ± 3 | 27 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 29 ± 2 | 28 ± 2 | 27 ± 2 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 29 ± 3 | 28 ± 2 | 28 ± 2 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 29 ± 1 | 28 ± 2 | 28 ± 2 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 29 ± 2 | 29 ± 2 | 27 ± 1 | <0.001 * |
| MoCA | 25 ± 2 | 22 ± 3 | 21 ± 4 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 25 ± 2 | 23 ± 2.5 | 23 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 25 ± 2 | 23 ± 3 | 22 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 25 ± 2 | 23 ± 3 | 22 ± 3.5 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 26 ± 2 | 23 ± 3 | 23 ± 2 | <0.001 * |
| Multidimensional cognition (n = 1002) | ||||
| AVLT-SR | 6 ± 4 | 5 ± 4 | 5 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 5.5 ± 3 | 5 ± 3 | 4 ± 2 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 6 ± 3 | 5 ± 3.75 | 6 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 6 ± 3 | 5 ± 4 | 5 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 6 ± 3 | 4 ± 5 | 4 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| AVLT-LR | 5 ± 4 | 4 ± 4 | 4 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 4 ± 3.75 | 4 ± 3 | 3 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 6 ± 4 | 4 ± 3 | 4 ± 4 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 5 ± 4 | 4 ± 3 | 3.5 ± 4.75 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 5.5 ± 3 | 3 ± 4 | 4 ± 3 | <0.001 * |
| SDMT | 36 ± 17 | 35 ± 13.5 | 31 ± 12 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 36 ± 13 | 35 ± 13 | 30.5 ± 10 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 38 ± 20 | 35 ± 14.75 | 32 ± 16 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 37 ± 15 | 36 ± 14.25 | 31 ± 14 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 35 ± 19.5 | 31.5 ± 8.75 | 31 ± 12 | <0.001 * |
| DSF | 8 ± 2 | 7 ± 1 | 8 ± 1 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 8 ± 2 | 8 ± 1 | 8 ± 1 | 0.001 * |
| Famale | 8 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 | 8 ± 2 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 8 ± 2 | 7 ± 1 | 8 ± 2 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 8 ± 1 | 7 ± 1.25 | 8 ± 1 | 0.015 * |
| DSB | 4 ± 1 | 4 ± 1 | 4 ± 1 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 4 ± 2 | 4 ± 2 | 4 ± 1 | 0.004* |
| Famale | 4 ± 1 | 4 ± 1 | 4 ± 1 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 4 ± 1 | 4 ± 1.25 | 4 ± 1 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 4 ± 2 | 3 ± 1 | 4 ± 1 | <0.001 * |
| TMT-A | 60 ± 30 | 62 ± 35 | 70 ± 39 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 57 ± 18.25 | 59 ± 26.5 | 67 ± 28 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 62 ± 34 | 64.5 ± 38 | 76 ± 39 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 60 ± 29 | 62 ± 34.75 | 70.5 ± 39 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 57.5 ± 37.5 | 66.5 ± 25.75 | 68 ± 35 | <0.001 * |
| TMT-B | 144 ± 72 | 161 ± 90 | 186 ± 94 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 142 ± 60.25 | 156 ± 88.5 | 175.5 ± 90.75 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 147 ± 75 | 170 ± 99.75 | 190 ± 103 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 140 ± 72 | 160 ± 90.25 | 190.5 ± 93 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 149 ± 75.75 | 170.5 ± 108.25 | 160 ± 83 | <0.001 * |
| SCWT-TIE | 36 ± 13 | 35 ± 18.5 | 36 ± 18 | 0.774 |
| Male | 40 ± 18 | 42 ± 23.5 | 43.5 ± 21.5 | 0.370 |
| Famale | 34 ± 13 | 33 ± 15 | 32 ± 16 | 0.539 |
| <65 y | 35 ± 13 | 34 ± 17 | 35 ± 18 | 0.807 |
| ≥65 y | 39.5 ± 18 | 39.5 ± 19 | 42 ± 22 | 0.723 |
| SCWT-RIE | 0 ± 2 | 0 ± 2 | 0 ± 2 | 0.848 |
| Male | 0 ± 2 | 0 ± 2 | 0 ± 3.75 | 0.508 |
| Famale | 0 ± 2 | 0 ± 3 | 0 ± 2 | 0.351 |
| <65 y | 0 ± 2 | 0 ± 2 | 0 ± 2.75 | 0.932 |
| ≥65 y | 0 ± 1.75 | 1 ± 4 | 0 ± 1 | 0.158 |
| Index | Control | MCI | MPS | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle function (n = 1023) | ||||
| Five-time chair stand test (s) | 9.31 ± 2.43 | 9.70 ± 2.55 | 13.24 ± 2.77 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 8.99 ± 2.27 | 9.61 ± 2.36 | 13.59 ± 2.84 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 9.40 ± 2.55 | 9.75 ± 2.66 | 12.98 ± 2.79 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 9.24 ± 2.32 | 9.59 ± 2.58 | 12.75 ± 2.80 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 9.35 ± 2.44 | 9.80 ± 2.42 | 13.52 ± 2.99 | <0.001 * |
| Handgrip strength (kg) | 26.10 ± 13.00 | 25.60 ± 11.43 | 22.40 ± 10.35 | <0.001 * |
| Male | 37.00 ± 8.60 | 35.35 ± 8.28 | 31.10 ± 7.15 | <0.001 * |
| Famale | 22.95 ± 5.40 | 22.70 ± 4.65 | 18.90 ± 6.50 | <0.001 * |
| <65 y | 25.50 ± 9.27 | 25.40 ± 11.00 | 22.50 ± 9.70 | <0.001 * |
| ≥65 y | 29.50 ± 13.40 | 26.90 ± 12.10 | 22.30 ± 11.40 | <0.001 * |
| 6-meter walk (m/s) | 1.13 ± 0.44 | 1.02 ± 0.45 | 1.01 ± 0.30 | 0.013 * |
| Male | 0.83 ± 0.21 | 0.82 ± 0.16 | 0.94 ± 0.20 | 0.031 * |
| Famale | 0.85 ± 0.23 | 0.84 ± 0.23 | 0.95 ± 0.25 | 0.306 |
| <65 y | 0.85 ± 0.24 | 0.83 ± 0.15 | 0.89 ± 0.19 | 0.056 |
| ≥65 y | 0.83 ± 0.19 | 0.83 ± 0.22 | 0.97 ± 0.27 | <0.001 * |
| Muscle mass (n = 528) | ||||
| Waistline (cm) | 85.00 ± 10.50 | 84.00 ± 11.13 | 86.00 ± 12.55 | 0.347 |
| Male | 90.10 ± 7.81 | 88.08 ± 7.88 | 88.39 ± 7.65 | 0.776 |
| Famale | 83.00 ± 10.13 | 82.00 ± 10.50 | 84.00 ± 11.00 | 0.256 |
| <65 y | 83.50 ± 13.55 | 83.00 ± 11.00 | 84.00 ± 13.00 | 0.631 |
| ≥65 y | 85.50 ± 10.00 | 85.00 ± 11.00 | 87.00 ± 11.50 | 0.306 |
| Hipline (cm) | 97.00 ± 8.75 | 96.00 ± 7.00 | 97.00 ± 8.00 | 0.488 |
| Male | 101.00 ± 6.60 | 98.00 ± 5.80 | 98.00 ± 8.00 | 0.330 |
| Famale | 96.40 ± 7.78 | 95.00 ± 7.13 | 96.00 ± 8.00 | 0.569 |
| <65 y | 97.00 ± 9.00 | 96.00 ± 5.50 | 96.00 ± 9.00 | 0.644 |
| ≥65 y | 97.50 ± 7.50 | 96.00 ± 8.00 | 97.00 ± 7.00 | 0.443 |
| Calf circumference (cm) | 34.50 ± 4.10 | 34.00 ± 3.25 | 34.00 ± 3.50 | 0.425 |
| Male | 36.00 ± 4.30 | 35.75 ± 4.88 | 35.50 ± 3.50 | 0.440 |
| Famale | 33.50 ± 4.08 | 33.50 ± 3.00 | 33.00 ± 3.00 | 0.505 |
| <65 y | 34.25 ± 4.35 | 34.00 ± 3.00 | 34.00 ± 3.50 | 0.194 |
| ≥65 y | 34.50 ± 3.80 | 34.00 ± 4.00 | 34.00 ± 4.00 | 0.663 |
| Muscle mass of right upper limb (kg) | 2.14 ± 0.92 | 2.16 ± 0.79 | 2.18 ± 0.93 | 0.557 |
| Male | 2.93 ± 0.71 | 2.90 ± 0.59 | 2.91 ± 0.56 | 0.839 |
| Famale | 2.01 ± 0.35 | 2.00 ± 0.31 | 1.92 ± 0.46 | 0.079 |
| <65 y | 2.09 ± 0.64 | 2.13 ± 0.70 | 2.04 ± 0.76 | 0.150 |
| ≥65 y | 2.38 ± 0.96 | 2.31 ± 0.86 | 2.25 ± 0.93 | 0.817 |
| Muscle mass of left upper limb (kg) | 2.12 ± 0.89 | 2.12 ± 0.76 | 2.12 ± 0.90 | 0.658 |
| Male | 2.93 ± 0.43 | 2.87 ± 0.40 | 2.84 ± 0.46 | 0.851 |
| Famale | 1.97 ± 0.38 | 1.97 ± 0.28 | 1.88 ± 0.44 | 0.120 |
| <65 y | 2.06 ± 0.65 | 2.10 ± 0.67 | 1.99 ± 0.70 | 0.146 |
| ≥65 y | 2.35 ± 0.84 | 2.23 ± 0.79 | 2.23 ± 0.98 | 0.830 |
| Muscle mass of right lower limb (kg) | 6.37 ± 2.15 | 6.44 ± 1.96 | 6.37 ± 2.35 | 0.491 |
| Male | 8.39 ± 1.37 | 8.07 ± 1.24 | 8.10 ± 1.32 | 0.354 |
| Famale | 6.05 ± 0.83 | 5.97 ± 0.96 | 5.67 ± 1.03 | 0.066 |
| <65 y | 6.22 ± 1.35 | 6.34 ± 1.67 | 6.05 ± 1.98 | 0.235 |
| ≥65 y | 7.05 ± 2.66 | 6.66 ± 2.08 | 6.55 ± 2.66 | 0.818 |
| Muscle mass of left lower limb (kg) | 6.29 ± 2.10 | 6.43 ± 2.02 | 6.38 ± 2.24 | 0.465 |
| Male | 8.25 ± 1.55 | 8.04 ± 1.24 | 8.03 ± 1.32 | 0.412 |
| Famale | 5.99 ± 0.78 | 5.93 ± 0.95 | 5.70 ± 1.04 | 0.061 |
| <65 y | 6.22 ± 1.48 | 6.32 ± 1.67 | 6.06 ± 1.75 | 0.210 |
| ≥65 y | 7.11 ± 2.38 | 6.70 ± 2.20 | 6.57 ± 2.50 | 0.830 |
| Limb ASM | 17.08 ± 5.78 | 17.10 ± 5.51 | 17.11 ± 6.58 | 0.512 |
| Male | 22.49 ± 3.71 | 21.87 ± 3.77 | 21.95 ± 3.49 | 0.542 |
| Famale | 15.74 ± 2.44 | 16.01 ± 2.49 | 15.07 ± 2.89 | 0.054 |
| <65 y | 16.66 ± 3.85 | 16.86 ± 4.41 | 16.08 ± 5.48 | 0.199 |
| ≥65 y | 18.77 ± 6.75 | 18.03 ± 6.05 | 17.43 ± 7.11 | 0.848 |
| ASM correction | 6.62 ± 1.44 | 6.64 ± 1.22 | 6.63 ± 1.48 | 0.679 |
| Male | 7.65 ± 0.83 | 7.51 ± 0.89 | 7.69 ± 0.96 | 0.900 |
| Famale | 6.23 ± 0.80 | 6.31 ± 0.66 | 6.11 ± 0.76 | 0.081 |
| <65 y | 6.40 ± 1.14 | 6.51 ± 1.19 | 6.40 ± 1.18 | 0.190 |
| ≥65 y | 6.98 ± 1.43 | 6.75 ± 1.30 | 6.70 ± 1.57 | 0.758 |
| Upper arm circumference (cm) | 30.60 ± 4.00 | 30.40 ± 3.50 | 30.40 ± 3.63 | 0.801 |
| Male | 31.50 ± 2.30 | 31.45 ± 3.52 | 31.60 ± 3.60 | 0.940 |
| Famale | 29.90 ± 3.60 | 29.60 ± 2.80 | 29.90 ± 3.50 | 0.936 |
| <65 y | 30.25 ± 4.55 | 30.50 ± 3.00 | 29.90 ± 3.75 | 0.673 |
| ≥65 y | 31.00 ± 2.90 | 30.40 ± 3.70 | 30.90 ± 3.60 | 0.348 |
| Fat-free circumference of upper arm (cm) | 24.10 ± 3.00 | 23.90 ± 2.73 | 24.10 ± 3.25 | 0.954 |
| Male | 26.30 ± 1.20 | 26.00 ± 2.50 | 26.20 ± 2.45 | 0.966 |
| Famale | 23.20 ± 1.85 | 23.30 ± 1.60 | 23.30 ± 2.10 | 0.831 |
| <65 y | 23.40 ± 2.90 | 23.90 ± 2.30 | 23.80 ± 2.85 | 0.306 |
| ≥65 y | 24.60 ± 2.70 | 24.00 ± 3.00 | 24.30 ± 3.10 | 0.565 |
| Index (μmol/L) | Control (n = 29) | MCI (n = 47) | MPS (n = 27) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27-OHC | 0.0464 (0.0346,0.0816) | 0.0492 (0.0324,0.0700) | 0.0728 (0.0503,0.0789) | 0.033 * |
| 4β-OHC | 0.6369 (0.4988,1.2422) | 0.8150 (0.6061,1.1742) | 1.0774 (0.6927,1.4093) | 0.107 |
| 4α-OHC | 0.1223 (0.0786,0.2955) | 0.1407 (0.0949,0.2788) | 0.1540 (0.0961,0.2646) | 0.793 |
| 7α/β-OHC | 0.0061 (0.0042,0.0084) | 0.0070 (0.0054,0.0095) | 0.0094 (0.0059,0.0148) | 0.009 * |
| 24S-OHC | 0.6225 (0.4836,0.7844) | 0.6073 (0.4564,0.74770) | 0.5640 (0.4178,0.7263) | 0.643 |
| 25-OHC | 0.0011 (0.0007,0.0034) | 0.0018 (0.0007,0.0097) | 0.0009 (0.0006,0.0026) | 0.155 |
| 7k-25-OHC | 0.0376 (0.0251,0.0744) | 0.0637 (0.0386,0.1033) | 0.0704 (0.0467,0.1098) | 0.012 * |
| 7k-27-OHC | 0.0457 (0.0259,0.0632) | 0.0529 (0.0353,0.0769) | 0.0595 (0.0515,0.0842) | 0.286 |
| 5α-6KC | 0.0109 (0.0072,2.6184) | 0.0103 (0.0051,0.0161) | 0.0083 (0.0046,0.0131) | 0.082 |
| 7α,25-diOHC | 0.0105 (0.0064,0.0210) | 0.0153 (0.0101,0.0219) | 0.0126 (0.0076,0.0205) | 0.084 |
| 7-KC | 0.0657 (0.0316,0.2580) | 0.1099 (0.0530,0.2571) | 0.1447 (0.0718,0.2100) | 0.235 |
| 24S,25-epoxy | 0.0726 (0.0567,0.2303) | 0.1027 (0.0586,0.1546) | 0.1166 (0.0732,0.1452) | 0.575 |
| 5α,6α-epoxy | 0.0491 (0.0310,0.0723) | 0.0571 (0.0374,0.0756) | 0.0763 (0.0615,0.1142) | 0.001 * |
| 5β,6β-epoxy | 0.1518 (0.1111,0.2004) | 0.1686 (0.0961,0.2630) | 0.2174 (0.1215,0.2963) | 0.105 |
| C4 | 0.0363 (0.0286,0.0633) | 0.0530 (0.0312,0.0838) | 0.0423 (0.0232,0.0678) | 0.342 |
| 15-HC | 0.0477 (0.0211,0.0671) | 0.0382 (0.0211,0.0702) | 0.0250 (0.0148,0.0428) | 0.048 * |
| 3β,5α,6β-triol | 0.0967 (0.0087,0.2582) | 0.1145 (0.0501,0.3500) | 0.1099 (0.0689,0.1946) | 0.466 |
| 3β,5α,6α-triol | 0.1474 (0.0160,0.3346) | 0.1590 (0.0469,0.6325) | 0.1827 (0.0669,0.2539) | 0.720 |
| C-4,6-dien-3 | 0.5965 (0.0523,1.3723) | 0.4140 (0.0437,1.6658) | 0.0794 (0.0376,0.6920) | 0.418 |
| 6α-OHC | 2.0950 (0.8482,4.3725) | 1.5500 (0.8110,3.8313) | 1.2473 (0.7175,2.2916) | 0.422 |
| 27-CA | 0.0033 (0.0026,0.0395) | 0.0062 (0.0019,0.0138) | 0.0038 (0.0023,0.0095) | 0.939 |
| 7-HOCA | 0.0004 (0.0002,0.0017) | 0.0007 (0.0003,0.0018) | 0.0006 (0.0003,0.0012) | 0.550 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ju, M.; Feng, W.; Guo, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, T.; Yu, H.; Qi, C.; Liu, M.; Tao, J.; Xiao, R. The Link Between Oxysterols and Gut Microbiota in the Co-Dysfunction of Cognition and Muscle. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071277
Ju M, Feng W, Guo Z, Yang K, Wang T, Yu H, Qi C, Liu M, Tao J, Xiao R. The Link Between Oxysterols and Gut Microbiota in the Co-Dysfunction of Cognition and Muscle. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071277
Chicago/Turabian StyleJu, Mengwei, Wenjing Feng, Zhiting Guo, Kexin Yang, Tao Wang, Huiyan Yu, Chengyan Qi, Miao Liu, Jiaxuan Tao, and Rong Xiao. 2025. "The Link Between Oxysterols and Gut Microbiota in the Co-Dysfunction of Cognition and Muscle" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071277
APA StyleJu, M., Feng, W., Guo, Z., Yang, K., Wang, T., Yu, H., Qi, C., Liu, M., Tao, J., & Xiao, R. (2025). The Link Between Oxysterols and Gut Microbiota in the Co-Dysfunction of Cognition and Muscle. Nutrients, 17(7), 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071277






