Oral Zinc Supplementation for the Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
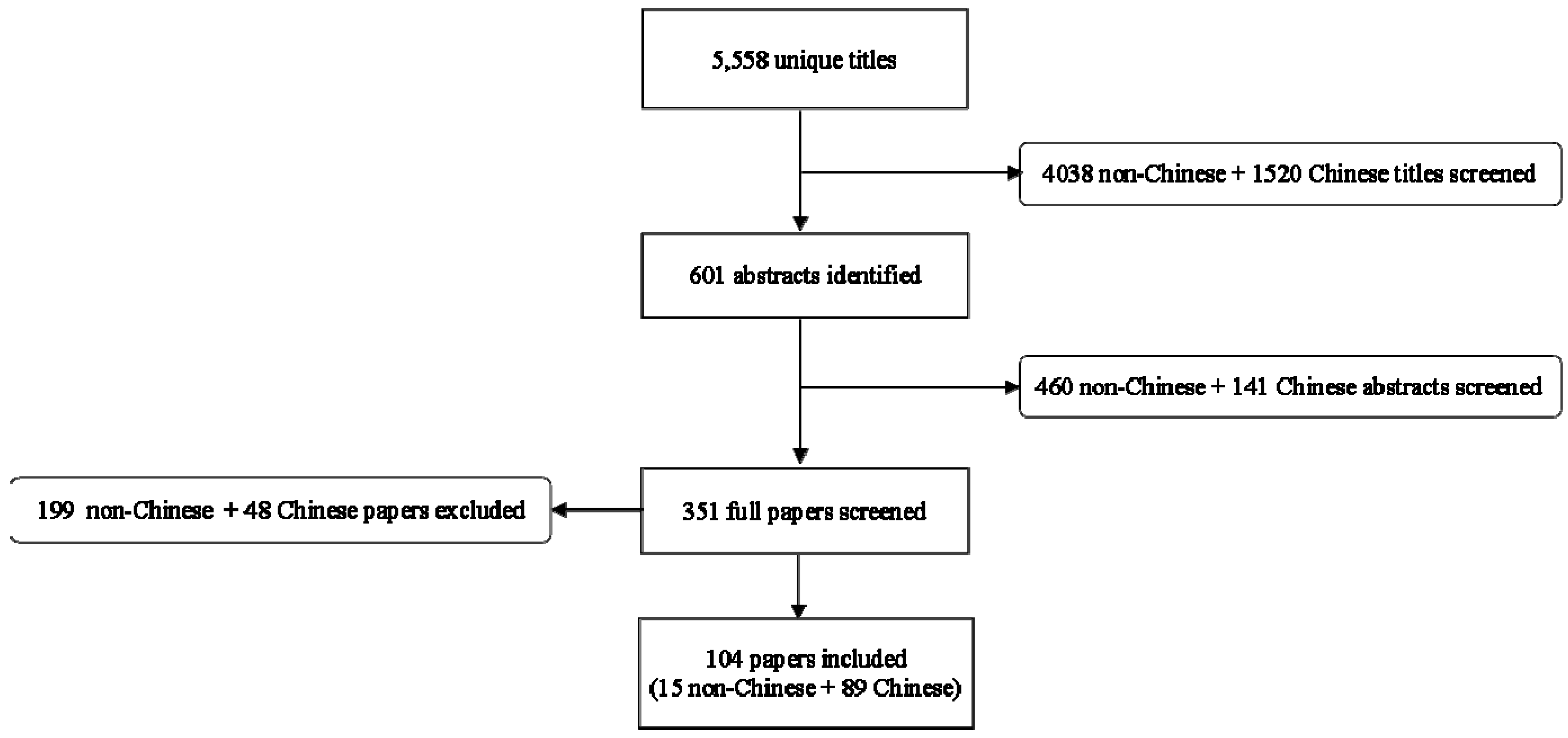
3. Results
| Author [Reference] | Year Published | Country | Trial Setting | Specific Causative Organisms | Age Group (months) | Sample Size | Zinc Salt | Tablet or Syrup | Daily Zinc Dose | Length of Supplementation (days) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc Group | Control Group | ||||||||||
| Al Sonboli [17] | 2003 | Brazil | Hospital | Unknown | 3–60 | 37 | 37 | Not Listed | Tablet | 3–5 mos: 22.5 mg 6–60 mos: 45 mg | 5 |
| Bahl [7] | 2002 | India | Community | Unknown | 6–35 | 404 | 401 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 6–11 mos: 15 mg 12–35 mos: 30 mg | 14 |
| Brooks [16] | 2005 | Bangladesh | Hospital | Unknown | 1–6 | 91 | 93 | Zinc Acetate | Syrup | 20 mg | Duration of episode |
| Brooks [16] | 2005 | Bangladesh | Hospital | Unknown | 1–6 | 91 | 93 | Zinc Acetate | Syrup | 5 mg | Duration of episode |
| Dutta [23] | 2011 | India | Hospital | Unknown | 6–24 | 44 | 41 | Not Listed | Syrup | 40 mg | 14 |
| Elnemr [21] | 2007 | Yemen | Hospital | Unknown | 3–24 | 88 | 92 | Zinc Acetate | Syrup | 20 mg | 14 |
| Faruque [12] | 1999 | Bangladesh | Hospital | Unknown | 6–24 | 343 | 341 | Zinc Acetate | Syrup | 14.2 mg | 15 |
| Fischer Walker [19] | 2006 | Pakistan | Hospital | Unknown | 1–5 | 281 | 279 | Zinc Sulfate | Tablet | 10 mg | 14 |
| Fischer Walker [19] | 2006 | India | Hospital | Unknown | 1–5 | 186 | 187 | Zinc Sulfate | Tablet | 10 mg | 14 |
| Fischer Walker [19] | 2006 | Ethiopia | Hospital | Unknown | 1–5 | 87 | 90 | Zinc Sulfate | Tablet | 10 mg | 14 |
| Larson [18] | 2005 | Bangladesh | Hospital | Unknown | 3–59 | 267 | 266 | Zinc Sulfate | Tablet | 20 mg | 10 |
| Patel [20] | 2009 | India | Hospital | Unknown | 6–59 | 264 | 271 | Zinc Sulfate | Syrup | 20 mg | 14 |
| Patro [22] | 2010 | Poland | Hospital | Unknown | 3–48 | 81 | 79 | Zinc Sulfate | Syrup | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–48 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Polat [15] | 2003 | Turkey | Hospital | Unknown | 2–29 | 52 | 54 | Zinc Sulfate | Syrup | 20 mg | 10 |
| Roy [13] | 1999 | Bangladesh | Hospital | Unknown | 3–24 | 32 | 35 | Zinc Acetate | Syrup | 20 mg | 14 |
| Sachdev [5] | 1988 | India | Hospital | Unknown | 6–18 | 25 | 25 | Zinc Sulfate | Tablet | 40 mg | Not Listed |
| Sazawal [6] | 1995 | India | Hospital | Unknown | 6–35 | 456 | 481 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Strand [14] | 2002 | Nepal | Community | Unknown | 6–35 | 442 | 449 | Not Listed | Syrup | 6–11 mos: 15 mg 12–35 mos: 30 mg | From enrolment until 7 days after episode subsided |
| Zhao [24] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 4–36 | 40 | 40 | Licorzinc | Tablet | 4–5 mos: 10.8 mg 6–12 mos: 14.4 mg 13–36 mos: 21.6 mg | Not Listed |
| Zhang [25] | 2009 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–24 | 60 | 60 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 20 mg | Duration of episode |
| Lin [26] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 1.5–36 | 58 | 58 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 1.5–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | Duration of episode |
| Zhou [27] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–24 | 42 | 40 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 20 mg | 14 |
| Yang [28] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–36 | 42 | 40 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Liu [29] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 5–18 | 40 | 40 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 5 mos: 10 mg 6–18 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Chen [30] | 2006 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 0–24 | 30 | 30 | Zinc gluconate | Not Listed | 10 mg | Not Listed |
| Liu [31] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6.8–22 | 90 | 90 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Liu [32] | 2009 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–36 | 112 | 108 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 20 mg | 10 |
| Fu [33] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 2–24 | 98 | 102 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 5 mg | Not Listed |
| Zhou [34] | 2008 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 2–48 | 40 | 40 | Licorzinc | Not Listed | 2–5 mos: 7.5 mg 6–12 mos: 11.25 mg 13–48 mos: 18.75 mg | 10–14 |
| Chen [35] | 2008 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 4–48 | 60 | 60 | Licorzinc | Not Listed | 4–5 mos: 7.2 mg 6–48 mos: 10.8 mg | Not Listed |
| Guan [36] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 1.5–45.6 | 45 | 45 | Licorzinc | Not Listed | 1.5–5 mos: 7.5 mg 6–11 mos: 11.25 mg 12–45.6 mos: 18.75 mg | 10–14 |
| Wu [37] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 4–13 | 46 | 46 | Licorzinc | Not Listed | 4–5 mos: 10 mg 6–13 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Zhou [38] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–24 | 65 | 60 | Licorzinc | Tablet | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Luo [39] | 2009 | China | Hospital | rotavirus | 6–36 | 55 | 50 | Licorzinc | Tablet | 18.75 mg | Not Listed |
| Zhang [40] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 5–48 | 50 | 50 | Licorzinc | Not Listed | Not Listed * | Not Listed |
| Ju [41] | 2007 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–36 | 40 | 38 | Licorzinc | Tablet | 6–12 mos: 11–25 mg 13–36 mos: 15 mg | Not Listed |
| Wang [42] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–36 | 30 | 30 | Licorzinc | Tablet | Not Listed * | 3 |
| Hong [43] | 2009 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 3–60 | 140 | 120 | Zinc Sulfate | Syrup | 3–11 mos: 20 mg 12–36 mos: 30 mg 37–60 mos: 40 mg | Not Listed |
| Lin [44] | 1994 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0.5–24 | 46 | 58 | Zinc Sulfate | Syrup | 10–14 mg/kg * | Not Listed |
| Yan [45] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 5–36 | 70 | 50 | Zinc Sulfate | Syrup | 5 mos: 50 mg 6–36 mos: 100 mg | Not Listed |
| He [46] | 1997 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–36 | 52 | 58 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Wei [47] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–36 | 44 | 42 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Yang [48] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–36 | 80 | 80 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Pu [49] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 0–24 | 38 | 34 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Zhang [50] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 3–36 | 53 | 53 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Sun [51] | 2008 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 1.5–36 | 45 | 45 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 1.5–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Zhang [52] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–36 | 90 | 90 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Lin [53] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–54 | 28 | 20 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 6–54 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| Liu [54] | 2009 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–36 | 95 | 91 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Qiao [55] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–36 | 73 | 72 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| Zhang [56] | 2007 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–24 | 85 | 90 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Zhao [57] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–24 | 70 | 70 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Cai [58] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–24 | 88 | 84 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| Zhang [59] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–17 | 120 | 120 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Qiao [60] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–24 | 85 | 85 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Zhong [61] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 3–48 | 50 | 50 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–48 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Wang [62] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 0–24 | 60 | 60 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Yang [63] | 2008 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 0–36 | 164 | 168 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Zhao [64] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–36 | 60 | 60 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 35 mg | 10 |
| Ma [65] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 4–42 | 41 | 41 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Chen [66] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 0–36 | 93 | 93 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Hu [67] | 2009 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 4–36 | 60 | 60 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 4–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Yuan [68] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 1–36 | 100 | 100 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 1–12 mos: 70 mg 13–36 mos: 140 mg | 14 |
| Tan [69] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–36 | 50 | 35 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Liu [70] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–36 | 89 | 77 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Hu [71] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–60 | 108 | 100 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–60 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| Li [72] | 2008 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–36 | 40 | 38 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 6–12 mos: 7.5 mg 13–36 mos: 15 mg | 3 |
| Gao [73] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–36 | 74 | 74 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| Wu [74] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–60 | 20 | 20 | Zinc Sulfate | Syrup | 10 mg | 10 |
| Wu [74] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–60 | 20 | 20 | Zinc Sulfate | Not Listed | 10 mg | 10 |
| Liu [75] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–60 | 54 | 53 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–60 mos: 20 mg | 3–5 |
| Chen [76] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 5–36 | 42 | 20 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Ma [77] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 2–36 | 63 | 63 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 2–5 mos: 70 mg 6–36 mos: 140 mg | 10–14 |
| Lu [78] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–18 | 120 | 140 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 140 mg | 10–14 |
| Ma [79] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–36 | 58 | 52 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Ao [80] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 0–24 | 87 | 80 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Gu [81] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–60 | 56 | 60 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–60 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Wen [82] | 2006 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–24 | 30 | 29 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Wang [83] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–36 | 60 | 60 | Licorzinc | Not Listed | 10–20 mg * | Duration of episode |
| Liu [84] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 8–30 | 90 | 90 | Licorzinc | Not Listed | 8–30 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Liu [85] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–60 | 100 | 100 | Licorzinc | Tablet | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–60 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Tong [86] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 2–36 | 98 | 98 | Licorzinc | Not Listed | 2–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Qiu [87] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 1–24 | 53 | 52 | Licorzinc | Tablet | 1–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| Kong [88] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3–30 | 35 | 35 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 3–5 mos: 10 mg 6–11 mos: 15 mg 12–30 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| He [89] | 2007 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 5–22 | 60 | 63 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Kang [90] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–36 | 92 | 80 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 20 mg | 14 |
| Su [91] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–36 | 97 | 97 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Huang [92] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 2–36 | 100 | 100 | Not Listed | Tablet | 2–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Zhang [93] | 2006 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–36 | 83 | 63 | Licorzinc | Syrup | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Wang [94] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 4–30 | 60 | 60 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 10 mg | Not Listed |
| Lin [95] | 2008 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0.5–34 | 60 | 60 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 0.5–5 mos: 140 mg 6–34 mos: 280 mg | 10–14 |
| Yan [96] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–60 | 57 | 57 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 20 mg | 10 |
| Yu [97] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–36 | 40 | 40 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Zhang [98] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 4–36 | 128 | 128 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 4–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| Xu [99] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 2–36 | 84 | 83 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 2–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 14 |
| Tan [100] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 3.5–60 | 55 | 55 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 3.5–5 mos: 10 mg 6–60 mos: 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Shen [101] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 2.5–40 | 46 | 42 | Zinc Gluconate | Not Listed | 2.5–5 mos: 10 mg 6–40 mos: 20 mg | Duration of episode |
| Wang [102] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–48 | 52 | 51 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Chen [103] | 2011 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 1–36 | 50 | 50 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 1–5 mos: 5 mg 6–36 mos: 10 mg | Not Listed |
| Meng [104] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–24 | 90 | 90 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 0–5 mos: 2.5 mg 6–12 mos: 5 mg 13–24 mos: 10 mg | Not Listed |
| Zhong [105] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 1–24 | 60 | 60 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 1–5 mos: 2.5 mg 6–12 mos: 5 mg 13–24 mos: 7.5 mg | 5–7 |
| Xie [106] | 2010 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–36 | 128 | 124 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Fan [107] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–36 | 163 | 121 | Not Listed | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | 10 |
| Zhou [108] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Rotavirus | 6–24 | 75 | 75 | Zinc Gluconate | Syrup | 20 mg | 10–14 |
| Zhao [109] | 2008 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–36 | 44 | 43 | Zinc Gluconate | Tablet | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–24 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Wan [110] | 2006 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–36 | 26 | 24 | Not Listed | Not Listed | Not Listed | Not Listed |
| Yang [111] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 6–60 | 60 | 60 | Not Listed | Not Listed | 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Luo [112] | 2012 | China | Hospital | Unknown | 0–36 | 168 | 196 | Not Listed | Not Listed | 0–5 mos: 10 mg 6–36 mos: 20 mg | Not Listed |
| Outcome | Study Sites 1 | Pooled Mean (95% CI) 2 | Percent Difference 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Zinc Group | Control Group | (%) | |
| Duration of Episode (days) | 13 | 3.51 (3.43–3.60) | 3.67 (3.59–3.76) | −4.4 (−7.8, −1.0) |
| Duration of Hospitalization (days) | 1 | 2.00 (1.99–2.01) | 3.17 (2.38–3.96) | −36.9 (−52.6, −21.2) |
| Stool Output (mL) | 2 | 391.2 (388.5–393.8) | 388.8 (386.2–391.5) | 0.6 (−0.3, 1.6) |
| Stool Frequency (Number per day) | 6 | 5.04 (4.88–5.19) | 5.36 (5.20–5.52) | −6.0 (−9.9, −2.0) |
| Outcome | Study Sites 1 | Pooled Estimate Percentage (95% CI) 2 | Pooled Relative Risk 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Zinc Group | Control Group | RR (95% CI) | |
| Episodes >3 days (%) | 3 | 29.7 (26.7–32.7) | 39.5 (36.3–42.7) | 0.78 (0.67–0.90) |
| Episodes >7 days (%) | 6 | 10.3 (8.9–11.7) | 14.9 (13.2–16.5) | 0.74 (0.55–0.99) |
| Vomiting (%) | 3 | 18.8 (16.0–21.6) | 9.4 (7.3–11.4) | 1.83 (1.40–2.39) |
| Outcome | Specific Causative Pathogens | Study Sites 1 | Pooled Mean (95% CI) 2 | Percent Difference 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Zinc Group | Control Group | (%) | ||
| Duration of Episode (days) | Unknown | 40 | 2.96 (2.90–3.03) | 4.68 (4.60–4.77) | −36.8 (−38.7, −34.8) |
| Rotavirus | 24 | 3.45 (3.36–3.54) | 5.01 (4.89–5.12) | −31.1 (−33.5, −28.8) | |
| Duration of Hospitalization (days) | Unknown | 10 | 4.65 (4.50–4.80) | 6.43 (6.25–6.61) | −27.7 (−30.8, −24.6) |
| Rotavirus | 2 | 4.15 (3.79–4.51) | 6.1 (5.66–6.54) | −32.0 (−39.6, −24.3) | |
| Duration of Fever (days) | Unknown | 13 | 1.90 (1.80–1.99) | 2.81 (2.70–2.92) | −32.4 (−36.5, −28.2) |
| Rotavirus | 4 | 1.96 (1.78–2.14) | 3.18 (2.95–3.41) | −38.4 (−45.6, −31.2) | |
| Duration of Vomiting (days) | Unknown | 6 | 1.15 (1.05–1.25) | 1.53 (1.41–1.64) | −24.8 (−33.3, −16.4) |
| Rotavirus | 3 | 1.84 (1.64–2.04) | 2.49 (2.26–2.72) | −26.1 (−36.6, −15.6) | |
| Stool Output (mL) | Unknown | 1 | 40 (38.1–41.9) | 70 (68.0–72.0) | −42.9 (−46.0, −39.7) |
| Rotavirus | 1 | 278.4 (256.8–300.0) | 425.4 (382.1–468.7) | −34.6 (−42.9, −26.2) | |
| Stool Frequency (Number per day) | Unknown | 1 | 4 (3.8–4.2) | 8 (7.6–8.4) | −50.0 (−53.5, −46.5) |
| Rotavirus | 2 | 3.74 (3.30–4.18) | 4.27 (3.77–4.77) | −12.4 (−27.0, 2.1) | |
| Outcome | Specific Causative Pathogens | Study Sites 1 | Pooled Estimate Percentage (95% CI) 2 | Relative Risk 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Zinc Group | Control Group | RR (95% CI) | ||
| Episodes >3 days (%) | Unknown | 44 | 31.4 (29.4–33.5) | 49.2 (46.6–51.8) | 0.73 (0.66–0.79) |
| Rotavirus | 29 | 31.8 (29.5–34.1) | 50.3 (47.4–53.3) | 0.70 (0.63–0.78) | |
| Episodes >7 days (%) | Unknown | 1 | 26.9 (-) | 39.2 (-) | 0.75 (0.42–1.37) |


| Number of Studies | Design | Limitations | Consistency | Directness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generalizability to Population of Interest | Generalizability to Intervention of Interest | ||||
| Diarrhea Duration (mean): Moderate outcome-specific quality 1 | |||||
| 53 non-specific 24 Rotavirus | RCT | Chinese studies not placebo-controlled (−0.5) | All but 4 studies showing decreased mean duration of diarrhea among zinc-treated children (+1) | Mostly South Asia and China (−0.5) | Generalizable |
| Diarrhea Duration (>3 days): Moderate outcome-specific quality 1 | |||||
| 47 non-specific 29 Rotavirus | RCT | Chinese studies not placebo-controlled (−0.5) | All studies showing decreased risk of diarrhea duration >3 days among zinc-treated children (+1) | Mostly South Asia and China (−0.5) | Generalizable |
| Diarrhea Duration (>7 days): Moderate outcome-specific quality 1 | |||||
| 7 non-specific | RCT | Chinese studies not placebo-controlled (−0.5) | All but one study showing decreased risk of diarrhea duration >7 days among zinc-treated children (+1) | Mostly South Asia and China (−0.5) | Generalizable |
| Hospitalizations Duration: Moderate outcome-specific quality 1 | |||||
| 11 non-specific 2 Rotavirus | RCT | Chinese studies not placebo-controlled (−0.5) | All studies showing decreased mean duration of hospitalization among zinc-treated children (+1) | Only one non-Chinese study (−0.5) | Generalizable |
| Stool Output: Moderate outcome-specific quality 1 | |||||
| 3 non-specific 1 Rotavirus | RCT | Chinese studies not placebo-controlled (−0.5) | All but one study showing decreased stool output among zinc-treated children (+1) | Only South Asia and China (−0.5) | Generalizable |
| Stool Frequency: Moderate outcome-specific quality 1 | |||||
| 7 non-specific 2 Rotavirus | RCT | Chinese studies not placebo-controlled (−0.5) | All but three studies showing decreased stool frequency among zinc-treated children (+1) | Mostly South Asia and China (−0.5) | Generalizable |
| Vomiting: Moderate outcome-specific quality1 | |||||
| 3 non-specific | RCT | None | All studies showing increased vomiting among zinc-treated children (+1) | No Chinese studies (−0.5) | Generalizable |
| Vomiting Duration: Moderate outcome-specific quality1 | |||||
| 6 non-specific 3 Rotavirus | RCT | Chinese studies not placebo-controlled (−0.5) | All but one study showing decreased duration of vomiting among zinc-treated children (+1) | No non-Chinese studies (−0.5) | Generalizable |
| Fever Duration: Moderate outcome-specific quality1 | |||||
| 13 non-specific 4 Rotavirus | RCT | Chinese studies not placebo-controlled (−0.5) | All studies showing decreased duration of fever among zinc-treated children (+1) | No non-Chinese studies (−0.5) | Generalizable |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Authors’ Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fischer-Walker, C.; Lamberti, L.; Roth, D.; Black, R. Zinc and fectious Diseases. In Zinc in Human Health; Rink, L., Ed.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 234–253. [Google Scholar]
- WHO/UNICEF. Joint Statement: Clinical Management of Acute Diarrhoea; WHO/UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzerini, M.; Ronfani, L. Oral zinc for treating diarrhoea in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer Walker, C.L.; Black, R.E. Zinc for the treatment of diarrhoea: Effect on diarrhoea morbidity, mortality and incidence of future episodes. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, i63–i69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, H.P.; Mittal, N.K.; Mittal, S.K.; Yadav, H.S. A controlled trial on utility of oral zinc supplementation in acute dehydrating diarrhea in infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1988, 7, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazawal, S.; Black, R.E.; Bhan, M.K.; Bhandari, N.; Sinha, A.; Jalla, S. Zinc supplementation in young children with acute diarrhea in India. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, R.; Bhandari, N.; Saksena, M.; Strand, T.; Kumar, G.T.; Bhan, M.K.; Sommerfelt, H. Efficacy of zinc-fortified oral rehydration solution in 6- to 35-month-old children with acute diarrhea. J. Pediatr. 2002, 141, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S. Efficacy and effectiveness of 20 child health interventions in China: Systematic review of Chinese literature. J. Glob. Health 2011, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Stata Statistical Software, release 12, StataCorp LP: College Station, TX, USA, 2011.
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Interaction revisited: The difference between two estimates. BMJ 2003, 326, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.; Fischer-Walker, C.; Bryce, J.; Bahl, R.; Cousens, S. Standards for CHERG reviews of intervention effects on child survival. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, i21–i31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruque, A.S.; Mahalanabis, D.; Haque, S.S.; Fuchs, G.J.; Habte, D. Double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of zinc or vitamin A supplementation in young children with acute diarrhoea. Acta Paediatr. 1999, 88, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Tomkins, A.M.; Haider, R.; Behren, R.H.; Akramuzzaman, S.M.; Mahalanabis, D.; Fuchs, G.J. Impact of zinc supplementation on subsequent growth and morbidity in Bangladeshi children with acute diarrhoea. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 529–534. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, T.A.; Chandyo, R.K.; Bahl, R.; Sharma, P.R.; Adhikari, R.K.; Bhandari, N.; Ulvik, R.J.; Molbak, K.; Bhan, M.K.; Sommerfelt, H. Effectiveness and efficacy of zinc for the treatment of acute diarrhea in young children. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, T.B.; Uysalol, M.; Cetinkaya, F. Efficacy of zinc supplementation on the severity and duration of diarrhea in malnourished Turkish children. Pediatr. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2003, 45, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W.A.; Santosham, M.; Roy, S.K.; Faruque, A.S.; Wahed, M.A.; Nahar, K.; Khan, A.I.; Khan, A.F.; Fuchs, G.J.; Black, R.E. Efficacy of zinc in young infants with acute watery diarrhea. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sonboli, N.; Gurgel, R.Q.; Shenkin, A.; Hart, C.A.; Cuevas, L.E. Zinc supplementation in Brazilian children with acute diarrhoea. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2003, 23, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.P.; Hoque, A.B.; Khan, A.M.; Saha, U.R. Initiation of zinc treatment for acute childhood diarrhoea and risk for vomiting or regurgitation: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2005, 23, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer Walker, C.L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Bhandari, N.; Teka, T.; Shahid, F.; Taneja, S.; Black, R.E. Zinc supplementation for the treatment of diarrhea in infants in Pakistan, India and Ethiopia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Dibley, M.J.; Mamtani, M.; Badhoniya, N.; Kulkarni, H. Zinc and copper supplementation in acute diarrhea in children: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. BMC Med. 2009, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnemr, M.A.M.; Abdullah, A.K. Effect of zinc supplementation on morbidity due to acute diarrhoea in infants and children in Sanaa, Yemen: A randomized controlled double blind clinical trial. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2007, 7, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Patro, B.; Szymanski, H.; Szajewska, H. Oral zinc for the treatment of acute gastroenteritis in Polish children: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 984–988. e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Mitra, U.; Dutta, S.; Naik, T.N.; Rajendran, K.; Chatterjee, M.K. Zinc, vitamin A, and micronutrient supplementation in children with diarrhea: A randomized controlled clinical trial of combination therapy versus monotherapy. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Sun, W. 40 Cases of oral licorzinc asist treatment of diarrhea. Chin. J. Esthet. Med. 2011, 20, 455. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. The effect of supplement zinc orally assist treatment on autumal diarrhea. Mod. Hosp. 2009, 9, 54–56. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M. Observation ofthe therapeutic efficiacy of oral zinc supplement with infantile rotaviral enteritis. Contemp. Med. 2010, 16, 8–10. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Ouyang, J. Analysis on the therapeutic and preventative effects of zinc supplement on rotavirus enteritis in children. J. Xianning Univ. 2010, 24, 401–403. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Clinical analysis of oral zinc adjuvant treatment for infants with acute diarrhea. China Mod. Med. 2011, 18, 7. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G. Clinical observation on the therapeutic efficacy of oral zinc supplement in infants with acute diarrhea. J. Qiaihar Med. Coll. 2010, 31, 1416. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Bao, Y.; Gao, S. The comparison of the therapeutic effects on children diarrhea treated with smecta and oral zinc. J. Pediatr. Pharm. 2006, 12, 26–27. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Nie, X. Chinical observation on the therapeutic efficacy of oral zinc supplement in infants with diarrhea. Pract. Clin. Med. 2011, 12, 86–88. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lan, X. Therapeutic effect of oral Zinc preparation on infantile diarrhea. Int. Med. Health Guid. News 2009, 15, 74–75. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, W. Chinical analysis on the therapeutic efficacy of oral zinc supplement in infants with rotavirus enteritis. Guide China Med. 2010, 8, 260–262. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G. Clinical efficacy of licorzinc in treatment of infantile acute diarrhea. Youjiang Med. J. 2008, 36, 573–574. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Clinical efficacy of licorzinc in treatment of infantile autumal diarrhea. J. Huaihai Med. 2008, 26, 442. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Yingwei, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Y. Clinical efficacy of licorzinc in treatment of infantile rotavirus enteritis. Stud. Trace Elem. Health 2012, 29, 21–22. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Li, F. 46 Cases of licorzinc in treatment of infantile rotavirus enteritis. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2010, 31, 296–297. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. Clinical observation of licorzinc treatment for children with diarrhea. Contemp. Med. 2010, 16, 20–21. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.E.A. Clinical observations on curative effects of licorzinc particles in adjuvant treating rotavirus enteritis. Clin. J. Med. Off. 2009, 37, 862–863. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, M. Observation of therapeutic effect of licorzinc granules adjuvant treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. Gems Health 2010, 5, 127–128. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Teng, L. Observation of therapeutic effect of licorzinc granules adjuvant treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. Shanxi Med. J. 2007, 36, 661. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Observation of therapeutic effect of licorzinc granules treatment for 30 cases of children with autumn diarrhea. Chin. Pediatr. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2012, 4, 168–169. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shen, C. Clinical analysis of zinc sulfate adjuvant treatment for children with rotavirus enteritis. Zhejiang Clin. Med. J. 2009, 11, 845–846. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc sulfate treatment for 46 cases of autumn diarrhea. Stud. Trace Elem. Health 1994, 11, 61–62. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Liu, Y. Clinical analysis on efficacy of zinc sulfate in adjuvant treating 120 children with diarrhea. J. Taishan Med. Coll. 2011, 32, 303. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Quan, Y.; Li, S. Determination of zinc in hair from infant patients with diarrhea and observation of curative effect with a supply of zinc. Guangdong Trace Elem. Sci. 1997, 4, 42–43. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate treatment for children with acute diarrhea. Youjiang Med. J. 2011, 39, 50–52. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Xu, L.; Huang, Z. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for children with acute diarrhea. Chin. Community 2012, 14, 186. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Z. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2010, 9, 1016–1017. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Analysis of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for children with rotavirus enteritis. China Mod. 2011, 49, 123–124. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, H.; Bian, X. Rotavirus enteritis suooprtive treated by glucoside zinc. J. Appl. Clin. Pediatr. 2008, 23, 1532–1533. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; He, J. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for children with rotavirus enteritis. J. Med. Theory Pract. 2011, 24, 2319–2320. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Deng, J. Effect of zinc gluconate tablets on serum zinc and diarrhea of children with rotariras enteritis. J. Hainan Med. Univ. 2010, 16, 491–493. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. Clinical observation of zinc gluconate’s effect on acute diarrhea of children. Sichuan Med. J. 2009, 30, 696–697. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, J.; Wu, B. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate treatment for children with acute diarrhea. Shanghai J. Prev. Med. 2011, 23, 581–582. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, J. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. Chin. Pract. J. Rural. 2007, 14, 29–30. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Gao, Z. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. J. Clin. Res. 2012, 25, 463–464. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, A. The effect of zinc gluconate on infants with acutie diarrhea. Med. J. Qilu 2011, 26, 255–256. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Observation of curative effect of zinc gluconate in treatment of children rotavirus enteritis. Guide China Med. 2012, 10, 218–219. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, R. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. Shanxi Med. J. 2012, 41, 380–381. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z. Therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate on infantile rotavirus enteritis. Contemp. Med. 2012, 18, 130–131. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Observation of clinical efficacy of zinc gluconate on infantile rotavirus enteritis. China Med. Pharm. 2011, 1, 94–95. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Y.; Mei, Q. Clinical observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate on infantile rotavirus diarrhea. Chongqing Med. 2008, 37, 2442–2443. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Clinical observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate on infantile rotavirus diarrhea. China Foreign Med. Treat. 2012, 13, 113. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z. Validity and security of zinc gluconate on infantile rotavirus diarrhea. China J. Pharm. Econ. 2012, 2, 273–274. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Su, H. Efficacy and safety analysis of zinc gluconate in treatment of children with rotavirus diarrhea. Contemp. Med. 2012, 18, 144–145. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, A. Observation of clinical efficacy of zinc gluconate on 60 cases with infantile acute duarrhea. Pract. Clin. Med. 2009, 10, 85. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Guan, J. Therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment on infantile acute diarrhea. Pract. Clin. Med. 2011, 12, 76–77. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. Anhui Med. J. 2011, 32, 802–803. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Clinical treatment and analysis in 69 Children with chronic diarrhea. Chin. Manip. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 3, 245–246. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Deng, H. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate granules for children with acute diarrhea. Chin. Foreign Women Health 2011, 19, 205. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Feng, G. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate granules for children with autumn diarrhea. China Pharm. 2008, 11, 218–219. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R. Clinical observation of supplemental zinc to treat 74 children with acute diarrhea. Asia Pac. Tradit. Med. 2012, 8, 58–59. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H. The effect of zinc supplementation on children with diarrhea. Strait Pharm. J. 2011, 23, 156–158. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Observation of therapeutic effects of zinc supplementation in treatment of children with acute diarrhea. Chin. J. Mod. Drug Appl. 2011, 5, 27–28. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wang, P. Clinical analysis of zinc supplementation to treat infant diarrhea. Chin. J. Misdiagn. 2010, 10, 7582. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K. Clinical observation of zinc supplementation to treat children with acute diarrhea. Chin. Foreign Med. Res. 2012, 10, 32–33. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J. Clinical observation of zinc supplementation in treatment of autumn diarrhea. Med. Recapitul. 2012, 18, 1101–1102. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Yang, H. Clinical analysis of zinc preparation adjuvant treatment for children with acute diarrhea. Matern. Child Health Care China 2012, 27, 3847–3848. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ao, Z.; Wang, J.; Lin, L. Formulation adjuvant therapy efficacy in children with diarrhea. Hebei Med. 2012, 18, 1091–1093. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Shen, H.; Zhao, P. Effect of zinc gluconate on acute diarrhea in children. J. Clin. Pediatr. 2011, 29, 249–251. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, C. Zinc supplement in adjuvant treatment of children acute diarrhea. Chin. J. Prim. Med. Pharm. 2006, 13, 1208. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Wu, X. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc adjuvant treatment for infantile autumn diarrhea. China Med. Pharm. 2011, 1, 66–98. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R. Zinc therapy in the treatment of children with rotavirus enteritis. Jilin Med. J. 2012, 33, 5648. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G. Observation of therapeutic effects of zinc supplementation in treatment of children with acute diarrhea. J. Med. Theory Pract. 2012, 25, 2287–2288. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tong, W. Observation of therapeutic effects of zinc supplementation in treatment of children with diarrhea. China Health Ind. 2011, 8, 84. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y. Serum zinc level of children with rotaviral diarrhea before and after zinc supplementation and clinical efficacy of the therapy. Chin. J. Woman Child Health Res. 2010, 21, 616–617. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X. Cinical analysis of combination of lysine hydrochloride and zinc gluconate granules with ribavirin for children with diarrhea in autumn and winter. Inn. Mong. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2011, 30, 8. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- He, Y. Observation of therapeutic effects of oral zinc supplementation adjuvant treatment for 60 cases of rotavirus enteritis. Zhejiang J. Clin. Med. 2007, 9, 1635. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C. Serum zinc levels and zinc supplementation treatment of young children with rotaviral enteritis. J. Kunming Med. Univ. 2010, 31, 109–113. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Su, M. Observation of effect of serum zinc levels and zinc supplementation treatment of young children with rotaviral enteritis. China Health Ind. 2012, 6, 76–77. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z. Observation of therapeutic effects of zinc adjuvant treatment for 200 cases of infantile rotavirus enteritis. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2010, 19, 80. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Observation of therapeutic effect of licorzinc granules with smectite powder for infantile diarrhea. Jiangxi Med. J. 2006, 41, 500–501. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc treatment for infantile diarrhea. China Health Care Nutr. 2012, 5, 249. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for 60 cases of infantile acute diarrhea. Chin. Community 2008, 24, 29. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for children with acute diarrhea. China Foreign Med. Treat. 2011, 30, 118–119. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J. Clinical observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for 80 cases of children with diarrhea. Jilin Med. J. 2012, 26, 5644. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Effect of zinc gluconate among the treatment for infantile rotavirus diarrhea. Chin. J. Midiagn. 2011, 11, 7848. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate treatment for children with rotavirus enteritis. Jiangsu Med. J. 2010, 36, 2327–2328. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc gluconate treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. Med. J. Chin. People Health 2010, 22, 1122. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D. Clinical observation of therapeutic Effect of zinc gluconate on infantile rotavirus enteritis. Guide China Med. 2012, 10, 46–47. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Study of effect of zinc gluconate combined with Saccharomyces boulardii Sachets in treatment for children with autumn diarrhea. Contemp. Med. 2010, 16, 141–142. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L. Clinical observation of therapeutic effect of Lysine and zinc gluconate adjuvant treatment for infantile acute diarrhea. Chin. J. Mod. Drug Appl. 2011, 5, 85–86. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F. Observation of therapeutic effect of Lysine and zinc gluconate treatment for infantile autumn and winter diarrhea. Chin. Community 2012, 14, 152. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L. Observation of therapeutic effect of Lysine and zinc gluconateadjuvant treatment for infantile acute diarrhea. Chin. J. Aesthet. Med. 2010, 19, 258. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J. Serum zinc level of rotaviral enteritis in children and the significance of zinc treatment. J. Pediatr. Pharm. 2010, 16, 18–20. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J. Application of zinc preparation in treatment for infantile diarrhea. Chin. J. Misdiagn. 2012, 12, 1306. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X. Therapeutic effect of zinc in the prevention and treatment of children rotvirus enteritis. Chin. Gen. Pract. 2012, 15, 1393–1394. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Observation of effect of zinc preparation adjuvant treatment for infantile acute diarrhea. Zhejiang J. Prev. Med. 2008, 20, 44. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H. Observation of therapeutic effect of Treasured zinc and selenium in adjuvant treatment for infantile diarrhea. Shandong Med. J. 2006, 46, 65. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc preparation in adjuvant treatment for infantile autumn diarrhea. Health World 2012, 2, 244. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y. Observation of therapeutic effect of zinc adjuvant treatment for 168 cases of infantile acute diarrhea. Public Med. Forum Mag. 2012, 16, 3338. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.B.; Dibley, M.J.; Mamtani, M.; Badhoniya, N.; Kulkarni, H. Influence of zinc supplementation in acute diarrhea differs by the isolated organism. Int. J. Pediatr. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer Walker, C.L.; Rudan, I.; Liu, L.; Nair, H.; Theodoratou, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Campbell, H.; Black, R.E. Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea. Lancet 2013, 381, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqui, A.H.; Black, R.E.; El Arifeen, S.; Yunus, M.; Chakraborty, J.; Ahmed, S.; Vaughan, J.P. Effect of zinc supplementation started during diarrhoea on morbidity and mortality in Bangladeshi children: Community randomised trial. BMJ 2002, 325, 1059. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.K.; Tomkins, A.M.; Mahalanabis, D.; Akramuzzaman, S.M.; Haider, R.; Behrens, R.H.; Fuchs, G. Impact of zinc supplementation on persistent diarrhoea in malnourished Bangladeshi children. Acta Paediatr. 1998, 87, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine, O. Effect of zinc supplementation on clinical course of acute diarrhoea. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2001, 19, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamberti, L.M.; Walker, C.L.F.; Chan, K.Y.; Jian, W.-Y.; Black, R.E. Oral Zinc Supplementation for the Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4715-4740. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5114715
Lamberti LM, Walker CLF, Chan KY, Jian W-Y, Black RE. Oral Zinc Supplementation for the Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2013; 5(11):4715-4740. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5114715
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamberti, Laura M., Christa L. Fischer Walker, Kit Y. Chan, Wei-Yan Jian, and Robert E. Black. 2013. "Oral Zinc Supplementation for the Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 5, no. 11: 4715-4740. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5114715
APA StyleLamberti, L. M., Walker, C. L. F., Chan, K. Y., Jian, W.-Y., & Black, R. E. (2013). Oral Zinc Supplementation for the Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 5(11), 4715-4740. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5114715




