Gender Differences in Exercise Dependence and Eating Disorders in Young Adults: A Path Analysis of a Conceptual Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Analysis
| Variable Categories | At-Risk | Nondependent Symptomatic | Nondependent Asymptomatic |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 17) | (n = 268) | (n = 235) | |
| Males (n, %) | 10 (59) | 127 (48) | 89 (38) |
| Caucasian (n, %) | 4 (24) | 111 (42) | 78 (34) |
| African American (n, %) | 3 (18) | 54 (21) | 57 (25) |
| Hispanic (n, %) | 6 (35) | 30 (12) | 25 (11) |
| Asian (n, %) | 1 (6) | 29 (11) | 29 (12) |
| Mixed ethnicity (n, %) | 3 (17) | 37 (14) | 43 (18) |
| Aerobic exercise: hours/week (mean ± SD) * | 6.1 ± 5.1 † | 3.9 ± 3.2 †,‡ | 2.3 ± 2.5 †,‡ |
| Strength training: hours/week (mean ± SD) * | 5.9 ± 4.4 † | 2.8 ± 2.6 †,‡ | 1.0 ± 1.5 †,‡ |
| Flexibility exercise: hours/week (mean ± SD) * | 2.2 ± 2.6 † | 1.6 ± 2.8 ‡ | 0.9 ± 1.5 †,‡ |
| METS/week (mean ± SD) * | 84.1 ± 51.6 † | 49.0 ± 35.9 †,‡ | 25.2 ± 24.0 †,‡ |
| EAT-score (mean ± SD) * | 14.4 ± 10.3 † | 8.6 ± 7.6 † | 6.9 ± 6.1 † |
| EDS-21 score (mean ± SD) * | 94.8 ± 11.6 † | 57.6 ± 11.4 †,‡ | 32.0 ± 7.6 †,‡ |
3.2. Exploratory Analysis
3.3. Model Specification
3.4. Model Modification

| Descriptive Characteristics | Mean ± SD | SE | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both Sexes | ||||
| EAT-26 | 8.1 ± 7.3 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 4.7 |
| EXD | 47.3 ± 18.2 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.4 |
| METS | 39.5 ± 34.7 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 5.8 |
| Log METS | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 0.02 | −1.3 | 1.6 |
| Males | ||||
| EAT-26 | 6.6 ± 6.3 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 9.6 |
| EXD | 50.0 ± 18.9 | 1.2 | 0.5 | −0.06 |
| METS | 45.5 ± 36.9 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 3.8 |
| Log METS | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 0.03 | −1.4 | 2.4 |
| Females | ||||
| EAT-26 | 9.1 ± 7.8 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 3.0 |
| EXD | 45.3 ± 17.3 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
| METS | 35.2 ± 32.2 | 1.9 | 2.5 | 8.8 |
| Log METS | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 0.03 | −1.3 | 1.3 |
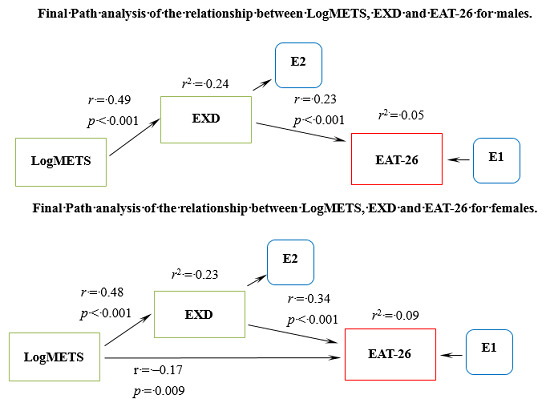
3.5. Gender Specific Analysis



4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cook, B.; Hausenblas, H.A.; Freimuth, M. Exercise Addiction and Compulsive Exercising: Relationship to Eating Disorders, Substance Use Disorders, and Addictive Disorders; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hausenblas, H.A.; Symons Downs, D. Exercise dependence: A systematic review. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2002, 3, 89–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bamber, D.; Cockerill, I.M.; Rodgers, S.; Carroll, D. It’s exercise or nothing: A qualitative analysis of exercise dependence. Br. J. Sport Med. 2000, 34, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Bamber, D.; Cockerill, I.M.; Rodgers, S.; Carroll, D. Diagnostic criteria for exercise dependence in women. Br. J. Sport Med. 2003, 37, 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, P.S.; Thompson, R.A. The Exercise Balance: What’s Too Much, What’s Too Little, and What’s Just Right for You! Gürze Books: Carlsbad, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Glasser, W. Positive Addiction; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, J.H.; Lindner, K.J.; Blaydon, M. Exercise Dependence; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi, E. Exercise addiction. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, B.; Hausenblas, H.; Tuccitto, D.; Giacobbi, P. Eating disorders and exercise: A structural equation modeling analysis of a conceptual model. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2011, 19, 216–225. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, B.; Hausenblas, H. The role of exercise dependence for the relationship between exercise behavior and eating pathology: Mediator or moderator? J. Health Psychol. 2008, 13, 495–502. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, H.; Lane, A.; Matheson, H. Validity of the eating attitudes test among exercisers. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2004, 3, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, A. Compulsive Exercise and the Eating Disorders: Toward an Integrated Theory of Activity; Brunner/Mazel: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, B.; Karr, T.M.; Zunker, C.; Mitchell, J.E.; Thompson, R.; Sherman, R.; Crosby, R.D.; Cao, L.; Erickson, A.; Wonderlich, S.W. Primary and Secondary Exercise Dependence in a Community-Based Sample of Road Race Runners. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 35, 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- De Coverley Veale, D.M.E. Exercise dependence. Br. J. Addict. 1987, 82, 735–740. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, H.G., Jr.; Gruber, A.J.; Choi, P.; Olivardia, R.; Phillips, K.A. Muscle dysmorphia: An underrecognized form of body dysmorphic disorder. Psychosomatics 1997, 38, 548–557. [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, L.K. Exercise Addiction; Lucent Books: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Grosvenor, M.B.; Smolin, L.A. Visualizing Nutrition—Everyday Choices, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, H.; Haycraft, E.; Willis, A.-M.; Meyer, C. Compulsive Exercise: The Role of Personality, Psychological Morbidity, and Disordered Eating. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2011, 44, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Slane, J.D.; Burt, S.A.; Klump, K.L. Genetic and Environmental Influences on Disordered Eating and Depressive Symptoms. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2011, 44, 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- National Eating Disorders Association. Available online: http://www.nationaleatingdisorders.org/information-resources/general-information.php#facts-statistics (accessed on 10 June 2014).
- Hoek, H.W. Incidence, prevalence and mortality of anorexia nervosa and other eating disorders. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2006, 19, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Smolak, L.; Murnen, S.K.; Ruble, A.E. Female athletes and eating problems: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2000, 27, 371–380. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, S.A.; Crow, S.J.; le Grange, D.; Swendsen, J.; Merikangas, K.R. Prevalence and Correlates of Eating Disorders in Adolescents. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 714–723. [Google Scholar]
- Timko, C.A.; Hormes, J.M.; Chubski, J. Will the real vegetarians please stand up? An investigation of dietary restraint and eating disorder symptoms in vegetarians versus non-vegetarians. Appetite 2012, 58, 982–990. [Google Scholar]
- Hausenblas, H.A.; Symons Downs, D. How much is too much? The development and validation of the exercise dependence scale. Psychol. Health 2002, 17, 387–404. [Google Scholar]
- Symons Downs, D.; Hausenblas, H.A.; Nigg, C. Factorial Validity and Psychometric Examination of the Exercise Dependence Scale-Revised. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2004, 8, 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Garner, D.M.; Olmsted, M.P.; Bohr, Y.; Garfinkel, P.E. The eating attitudes test: Psychometric features and clinical correlates. Psychol. Med. 1982, 12, 871–878. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Whitt, M.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Strath, S.J.; O’Brien, W.L.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Schmitz, K.H.; Emplaincourt, P.O.; et al. Compendium of Physical Activities: An update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2000, 32, S498–S516. [Google Scholar]
- Buhi, E.R.; Goodson, P.; Neilands, T.B. Structural Equation Modeling: A primer for Health Behavior Researchers. Am. J. Health Behav. 2007, 31, 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, R.M. Applied Statistics—From Bivariate Trough Multivariate Techniques; SAGE Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Anderson, R.E.; Tatham, R.L.; Black, W.C. Multivariate Data Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, M.; Tsuboi, K.; Dennerstein, L. Prevalence of eating disorders: A comparison of western and non-western countries. MedGenMed 2004, 6, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Striegel-Moore, R.H.; Rosselli, F.; Perrin, N.; DeBar, L.; Wilson, G.T.; May, A.; Kraemer, H.C. Gender Difference in the Prevalence of Eating Disorder Symptoms. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2009, 42, 471–474. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, B.; Hausenblas, H.A.; Rossi, J. The moderating effect of gender on ideal-weight goals and exercise dependence symptoms. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, S.; Hausenblas, H.A.; Olivia, P.; Cuzzocrea, F.; Larcan, R. The role of age, gender, mood states and exercised fereqency on exercise dependence. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- Bollen, K.A. Structural Equations with Latent Variables; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Godin, G.; Shephard, R.J. A simple method to assess exercise behavior in the community. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 1985, 10, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meulemans, S.; Pribis, P.; Grajales, T.; Krivak, G. Gender Differences in Exercise Dependence and Eating Disorders in Young Adults: A Path Analysis of a Conceptual Model. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4895-4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114895
Meulemans S, Pribis P, Grajales T, Krivak G. Gender Differences in Exercise Dependence and Eating Disorders in Young Adults: A Path Analysis of a Conceptual Model. Nutrients. 2014; 6(11):4895-4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114895
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeulemans, Shelli, Peter Pribis, Tevni Grajales, and Gretchen Krivak. 2014. "Gender Differences in Exercise Dependence and Eating Disorders in Young Adults: A Path Analysis of a Conceptual Model" Nutrients 6, no. 11: 4895-4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114895
APA StyleMeulemans, S., Pribis, P., Grajales, T., & Krivak, G. (2014). Gender Differences in Exercise Dependence and Eating Disorders in Young Adults: A Path Analysis of a Conceptual Model. Nutrients, 6(11), 4895-4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114895