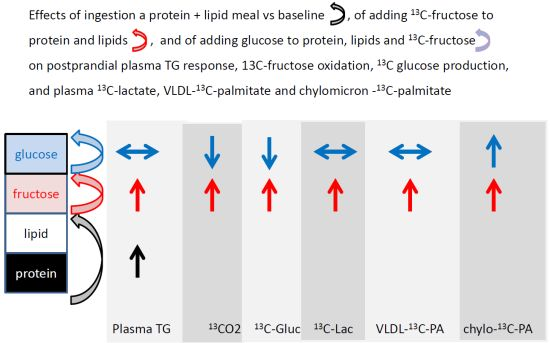
Metabolic Fate of Fructose Ingested with and without Glucose in a Mixed Meal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Subjects Inclusion
| Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 26.4 ± 1.0 |
| Body weight (kg) | 63.7 ± 2.4 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.9 ± 0.7 |
| Body fat (%) | 20.6 ± 1.9 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 118 ± 3 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 70 ± 3 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 74 ± 3 |
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Metabolic Tests

2.4. Analytical Procedures
2.5. Calculations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric Variables and Fasting Parameters
| ProLip | Fr | Fr + G | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma glucose (mmol/L) | 4.74 ± 0.15 | 4.79 ± 0.08 | 4.67 ± 0.10 |
| Plasma insulin (pmol/L) | 54.2 ± 5.6 | 57.4 ± 4.7 | 54.3 ± 3.6 |
| Body weight (kg) | 63.4 ± 2.4 | 63.7 ± 2.4 | 63.6 ± 2.4 |
| Lean body mass (kg) | 51.1 ± 2.4 | 50.0 ± 2.5 | 50.4 ± 2.5 |
| Fat mass (kg) | 12.3 ± 1.1 | 13.7 ± 0.8 | 13.0 ± 1.0 |
3.2. Effects on Carbohydrate Metabolism



| ProLip | Fr | Fr + G | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRa (g/360 min) | 50.98 ± 2.47 | 53.78 ± 2.20 | 69.86 ± 2.51 *,$ |
| Fructose oxidation (g/360 min) | 12.64 ± 0.67 | 11.30 ± 0.74 $ | |
| Total carbo. ox. (g/360 min) | 25.92 ± 1.93 | 22.16 ± 1.91 | 25.87 ± 4.73 |
| GNGf (g/360 min) | 9.03 ± 0.15 | 6.54 ± 0.17 $ | |
| NOFD (g/6 h) | 21.78 ± 0.96 | 22.90 ± 0.97 $ |
3.3. Effects on Lipid Metabolism


3.4. Effects on Energy Expenditure and Diet-Induced Thermogenesis
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolic Fate of Fructose Ingested together with Equimolar Amounts of Glucose
4.2. Modulation of Fructose Metabolism by Glucose
4.3. Effects of Fructose and Glucose on Dietary Lipid Handling
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elliott, S.S.; Keim, N.L.; Stern, J.S.; Teff, K.; Havel, P.J. Fructose, weight gain, and the insulin resistance syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 911–922. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, M.B.; Kimmons, J.E.; Gillespie, C.; Welsh, J.; Blanck, H.M. Dietary fructose consumption among US children and adults: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Medscape J. Med. 2008, 10, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, G.A. Soft drink consumption and obesity: It is all about fructose. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2010, 21, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizeau, M.E.; Pagliassotti, M.J. Hepatic adaptations to sucrose and fructose. Metabolism 2005, 54, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappy, L.; Lê, K.A. Metabolic effects of fructose and the worldwide increase in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarue, J.; Normand, S.; Pachiaudi, C.; Beylot, M.; Lamisse, F.; Riou, J.P. The contribution of naturally labelled 13C fructose to glucose appearance in humans. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounian, P.; Schneiter, P.; Henry, S.; Jéquier, E.; Tappy, L. Effects of infused fructose on endogenous glucose production, gluconeogenesis, and glycogen metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, E710–E717. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, C.; Jacot-Descombes, D.; Lecoultre, V.; Fielding, B.A.; Carrel, G.; Lê, K.A.; Schneiter, P.; Bortolotti, M.; Frayn, K.N.; Tappy, L. Sex differences in lipid and glucose kinetics after ingestion of an acute oral fructose load. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, L.H.; Hultman, E. Liver and muscle glycogen in man after glucose and fructose infusion. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1974, 33, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.F.; Fielding, B.A.; Frayn, K.N. Mechanisms for the acute effect of fructose on postprandial lipemia. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, E.J.; Skokan, L.E.; Timlin, M.T.; Dingfelder, C.S. Dietary sugars stimulate fatty acid synthesis in adults. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Haidari, M.; Leung, N.; Mahbub, F.; Uffelman, K.D.; Kohen-Avramoglu, R.; Lewis, G.F.; Adeli, K. Fasting and postprandial overproduction of intestinally derived lipoproteins in an animal model of insulin resistance. Evidence that chronic fructose feeding in the hamster is accompanied by enhanced intestinal de novo lipogenesis and ApoB48-containing lipoprotein overproduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 30, 31646–31655. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, G.F.; Uffelman, K.; Naples, M.; Szeto, L.; Haidari, M.; Adeli, K. Intestinal lipoprotein overproduction, a newly recognized component of insulin resistance, is ameliorated by the insulin sensitizer rosiglitazone: Studies in the fructose-fed Syrian golden hamster. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, L.; Lecoultre, V.; Theytaz, F.; Campos, V.; Hodson, L.; Schneiter, P.; Mittendorfer, B.; Patterson, B.W.; Fielding, B.A.; Gerber, P.A.; et al. Exercise prevents fructose-induced hypertriglyceridemia in healthy young subjects. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faeh, D.; Minehira, K.; Schwarz, J.M.; Periasamy, R.; Park, S.; Tappy, L. Effect of fructose overfeeding and fish oil administration on hepatic de novo lipogenesis and insulin sensitivity in healthy men. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, J.; Chen, Y.D.; Zhou, M.Y.; Wang, T.; Reaven, G.M. Effect of variations in oral fat and carbohydrate load on postprandial lipemia. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Corpe, C.P.; Burant, C.F.; Hoekstra, J.H. Intestinal fructose absorption: Clinical and molecular aspects. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999, 28, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, O.P.; Cherrington, A.D. Effects of fructose on hepatic glucose metabolism. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2003, 6, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Elia, M.; Livesey, G. Energy expenditure and fuel selection in biological systems: The theory and practice of calculations based on indirect calorimetry and tracer methods. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1992, 70, 68–131. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, K.F.; Laurent, D.; Yu, C.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I. Stimulating effects of low-dose fructose on insulin-stimulated hepatic glycogen synthesis in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerton, A.S.; Roberts, R.; Fielding, B.A.; Hodson, L.; Blaak, E.E.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; Gilbert, M.; Karpe, F.; Frayn, K.N. Preferential uptake of dietary fatty acids in adipose tissue and muscle in the postprandial period. Diabetes 2007, 56, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquot, N.; Schneiter, P.H.; Jéquier, E.; Gaillard, R.; Lefèbvre, P.J.; Scheen, A.; Tappy, L. Effects of ingested fructose and infused glucagon on endogenous glucose production in obese NIDDM patients, obese non-diabetic patients, and healthy subjects. Diabetologia 1996, 39, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Bjorkman, O.; Reichard, G.; Pilo, A.; Olsson, M.; Wahren, J.; DeFronzo, R.A. The disposal of an oral glucose load in healthy subjects. A quantitative study. Diabetes 1985, 34, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Z.; Empie, M.W. Fructose metabolism in humans—What isotopic tracer studies tell us. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2012, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzo, R.; Bianco, F.; Falcone, I.; Coppola, P.; Liverini, G.; Iossa, S. Increased hepatic de novo lipogenesis and mitochondrial efficiency in a model of obesity induced by diets rich in fructose. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Dash, S.; Morgantini, C.; Lewis, G.F. Novel role of enteral monosaccharides in intestinal lipoprotein production in healthy humans. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, P.H.; de Boer, B.C.; Haddeman, E.; Houtsmuller, U.M.; Hülsmann, W.C. Effect of dietary fat composition on the metabolism of triacylglycerol-rich plasma lipoproteins in the postprandial phase in meal-fed rats. J. Lipid Res. 1988, 29, 541–551. [Google Scholar]
- Lê, K.A.; Ith, M.; Kreis, R.; Faeh, D.; Bortolotti, M.; Tran, C.; Boesch, C.; Tappy, L. Fructose overconsumption causes dyslipidemia and ectopic lipid deposition in healthy subjects with and without a family history of type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.R.; Newnham, E.; Barrett, J.S.; Shepherd, S.J.; Muir, J.G. Review article: Fructose malabsorption and the bigger picture. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 349–363. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, H.F.; Butler, R.N.; Brooks, D.A. Intestinal fructose transport and malabsorption in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G202–G206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudgins, L.C.; Parker, T.S.; Levine, D.M.; Hellerstein, M.K. A dual sugar challenge test for lipogenic sensitivity to dietary fructose. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Ishida, T.; Yasuda, T.; Monguchi, T.; Sasaki, M.; Kondo, K.; Hasokawa, M.; Nakajima., H.; Haraguchi, Y.; Sun, L.; Shinohara, M.; Toh, R.; Nishimura, K.; Hirata, K. Fasting serum concentration of apolipoprotein B48 represents residual risks in patients with new-onset and chronic coronary artery disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 421, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Theytaz, F.; De Giorgi, S.; Hodson, L.; Stefanoni, N.; Rey, V.; Schneiter, P.; Giusti, V.; Tappy, L. Metabolic Fate of Fructose Ingested with and without Glucose in a Mixed Meal. Nutrients 2014, 6, 2632-2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6072632
Theytaz F, De Giorgi S, Hodson L, Stefanoni N, Rey V, Schneiter P, Giusti V, Tappy L. Metabolic Fate of Fructose Ingested with and without Glucose in a Mixed Meal. Nutrients. 2014; 6(7):2632-2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6072632
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheytaz, Fanny, Sara De Giorgi, Leanne Hodson, Nathalie Stefanoni, Valentine Rey, Philippe Schneiter, Vittorio Giusti, and Luc Tappy. 2014. "Metabolic Fate of Fructose Ingested with and without Glucose in a Mixed Meal" Nutrients 6, no. 7: 2632-2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6072632
APA StyleTheytaz, F., De Giorgi, S., Hodson, L., Stefanoni, N., Rey, V., Schneiter, P., Giusti, V., & Tappy, L. (2014). Metabolic Fate of Fructose Ingested with and without Glucose in a Mixed Meal. Nutrients, 6(7), 2632-2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6072632