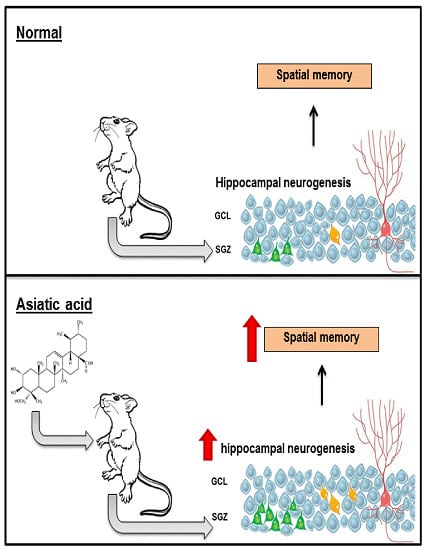
Effects of Asiatic Acid on Spatial Working Memory and Cell Proliferation in the Adult Rat Hippocampus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatments
2.2. Behavioral Testing
2.3. Tissue Preparation
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Immunoblotting
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Asiatic Acid on Spatial Working Memory


3.2. Effect of Asiatic Acid on Cell Proliferation in the SGZ


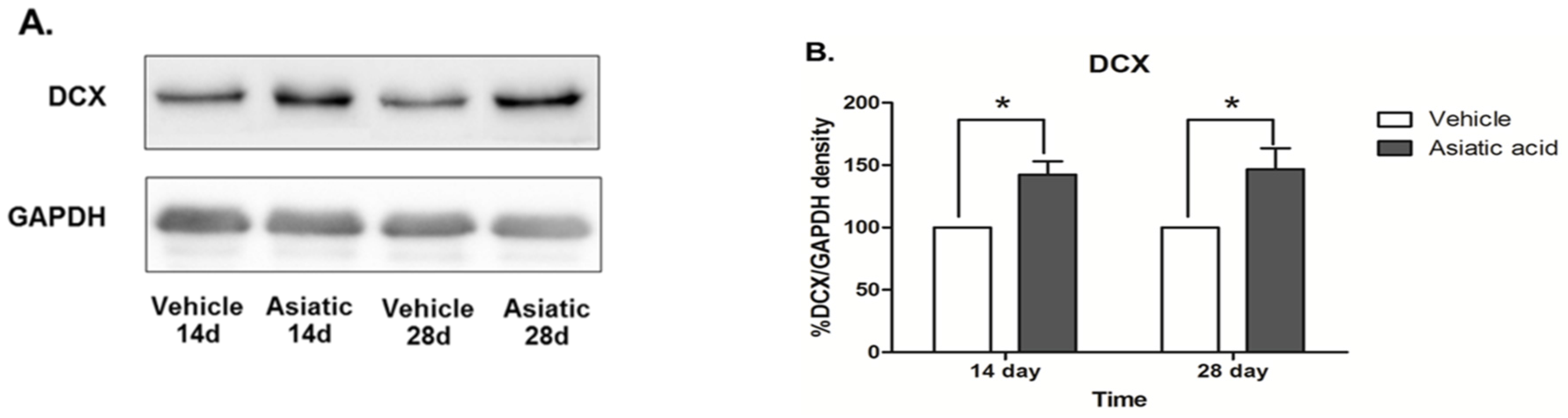
3.3. Effect of Asiatic Acid on Hippocampal Notch1 and DCX

4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, C.J.; Qin, L.P. Chemical components of centella asiatica and their bioactivities. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2007, 5, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, M.N.; Abdullah, J.; Habsah, M.; Ghani, R.I.; Rammes, G. Inhibitory effect of asiatic acid on acetylcholinesterase, excitatory post synaptic potential and locomotor activity. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, M.N.; Habsah, M.; Zamzuri, I.; Rammes, G.; Hasnan, J.; Abdullah, J. Effects of asiatic acid on passive and active avoidance task in male spraque-dawley rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Dou, Y.; Xia, B.; Rong, W.; Rimbach, G.; Lou, Y. Asiatic acid protects primary neurons against C 2-ceramide-induced apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 679, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.E. Centella asiatica (L.) Urban: From traditional medicine to modern medicine with neuroprotective potential. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 946259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.K.; Kim, S.R.; Sung, S.H.; Lim, D.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.; Park, H.K.; Je, S.; Ki, Y.C. Asiatic acid derivatives protect cultured cortical neurons from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 2000, 108, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, R.G.; Senut, M.C.; Zemke, D.; Min, J.; Frenkel, M.B.; Greenberg, E.J.; Yu, S.W.; Ahn, N.; Goudreau, J.; Kassab, M.; et al. Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene from centella asiatica, is neuroprotective in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Bae, O.N.; Weinstock, S.; Kassab, M.; Majid, A. Neuroprotective effect of asiatic acid in rat model of focal embolic stroke. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, G.L.; Song, H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taupin, P. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system: Functionality and potential clinical interest. Med. Sci. Monit. 2005, 11, RA247–RA252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Curtis, M.A.; Kam, M.; Nannmark, U.; Anderson, M.F.; Axell, M.Z.; Wikkelso, C.; Holtas, S.; van Roon-Mom, W.M.; Bjork-Eriksson, T.; Nordborg, C.; et al. Human neuroblasts migrate to the olfactory bulb via a lateral ventricular extension. Science 2007, 315, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toni, N.; Laplagne, D.A.; Zhao, C.; Lombardi, G.; Ribak, C.E.; Gage, F.H.; Schinder, A.F. Neurons born in the adult dentate gyrus form functional synapses with target cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabatake, Y.; Sailor, K.A.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H. Adult neurogenesis and hippocampal memory function: New cells, more plasticity, new memories? Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 18, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, T.A.; Amin, E.; Pearce, J.M.; Brown, M.W.; Aggleton, J.P. Novel spatial arrangements of familiar visual stimuli promote activity in the rat hippocampal formation but not the parahippocampal cortices: A c-Fos expression study. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich-Hunsaker, N.J.; Hunsaker, M.R.; Kesner, R.P. The interactions and dissociations of the dorsal hippocampus subregions: How the dentate gyrus, CA3, and CA1 process spatial information. Behav. Neurosci. 2008, 122, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, N.; Teixeira, C.M.; Wang, A.H.; Frankland, P.W. Preferential incorporation of adult-generated granule cells into spatial memory networks in the dentate gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, L.; ElBeltagy, M.; Umka, J.; Markwick, R.; Startin, C.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P. Fluoxetine reverses the memory impairment and reduction in proliferation and survival of hippocampal cells caused by methotrexate chemotherapy. Psychopharmacology 2011, 215, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ELBeltagy, M.; Mustafa, S.; Umka, J.; Lyons, L.; Salman, A.; Dormon, K.; Allcock, C.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P. The effect of 5-fluorouracil on the long term survival and proliferation of cells in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 88, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.; Walker, A.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P.M. 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy affects spatial working memory and newborn neurons in the adult rat hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umka, J.; Mustafa, S.; ElBeltagy, M.; Thorpe, A.; Latif, L.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P.M. Valproic acid reduces spatial working memory and cell proliferation in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encinas, J.M.; Vaahtokari, A.; Enikolopov, G. Fluoxetine targets early progenitor cells in the adult brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8233–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, S.L.; Aggleton, J.P. Extending the spontaneous preference test of recognition: Evidence of object-location and object-context recognition. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 99, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.V.; Sleight, A.J.; Woolley, M.L.; Topham, I.A.; Marsden, C.A.; Fone, K.C.F. 5-HT 6 receptor antagonists reverse delay-dependent deficits in novel object discrimination by enhancing consolidation—An effect sensitive to nmda receptor antagonism. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weible, A.P.; Rowland, D.C.; Pang, R.; Kentros, C. Neural correlates of novel object and novel location recognition behavior in the mouse anterior cingulate cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 102, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhew, T.M.; Burton, G.J. Methodological problems in placental morphometry: Apologia for the use of stereology based on sound sampling practice. Placenta 1988, 9, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELBeltagy, M.; Mustafa, S.; Umka, J.; Lyons, L.; Salman, A.; Chur-Yoe, G.T.; Bhalla, N.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P.M. Fluoxetine improves the memory deficits caused by the chemotherapy agent 5-fluorouracil. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.J.; Herbert, J. Stimulation of neurogenesis in the hippocampus of the adult rat by fluoxetine requires rhythmic change in corticosterone. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, E.; Beylin, A.; Tanapat, P.; Reeves, A.; Shors, T.J. Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouche, S.; Bontempi, B.; Roullet, P.; Rampon, C. Recruitment of adult-generated neurons into functional hippocampal networks contributes to updating and strengthening of spatial memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5919–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Asselen, M.; Kessels, R.P.C.; Neggers, S.F.W.; Kappelle, L.J.; Frijns, C.J.M.; Postma, A. Brain areas involved in spatial working memory. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.R.; Koo, K.A.; Lee, M.K.; Park, H.G.; Jew, S.S.; Cha, K.H.; Kim, Y.C. Asiatic acid derivatives enhance cognitive performance partly by improving acetylcholine synthesis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.F.; Xiong, Y.Y.; Liu, J.K.; Qian, J.J.; Zhu, L.; Gao, J. Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene in centella asiatica, attenuates glutamate-induced cognitive deficits in mice and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, G.L.; Amin, E.; Aggleton, J.P. Qualitatively different hippocampal subfield engagement emerges with mastery of a spatial memory task by rats. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 2008, 132, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehninger, D.; Kempermann, G. Neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 331, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, V.; Saravanan, R. Efficacy of asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene on attenuating the key enzymes activities of carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Koh, H.C.; Chang, M.Y.; Park, C.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.H. Erythropoietin and bone morphogenetic protein 7 mediate ascorbate-induced dopaminergic differentiation from embryonic mesencephalic precursors. Neuroreport 2003, 14, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Studer, L.; Csete, M.; Lee, S.H.; Kabbani, N.; Walikonis, J.; Wold, B.; McKay, R. Enhanced proliferation, survival, and dopaminergic differentiation of cns precursors in lowered oxygen. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7377–7383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morrison, S.J.; Csete, M.; Groves, A.K.; Melega, W.; Wold, B.; Anderson, D.J. Culture in reduced levels of oxygen promotes clonogenic sympathoadrenal differentiation by isolated neural crest stem cells. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7370–7376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.S.; Shetty, A.K. Efficacy of doublecortin as a marker to analyse the absolute number and dendritic growth of newly generated neurons in the adult dentate gyrus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couillard-Despres, S.; Winner, B.; Schaubeck, S.; Aigner, R.; Vroemen, M.; Weidner, N.; Bogdahn, U.; Winkler, J.; Kuhn, H.G.; Aigner, L. Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect neurogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, F.; Koulakoff, A.; Boucher, D.; Chafey, P.; Schaar, B.; Vinet, M.C.; Friocourt, G.; McDonnell, N.; Reiner, O.; Kahn, A.; et al. Doublecortin is a developmentally regulated, microtubule-associated protein expressed in migrating and differentiating neurons. Neuron 1999, 23, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, J.G.; Lin, P.T.; Flanagan, L.A.; Walsh, C.A. Doublecortin is a microtubule-associated protein and is expressed widely by migrating neurons. Neuron 1999, 23, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, T.; Jagasia, R.; Herrmann, A.; Matile, H.; Borroni, E.; Francis, F.; Kuhn, H.G.; Czech, C. Analysis of adult neurogenesis: Evidence for a prominent “non-neurogenic” dcx-protein pool in rodent brain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberi, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Badie, R.; Smith-Hicks, C.; Wu, J.; Pierfelice, T.J.; Abazyan, B.; Mattson, M.P.; Kuhl, D.; et al. Activity-induced notch signaling in neurons requires Arc/Arg3.1 and is essential for synaptic plasticity in hippocampal networks. Neuron 2011, 69, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chan, S.L.; Miele, L.; Yao, P.J.; Mackes, J.; Ingram, D.K.; Mattson, M.P.; Furukawa, K. Involvement of notch signaling in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9458–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breunig, J.J.; Silbereis, J.; Vaccarino, F.M.; Sestan, N.; Rakic, P. Notch regulates cell fate and dendrite morphology of newborn neurons in the postnatal dentate gyrus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20558–20563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.M.; Honjo, T.; Silva, A.J. Learning and memory deficits in notch mutant mice. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stump, G.; Durrer, A.; Klein, A.L.; Lutolf, S.; Suter, U.; Taylor, V. Notch1 and its ligands delta-like and jagged are expressed and active in distinct cell populations in the postnatal mouse brain. Mech. Dev. 2002, 114, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.M.; Drew, C.; Silva, A.J. Notch to remember. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sirichoat, A.; Chaijaroonkhanarak, W.; Prachaney, P.; Pannangrong, W.; Leksomboon, R.; Chaichun, A.; Wigmore, P.; Welbat, J.U. Effects of Asiatic Acid on Spatial Working Memory and Cell Proliferation in the Adult Rat Hippocampus. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8413-8423. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7105401
Sirichoat A, Chaijaroonkhanarak W, Prachaney P, Pannangrong W, Leksomboon R, Chaichun A, Wigmore P, Welbat JU. Effects of Asiatic Acid on Spatial Working Memory and Cell Proliferation in the Adult Rat Hippocampus. Nutrients. 2015; 7(10):8413-8423. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7105401
Chicago/Turabian StyleSirichoat, Apiwat, Wunnee Chaijaroonkhanarak, Parichat Prachaney, Wanassanan Pannangrong, Ratana Leksomboon, Amnart Chaichun, Peter Wigmore, and Jariya Umka Welbat. 2015. "Effects of Asiatic Acid on Spatial Working Memory and Cell Proliferation in the Adult Rat Hippocampus" Nutrients 7, no. 10: 8413-8423. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7105401
APA StyleSirichoat, A., Chaijaroonkhanarak, W., Prachaney, P., Pannangrong, W., Leksomboon, R., Chaichun, A., Wigmore, P., & Welbat, J. U. (2015). Effects of Asiatic Acid on Spatial Working Memory and Cell Proliferation in the Adult Rat Hippocampus. Nutrients, 7(10), 8413-8423. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7105401