Height, Zinc and Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Schoolchildren: A Study in Cuba and Cambodia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population Cuba
2.2. Study Population Cambodia
2.3. Height for Age
2.4. Parasitology and Treatment
2.5. Plasma Zinc and Inflammation
2.6. Hair Zinc
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Populations
| Cuba (N = 1389) | Cambodia (N = 2471) | |
|---|---|---|
| n (%) or mean ± sd | n (%) or mean ± sd | |
| Age (years) | 8.14 ± 2.07 | 9.68 ± 2.27 |
| Sex (female) | 640 (47.0%) | 1236 (50.0%) |
| Height for age z-score | 0.06 ± 1.04 | −1.81 ± 1.05 |
| Stunted | 21 (1.6%) | 1056 (42.9%) |
| STH infection a | 114 (8.4%) | 302 (16.8%) |
| Ascaris lumbricoides | 70 (5.2%) | 5 (0.3%) |
| Light (<5.000 epg) | 55 (4.1%) | 5 (0.3%) |
| Moderate (5.000–50.000 epg) | 15 (1.1%) | 0 |
| Heavy (>50.000 epg) | 0 | 0 |
| Trichuris trichiura | 42 (3.1%) | 6 (0.3%) |
| Light (<1.000 epg) | 38 (2.8%) | 6 (0.3%) |
| Moderate (1.000–10.000 epg) | 2 (0.1%) | 0 |
| Heavy (>10.000 epg) | 2 (0.1%) | 0 |
| Hookworm | 15 (1.1%) | 293 (16.3%) |
| Light (<2.000 epg) | 13 (1.0%) | 283 (15.8%) |
| Moderate (2.000–4.000 epg) | 0 | 9 (0.5%) |
| Heavy (>4.000 epg) | 2 (0.1%) | 1 (0.1%) |
| Hair zinc (μg g−1) | 113 (91–137) b | n.a. |
| Zinc deficiency c | 28 (12.2%) | n.a. |
| Plasma zinc d (μmol L−1) | n.a. | 7.65 ± 1.69 |
| Zinc deficiency e | n.a. | 1884 (92.8%) |
| Inflammation | ||
| No inflammation | n.a. | 1450 (60.5%) |
| Only CRP elevated | n.a. | 8 (0.3%) |
| Only AGP elevated | n.a. | 816 (34.1%) |
| CRP & AGP elevated | n.a. | 122 (5.1%) |
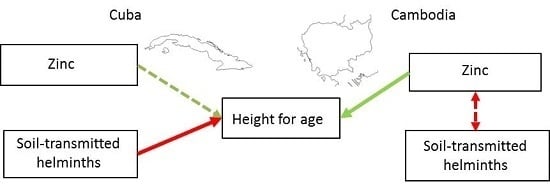
3.2. Associations between Height for Age, Zinc and STH Infection
| N | Zinc concentration | N | Height for age z score (mean ± sd) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cuba | STH uninfected | 160 | 112.55 (88.3–136.0) a | 1251 | 0.11 ± 0.97 |
| STH infected | 70 | 113.35 (94.4–143.7) a | 117 | −0.31 ± 1.16 | |
| Cambodia | STH uninfected | 1239 | 7.74 ± 1.70 b | 1450 | −1.81 ± 1.05 |
| STH infected | 254 | 7.52 ± 1.70 b | 296 | −1.84 ± 1.09 |
| independent variable | N | aB a | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cuba b | STH infection | 226 | −0.483 | 0.001 |
| Zinc | 0.335 | 0.082 | ||
| Cambodia c | STH infection | 1448 | −0.008 | 0.902 |
| Zinc | 0.033 | 0.029 |
| Variable | N | aB | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cuba a | STH infection | 230 | 0.068 | 0.206 |
| Cambodia b | STH infection | 1795 | −0.233 | 0.051 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Working Group. Use and interpretation of anthropometric indicators of nutritional-status. Bull. World Health Org. 1986, 64, 929–941. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Mathers, C.; Rivera, J.; Maternal and Child Undernutrition Study Group. Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Katz, J.; Martorell, R.; et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.K. Immune responses in parasitic diseases. Part b: Mechanisms. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1982, 4, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundy, D.A.; Golden, M.H. The impact of host nutrition on gastrointestinal helminth populations. Parasitology 1987, 95, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Zinc Nutrition Consultative; Brown, K.H.; Rivera, J.A.; Bhutta, Z.; Gibson, R.S.; King, J.C.; Lonnerdal, B.; Ruel, M.T.; Sandtrom, B.; Wasantwisut, E.; et al. International zinc nutrition consultative group (izincg) technical document #1. Assessment of the risk of zinc deficiency in populations and options for its control. Food Nutr. Bull. 2004, 25, S99–S203. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; International Atomic Energy Agency. Trace elements in Human Nutrition and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; p. 343. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer Walker, C.L.; Black, R.E. Functional indicators for assessing zinc deficiency. Food Nutr. Bull. 2007, 28, S454–S479. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, R.S. A historical review of progress in the assessment of dietary zinc intake as an indicator of population zinc status. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotez, P.J.; Kamath, A. Neglected tropical diseases in sub-saharan africa: Review of their prevalence, distribution, and disease burden. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Al-Adhroey, A.H.; Ithoi, I.; Abdulsalam, A.M.; Surin, J. The nutritional impacts of soil-transmitted helminths infections among Orang Asli schoolchildren in rural Malaysia. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethony, J.; Brooker, S.; Albonico, M.; Geiger, S.M.; Loukas, A.; Diemert, D.; Hotez, P.J. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: Ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet 2006, 367, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, S.; Hotez, P.J.; Bundy, D.A. Micronutrient supplementation and deworming in children with geohelminth infections. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongsbak, K.; Wahed, M.A.; Friis, H.; Thilsted, S.H. Acute phase protein levels, T. trichiura, and maternal education are predictors of serum zinc in a cross-sectional study in bangladeshi children. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2262–2268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koski, K.G.; Scott, M.E. Gastrointestinal nematodes, nutrition and immunity: Breaking the negative spiral. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2001, 21, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinuon, M.; Anantaphruti, M.T.; Socheat, D. Intestinal helminthic infections in schoolchildren in cambodia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2003, 34, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franco, M.; Bilal, U.; Ordunez, P.; Benet, M.; Morejon, A.; Caballero, B.; Kennelly, J.F.; Cooper, R.S. Population-wide weight loss and regain in relation to diabetes burden and cardiovascular mortality in cuba 1980–2010: Repeated cross sectional surveys and ecological comparison of secular trends. BMJ 2013, 346, f1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wordemann, M.; Polman, K.; Menocal Heredia, L.T.; Diaz, R.J.; Madurga, A.M.; Nunez Fernandez, F.A.; Cordovi Prado, R.A.; Espinosa, A.R.; Duran, L.P.; Gorbea, M.B.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of intestinal parasites in cuban children. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2006, 11, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a who growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Org. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, N.; Chaves, A.; Pellegrino, J. A simple device for quantitative stool thick-smear technique in schistosomiasis mansoni. Rev. do Inst. de Med. Trop. de Sao Paulo 1972, 14, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Nunez Fernández, F.A.; Sanjurjo González, E.; Finlay, C.M.; Gálvez Oviedo, D. Estudio de dosis única de Mebendazol, para tratamiento de Trichuris trichiura y Necator americanus en las comunidades. Rev. Cuba. de Med. Trop. 1989, 41, 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Vercruysse, J.; Behnke, J.M.; Albonico, M.; Ame, S.M.; Angebault, C.; Bethony, J.M.; Engels, D.; Guillard, B.; Hoa, N.T.V.; Kang, G.; et al. Assessment of the anthelmintic efficacy of albendazole in school children in seven countries where soil-transmitted helminths are endemic. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e94823. [Google Scholar]
- Erhardt, J.G.; Estes, J.E.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Biesalski, H.K.; Craft, N.E. Combined measurement of ferritin, soluble transferrin receptor, retinol binding protein, and c-reactive protein by an inexpensive, sensitive, and simple sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3127–3132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wieringa, F.T.; Dijkhuizen, M.A.; West, C.E.; Northrop-Clewes, C.A.; Muhilal. Estimation of the effect of the acute phase response on indicators of micronutrient status in indonesian infants. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 3061–3066. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Haese, P.C.; Lamberts, L.V.; Vanheule, A.O.; De Broe, M.E. Direct determination of zinc in serum by zeeman atomic absorption spectrometry with a graphite furnace. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 2439–2443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hambidge, K.M.; Hambidge, C.; Jacobs, M.; Baum, J.D. Low levels of zinc in hair, anorexia, poor growth, and hypogeusia in children. Pediatr. Res. 1972, 6, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, J.L.; Caamano, M.C.; Montoya, Y.A.; de Lourdes Solano, M.; Santos, J.I.; Long, K.Z. Interaction of zinc or vitamin a supplementation and specific parasite infections on mexican infants’ growth: A randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei, A.; Houser, R.; Bulusu, S.; Joshi, T.; Hamer, D. Nutritional status of primary schoolchildren in garhwali himalayan villages of india. Food Nutr. Bull. 2010, 31, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Gier, B.; Campos Ponce, M.; van de Bor, M.; Doak, C.M.; Polman, K. Helminth infections and micronutrients in school-age children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, P.; Utzinger, J.; Hattendorf, J.; Steinmann, P. Influence of nutrition on infection and re-infection with soil-transmitted helminths: A systematic review. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.; Hewitt, G.; Tuffrey, V.; de Silva, N. A review and meta-analysis of the impact of intestinal worms on child growth and nutrition. Matern. Child Nutr. 2008, 4, 118–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papier, K.; Williams, G.M.; Luceres-Catubig, R.; Ahmed, F.; Olveda, R.M.; McManus, D.P.; Chy, D.; Chau, T.N.; Gray, D.J.; Ross, A.G. Childhood malnutrition and parasitic helminth interactions. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grantham-McGregor, S.; Cheung, Y.B.; Cueto, S.; Glewwe, P.; Richter, L.; Strupp, B.; International Child Development Steering Group. Developmental potential in the first 5 years for children in developing countries. Lancet 2007, 369, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpe, P.S.; Petri, W.A. Environmental enteropathy: Critical implications of a poorly understood condition. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshage, H. Cytokines and the hepatic acute phase response. J. Pathology 1997, 181, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo-Wilson, E.; Imdad, A.; Junior, J.; Dean, S.; Bhutta, Z.A. Preventive zinc supplementation for children, and the effect of additional iron: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, N.M.; Fekete, K.; Decsi, T. Methods of assessment of zinc status in humans: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 2040S–2051S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, M.H. Proposed recommended nutrient densities for moderately malnourished children. Food Nutr. Bull. 2009, 30, S267–S342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thurnham, D.I. Interactions between nutrition and immune function: Using inflammation biomarkers to interpret micronutrient status. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Gier, B.; Mpabanzi, L.; Vereecken, K.; Van der Werff, S.D.; D'Haese, P.C.; Fiorentino, M.; Khov, K.; Perignon, M.; Chamnan, C.; Berger, J.; et al. Height, Zinc and Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Schoolchildren: A Study in Cuba and Cambodia. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3000-3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7043000
De Gier B, Mpabanzi L, Vereecken K, Van der Werff SD, D'Haese PC, Fiorentino M, Khov K, Perignon M, Chamnan C, Berger J, et al. Height, Zinc and Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Schoolchildren: A Study in Cuba and Cambodia. Nutrients. 2015; 7(4):3000-3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7043000
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Gier, Brechje, Liliane Mpabanzi, Kim Vereecken, Suzanne D. Van der Werff, Patrick C. D'Haese, Marion Fiorentino, Kuong Khov, Marlene Perignon, Chhoun Chamnan, Jacques Berger, and et al. 2015. "Height, Zinc and Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Schoolchildren: A Study in Cuba and Cambodia" Nutrients 7, no. 4: 3000-3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7043000
APA StyleDe Gier, B., Mpabanzi, L., Vereecken, K., Van der Werff, S. D., D'Haese, P. C., Fiorentino, M., Khov, K., Perignon, M., Chamnan, C., Berger, J., Parker, M. E., Díaz, R. J., Núñez, F. A., Rivero, L. R., Gorbea, M. B., Doak, C. M., Ponce, M. C., Wieringa, F. T., & Polman, K. (2015). Height, Zinc and Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections in Schoolchildren: A Study in Cuba and Cambodia. Nutrients, 7(4), 3000-3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7043000