Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency after Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
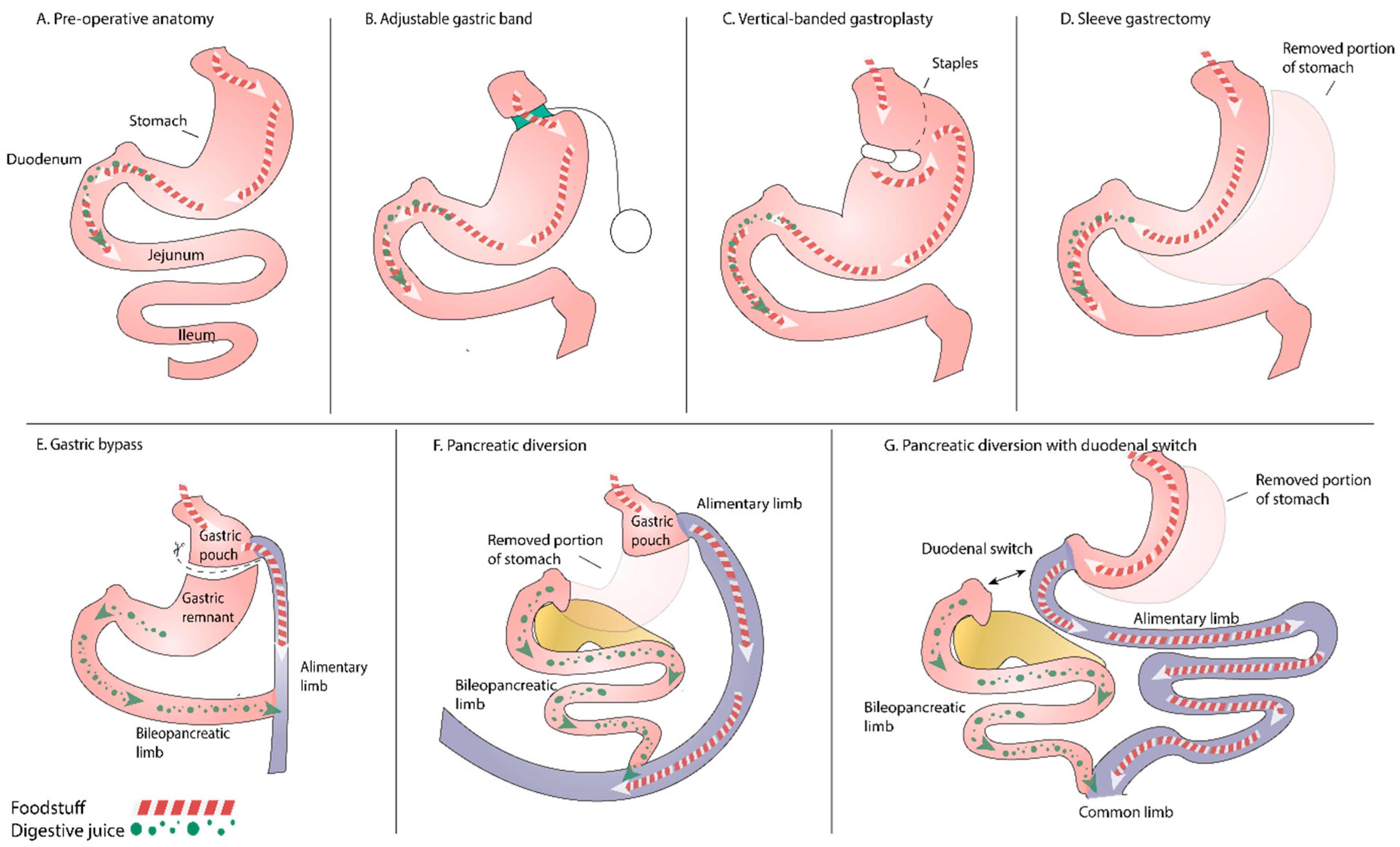
2. Bariatric Surgery
- food limitation operations (restrictive procedures): vertical-banded gastroplasty, adjustable gastric banding, proximal gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy;
- operations limiting absorption of macronutrients (limiting energy absorption): biliopancreatic diversion; and
- combined restrictive/malabsorptive operations: biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch or distal gastric bypass.
3. Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency
4. Exocrine Pancreatic Function after Digestive Surgery
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsigos, C.; Hainer, V.; Basdevant, A.; Finer, N.; Fried, M.; Mathus-Vliegen, E.; Micic, D.; Maislos, M.; Schutz, Y.; Toplak, H.; et al. Management of obesity in adults: European clinical practice guidelines. Obes. Facts 2008, 1, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, M.; Hainer, V.; Basdevant, A.; Buchwald, H.; Deitel, M.; Finer, N.; Greve, J.W.; Horber, F.; Mathus-Vlieqen, E.; Scopinaro, N.; et al. Interdisciplinary European guidelines on surgery of severe obesity. Obes. Facts 2008, 1, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.; Liddle, R.A. Recent advances in pancreatic endocrine and exocrine secretion. Curr. Opion. Gastroenterol. 2011, 27, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, J.; Nawrot-Porabka, K.; Leja-Szpak, A.; Konturek, S.J. Brain-gut axis in the modulation of pancreatic enzyme secretion. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Love, J.A.; Yi, E.; Smith, T.G. Autonomic pathways regulating pancreatic exocrine secretion. Auton. Neurosci. 2007, 133, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Hamdah, R.; Rabiee, A.; Meneilly, G.S.; Shannon, R.P.; Andersen, D.K.; Elahi, D. Clinical review: The extrapancreatic effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and related peptides. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapica, M.; Puzio, I.; Kato, I.; Kuwahara, A.; Zabielski, R. Role of feed-regulating peptides on pancreatic exocrine secretion. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 59 (Suppl. 2), 145–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.V.; Ren, P.G.; Avsian-Kretchmer, O.; Luo, C.W.; Rauch, R.; Klein, C.; Hsueh, A.J. Obestatin, a peptide encoded by the ghrelin gene, opposes ghrelin’s effects on food intake. Science 2005, 310, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.; Masri, B.; Daviaud, D.; Gesta, S.; Guigne, C.; Mazzucotelli, A.; Castan-Laurell, I.; Tack, I.; Knibiehler, B.; Carpéné, C.; et al. Apelin, a newly identified adipokine up-regulated by insulin and obesity. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1764–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Anini, Y.; Wei, W.; Qi, X.; OCarroll, A.M.; Mochizuki, T.; Wang, H.Q.; Hellmich, M.R.; Englander, E.W.; Greeley, G.H., Jr.; et al. Apelin, a new enteric peptide: Localization in the gastrointestinal tract, ontogeny, and stimulation of gastric cell proliferation and of cholecystokinin secretion. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susaki, E.; Wang, G.; Cao, G.; Wang, H.Q.; Englander, E.W.; Greeley, G.H., Jr. Apelin cells in the rat stomach. Regul. Pept. 2005, 129, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xanthakos, S.A. Nutritional deficiencies in obesity and after bariatric surgery. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 56, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, A.K. Consumption of energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods by adult Americans: Nutritional and health implications. The third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kapica, M.; Jankowska, A.; Antushevich, H.; Pietrzak, P.; Bierla, J.B.; Dembinski, A.; Zabielski, R. The effect of exogenous apelin on the secretion of pancreatic juice in anaesthetized rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 63, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Jayasena, C.N.; Bloom, S.R. Obesity and appetite control. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 824305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angrisani, L.; Santonicola, A.; Iovino, P.; Formisano, G.; Buchwald, H.; Scopinaro, N. Bariatric Surgery Worldwide 2013. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elrazek, A.E.; Elbanna, A.E.; Bilasy, S.E. Medical management of patients after bariatric surgery: Principles and guidelines. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 6, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, L.; Lindroos, A.K.; Peltonen, M.; Torgerson, J.; Bouchard, C.; Carlsson, B.; Dahlgren, S.; Larsson, B.; Narbro, K.; Sjöström, C.D.; et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, L.; Narbro, K.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Karason, K.; Larsson, B.; Wedel, H.; Lystig, T.; Sullivan, M.; Bouchard, C.; Carlsson, B.; et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchwald, H.; Avidor, Y.; Braunwald, E.; Jensen, M.D.; Pories, W.; Fahrbach, K. Bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2004, 292, 1724–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Tsugawa, Y.; Faridi, M.K.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Hasegawa, K. Reduced Risk of Acute Exacerbation of COPD after Bariatric Surgery: A Self-Controlled Case Series Study. Chest 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier-Larouche, T.; Carreau, A.M.; Carpentier, A.C. Early Metabolic Improvement after Bariatric Surgery: The First Steps toward Remission of Type 2 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevedo, M.D.P.; Palermo, M.; Serra, E.; Ackermann, M.A. Metabolic surgery: Gastric bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, O.; Sirveaux, M.A.; Brunaud, L.; Reibel, N.; Quilliot, D. Medical follow up after bariatric surgery: Nutritional and drug issues. General recommendations for the prevention and treatment of nutritional deficiencies. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolin, R.E.; LaMarca, L.B.; Kenler, H.A.; Cody, R.P. Malabsorptive gastric bypass in patients with superobesity. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2002, 6, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.R. The neurological complications of bariatric surgery. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brolin, R.E.; Gorman, J.H.; Gorman, R.C.; Petschenik, A.J.; Bradley, L.J.; Kenler, H.A.; Cody, R.P. Are vitamin B12 and folate deficiency clinically important after roux-en-Y gastric bypass? J. Gastrointest. Surg. 1998, 2, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, S.; Baz, W.; Badine, E.; Nakhl, F.; McMullen, H.; Nicastro, J.; Forte, F.; Terjanian, T.; Dai, Q. Need for parenteral iron therapy after bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2008, 4, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Drygalski, A.; Andris, D.A.; Nuttleman, P.R.; Jackson, S.; Klein, J.; Wallace, J.R. Anemia after bariatric surgery cannot be explained by iron deficiency alone: Results of a large cohort study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2011, 7, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J. Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, 2nd ed.; UNIMED: Bremen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lohr, J.M.; Dominguez-Munoz, E.; Rosendahl, J.; Besselink, M.; Mayerle, J.; Lerch, M.M.; Haas, S.; Akisik, F.; Kartalis, N.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; et al. United European Gastroenterology evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and therapy of chronic pancreatitis (HaPanEU). United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 153–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankisch, P.G.; Schmidt, I.; Konig, H.; Lehnick, D.; Knollmann, R.; Lohr, M.; Liebe, S. Faecal elastase 1: Not helpful in diagnosing chronic pancreatitis associated with mild to moderate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Gut 1998, 42, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, S.; Krins, S.; Knauerhase, A.; Lohr, M. Altered bone metabolism and bone density in patients with chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. JOP J. Pancreas 2015, 16, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Moneo, E.; Stigliano, S.; Hedstrom, A.; Kaczka, A.; Malvik, M.; Waldthaler, A.; Maisonneuve, P.; Simon, P.; Capurso, G. Deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins in chronic pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindkvist, B.; Phillips, M.E.; Dominguez-Munoz, J.E. Clinical, anthropometric and laboratory nutritional markers of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: Prevalence and diagnostic use. Pancreatology 2015, 15, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeds, J.S.; Hopper, A.D.; Hurlstone, D.P.; Edwards, S.J.; McAlindon, M.E.; Lobo, A.J.; Donnelly, M.T.; Morley, S.; Sanders, D.S. Is exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in adult coeliac disease a cause of persisting symptoms? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madzak, A.; Olesen, S.S.; Wathle, G.K.; Haldorsen, I.S.; Drewes, A.M.; Frokjaer, J.B. Secretin-Stimulated Magnetic Resonance Imaging Assessment of the Benign Pancreatic Disorders: Systematic Review and Proposal for a Standardized Protocol. Pancreas 2016, 45, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Murakami, Y.; Uemura, K.; Hayashidani, Y.; Sudo, T.; Ohge, H.; Sueda, T. Predictive factors for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency after pancreatoduodenectomy with pancreaticogastrostomy. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2009, 13, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, S.; Malfertheiner, P. Exocrine and endocrine pancreatic insufficiency after pancreatic surgery. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2004, 18, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Buchler, M.; Glasbrenner, B.; Schafmayer, A.; Ditschuneit, H. Adaptive changes of the exocrine pancreas and plasma cholecystokinin release following subtotal gastric resection in rats. Digestion 1987, 38, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friess, H.; Bohm, J.; Muller, M.W.; Glasbrenner, B.; Riepl, R.L.; Malfertheiner, P.; Büchler, M.W. Maldigestion after total gastrectomy is associated with pancreatic insufficiency. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1996, 91, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keller, J.; Layer, P. Human pancreatic exocrine response to nutrients in health and disease. Gut 2005, 54 (Suppl. 6), vi1–vi28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borbely, Y.; Plebani, A.; Kroll, D.; Ghisla, S.; Nett, P.C. Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2016, 12, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullo, L.; Costa, P.L.; Ventrucci, M.; Mattioli, S.; Viti, G.; Labo, G. Exocrine pancreatic function after total gastrectomy. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1979, 14, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armbrecht, U.; Lundell, L.; Stockbrugger, R.W. The benefit of pancreatic enzyme substitution after total gastrectomy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1988, 2, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujasinovic, M.; Kunst, G.; Breznikar, B.; Rozej, B.; Tepes, B.; Rudolf, S.; Kuster, A. Is pancreatic exocrine insufficiency a cause of malabsorption in patients after bariatric surgery? JOP J. Pancreas 2016, 17, 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Munoz, J.E.; Hardt, P.D.; Lerch, M.M.; Lohr, M.J. Potential for Screening for Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency Using the Fecal Elastase-1 Test. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Hormone | Action on Pancreas Exocrine Secretion | Action on Food Intake |
|---|---|---|
| Cholecystokinin (CCK) | Released from enteroendocrine I cells in duodenal and ileal mucosa. Stimulates pancreatic exocrine secretion. Vagal afferent nerve fibers express several receptors for CCK. | CCK was the first gut hormone found to be implicated in appetite control. Some studies suggest that leptin and CCK may interact synergistically to induce short-term inhibition of food intake and long-term reduction of body weight. |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) | Released from the small intestine; inhibits hypoglycemia-stimulated exocrine secretion by direct activation of dorsal vagal complex. | GLP-1 reduces food intake, suppresses glucagon secretion and delays gastric emptying. Intravenous administration of GLP-1 is associated with a dose-dependent reduction of food intake in both normal weight and obese subjects. |
| Serotonin | Could activate vagal afferents to initiate enteropancreatic reflex and to stimulate pancreatic exocrine secretion. Vagal afferent nerve fibers express several receptors for serotonin. | None. |
| Leptin | Mainly produced and secreted by adipocytes. Controversial effect on pancreas. Could activate vagal afferents to initiate enteropancreatic reflex and stimulate pancreatic exocrine secretion. Intravenous application in rats reduces pancreatic secretion by inhibiting neurohormonal CCK-vagal-dependent mechanism. Leptin administrated in duodenum significantly stimulates pancreatic protein secretion. Significantly reduces the severity of acute pancreatitis. Vagal afferent nerve fibers express several receptors for leptin. | Regulation of food intake, energy expenditure and body weight homeostasis. |
| Ghrelin | Controversial effect on pancreas. Central administration in rats could activate vagal afferents to initiate enteropancreatic reflex and to stimulate pancreatic exocrine secretion. Intravenous administration in rats reduced pancreatic enzyme secretion. Vagus-dependent cholinergic pathway. | Strongly stimulates food intake. Increases adipogenesis. |
| Melatonin | Produced in the pineal gland and in the enteroendocrine cells of gastrointestinal mucosa and secreted into the duodenal lumen with the bile. Protects pancreas against acute damage. Dose-dependent stimulation of pancreatic exocrine secretion. | None. |
| Apelin | Stimulates CCK secretion. Intravenous application in rats leads to significant dose-dependent inhibition of pancreatic secretion. Intraduodenal application stimulates pancreatic secretion. Neurohormonal, CCK1-vagal-dependent mechanism. | Apelin is expressed in adipose tissue, suggesting adipokine functions. |
| Obestatin | May stimulate pancreatic protein output and trypsin activity following intravenous and intraduodenal administration (effect is dose-dependent). | Appears to have opposite actions to ghrelin on the regulation of food intake, emptying the stomach, and body weight in rodents. |
| Orexin-A and -B | Stimulation of pancreas exocrine secretion with orexin-A and no effect with orexin-B. Controlled by dorsal vagal complex. | Involved in the control of feeding. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vujasinovic, M.; Valente, R.; Thorell, A.; Rutkowski, W.; Haas, S.L.; Arnelo, U.; Martin, L.; Löhr, J.-M. Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency after Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111241
Vujasinovic M, Valente R, Thorell A, Rutkowski W, Haas SL, Arnelo U, Martin L, Löhr J-M. Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency after Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients. 2017; 9(11):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111241
Chicago/Turabian StyleVujasinovic, Miroslav, Roberto Valente, Anders Thorell, Wiktor Rutkowski, Stephan L. Haas, Urban Arnelo, Lena Martin, and J.-Matthias Löhr. 2017. "Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency after Bariatric Surgery" Nutrients 9, no. 11: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111241
APA StyleVujasinovic, M., Valente, R., Thorell, A., Rutkowski, W., Haas, S. L., Arnelo, U., Martin, L., & Löhr, J.-M. (2017). Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency after Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients, 9(11), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111241




