Ultrasonographic and Three-Dimensional Analyses at the Glabella and Radix of the Nose for Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection Procedures into the Procerus Muscle
Abstract
1. Introduction
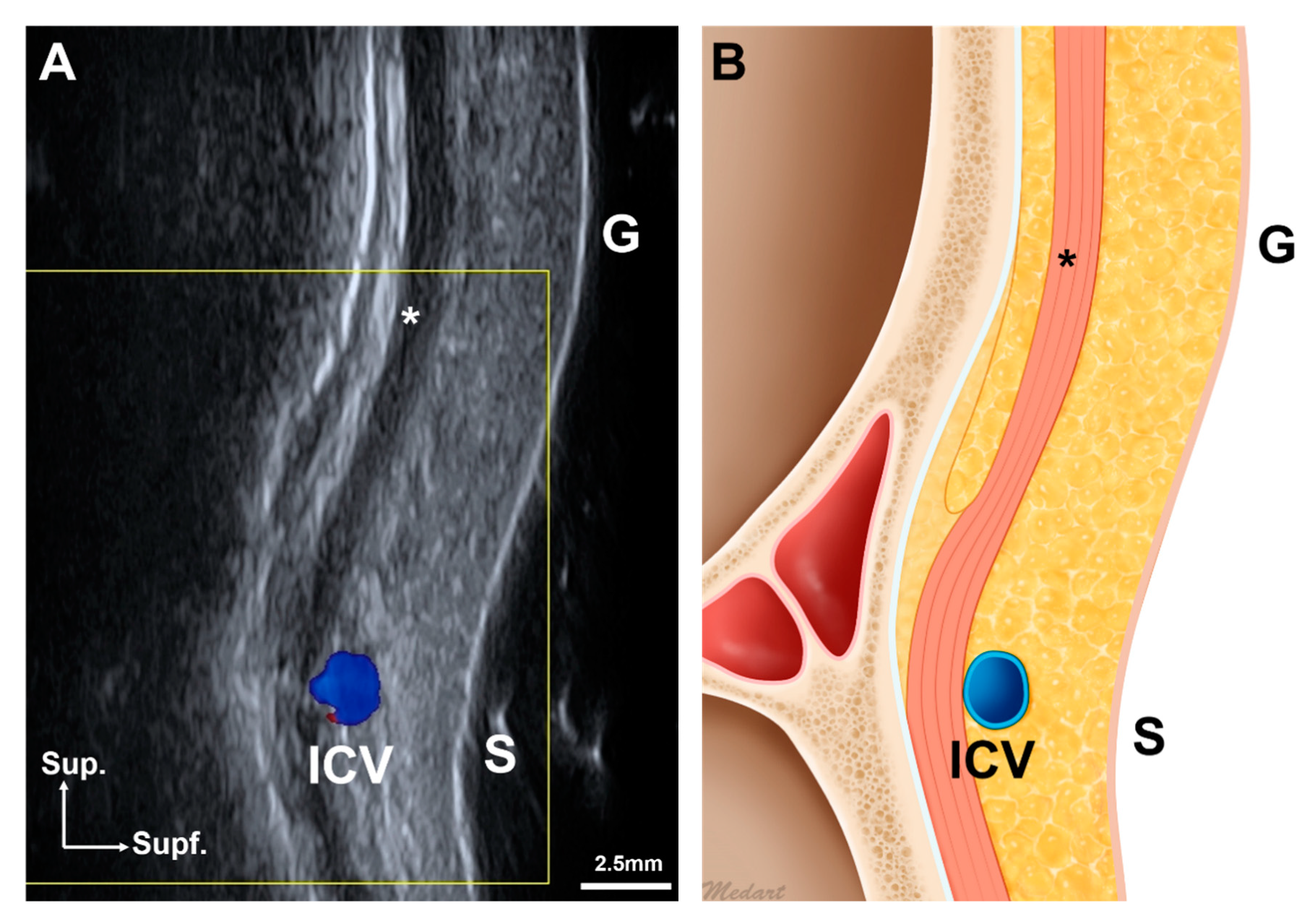
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
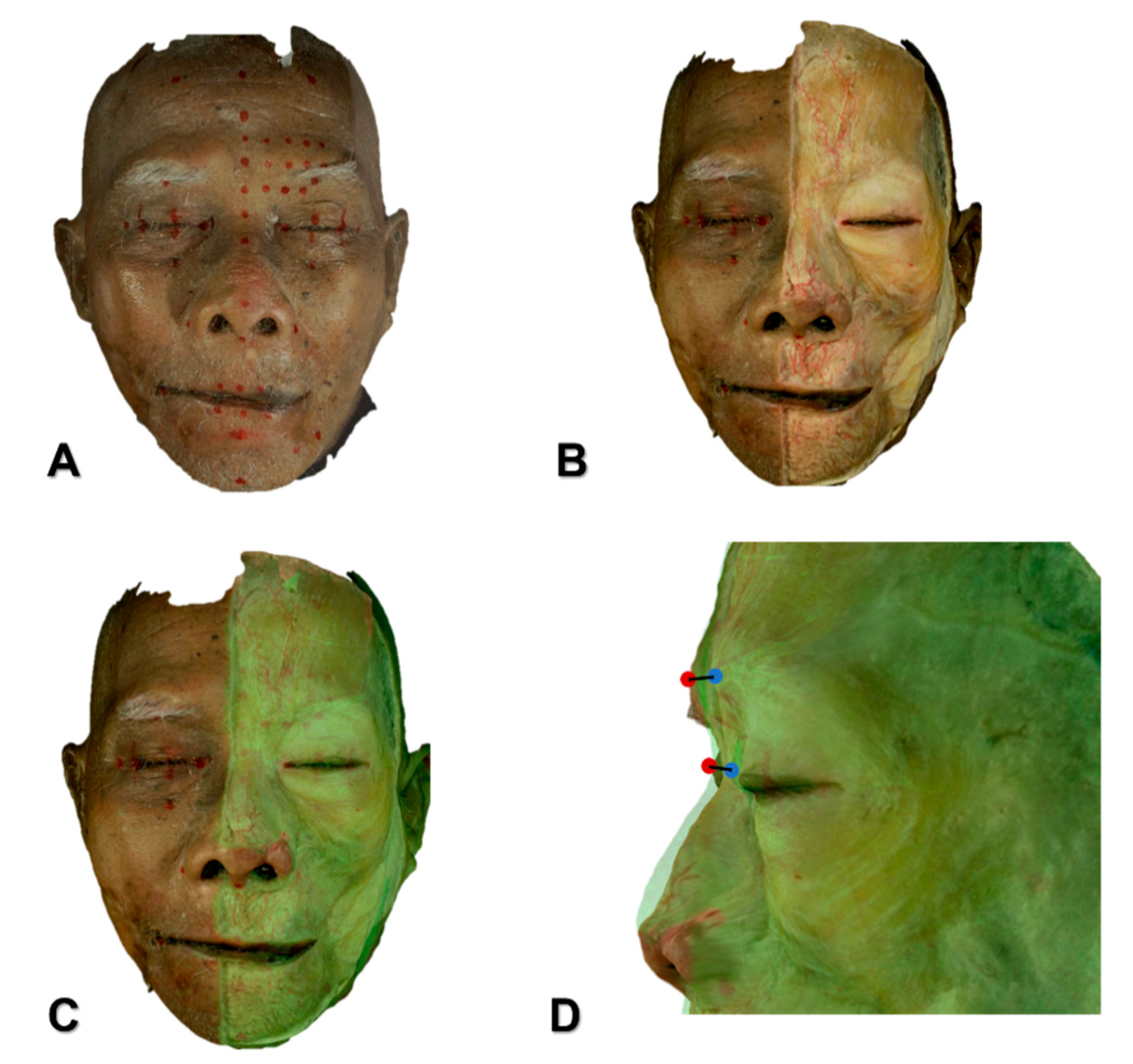
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. 3D Scanning Using a Structured-Light Scanner for Analyzing the Depth of the Procerus
5.2. US Analyses of the Procerus and the ICV
5.3. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alster, T.S.; Lupton, J.R. Botulinum toxin type B for dynamic glabellar rhytides refractory to botulinum toxin type A. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2003, 29, 516–518. [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers, J.D.; Lowe, N.J.; Menter, M.A.; Gibson, J.; Eadie, N.; Botox Glabellar Lines, I.I.S.G. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin type A for patients with glabellar lines. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 112, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, J.E.; Easthope, S.E. Botulinum toxin A (Botox Cosmetic): A review of its use in the treatment of glabellar frown lines. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 4, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.M.; Krishnamurthy, K. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Procerus Muscle; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, M.S. Anatomical relationships of the procerus with the nasal ala and the nasal muscles: Transverse part of the nasalis and levator labii superioris alaeque nasi. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2017, 39, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruthers, A.; Carruthers, J. Eyebrow height after botulinum toxin type A to the glabella. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2007, 33, S26–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, S. Different Glabellar Contraction Patterns in Chinese and Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Treating Glabellar Lines: A Pilot Study. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2017, 43, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, A.; Quadros, T. An observational study on glabellar wrinkle patterns in Indians. Indian J. Derm. Venereol Leprol 2019, 85, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.; Jin, S.; Park, J.H.; Chung, I.H. Innervation of the procerus muscle. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2006, 17, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Imanishi, N.; Nakajima, T.; Nakajima, H.; Aiso, S.; Kishi, K. Venous architecture of the glabellar to the forehead region. Clin. Anat. 2013, 26, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kang, I.W.; Won, S.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Hu, K.S.; Tansatit, T.; Kim, H.J. Description of a novel anatomic venous structure in the nasoglabellar area. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, 633–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.Y.; Yang, C.J. A case report of cavernous sinus thrombosis after trauma. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 95, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tronstad, L.; Olsen, I. Brain abscesses caused by oral infection. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1999, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochazka, V.; Cizek, V.; Kacirova, R. Cavernous sinus dural fistula treated by transvenous facial vein approach. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2004, 10, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.H.; Gil, Y.C.; Hu, K.S.; Kim, H.J. Validity and reliability of a structured-light 3D scanner and an ultrasound imaging system for measurements of facial skin thickness. Clin. Anat. 2017, 30, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Youn, K.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.J. Ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Injection for Correcting Asymmetrical Smiles. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2018, 38, NP130–NP134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, K.W.; Hu, K.S.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, H.J. Ultrasonography of the internal architecture of the superficial part of the masseter muscle in vivo. Clin. Anat. 2019, 32, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koerte, I.K.; Schroeder, A.S.; Fietzek, U.M.; Borggraefe, I.; Kerscher, M.; Berweck, S.; Reiser, M.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; Heinen, F. Muscle atrophy beyond the clinical effect after a single dose of OnabotulinumtoxinA injected in the procerus muscle: A study with magnetic resonance imaging. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 39, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenc, Z.P.; Smith, S.; Nestor, M.; Nelson, D.; Moradi, A. Understanding the functional anatomy of the frontalis and glabellar complex for optimal aesthetic botulinum toxin type A therapy. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2013, 37, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Andersson, M.; Punga, A.R. Correlation of botulinum toxin dose with neurophysiological parameters of efficacy and safety in the glabellar muscles: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2014, 94, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Arndt, K.A.; Dover, J.S. Severe, intractable headache after injection with botulinum a exotoxin: Report of 5 cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 46, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Gaon, N.; Wortsman, X.; Penaloza, O.; Carrasco, J.E. Comparison of clinical marking and ultrasound-guided injection of Botulinum type A toxin into the masseter muscles for treating bruxism and its cosmetic effects. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Seo, K.K.; Lee, H.-K.; Kim, J. Clinical Anatomy for Botulinum Toxin Injection. In Clinical Anatomy of the Face for Filler and Botulinum Toxin Injection; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 55–92. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, K.W.; Gil, Y.C.; Hu, K.S.; Kim, H.J. Ultrasonographic Analyses of the Forehead Region for Injectable Treatments. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.S.; Gil, Y.C.; Tanvaa, T.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, H.J. Regional thickness of facial skin and superficial fat: Application to the minimally invasive procedures. Clin. Anat. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Site | Measurement Method | Depth from Skin Surface to the Procerus (mm) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glabella | Ultrasonography (n = 55) | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 0.144 |
| 3D scanning (n = 45) | 4.1 ± 1.3 | ||
| Sellion | Ultrasonography (n = 69) | 2.7 ± 0.6 | 0.063 |
| 3D scanning (n = 45) | 3.0 ± 1.1 |
| Site Measurement | Type I | Type II | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 55 (79.7%) | n = 14 (20.3%) | ||
| Glabella | Depth | 3.8 ± 0.7 mm | |
| Thickness | 1.1 ± 0.5 mm | ||
| Sellion | Depth | 2.7 ± 0.5 mm | 2.7 ± 0.9 mm |
| Thickness * | 1.6 ± 0.6 mm | 1.3 ± 0.4 mm | |
| Width | 10.1 ± 2.0 mm | 10.2 ± 1.2 mm | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, K.-L.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, H.-J. Ultrasonographic and Three-Dimensional Analyses at the Glabella and Radix of the Nose for Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection Procedures into the Procerus Muscle. Toxins 2019, 11, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100560
Cho Y, Lee H-J, Lee K-W, Lee K-L, Kang JS, Kim H-J. Ultrasonographic and Three-Dimensional Analyses at the Glabella and Radix of the Nose for Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection Procedures into the Procerus Muscle. Toxins. 2019; 11(10):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100560
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Younghoon, Hyung-Jin Lee, Kang-Woo Lee, Kyu-Lim Lee, Jae Seung Kang, and Hee-Jin Kim. 2019. "Ultrasonographic and Three-Dimensional Analyses at the Glabella and Radix of the Nose for Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection Procedures into the Procerus Muscle" Toxins 11, no. 10: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100560
APA StyleCho, Y., Lee, H.-J., Lee, K.-W., Lee, K.-L., Kang, J. S., & Kim, H.-J. (2019). Ultrasonographic and Three-Dimensional Analyses at the Glabella and Radix of the Nose for Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection Procedures into the Procerus Muscle. Toxins, 11(10), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100560








