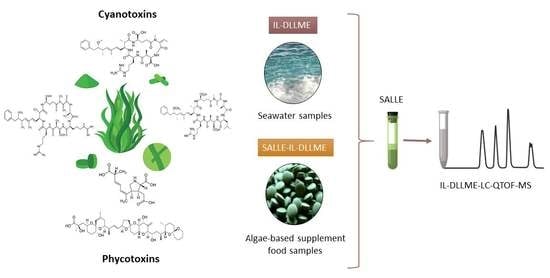
Determination of Cyanotoxins and Phycotoxins in Seawater and Algae-Based Food Supplements Using Ionic Liquids and Liquid Chromatography with Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of LC-Q-TOF-MS Conditions
2.2. Optimization of the Microextraction Procedure
2.3. Method Validation
2.4. Analysis of Seawater and Algae-Based Dietary Supplement Food Samples
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Instrumentation
4.3. Samples
4.4. Analytical Procedure
4.4.1. Water Samples
4.4.2. Dietary Algae-Based Food Supplement Samples
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tamele, I.J.; Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, V. The incidence of marine toxins and the associated seafood poisoning episodes in the african countries of the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea. Toxins 2019, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svirčev, Z.; Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Mijović, B.; Codd, G.A.; Meriluoto, J. Toxicology of microcystins with reference to cases of human intoxications and epidemiological investigations of exposures to cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stutts, W.L.; Deeds, J.R.; Marsan, D.W.; Conrad, S.M.; Stutts, W.L.; Parker, C.H. Evaluation of microcystin contamination in blue-green algal dietary supplements using a protein phosphatase inhibition-based test kit. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00573. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ajani, P.; Harwood, D.; Murray, S. Recent trends in marine phycotoxins from Australian coastal waters. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; Pol-Hofstad, I.E.; Poelman, M.; Mulder, P.P.J.; van den Top, H.J.; Dde Boer, J. Marine toxins: Chemistry, toxicity, occurrence and detection, with special reference to the Dutch situation. Toxins 2010, 2, 878–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, E.U. Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2004, 139, 55–205. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; ISBN 9789241545808. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen, K.K.; Kankaanpa, H.; Leinio, S.; Sipia, V.O. Accumulation of nodularin-like compounds from the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena and changes in acetylcholinesterase activity in the clam Macoma balthica during short-term laboratory exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 64, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeger, S.J.; Shaw, G.; Hitzfeld, B.C.; Dietrich, D.R. Occurrence and elimination of cyanobacterial toxins in two Australian drinking water treatment plants. Toxicon 2004, 43, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Hrudey, S.; Li, X.-F. Determination of microcystins in water using integrated solid-phase microextraction with microbore high-performance liquid chromatography—Electrospray quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2006, 44, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasurendra, A.M.; Palagama, D.S.W.; Rohanifar, A.; Isailovic, D.; Kirchhoff, J.R.; Anderson, J.L. Solid-phase extraction, quantification, and selective determination of microcystins in water with a gold-polypyrrole nanocomposite sorbent material. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1560, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Shi, X.; Dou, A.; Zou, C.; He, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Lu, X.; Xu, G. A fully automated system with on-line micro solid-phase extraction combined with capillary liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for high throughput analysis of microcystins and nodularin-R in tap water and lake water. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, S.; Aga, D.S. Recent advances in the sample preparation, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometric analysis and environmental fate of microcystins in water. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allis, O.; Healy, B.M.; Mu, P.; Lehane, M.; Aine, N.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Determination of toxic cyclic heptapeptides by liquid chromatography with detection using ultra-violet, protein phosphatase assay and tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Ammerman, J.L.; Aldstadt, J.H., III. Monolithic solid-phase extraction for the rapid on-line monitoring of microcystins in surface waters. Microchem. Acta 2009, 164, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yan, F.; Chen, F.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, L. C18-functionalized magnetic silica nanoparticles for solid phase extraction of microcystin-LR in reservoir water samples followed by HPLC-DAD determination. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. 2014, 38, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, V.; Babica, P.; Todorova, D.; Bratanova, Z.; Marðµlek, B. Contamination of some reservoirs and lakes in Republic of Bulgaria by microcystins. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2006, 34, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, F.M.; de Macedo, A.N.; Vieira, E.M. Determination of microcystin-LR in cyanobacterial blooms from the Mogi Guacu River (Brazil) by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2014, 37, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.P.; Bobbitt, J.M.; Taylor, R.B.; Lovin, L.M.; Conkle, J.L.; Chambliss, C.K.; Brooks, B.W. Determination of microcystins, nodularin, anatoxin-a, cylindrospermopsin, and saxitoxin in water and fish tissue using isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1599, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, Z.; Gao, J.; Tong, P.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L. Metal–organic framework UiO-66 modified magnetite@silica core–shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of domoic acid from shellfish samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1400, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, M.; Wang, M.; Tong, P.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, L. Magnetic porous β-cyclodextrin polymer for magnetic solid-phase extraction of microcystins from environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1503, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Reversed-phase/weak anion exchange magnetic mesoporous microspheres for removal of matrix effects in lipophilic marine biotoxins analysis by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Y. Development and application of immunoaffinity column purification and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of domoic acid in shellfish. Toxins 2019, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchy, P.; Berry, J. Detection of total microcystin in fish tissues based on lemieux oxidation and recovery of 2-methyl-3-methoxy-4-phenylbutanoic acid (MMPB) by solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (SPME-GC/MS). Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2012, 92, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Neill, A.O.; Maskrey, B.H.; Coates, L.; Texeira Alves, M.; Kelly, R.J.; Hatfield, R.G.; Rowland-Pilgrim, S.J.; Lewis, A.M.; Algoet, M.; et al. Variability and profiles of lipophilic toxins in bivalves from Great Britain during five and a half years of monitoring: Okadaic acid, dinophysis toxins and pectenotoxins. Harmful Algae 2018, 77, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.; Foss, A.; Miller, M.A.; Gibson, Q. Detection of cyanotoxins (microcystins/nodularins) in livers from estuarine and coastal bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Northeast Florida. Harmful Algae 2018, 76, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, S.; Flinois, C.; Maisonnette, C.; Leberre, B. Variations in the microcystin production of Planktothrix rubescens (Cyanobacteria) assessed from a four-year survey of Lac du Bourget (France) and from laboratory experiments. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 50, 418–428. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, K.-F.; Hon-wah Lam, M.; Lam, P.K.S.; Wong, B.S.F. Determination of microcystins in cyanobacterial blooms by solid-phase microextraction–high-performance liquid chromatography. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán, E.; Ibáñez, M.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernández, F. Determination of six microcystins and nodularin in surface and drinking waters by on-line solid phase extraction–ultra high pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1266, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lian, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Tian, Y.; Guo, X.; Lou, D. Analysis of microcystins using high-performance liquid chromatography and magnetic solid-phase extraction with silica-coated magnetite with cetylpyridinium chloride. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Clark, K.D.; Anderson, J.L. Rapid and sensitive analysis of microcystins using ionic liquid-based in situ dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1406, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavagadhi, S.; Basheer, C.; Balasubramanian, R. Application of ionic-liquid supported cloud point extraction for the determination of microcystin-leucine–arginine in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 686, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Diana Di Mavungu, J.; Uka, V.; Malysheva, S.V.; Cary, J.W.; Ehrlich, K.C.; Vanhaecke, L.; Bhatnagar, D.; De Saeger, S. Use of UHPLC high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry to investigate the genes involved in the production of secondary metabolites in Aspergillus flavus. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 1656–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Decision 2002/657/EC of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. Union 2002, L221, 8–36. [Google Scholar]



| Compound | tR (min) | m/z Theoretical | m/z Experimental | Error (ppm) | Q1, m/z | Q2, m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domoic acid (DA) | 6.22 | 312.1447 | 312.1440 | −2.2 | 161.0963 | 266.1382 |
| Microcystine-RR (MC-RR) | 12.55 | 1038.5736 | 1038.5707 | −2.8 | 135.0803 | 620.3387 |
| Nodularin (NOD) | 13.70 | 825.4511 | 825.4499 | −1.5 | 135.0803 | 691.3774 |
| Microcystine-LR (MC-LR) | 14.46 | 995.5566 | 995.5552 | −1.4 | 135.0803 | 861.4811 |
| Okadaic acid (OA) | 18.33 | 805.4738 | 805.4714 | −3.0 | 769.4508 | 787.4621 |
| Compound | Seawater Limits of Detection (LD), ng mL−1 | Food Supplements LD, ng g−1 | Relative Standard Deviations (RSD), % |
|---|---|---|---|
| DA | 0.39 | 13 | 8.2 |
| MC-RR | 1.4 | 52 | 10 |
| NOD | 0.22 | 7.5 | 9.5 |
| MC-LR | 0.33 | 11 | 7.7 |
| OA | 1.5 | 49 | 8.9 |
| Compound | Seawater, ng mL−1 | Food Supplement, ng g−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 300 | 900 | |
| DA | 94.3 | 99.2 | 84.4 | 105 |
| MC-RR | 118 | 102 | 87.4 | 103 |
| NOD | 94.8 | 99.3 | 81.7 | 102 |
| MC-LR | 108 | 101 | 113 | 99.1 |
| OA | 112 | 88.0 | 91.5 | 101 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giménez-Campillo, C.; Pastor-Belda, M.; Campillo, N.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Hernández-Córdoba, M.; Viñas, P. Determination of Cyanotoxins and Phycotoxins in Seawater and Algae-Based Food Supplements Using Ionic Liquids and Liquid Chromatography with Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2019, 11, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100610
Giménez-Campillo C, Pastor-Belda M, Campillo N, Arroyo-Manzanares N, Hernández-Córdoba M, Viñas P. Determination of Cyanotoxins and Phycotoxins in Seawater and Algae-Based Food Supplements Using Ionic Liquids and Liquid Chromatography with Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Toxins. 2019; 11(10):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100610
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiménez-Campillo, Claudia, Marta Pastor-Belda, Natalia Campillo, Natalia Arroyo-Manzanares, Manuel Hernández-Córdoba, and Pilar Viñas. 2019. "Determination of Cyanotoxins and Phycotoxins in Seawater and Algae-Based Food Supplements Using Ionic Liquids and Liquid Chromatography with Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry" Toxins 11, no. 10: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100610
APA StyleGiménez-Campillo, C., Pastor-Belda, M., Campillo, N., Arroyo-Manzanares, N., Hernández-Córdoba, M., & Viñas, P. (2019). Determination of Cyanotoxins and Phycotoxins in Seawater and Algae-Based Food Supplements Using Ionic Liquids and Liquid Chromatography with Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Toxins, 11(10), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100610