Curine Inhibits Macrophage Activation and Neutrophil Recruitment in a Mouse Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Curine Inhibits Neutrophil Recruitment in LPS-Challenged Mice
2.2. Curine Inhibits Inflammatory Mediator Production in Vivo
2.3. Curine Inhibits Macrophage Activation in Vitro
2.4. Effects of Calcium Influx Inhibition on Macrophage Activation
2.5. Curine Inhibits Nitric Oxide (NO) Production by Regulating iNOS Expression in Macrophages
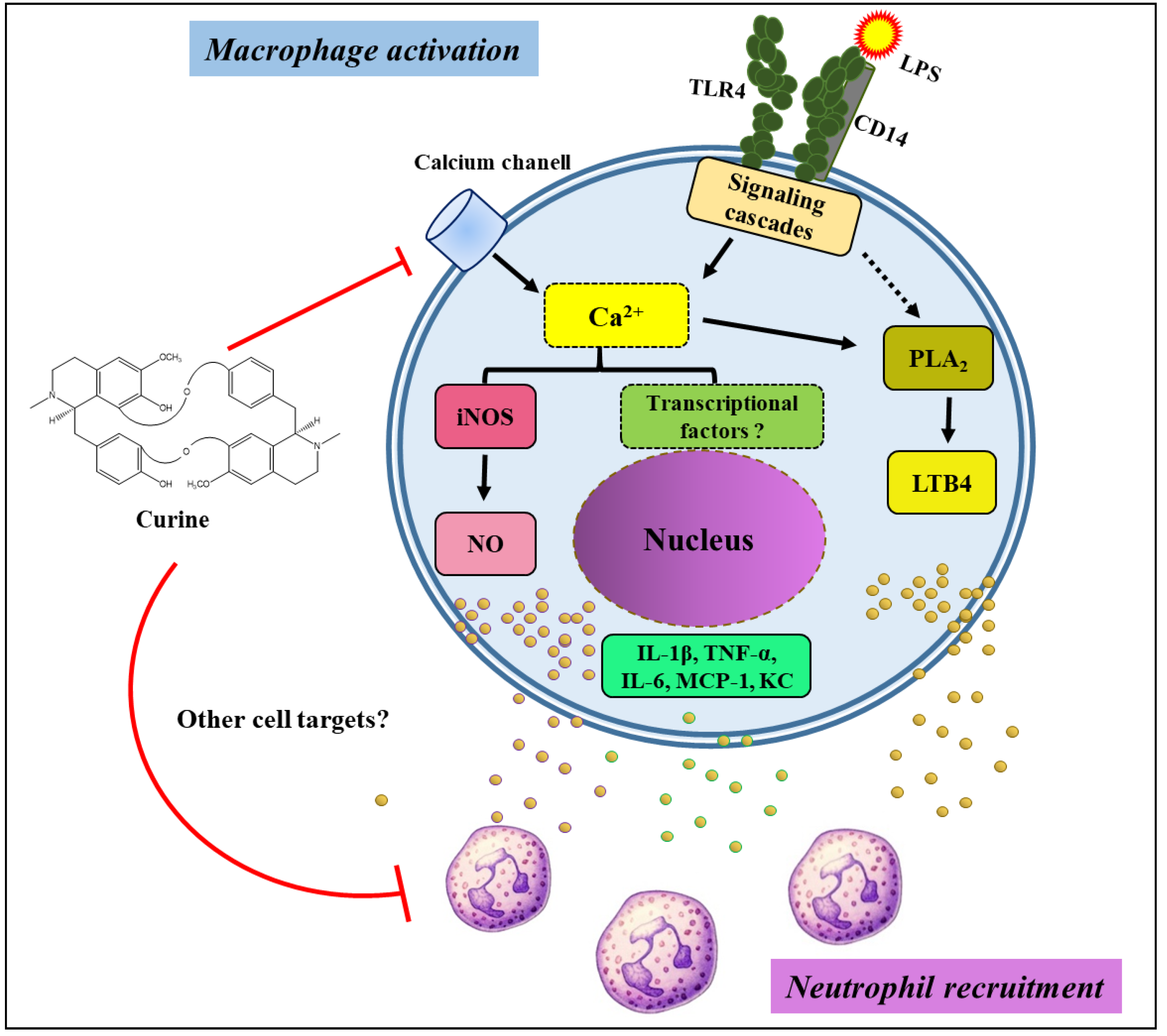
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Curine Solution
4.2. Animals
4.3. Treatments
4.4. LPS-Induced Pleurisy
4.5. Leukocyte Counting
4.6. Peritoneal Macrophage Cultures
4.7. Cytokine and LTB4 Analysis
4.8. Nitrite Quantification
4.9. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borregaard, N. Neutrophils, from marrow to microbes. Immunity 2010, 33, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dean, J.L.E.; Brook, M.; Clark, A.R.; Saklatvala, J. p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Regulates Cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA Stability and Transcription in Lipopolysaccharide-treated Human Monocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Ha, I.; Kim, K.; Park, D.; Lee, M.Y. Production of TLRs triggered pro-inflammatory cytokines through calcium dependent and independent pathways in HaCaT cells. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 184.6. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.P.; Nicholls, A.J.; Wong, C.H.Y. Partners in crime: neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages in inflammation and disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 371, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Tao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ye, W.; Zhao, D.; Fu, L.; Tian, C.; Yang, J.; He, F.; et al. Neutrophils promote the development of reparative macrophages mediated by ROS to orchestrate liver repair. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dias, C.S.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Lemos, V.S.; Cortes, S.F. Mechanisms involved in the vasodilator effect of curine in rat resistance arteries. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, P.M. Dicionário Das Plantas Úteis do Brasil e das Exóticas Cultivadas; Instituto Brasileiro de Desenvolvimento Florestal, Ministério da Agricultura: Brasília, Brasil, 1984.
- Souto, A.L.; Tavares, J.F.; Silva, M.S.; Diniz, M.F.; Athayde-Filho, P.F.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M. Anti-inflammatory activity of alkaloids: An update from 2000 to 2010. Molecules 2011, 16, 8515–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, D.N.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Lemos, V.S.; Côrtes, S.F. Mechanism of the vasodilator effect of 12-O-methylcurine in rat aortic rings. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, M.A.; Pinho, J.F.; de-Lira, D.P.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Araújo, D.A.; Cortes, S.F.; Lemos, V.S.; Cruz, J.S. Curine, abisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid, blocks L-type Ca2+ channels and decreases intracellular Ca2+ transients in A7r5 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 669, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Calheiros, A.S.; Vieira-de-Abreu, A.; Carvalho, K.I.M.; Mendes, D.S.; Bandeira-Melo, C.; Martins, M.A.; Dias, C.S.; Piuvezam, M.R.; Bozza, P.T. Curine inibits eosinophil activation and airway hyper-responsiveness in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 273, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Leite, F.C.; Costa, H.F.; Calheiros, A.S.; Torres, R.C.; de Azevedo, C.T.; Martins, M.A.; Dias, C.S.; Bozza, P.T.; Piuvezam, M.R. Curine inhibits mast cell-dependent responses in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leite, F.C.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Costa, H.F.; Salgado, P.R.; Calheiros, A.S.; Carneiro, A.B.; de Almeida, R.N.; Dias Cda, S.; Bozza, P.T.; Piuvezam, M.R. Curine, an Alkaloid Isolated from Chondrodendron platyphyllum Inhibits Prostaglandin E2 in Experimental Models of Inflammation and Pain. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.I.; Liao, J.C.; Kuo, L. Arginase modulates nitric oxide production in activated macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Piuvezam, M.R.; Moura, M.D.; Silva, M.S.; Batista-Lima, K.V.; Leitão-da-Cunha, E.V.; Fechine, I.M.; Takemura, O.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of alkaloids: A twenty-century review. Braz. J. Pharmacogn. 2006, 16, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Piuvezam, M.R.; Bozza, P.T. Anti-allergic properties of curine, a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid. Molecules 2015, 20, 4695–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosendey, M.A.E.; Bermudez, J.A.Z.; Reis, A.L.A.; Silva, H.F.; Oliveira, M.A.; Luiza, V.L. Assistência farmacêutica na atenção básica de saúde: A experiência de três estados brasileiros. Cad. Saúde Pública 2000, 16, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rainsford, K.D. Anti-inflammatory drugs in the 21st century. Sub-Cel. Biochem. 2007, 42, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amulic, B.; Cazalet, C.; Hayes, G.L.; Metzler, K.D.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Function: From Mechanisms to Disease. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 459–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, K.V.; Poluri, K.M.; Dutta, A.K.; Sepuru, K.M.; Troshkina, A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Rajarathnam, K. Chemokine CXCL1 mediated neutrophil recruitment: Role of glycosaminoglycan interactions. Sci. Rep. 2010, 6, 33123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmblad, J.; Malmsten, C.L.; Udén, A.M.; Rådmark, O.; Engstedt, L.; Samuelsson, B. Leukotriene B4 is a potent and stereospecific stimulator of neutrophil chemotaxis and adherence. Blood 1981, 58, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afonso, P.V.; Janka-Junttila, M.; Lee, Y.J.; McCann, C.P.; Oliver, C.M.; Aamer, K.A.; Losert, W.; Cicerone, M.T.; Parent, C.A. LTB4 is a signal-relay molecule during neutrophil chemotaxis. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, A.P.; Pinheiro, C.S.; Luna-Gomes, T.; Alves, L.R.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Porto, B.N.; Barja-Fidalgo, C.F.; Benjamim, C.F.; Peters-Golden, M.; Bandeira-Melo, C.; et al. Leukotriene B4 mediates neutrophil migration induced by heme. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6562–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doukas, J.; Pober, J.S. IFN-gamma enhances endothelial activation induced by tumor necrosis factor but not IL-1. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Marfaing-Koka, A.; Devergne, O.; Gorgone, G.; Portier, A.; Schall, T.J.; Galanaud, P.; Emilie, D. Regulation of the production of the RANTES chemokine by endothelial cells. Synergistic induction by IFN-gamma plus TNF-alpha and inhibition by IL-4 and IL-13. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammatory Mechanisms: The Molecular Basis of Inflammation and Disease. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophages in inflammation and Allergy. Curr. Drug Targets 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soehnlein, O.; Weber, C.; Lindbom, L. Neutrophil granule proteins tune monocytic cell function. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Kumar, S.; Jyoti, A.; Srinag, B.S.S.; Keshari, R.S.; Saluja, R.; Verma, A.; Mitra, K.; Barthwal, M.K.; Krishnamurthy, H.; et al. Nitric oxide donors release extracellular traps from human neutrophils by augmenting free radical generation. Nitric Oxide 2010, 22, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, S.; Palmer, R.M.J.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 109–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zumerle, S.; Calı, B.; Munari, F.; Angioni, R.; Virgilio, F.D.; Molon, B.; Viola, A. Intercellular Calcium Signaling Induced by ATP Potentiates Macrophage Phagocytosis. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desai, B.M.; Leitinger, N. Purinergic and calcium signaling in macrophage function and plasticity. Front. Immunol. 2010, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cunha, F.Q.; Poole, S.; Lorenzetti, B.B.; Ferreira, S.H. The pivotal role of tumour necrosis factor alpha in the development of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 107, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.H.; Lorenzetti, B.B.; Bristow, A.F.; Poole, S. Interleukin-1β as a potent hyperalgesic agent antagonized by a tripeptide analogue. Nature 1988, 334, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, Y.; Picolo, G.; Gutierrez, V.P.; Ferreira, S.H. Pain and analgesia: The dual effect of nitric oxide in the nociceptive system. Nitric Oxide 2011, 25, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambu, L.; Martin, M.T.; Razafimahefa, D.; Ramanitrahasimbola, D.; Rasoanaivo, P.; Frappier, F. Spectral characterisation and antiplasmodial activity of bisbenzylisoquinolines from Isolona ghesquiereina. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação animal (CONCEA). Procedimentos–Roedores E Lagomorfos Mantidos Em Instalações de Instituições de Ensino Ou Pesquisa Científica. Resolução Normativa N° 33, de 18 de Novembro de 2016. Available online: http://www.in.gov.br/materia/-/asset_publisher/Kujrw0TZC2Mb/content/id/22073702/do1-2016-11-21-resolucao-normativa-n-33-de-18-de-novembro-de-2016-22073453 (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- McIntyre, K. Rodent gavage technique concerns: Avoiding excess mortality. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2001, 40, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Laranjeira, A.P.; Silva, A.R.; Gomes, R.N.; Penido, C.; Henriques, M.G.M.O.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Bozza, P.T. Mechanisms of allergen- and LPS-induced bone marrow eosinophil mobilization and eosinophil accumulation into the pleural cavity: A role for CD11b/CD18 complex. Inflamm. Res. 2001, 50, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Carvalho Leite, F.; Surrage Calheiros, A.; de Brito Carneiro, A.; Alves Azeredo, J.; Fernandes de Assis, E.; da Silva Dias, C.; Regina Piuvezam, M.; T. Bozza, P. Curine Inhibits Macrophage Activation and Neutrophil Recruitment in a Mouse Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation. Toxins 2019, 11, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120705
Ribeiro-Filho J, Carvalho Leite F, Surrage Calheiros A, de Brito Carneiro A, Alves Azeredo J, Fernandes de Assis E, da Silva Dias C, Regina Piuvezam M, T. Bozza P. Curine Inhibits Macrophage Activation and Neutrophil Recruitment in a Mouse Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation. Toxins. 2019; 11(12):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120705
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro-Filho, Jaime, Fagner Carvalho Leite, Andrea Surrage Calheiros, Alan de Brito Carneiro, Juliana Alves Azeredo, Edson Fernandes de Assis, Celidarque da Silva Dias, Márcia Regina Piuvezam, and Patrícia T. Bozza. 2019. "Curine Inhibits Macrophage Activation and Neutrophil Recruitment in a Mouse Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation" Toxins 11, no. 12: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120705
APA StyleRibeiro-Filho, J., Carvalho Leite, F., Surrage Calheiros, A., de Brito Carneiro, A., Alves Azeredo, J., Fernandes de Assis, E., da Silva Dias, C., Regina Piuvezam, M., & T. Bozza, P. (2019). Curine Inhibits Macrophage Activation and Neutrophil Recruitment in a Mouse Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation. Toxins, 11(12), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120705






