Astaxanthin Protects OTA-Induced Lung Injury in Mice through the Nrf2/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physiological Index
2.2. Mice Lung Organ Ratios
2.3. Pathological Changes in Lung Organ
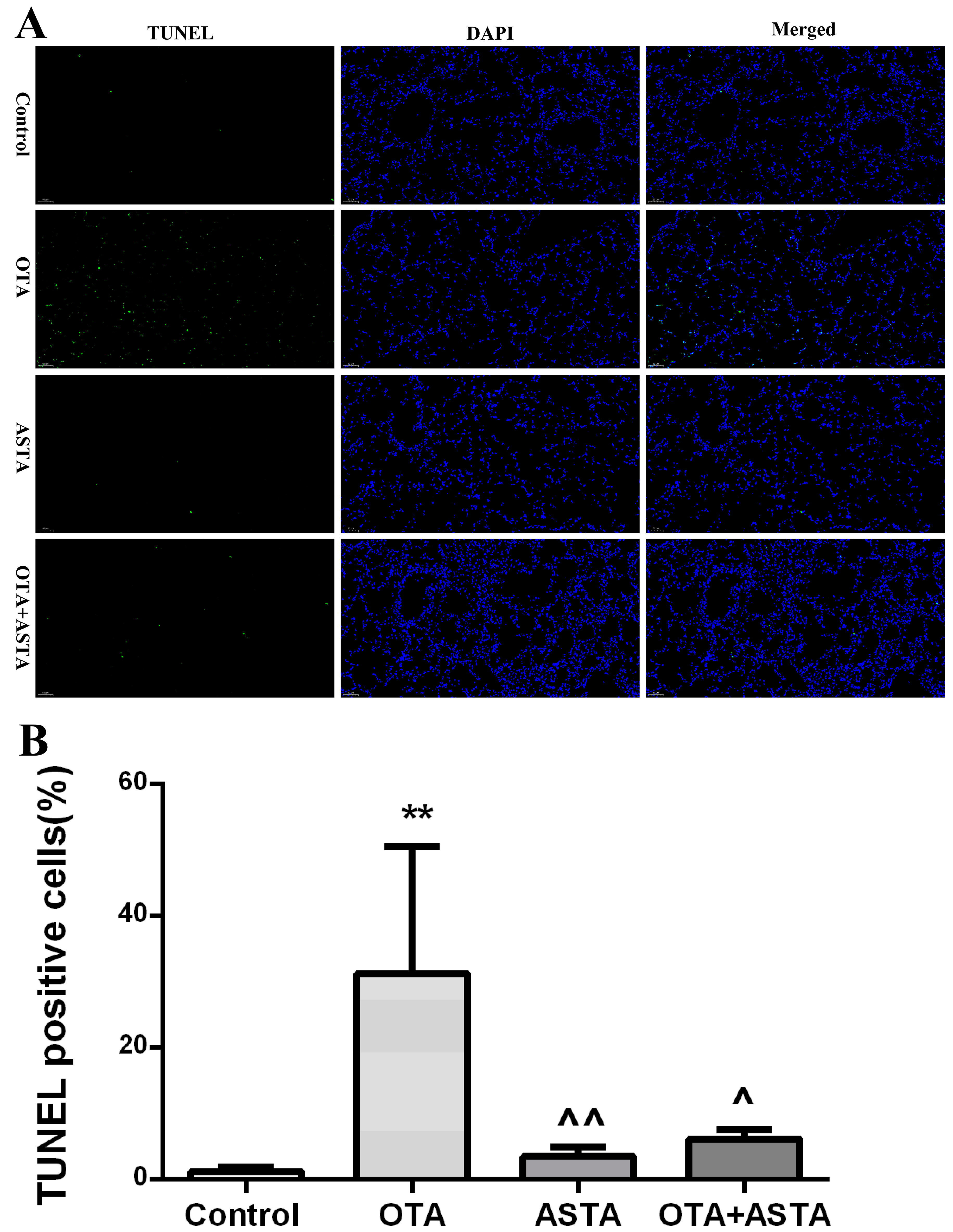
2.4. Analysis of Apoptosis by TUNEL in Mouse Lung
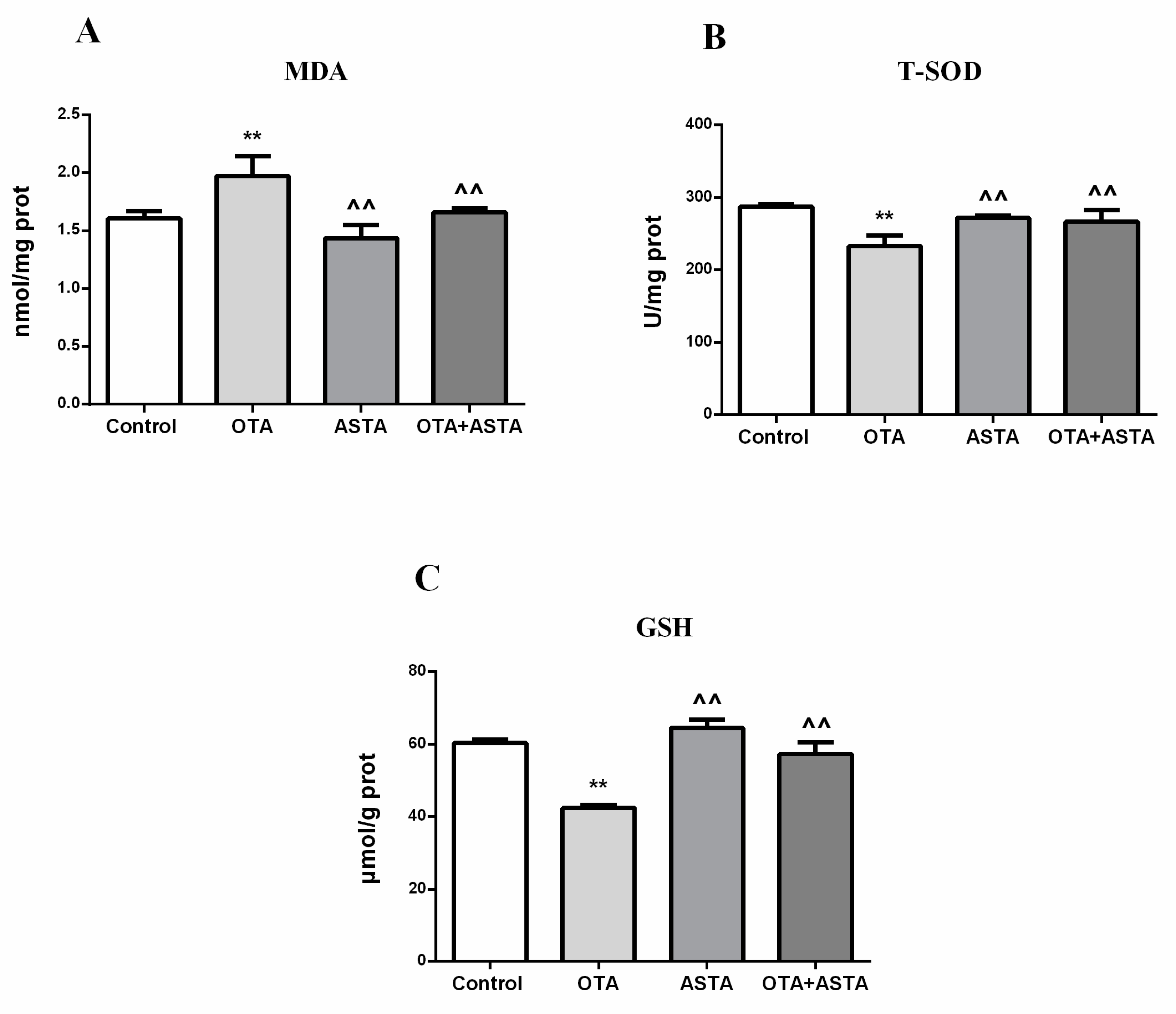
2.5. Changes of the Oxidation Index in the Lungs
2.6. Changes in Inflammation Markers in the Lungs
2.7. Changes in the Expression of Nrf2, Keap1, HO-1, and MnSOD in Mice Lungs
2.8. Changes in the Expression of TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB in Mice Lungs
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals
5.2. Experimental Design and Treatment
5.3. Pulmonary Organ Indices
5.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
5.5. TUNEL Apoptosis Analysis
5.6. Oxidation Assays in Mice Lungs
5.7. Inflammation Indices in Mice Lungs
5.8. Western Blot Analysis
5.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ringot, D.; Chango, A.; Schneider, Y.J.; Larondelle, Y. Toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics of ochratoxin A, an update. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 159, 18–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Su, J.; Lin, J.; Qian, G.; Chen, X.; Song, S.; Huang, K. Activation of AMPK-dependent SIRT-1 by astragalus polysaccharide protects against ochratoxin A-induced immune stress in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Novotna, E. Toxicity of the mycotoxin ochratoxin A in the light of recent data. Toxin Rev. 2013, 32, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. Ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 51, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, V.; Reunova, O.; Velasquez, A.; Harbison, R.; Sanchez-Ramos, J. Acute neurotoxic effects of the fungal metabolite ochratoxin-A. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sava, V.; Velasquez, A.; Song, S.; Sanchez-Ramos, J. Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells In Vitro Are Vulnerable to the Mycotoxin Ochratoxin-A. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 98, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Malir, J.; Toman, J. Ochratoxin A: 50 Years of Research. Toxins 2016, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinelli, E.; Adlouni, C.E.; Pipy, B.; Quartulli, F.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Roles of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenases in ochratoxin A genotoxicity in human epithelial lung cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1999, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, N.; Guarnieri, A.; Loi, F.; Sacchi, G.; Mangiarotti, A.M.; Di Paolo, M. Acute renal failure from inhalation of mycotoxins. Nephron 1993, 64, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, J.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; De Saeger, S.; Wu, A. Combinatorial approach of LC-MS/MS and LC-TOF-MS for uncovering in vivo kinetics and biotransformation of ochratoxin A in rat. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 925, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Pyo, M.C.; Shin, H.S.; Ryu, D.; Lee, K.W. Renal toxicity through AhR, PXR, and Nrf2 signaling pathway activation of ochratoxin A-induced oxidative stress in kidney cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouaziz, C.; Sharaf el dein, O.; Martel, C.; El Golli, E.; Abid-Essefi, S.; Brenner, C.; Lemaire, C.; Bacha, H. Molecular events involved in ochratoxin A induced mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis, modulation by Bcl-2 family members. Environ. Toxicol. 2011, 26, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaug, M.A.; Eduard, W.; Størmer, F.C. Ochratoxin A in airborne dust and fungal conidia. Mycopathologia 2001, 151, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okutan, H.; Aydin, G.; Ozcelik, N. Protective role of melatonin in ochratoxin a toxicity in rat heart and lung. J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2004, 24, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creppy, E.E.; Röschenthaler, R.; Dirheimer, G. Inhibition of protein synthesis in mice by ochratoxin A and its prevention by phenylalanine. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1984, 22, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Martin, M.; Bartsch, H.; Rahimtula, A.D. Perturbation of liver microsomal calcium homeostasis by ochratoxin A. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1989, 38, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Xing, L.; Shen, H.; Wu, S.; Lian, H.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X. Ochratoxin A induces oxidative DNA damage and G1 phase arrest in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashkow, F.J.; Watumull, D.G.; Campbell, C.L. Astaxanthin: A novel potential treatment for oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, S58–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Seo, J.M.; Nguyen, A.; Pham, T.X.; Park, H.J.; Park, Y.; Kim, B.; Bruno, R.S.; Lee, J. Astaxanthin-rich extract from the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis lowers plasma lipid concentrations and enhances antioxidant defense in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, G.; Sankawa, U.; Goto, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. Astaxanthin, a Carotenoid with Potential in Human Health and Nutrition. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, Y.M. Antioxidant Activities of Astaxanthin and Related Carotenoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuzawa, K.; Inokami, Y.; Tokumura, A.; Terao, J.; Suzuki, A. Rate constants for quenching singlet oxygen and activities for inhibiting lipid peroxidation of carotenoids and α-tocopherol in liposomes. Lipids 1998, 33, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinsky, N.I. Antioxidant functions of carotenoids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1989, 7, 617–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhn, K.; Hyeyoung, K. Inhibitory Effect of Astaxanthin on Oxidative Stress-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction-A Mini-Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1137. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.L.; Han, X.D.; Li, Y.; Chu, X.F.; Miao, W.M.; Zhang, J.L.; Fan, S.J. Astaxanthin attenuates total body irradiation-induced hematopoietic system injury in mice via inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Guo, S.; Zhou, H.; Han, R.; Wu, P.; Han, C. Astaxanthin protects against early burn-wound progression in rats by attenuating oxidative stress-induced inflammation and mitochondria-related apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.X.; Zhou, H.L.; Huang, C.L.; You, C.G.; Fang, Q.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.G.; Han, C.M. Astaxanthin attenuates early acute kidney injury following severe burns in rats by ameliorating oxidative stress and mitochondrial-related apoptosis. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2105–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, B.; Lin, S.; Jing, L.; Mao, C.; Xu, P.; Lv, C.; Liu, W.; Zuo, J. Astaxanthin inhibits apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells type II in vivo and in vitro through the ROS-dependent mitochondrial signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 2198–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, W. Effects of astaxanthin and esterified glucomannan on hematological and serum parameters, and liver pathological changes in broilers fed aflatoxin-B1-contaminated feed. Anim. Sci. J. 2014, 85, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Shen, T.F.; Pang, V.F.; Chen, B.J. Effects of aflatoxin and carotenoids on growth performance and immune response in mule ducklings. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 128, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradelet, S.; Astorg, P.; Bon, A.-M.L.; Bergès, R.; Suschetet, M. Modulation of aflatoxin B1 carcinogenicity, genotoxicity and metabolism in rat liver by dietary carotenoids: Evidence for a protective effect of CYP1A inducers. Cancer Lett. 1997, 114, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peteri, Z.; Teren, J.; Vagvolgyi, C.; Varga, J. Ochratoxin degradation and adsorption caused by astaxanthin-producing yeasts. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Wu, R.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, C.S.; Zhang, W.D.; Ge, W.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.Y.; Zou, S.H.; Shen, W. Ochratoxin A exposure decreased sperm motility via the AMPK and PTEN signaling pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 340, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Ochratoxin A and aristolochic acid involvement in nephropathies and associated urothelial tract tumours. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2009, 60, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Pyo, M.C.; Ryu, D.; Lee, K.W. Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity through Phase I and Phase II Reactions Regulated by AhR in Liver Cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrenti, V.; Di Giacomo, C.; Acquaviva, R.; Barbagallo, I.; Bognanno, M.; Galvano, F. Toxicity of ochratoxin a and its modulation by antioxidants: A review. Toxins 2013, 5, 1742–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, J.H.; Hope, B.E. A review of the diagnosis and treatment of Ochratoxin A inhalational exposure associated with human illness and kidney disease including focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 835059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, Y.C. Impact of oxidative stress on lung diseases. Respirology 2009, 14, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykiotis, G.P.; Habeos, I.G.; Samuelson, A.V.; Bohmann, D. The role of the antioxidant and longevity-promoting Nrf2 pathway in metabolic regulation. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachev, V.O.; Menshchikova, E.B.; Zenkov, N.K. Mechanism of the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling system. Biochemistry 2011, 76, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kensler, T.W.; Wakabayashi, N.; Biswal, S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykiotis, G.P.; Bohmann, D. Stress-activated cap ‘n’collar transcription factors in aging and human disease. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, re3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Li, J.; Johnson, D.A.; Stein, T.D.; Kraft, A.D.; Calkins, M.J.; Jakel, R.J.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2, a multi-organ protector? FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M. Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiprasongsuk, A.; Janjetovic, Z.; Kim, T.K.; Jarrett, S.G.; D’Orazio, J.A.; Holick, M.F.; Tang, E.K.Y.; Tuckey, R.C.; Panich, U.; Li, W.; et al. Protective effects of novel derivatives of vitamin D3 and lumisterol against UVB-induced damage in human keratinocytes involve activation of Nrf2 and p53 defense mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Hao, S.; Gan, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Huang, K. In vitro immune toxicity of ochratoxin A in porcine alveolar macrophages: A role for the ROS-relative TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 272, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Tang, S.; Su, F. Dioscin inhibits ischemic strokeinduced inflammation through inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NFkappaB signaling pathway in a rat model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Su, R.; Song, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, L.; Ma, J.; Yang, H. Positive Correlation between Enhanced Expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB with Insulin Resistance in Placentae of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirshahrokhi, K.; Khalili, A.R. Carvedilol attenuates paraquat-induced lung injury by inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokine MCP-1, NF-kappaB activation and oxidative stress mediators. Cytokine 2016, 88, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibi, D.; Kijima, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Jin, M.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Yanai, T.; Nishikawa, A.; Umemura, T. Effects of p53 knockout on ochratoxin A-induced genotoxicity in p53-deficient gpt delta mice. Toxicology 2013, 304, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Meng, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Gao, M. Astaxanthin ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis and peritubular capillary rarefaction in unilateral ureteral obstruction. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3168–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Wang, M.; Cui, G.; Li, L.; Jiao, D.; Yao, B.; Xu, K.; Chen, Y.; Long, M.; Yang, S.; et al. Astaxanthin Protects OTA-Induced Lung Injury in Mice through the Nrf2/NF-κB Pathway. Toxins 2019, 11, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090540
Xu W, Wang M, Cui G, Li L, Jiao D, Yao B, Xu K, Chen Y, Long M, Yang S, et al. Astaxanthin Protects OTA-Induced Lung Injury in Mice through the Nrf2/NF-κB Pathway. Toxins. 2019; 11(9):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090540
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Weixiang, Mingyang Wang, Gengyuan Cui, Lin Li, Danyang Jiao, Beibei Yao, Ketao Xu, Yueli Chen, Miao Long, Shuhua Yang, and et al. 2019. "Astaxanthin Protects OTA-Induced Lung Injury in Mice through the Nrf2/NF-κB Pathway" Toxins 11, no. 9: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090540
APA StyleXu, W., Wang, M., Cui, G., Li, L., Jiao, D., Yao, B., Xu, K., Chen, Y., Long, M., Yang, S., & He, J. (2019). Astaxanthin Protects OTA-Induced Lung Injury in Mice through the Nrf2/NF-κB Pathway. Toxins, 11(9), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090540





