Qualifying the T-2 Toxin-Degrading Properties of Seven Microbes with Zebrafish Embryo Microinjection Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
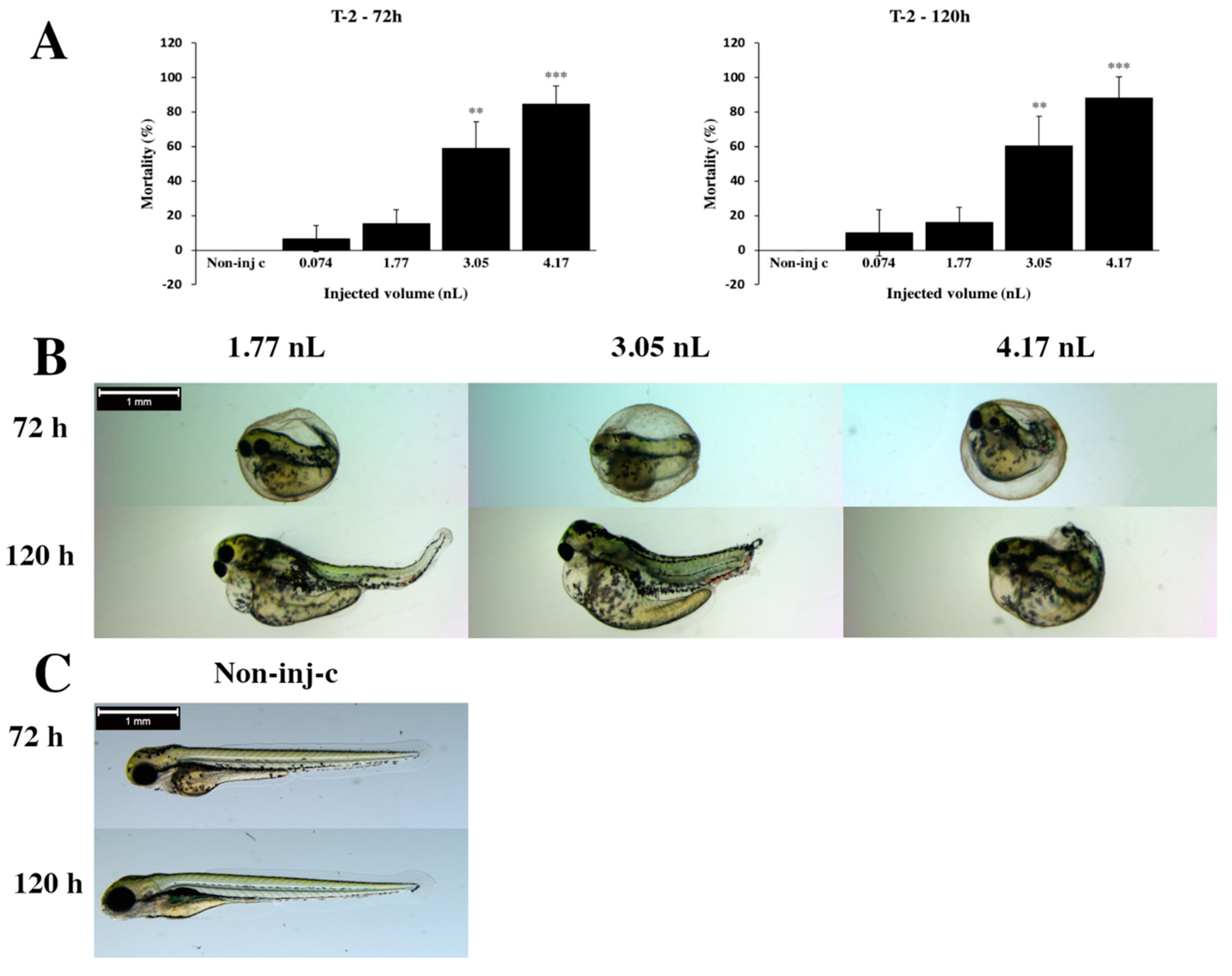
2.1. Effects of T-2 on Injected Zebrafish Embryos
2.2. Effects of Bacterial Metabolites and Degradation Products on Injected Embryos
2.3. Analytical Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Material and Methods
5.1. Animal Protection
5.2. Bacterial Experiments
5.3. Analytical Measurement
5.4. Maintenance of Zebrafish and Egg Collection
5.5. Microinjection
5.6. Toxicological Endpoints
5.7. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marroquin-Cardona, A.; Johnson, N.; Phillips, T.D.; Hayes, A.W. Mycotoxins in a changing global environment—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 69, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, E.; Schatzmayr, G.; Tassis, P.; Tzika, E.; Marin, D.E.; Taranu, I.; Tabuc, C.; Nicolau, A.I.; Aprodu, I.; Puel, O.; et al. Current Situation of Mycotoxin Contamination and Co-occurrence in Animal Feed—Focus on Europe. Toxins 2012, 4, 788–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pestka, J.J. Application of immunology to the analysis and toxicity assessment of mycotoxins. Food Agric. Immunol. 1994, 6, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F. Measuring the economic impacts of Fusarium toxins in animal feeds. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, T.; Young, J.C.; Boland, G.J.; Scott, P.M. Chemical and biological transformations for detoxification of trichothecene mycotoxins in human and animal food chains: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, E.M. Managing the risk of mycotoxins in modern feed production. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2007, 133, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.; Binder, E.M.; Heidler, D.; Krska, R. Structural characterization of metabolites after the microbial degradation of type A trichothecenes by the bacterial strain BBSH 797. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mycotoxins: Risks in Plant, Animal, and Human Systems; CAST Report; Council for Agricultural Science and Technology: Ames, IA, USA, 2003; ISBN 1-887383-22-0.
- Hsu, I.-C.; Smalley, E.B.; Strong, F.M.; Ribelin, W.E. Identification of T-2 Toxin in Moldy Corn Associated with a Lethal Toxicosis in Dairy Cattle. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalantari, H.; Moosavi, M. Review on T-2 Toxin. Jundishapur J. Natl. Pharm. Prod. 2010, 5, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on Fusarium Toxins Part 5: T-2 Toxin and HT-2 Toxin; European Comission: Brussels, Belgium, 2001.
- Selected Mycotoxins: Ochratoxins, Trichothecenes, Ergot; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1990; ISBN 92-4-157105-5.
- Boonchuvit, B.; Hamilton, P.B.; Burmeister, H.R. Interaction of T-2 Toxin with Salmonella Infections of Chickens. Poult. Sci. 1975, 54, 1693–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, K.; Kondo, E. Decreased Resistance to Mycobacterial Infection in Mice Fed a Trichothecene Compound (T-2 Toxin). Jpn. J. Med Sci. Biol. 1984, 37, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarom, R. T-2 toxin effect on bacterial infection and leukocyte functions. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1984, 75, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesan, V.; Rukmini, C.; Vijayaraghavan, M.; Tulpule, P. Immune studies with T-2 toxin: Effect of feeding and withdrawal in monkeys. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1982, 20, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poston, H.A.; Coffin, J.L.; Combs, G.F. Biological effects of dietary T-2 toxin on rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Aquat. Toxicol. 1982, 2, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Huang, L.; Peng, S. T-2 toxin induces developmental toxicity and apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardall, J.M.; Miller, J.D. Diseases in Humans with Mycotoxins as Possible Causes. In Mycotoxins in Grain: Compounds Other than Aflatoxin; Miller, J., Trenholm, H., Eds.; Eagan Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1994; p. 552. ISBN 0962440752. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, R.; Ramakrishna, Y.; Beedu, S.; Munshi, K. Outbreak of Trichothecene Mycotoxicosis Associated with Consumption of Mould-Damaged Wheat Products in Kashmir Valley, India. Lancet 1989, 333, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffe, A.Z. Toxicity of Fusarium Poae and F. sporotrichioides and Its Relation to Alimentary Toxic Aleukia. In Mycotoxins; Purchase, I.F.H., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1974; pp. 229–262. [Google Scholar]
- Bata, A. Detoxification of mycotoxin-contaminated food and feed by microorganisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, M.J.; White, D.G. Identifying Sources of Resistance to Aflatoxin and Fumonisin Contamination in Corn Grain. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2004, 23, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkvold, G.P. Cultural Andgeneticapproaches Tomanagingmycotoxins Inmaize. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2003, 41, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Sinha, K. Insect pests, Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin contamination in stored wheat: A survey at North Bihar (India). J. Stored Prod. Res. 1990, 26, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champeil, A.; Fourbet, J.; Doré, T.; Rossignol, L. Influence of cropping system on Fusarium head blight and mycotoxin levels in winter wheat. Crop. Prot. 2004, 23, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, J.W.; Cole, R.J. Effect of application of nontoxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus on subsequent aflatoxin contamination of peanuts in storage. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2002, 38, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jard, G.; Liboz, T.; Mathieu, F.; Guyonvarc’H, A.; Lebrihi, A. Review of mycotoxin reduction in food and feed: From prevention in the field to detoxification by adsorption or transformation. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 1590–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerre, P. Interest of the treatments of raw materials and usage of adsorbents to decontaminate animal food containing mycotoxins. Rev. Méd. Vét. 2000, 151, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Kabak, B.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Var, I. Strategies to Prevent Mycotoxin Contamination of Food and Animal Feed: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, P.A.; Rice, J.L.G.; Ross, P.F. Fumonisin B1, B2 and B3 content of Iowa, Wiscinsin, Illinois corn and screenings. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, E.P.; Szafraniec, L.L. Hypochlorite-Promoted Transformations of Trichothecenes, 3. Deoxynivalenol. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freimund, S.; Sauter, M.; Rys, P. Efficient Adsorption of the Mycotoxins Zearalenone and T?2 Toxin on a Modified Yeast Glucan. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2003, 38, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorska, J.E.; Pappas, A.C.; Karadas, F.; Speake, B.K.; Surai, P.F. Protective effect of modified glucomannans and organic selenium against antioxidant depletion in the chicken liver due to T-2 toxin-contaminated feed consumption. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 145, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubena, L.F.; Edrington, T.S.; Harvey, R.; Buckley, S.; Phillips, T.D.; Rottinghaus, G.; Casper, H.H. Individual and combined effects of fumonisin B1 present in Fusarium moniliforme culture material and T-2 toxin or deoxynivalenol in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 1997, 76, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, M.; Devegowda, G. Influence of esterified-glucomannan on performance and organ morphology, serum biochemistry and haematology in broilers exposed to individual and combined mycotoxicosis (aflatoxin, ochratoxin and T-2 toxin). Br. Poult. Sci. 2000, 41, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, A.; Aly, S. Biological detoxification of mycotoxins: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserhati, M.; Kriszt, B.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Hahn, J.; Toth, S.; Nagy, I.; Kukolya, J. Mycotoxin-degradation profile of Rhodococcus strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeton, S.; Bull, A.T. Biotransformation and detoxification of T-2 toxin by soil and freshwater bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueno, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Ishii, K.; Tashiro, F.; Minoda, Y.; Omori, T.; Komagata, K. Metabolism of T-2 toxin in Curtobacterium sp. strain 114-2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuca, K.; Dohnal, V.; Jezkova, A.; Jun, D. Metabolic pathways of T-2 toxin. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher-Wolz, U.; Heine, K.; Schneider, K. Report on toxicity data on trichothecene mycotoxins HT-2 and T-2 toxins. EFSA Support. Publ. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Dohnal, V.; Huang, L.; Ramalho, T.C.; Yuan, Z. Metabolic pathways of trichothecenes. Drug Metab. Rev. 2010, 42, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudergue, C.; Burel, C.; Dragacci, S.; Favrot, M.; Fremy, J.; Massimi, C.; Prigent, P.; Debongnie, P.; Pussemier, L.; Boudra, H.; et al. Review of mycotoxin-detoxifying agents used as feed additives: Mode of action, efficacy and feed/food safety. EFSA Support. Publ. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Statement on the establishment of guidelines for the assessment of additives from the functional group ‘substances for reduction of the contamination of feed by mycotoxins’. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csenki-Bakos, Z.; Garai, E.; Risa, A.; Cserháti, M.; Bakos, K.; Márton, D.; Bokor, Z.; Kriszt, B.; Urbányi, B. Biological evaluation of microbial toxin degradation by microinjected zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, S.; Keddig, N.; Hanel, R.; Kammann, U. Microinjection into zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio)—A useful tool in aquatic toxicity testing? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, M.; Negi, B.; Kaushik, N.; Adhikari, A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. T-2 mycotoxin: Toxicological effects and decontamination strategies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33933–33952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueno, Y. Toxicological features of T-2 toxin and related trichothecenes. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1984, 4, S124–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.-C.; Gentry, P. LD50 values and serum biochemical changes induced by T-2 toxin in rats and rabbits. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1984, 73, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.S.; Mirocha, C.J.; Kurtz, H.J.; Weaver, G.; Bates, F.; Shimoda, W.; Burmeister, H.R. Acute Toxicity of T-2 Toxin in Broiler Chicks and Laying Hens. Poult. Sci. 1977, 56, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y. Trichothecene Mycotoxins Mycology, Chemistry, and Toxicology. In Advances in Nutritional Research; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 301–353. [Google Scholar]
- Jewers, K. Mycotoxins and Their Effect on Poultry Production. In L’aviculture en Méditerranée; Saveur, B., Ed.; Montpellier CIHEAM: Belgrade, Yugoslavia, 1990; pp. 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Devreese, M.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Different methods to counteract mycotoxin production and its impact on animal health. Vlaams Diergeneeskundig Tijdschrift 2013, 82, 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, K.; Ishigami, N.; Sehata, S. T-2 Toxin-induced Toxicity in Pregnant Mice and Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2146–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyatt, R.D.; Weeks, B.A.; Hamilton, P.B.; Burmeister, H.R. Severe Oral Lesions in Chickens Caused by Ingestion of Dietary Fusariotoxin T-21. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheeke, P.R. Endogenous toxins and mycotoxins in forage grasses and their effects on livestock. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Háhn, J.; Szoboszlay, S.; Tóth, G.; Kriszt, B. Assessment of bacterial biodetoxification of herbicide atrazine using Aliivibrio fischeri cytotoxicity assay with prolonged contact time. Ecotoxicology 2017, 52, 279–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachitha, P.; Khanum, F. T-2 mycotoxin induced toxicity: A review. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2014, 6, 10798–10806. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Lee, H.-H.; Youn, K.; Kim, S.; Jung, B.; Lee, J.; Seo, Y.-S. Transcriptome analyses to understand effects of the Fusarium deoxynivalenol and nivalenol mycotoxins on Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 192, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| T-2 Concentration of Degradation Samples (mg/L) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supernatant | Pellet | |||||||||||
| A | B | C | Mean | SD | A | B | C | Mean | SD | |||
| AK38 | 5.81 | 5.49 | 4.94 | 5.42 | 0.44 | AK38 | 2.53 | 1.55 | 1.11 | 1.73 | 0.73 | |
| N774 | 2.29 | 0.18 | 1.68 | 1.39 | 1.09 | N774 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| N58 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | N58 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| NI2 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | NI2 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| NI1 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | NI1 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| N361 | 6.61 | 6.48 | 5.78 | 6.29 | 0.45 | N361 | 0.78 | 0.48 | 1.26 | 0.87 | 0.39 | |
| NZS14 | 0.03 | 2.43 | 1.89 | 1.45 | 1.26 | NZS14 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garai, E.; Risa, A.; Varga, E.; Cserháti, M.; Kriszt, B.; Urbányi, B.; Csenki, Z. Qualifying the T-2 Toxin-Degrading Properties of Seven Microbes with Zebrafish Embryo Microinjection Method. Toxins 2020, 12, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070460
Garai E, Risa A, Varga E, Cserháti M, Kriszt B, Urbányi B, Csenki Z. Qualifying the T-2 Toxin-Degrading Properties of Seven Microbes with Zebrafish Embryo Microinjection Method. Toxins. 2020; 12(7):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070460
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarai, Edina, Anita Risa, Emese Varga, Mátyás Cserháti, Balázs Kriszt, Béla Urbányi, and Zsolt Csenki. 2020. "Qualifying the T-2 Toxin-Degrading Properties of Seven Microbes with Zebrafish Embryo Microinjection Method" Toxins 12, no. 7: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070460
APA StyleGarai, E., Risa, A., Varga, E., Cserháti, M., Kriszt, B., Urbányi, B., & Csenki, Z. (2020). Qualifying the T-2 Toxin-Degrading Properties of Seven Microbes with Zebrafish Embryo Microinjection Method. Toxins, 12(7), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070460




