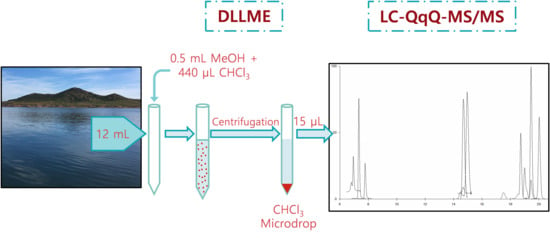
Monitoring Lipophilic Toxins in Seawater Using Dispersive Liquid—Liquid Microextraction and Liquid Chromatography with Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
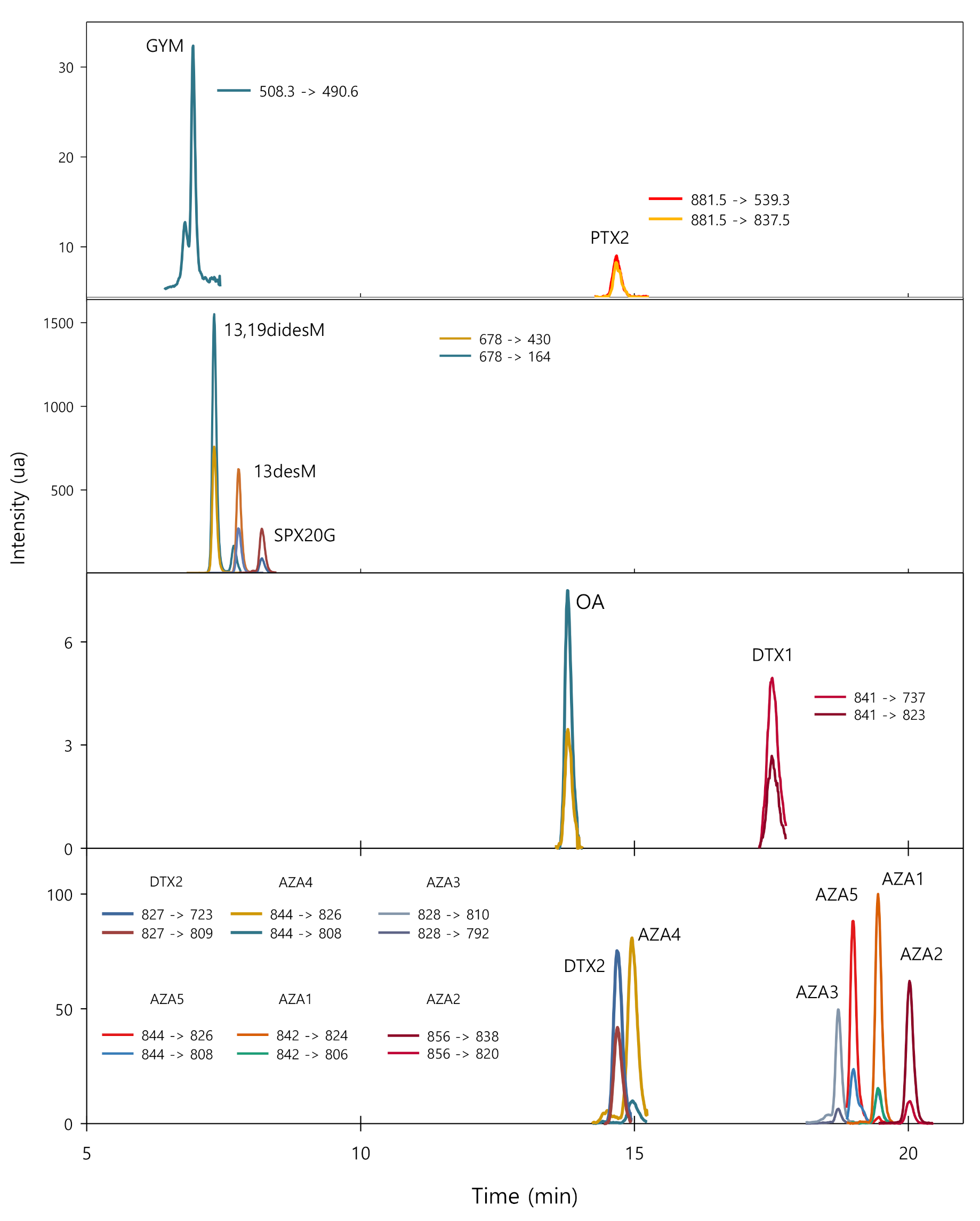
2.1. Chromatographic Separation and MS Conditions
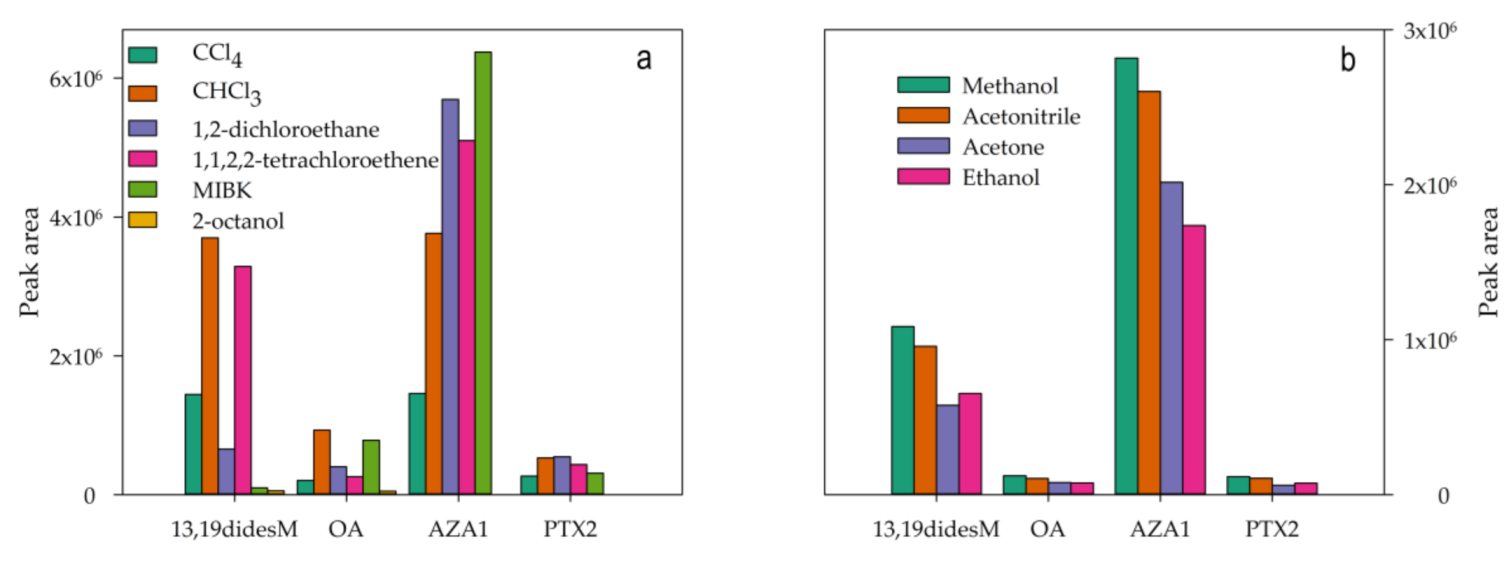
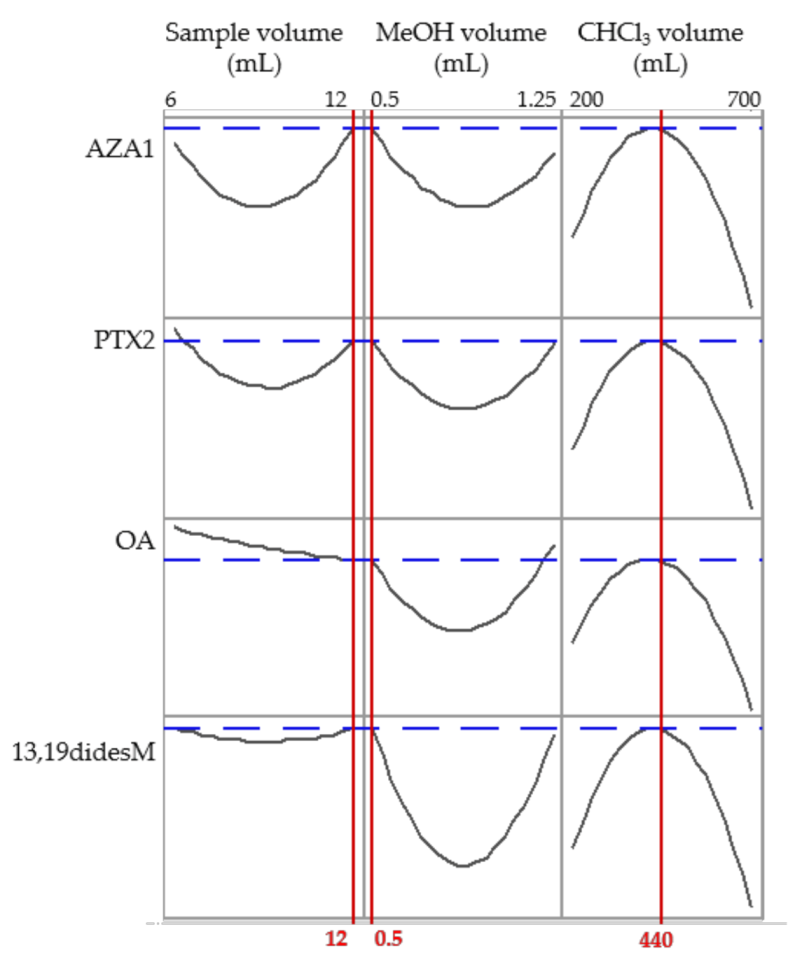
2.2. Optimization of the DLLME Procedure
2.3. Validation of the Procedure and Matrix Effect
2.4. Analysis of Seawater Samples
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Instrumentation
4.3. Samples
4.4. Analytical Procedure
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humbert, J.F. Advances in the detection of phycotoxins and cyanotoxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1653–1654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orellana, G.; Van Meulebroek, L.; De Rijcke, M.; Janssen, C.R.; Vanhaecke, L. High resolution mass spectrometry-based screening reveals lipophilic toxins in multiple trophic levels from the North Sea. Harmful Algae 2017, 64, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamee, S.E.; Medlin, L.K.; Kegel, J.; McCoy, G.R.; Raine, R.; Barra, L.; Ruggiero, M.V.; Kooistra, W.H.C.F.; Montresor, M.; Hagstrom, J.; et al. Distribution, occurrence and biotoxin composition of the main shellfish toxin producing microalgae within European waters: A comparison of methods of analysis. Harmful Algae 2016, 55, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernández, R.; Mamán, L.; Jaén, D.; Fuentes, L.F.; Ocaña, M.A.; Gordillo, M.M. Dinophysis species and diarrhetic shellfish toxins: 20 years of monitoring program in Andalusia, South of spain. Toxins 2019, 11, 189. [Google Scholar]
- Palenzuela, J.M.T.; Vilas, L.G.; Bellas, F.M.; Garet, E.; González-Fernández, Á.; Spyrakos, E. Pseudo-nitzschia blooms in a coastal upwelling system: Remote sensing detection, toxicity and environmental variables. Water 2019, 11, 1954–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Paches, M.; Aguado, D.; Martínez-Guijarro, R.; Romero, I. Long-term study of seasonal changes in phytoplankton community structure in the western Mediterranean (Valencian Community). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14266–14276. [Google Scholar]
- Alcolea, A.; Contreras, S.; Hunink, J.E.; García-Aróstegui, J.L.; Jiménez-Martínez, J. Hydrogeological modelling for the watershed management of the Mar Menor coastal lagoon (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 901–914. [Google Scholar]
- Soria, J.; Caniego, G.; Hernández-Sáez, N.; Dominguez-Gomez, J.A.; Erena, M. Phytoplankton distribution in Mar Menor coastal lagoon (SE Spain) during 2017. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 600–618. [Google Scholar]
- Alarcan, J.; Biré, R.; Le Hégarat, L.; Fessard, V. Mixtures of lipophilic phycotoxins: exposure data and toxicological assessment. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Fessard, V.; Le Hégarat, L. A strategy to study genotoxicity: Application to aquatic toxins, limits and solutions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Regulation 2019/627 of 15 March 2019 laying down uniform practical arrangements for the performance of official controls on products of animal origin intended for human consumption. Off. J. Eur. Union L 2019, 131, 51–100. [Google Scholar]
- Puech, L.; Dragacci, S.; Gleizes, E.; Fremy, J.M. Use of immunoaffinity columns for clean-up of diarrhetic toxins (okadaic acid and dinophysistoxins) extracts from shellfish prior to their analysis by HPLC/fluorimetry. Food Addit. Contam. 1999, 16, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilliam, M.A. Analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins in shellfish tissue by liquid chromatography with fluorometric and mass spectrometric detection. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regueiro, J.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Álvarez, G.; Blanco, J. Automated on-line solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Gong, L.; Baibado, J.T.; Dong, W.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Cheung, H.Y. Graphene based pipette tip solid phase extraction of marine toxins in shellfish muscle followed by UPLC-MS/MS analysis. Talanta 2013, 116, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- These, A.; Scholz, J.; Preiss-Weigert, A. Sensitive method for the determination of lipophilic marine biotoxins in extracts of mussels and processed shellfish by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on enrichment by solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4529–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, A.; Li, D.; Zhao, J. Determination of lipophilic marine toxins in fresh and processed shellfish using modified QuEChERS and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fux, E.; McMillan, D.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Development of an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the detection of lipophilic marine toxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1157, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yao, J.; Guo, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhai, Y. Distribution of marine lipophilic toxins in shellfish products collected from the chinese market. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4281–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroney, C.; Lehane, M.; Braña-Magdalena, A.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Comparison of solid-phase extraction methods for the determination of azaspiracids in shellfish by liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 963, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Shi, Q.; Cao, W.; Zheng, X.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L. Determination of typical lipophilic marine toxins in marine sediments from three coastal bays of China using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after accelerated solvent extraction. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Cao, W.; Sun, C.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X. Screening of lipophilic marine toxins in marine aquaculture environment using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Hong, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y. Polymeric ion exchange material based dispersive micro solid-phase extraction of lipophilic marine toxins in seawater followed by the Q Exactive mass spectrometer analysis using a scheduled high resolution parallel reaction monitoring. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, R.C.; Kong, F.-Z.; Li, C.; Dai, L.; Chen, Z.-F.; Zhou, M.J. Lipophilic marine toxins discovered in the Bohai Sea using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilliam, M.A.; Xie, M.; Hardstaff, W.R. Rapid extraction and cleanup for liquid chromatography determination of domoic acid in unsalted seafood. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Han, T.; Li, X.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Song, X.; Zhou, D.; Wang, X. Occurrence and distribution of marine natural organic pollutants: Lipophilic marine algal toxins in the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Detection, occurrence and monthly variations of typical lipophilic marine toxins associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in the coastal seawater of Qingdao City, China. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch-Orea, C.; Sanchís, J.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Analysis of lipophilic marine biotoxins by liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry in seawater from the Catalan Coast. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5451–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendong, Z.; Kadiri, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Nézan, E.; Mazzeo, A.; Hess, P. Algal toxin profiles in Nigerian coastal waters (Gulf of Guinea) using passive sampling and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2016, 114, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Reversed-phase/weak anion exchange magnetic mesoporous microspheres for removal of matrix effects in lipophilic marine biotoxins analysis by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Campillo, C.; Pastor-Belda, M.; Campillo, N.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Hernández-Córdoba, M.; Viñas, P. Determination of cyanotoxins and phycotoxins in seawater and algae-based food supplements using ionic liquids and liquid chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Toxins 2019, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerssen, A.; McElhinney, M.A.; Mulder, P.P.J.; Bire, R.; Hess, P.; De Boer, J. Solid phase extraction for removal of matrix effects in lipophilic marine toxin analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, I.; Alfonso, A.; González-Jartín, J.M.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. A single run UPLC-MS/MS method for detection of all EU-regulated marine toxins. Talanta 2018, 189, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domènech, A.; Cortés-Francisco, N.; Palacios, O.; Franco, J.M.; Riobó, P.; Llerena, J.J.; Vichi, S.; Caixach, J. Determination of lipophilic marine toxins in mussels. Quantification and confirmation criteria using high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1328, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Sun, G.; Qiu, J.; Fan, L. Lipophilic shellfish toxins in Dinophysis caudata picked cells and in shellfish from the East China Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana, G.; Van Meulebroek, L.; Van Vooren, S.; De Rijcke, M.; Vandegehuchte, M.; Janssen, C.R.; Vanhaecke, L. Quantification and profiling of lipophilic marine toxins in microalgae by UHPLC coupled to high-resolution orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6345–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; John, U.; Cembella, A. LC-MS-MS aboard ship: Tandem mass spectrometry in the search for phycotoxins and novel toxigenic plankton from the North Sea. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, P.; Wright, E.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry of domoic acid and lipophilic shellfish toxins with selected reaction monitoring and optional confirmation by library searching of product ion spectra. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josić, D.; Rešetar, D.; Peršurić, Ž.; Martinović, T.; Kraljevic Pavelić, S. Detection of microbial toxins by -omics methods: A growing role of proteomics. In Proteomics for Microbial Toxin Identification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 497–505. ISBN 9780128040577. [Google Scholar]

| Time (min) | Solvent B (%) | Flow Rate (mL min−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 60 | 0.3 |
| 8 | 60 | 0.3 |
| 8.5 | 75 | 0.3 |
| 15 | 75 | 0.3 |
| 15.5 | 75 | 0.4 |
| 20 | 85 | 0.4 |
| 20.5 | 95 | 0.5 |
| 26 | 95 | 0.5 |
| 31 | 25 | 0.5 |
| Compound | Retention Time (min) | Multiple Reaction Monitoring Transition (m/z) | Fragmentation Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GYM | 6.93 | 508.3 → 490.6 1 | 200 | 40 |
| 13,19didesM | 7.32 | 678 → 430 1 678 → 164 (194) | 200 200 | 50 40 |
| 13desM | 7.72 | 692 → 164 1 692 → 444 (44) | 200 200 | 50 20 |
| SPX20G | 8.12 | 706 → 688 1 706 → 670 (33) | 190 190 | 30 35 |
| OA | 13.8 | 827 → 723 1 827 → 809 (47) | 190 190 | 55 45 |
| DTX2 | 14.7 | 827 → 723 1 827 → 809 (40) | 190 190 | 55 45 |
| PTX2 | 14.8 | 881.5 → 539.3 1 881.5 → 837.5 (99) | 230 230 | 60 70 |
| AZA4 | 15.0 | 844 → 826 1 844 → 808 (12) | 190 190 | 30 45 |
| DTX1 | 17.5 | 841 → 737 1 841 → 823 (50) | 190 190 | 45 55 |
| AZA3 | 18.6 | 828 → 810 1 828 → 792 (13) | 190 190 | 30 45 |
| AZA5 | 19.0 | 844 → 826 1 844 → 808 (37) | 180 180 | 30 40 |
| AZA1 | 19.4 | 842 → 824 1 842 → 806 (17) | 190 190 | 30 45 |
| AZA2 | 20.0 | 856 → 838 1 856 → 820 (17) | 190 190 | 30 45 |
| Assay | Point Type | Sample (mL) | MeOH (mL) | CHCl3 (µL) | Assay | Point Type | Sample (mL) | MeOH (mL) | CHCl3 (µL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cubic | 6 | 2 | 200 | 11 | Central | 9 | 1.25 | 450 |
| 2 | Cubic | 12 | 0.5 | 700 | 12 | Cubic | 12 | 2 | 700 |
| 3 | Cubic | 12 | 2 | 200 | 13 | Axial | 9 | 1.25 | 575 |
| 4 | Central | 9 | 1.25 | 450 | 14 | Axial | 9 | 1.25 | 325 |
| 5 | Cubic | 12 | 0.5 | 200 | 15 | Central | 9 | 1.25 | 450 |
| 6 | Cubic | 6 | 0.5 | 200 | 16 | Axial | 9 | 1.625 | 450 |
| 7 | Central | 9 | 1.25 | 450 | 17 | Axial | 10.5 | 1.25 | 450 |
| 8 | Cubic | 6 | 2 | 700 | 18 | Axial | 7.5 | 1.25 | 450 |
| 9 | Central | 9 | 1.25 | 450 | 19 | Axial | 9 | 0.875 | 450 |
| 10 | Cubic | 6 | 0.5 | 700 | 20 | central | 9 | 1.25 | 450 |
| Compound | Linearity Range (ng L−1) | Limit of Detection (ng L−1) | Limit of Quantitation (ng L−1) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GYM | 2.5–1000 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 0.1 |
| 13,19didesM | 1.0–1000 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 3.1 |
| 13desM | 1.0–1000 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| SPX20G | 3.5–1000 | 1.0 | 3.3 | 0.9 |
| OA | 5.0–1500 | 1.4 | 4.7 | 0.8 |
| DTX2 | 4.0–1000 | 1.1 | 3.7 | 1.9 |
| PTX2 | 4.5–1000 | 1.1 | 3.7 | 2.3 |
| AZA4 | 4.5–1000 | 1.3 | 4.3 | 5.1 |
| DTX1 | 20–5000 | 5.7 | 19 | 7.5 |
| AZA3 | 3.0–1000 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 2.1 |
| AZA5 | 1.0–1000 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.8 |
| AZA1 | 1.0–1000 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| AZA2 | 2.0–1000 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 3.6 |
| Compound | Level (ng·L−1) | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Compound | Level (ng·L−1) | Sample 1 | Sample 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GYM | 10 50 | 100 98 | 112 102 | AZA4 | 10 50 | 121 114 | 104 120 |
| 13,19didesM | 10 50 | 89 92 | 90 94 | DTX1 | 50 100 | 90 106 | 123 93 |
| 13desM | 10 50 | 95 96 | 98 97 | AZA3 | 10 50 | 101 106 | 113 106 |
| SPX20G | 10 50 | 82 119 | 114 121 | AZA5 | 10 50 | 104 101 | 104 104 |
| OA | 10 50 | 111 99 | 109 96 | AZA1 | 10 50 | 105 95 | 107 112 |
| DTX2 | 10 50 | 90 105 | 118 90 | AZA2 | 10 50 | 101 99 | 115 102 |
| PTX2 | 10 50 | 96 102 | 112 112 |
| Sample Treatment | Limit of Detection Range (ng L−1) | Ref. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | Sample Volume (mL) | Solvent Consumption | Time (min) | GYM | SPXs | OA and DTXs | PTXs | AZAs | |
| SPE | 500 | 10 mL MeOH | 532 | 1410 | 250 | 171–657.5 | 129 | 1237–1283 | [22] |
| SPE | 300 | 6 mL MeOH + 9 mL NH4OH/MeOH | 338 | 25 | 23.5 | 34.2–128.9 | 60.6 | 8.5–82.4 | [26] |
| SPE | 200 | 9 mL MeOH | 238 | - | - | 68 | 13 | - | [27] |
| SPE | 500 | 10 mL MeOH | 520 | - | - | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.002–0.003 | [28] |
| DMSPE | 50 | 1.5 mL NH4OH/AcN + 1.5 mL FA/AcN | - | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.2 | - | 0.03 | [23] |
| IL-DLLME | 10 | 0.5 mL AcN | 3 | - | - | 1500 | - | - | [31] |
| DLLME | 12 | 0.5 mL MeOH + 0.44 mL CHCl3 | 5 | 0.7 | 0.2–1 | 1.1–5.7 | 1.1 | 0.2–1.3 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oller-Ruiz, A.; Campillo, N.; Hernández-Córdoba, M.; Gilabert, J.; Viñas, P. Monitoring Lipophilic Toxins in Seawater Using Dispersive Liquid—Liquid Microextraction and Liquid Chromatography with Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2021, 13, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010057
Oller-Ruiz A, Campillo N, Hernández-Córdoba M, Gilabert J, Viñas P. Monitoring Lipophilic Toxins in Seawater Using Dispersive Liquid—Liquid Microextraction and Liquid Chromatography with Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Toxins. 2021; 13(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleOller-Ruiz, Ainhoa, Natalia Campillo, Manuel Hernández-Córdoba, Javier Gilabert, and Pilar Viñas. 2021. "Monitoring Lipophilic Toxins in Seawater Using Dispersive Liquid—Liquid Microextraction and Liquid Chromatography with Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry" Toxins 13, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010057
APA StyleOller-Ruiz, A., Campillo, N., Hernández-Córdoba, M., Gilabert, J., & Viñas, P. (2021). Monitoring Lipophilic Toxins in Seawater Using Dispersive Liquid—Liquid Microextraction and Liquid Chromatography with Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Toxins, 13(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010057