Genetic Manipulation of the Ergot Alkaloid Pathway in Epichloë festucae var. lolii and Its Effect on Black Beetle Feeding Deterrence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Molecular Screening of Transformants to Identify Gene Deletions in the Ergot Alkaloid Pathway
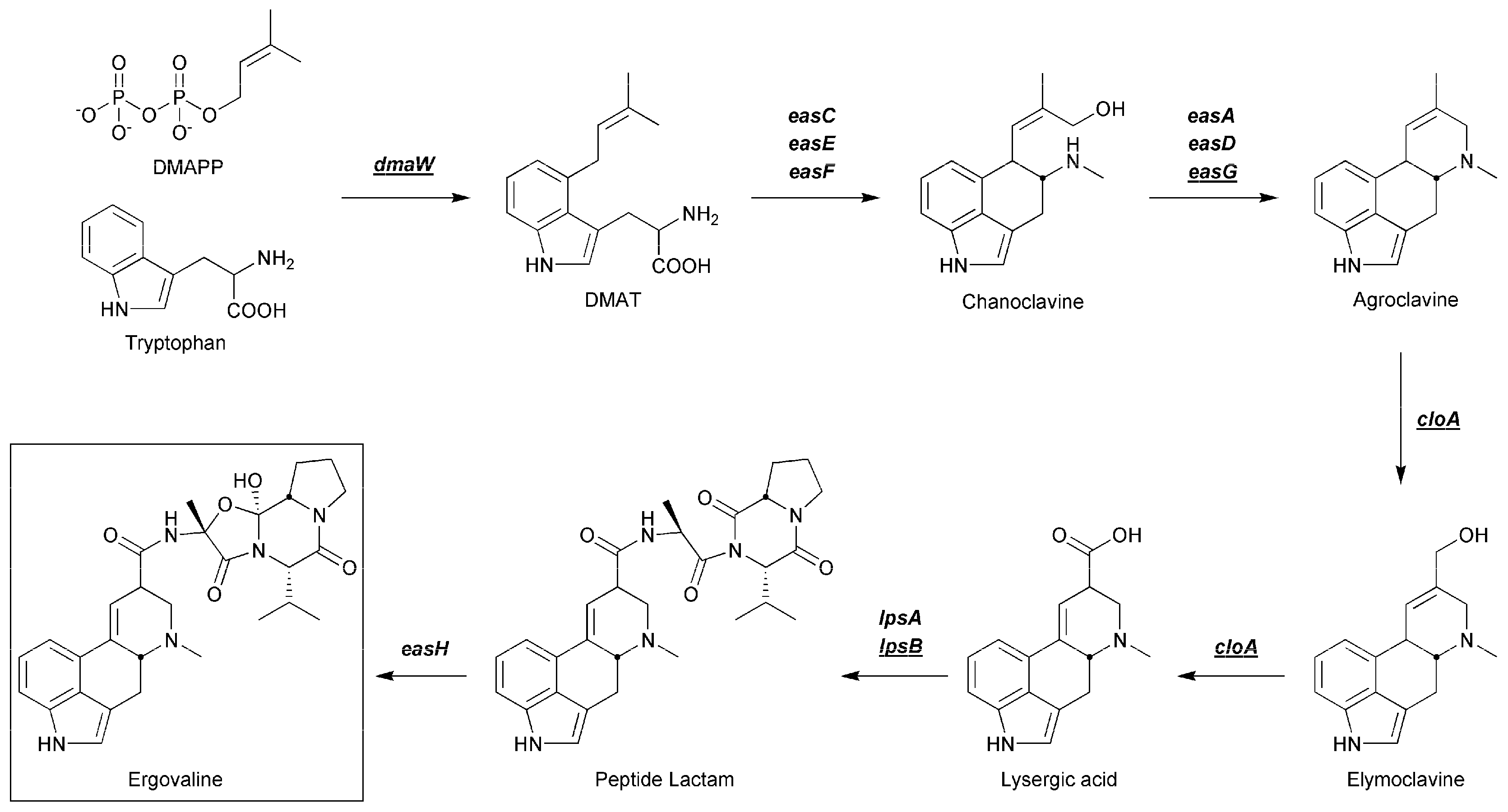
2.2. Analysis of Ergot Alkaloids in Gene Deletion Strains
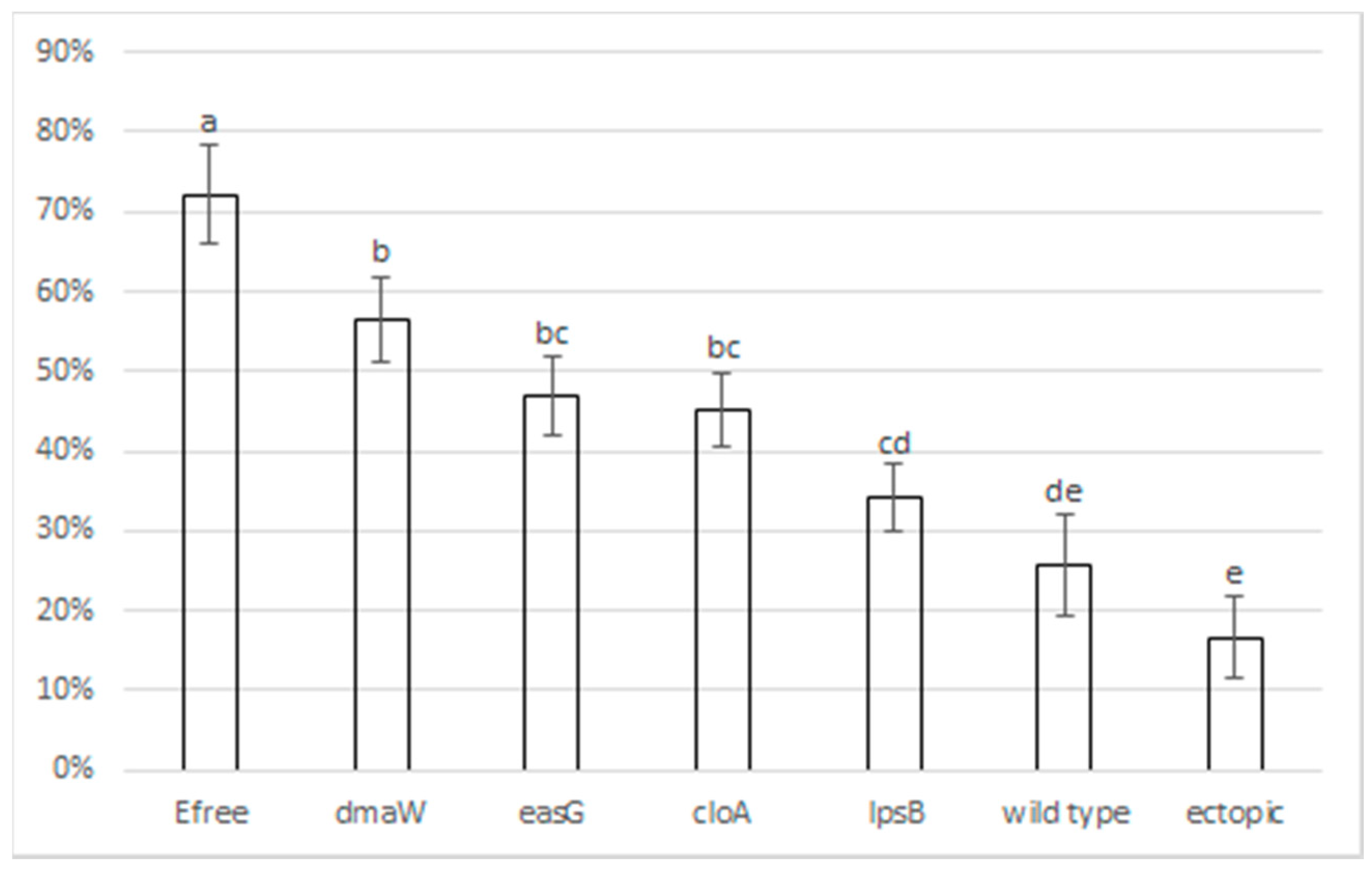
2.3. Black Beetle Feeding Deterrence
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Strains
3.2. Fungal Strains and Growth Conditions
3.3. Plant Growth and Endophyte Inoculation
3.4. Genomic DNA and Plasmid Isolation
3.5. Preparation of Gene Deletion Constructs
3.6. Fungal Protoplasting and Transformation
3.7. Molecular Analysis of Transformants
3.8. Black Beetle Insect Feeding Assay
3.9. Sample Preparation for Chemical Analysis
3.10. Solid-Phase Extraction Clean-Up
3.11. Analysis for Epichloë Ergot Alkaloids
3.12. Data Processing
3.13. Methods of Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schardl, C.L.; Leuchtmann, A.; Chung, K.-R.; Penny, D.; Siegel, M.R. Coevolution by common descent of fungal symbionts (Epichloë spp.) and grass hosts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schardl, C.L. The Epichloae, symbionts of the grass subfamily Poöideae. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2010, 97, 646–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schardl, C.L.; Phillips, T.D. Protective Grass Endophytes: Where are they from and where are they going? Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hume, D.E.; Ryan, G.D.; Gibert, A.; Helander, M.; Mirlohi, A.; Sabzalian, M.R. Epichloë fungal endophytes for grassland ecosystems. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 233–305. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.J.; de Bonth, A.C.M.; Briggs, L.R.; Caradus, J.R.; Finch, S.C.; Fleetwood, D.J.; Fletcher, L.R.; Hume, D.E.; Johnson, R.D.; Popay, A.J.; et al. The exploitation of epichloae endophytes for agricultural benefit. Fungal Divers. 2013, 60, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, C.M.; Barratt, B.I.; Bell, N.; Goldson, S.L.; Hardwick, S.; Jackson, M.; Jackson, T.A.; Phillips, C.B.; Popay, A.J.; Rennie, G. Quantifying the economic cost of invertebrate pests to New Zealand’s pastoral industry. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 62, 255–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popay, A.; Baltus, J. Black Beetle Damage to Perennial Ryegrass Infected with AR1 Endophyte. In Proceedings of the Conference—New Zealand Grassland Association, Hamilton, New Zealand, 30 October–1 November 2001; Volume 63, pp. 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Popay, A.; Thom, E. Endophyte effects on major insect pests in Waikato dairy pasture. In Proceedings of the New Zealand Grassland Association, Waitangi, New Zealand, 3–5 November 2009; Volume 71, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Schardl, C.; Young, C.; Hesse, U.; Amyotte, S.; Andreeva, K.; Calie, P.; Fleetwood, D.; Haws, D.; Moore, N.; Oeser, B.; et al. Plant-symbiotic fungi as chemical engineers: Multi-genome analysis of the Clavicipitaceae reveals dynamics of alkaloid loci. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duringer, J.; DeLorme, M.; Lehner, A.; Craig, A. A review of the ergot alkaloids found in endophyte-infected tall fescue and perennial ryegrass and their metabolism after ingestion by livestock. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Fungal Endophytes of Grasses, Christchurch, New Zealand, 25–28 March 2007; p. 377382. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhards, N.; Neubauer, L.; Tudzynski, P.; Li, S.-M. Biosynthetic pathways of ergot alkaloids. Toxins 2014, 6, 3281–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerre, P. Ergot alkaloids produced by endophytic fungi of the genus Epichloë. Toxins 2015, 7, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakubczyk, D.; Cheng, J.Z.; O’Connor, S.E. Biosynthesis of the ergot alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, O.J.-P.; Miles, C.O.; Prestidge, R.A. Ergopeptine alkaloids and Neotyphodium lolii-mediated resistance in perennial ryegrass against adult Heteronychus arator (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1997, 90, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, O.-P.; Christensen, M.; Prestidge, R. Effect of selected isolates of Acremonium endophytes on adult black beetle (Heteronychus arator) feeding. In Proceedings of the New Zealand Plant Protection Conference, Waitangi, New Zealand, 9–11 August 1994; Volume 47, pp. 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, L. Non-toxic endophytes in ryegrass and their effect on livestock health and production. Ryegrass Endophyte Essent. N. Z. Symbiosis Grassl. Res. Pract. Ser. 1999, 7, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, J.; Nicol, A. Ergovaline, an endophytic alkaloid. 1. Animal physiology and metabolism. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2016, 56, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallwey, C.; Li, S.-M. Ergot alkaloids: Structure diversity, biosynthetic gene clusters and functional proof of biosynthetic genes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-J.; Han, M.-Y.; Gong, T.; Yang, J.-L.; Zhu, P. Recent progress in ergot alkaloid research. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 27384–27396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coyle, C.M.; Panaccione, D.G. An ergot alkaloid biosynthesis gene and clustered hypothetical genes from Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3112–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panaccione, D.G. Origins and significance of ergot alkaloid diversity in fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 251, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleetwood, D.J.; Scott, B.; Lane, G.A.; Tanaka, A.; Johnson, R.D. A complex ergovaline gene cluster in Epichloë endophytes of grasses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorenz, N.; Haarmann, T.; Pazoutova, S.; Jung, M.; Tudzynski, P. The ergot alkaloid gene cluster: Functional analyses and evolutionary aspects. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.A.; Schardl, C.L.; Panaccione, D.G.; Florea, S.; Takach, J.E.; Charlton, N.D.; Moore, N.; Webb, J.S.; Jaromczyk, J. Genetics, genomics and evolution of ergot alkaloid diversity. Toxins 2015, 7, 1273–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Panaccione, D.G.; Schardl, C.L. Phylogenetic analyses reveal monophyletic origin of the ergot alkaloid gene dmaW in fungi. Evol. Bioinform. 2009, 5, EBO-S2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Z.; Coyle, C.M.; Panaccione, D.G.; O’Connor, S.E. Controlling a structural branch point in ergot alkaloid biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12835–12837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matuschek, M.; Wallwey, C.; Xie, X.; Li, S.-M. New insights into ergot alkaloid biosynthesis in Claviceps purpurea: An agroclavine synthase EasG catalyses, via a non-enzymatic adduct with reduced glutathione, the conversion of chanoclavine-I aldehyde to agroclavine. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4328–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.L.; Panaccione, D.G. Biosynthesis of the pharmaceutically important fungal ergot alkaloid dihydrolysergic acid requires a specialized allele of cloA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00805–e00817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panaccione, D.G.; Johnson, R.D.; Wang, J.; Young, C.A.; Damrongkool, P.; Scott, B.; Schardl, C.L. Elimination of ergovaline from a grass–Neotyphodium endophyte symbiosis by genetic modification of the endophyte. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12820–12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleetwood, D.J. Molecular Characterisation of the EAS Gene Cluster for Ergot Alkaloid Biosynthesis in Epichloë Endophytes of Grasses: A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Molecular Genetics at Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand; Massey University: Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Popay, A.; Hume, D. Endophytes improve ryegrass persistence by controlling insects. Pasture Persistence Grassl. Res. Pract. Ser. 2011, 15, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Bastias, D.A.; Martínez-Ghersa, M.A.; Ballaré, C.L.; Gundel, P.E. Epichloë fungal endophytes and plant defenses: Not just alkaloids. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, K.; Cheplick, G.P. Effect of ergot alkaloids from fungal endophyte-infected grasses on fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). J. Chem. Ecol. 1989, 15, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, S.C.; Munday, J.S.; Sprosen, J.M.; Bhattarai, S. Toxicity studies of chanoclavine in mice. Toxins 2019, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glatt, H.; Eich, E.; Pertz, H.; Becker, C.; Oesch, F. Mutagenicity experiments on agroclavines, new natural antineoplastic compounds. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 1811–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latch, G.C.M.; Christensen, M.J. Artificial infection of grasses with endophytes. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1985, 107, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, W.R.; Schmid, J.; Singh, J.; Faville, M.J.; Johnson, R.D. A morphological change in the fungal symbiont Neotyphodium lolii induces dwarfing in its host plant Lolium perenne. Fungal Biol. 2012, 116, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.D.; Schardl, C.L.; Songlin, P.J.; Mogen, K.L.; Siegel, M.R. The β-tubulin gene of Epichloë typhina from perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne). Curr. Genet. 1990, 18, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama, M.; Forester, N.; Ariyawansa, K.; Voisey, C.; Johnson, L.; Johnson, R.; Fleetwood, D. Efficient targeted mutagenesis in Epichloë festucae using a split marker system. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 134, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.K.; Nielsen, B.D. Nutritional requirements for growth of a fungus endophyte of tall fescue grass. Mycologia 1986, 78, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.; Bryant, M.; Christensen, M.; Tapper, B.; Bryan, G.; Scott, B. Molecular cloning and genetic analysis of a symbiosis-expressed gene cluster for lolitrem biosynthesis from a mutualistic endophyte of perennial ryegrass. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2005, 274, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Chanoclavine (mg/kg) | Agroclavine (mg/kg) | Elymoclavine (mg/kg) | Lysergic Acid (Relative to Ev) | Ergovaline (mg/kg) | Peramine (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR5 dmaW KO15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 29.76 |
| AR5 dmaW KO20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 22.60 |
| AR5 easG KO3 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 16.18 |
| AR5 easG KO20 | 0.69 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 21.38 |
| AR5 cloA KO6 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 22.10 |
| AR5 cloA KO32 | 0.86 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 25.71 |
| AR5 lpsB KO10 | 0.89 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.00 | 25.78 |
| AR5 lpsB KO11 | 0.85 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 31.62 |
| AR5 dmaW E1 | 0.77 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 17.42 | 31.59 |
| AR5 easG E14 | 0.88 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 22.10 | 28.81 |
| AR5 cloA E4 | 0.87 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 13.42 | 27.64 |
| AR5 lpsB E9 | 1.16 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 14.01 | 25.47 |
| AR5 WT | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 4.50 | 9.24 |
| E free | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hudson, D.; Mace, W.; Popay, A.; Jensen, J.; McKenzie, C.; Cameron, C.; Johnson, R. Genetic Manipulation of the Ergot Alkaloid Pathway in Epichloë festucae var. lolii and Its Effect on Black Beetle Feeding Deterrence. Toxins 2021, 13, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020076
Hudson D, Mace W, Popay A, Jensen J, McKenzie C, Cameron C, Johnson R. Genetic Manipulation of the Ergot Alkaloid Pathway in Epichloë festucae var. lolii and Its Effect on Black Beetle Feeding Deterrence. Toxins. 2021; 13(2):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020076
Chicago/Turabian StyleHudson, Debbie, Wade Mace, Alison Popay, Joanne Jensen, Catherine McKenzie, Catherine Cameron, and Richard Johnson. 2021. "Genetic Manipulation of the Ergot Alkaloid Pathway in Epichloë festucae var. lolii and Its Effect on Black Beetle Feeding Deterrence" Toxins 13, no. 2: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020076





