Cell-Based Reporter Release Assay to Determine the Activity of Calcium-Dependent Neurotoxins and Neuroactive Pharmaceuticals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
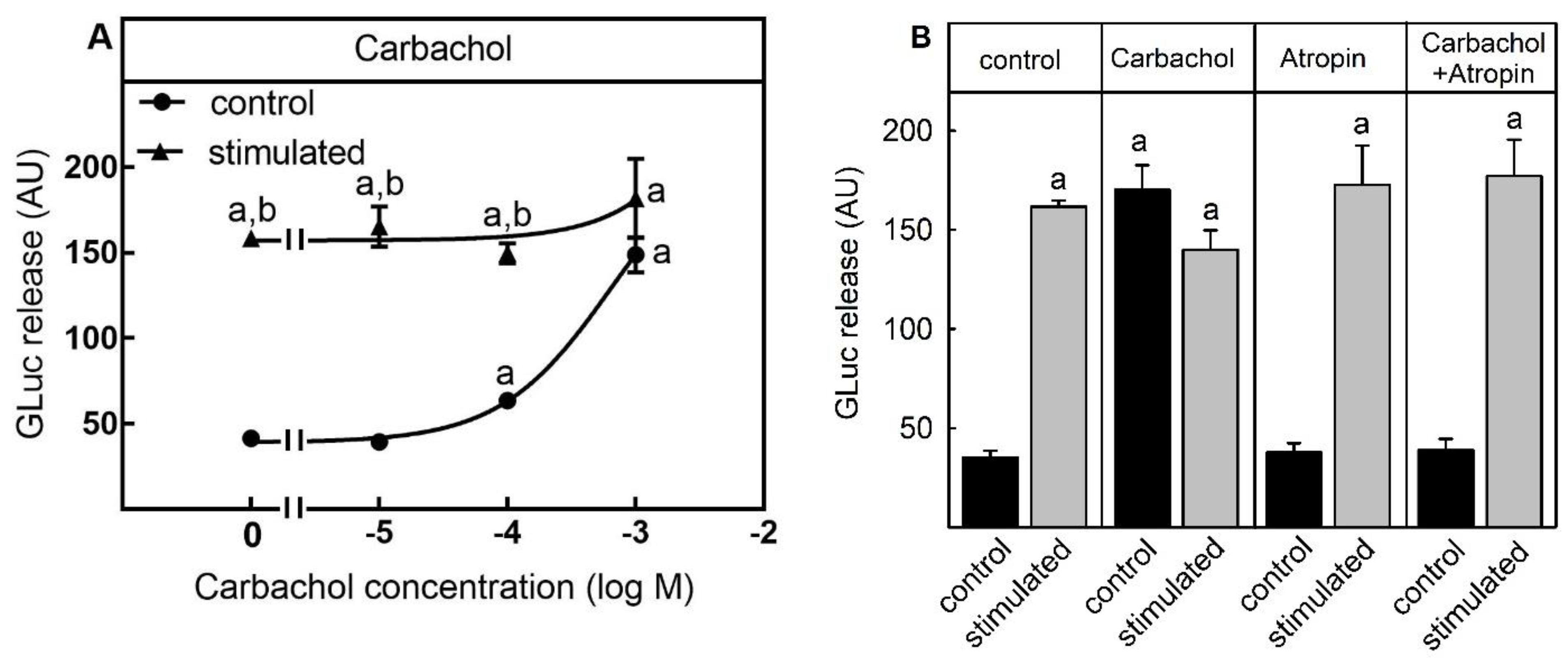
2.1. Suitability for Testing Compounds Leading to Neurotransmitter Release by an Increase of Intracellular Ca2+-Concentration from Intracellular Stores
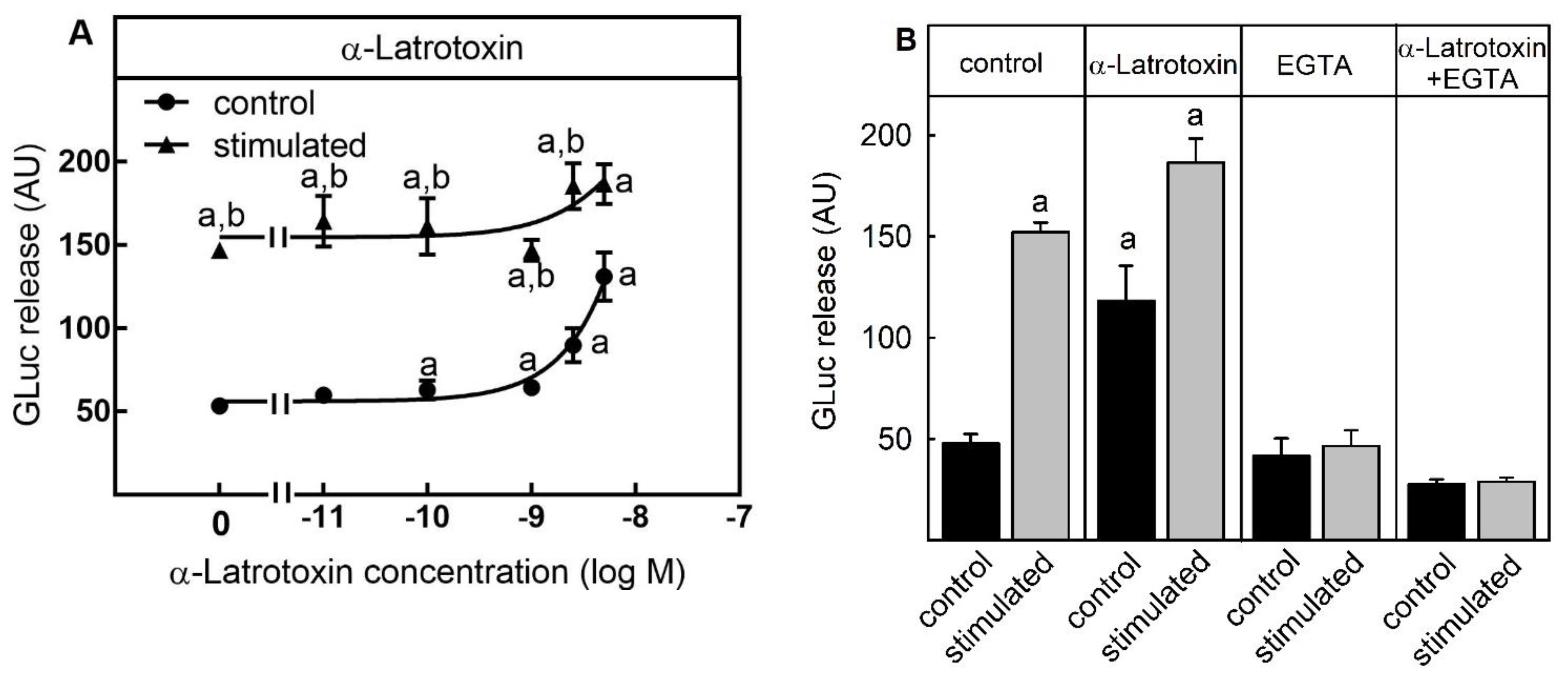
2.2. Suitability for Testing Compounds Leading to Neurotransmitter Release by an Increase of Intracellular Ca2+-Concentration by Ca2+-Channel-Forming Neurotoxins
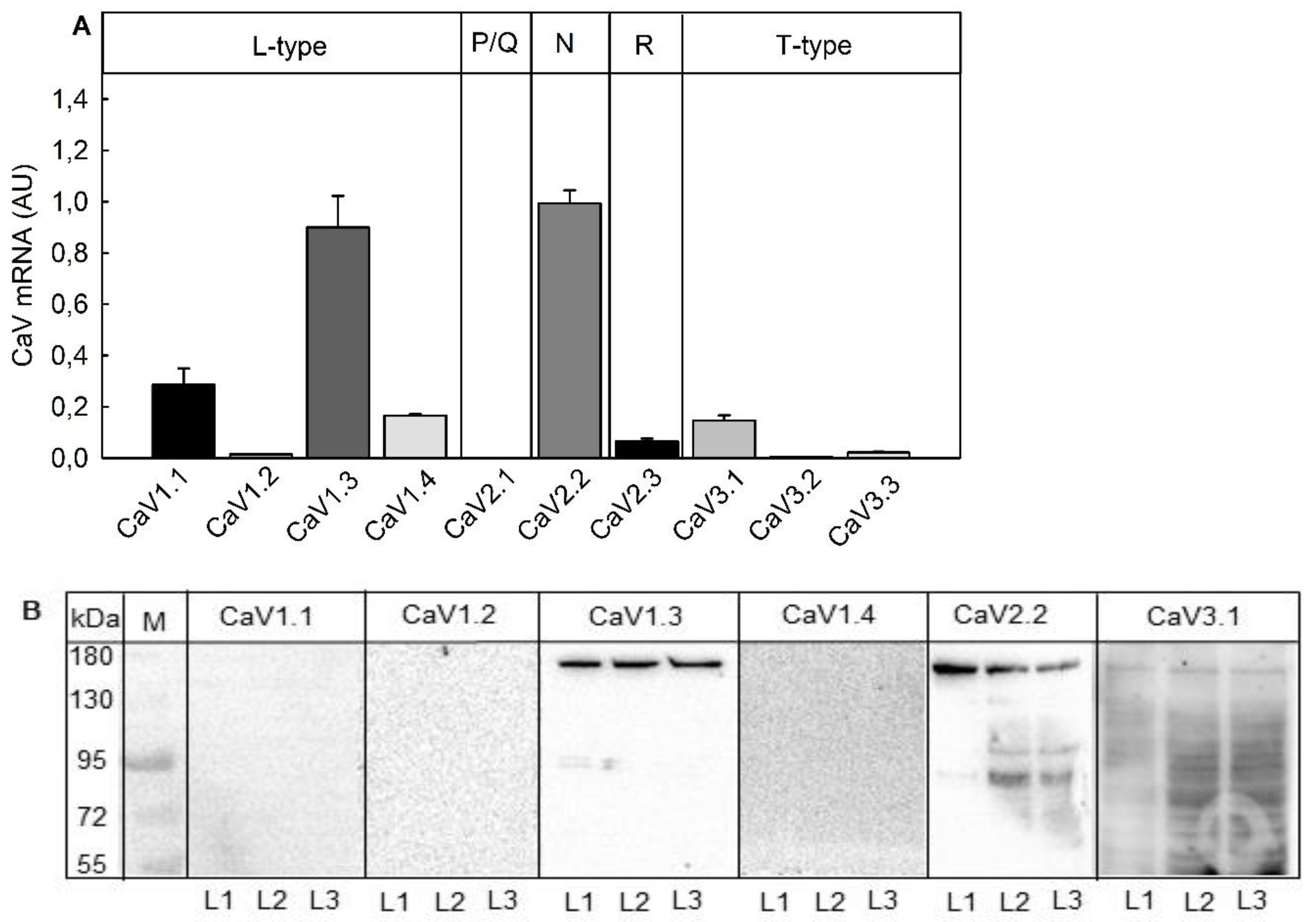
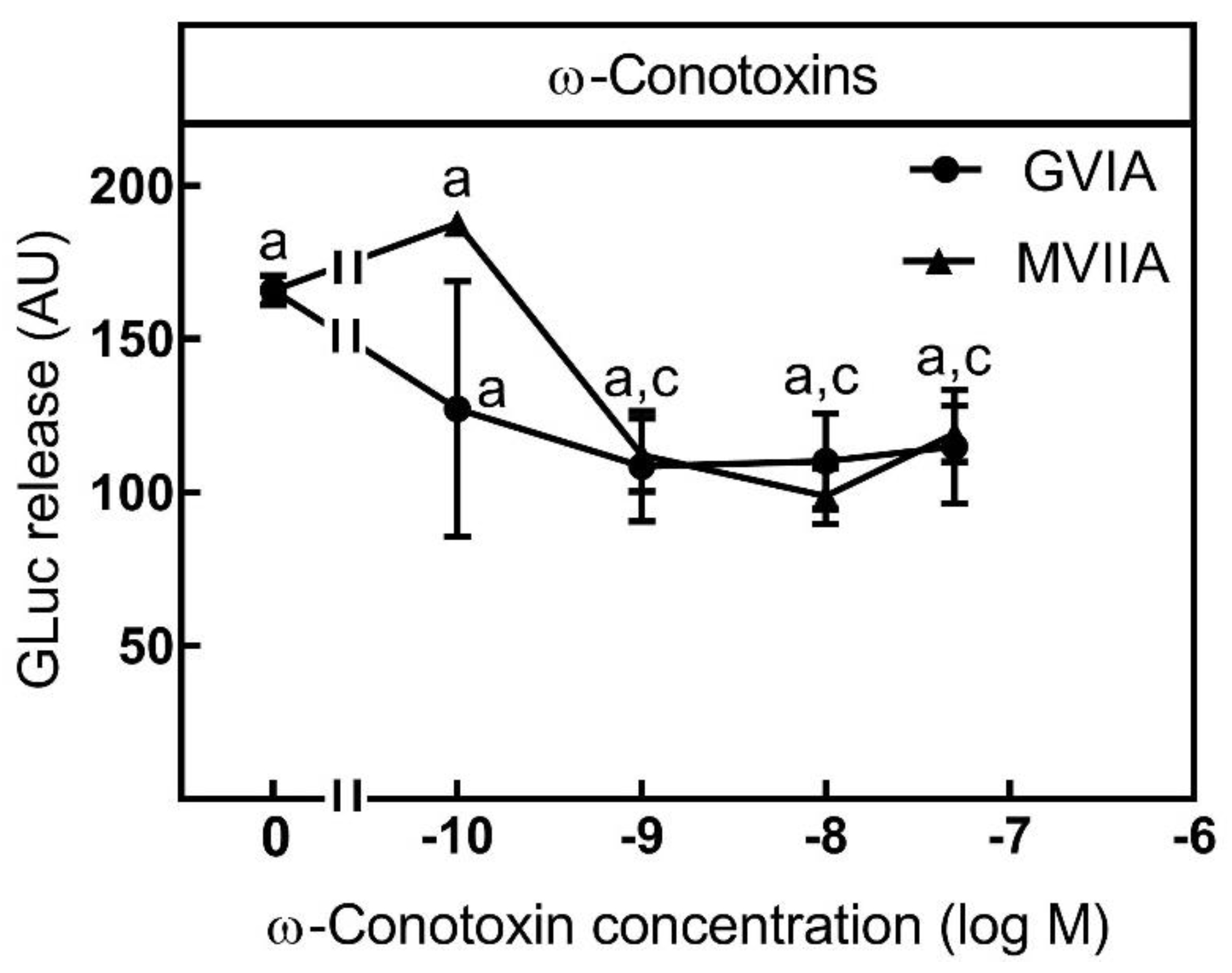
2.3. Suitability for Testing Compounds Leading to an Inhibition of Neurotransmitter Release by Blocking Voltage-Gated Ca2+-Channels (VGCC)
3. Discussion
3.1. Suitability of the Assay for Compounds Stimulating Neurotransmitter Release
3.2. Suitability of the Assay for Compounds Inhibiting Neurotransmitter Release
3.3. Cytotoxicity of Compounds Inhibiting Neurotransmitter Release
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Cell Culture
5.3. Luciferase Release from Cells Treated with Neurotoxins or NeuroActive Pharmaceuticals
5.4. Real-Time RT-PCR
5.5. Western Blot Analysis
5.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dragicevic, E.; Schiemann, J.; Liss, B. Dopamine midbrain neurons in health and Parkinson’s disease: Emerging roles of voltage-gated calcium channels and ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Neuroscience 2015, 284, 798–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, R.; Montagut-Bordas, C.; Dickenson, A.H. Calcium channel modulation as a target in chronic pain control. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2173–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanou, E.; Catterall, W.A. Calcium Channels, Synaptic Plasticity, and Neuropsychiatric Disease. Neuron 2018, 98, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binz, T. Clostridial neurotoxin light chains: Devices for SNARE cleavage mediated blockade of neurotransmission. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 364, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahamimoff, R.; Erulkar, S.D.; Lev-Tov, A.; Meiri, H. Intracellular and extracellular calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular synapse. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1978, 307, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Südhof, T.C. The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 27, 509–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dolphin, A.C.; Lee, A. Presynaptic calcium channels: Specialized control of synaptic neurotransmitter release. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J. Conotoxins as selective inhibitors of neuronal ion channels, receptors and transporters. IUBMB Life 2004, 56, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, S.; Alewood, P.F. Targeting voltage-gated calcium channels: Developments in peptide and small-molecule inhibitors for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 970–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathe-Neuschäfer-Rube, A.; Neuschäfer-Rube, F.; Genz, L.; Püschel, G.P. Botulinum neurotoxin dose-dependently inhibits release of neurosecretory vesicle-targeted luciferase from neuronal cells. ALTEX 2015, 32, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathe-Neuschäfer-Rube, A.; Neuschäfer-Rube, F.; Haas, G.; Langoth-Fehringer, N.; Püschel, G.P. Cell-Based Reporter Release Assay to Determine the Potency of Proteolytic Bacterial Neurotoxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Südhof, T.C. alpha-Latrotoxin and its receptors: Neurexins and CIRL/latrophilins. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 933–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S. Pharmacological Inhibition of Voltage-gated Ca(2+) Channels for Chronic Pain Relief. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catterall, W.A.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Snutch, T.P.; Striessnig, J. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soward, A.L.; Vanhaleweyk, G.L.; Serruys, P.W. The haemodynamic effects of nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem in patients with coronary artery disease. A review. Drugs 1986, 32, 66–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakulendran, S.; Hanna, M.G. The Role of Calcium Channels in Epilepsy. Cold. Spring. Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a022723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, R. Muscarinic receptors in the stomach. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1980, 66, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.A.; Abogadie, F.C.; Allen, T.G.; Buckley, N.J.; Caulfield, M.P.; Delmas, P.; Haley, J.E.; Lamas, J.A.; Selyanko, A.A. Muscarinic mechanisms in nerve cells. Life Sci. 1997, 60, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, M.P.; Birdsall, N.J. International Union of Pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998, 50, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caulfield, M.P. Muscarinic receptors-characterization, coupling and function. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 58, 319–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.G.; Nahorski, S.R. Carbachol-stimulated calcium entry in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells: Which route? J. Physiol. Paris. 1992, 86, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.L.; Bohnen, N.I. Cholinergic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, A.; Behrens, C.J.; Heinemann, U. Cholinergic dysfunction in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2007, 48 (Suppl. 5), 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnen-Johannsen, K.L.; Kayser, O. Tropane Alkaloids: Chemistry, Pharmacology, Biosynthesis and Production. Molecules 2019, 22, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spinks, A.; Wasiak, J. Scopolamine (hyoscine) for preventing and treating motion sickness. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 15, CD002851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langmead, C.J.; Watson, J.; Reavill, C. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors as CNS drug targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hofmann, J.; Fish, I.; Schaake, B.; Eitel, K.; Bartuschat, A.; Kaindl, J.; Rampp, H.; Banerjee, A.; Hübner, H.; et al. Structure-guided development of selective M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12046–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Randáková, A.; Rudajev, V.; Doležal, V.; Boulos, J.; Jakubík, J. Novel long-acting antagonists of muscarinic ACh receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, G.J. Black and brown widow spider bites in South Africa. A series of 45 cases. S. Afr. Med. J. 1993, 83, 399–405. [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco, E.; Rigoni, M.; Caccin, P.; Grishin, E.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Calcium overload in nerve terminals of cultured neurons intoxicated by alpha-latrotoxin and snake PLA2 neurotoxins. Toxicon 2009, 54, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duregotti, E.; Zanetti, G.; Scorzeto, M.; Megighian, A.; Montecucco, C.; Pirazzini, M.; Rigoni, M. Snake and Spider Toxins Induce a Rapid Recovery of Function of Botulinum Neurotoxin Paralysed Neuromuscular Junction. Toxins 2015, 7, 5322–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.J.; Berecki, G. Mechanisms of conotoxin inhibition of N-type (Ca(v)2.2) calcium channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Lipscombe, D. Neuronal Ca(V)1.3alpha(1) L-type channels activate at relatively hyperpolarized membrane potentials and are incompletely inhibited by dihydropyridines. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 5944–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilijic, E.; Guzman, J.N.; Surmeier, D.J. The L-type channel antagonist isradipine is neuroprotective in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 43, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anekonda, T.S.; Quinn, J.F. Calcium channel blocking as a therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease: The case for isradipine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sousa, S.R.; Vetter, I.; Ragnarsson, L.; Lewis, R.J. Expression and pharmacology of endogenous Cav channels in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH CaV 1.1 CaV 1.2 CaV 1.3 CaV 1.4 CaV 2.1 CaV 2.2 CaV 2.3 CaV 3.1 CaV 3.2 CaV 3.3 | 5′-TGATGACATCAAGAAGGTGG 5′-ACCATTGAGGAAGAGGCAGC 5′-TGCCCTTGCATCTGGTTCAT 5′-CCCAGGCAGAAACATCGACT 5′-CTTGGTGGAGGCTGTGCTTA 5′-CCTGAGCATGACCACCCAAT 5′-TACAAGACGGCCAACTCCTC 5′-AGACGCTCACTTTCGAAGCA 5′-GCTGGATGAGCAGAGGAGAC 5′-CTCAGGGCTTCCTGGACAAG 5′-GAAGAGATGAGGGTCGCAGG | 5′-TTACTCCTTGGAGGCCATGT 5′-CATAGGCGACATTGGCGTTG 5′-ATCAAGACCGCTTCCACCAG 5′-CTGCCATGATCTGTTGCTGC 5′-TATTGAGCAGTTGGGGAGGG 5′-CATGTGCTCTCGGCCCTC 5′-TCAGGGAGGACACGTAGGAA 5′-TTGTTGACAGCCCCACACAT 5′-ATCTTTCTTTGGGGAGGGCG 5′-CCGTCCAAGAAAGGGTCTCC 5′-GCCAGAATCCCAGAGCATCA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pathe-Neuschäfer-Rube, A.; Neuschäfer-Rube, F.; Püschel, G.P. Cell-Based Reporter Release Assay to Determine the Activity of Calcium-Dependent Neurotoxins and Neuroactive Pharmaceuticals. Toxins 2021, 13, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040247
Pathe-Neuschäfer-Rube A, Neuschäfer-Rube F, Püschel GP. Cell-Based Reporter Release Assay to Determine the Activity of Calcium-Dependent Neurotoxins and Neuroactive Pharmaceuticals. Toxins. 2021; 13(4):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040247
Chicago/Turabian StylePathe-Neuschäfer-Rube, Andrea, Frank Neuschäfer-Rube, and Gerhard P. Püschel. 2021. "Cell-Based Reporter Release Assay to Determine the Activity of Calcium-Dependent Neurotoxins and Neuroactive Pharmaceuticals" Toxins 13, no. 4: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040247
APA StylePathe-Neuschäfer-Rube, A., Neuschäfer-Rube, F., & Püschel, G. P. (2021). Cell-Based Reporter Release Assay to Determine the Activity of Calcium-Dependent Neurotoxins and Neuroactive Pharmaceuticals. Toxins, 13(4), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040247





