Abstract
Meteorus pulchricornis (Ichneumonoidea, Braconidae) is an endoparasitoid wasp of lepidopteran caterpillars. Its parasitic success relies on vesicles (named M. pulchricornis Virus-Like Particles or MpVLPs) that are synthesized in the venom gland and injected into the parasitoid host along with the venom during oviposition. In order to define the content and understand the biogenesis of these atypical vesicles, we performed a transcriptome analysis of the venom gland and a proteomic analysis of the venom and purified MpVLPs. About half of the MpVLPs and soluble venom proteins identified were unknown and no similarity with any known viral sequence was found. However, MpVLPs contained a large number of proteins labelled as metalloproteinases while the most abundant protein family in the soluble venom was that of proteins containing the Domain of Unknown Function DUF-4803. The high number of these proteins identified suggests that a large expansion of these two protein families occurred in M. pulchricornis. Therefore, although the exact mechanism of MpVLPs formation remains to be elucidated, these vesicles appear to be “metalloproteinase bombs” that may have several physiological roles in the host including modifying the functions of its immune cells. The role of DUF4803 proteins, also present in the venom of other braconids, remains to be clarified.
Keywords:
Meteorus pulchricornis; parasitoid wasp; Braconidae; venomics; virus-like particles (VLPs); proteomic; transcriptomic; metalloproteases; DUF-4803 proteins Key Contribution:
Endoparasitoid wasps are natural regulators of many agronomic insect pests. Their reproductive success relies on the venom and/or on virus-like particles they inject at oviposition, which are important for controlling host immunity, metabolism and development. In Meteorus pulchricornis, an endoparasitoid wasp of many lepidopteran species, vesicles resembling ovarian viral particles of other Ichneumonoidea species are synthetized in the venom gland. This work shows that these vesicles are enriched in metalloprotease-like proteins that may play an important role in the reported alteration of host immune cells. The vesicles of M. pulchricornis differ from those described in other species of Ichneumonoidea endoparasitoids in that their production in the venom gland does not appear to involve an endogenous viral machinery.
1. Introduction
Meteorus pulchricornis (Ichneumonoidea, Braconidae, Euphorinae) is an endoparasitoid wasp that develops in the larval stages of a large number of lepidopteran species including several pests such as Helicoverpa armigera [1,2]. M. pulchricornis is widely distributed in Europe and thelytokous strains can be found in Japan and New-Zealand [2,3]. M. pulchricornis lays eggs in host caterpillars that continue to develop after parasitism (koinobiont lifestyle). To ensure successful parasitism, koinobiont endoparasitoids such as M. pulchricornis rely on various strategies to modulate the host internal physiological conditions in order to make them more suitable to the development of their eggs and larvae. These strategies comprise the production of factors in the female genital tract or by specialized embryonic cells released in the parasitized insect, the teratocytes [4]. Female-derived factors include proteins or vesicles made in the venom gland or in specialized ovarian tissues [5,6,7].
Virus-like particles produced in the calyx of female ovaries have been extensively studied in ichneumonid and braconid wasps. In these species, the particles are produced by viral machineries imbedded in wasp chromosomes as a result of virus genome integration events that occurred during wasp evolution [8,9,10,11,12,13]. These parasitoid ovarian particles contain either DNA molecules or proteins, and they originate from independent integration events. The best known are those from the polydnavirus (PDV) family. PDV particles enclose circular dsDNA molecules carrying wasp genes that are expressed in the cells of different tissues of the parasitized host. The products of these genes ensure successful parasitism by suppressing host immune responses and/or altering host larval development.
Unlike other braconid endoparasitoid species, M. pulchricornis females do not produce viral particles in their ovaries. However, electron microscopy studies have indicated that the lumen of their venom glands and their reservoir are filled with numerous vesicles resembling virus particles, which have been named MpVLPs [14,15]. MpVLPs are produced in the cells of the venom gland and then stored in the venom reservoir. Injection of purified MpVLPs in Pseudaletia separata (Mythimna separata) host larvae strongly decreased the ability of host hemocytes to encapsulate fluorescent latex beads, and one specific type of hemocytes, granulocytes, showed rapid cytoskeleton change followed by apoptosis [14,15,16]. Therefore, MpVLPs appear to play an important role in parasitoid success by modulating the host immune response and protecting the parasitoid egg from the host encapsulation response.
MpVLPs have been described as single-membrane vesicles approximately 150 nm in diameter filled with electron-dense material that does not contain nucleic acids [15]. This feature makes them more similar to virus-like particles produced in the ovaries of the ichneumonid Venturia canescens [10] than to PDVs from other Braconids. Interestingly, up to now, and with the exception of Meteorus spp., only parasitoid species in the family Figitidae (mainly Leptopilina and Ganaspis species) have been reported to form vesicles in their venom gland [17,18]. Figitidae vesicles are also uniquely filled with proteins that target specialized host immune cells [19,20]. However, and in contrast to our current knowledge on VLPs/PDVs produced in wasp ovaries, a clear demonstration of the origin (cellular or viral derived) and exact mechanism of biogenesis of these wasp venom vesicles remains to be obtained [19,21,22,23].
To gain further insights on the nature and origin of M. pulchricornis venom and MpVLPs, we investigated in the present study the transcriptome of the venom gland and the proteome of the venom and purified MpVLPs. The aim was to complement a prior published study on the venom gland transcriptome that was based only on sequencing of a low number of clones (473 clones) from a conventional cDNA library of venom gland filaments [24]. In this previous study, many of the sequences were related to cellular components or unknown. Of these, several were selected to be knockdown by RNA interference and two, which were immunolocalized with MpVLPs, slightly affected the adhesion and spreading of host plasmatocytes suggesting these proteins may be involved in host immune suppression. However, single and double KO of these genes did not affect the success of wasp parasitism.
Here, Illumina sequencing of the M. pulchricornis venom gland transcriptome yielded nearly 17,000 predicted coding sequences (CDS). This database was used for proteomic analysis of the total venom extracted from the venom reservoir and MpVLPs purified from this venom. Among the most abundant proteins found in the venom and composing the MpVLPs, we identified a high number of Zn-metalloproteases and proteins containing the Domain-of-Unknown-Function-4803 (DUF4803) suggesting that a large expansion of these two protein families had occurred in M. pulchricornis lineage. Interestingly, since MpVLPs affect host immune cells and wasp metalloproteases have been implicated in impairing host cell immune functions, it is tempting to suggest a role for MpVLPs metalloproteases in this process. We did not find genes from known viruses abundantly expressed in the transcriptome of the M. pulchricornis venom gland, nor did we find viral proteins in the proteomic analyses of venom and MpVLPs. Although not definitive, these data suggest that MpVLPs do not have a viral origin in contrast to the ovarian calyx particles described in other braconids.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. M. pulchricornis Venom Gland and MpVLPs Secretion
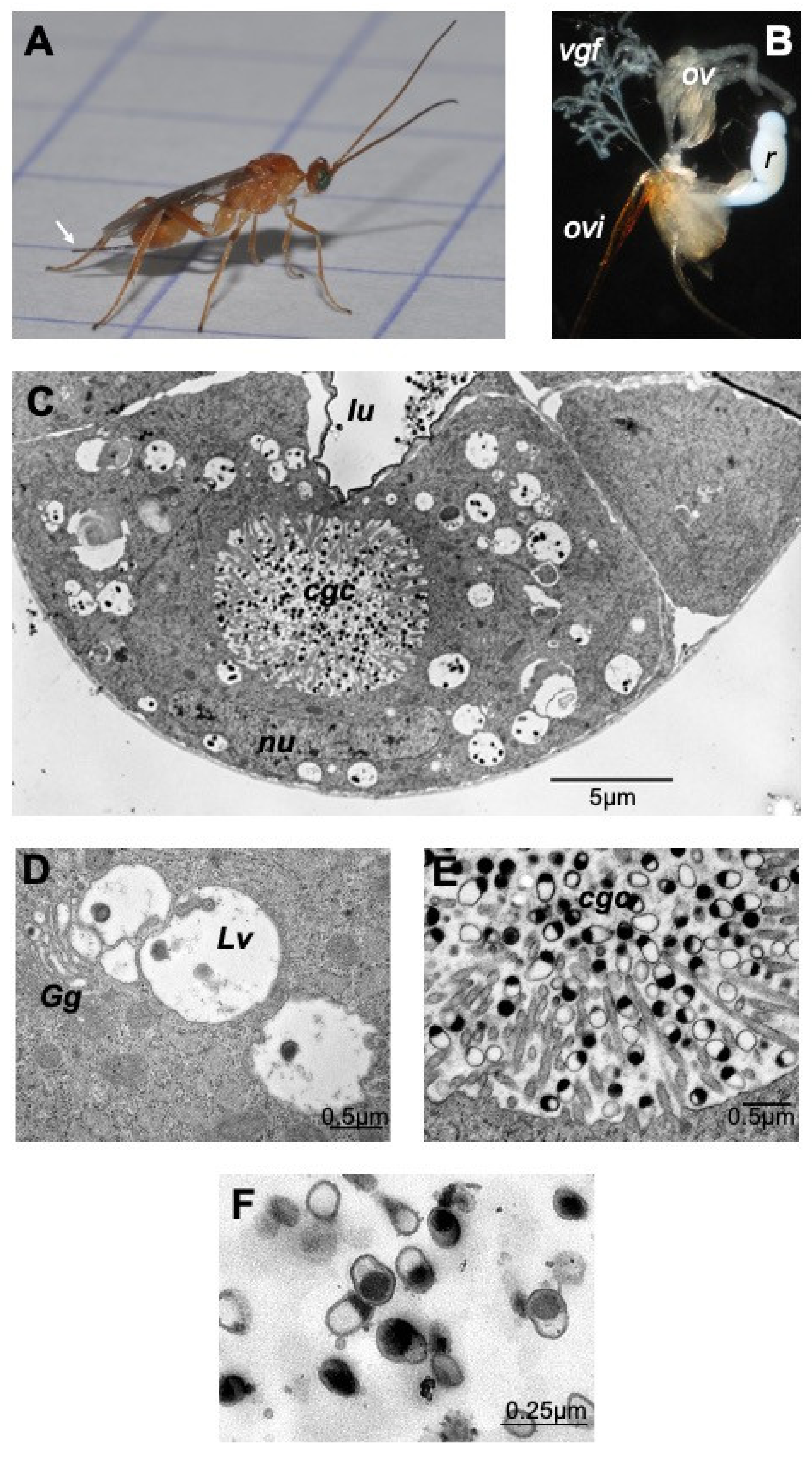
The dissected venom apparatus from M. pulchricornis female wasps (Figure 1A) consists of two filamentous venom glands and a large milky reservoir (Figure 1B). Observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), the cells of the gland (Figure 1C) show the classic type of glandular venom cells with an internal secretory cell canal (cell glandular canal, cgc) surrounded by microvilli [25]. The glandular cells showed a normal nucleus and had a cytoplasm filled with large vesicles, very often in close proximity to the Golgi apparatus (Figure 1D). The center of the cell canal in this species was packed with vesicles filled or half filled with an electron dense material, the MpVLPs (Figure 1E). These secreted vesicles were further observed in the lumen of the collecting duct running at the center of the gland where the cell duct opens (Figure 1C). These large vesicles enclosed small membranous vesicles filled with dark material, which may represent the precursor of secreted MpVLPs. MpVLPs purified by centrifugation (Figure 1F) from the venom in the reservoir (Figure 1B) have the same appearance as those observed in the secretory cell canal and the gland collecting duct, indicating that the purification procedure did not induce significant changes.
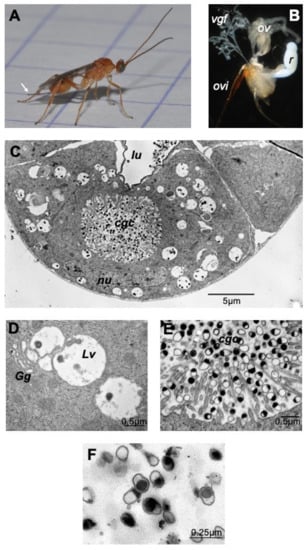
Figure 1.
The venom apparatus of Meteorus pulchricornis. From the female wasp (A) the venom apparatus (B) was obtained by pulling out the ovipositor (ovi; white arrow in A). The ovarioles (ov), the two filamentous venom glands (vgf) and the large unique milky venom reservoir (r) are clearly visible. (C) TEM observation of a cross section of a venom gland filament showing a glandular cell with the secretory cell glandular canal (cgc) at its center that ends in the lumen of the collecting gland duct (lu). The nucleus (nu) surrounded by its nuclear envelope had and apparent normal shape. (D) MpVLPs may derive from the small electron dense vesicles contained within large cytoplasmic vesicles (Lv) found associated with the Golgi apparatus (Gg). (E) The internal canal (cgc) of the secretory gland cell, lined by microvilli, is filled with secreted mature MpVLPs. (F) MpVLPs purified by centrifugation of venom collected from M. pulchricornis venom reservoir (MpVLPs average longer diameter 250 nm, n = 20). These vesicles were apparently single membraned vesicles (membrane mean width 30 ± 13 nm, n = 17).
2.2. Analysis of M. pulchricornis Venom Gland Transcriptome
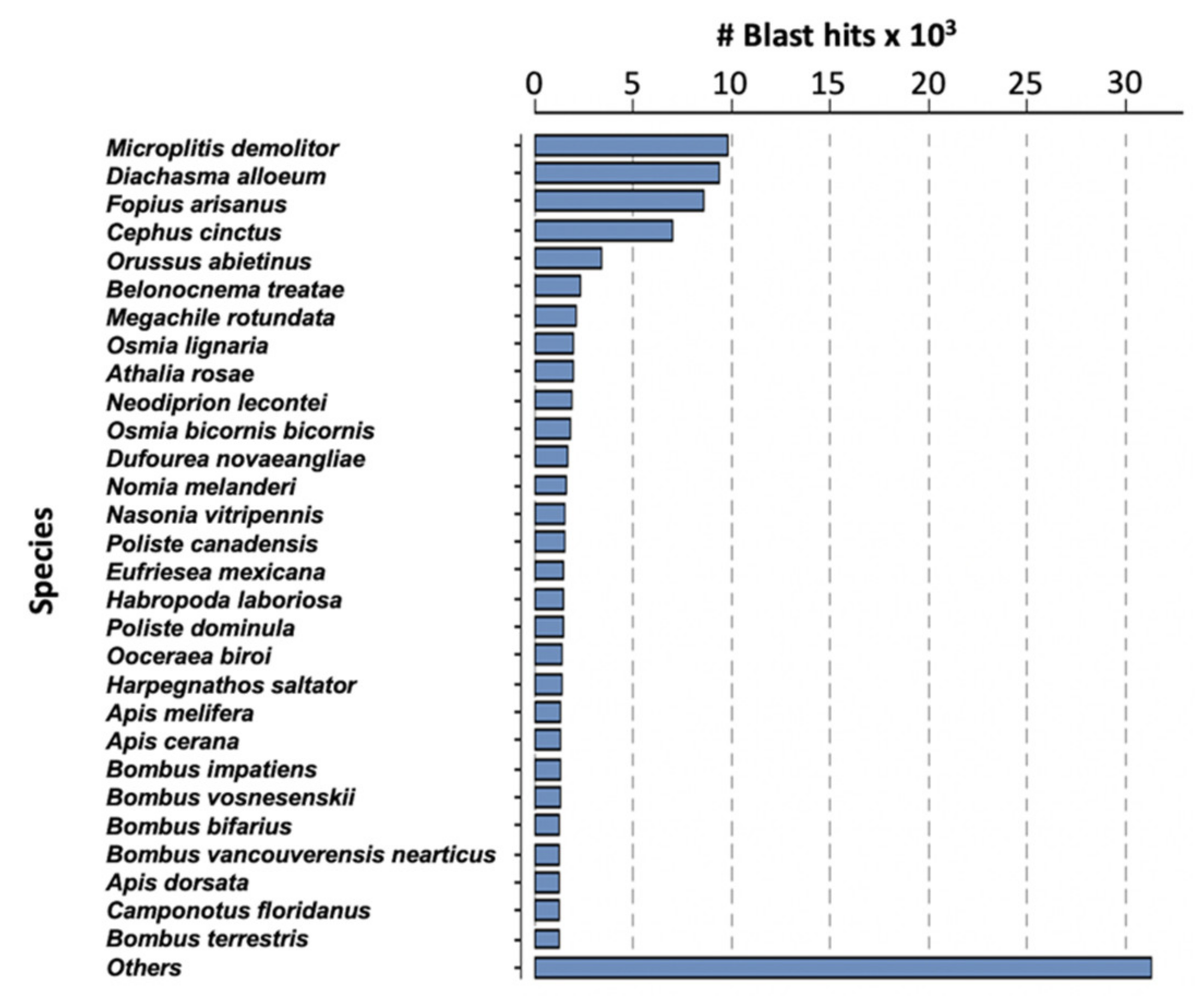
Assembly of the filamentous venom gland transcriptome yielded 14,926 contigs corresponding to 16,828 predicted coding sequences (CDS) (Table S1). The difference can be explained by the existence of chimeric contigs containing two or more tandem reading frames or with forward and reverse phase sequences for instance. The average length of the predicted CDS was 855 nucleotides (median 555 nt). Analyses were made on the 16,828 predicted proteins and, after BlastP similarity searches against the NCBI NR database, a total of 10,096 of these proteins matched a known protein. The highest number of matches was obtained with Microplitis demolitor, followed by Diaschama alloeum and Fopius arisanus which belong to the same braconid family as M. pulchricornis (Figure 2).
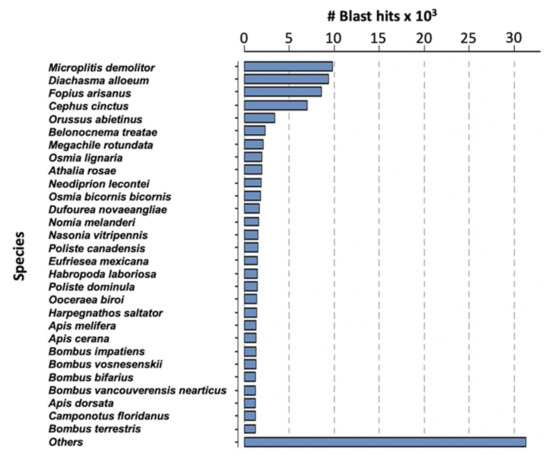
Figure 2.
Species classified by the number of hits reported for M. pulchricornis CDS protein sequences against the NCBI NR database.
To estimate the extent to which the M. pulchricornis transcriptomic dataset included orthologs from other related or distantly related parasitoid species (Figure S1A), orthology relationships were searched by Orthofinder using as input the venom CDSs of M. pulchricornis and predicted proteins from a series of available parasitoid genomes (the braconids Aphidius ervi Haliday, Cotesia congregate Say, Diachasma alloeum, Fopius arisanus, Lysiphlebus fabarum Marshall and Microplitis demolitor Wilkinson, the ichneumonids Campoletis sonorensis Cameron, Hyposoter didymator Thunberg and Venturia canescens Gravenhorst, the pteromalid Nasonia vitripennis Walker, plus Apis mellifera L. and Drosophila melanogaster Meigen as non-parasitoid species) and braconid venom gland transcriptomes (Liragathis javana Bhat & Gupta, Psyttalia concolor Szepligeti, Bracon nigricans Szepligeti) (see Table S2). This analysis showed that among the 16,828 predicted M. pulchricornis proteins, a total of 11,767 CDSs (70%) were distributed into 8315 orthogroups composed of 2 to 471 members while 5061 CDSs could not be assigned to an orthogroup (see Table S1).
Of the 8315 orthogroups identified by Orthofinder, 122 contained only M. puchricornis proteins (from two to 99 sequences/orthogroups). The most abundant was OG000306 (99 proteins), which included proteins with similarities with metalloproteases or with the previously described hypothetical BAL70303.1 protein from M. pulchricornis, followed by OG0005090 (34 proteins) and OG0006398 (30 proteins), which corresponded to uncharacterized proteins. The majority of the orthogroups thus included sequences from other species, although in variable number. Orthogroups with a large majority of M. pulchricornis proteins included OG0000843 (67 of 68 entries were M. pulchricornis sequences), OG0001872 (50 of 51 entries) or OG0005678 (30 of 32 entries). All three also included sequences displaying similarities to metalloproteases or the BAL70303.1 protein (like OG000306 above). Note that the richest orthogroups (for instance OG0000003 (471 entries) or OG0000005 (327 entries)) were mainly composed of cellular proteins with orthologs from almost all analyzed species.
Then, to obtain functional labels, the 16,828 proteins were aligned against NCBI NR and scanned against the InterPro protein signatures database. We used Blast2GO to assign Gene Ontology (GO) IDs and EC numbers. GO IDs could be assigned to 45.61% of the input sequences, revealing that cellular and metabolic processes are the most represented among GOs (Figure S1B). Among enzymes, hydrolases were the most represented in the analyzed dataset, followed by transferases and oxidoreductases, and among them, peptidases formed the most important subclass (Figure S1C).
At last, Blast searches of viral sequences deposited at NCBI yielded 1031 CDS corresponding to 563 different viral proteins (Table S1). None of the viral hits corresponded to sequences previously described as involved in the production of viral particles in other braconid or ichneumonid species. Of these 1031 proteins, 1019 belonged to orthogroups comprising from two to 280 sequences from different parasitoid species. In addition, almost all displayed similarities with cellular proteins, which suggests that these CDS actually correspond to cellular genes that matched with virus acquired cellular genes. For the 12 sequences not assigned to an orthogroup, more than half had a collagen alpha domain and therefore could also be cellular proteins. All this indicates that none of these sequences was specific to M. pulchricornis and could be directly responsible for MpVLPs formation.
2.3. Search for M. pulchricornis Genes a Priori Preferentially Transcribed in the Venom Gland
Transcript levels of each protein-encoding sequence identified in the venom gland dataset were represented by the read coverage estimated by transcripts per kilobase million (TPM) to account for variability in CDS sequence length. For all 16,828 protein-encoding CDSs, TPMv (v for venom) ranged from 0.04 to 70,872 (Table S1), corresponding to a total number of reads ranging from 3 to 8,567,976. Only a minority of sequences (>1%) had a TPMv > 1000 indicative of a high level of transcription (Table 1; Table S1). The vast majority (∼96%) had a TPMv < 100, suggesting they were relatively poorly expressed in the M. pulchricornis venom gland (Table 1).

Table 1.
Sequencing coverage of predicted M. pulchricornis venom gland CDS (TPMv; number of sequences for given TPM (Transcripts Per Kilobase Million) ranges in venom gland transcriptome).
To assess which sequences may be preferentially transcribed in the venom gland of M. pulchricornis compared to other tissues, the sequences were first used to search a previously published RNAseq obtained from antennae tissues [26]. Among the 16,828 CDS sequences in the venom, 16,091 (95.6%) were also found in the antennae. However, the corresponding TPMs in antennae (TPMa) were highly variable, ranging from 0.029 to 18,499 (Table S1).
Of the 39 CDSs that were highly expressed in the venom gland (TPMv > 5000), 37 had a low coverage in the antennae (TPMa < 200), suggesting that they potentially correspond to genes more specifically transcribed in the venom gland compared to antennae. Contrariwise, the CDS most expressed in the antennae were poorly expressed in the venom gland and encoded odorant binding proteins or odorant-binding related proteins, which are proteins that play an important role in olfaction and are known to be abundant in olfactory organs [27]. Only four of these 39 CDSs had a match in the NCBI NR database with a protein of known function (Table 2; Table S1) and 12 had similarities with genes previously identified in the EST library of the venom gland of M. pulchricornis [24]. Most of the highly expressed CDSs (n = 24) belonged to orthogroups composed mostly by sequences from M. pulchricornis although they also contained sequences from other parasitoid species (Table 2).

Table 2.
List of the 39 CDS highly expressed in M. pulchricornis venom gland (TPMv > 5000). CDS with TPMv/TPMa ratio > 500 are indicated in pink, in orange 500 > ratio > 200 and in green ratio < 50.
The most highly expressed CDS in the venom gland were contigs 60.p3, 64, 32 and 338. All four encoded proteins with similarities to hypothetical proteins previously identified in the M. pulchricornis venom gland [24]. Homologs were only identified in the transcriptome of L. javana venom gland for contig 60.p3, 64 and 338 (Table S1). Contig 60.p3 and contig 338 encoded a 55 AA-long and a 136 AA-long sequences, respectively, that matched with the hypothetical 136 AA protein from M. pulchricornis. The product of contig 338 was 79% identical to BAL70305.1 (E = 6 × 10−70) while that of contig 60.p3 corresponded only with the N-terminus (including a putative signal peptide) of BAL70305.1. Contig 64 encoded a 123 AA sequence protein 96% identical to the C-terminus of the hypothetical protein BAL70301.1 of M. pulchricornis. Finally, contig 32 encoded a protein of 172 AA that was 97% identical to BAL70307.1 (10−115) of M. pulchricornis.
Among the CDSs with high TPMv values, four can be pointed out because of their high TPMv/TPMa ratio, suggesting that they are highly overexpressed in the venom gland relative to the antennae: contigs 52, 21, 155 and 49. Contigs 52 and 49 both matched with 97% identity with the hypothetical BAL70302.1 protein from M. pulchricornis, contig 21 to a 5′-nucleotidase (5NUC-like protein) from A. cerana, whereas contig 155 had no hit in the NCBI NR database.
2.4. Proteomic Analysis
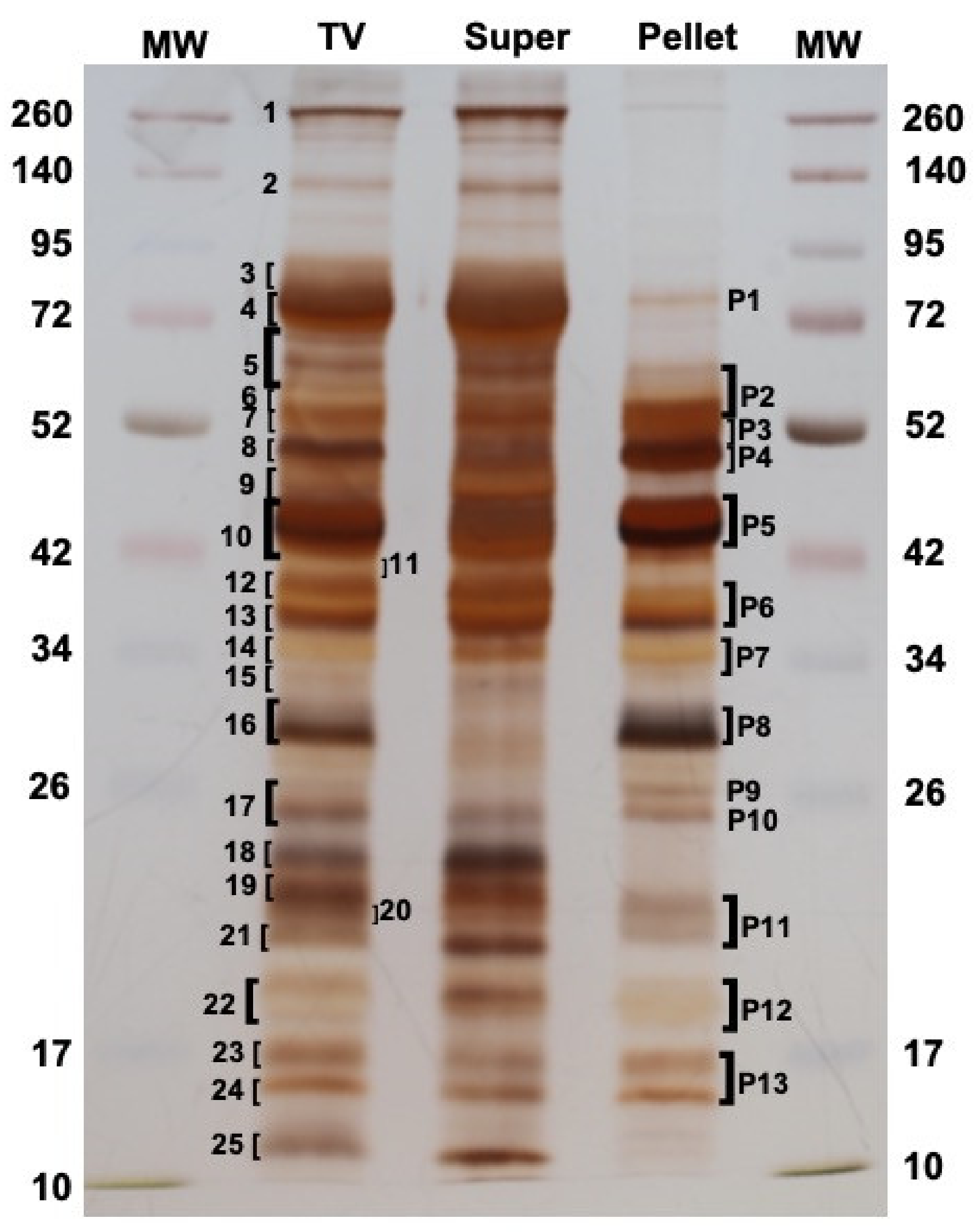
To define exactly which proteins were present in M. pulchricornis MpVLPs, the total venom (TV) was extracted from venom reservoirs and analyzed directly, or fractionated by centrifugation at 15,000× g into supernatant (Super) and pellet, with the later fraction containing only purified MpVLPs (see Figure 1F). When the proteins of each sample were separated by SDS-PAGE (Figure 3), some of the bands present in TV were strongly decreased or absent in the supernatant fraction while they were highly enriched in the pellet fraction of MpVLPs (such as bands P4, P5, P8, P9, P10, P11 and P12), indicating that MpVLPs had a specific protein profile.
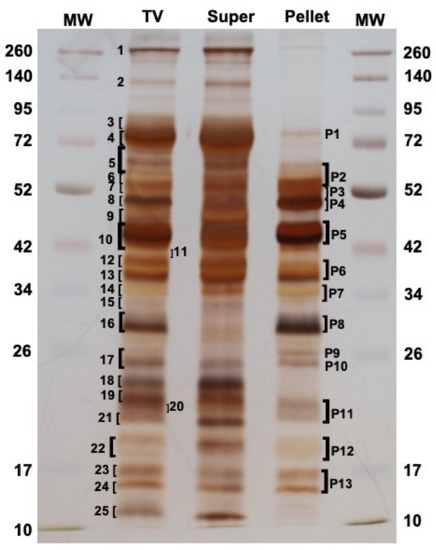
Figure 3.
Protein profile of total venom (TV) compared to the supernatant (Super) and the MpVLPs pellet fractions obtained after centrifugation. A total of 25 and 13 bands were cut off for TV and the washed 15,000 g Pellets (MpVLPs) lanes, respectively, to be submitted to the MS-MS analysis. Left and right lanes correspond to molecular weight markers (MW in kDa). 12% SDS-PAGE in reducing conditions and gel was silver stained.
Following separation by SDS-PAGE, a number of major protein bands were selected from the TV and MpVLPs samples (bands 1 to 25 for TV lane, bands P1 to P13 for Pellet lane; Figure 3). These bands were cut off from the gel, digested with trypsin, then submitted to mass spectrometry (see Materials and Methods). Protein identification was carried out using MASCOT searches against predicted translated contig sequences from the venom gland transcriptome. For TV, the peptides matched with 1354 different potential proteins and for MpVLPs with 516 different proteins. For subsequent analyses, we chose to focus on the 60 proteins with the highest Mascot proteomic scores (correlated to protein abundance according to spectral counting method, see material and method) for each of the two samples. Of these 120 sequences, 27 were common to both TV and MpVLPs samples, resulting in a total of 93 unique proteins. Note that because the TV sample included both MpVLPs and soluble proteins, we considered as “MpVLPs proteins” those that were enriched in the MpVLP sample plus those that were common to both samples (n = 60). Proteins present only in the TV were considered “soluble venom proteins” (n = 33).
BlastP similarity searches against the NCBI NR database indicated that most of the identified proteins had no matches or corresponded to proteins with no predicted functions (see Table 3 and Table 4 below). However, a large proportion of MpVLPs proteins has a predicted metalloprotease domain, while a large number of soluble venom proteins has a domain of Unknown Function 4803 (DUF4803). No hit was returned when MpVLPs peptides were blasted to the virus protein databank at Uniprot (Viralzone including polyDNAviridae).

Table 3.
Names and functions of the most abundant MpVLPs proteins. They are classified starting from the most abundant MpVLP protein using the Mascot “ranks” that ranged from 1 (the most abundant) to 516 (the less abundant) for MpVLPs and from 1 to 1354 for TV CDS/proteins, respectively.

Table 4.
Names and functions of the most abundant venom soluble proteins. Mascot “ranks” range from 1 (the most abundant) to 1354 (the less abundant) for TV CDS/proteins and from 1 to 516 for MpVLP CDS/proteins.
2.5. The MpVLPs Proteins
The most represented protein family in MpVLPs was formed by the 32 sequences with correspondence to metalloprotease-like proteins (Table 3). This group included proteins with predicted metalloprotease domains, with similarities to the BAL70303.1 protein from M. pulchricornis (which includes a cysteine-rich ADAM domain), or sequences with no clear domain homology, but which were clustered in an orthogroup containing metalloproteases (Table 3).
However, based on Mascot scores, the most abundant proteins in MpVLPs were those encoded by contig 38 and contained a DUF4803 (Table 3). Contig 38 contained two proteins (named 38.p1 and 38.p2) in tandem on the same reading frame separated by an insertion. Both were DUF4803 containing proteins, and for both a high peptide coverage was obtained by MS-MS (Figure S2) explaining the very high Mascot score for this contig. One of the CDSs (38.p1) had a very high TMPv while the second one (38.p2) was tenfold less expressed. These two proteins belonged to two different orthogroups but showed 31% identity (E = 2 × 10−60) and both had a predicted C-ter transmembrane domain. They were also related to proteins of unknown function from different species of parasitoid wasps, although with low E-values (from E = 2 × 10−12), which may be due to the fact that all contained the DUF4803 domain. Two other proteins have DUF4803 domains (contig 72 and 897), making a total of four proteins of this family detected in MpVLPs. The third most abundant protein is encoded by contig 35. This unknown protein of 349 amino acids had no predicted signal peptide but a putative C-terminus transmembrane domain. The fourth and fifth most abundant MpVLPs proteins were encoded by contig 29 and 39, respectively. These proteins had no known function, domain, or peptide signal. The protein in contig 29 encoded a full-length protein that was 93% identical to BAL70308.1, and the protein in contig 39 was 98% identical to BAL70290.1 but has also some identity with BAL70306.1 (34% identity; E = 2 × 10−19) and BAL70304.1 (34%; E = 4 × 10−10). The abundant MpVLPs proteins also included proteins without a match in the NCBI database of proteins but having a predicted domain (3 with Calycin/Lipocalin domains and one with Serine protease inhibitor SERPIN domain).
Only four of the MpVLPs proteins have a clear match in the NCBI NR database. This is the case for a pancreatic lipase-like (contig 554), or a hyaluronidase (contig 293). Contig 6.p3 (and also 6.p2) and contig 1039 correspond to fibrillin-like proteins; they were about 35% identical to each other and all three have a predicted signal peptide. Fibrillins are high molecular weight secreted cysteine-rich glycoproteins (about 350 kDa) that contain numerous EGF-like calcium-binding domains [28]. The M. pulchricornis proteins corresponded to fibrillins mainly because of the high number of cysteine residues in their sequences (24 conserved cysteine positions out of the 29–31 cysteines of these sequences). Whether these proteins are derived from a fibrillin or are individual cysteine-rich proteins remains to be determined.
At last, all MpVLPs CDSs for proteins found in proteomics showed medium to high TPMv and were also expressed in antennae, although at a much lower level (TPMa ranging from 0.3 to 131). For nine of the twelve first MpVLPs proteins, a good correlation could be observed between the level of expression in the venom gland (TPMv > 5000) and the Mascot scores. Interestingly, the most abundant proteins in the purified MpVLPs were also the most abundant in the TV sample, indicating the importance of the vesicles and their content in the venom composition.
2.6. The Venom Soluble Proteins
Soluble proteins are those that are highly enriched in the TV sample compared with MpVLPs and represented 33 proteins (Table 4). Of these, 10 contained a DUF4803 domain and one, although lacking the domain, had a high identity to the venom protein 2 of Microctonus hyperodae Loan, which is also a DUF4803-containing protein. Four proteins were tagged metalloproteases or belonged to an orthogroup of metalloproteases, including a member of Neprylisin (contig 6971). Two proteins had a lipocalin domain and one could be an odorant binding protein (OBP) that are from the same protein family. Two matched with a pancreatic lipase-related protein, two with apolipophorins. One corresponded to a 5′ Nucleotidase (5NUC), one to a γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT), one to a cysteine-rich secretory proteins, antigen 5, and pathogenesis-related 1 proteins (CAP) domain protein. Several of the CDSs matched with proteins generally considered to be cytoplasmic proteins such as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, 14-3-3 protein, myosin, aldose reductase and arginine kinase.
A surprising result was that, in contrast to MpVLPs, many of the contigs encoding the most enriched soluble proteins had low TPMv, and in some cases even appeared to be more expressed in the antennae than in the venom gland (i.e., arginine kinase and OBP). Based on their TPMv values, three groups of venom-soluble proteins could be defined: those with TPMv > 1000 (10 contigs) and those with TPMv < 100 (16 contigs), with the remaining seven contigs ranging between 112 and 581. For example, almost all CDSs encoding DUF4803 domain-containing proteins were weakly expressed in the venom gland (except contig 275). Conversely, those encoding metalloproteases, even with a low Mascot score, were highly expressed with the exception of neprilysin whose expression was very low in both venom gland and antennae.
The most expressed CDS was contig 21 encoding the 5NUC-like protein, while among the least expressed were those encoding GGT, OBP, myosin, arginine kinase, neprylisin and apolipophorins. Some of these proteins such as arginine kinase, OBP and apolipophorins play an important role in lipid transport and immune response in insects and usually circulate in the hemolymph [29,30]. Their presence in the venom could therefore result from a contamination during venom collection, yet other classically abundant hemolymph proteins (i.e., HSP chaperones and phenoloxidases) were absent from the data. Another possibility is that these proteins entered passively or were concentrated in the venom by a specific transport process, but this remains to be ascertained. Another possibility for some of these proteins is that, because the venom is enclosed and separated from the rest of the body fluids, the released cellular proteins may have accumulated in this fluid. However, this does not exclude that these proteins may play a role in the envenomation. For example, arginine kinase, which plays a critical role in maintaining insect cellular energy homeostasis, has been found in almost all hymenopteran venoms. Once injected by the wasp, it can modulate the host extracellular ATP/ADP ratio, which may significantly affect the host purinergic signaling-activated innate immune response [31].
2.7. The Most Represented Venom Proteins: Metalloproteases and DUF4803 Proteins
2.7.1. The Venom Metalloproteases
Metalloproteases were found in large numbers in the transcriptomic analysis of the M. pulchricornis venom gland and a total of 36 putative metalloproteases were found by proteomics. The majority (n = 32) were enriched in MpVLPs. In addition, a neprylisin-like protein (contig 6971) was detected in the soluble fraction and will be discussed in more details below.
Metalloproteinases are toxins described in the venom of almost all venomous animals [32] and also used as virulence factors by bacteria [33]. The best studied example for the role of these enzymes in envenomation is that of snake bites where injected metalloproteinases interfere with the hemostatic system, resulting in hemorrhage [34]. Snake venom metalloproteinases also induce local myonecrosis, skin lesions, and an inflammatory response [35]. Metalloproteases have also been identified in the venom of hymenopteran wasp and bee species [36,37,38,39]. These metallopeptidases have been suggested to have a wide range of functions, including nutrition, suppression of host cellular defense, and degradation of host defense molecules.
Metalloproteases include a number of families that differ in their structure and catalytic domains. A disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motif (ADAM-TS) are normally multidomain proteins of more than 800 AA that typically comprise: (i) a signal peptide, (ii) a pro-domain, (iii) a catalytic domain with a reprolysin-type zinc-binding motif (HEXXHXXG/N/SXXHD), and (iv) a disintegrin-like domain. The disintegrin domain may be followed in some proteins by an ADAM-cysteine rich (ADAM-CR) domain and a C-terminus of varying length [40,41,42]. The different domains can be cleaved from the catalytic domain after secretion to give rise to the mature protein [43]. Collagenase/matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are also multidomain proteins and can have a lower molecular weight ranging from 25 to >100 kDa. The metal ligands and active site of MMPs show a similar HEXXHXXGXX motif [44] and their substrate and cleavage sequence specificity overlap with that of ADAMs. However, some metalloproteases, for instance snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs), can be much shorter. Indeed, SVMPs can be divided into three classes: Class I SVMPs range from 20 to 30 kDa and contain only a pro-domain and the proteinase domain. Class II is 30–60 kDa, contains the pro, proteinase and disintegrin domains and Class III, 60–100 kDa, contains the pro, proteinase, disintegrin-like and cysteine-rich domains structure [45,46].
The putative metalloproteases sequences from M. pulchricornis venom ranged from 126 AA (contig 379.p2) to 592 AA (contig 375) suggesting that some sequences may be incomplete or represent the N- and C-terminus of the same protein. They shared from zero to about 70% identity, certainly due to differences in sequence length but nonetheless suggesting a high divergence among them (Figure S3). A putative N-terminus Methionine could be assigned to 18 sequences and a predicted signal peptide sequence to 11 of them (Table S3). Despite their variable length, most of the M. pulchricornis predicted metalloproteases have a labeled catalytic domain such as collagenase (matrix metalloprotease; MMPs), A disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM, ADAM-TS, reprolysin) or an ADAM-cysteine rich domain (ADAM-CR) (see Table S3). Of the 36 metalloprotease sequences, six had the canonical zinc-binding/catalytic site motif and 17 had a more or less degenerate motif. Most sequences had a furin cleavage site in their N-terminus between the pro- and the catalytic domain and the conserved triad of amino acids (E-D-N) involved in the first Ca2+ binding site of ADAMs (Figure S3). In addition, 22 of them showed a putative ‘Met-turn’, downstream of the catalytic site position, although not always in the V/IMA/S canonical motif but mainly L/IMD/Q motif [42]. After this Met-turn, 24 of the sequences showed the conserved proline marking the end of the metalloproteinase domain and then their C-terminus region contained up to seven conserved cysteine residues suggesting the presence of a disintegrin/cysteine-rich domain. None of these sequences have other EGF, transmembrane or cytoplasmic domains and are therefore structurally closer to class II SVMPs. Interestingly the 121 AA sequence from M. pulchricornis BAL70303.1 that contained 10 Cysteine residues aligned with this disintegrin/cysteine-rich domain in the other sequences, suggesting it may be an incomplete sequence that contains only this domain like our contigs 379 and 1198 (Figure S3). Whether an evolution leading to different classes of metalloproteinases as described in SVMPs has occurred in M. pulchricornis will necessitate to obtain the complete genome to have access to full length CDSs.
Several neprylisin-like CDSs from M. pulchricornis were distributed in different orthogroups, OG0017160 (7/7), OG0000177 (9/114), OG0000299 (12/99 contigs), OG0008057 (2/25), OG0002203 (1/49), OG0013455 (1/10), but only one neprilysin encoded by contig 6971 (named MpNEP) was found as a venom soluble protein. Neprilysins, also known as neutral endopeptidases, are normally membrane bound proteins, but their ectodomain can be released from the cell surface, producing a free circulating enzyme [47]. Such a mechanism may explain its presence in the soluble fraction of the venom. MpNEP had a low Mascot score and, as previously described, had a very low TMPv value in the venom gland (TPMv = 1) suggesting that it may be not synthesized in this tissue. However, since the protein had a conserved active site (Table S3) it could, even in small amounts, have an effect on the parasitoid’s host. NEP and NEP-like enzymes are involved in the processing of various neuropeptides and peptide hormones and play a role in the regulation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in insects [48,49,50]. Neprilysin-like enzymes have been commonly found in wasp parasitoid venoms [51,52,53] and a 94 kDa neprilysin−like protein (VcNEP) was found to be associated with virus−like particles produced in the calyx region of V. canescens [54]. This VcNEP has been suggested to induce cell adhesion and hemocyte spreading of the host Ephestia kuehniella Zeller. Contrariwise, injection of a recombinant neprilysin from the venom of the endoparasitoid wasp Cotesia vestalis Haliday (previously Cotesia plutellae) disrupted immune responses against E. coli in its host Plutella xylostella L. [53]. Although the role of neprilysin in parasitoid venoms remains to be clarified, this enzyme is known to play a role in the venom of snakes and solitary and social wasps, in the physiological clearance of natriuretic and vasodilatory neuropeptides [55,56]. Neprilysin-like enzymes present in spider venoms may also play a role in extracellular matrix degradation or cell apoptosis [57,58]. Similar effects of MpNEP can be expected in wasp hosts.
2.7.2. The DUF4803 Containing Proteins
A total of 14 proteins identified in M. pulchricornis venom by mass spectrometry contained a predicted DUF4803 domain (Table S4). In addition, we identified one contig (1164) that encoded a CDS lacking the DUF4803 domain but that matched with DUF4803-containing proteins. On this basis, 11 DUF4803 proteins were enriched in the soluble fraction of venom while four were enriched in MpVLPs. These proteins belonged to 10 different orthogroups, four of which contained only two to 34 CDSs from M. pulchricornis, three were shared with only L. javana, and three with one or more other species (Table S1). The DUF4803 (PF16061; IPR032062) protein family contains only arthropods proteins. Among them, 83 proteins have been reported in Hymenoptera (wasps, bees, ants …) including 56 in parasitoids (33 in Chalcidoidea and 23 in Braconidae). However, DUF4803 proteins are also found in venom-less insects such as Drosophila, suggesting a ubiquitous role for this domain. Indeed, DUF4803 proteins are typically between 350 and 690 amino acids and can have several other domains such as immunoglobulin, protein phosphatase or zinc finger domains, suggesting potential different functions or localizations.
Comparison of the 15 MS-MS-validated M. pulchricornis DUF4803 venom protein sequences showed an identity ranging from 9% to 53%, suggesting a large divergence between them. Protein sequence alignment showed a specific motif of highly conserved cysteine residues (Figure S4), in particular the characteristic DUF4803 CxxCxCxC motif, yet however the other suggested canonical motif RRY was not well conserved. A VI/VTGIK/RF motif present at the end of the DUF domain is duplicated in the C- terminus of the sequences suggesting a partial duplication of the domain. None of these venom DUF4803 proteins have another known domain.
Although DUF4803 proteins were previously found in proteomics in the venom of parasitoid wasps of the braconid species such as B. nigricans [59], Psyttalia lounsburyi Silvestri [51] and A. ervi [60] the role(s) they may play in parasitic success remains to be understood.
2.8. Other Venom Proteins of Interest
2.8.1. The 5′ Nucleotidase (5NUC)
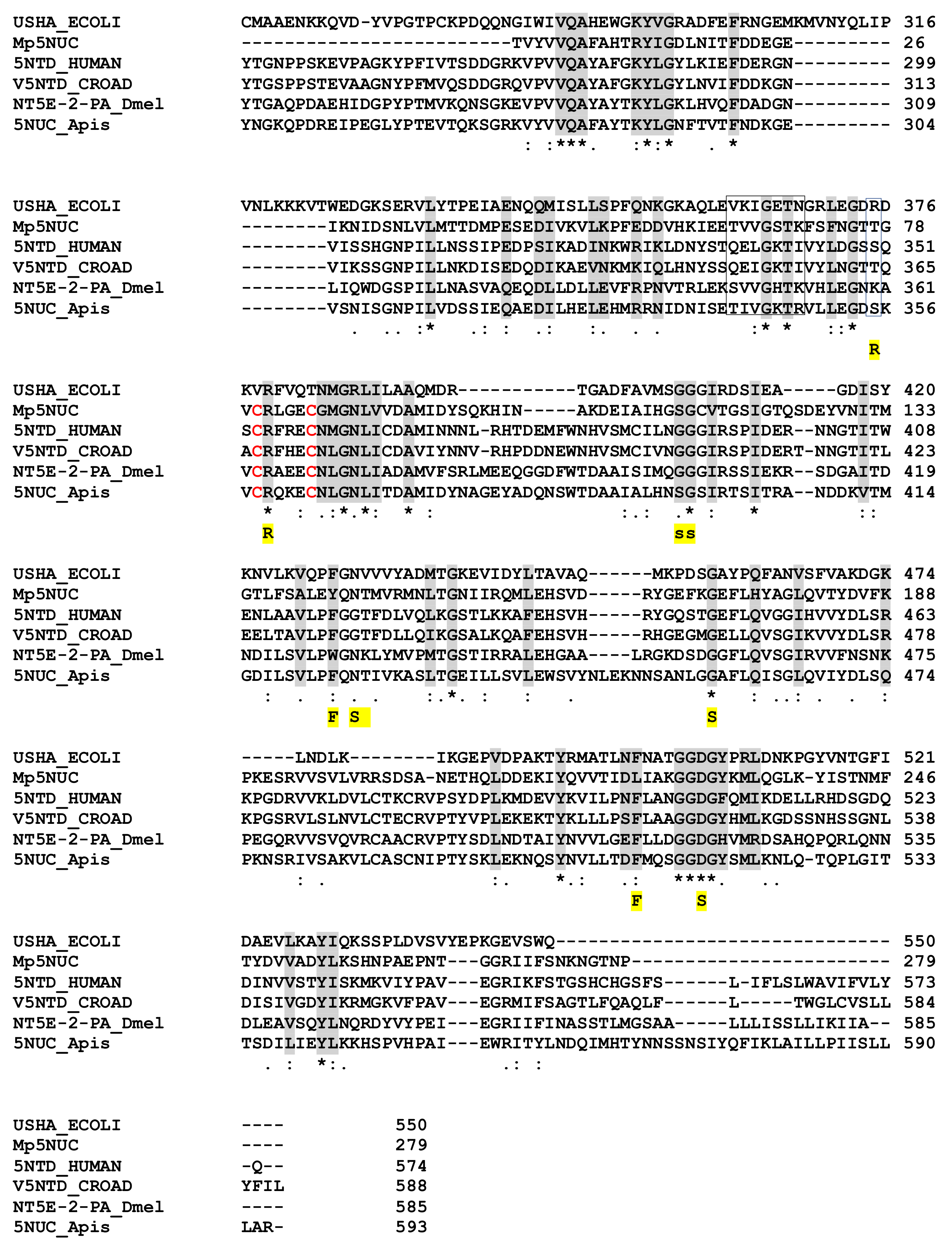
The 179 AA M. pulchricornis venom 5NUC protein encoded by contig 21 (which is 96% identical to the protein encoded by contig 19) found in the soluble fraction was found to be incomplete since it matched only the C-terminus domain of ecto-5NUC from bacteria, Hymenoptera and vertebrate sequences, including snakes and human CD73 (Figure 4). Therefore, the catalytic and ion binding sites were absent but some of the important features of the enzyme were retained [61]. The M. pulchricornis protein was not predicted to have a GPI anchor like human CD73 ecto-5NUC.
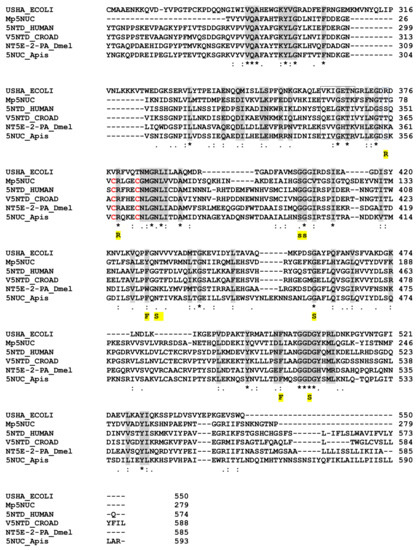
Figure 4.
Sequence alignment of nucleotidases from M. pulchricornis, human, E.coli, snake, drosophila and bee. Important conserved residues or motifs are shaded in grey or boxed. Functionally important residues are marked below the alignment with the following labels: “R” indicates the three arginine in the active site of the E. coli enzyme; “F”, the phenylalanines that bind the adenine moiety; “S” the residues that interact with the substrate and “s” those involved in non-polar interactions (from [61]). The only two cysteines in MpNUC that can form a bond are in red. USHA.ECOLI, Protein UshA Escherichia coli P07024 (uniport); 5NTD.HUMAN, 5’-nucleotidase Homo sapiens P21589; V5NTD.CROAD, Crotalus adamanteus venom 5’-nucleotidase F8S0Z7; NT5E-2PA, D. melanogaster Q8SZY4; 5NUC.Apis, protein 5NUC Apis mellifera XP.394018 (NCBI). Identical amino acids are indicated by a star, conservation by a colon and substitution by a dot.
The 5′-nucleotidase is a ubiquitously distributed enzyme in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. It is commonly found in the venoms of bees, wasps and ants [39,62] and is present in the venom or used as a virulence factor by various other species. For example, in snake venom, this enzyme has an anticoagulant effect and inhibits platelet aggregation in humans. In animals, the cytosolic and extracellular 5NUC enzymes (which are bound to the membrane by a GPI anchor) are structurally unrelated [63,64]. There is also a soluble form of these ecto-enzymes that is shed from the membrane by the action of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase. The ecto-5NUC catalytic domain of snake venom belongs to a superfamily of dinuclear metallophosphoesterases, which hydrolyze very different substrates, including phosphoproteins, nucleotides and nucleic acids. In humans, two 5NUCs, CD39 and CD73, have complementary activity: CD39 hydrolyses both ATP and ADP and produces AMP while CD73 uses AMP and generates adenosine [65].
Because in insects adenosine is involved in a broad range of physiological processes, including cell growth, differentiation and immunosuppression, 5’nucleotidase may have an immunoregulatory role when injected into the host by converting AMP to adenosine [61]. In D. melanogaster, extracellular adenosine is involved in the release of glucose from glycogen, a systemic metabolic switch required for effective resistance to pathogens [31]. 5NUC may have a different role in parasitoid wasp venoms but, based on the actions described, it may interfere with host immunity directly through adenosine production or depletion of circulating ATP or indirectly by modulating host metabolism to promote parasitoid larval development.
2.8.2. The Calycin/Lipocalin Proteins
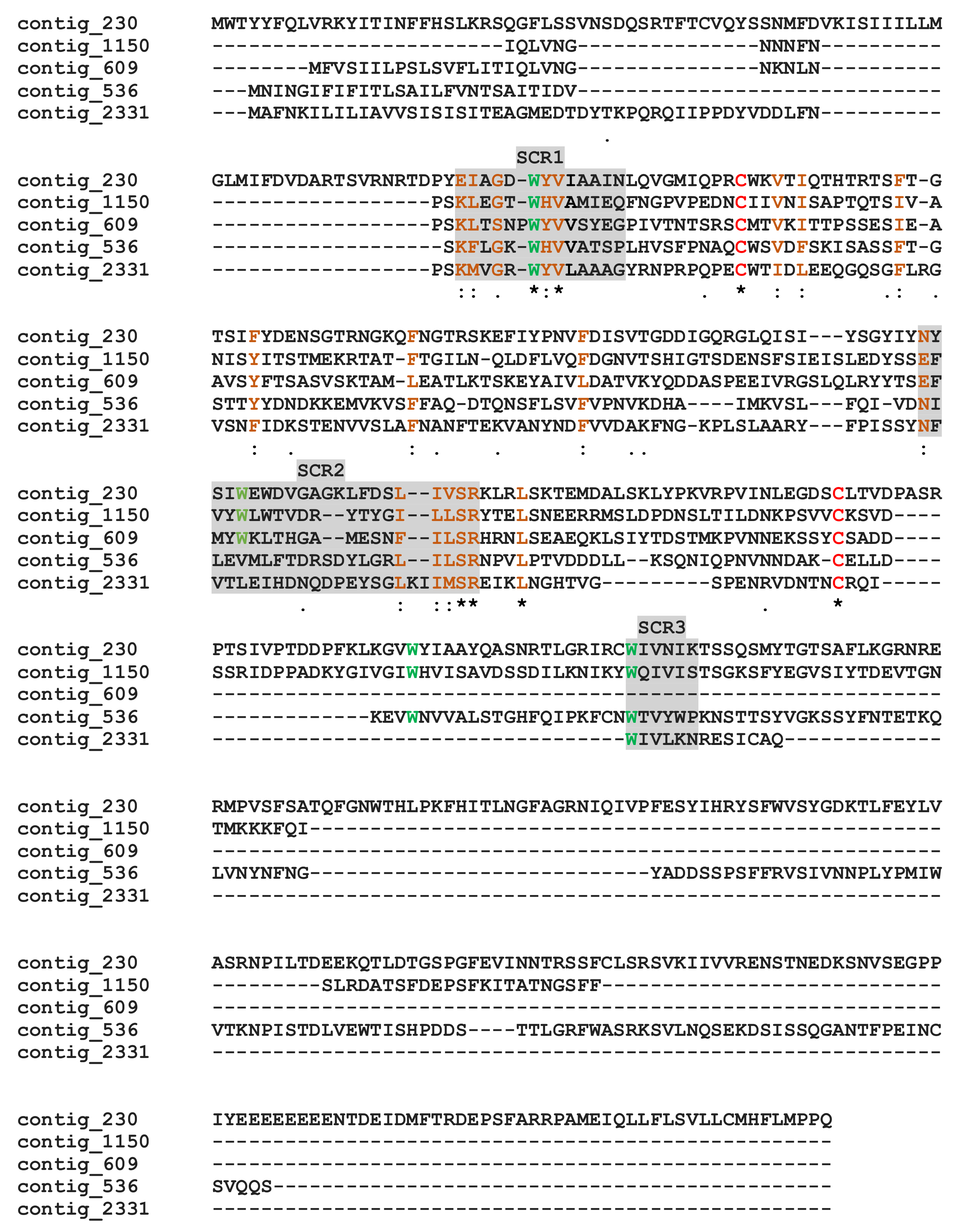
M. pulchricornis venom contained proteins with a calycins/lipocalin domain: three are enriched in the soluble protein fraction (contig 2331, 536 and 609) and two in MpVLPs (contig 1150 and 230). Calycins form a large protein superfamily consisting of a heterogeneous group of secreted proteins, including lipocalins and fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs), which bind a wide variety of small hydrophobic ligands and exhibit high functional diversity [66,67]. Calycins/lipocalins are quite diverse and have little sequence identity, except for characteristic short conserved motifs (SCRs) that may be receptor-binding sites for hydrophobic compounds [68,69]. The M. pulchricornis sequences shared only between 15–33% identity, but when these sequences were compared to well-described lipocalins [69], the three putative SCRs could be located (Figure 5). In all lipocalins, SCR1 is the most conserved motif, and the M. pulchricornis sequences display the central SCR1 motif GXWH/Y found in classical lipocalins such as retinol binding protein [70]. The positions of the other two SCRs are indicated but are much less conserved (even in canonical lipocalin sequences). Some amino acid identities/similarities can be found in the SCR2 region and a degenerated SCR3 appears to be present only in the four longest sequences. The M. pulchricornis proteins also showed two classically conserved cysteines that may form a disulfide bond but lack the CXXXC motif found in OBPs (Figure 5).
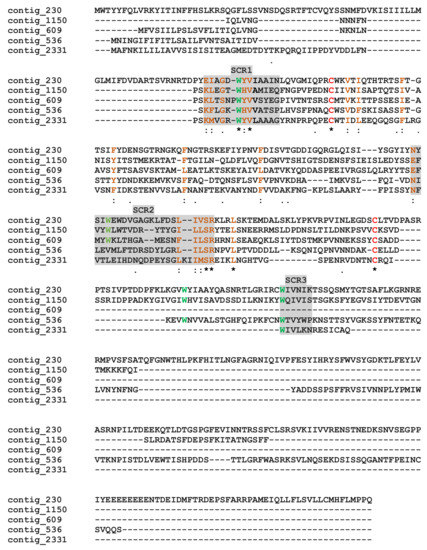
Figure 5.
Alignment of the putative M. pulchricornis venom lipocalins. Grey boxes indicate the three putative lipocalin structural regions (SCR1, 2, 3). In green, the hydrophobic tryptophan (W) retrieved in SCRs, in red the cysteines. Identical amino acids are indicated by a star, conservation by a colon and substitution by a dot.
Proteins of the lipocalin superfamily have been identified in the venom of the parasitoids Chelonus inanitus L., Pteromalus puparum L., and N. vitripennis and various other hymenopteran species. In P. puparum, OBP-like mRNA expression in the venom apparatus is upregulated after feeding and parasitism, suggesting a role in venom gland metabolism or host interaction (or both) [71]. The main ant venom allergen of Dinoponera quadriceps Kempf and the fire ant Solenopsis invicta Buren are OBP/PBP-like capable of triggering anaphylaxis [72]. The role(s) that lipocalins may play in the host after wasp venom injection remains to be analyzed, but this type of molecules, with their different functions such as retinoids, arachidonic acid and steroids transport, pheromone transport and prostaglandin synthesis, play many different roles in metabolism and physiological regulation [66,67]. Lipocalins are also members of the calycins superfamily, which includes avidins, a group of metalloproteinase inhibitors, and triabin, which is found in several groups of hematophagous arthropods and has various anti-hemostatic functions by interfering with the assembly of procoagulant complexes, preventing platelet activation and aggregation, and sequestering amines such as serotonin (for review [32]).
To this group of lipocalins proteins we can add the protein encoded by contig 267 with a juvenile hormone binding protein domain (JHBP) found in MpVLPs. This protein did not blast with known JHBPs but with several parasitoid proteins with tandemly repeated JHBP domains. The sequence also lacked the cysteine residues forming the two bonds in the JHBP proteins. The CDS of contig 267 has a TMPv of 2950 suggesting high expression in the venom gland. In the hemolymph, the JHBP protein transports Juvenile Hormone from the sites of its synthesis to target tissues and protect it from hydrolysis. Juvenile hormone (JH) has a profound effect on insect embryogenesis, larval development and reproductive maturation of adult forms. Once injected, this protein can bind to the host JH to block its development and molting. However, since M. pulchricornis contig 267 does not have the classical characteristics of the JHBP protein and the structure of the JHBP domain resembles that found in some mammalian lipid-binding tandem-repeat proteins that increase bacterial permeability, it cannot be ruled out that this protein may have one of these other roles.
2.8.3. The GGTs
A γ-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT) was found with a high score in soluble venom proteins. Among the proteins present in braconid venom, it is suggested that a GGT play an important role in the success of the parasitoid A. ervi: once injected, venom GGT1 can target the reproductive tract of the female aphid host, leading to ovarian degeneration and decreased fertility [73]. GGTs are normally cell surface hydrolases that cleave glutathione and other γ-glutamyl compounds and are essential in cysteine homeostasis, but like neprilysin, they can be cleaved and released into the surrounding environment [74].
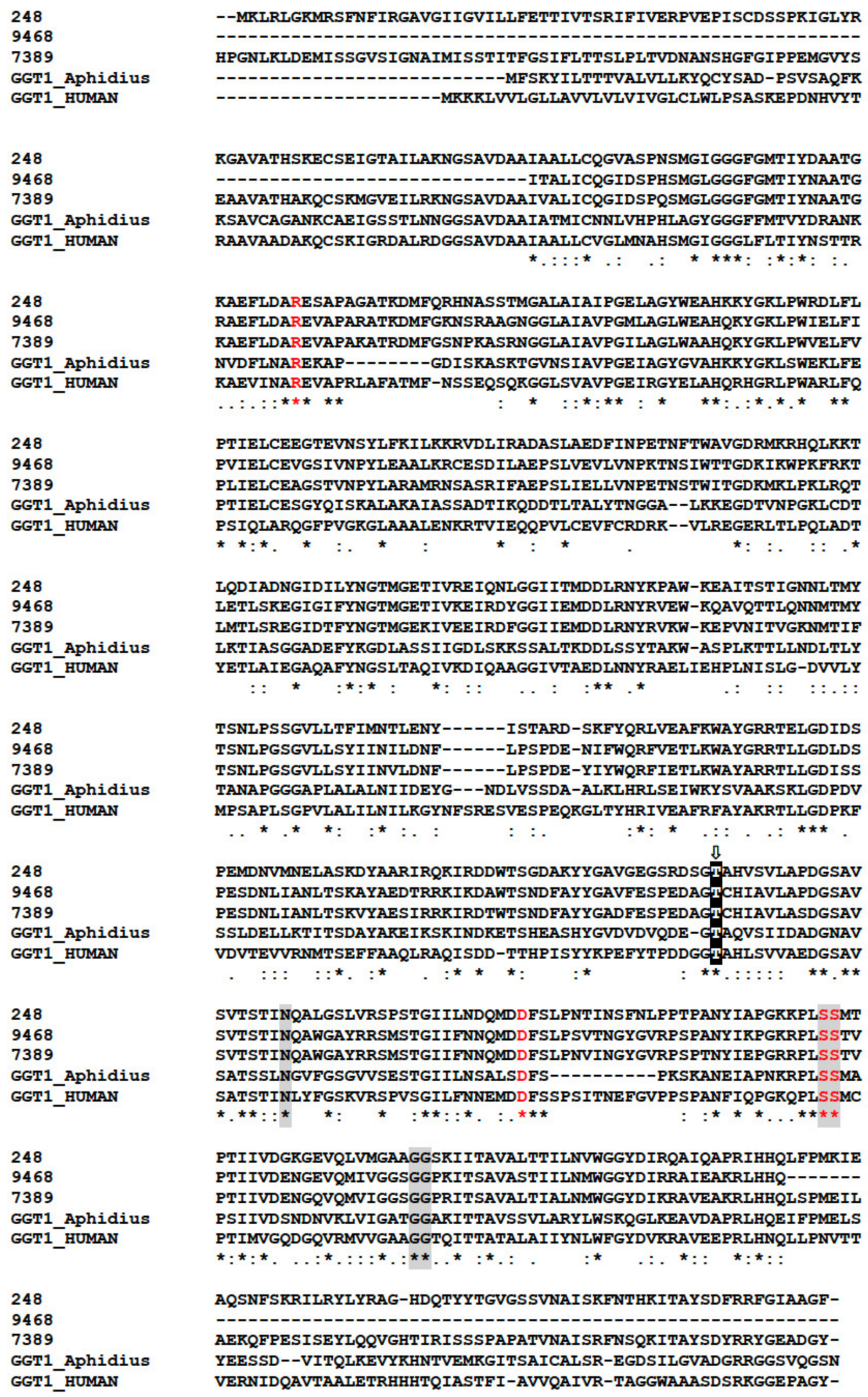
In our analysis, GGTs formed the orthogroup OG0000441 (Table S1) encompassing 87 sequences from various Hymenoptera including six from M. pulchricornis. Five of the six M. pulchricornis sequences blasted with high e-values with GGTs from the braconid M. demolitor (NCBI ID: XP.008555551.1) and four of these GGTs sequences were found in the M. pulchricornis venom proteome (CDSs from contig 11339, 248, 9468, 7389). Two of the encoded proteins were 100% identical (contig 11339 and 248). The other two were 80% identical to each other and 62% (for 9468) and 55% (for 7389), respectively, with the 11339/248 CDS sequence. The three sequences were compared with those of GGT1 from Aphidius ervi venom and human GGT1 (Figure 6). The main feature of the GGTs was retrieved in the M. pulchricornis sequences, suggesting that they function like GGT1 in venom and may have a similar function to that in A. ervi venom. However, none of the GGTs in the M. pulchricornis sequences had AA mutations that have been found in some A. ervi venom isoform sequences, mutations that reduced the enzymatic activity of human GGT [60]. Interestingly, a very high number of OG0000441 members (49/87) were predicted in the transcriptome of the venom gland of the ichneumonid Pimpla turionellae L., suggesting strong GGT amplification in this species.
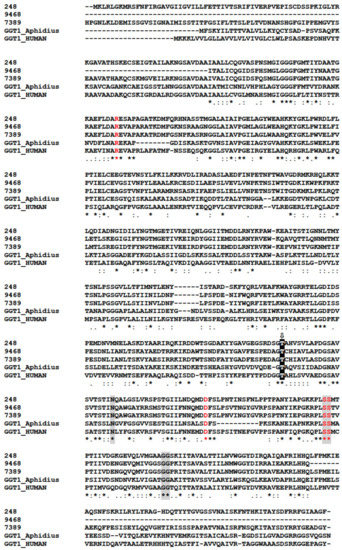
Figure 6.
Clustal alignment of the M. pulchricornis GGTs with the human (CAG30380.1) and A. ervi (CAL69624.1) GGT1 sequences. The catalytic threonine residue that forms the N-terminus of the small subunit (T381) after autocleavage to form the mature heterodimeric enzyme is highlighted with a black box containing a white “T” with an arrow above. Residues proposed to interact with glutathione in human GGT1 are shaded in grey and residues that significantly reduced human GGT enzymatic activity by site-directed mutagenesis are in red. Identical amino acids are indicated by a star, conservation by a colon and substitution by a dot.
2.8.4. Pancreatic Lipase Like Proteins
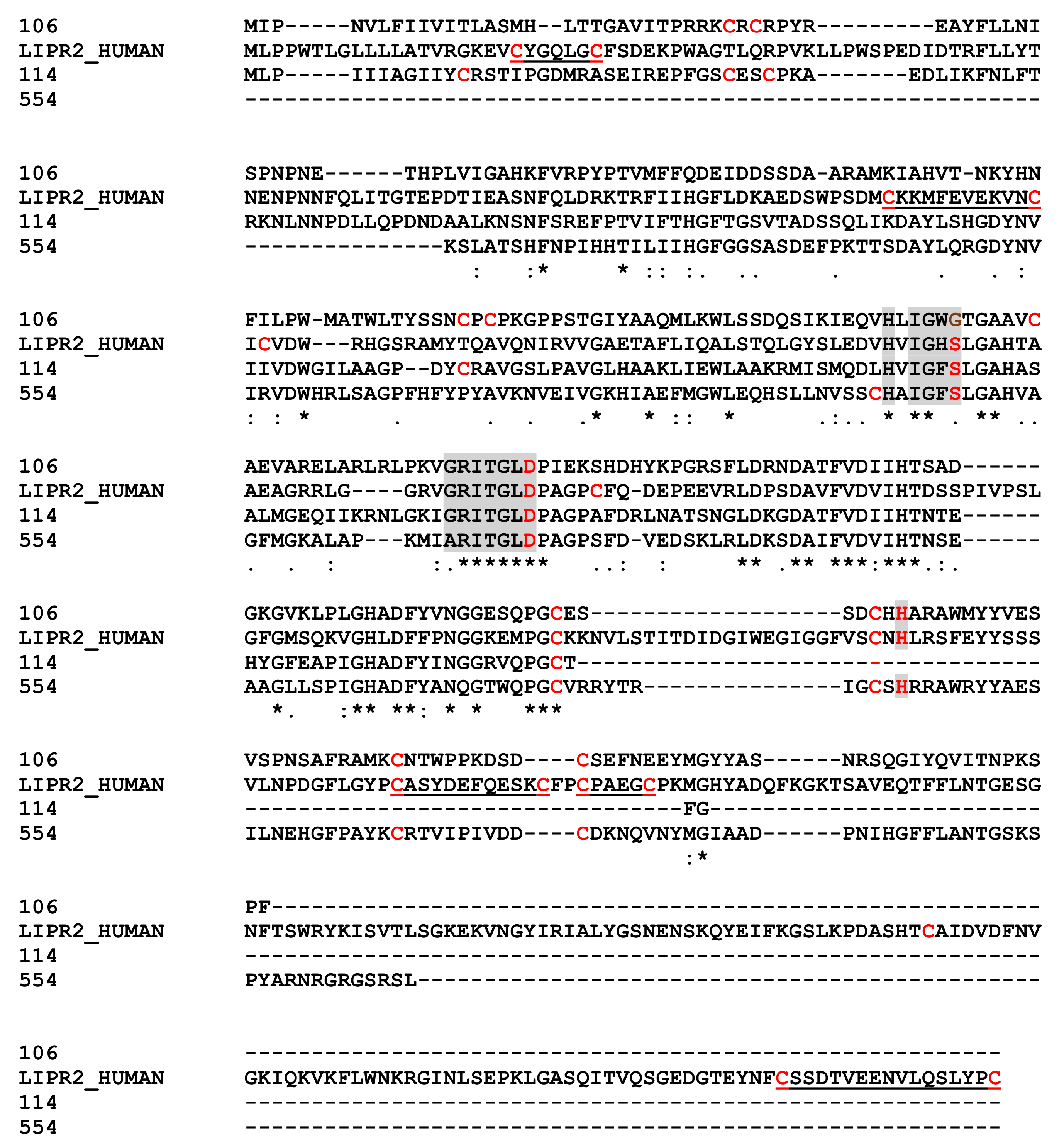
One soluble protein and one in MpVLPs matched with pancreatic lipase-relative protein 2-like (PLRP2-like) and one soluble protein with a triacylglycerol lipase. These sequences had 35% (contig 106 versus 114 and 554) to 49% (114 versus 154) identity. When compared with human pancreatic lipase-related protein 2/PNLIPRP2 (Figure 7) the three important active site residues (S,D,H) could be retrieved for at least two of the three sequences, with the first serine replaced by a glycine in the contig 106 protein [75]. While at least four of the cysteine residues were conserved, most of those involved in disulfide bonds in the human protein were absent. Lipases are widely distributed in animals, plants and prokaryotes. Pancreatic lipases (EC 3.1.1.3) are one of the three tissue-specific isozymes described in higher vertebrates [75]. They hydrolyze long chain triacyl-glycerol to free fatty acids and monoacylglycerols at the lipid–water interface and therefore play a crucial role in controlling lipid uptake, transport and utilization. Members of the lipase family have been found in the venom of insects including social Hymenoptera (bees, wasps and ants) and various other species such as snakes. In general, these major lipases were from the phospholipase-A family, which uses a different catalytic mechanism to hydrolyze acyl-ester bonds of phosphatidylcholine.
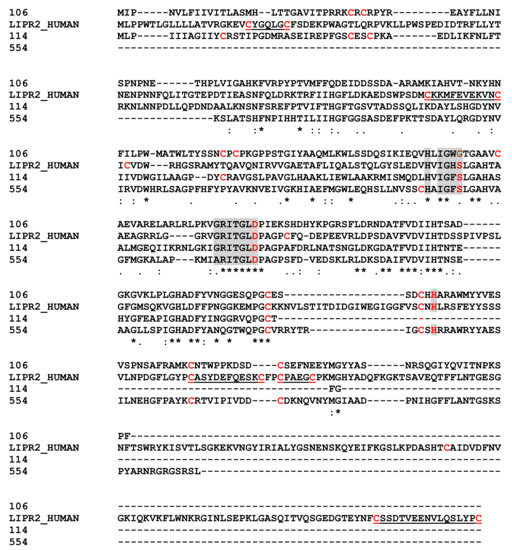
Figure 7.
Sequence Alignments for Pancreatic Lipase Sequences. Key active site residues from Human Pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 (P54317) are in red shaded in grey; in shaded grey, amino acids conserved around the active site residues. The underline human sequence residues represent the two bonds between cysteines. Identical amino acids are indicated by a star, conservation by a colon and substitution by a dot.
In vertebrates, PLRP2 enzymes are mainly digestive. These enzymes participate in the hydrolysis of triglycerides, phospholipids and vitamin A esters and also have a high activity on monogalactosyl diglyceride [76], the major lipids of plant cells. Recently PLRP2-like proteins have been described in the ectoparasitoid wasp P. puparum, and for four of them peptides were found in the venom proteome [77]. Based on the functions of PLRPs, PLRP2-like found in M. pulchricornis venom may contribute to hijacking host lipid metabolism for the benefit of endoparasitoid eggs/larvae.
2.8.5. Hyaluronidase
A hyaluronidase protein was present in MpVLPs although its activity may be reduced due to an AA replacement in the active site (Figure 8). Hyaluronidases are found from bacteria to mammals. In mammals, these enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of hyaluronan (HA) and chondroitin sulphates from the extracellular matrix. This property of increasing tissue permeability has led to the suggestion that hyaluronidases present in the venom of bees, stinging wasps, snakes and other species, along with phospholipases, facilitate the diffusion of other venom components throughout the body [78,79]. Although HA is widely distributed in vertebrates, it has apparently not been found in invertebrates, including insect species [80]. Therefore, the potential role of hyaluronidase in host after parasitoid oviposition requires further attention, including whether it can act on other glycosaminoglycans components of the insect matrix such as chitin, chondroitin or chondroitin sulfate, which can be degraded by hyaluronidase [80].

Figure 8.
Alignment of hyaluronidases from M. pulchricornis (Hyal-Mp from contig 293), Human (Hyaluronidase 2, HYAL2-HUMAN, Q12891), bee (Apis mellifera, Q08169) and Cotesia congregata (CCQ71107). The putative active-site residues Asp(D), Glu(E), and Glu(E) (shaded in grey) of the hyaluronidase were conserved in the M. pulchricornis sequence, although a conservative replacement E → N occurred that may affect its activity [81]. The four cysteine residues forming two disulfide bridges are also conserved (in red). Identical amino acids are indicated by a star, conservation by a colon and substitution by a dot.
2.8.6. CAP Domains Protein
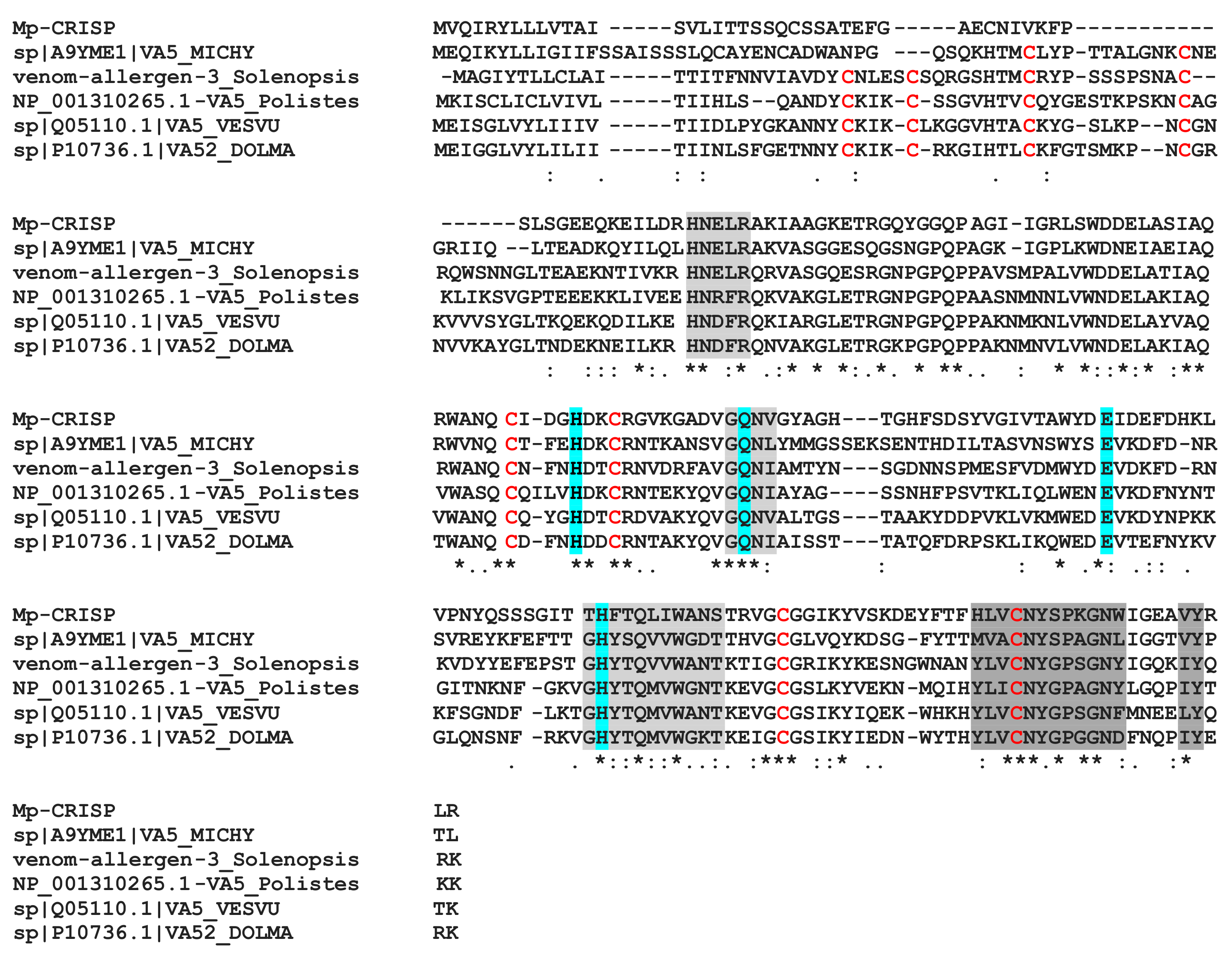
The MpVLPs protein from contig 2455 contains three CAP domains (cysteine-rich secretory proteins or CRISPs), antigen 5 (Ag5), and pathogenesis-related 1 (PR-1) proteins). CAP domain proteins are distributed in a wide range of organisms and have a wide range of functions [82]. CRISPs are found in the majority of snake venoms where they disrupt prey homeostasis through several mechanisms, including inhibition of ion channels and angiogenesis [83]. In snakes, CRISP genes have undergone accelerated evolution aided by strong positive selection and directional mutagenesis [84]. PR-1 proteins are ubiquitous in plant species and it is suggested that PR-1 has a broad antimicrobial function. Antigens 5 are proteins of unknown function in Hymenoptera venoms with strong allergenic potency [85]. When we aligned the first CAP domain of contig 2455 with the Hymenoptera antigen 5 sequences (which have only one domain), we obtained a good match with about 35–40% identity (Figure 9). To date, the role of CAP domain proteins in parasitoids venom is unknown.
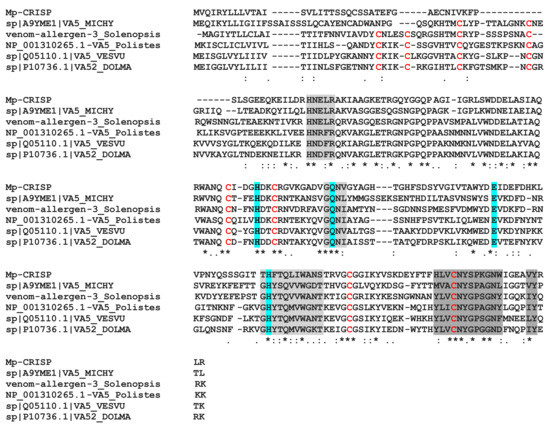
Figure 9.
Alignment of the first CAP domain of contig 2455 (Mp-CRISP) with selected sequences of hymenoptera antigen 5 allergens. The CAP signature motifs are shaded in grey and conserved residues that form the putative active site are shaded in cyan [85]. Cysteine residues that form disulphide bridges in Ag5 proteins are marked in red. Asterisks, colons and periods indicate identical, conserved and semi-conserved residues, respectively. Sequence from Vespula vulgaris (VA5.VESVU, Q05110.1), Dolichovespula maculata (bald-faced hornet)(VA52.DOLMA, P10736.1), Polistes dominula (European paper wasp) (VA5.polistes, NP.001310265.1), and Microctonus hyperodae (A9YME1.1).
2.8.7. The SERPIN
The MpVLPs contig 590 encodes a serine proteinase inhibitor (SERPIN) domain protein. SERPINs participate in a suicide inhibitory mechanism that permanently inactivate proteinases [86]. They share a conserved core structure critical for their inhibitory function. The structure of contig 590 corresponds to α-1-antitrypsin, the human prototype being SERPINA1. In the native conformation, the reactive center loop (RCL) of SERPINs, a short flexible strand recognized by proteases, is exposed for interaction. After recognition, an initial noncovalent complex is formed and then a covalent bond is established upon cleavage of the peptide bond between AA P1 and P1′ (see Figure 10). Besides Ser P1′, only one other AA is conserved in the M. pulchricornis RCL compared to human SERPINA1. The conserved alanine rich hinge important for the inhibitory function of SERPINs [86] is also absent suggesting that SERPIN from contig 590 is potentially non inhibitory. The role of SERPINS in arthropods has been studied mainly for their functions in innate immune responses [87]. For example, SERPINs are involved in the phenoloxidase activation cascade and inhibition of this cascade by a Leptopilina boulardi Barbotin, Carton & Kelner venom SERPIN, LbSPN, is part of the success of this wasp in some Drosophila species [88]. Interestingly, in two well-studied strains of L. boulardi, LbSPN retain its active RCL in one strain but not in the other [20], suggesting, as with M. pulchricornis, a possible different role for this protein than protease inhibition.

Figure 10.
Amino acid sequence alignments of contig 590 protein (Mp_SERPIN) and human SERPINA1 (P01009|A1AT_HUMAN Alpha-1-antitrypsin). The RCL position of the human sequence is underlined. The cleavage site is situated between the position P1 (Met) and P1′ (Ser) of the human sequence, only the Ser is conserved in Mp_SERPIN. The important Alanine-rich hinge site shaded in grey is also absent from contig 590. Asterisks, colons and periods indicate identical, conserved and semi-conserved residues, respectively.
3. Conclusions
As in many parasitoid wasp venoms studied to date, the most represented class of proteins in M. pulchricornis venom corresponded to “uncharacterized” proteins or proteins with no hit in the database. Although a number of these M. pulchricornis proteins have already been described in the venom glands of other venomous species, they currently have no determined function. Most of the known proteins or proteins with a known functional domain have also been found in the venom of different species and may have the same suggested role, keeping in mind that in most cases the described role is a defensive one against a vertebrate organism with a different physiology from that of the host insect caterpillar.
Overall, the main conclusions of the present study are (i) the relative preponderance of metalloproteases in the MpVLPs and of DUF4803 domain proteins in the soluble fraction of the venom, and the high diversity of these two main families of venom proteins produced in venom glands, (ii) the lack of evidence of a viral origin for MpVLPs.
Zinc metalloproteases are abundant in M. pulchricornis and particularly well represented in MpVLPs. Metalloproteases are common in parasitoids venoms, and a number of studies have been done to understand their role. One example is the venom metalloprotease from Microplitis mediator (named VRF1): the C-terminus fragment, which contains the catalytic domain, enters the hemocytes of the host Helicoverpa armigera where it cleaves the NF-κB Dorsal factor, a process related to the modulation of wasp egg encapsulation by the host [89]. In the ectoparasitoid wasp Eulophus pennicornis, three genes encoding metalloproteinases with a C−terminus reprolysin domain are expressed in the venom gland and injection of one of these recombinant metalloproteases into the larval host Lacanobia oleracea resulted in partial mortality of the insects, with the surviving ones exhibiting delayed development and growth [37]. In N. vitripennis, an in vitro study indicated also that venom metalloproteases may be involved in apoptosis of insect cultured cells [90]. From these examples, and based on the elevated number of metalloproteases incorporated into MpVLPs, it could be suggested that MpVLPs are a sort of “metalloprotease bomb” that, once injected into the host, enter host immune cells or other cells to impair the immune response and/or development as well as other physiological functions. This is consistent with the reported in vitro effect of MpVLPs in inhibiting the attachment and the spreading of host hemocytes and ultimately inducing their apoptosis [14,15].
Another family of proteins that is abundant in the venom of M. pulchricornis, particularly in the soluble fraction, is the DUF4803 containing proteins family. Unfortunately, no functional information is currently available for these proteins, which are also present in the venom of other braconid species. Therefore, these proteins most probably deserve to be studied in more detail in the future in order to determine their function in parasitoid venoms.
Our study showed that members of the metalloprotease and DUF4803 families are highly represented in the venom proteome of M. pulchricornis and in the transcriptome of the venom gland. In Hymenoptera and other venomous taxa, the venom protein cocktail is classically enriched through gene duplication, thereby increasing its functional divergence through evolution of new functions or neofunctionalization [32,91]. One of the best examples is the snake venom family of metalloproteinases: in some species, these proteins have expanded massively from a single copy to 31 genes in tandem through gene duplication events [46]. This expansion has been accompanied by mutations within the active sites, suggesting that some proteins have lost their metalloprotease function and may have evolved other functions. The evolution of venom genes through processes including multi-functionalization, co-option, and gene duplication has also been suggested in parasitoids [92]. Therefore, similar types of evolutionary mechanisms may have occurred in the lineage of M. pulchricornis resulting in an increase of the diversity of its venom proteins, and/or potentially the appearance of new functions for some of the venom proteins. Studies of species related to Meteorus species will be of interest to resolve this issue.
Finally, our study did not find any candidate viral gene or protein that could be linked to the production of MpVLPs. The approach undertaken here is similar to that performed in species producing virus-derived particles such as PDVs or VLPs in their ovarian calyx. Indeed, in these models, the endogenous virus was detected both by the transcriptomic analyses of the producing tissue and by the proteomic analyses of the purified particles. In the present work, we did not find any specific viral gene expressed in the venom gland nor a viral protein in MpVLPs. The hypothesis is therefore that either M. pulchricornis VLPs are formed by a viral machinery derived from an as yet undetermined virus and therefore whose sequences are absent from public databases, or that MpVLPs are produced directly by a specific pathway in the venom gland cell that remains to be deciphered.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insects
M. pulchricornis cocoons (about 10 cocoons) were recovered from Spodoptera sp. larvae collected in 2015 in the South of France. Mated adult females were used to parasitize larvae of a laboratory strain of Spodoptera littoralis Boisduval. Parasitized hosts were reared under a long-day photoperiod (16 h light: 8 h dark) at 25 °C until emergence of wasps. Female wasps used in the different experiments were at least 3 days-old. The reproductive apparatus was obtained from cooled anaesthetized female wasps by traction on the ovipositor and venom glands separated by dissection under a binocular.
4.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
Venom glands and 15,000× g MpVLP pellets were processed for transmission electron microscopy as described in [21]. Briefly, samples were fixed in sodium cacodylate (0.1 M, pH 7.2) for MpVLPs or in Insect Ringer for venom apparatus (KCl 182 mM; NaCl 46 mM; CaCl2 3 mM; Tris-HCl 10 mM)) supplemented with 5% glutaraldehyde and stored for 24 h at 4 °C. Post-fixation was done with 2% osmium tetroxide in the same buffers, followed by dehydration in a graded ethanol series prior to inclusion in Epon and ultrathin section. The sections were contrasted with uranyl acetate and lead citrate before observation (1010, JEOL, Croissy, France and EM10CR, 80 kV, Zeiss, Marly le Roi, France).
4.3. Sequencing and Sequence Analyses
For transcriptomics, total RNA was extracted from 30 venom glands using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Courtaboeuf, France) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After polyA selection, mRNA was fragmentated and the cDNA strand was synthesized using random primers. End repair, phosphorylation and A-tailing were done and, after ligation of adapters, a PCR amplification. Sequencing of PCR products was performed using Illumina RNA-Seq (HiSeq, 2 × 125 pb; Genewiz, Paris, France). The quality of the raw Illumina reads was controlled using FastQC software (mean quality score 36), and the reads were cleaned by removing low-quality sequences and reads containing N or adaptor sequences. De novo assembly was performed using CLC Genomics Server 8 (257,921,401 total reads; 206,153,609 matched reads; 177,571,432 reads in pairs; 14,926 contigs with 37% GC). The average length of the transcripts was 1604 bp and the N50 is 2153 bp. Raw transcriptomic reads of M. pulchricornis (PRJNA733444) and L. javana (PRJNA734452) are deposited at NCBI. The accession/description of the other species genomes and transcriptomes are in Table S2.
In order to calculate TPM values in venom glands and antennae, reads were aligned back to contigs with the Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA-MEM, v 0.7.17) [93] with default parameters. Raw counts were calculated with the samtools idxstats (v1.10) [94]. TPM for a transcript (i) was calculated using the formula:
TPM(I) = 1e6 × ((raw count(i)/transcript length(i))/sum(all dataset) (raw count/transcript length))
Peptides from transcriptomes of M. pulchricornis, B. nigricans, L. javana, P. turionellae and P. concolor were predicted with TransDecoder (v5.5; downloaded at https://github.com/brewsci/homebrew-bio/pkgs/container/bio%2Ftransdecoder, accessed on 17 July 2021), first by predicting the TransDecoder.LongOrfs ORFs with the -m 50 option, then by blasting the resulting longest ORFs (longest.orfs.pep) to the NCBI NR database (NR.2020-5-29), with DIAMOND (v2.0.6) [95] with the arguments: --max-target-seqs 1 --outfmt 6 --evalue 1e-5. Finally, we used the TransDecoder.Predict algorithm with the retain.blastp option with the DIAMOND results. Orthologs were identified by OrthoFinder (v2.3.8) [96] with the -S DIAMOND option and a database already built for previous analyses [97] and supplemented with the proteomes of C. Congregata [13], A. ervi and L. fabarum [98], and with the predicted peptides of M. puchricornis, B. nigricans, L. javana, P. turionellae, and P. concolor (see Table S2). Gene functions were obtained after a BLASTp of predicted peptides against NCBI NR (NR.2020-5-29) with DIAMOND (v2.0.6) and the arguments: --evalue 1e-8 --max-target-seqs 10 --masking 0, and InterProScan (v5.42-78) [99] with the options: -iprlookup -goterms --pathways -f xml -dp. Gene Ontology terms were assigned with Blast2GO CLI (v1.4.4) [100] using the results of Blastp and InterProScan.
4.4. Venom and VLPs Proteomic
Venom was obtained from the opening of 30 dissected reservoirs in a 50 µL drop in Insect Ringer supplemented with antiproteases (S8830; Sigma, Saint Quentin Fallavier, France) (IR + P). The extract was centrifuged at 500× g for 5 min. and the supernatant stored as total venom (TV). For MpVLPs purification, the supernatant centrifuged at 500× g was centrifuged again at 15,000× g for 10 min, the supernatant (Super) was removed and the pellet (Pellet) resuspended in 100 µL of IR + P and centrifuged again 10 min. at 15,000× g. The last pellet was resuspended in 50 µL of IR + P. All samples (TV, Super, and Pellet) were mixed with 4× Laemmli sample buffer with 10% β-mercaptoethanol [101]. Gel electrophoresis was carried out on a 12.5% acrylamide gel. After silver staining [102], gel slices were cut, washed with 50% acetonitrile, 50 mM NH4HCO3, and incubated overnight at 37 °C (with shaking) with 12.5 ng/mL trypsin (Promega, Charbonnières-les-Bains, France) in 25 mM NH4HCO3. The peptides were extracted three times with 50% acetonitrile, water containing 1% (v/v) formic acid and dried. Samples were analyzed online using a Q-orbitrap mass spectrometer (Q exactive, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Illkirch-Graffenstaden, France) coupled to an Ultimate 3000 HPLC (Dionex, Voisins-le-Bretonneux, France). Protein identification was performed using the Mascot v 2.3 algorithm (Matrix Science Inc., London, UK), by searching against the M. pulchricornis sequences. Peptides scoring higher than the identity score (p < 0.05) were considered significant. As the Mascot score for a protein is the summed score for the individual peptides, it can be used to estimate protein abundance. Such semiquantitative measure of protein abundance is called “spectral counting”, defined as the total number of spectra identified for a protein. Mass spectrometry proteomics raw data were deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium (http://proteomecentral.proteomexchange.org, 17 July 2021) via the MassIVE partner repository [103] with the dataset identifier PXD022771.
Mass spectrometry-matched sequences were manually verified and putative protein sequences blasted using BLASTp on NCBI NR for homologies (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 17 July 2021) using default values. Protein domains were obtained from PFAM (http://pfam.xfam.orgresults, accessed during the 2020–2021 years) during NCBI blast and were also searched or confirmed using HMMERSCAN with default set up [104]. The presence of a N-terminus signal peptide sequence was tested using SignalP-5.0 server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/, accessed during the 2020–2021 years) [105]. Sequence alignment was performed with MUSCLE (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/muscle/, accessed on 17 July 2021) [106].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/toxins13070502/s1, Figure S1: Phylogeny from Orthofinder and Blast2GO Short Reports (pdf file), Figure S2: Comparison of the CDSs encoded by contig 38 (pdf file), Figure S3: Sequence comparison of the venom metalloproteases (pdf file), Figure S4: Sequence comparison of the DUF4803 containing proteins (pdf file), Table S1: General analysis of the M. pulchricornis gland transcriptome (excel file), Table S2: Genomes and transcriptomes used in this study (pdf file), Table S3: Data and sequence of the venom metalloproteases (excel file), Table S4: Data and sequence of the venom DUF4803 containing proteins (excel file).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.-N.V., M.P. and J.-L.G.; investigation, A.-N.V., D.A.-S., M.B., M.R., M.F., F.L., S.R. and J.-L.G.; resources, M.F., D.A.-S., M.T., R.S., M.B., F.L., S.R.; writing—original draft preparation, A.-N.V., M.P., M.B., F.L. and J.-L.G.; writing—review and editing, All authors; funding acquisition, A.-N.V., M.P. and J.-L.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The transcriptomes of M. pulchricornis and L. javana were partially supported by the French National Agency of Research ANR-12-ADAP-0001 (ABC-PaPoGen) granted to A.-N.V. This research received also support from the Department of Plant Health (SPE) from the French National Institute for Research in Agriculture, Food and Environment (INRAE) and from the French Government through the “Investments for the Future” programs LABEX SIGNALIFE ANR-11-LABX-0028-01 and IDEX UCAJedi ANR-15-IDEX-01 (J.-L.G., M.P.).
Data Availability Statement
Raw transcriptomic reads of M. pulchricornis (PRJNA733444) and L. javana (PRJNA734452) are deposited at NCBI. Mass spectrometry proteomics raw data were deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium (http://proteomecentral.proteomexchange.org accessed on 17 July 2021) via the MassIVE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD022771.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Andrea Becchimanzi and Franco Pennacchio from the University of Napoli ‘Federico II’, Italy, for sharing the assembled transcriptome of Bracon nigricans.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Berry, J.A.; Walker, G.P. Meteorus Pulchricornis (Wesmael) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Euphorinae): An Exotic Polyphagous Parasitoid in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Zool. 2004, 31, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartnett, D.E.; MacDonald, F.H.; Martin, N.A.; Walker, G.P.; Ward, D.F. A Survey of the Adventive Parasitoid Meteorus Pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and Native Larval Parasitoids of Native Lepidoptera. N. Z. J. Zool. 2018, 61, 326–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeto, K. Systematic Studies on the Tribe Meteorini (Hymenoptera, Braconidae) from Japan V. The Pulchricornis Group of Genus Meteorus (1). Jpn. J. Entomol. 1989, 57, 581–595. [Google Scholar]
- Pennacchio, F.; Strand, M.R. Evolution of Developmental Strategies in Parasitic Hymenoptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Fisher, T.; Nusawardani, T. The Natural Genetic Engineering of Polydnaviruses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1178, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, J.-L.; Schmitz, A.; Colinet, D.; Poirié, M. Parasitoid Viruses. In Unique Attributes of Viruses and Virus-Like Particles Associated with Parasitoids; Beckage, N.E., Drezen, J.-M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Section B; pp. 181–192. ISBN 9780123848581. [Google Scholar]
- Herniou, E.A.; Huguet, E.; Thézé, J.; Bézier, A.; Periquet, G.; Drezen, J.M. When Parasitic Wasps Hijacked Viruses: Genomic and Functional Evolution of Polydnaviruses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bézier, A.; Herbinière, J.; Lanzrein, B.; Drezen, J.-M. Polydnavirus Hidden Face: The Genes Producing Virus Particles of Parasitic Wasps. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 101, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, A.-N.; Jouan, V.; Urbach, S.; Samain, S.; Bergoin, M.; Wincker, P.; Demettre, E.; Cousserans, F.; Provost, B.; Coulibaly, F.; et al. Analysis of Virion Structural Components Reveals Vestiges of the Ancestral Ichnovirus Genome. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichon, A.; Bézier, A.; Urbach, S.; Aury, J.M.; Jouan, V.; Ravallec, M.; Guy, J.; Cousserans, F.; Thézé, J.; Gauthier, J.; et al. Recurrent DNA Virus Domestication Leading to Different Parasite Virulence Strategies. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1501150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burke, G.R.; Walden, K.K.O.; Whitfield, J.B.; Robertson, H.M.; Strand, M.R. Genome Report: Whole Genome Sequence of the Parasitoid Wasp Microplitis DemolitorThat Harbors an Endogenous Virus Mutualist. G3 Genes Genom. Genet. 2003, 8, 2875–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strand, M.R.; Burke, G.R. Polydnaviruses: Evolution and Function. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2020, 34, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauthier, J.; Boulain, H.; van Vugt, J.J.F.A.; Baudry, L.; Persyn, E.; Aury, J.-M.; Noel, B.; Bretaudeau, A.; Legeai, F.; Warris, S.; et al. Chromosomal Scale Assembly of Parasitic Wasp Genome Reveals Symbiotic Virus Colonization. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Miura, K.; Tanaka, T. The Virus-like Particles of a Braconid Endoparasitoid Wasp, Meteorus Pulchricornis, Inhibit Hemocyte Spreading in Its Noctuid Host, Pseudaletia separata. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Tanaka, T. Virus-like Particles in Venom of Meteorus Pulchricornis Induce Host Hemocyte Apoptosis. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Miura, K.; Tanaka, T. Effects of the Virus-like Particles of a Braconid Endoparasitoid, Meteorus Pulchricornis, on Hemocytes and Hematopoietic Organs of Its Noctuid Host, Pseudaletia separata. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2009, 44, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizki, R.M.; Rizki, T.M. Parasitoid Virus-like Particles Destroy Drosophila Cellular Immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8388–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupas, S.; Brehelin, M.; Frey, F.; Carton, Y. Immune Suppressive Virus-like Particles in a Drosophila Parasitoid: Significance of Their Intraspecific Morphological Variations. Parasitology 1996, 113, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heavner, M.E.; Ramroop, J.; Gueguen, G.; Ramrattan, G.; Dolios, G.; Scarpati, M.; Kwiat, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Wang, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Novel Organelles with Elements of Bacterial and Eukaryotic Secretion Systems Weaponize Parasites of Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2869–2877.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colinet, D.; Deleury, E.; Anselme, C.; Cazes, D.; Poulain, J.; Azema-Dossat, C.; Belghazi, M.; Gatti, J.-L.; Poirié, M. Extensive Inter- and Intraspecific Venom Variation in Closely Related Parasites Targeting the Same Host: The Case of Leptopilina Parasitoids of Drosophila. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Goguet, E.; Ravallec, M.; Pierre, O.; Lemauf, S.; Volkoff, A.-N.; Gatti, J.-L.; Poirié, M. Venom Atypical Extracellular Vesicles as Interspecies Vehicles of Virulence Factors Involved in Host Specificity: The Case of a Drosophila Parasitoid Wasp. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Giovanni, D.; Lepetit, D.; Guinet, B.; Bennetot, B.; Boulesteix, M.; Couté, Y.; Bouchez, O.; Ravallec, M.; Varaldi, J. A Behavior-Manipulating Virus Relative as a Source of Adaptive Genes for Drosophila Parasitoids. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 2791–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morales, J.; Chiu, H.; Oo, T.; Plaza, R.; Hoskins, S.; Govind, S. Biogenesis, Structure, and Immune-Suppressive Effects of Virus-like Particles of a Drosophila Parasitoid, Leptopilina victoriae. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, K.; Sano, T.; Suzuki, M.; Tanaka, T.; Minakuchi, C.; Miura, K. The Major Constituents of the Venom Gland of a Braconid Endoparasitoid, Meteorus Pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2017, 52, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarese, R.; Morales, J.; Fimiarz, D.; Webb, B.A.; Govind, S. A Supracellular System of Actin-Lined Canals Controls Biogenesis And Release Of Virulence Factors In Parasitoid Venom Glands. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, S.; Liao, C.-W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, W.-M.; He, P.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F.-A. Candidate Chemosensory Genes Identified in the Endoparasitoid Meteorus Pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) by Antennal Transcriptome Analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2017, 22, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond Chemoreception: Diverse Tasks of Soluble Olfactory Proteins in Insects. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrenk, S.; Cenzi, C.; Bertalot, T.; Conconi, M.T.; Liddo, R.D. Structural and Functional Failure of Fibrillin-1 in Human Diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Handke, B.; Poernbacher, I.; Goetze, S.; Ahrens, C.H.; Omasits, U.; Marty, F.; Simigdala, N.; Meyer, I.; Wollscheid, B.; Brunner, E.; et al. The Hemolymph Proteome of Fed and Starved Drosophila Larvae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Song, Q.; Gu, P.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q. Proteomics of Larval Hemolymph in Bombyx Mori Reveals Various Nutrient-Storage and Immunity-Related Proteins. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajgar, A.; Dolezal, T. Extracellular Adenosine Modulates Host-Pathogen Interactions through Regulation of Systemic Metabolism during Immune Response in Drosophila. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.E.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; King, G.F.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Norman, J.A.; Lewis, R.J.; Norton, R.S.; et al. The Toxicogenomic Multiverse: Convergent Recruitment of Proteins into Animal Venoms. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Häse, C.C.; Finkelstein, R.A. Bacterial Extracellular Zinc-Containing Metalloproteases. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 57, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A.; Herrera, C. Hemorrhage Caused by Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: A Journey of Discovery and Understanding. Toxins 2016, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: Their Role in the Pathogenesis of Local Tissue Damage. Biochimie 2000, 82, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, F.L.; Vinson, S.B. Host Regulation and the Embryonic Development of the Endoparasitoid Toxoneuron Nigriceps (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 137, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.R.G.; Bell, H.A.; Hinchliffe, G.; Fitches, E.; Weaver, R.; Gatehouse, J.A. A Venom Metalloproteinase from the Parasitic Wasp Eulophus Pennicornis Is Toxic towards Its Host, Tomato Moth (Lacanobia Oleracae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danneels, E.L.; Rivers, D.B.; Graaf, D.C. De Venom Proteins of the Parasitoid Wasp Nasonia vitripennis: Recent Discovery of an Untapped Pharmacopee. Toxins 2010, 2, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danneels, E.L.; Vaerenbergh, M.V.; Debyser, G.; Devreese, B.; Graaf, D.C. de Honeybee Venom Proteome Profile of Queens and Winter Bees as Determined by a Mass Spectrometric Approach. Toxins 2015, 7, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, J.S.M.; Lisboa, A.B.P.; Santos, T.M.; Andrade, M.V.S.; Neves, V.B.S.; Teles-Souza, J.; Jesus, H.N.R.; Bezerra, T.G.; Falcão, V.G.O.; Oliveira, R.C.; et al. The Evolution of ADAM Gene Family in Eukaryotes. Genomics 2020, 112, 3108–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.R.; Handsley, M.M.; Pennington, C.J. The ADAM Metalloproteinases. Mol. Asp. Med. 2008, 29, 258–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seals, D.F.; Courtneidge, S.A. The ADAMs Family of Metalloproteases: Multidomain Proteins with Multiple Functions. Gene Dev. 2003, 17, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Almeida, M.T.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Nicolau, C.A.; Gomes-Neto, F.; Valente, R.H. Processing of Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: Generation of Toxin Diversity and Enzyme Inactivation. Toxins 2016, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laronha, H.; Caldeira, J. Structure and Function of Human Matrix Metalloproteinases. Cells 2020, 9, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S. ADAM and ADAMTS Family Proteins and Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: A Structural Overview. Toxins 2016, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giorgianni, M.W.; Dowell, N.L.; Griffin, S.; Kassner, V.A.; Selegue, J.E.; Carroll, S.B. The Origin and Diversification of a Novel Protein Family in Venomous Snakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10911–10920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Barallat, J.; Richards, A.M. A Test in Context: Neprilysin Function, Inhibition, and Biomarker. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.J.; Isaac, R.E.; Coates, D. The Neprilysin (NEP) Family of Zinc Metalloendopeptidases: Genomics and Function. BioEssays 2001, 23, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, R.E.; Bland, N.D.; Shirras, A.D. Neuropeptidases and the Metabolic Inactivation of Insect Neuropeptides. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 162, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, N.D.; Pinney, J.W.; Thomas, J.E.; Turner, A.J.; Isaac, R.E. Bioinformatic Analysis of the Neprilysin (M13) Family of Peptidases Reveals Complex Evolutionary and Functional Relationships. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathé-Hubert, H.; Colinet, D.; Deleury, E.; Belghazi, M.; Ravallec, M.; Poulain, J.; Dossat, C.; Poirié, M.; Gatti, J.-L. Comparative Venomics of Psyttalia lounsburyi and P. concolor, two Olive Fruit Fly Parasitoids: A Hypothetical Role for a GH1 β-Glucosidase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goecks, J.; Mortimer, N.T.; Mobley, J.A.; Bowersock, G.J.; Taylor, J.; Schlenke, T.A. Integrative Approach Reveals Composition of Endoparasitoid Wasp Venoms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, W.H.; Lee, D.-W. C-Terminal Conserved Motifs of Neprilysin1 in Cotesia plutellae Are Not Required for Immune Suppression of the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella (L.). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2019, 22, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, S.; Reineke, A.; Beck, M.; Schmidt, O. Isolation and Characterization of a Neprilysin-like Protein from Venturia Canescens Virus-like Particles. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.A.; Kim, K.; Kim, W.-J.; Bang, W.Y.; Ahn, N.-H.; Bae, C.-H.; Yeo, J.-H.; Lee, S.H. Characterization of Venom Components and Their Phylogenetic Properties in Some Aculeate Bumblebees and Wasps. Toxins 2020, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Chanhome, L.; Tan, N.H. Comparative Venom Gland Transcriptomics of Naja kaouthia (Monocled Cobra) from Malaysia and Thailand: Elucidating Geographical Venom Variation and Insights into Sequence Novelty. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Yu, S.; Wu, Y.; Shan, B. Effect of Spider Venom on Cell Apoptosis and Necrosis Rates in MCF-7 Cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2007, 26, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soraia, N.; De Oliveira, U.C.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Tashima, A.K.; Da Silva, P.I.J. Presence of a Neprilysin on Avicularia Juruensis (Mygalomorphae: Theraphosidae) Venom. Toxin Rev. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becchimanzi, A.; Avolio, M.; Bostan, H.; Colantuono, C.; Cozzolino, F.; Mancini, D.; Chiusano, M.L.; Pucci, P.; Caccia, S.; Pennacchio, F. Venomics of the Ectoparasitoid Wasp Bracon nigricans. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colinet, D.; Anselme, C.; Deleury, E.; Mancini, D.; Poulain, J.; Azema-Dossat, C.; Belghazi, M.; Tarès, S.; Pennacchio, F.; Poirié, M.; et al. Identification of the Main Venom Protein Components of Aphidius Ervi, a Parasitoid Wasp of the Aphid Model Acyrthosiphon pisum. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sträter, N. Ecto-5’-Nucleotidase: Structure Function Relationships. Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aili, S.R.; Touchard, A.; Hayward, R.; Robinson, S.D.; Pineda, S.S.; Lalagüe, H.; Mrinalini, V.I.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Kini, R.M.; Escoubas, P.; et al. An Integrated Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Venom Complexity of the Bullet Ant Paraponera clavata. Toxins 2020, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péterfi, O.; Boda, F.; Szabó, Z.; Ferencz, E.; Bába, L. Hypotensive Snake Venom Components—A Mini-Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhadrapura, L.D.; Cletus, J.M.D. The Pharmacological Role of Nucleotidases in Snake Venoms. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2010, 28, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, B.; Longhi, M.S.; Robson, S.C.; Stagg, J. The Ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73: Novel Checkpoint Inhibitor Targets. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flower, D.R. The Lipocalin Protein Family: Structure and Function. Biochem. J. 1996, 318, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, D.R.; North, A.C.; Sansom, C.E. The Lipocalin Protein Family: Structural and Sequence Overview. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1482, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganfornina, L.; Sanchez, D.; Flower, L.H.G.; Flower, D.R. The Lipocalin Protein Family: Protein Sequence, Structure and Relationship to the Calycin Superfamily. In Lipocalins; Åkerström, B., Borregaard, N., Flower, D.R., Salie, J.-P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; ISBN 9780429089886. [Google Scholar]
- Ganfornina, M.D.; Gutiérrez, G.; Bastiani, M.; Sánchez, D. A Phylogenetic Analysis of the Lipocalin Protein Family. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flower, D.R.; North, A.C.T.; Attwood, T.K. Structure and Sequence Relationships in the Lipocalins and Related Proteins. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Qian, C.; Fang, Q.; Ye, G.-Y. Venom of The Parasitoid Wasp Pteromalus puparum Contains an Odorant Binding Protein. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 88, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, D.O.C.; de Oliveira, Ú.C.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Pimenta, D.C.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Prieto-da-Silva, Á.R. Bottom-Up Proteomic Analysis of Polypeptide Venom Components of the Giant Ant Dinoponera quadriceps. Toxins 2019, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falabella, P.; Riviello, L.; Caccialupi, P.; Rossodivita, T.; Valente, M.T.; Stradis, M.L.D.; Tranfaglia, A.; Varricchio, P.; Gigliotti, S.; Graziani, F.; et al. A Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase of Aphidius Ervi Venom Induces Apoptosis in the Ovaries of Host Aphids. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistini, B.; Chailler, P.; Brière, N.; Beaudoin, A.R. Secretion of Gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase by the Pancreas: Evidence for a Membrane Shedding Process during Exocytosis. Life Sci. 1990, 47, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.S.; Cox, L.A. Bioinformatics and Evolution of Vertebrate Pancreatic Lipase and Related Proteins and Genes. J. Data Min. Genom. Proteom. 2012, 3, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbara, S.; Francine, F.; Philippe, G.; Dominique, L.; Paul, B.; Alain, D.C.; Bernard, L.; Robert, V.; Frédéric, C. Human Pancreatic Lipase-Related Protein 2 Is a Galactolipase. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 10138–10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Xiong, S.; Mei, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. A Chromosome-level Genome Assembly of the Parasitoid Wasp Pteromalus puparum. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1384–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordon, K.C.F.; Wiezel, G.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Arantes, E.C. Arthropod Venom Hyaluronidases: Biochemical Properties and Potential Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins 2015, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, J.W. A Brief Review of the Scientific History of Several Lesser-Known Snake Venom Proteins: L-Amino Acid Oxidases, Hyaluronidases and Phosphodiesterases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Sugahara, K.; Özbek, S. Evolution of Glycosaminoglycans. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marković-Housley, Z.; Miglierini, G.; Soldatova, L.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Müller, U.; Schirmer, T. Crystal Structure of Hyaluronidase, a Major Allergen of Bee Venom. Structure 2000, 8, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Chandler, D.E. Tracing the Evolutionary History of the CAP Superfamily of Proteins Using Amino Acid Sequence Homology and Conservation of Splice Sites. J. Mol. Evol. 2017, 85, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadokoro, T.; Modahl, C.M.; Maenaka, K.; Aoki-Shioi, N. Cysteine-Rich Secretory Proteins (CRISPs) from Venomous Snakes: An Overview of the Functional Diversity in a Large and Underappreciated Superfamily. Toxins 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunagar, K.; Johnson, W.E.; O’Brien, S.J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Evolution of CRISPs Associated with Toxicoferan-Reptilian Venom and Mammalian Reproduction. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1807–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blank, S.; Bazon, M.L.; Grosch, J.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B.; Brochetto-Braga, M.R.; Bilò, M.B.; Jakob, T. Antigen 5 Allergens of Hymenoptera Venoms and Their Role in Diagnosis and Therapy of Venom Allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthm. Rep. 2020, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanrattana, W.; Maas, C.; de Maat, S. SERPINs—From Trap to Treatment. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanost, M.R.; Jiang, H. Clip-Domain Serine Proteases as Immune Factors in Insect Hemolymph. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colinet, D.; Dubuffet, A.; Cazes, D.; Moreau, S.; Drezen, J.-M.; Poirié, M. A Serpin from the Parasitoid Wasp Leptopilina Boulardi Targets the Drosophila Phenoloxidase Cascade. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, R.-J.; Du, J.; Volovych, O.; Li, J.-C.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Lu, Z.; Zou, Z. A Metalloprotease Homolog Venom Protein from a Parasitoid Wasp Suppresses the Toll Pathway in Host Hemocytes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Formesyn, E.M.; Heyninck, K.; de Graaf, D.C. The Role of Serine- and Metalloproteases in Nasonia Vitripennis Venom in Cell Death Related Processes towards a Spodoptera Frugiperda Sf21 Cell Line. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.A.; Robinson, S.D.; Yeates, D.K.; Jin, J.; Baumann, K.; Dobson, J.; Fry, B.G.; King, G.F. Entomo-Venomics: The Evolution, Biology and Biochemistry of Insect Venoms. Toxicon 2018, 154, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarado, G.; Holland, S.R.; De Perez-Rasmussen, J.; Jarvis, B.A.; Telander, T.; Wagner, N.; Waring, A.L.; Anast, A.; Davis, B.; Frank, A.; et al. Bioinformatic Analysis Suggests Potential Mechanisms Underlying Parasitoid Venom Evolution and Function. Genomics 2020, 112, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows–Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. Subgroup, 1000 Genome Project Data Processing, The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchfink, B.; Reuter, K.; Drost, H.-G. Sensitive Protein Alignments at Tree-of-Life Scale Using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Phylogenetic Orthology Inference for Comparative Genomics. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legeai, F.; Santos, B.F.; Robin, S.; Bretaudeau, A.; Dikow, R.B.; Lemaitre, C.; Jouan, V.; Ravallec, M.; Drezen, J.-M.; Tagu, D.; et al. Genomic Architecture of Endogenous Ichnoviruses Reveals Distinct Evolutionary Pathways Leading to Virus Domestication in Parasitic Wasps. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, A.B.; Ballesteros, G.I.; Robin, S.; Schrader, L.; Bast, J.; Berghöfer, J.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Belghazi, M.; Bretaudeau, A.; Buellesbach, J.; et al. Functional Insights from the GC-Poor Genomes of Two Aphid Parasitoids, Aphidius Ervi and Lysiphlebus fabarum. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-Scale Protein Function Classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Williams, T.D.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Nueda, M.J.; Robles, M.; Talón, M.; Dopazo, J.; Conesa, A. High-Throughput Functional Annotation and Data Mining with the Blast2GO Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3420–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, J.H. Silver Stain for Proteins in Polyacrylamide Gels: A Modified Procedure with Enhanced Uniform Sensitivity. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 117, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, A. Proteomics Data Reuse with MassIVE-KB. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, S.C.; Luciani, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Park, Y.; Lopez, R.; Finn, R.D. HMMER Web Server: 2018 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, gky448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armenteros, J.J.A.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 Improves Signal Peptide Predictions Using Deep Neural Networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; mi Park, Y.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI Search and Sequence Analysis Tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).