In Vitro Effects of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Lytic Extracellular Compounds Produced by Alexandrium Strains on Hemocyte Integrity and Function in Mytilus edulis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
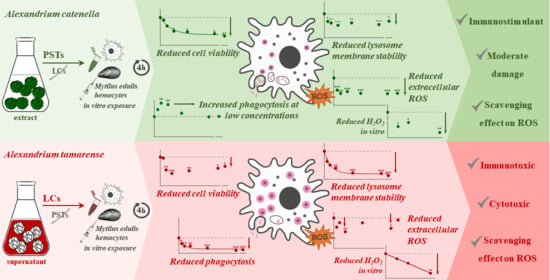
2. Results
2.1. PST and LC Effects on Hemocytes
2.1.1. Cytotoxicity
2.1.2. Cellular Function
2.2. Toxin Scavenger Function
2.2.1. In Vitro Chemical Effects of PST and LC on H2O2 Levels
3. Discussion
3.1. PST vs. LC: In Vitro Cytotoxic and Functional Effects
3.2. In Vitro vs. In Vivo Effects
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Preparation of PST Extracts and Extracellular LCs
5.2. Mussel Collection and Maintenance
5.3. Hemocyte Extraction and Manipulation
5.4. PST and LC Effects on Hemocytes
5.4.1. In Vitro Experimental Design
5.4.2. Cytotoxicity
5.4.3. Cellular Function
5.5. Scavenger Effects in PST and LC Treatments
5.5.1. In Vitro Chemical Effects of PST and LC Treatments on H2O2 Levels
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve molluscs: Occurrence, transfer kinetics, and biotransformation. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1998, 6, 315–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.; Díaz, P.A.; Godoy, M.; Araya, M.; Ganuza, I.; Pino, R.; Álvarez, F.; Rengel, J.; Hernández, C.; Uribe, E.; et al. Paralytic shellfish toxins in surf clams Mesodesma donacium during a large bloom of Alexandrium catenella dinoflagellates associated to an intense shellfish mass mortality. Toxins 2019, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landsberg, J.H. The effects of harmful algal blooms on aquatic organisms. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2010, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassudrie, M.; Hégaret, H.; Wikfors, G.H.; da Silva, P.M. Effects of marine harmful algal blooms on bivalve cellular immunity and infectious diseases: A review. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 108, 103660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schantz, E.J.; Mold, J.D.; Stanger, W.D.; Shavel, J.; Riel, F.J.; Bowden, J.P.; Lynch, J.M.; Wyler, R.S.; Riegel, B.; Sommer, H. Paralytic shellfish poison. VI. A Procedure for the isolation and purification of the poison from toxic clam and mussel tissues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 5230–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P. New saxitoxin analogues in the marine environment: Developments in toxin chemistry, detection and biotransformation during the 2000s. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, H.R. Marine toxins targeting ion channels. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 31–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiese, M.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic alkaloids: Saxitoxin and its analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, S.E.; Bricelj, V.M.; Lambert, C.; Paillard, C. Deleterious effects of a nonPST bioactive compound(s) from Alexandrium tamarense on bivalve hemocytes. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fast, M.D.; Cembella, A.D.; Ross, N.W. In Vitro transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in the clams Mya arenaria and Protothaca staminea. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Reiriz, M.J.; Navarro, J.M.; Contreras, A.M.; Labarta, U. Trophic interactions between the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella and Mytilus chilensis: Feeding and digestive behaviour to long-term exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaghy, L.; Lambert, C.; Choi, K.-S.; Soudant, P. Hemocytes of the carpet shell clam (Ruditapes decussatus) and the Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum): Current knowledge and future prospects. Aquaculture 2009, 297, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kádár, E. Haemocyte response associated with induction of shell regeneration in the deep-sea vent mussel Bathymodiolus azoricus (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 362, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hégaret, H.; Wikfors, G.H.; Soudant, P.; Lambert, C.; Shumway, S.E.; Bérard, J.B.; Lassus, P. Toxic dinoflagellates (Alexandrium fundyense and A. catenella) have minimal apparent effects on oyster hemocytes. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Ford, S.E.; Lambert, C.; Barbou, A.; Paillard, C. Effects of toxic Alexandrium tamarense on behavior, hemocyte responses and development of brown ring disease in Manila clams. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 430, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mello, D.F.; da Silva, P.M.; Barracco, M.A.; Soudant, P.; Hégaret, H. Effects of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum and its toxin (saxitoxin) on the functional activity and gene expression of Crassostrea gigas hemocytes. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberkorn, H.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Moal, J.; Suquet, M.; Guéguen, M.; Sunila, I.; Soudant, P. Effects of Alexandrium minutum exposure on nutrition-related processes and reproductive output in oysters Crassostrea gigas. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Núñez-Acuña, G.; Aballay, A.E.; Hégaret, H.; Astuya, A.P.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. Transcriptional responses of Mytilus chilensis exposed in vivo to saxitoxin (STX). J. Molluscan Stud. 2013, 79, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wootton, E.C.; Dyrynda, E.A.; Ratcliffe, N.A. Bivalve immunity: Comparisons between the marine mussel (Mytilus edulis), the edible cockle (Cerastoderma edule) and the razor-shell (Ensis siliqua). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2003, 15, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimany, E.; Sunila, I.; Hégaret, H.; Ramón, M.; Wikfors, G.H. Experimental exposure of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis, L.) to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense: Histopathology, immune responses, and recovery. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuya, A.; Carrera, C.; Ulloa, V.; Aballay, A.; Núñez-Acuña, G.; Hégaret, H.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. Saxitoxin modulates immunological parameters and gene transcription in Mytilus chilensis hemocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15235–15250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tillmann, U.; John, U. Toxic effects of Alexandrium spp. on heterotrophic dinoflagellates: An allelochemical defence mechanism independent of PSP-toxin content. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 230, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Bickmeyer, U.; Graeve, M.; Cembella, A. Mode of action of membrane-disruptive lytic compounds from the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Toxicon 2011, 58, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arzul, G.; Seguel, M.; Guzman, L.; Erard-Le Denn, E. Comparison of allelopathic properties in three toxic Alexandrium species. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 232, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Hansen, P.J. Allelopathic effects of Alexandrium tamarense on other algae: Evidence from mixed growth experiments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Muck, A.; Wielsch, N.; Svatoš, A.; Cembella, A. Isolation of activity and partial characterization of large non-proteinaceous lytic allelochemicals produced by the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Cembella, A. Preliminary characterization of extracellular allelochemicals of the toxic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense using a Rhodomonas salina bioassay. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haberkorn, H.; Lambert, C.; Le Goic, N.; Guéguen, M.; Moal, J.; Palacios, E.; Lassus, P.; Soudant, P. Effects of Alexandrium minutum exposure upon physiological and hematological variables of diploid and triploid oysters, Crassostrea gigas. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castrec, J.; Soudant, P.; Payton, L.; Tran, D.; Miner, P.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Huvet, A.; Quillien, V.; Boullot, F.; et al. Bioactive extracellular compounds produced by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum are highly detrimental for oysters. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borcier, E.; Morvezen, R.; Boudry, P.; Miner, P.; Charrier, G.; Laroche, J.; Hegaret, H. Effects of bioactive extracellular compounds and paralytic shellfish toxins produced by Alexandrium minutum on growth and behaviour of juvenile great scallops Pecten maximus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 184, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, V.; Langeloh, H.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Müller, A.; Bickmeyer, U.; Abele, D. Separate and combined effects of neurotoxic and lytic compounds of Alexandrium strains on Mytilus edulis feeding activity and hemocyte function. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estrada, N.; Ascencio, F.; Shoshani, L.; Contreras, R.G. Apoptosis of hemocytes from lions-paw scallop Nodipecten subnodosus induced with paralyzing shellfish poison from Gymnodinium catenatum. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi-Khalil, C.; Finkelstein, D.S.; Conejero, G.; Du Bois, J.; Destoumieux-Garzon, D.; Rolland, J.L. The paralytic shellfish toxin, saxitoxin, enters the cytoplasm and induces apoptosis of oyster immune cells through a caspase-dependent pathway. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Ren, D. Lysosomal physiology. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brentano, D.M.; Giehl, E.L.H.; Petrucio, M.M. Abiotic variables affect STX concentration in a meso-oligotrophic subtropical coastal lake dominated by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyceae). Harmful Algae 2016, 56, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Grand, F.; Kraffe, E.; Marty, Y.; Donaghy, L.; Soudant, P. Membrane phospholipid composition of hemocytes in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas and the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2011, 159, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detree, C.; Núñez-Acuña, G.; Roberts, S.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. Uncovering the complex transcriptome response of Mytilus chilensis against saxitoxin: Implications of harmful algal blooms on mussel populations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hannick, L.; Lin, S. Metatranscriptome profiling reveals versatile N-nutrient utilization, CO2 limitation, oxidative stress, and active toxin production in an Alexandrium fundyense bloom. Harmful Algae 2015, 42, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, H.S.; Wikfors, G.H.; Dam, H.G. Reactive oxygen species are linked to the toxicity of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium spp. to protists. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 66, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mardones, J.I.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Fish gill damage by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella from Chilean fjords: Synergistic action of ROS and PUFA. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.M.; Plummer, S. Production of extracellular reactive oxygen species by phytoplankton: Past and future directions. J. Plankton Res. 2018, 40, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oda, T.; Moritomi, J.; Kawano, I.; Hamaguchi, S.; Muramatsu, T.; Ishimatsu, A. Catalase- and Superoxide Dismutase-induced morphological changes and growth inhibition in the red tide phytoplankton Chattonella marina. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 2044–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hégaret, H.; Brokordt, K.B.; Gaymer, C.F.; Lohrmann, K.B.; García, C.; Varela, D. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella on histopathogical and escape responses of the Northern scallop Argopecten purpuratus. Harmful Algae 2012, 18, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basti, L.; Nagai, S.; Go, J.; Okano, S.; Nagai, K.; Watanabe, R.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, Y. Differential inimical effects of Alexandrium spp. and Karenia spp. on cleavage, hatching, and two larval stages of Japanese pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. Harmful Algae 2015, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hégaret, H.; Da Silva, P.M.; Wikfors, G.H.; Haberkorn, H.; Shumway, S.E.; Soudant, P. In Vitro interactions between several species of harmful algae and haemocytes of bivalve molluscs. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2011, 27, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, P.M.; Hégaret, H.; Lambert, C.; Wikfors, G.H.; Le Goïc, N.; Shumway, S.E.; Soudant, P. Immunological responses of the Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) with varying parasite (Perkinsus olseni) burden, during a long-term exposure to the harmful alga, Karenia selliformis, and possible interactions. Toxicon 2008, 51, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tillmann, U.; Alpermann, T.L.; da Purificação, R.C.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A. Intra-population clonal variability in allelochemical potency of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, M.; Erler, K.; Hiller, S.; Christian, B.; Luckas, B. Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) toxins in dietary supplements by application of a new HPLC/FD method. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 224, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Seguel, C.G.; Cembella, A.D. Toxin profile of Alexandrium catenella from the Chilean coast as determined by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novas, A.; Barcia, R.; Ramos-Martínez, J.I. After the Prestige oil spill modifications in NO production and other parameters related to the immune response were detected in hemocytes of Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 85, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, J.; Farley, S.; Pipe, R. Alteration of the immune response of the common marine mussel Mytilus edulis resulting from exposure to cadmium. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1995, 22, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. May 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaishi, F.M.; St-Jean, S.D.; Bishay, F.; Clarke, J.; Rabitto, I.D.S.; Ribeiro, C.A.D.O. Immunological responses, histopathological finding and disease resistance of blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) exposed to treated and untreated municipal wastewater. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchel, R.P.; Raftos, D.A.; Nair, S. Immunosuppressive effects of environmental stressors on immunological function in Pinctada imbricata. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, B.; Allam, B. Fluorometric measurement of oxidative burst in lobster hemocytes and inhibiting effect of pathogenic bacteria and hypoxia. J. Shellfish Res. 2006, 25, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, C. Toward a unified approach to dose-response modeling in ecotoxicology. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| PST | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cell Viability | 1.00 | ||||
| 2 | LMS | 0.68 * | 1.00 | |||
| 3 | Phagocytosis | 0.14 | −0.46 | 1.00 | ||
| 4 | Intracellular ROS | 0.68 * | 0.65 | −0.25 | 1.00 | |
| 5 | Extracellular H2O2 | 0.76 * | 0.91 ** | −0.30 | 0.82 * | 1.00 |
| LC | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 1 | Cell Viability | 1.00 | ||||
| 2 | LMS | 0.71 * | 1.00 | |||
| 3 | Phagocytosis | 0.69 | 0.98 *** | 1.00 | ||
| 4 | Intracellular ROS | 0.03 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 1.00 | |
| 5 | Extracellular H2O2 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.34 | −0.33 | 1.00 |
| PST | ng µL−1 | µM |
|---|---|---|
| STX | 4.3 | 14 |
| NEO | 63.5 | 200 |
| GTX 1/4 | 105.2 | 255 |
| GTX 2/3 | 0.7 | 2 |
| C1/C2 | 94.3 | 199 |
| Total concentration | 268.1 | 670 |
| µM/% | Cells mL−1 | |
|---|---|---|
| PST | 1250 | 6900 |
| 500 | 2760 | |
| 250 | 1380 | |
| 125 | 690 | |
| 62.50 | 345 | |
| 31.25 | 172.5 | |
| LC | 50 | 6800 |
| 25 | 3400 | |
| 12.5 | 1700 | |
| 5 | 680 | |
| 2.5 | 340 | |
| 1.25 | 170 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianchi, V.A.; Bickmeyer, U.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Müller, A.; Abele, D. In Vitro Effects of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Lytic Extracellular Compounds Produced by Alexandrium Strains on Hemocyte Integrity and Function in Mytilus edulis. Toxins 2021, 13, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080544
Bianchi VA, Bickmeyer U, Tillmann U, Krock B, Müller A, Abele D. In Vitro Effects of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Lytic Extracellular Compounds Produced by Alexandrium Strains on Hemocyte Integrity and Function in Mytilus edulis. Toxins. 2021; 13(8):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080544
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianchi, Virginia Angélica, Ulf Bickmeyer, Urban Tillmann, Bernd Krock, Annegret Müller, and Doris Abele. 2021. "In Vitro Effects of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Lytic Extracellular Compounds Produced by Alexandrium Strains on Hemocyte Integrity and Function in Mytilus edulis" Toxins 13, no. 8: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080544
APA StyleBianchi, V. A., Bickmeyer, U., Tillmann, U., Krock, B., Müller, A., & Abele, D. (2021). In Vitro Effects of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Lytic Extracellular Compounds Produced by Alexandrium Strains on Hemocyte Integrity and Function in Mytilus edulis. Toxins, 13(8), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080544