Evaluation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Marine Oyster Farming and Microalgae in the Atlantic Amazon Evidences Safety but Highlights Potential Risks of Shellfish Poisoning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Water
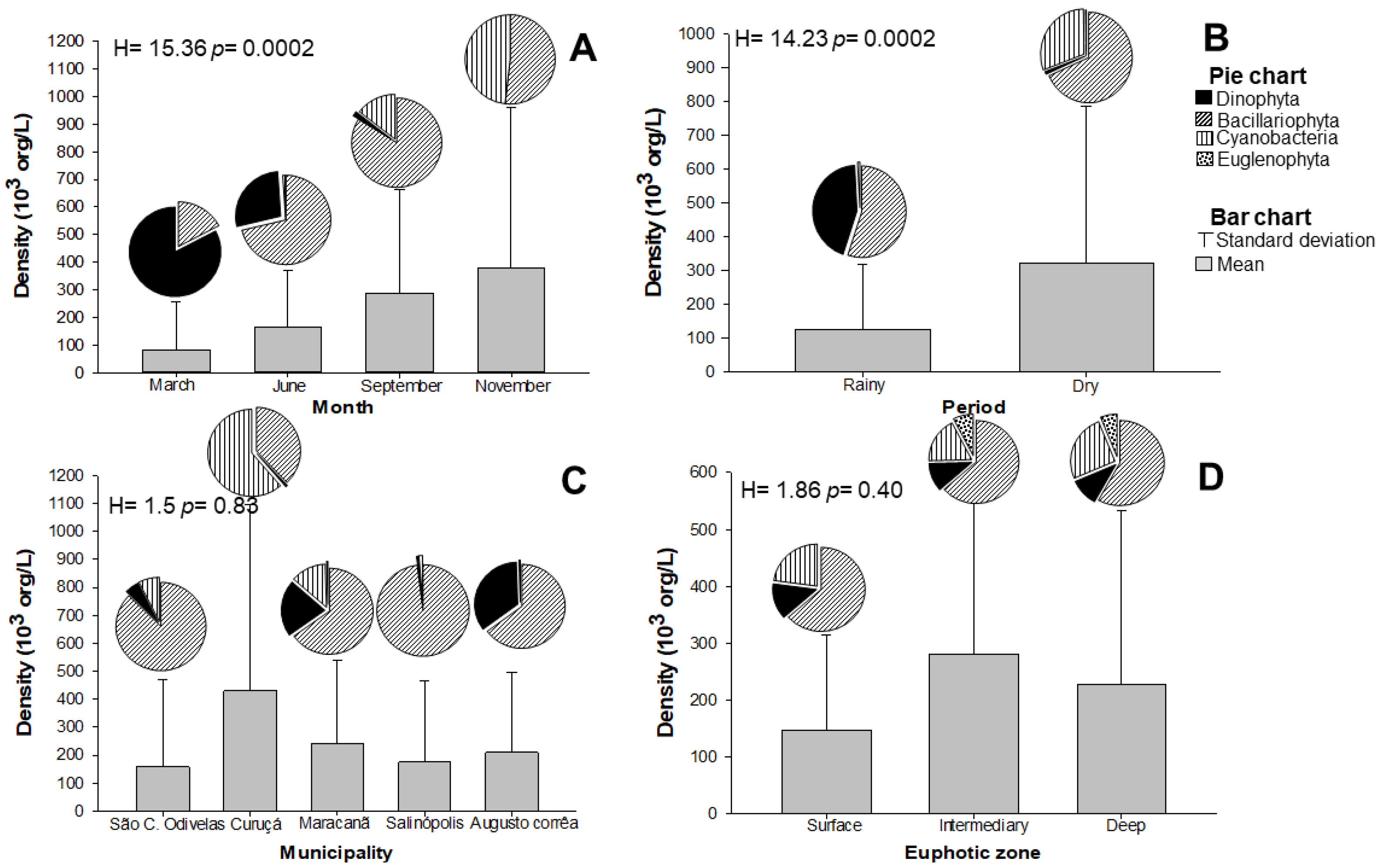
2.2. Microalgae
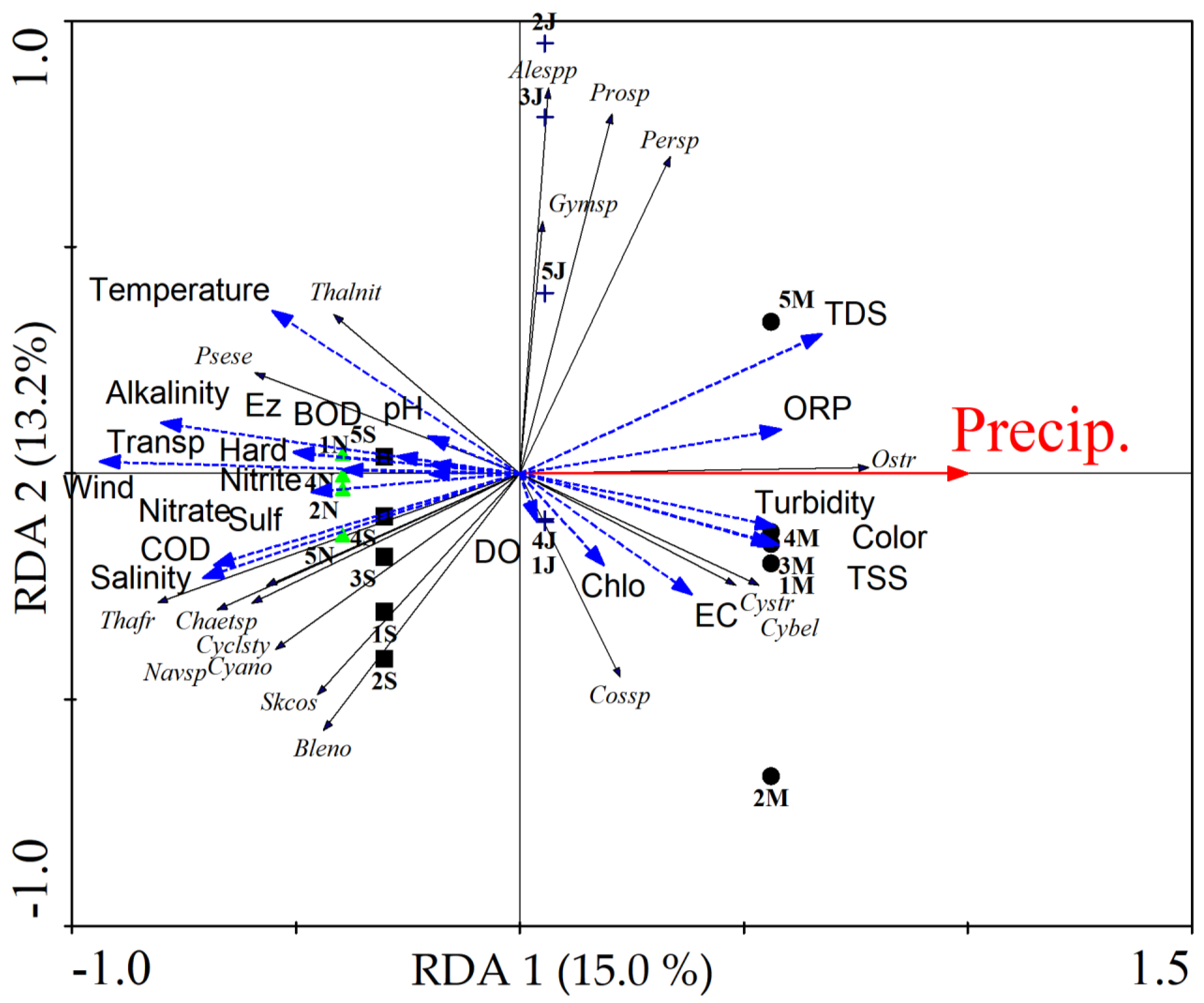
2.3. Redundancy Analysis
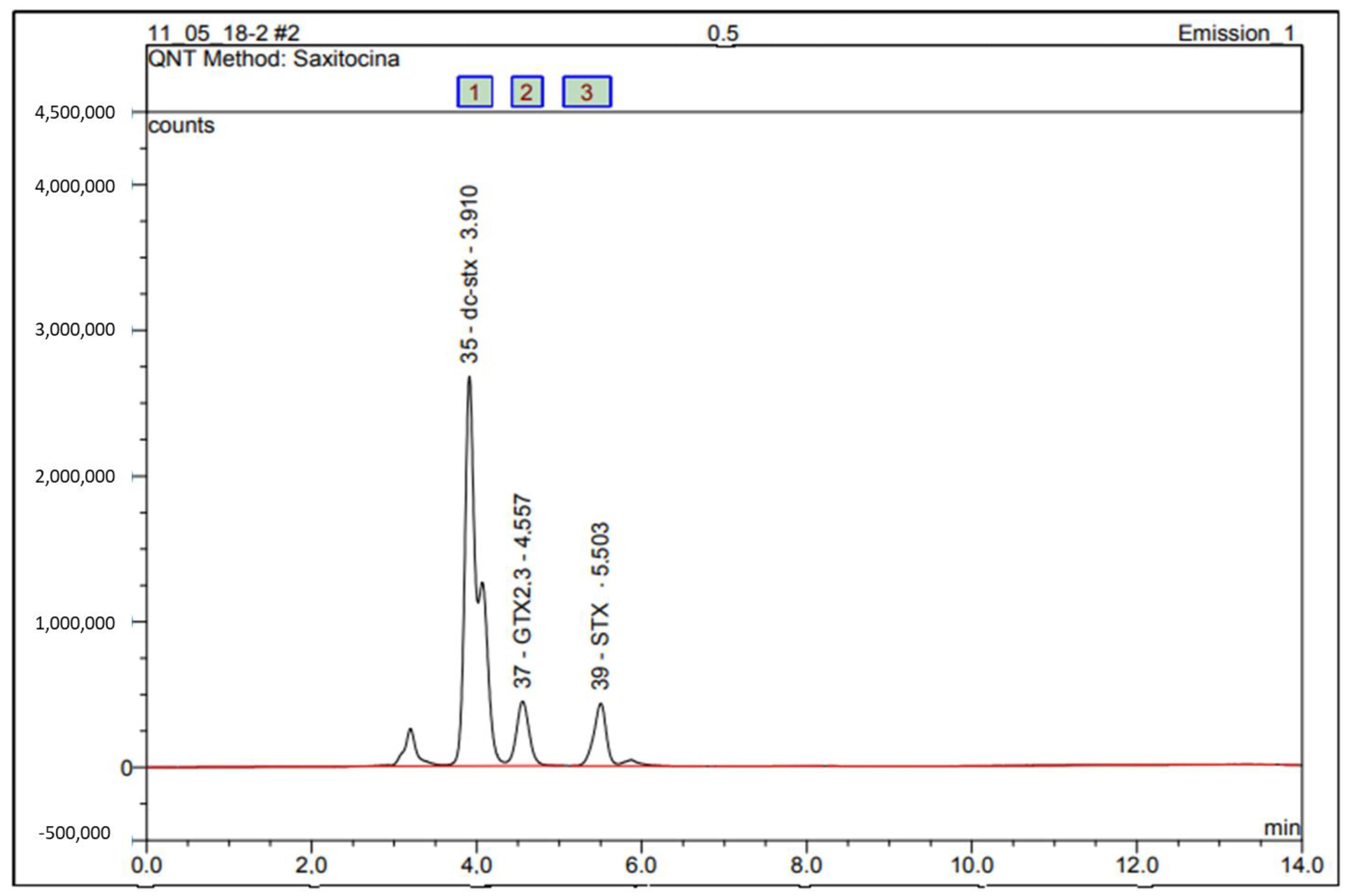
2.4. Identification of PSPs in Oysters by HPLC-FLD
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Site and Samples
5.2. Microalgae and Chlorophyll-A
5.3. Physicochemical Characteristics of Water
5.4. Statistical Analysis
5.5. Extraction and Clean-Up Procedure for Shellfish Samples
5.6. HPLC-FLD Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tamele, I.J.; Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, V. The Incidence of Marine Toxins and the Associated Seafood Poisoning Episodes in the African Countries of the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea. Toxins 2019, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Durán-Riveroll, L.M.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.J.; Leyva-Valencia, I.; López-Cortés, D.J.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, D.V. Paralytic toxin producing dinoflagellates in Latin America: Ecology and physiology. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020: Sustainability in Action; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.; McIntyre, L.; Ritson, M.; Stone, J.; Bronson, R.; Bitzikos, O.; Rourke, W.; Galanis, E. Outbreak of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning associated with mussels, British Columbia, Canada. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valbi, E.; Ricci, F.; Capellacci, S.; Casabianca, S.; Scardi, M.; Penna, A. A model predicting the PSP toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum occurrence in the coastal waters of the NW Adriatic Sea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z. Neurotoxins from marine dinoflagellates: A brief review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farabegoli, F.; Blanco, L.; Rodriguez, L.P.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Phycotoxins in Marine Shellfish: Origin, Occurrence and Effects on Humans. Mar.Drugs 2018, 16, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Campillo, C.; Pastor-Belda, M.; Campillo, N.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Hernandez-Cordoba, M.; Vinas, P. Determination of Cyanotoxins and Phycotoxins in Seawater and Algae-Based Food Supplements Using Ionic Liquids and Liquid Chromatography with Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2019, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Banack, S.A.; Wessel, R.A.; Lester, M.; Pim, J.G.; Cassani, J.R.; Cox, P.A. Toxin Analysis of Freshwater Cyanobacterial and Marine Harmful Algal Blooms on the West Coast of Florida and Implications for Estuarine Environments. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, S.; Silvestro, S.; Faggio, C. How the marine biotoxins affect human health. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.R.; Robertson, A.; Quilliam, M.A. Toxin profile of Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae) from the Portuguese coast, as determined by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2046–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wright, E.J.; Thomas, K.; Li, A.; McCarron, P.; Beach, D.G. Semiquantitation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins by Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Using Relative Molar Response Factors. Toxins 2020, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis Costa, P.; Braga, A.C.; Turner, A.D. Accumulation and Elimination Dynamics of the Hydroxybenzoate Saxitoxin Analogues in Mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis Exposed to the Toxic Marine Dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. Toxins 2018, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Botelho, M.J.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Gomes, S.S.; Sampayo, M.A.d.M. Two decades of marine biotoxin monitoring in bivalves from Portugal (1986–2006): A review of exposure assessment. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, H.; Ajani, P.; Murray, S.; Baker, P.; Webster, G.; Brett, S.; Zammit, A. Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxin Monitoring in Commercial Wild Harvest Bivalve Shellfish in New South Wales, Australia. Toxins 2018, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.M.; Magalhães, A.R.M.; Barracco, M.A. Pathologies in commercial bivalve species from Santa Catarina State, southern Brazil. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2012, 92, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futigami, L.d.S.; Dutra, M.d.O.; Verruck, S. Ocorrência de ficotoxinas diarreicas em ostras e mexilhões cultivados entre 2019 e 2020 em Governador Celso Ramos, SC. Rev. Bras. Agrotecnologia 2021, 11, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigozzi, L.; Freitas, V.S.; Salazar, V.A.; Verruck, S. Avaliação da presença de biotoxinas marinhas em moluscos bivalves na região da Costeira do Ribeirão em Florianópolis, Santa Catarina. Sci. Plena 2021, 17, 081501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.K.; Costa, L.D.F.; Yunes, J.S.; Resgalla, C., Jr.; Barufi, J.B.; Bastos, E.O.; Horta, P.A., Jr.; Rorig, L.R. Saxitoxins from the freshwater cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii can contaminate marine mussels. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. In Pesquisa Nacional de Saneamento Básico 2017: Abastecimento de Água e Esgotamento Sanitário; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, D.F.; Albernaz, A.L. Possible impacts of climate change on wetlands and its biota in the Brazilian Amazon. Braz. J Biol. 2014, 74, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.C.C.; Sousa-Felix, R.C.d.; Costa, R.M.d.; Jimenez, J.A. Challenges of the recreational use of Amazon beaches. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 165, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezequel, C.; Tedesco, P.A.; Darwall, W.; Dias, M.S.; Frederico, R.G.; Hidalgo, M.; Hugueny, B.; Maldonado-Ocampo, J.; Martens, K.; Ortega, H.; et al. Freshwater fish diversity hotspots for conservation priorities in the Amazon Basin. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 34, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, D.d.S.; Tagliaro, C.H.; Schneider, H.; Beasley, C.R. Oyster culture on the Amazon mangrove coast: Asymmetries and advances in an emerging sector. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.C.; Lacerda, L.D. Degradation and conservation of Brazilian mangroves, status and perspectives. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 125, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.M.S.; Barauna, R.A.; Marcon, D.J.; Lago, L.A.B.; Silva, A.; Lusio, J.; Tavares, R.D.S.; Tacao, M.; Henriques, I.; Schneider, M.P.C. Occurrence, antibiotic-resistance and virulence of E. coli strains isolated from mangrove oysters (Crassostrea gasar) farmed in estuaries of Amazonia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, O.L.L.; ModestoVeríssimo, S.M.; Rosa, A.M.B.P.d.; Iguchi, Y.B.; Nunes, E.d.S.C.d.L.; Moraes, C.M.d.; Cordeiro, C.A.M.; Xavier, D.d.A.; Pinto, A.S.O.; Joele, M.R.S.P.; et al. Effect of environmental factors on microbiological quality of oyster farming in Amazon estuaries. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, M.V.R.; Costa, S.S.; Schaan, A.P.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â.K.C.; Silva, A.; Graças, D.A.d.; Schneider, M.P.C.; Baraúna, R.A. Amazonia Seasons Have an Influence in the Composition of Bacterial Gut Microbiota of Mangrove Oysters (Crassostrea gasar). Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 602608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanajás, J.C.; Braga, C.C. Padrões espaço-temporal pluviométricos na Amazônia Oriental utilizando análise multivariada. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2012, 27, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassoni-Andrade, A.C.; Fleischmann, A.S.; Papa, F.; Paiva, R.C.D.d.; Wongchuig, S.; Melack, J.M.; Moreira, A.A.; Paris, A.; Ruhoff, A.; Barbosa, C.; et al. Amazon Hydrology From Space: Scientific Advances and Future. Rev. Geophys. 2021, 59, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, D.d.S.; Santos, M.d.L.S.; Tagliaro, C.H.; Beasley, C.R. Variation in environmental characteristics of waters among Amazon coast oyster culture units. Acta Amaz. 2020, 50, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, E.B.d.; Costa, V.B.d.; Pereira, L.C.C.; Costa, R.M.d. Variação temporal do fitoplâncton e dos parâmetros hidrológicos da zona de arrebentação da Ilha Canela (Bragança, Pará, Brasil). Acta Bot. Bras. 2009, 23, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosário, R.P. Análise de Processos Oceanográficos No Estuário do Rio Pará; Universidade Federal do Pará: Belém, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, B.O.d. Variação Nictemeral do Microfitoplâncton em um Estuário do Nordeste Paraense, Brasil; Universidade Federal do Pará: Belém, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, F.N.d.; Belúcio, L.F.; Pamplona, F.C.; Reis, L.T.L.; Veiga, G.D.d.; Melo, N.F.A.C.d. Microphytoplankton dynamics in Curuperé estuary at the Amazonian mangrove ecosystem. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2020, 46, e513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, D.d.S.; Paiva, R.d.S.; Pereira, L.C.C.; Costa, R.M.d. Microphytoplankton of the Marapanim Estuary (Pará, Northern Brazil). Trop. Oceanogr. 2010, 38, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sousa, E.B.d.; Costa, V.B.d.; Pereira, L.C.C.; Costa, R.M.d. Microfitoplâncton de águas costeiras amazônicas: Ilha Canela (Bragança, PA, Brasil). Acta Bot. Bras. 2008, 22, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, M.I.C.; Gomes, M.; Botelho, M.J.; Rudnitskaya, A. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins (PST)-Transforming Enzymes: A Review. Toxins 2020, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingone, A.; Escalera, L.; Aligizaki, K.; Fernandez-Tejedor, M.; Ismael, A.; Montresor, M.; Mozetic, P.; Tas, S.; Totti, C. Toxic marine microalgae and noxious blooms in the Mediterranean Sea: A contribution to the Global HAB Status Report. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Oliveira, P.B.; Moita, M.T.; David, H.; Caeiro, M.F.; Zingone, A.; Amorim, A.; Silva, A. Ocurrence of Ostreopsis in two temperate coastal bays (SW iberia): Insights from the plankton. Harmful Algae 2019, 86, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibiriçá, C.; Leite, I.P.; Batista, T.V.V.; Fernandes, L.F.; Chomerat, N.; Herve, F.; Hess, P.; Mafra, L.L., Jr. Ostreopsis cf. ovata Bloom in Currais, Brazil: Phylogeny, Toxin Profile and Contamination of Mussels and Marine Plastic Litter. Toxins 2019, 11, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.M.; de Carvalho, M.; Mestre, T.; Ferreira, J.J.; Coelho, M.; Peralta, R.; Vale, P. Paralytic shellfish poisoning due to ingestion of Gymnodinium catenatum contaminated cockles--application of the AOAC HPLC official method. Toxicon 2012, 59, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.L.; Pelerito, A.; Ribeiro, I.; Cordeiro, R.; Nuncio, M.S.; Vale, P. Paralytic shellfish poisoning due to ingestion of contaminated mussels: A 2018 case report in Caparica (Portugal). Toxicon X 2019, 4, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, M.A.; Tamanaha, M.S.; Beirão, L.H.; Proença, L.A.O. Toxinas paralisantes em mexilhão Perna perna em áreas de cultivo da costa sul do Brasil: Estudo de caso. Aliment. Nutr. Araraquara 2009, 17, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, D.A.d.; Zanette, G.B.; Neves, M.H.C.B.; Schramm, M.A.; Proença, L.A.d.O.; Oliveira, M.M.d. Cultivo de moluscos bivalves: Algas nocivas e bases para programa de monitoramento de ficotoxinas em fazenda de maricultura de Arraial do Cabo, RJ. Bol. Do Obs. Ambient. Alberto Ribeiro Lamego 2015, 9, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D. HABs in a changing world: A perspective on harmful algal blooms, their impacts, and research and management in a dynamic era of climactic and environmental change. Harmful Algae 2015, 2012, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lugliè, A.; Satta, C.T.; Pulina, S.; Bazzoni, A.M.; Padedda, B.M.; Nicola, S. Le problematiche degli Harmful Algal Blooms (HAB) in Sardegna. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2011, 18, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzoni, A.M.; Caddeo, T.; Pulina, S.; Padedda, B.M.; Satta, C.T.; Sechi, N.; Luglie, A. Spatial distribution and multiannual trends of potentially toxic microalgae in shellfish farms along the Sardinian coast (NW Mediterranean Sea). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, R.C.; Kong, F.Z.; Chen, Z.F.; Dai, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.C.; Wang, Y.F.; Yan, T.; Zhou, M.J. Paralytic shellfish toxins in phytoplankton and shellfish samples collected from the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon, A. Official method 2005.06 quantitative determination of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in shellfish using pre-chromatographic oxidation and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. In AOAC Official Methods for Analysis; International, A., Ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Oshima, Y. Chemical and enzymatic transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine organisms. In Harmful Marine Algal Blooms; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Gentien, P., Marcaillou, C., Eds.; Lavoisier Publishers: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Fisch, G.; Marengo, J.A.; Nobre, C.A. Uma revisão geral sobre o clima da Amazônia. Acta Amaz. 1998, 28, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Filho, P.W.M. The Amazon Macrotidal Mangrove Coast (AMMC): Morphological scenes, mapping and area quantification using remote sensing data. Rev. Bras. Geofísica 2005, 23, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.A. Textbook of Limnology, 4th ed.; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.; Bridgewater, L.; Association, A.P.H.; Association, A.W.W.; Federation, W.E. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Bicudo, C.E.M.; Menezes, M. Gêneros de Algas de Águas Continenetais do Brasil: Chave Para Identificação e Descrições, 2nd ed.; RiMa Editora: São Carlos, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, K.; Anagnostidis, K. Oscillatoriales. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa freshwater flora of central Europa. In Cyanoprocaryota 2. Teil/Part 2; Büdel, B., Gärtner, G., Krienitz, L., Schagerl, M., Eds.; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag: Berlim, Germany, 2007; p. 759. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Chroococcales. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropafreshwater flora of central Europa. In Cyanoprocaryota 1. Teil. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag: Berlim, German, 2008; pp. 1–556. [Google Scholar]
- Round, F.E.; Crawford, R.M.; Mann, D.G. Diatoms: Biology and Morphology of the Genera; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; p. 747. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, S.; Nishimura, T.; Uehara, K.; Sakanari, H.; Tawong, W.; Hariganeya, N.; Smith, K.; Rhodes, L.; Yasumoto, T.; Taira, Y.; et al. Phylogeography of ostreopsis along west Pacific coast, with special reference to a novel clade from Japan. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S.A.; Chomérat, N.; Horiguchi, T. Marine Benthic Dinoflagellates-Unveiling Their Worldwide Biodiversity; Schweizerbart Science Publisher: Stuttgart, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, D.; Gonglewski, N. Determining Suspended Solids Using a Spectrophotometer. Sew. Ind. Wastes 1959, 31, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil. Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. In Resolução CONAMA 357 de 17 de Março de 2005. Available online: www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/res/res05/res35705.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- INMET. Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia do Brasil. In Normais Climatológicas (1991–2020); INMET: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.; Ryan, P. Paleontological Statistics Software Package for education and data analsis PAST. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin, J.L. Ecologia Numérica: Uma Introdução à Análise Multivariada de Dados Ecológicos, 2nd ed.; Editora Interciência: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- McCune, B.; Mefford, M.J. PC-ORD. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data, Version 7.0 for Windows; Wild Blueberry Media: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, J.F.; Niedzwiadek, B.; Menard, C.; Lau, B.P.; Lewis, D.; Kuper-Goodman, T.; Carbone, S.; Holmes, C. Comparison of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry, ELISA, and phosphatase assay for the determination of microcystins in blue-green algae products. J. AOAC Int. 2001, 84, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Benford, D.; Cockburn, A.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Dogliotti, E.; Domenico, A.D.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L.; Fink-Gremmels, J.; Fürst, P.; Galli, C.; et al. Marine biotoxins in shellfish—Saxitoxin group. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 indicates oyster culture communities’ location). Geographic coordinates of the sampling points are provided in the methods section.
indicates oyster culture communities’ location). Geographic coordinates of the sampling points are provided in the methods section.
 indicates oyster culture communities’ location). Geographic coordinates of the sampling points are provided in the methods section.
indicates oyster culture communities’ location). Geographic coordinates of the sampling points are provided in the methods section.
| Sampling Points | Months | GTX1,4 (Mg STX Equiv./Kg) | GTX2,3 (Mg STX Equiv./Kg) | STX (Mg STX Equiv./Kg) | dc-STX (Mg STX Equiv./Kg) | NEO (Mg STX Equiv./Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| São Caetano de Odivelas | March | <LOD | <LOD | 0.00249 | <LOD | <LOD |
| June | <LOD | 0.0038 | 0.00052 | 0.00102 | <LOD | |
| September | <LOD | 0.0049 | 0.106 | 0.00046 | <LOD | |
| November | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Curuçá | March | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| June | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| September | <LOD | 0.0076 | <LOD | 0.0018 | <LOD | |
| November | <LOD | 0.031 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Maracanã | March | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| June | <LOD | 0.0044 | 0.000707 | 0.00273 | <LOD | |
| September | <LOD | 0.083 | 0.141 | 0.00032 | <LOD | |
| November | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Salinópolis | March | <LOD | <LOD | 0.00024 | <LOD | <LOD |
| June | <LOD | 0.003 | 0.00044 | <LOD | <LOD | |
| September | <LOD | <LOD | 0.421 | 0.001 | <LOD | |
| November | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | |
| Augusto Corrêa | March | <LOD | 0.018 | 0.0172 | 0.00059 | <LOD |
| June | <LOD | 0.012 | <LOD | 0.0018 | <LOD | |
| September | <LOD | 0.023 | 0.155 | 0.00103 | <LOD | |
| November | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves, F.A.d.S.; de Sousa, E.B.; Martins, M.P.; da Silva Rocha, C.C.; Faustino, S.M.M.; Mendes, R.A.; de Oliveira Lima, M.; Schneider, M.P.C. Evaluation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Marine Oyster Farming and Microalgae in the Atlantic Amazon Evidences Safety but Highlights Potential Risks of Shellfish Poisoning. Toxins 2022, 14, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100654
Alves FAdS, de Sousa EB, Martins MP, da Silva Rocha CC, Faustino SMM, Mendes RA, de Oliveira Lima M, Schneider MPC. Evaluation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Marine Oyster Farming and Microalgae in the Atlantic Amazon Evidences Safety but Highlights Potential Risks of Shellfish Poisoning. Toxins. 2022; 14(10):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100654
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves, Francisco Arimatéia dos Santos, Eliane Brabo de Sousa, Maíra Pompeu Martins, Cássia Christina da Silva Rocha, Silvia Maria Mathes Faustino, Rosivaldo Alcântara Mendes, Marcelo de Oliveira Lima, and Maria Paula Cruz Schneider. 2022. "Evaluation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Marine Oyster Farming and Microalgae in the Atlantic Amazon Evidences Safety but Highlights Potential Risks of Shellfish Poisoning" Toxins 14, no. 10: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100654
APA StyleAlves, F. A. d. S., de Sousa, E. B., Martins, M. P., da Silva Rocha, C. C., Faustino, S. M. M., Mendes, R. A., de Oliveira Lima, M., & Schneider, M. P. C. (2022). Evaluation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Marine Oyster Farming and Microalgae in the Atlantic Amazon Evidences Safety but Highlights Potential Risks of Shellfish Poisoning. Toxins, 14(10), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100654





