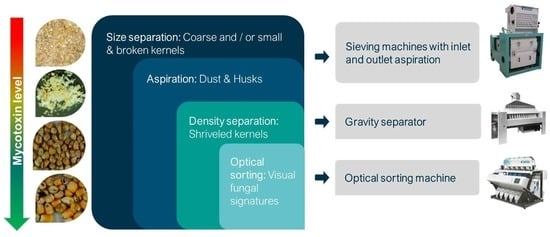
Industrial-Scale Cleaning Solutions for the Reduction of Fusarium Toxins in Maize
Abstract
Share and Cite
Pascale, M.; Logrieco, A.F.; Lippolis, V.; De Girolamo, A.; Cervellieri, S.; Lattanzio, V.M.T.; Ciasca, B.; Vega, A.; Reichel, M.; Graeber, M.; et al. Industrial-Scale Cleaning Solutions for the Reduction of Fusarium Toxins in Maize. Toxins 2022, 14, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110728
Pascale M, Logrieco AF, Lippolis V, De Girolamo A, Cervellieri S, Lattanzio VMT, Ciasca B, Vega A, Reichel M, Graeber M, et al. Industrial-Scale Cleaning Solutions for the Reduction of Fusarium Toxins in Maize. Toxins. 2022; 14(11):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110728
Chicago/Turabian StylePascale, Michelangelo, Antonio F. Logrieco, Vincenzo Lippolis, Annalisa De Girolamo, Salvatore Cervellieri, Veronica M. T. Lattanzio, Biancamaria Ciasca, Anna Vega, Mareike Reichel, Matthias Graeber, and et al. 2022. "Industrial-Scale Cleaning Solutions for the Reduction of Fusarium Toxins in Maize" Toxins 14, no. 11: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110728
APA StylePascale, M., Logrieco, A. F., Lippolis, V., De Girolamo, A., Cervellieri, S., Lattanzio, V. M. T., Ciasca, B., Vega, A., Reichel, M., Graeber, M., & Slettengren, K. (2022). Industrial-Scale Cleaning Solutions for the Reduction of Fusarium Toxins in Maize. Toxins, 14(11), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110728